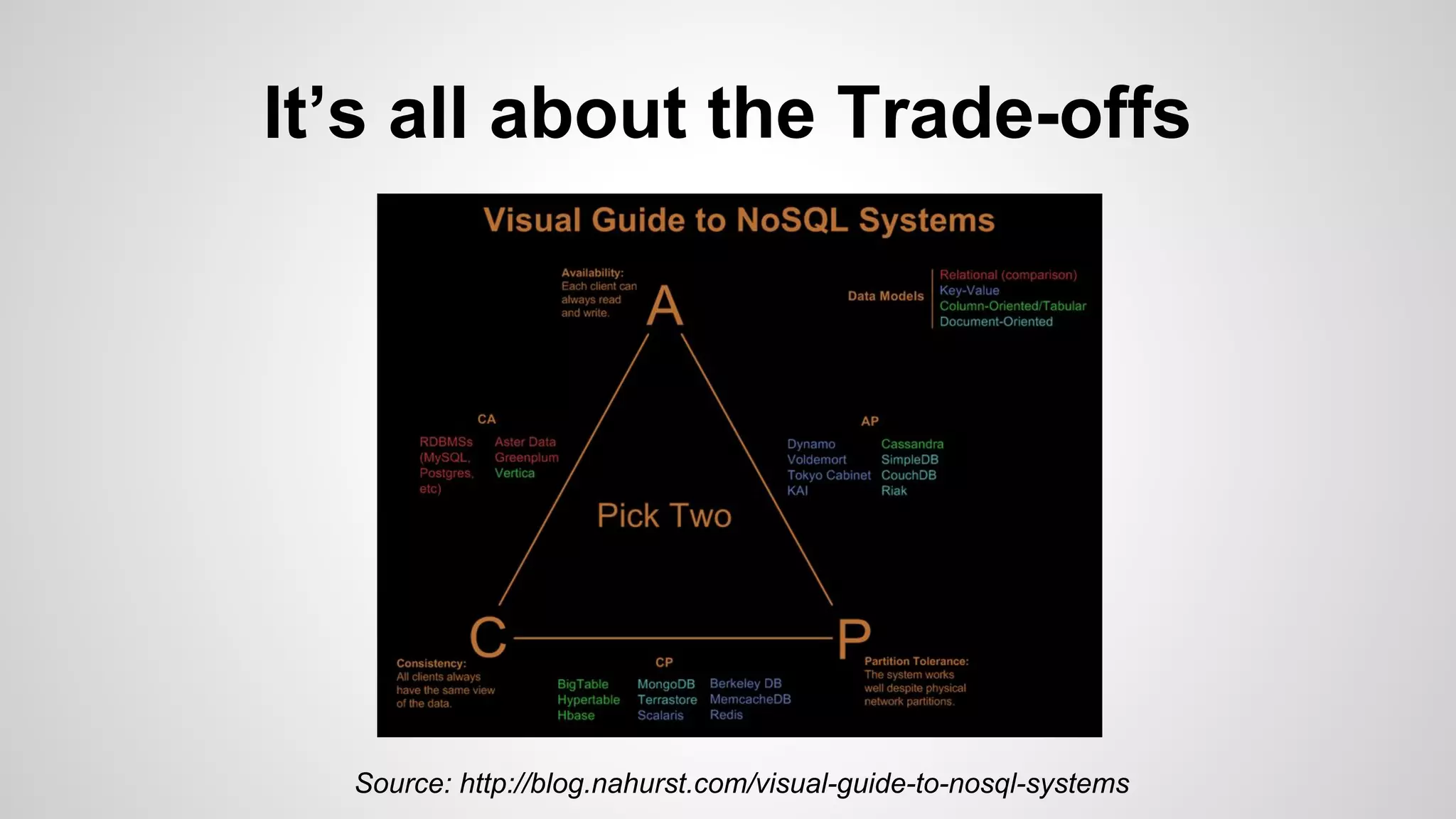
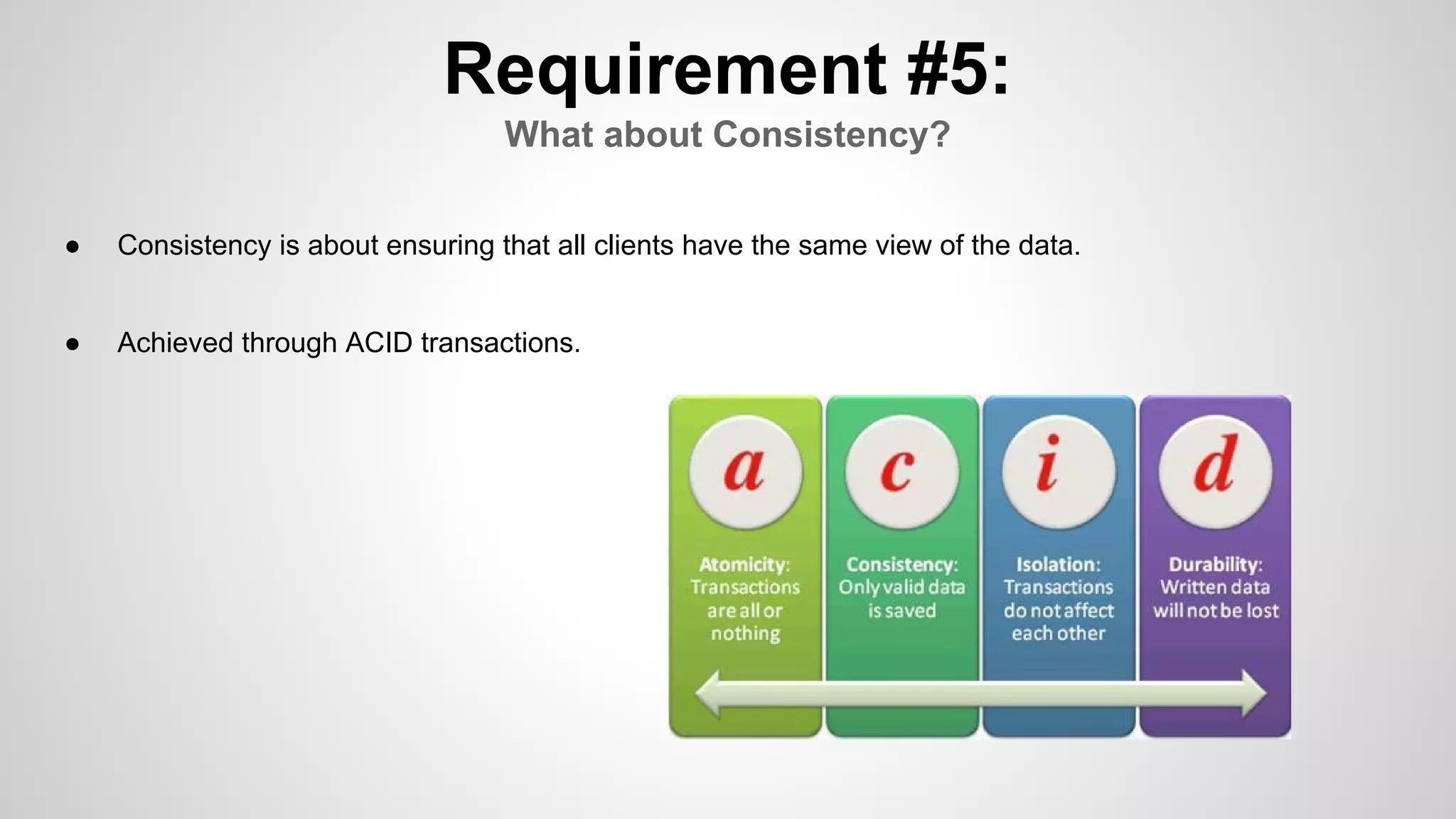
This document discusses relational databases and some of their key properties and tradeoffs. It notes that consistency, availability, and partition tolerance in shared data systems can only achieve two of the three properties at once, according to Brewer's CAP theorem. The document then examines different requirements like querying, transactions, consistency and scaling in the context of choosing a database for a startup's application. It provides an example use case of using PostgreSQL, Redis, and MongoDB together to address these requirements for a listings application called Kuai List.