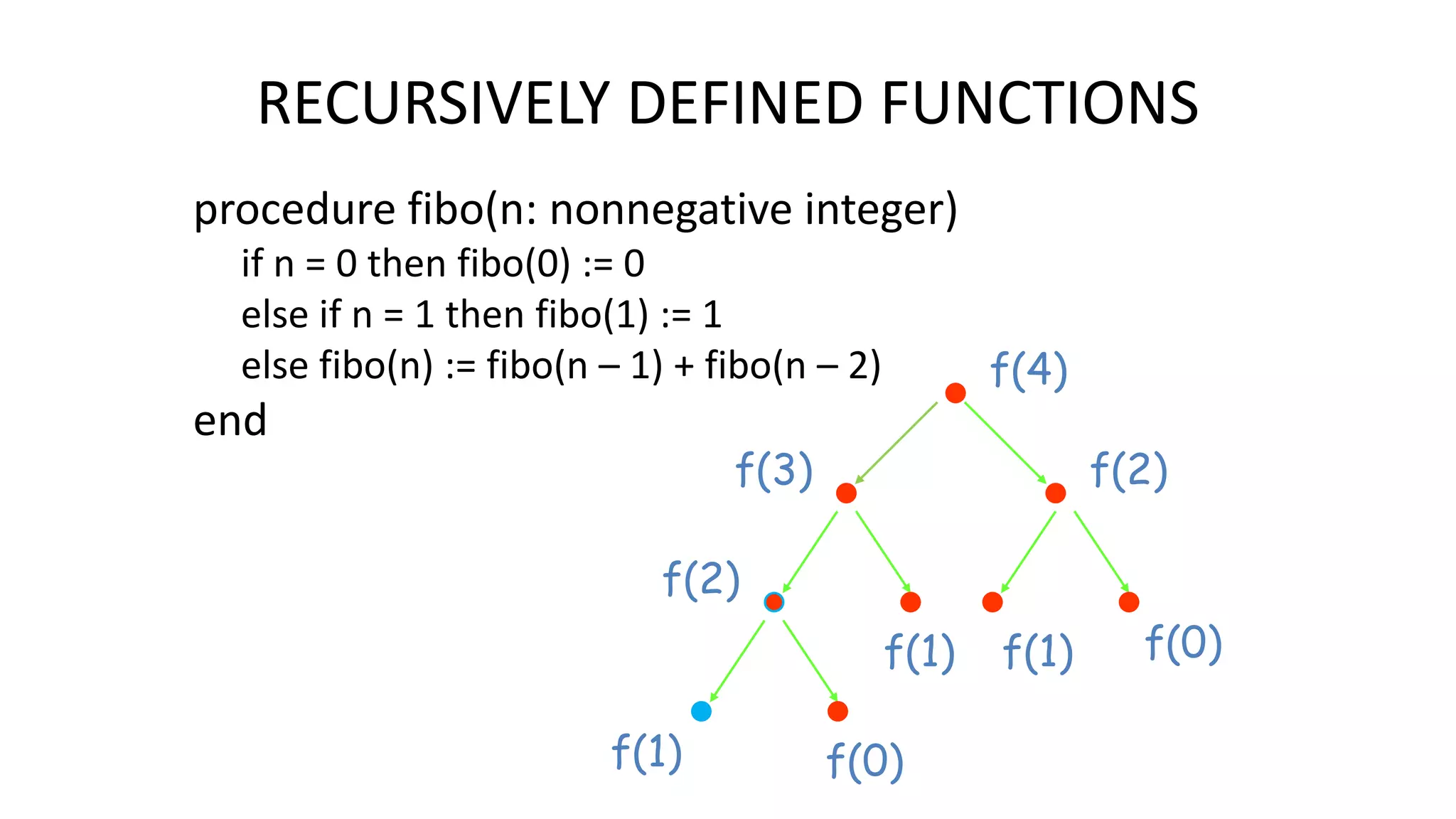
Recursion is a process where an object is defined in terms of smaller versions of itself. It involves a base case, which is the simplest definition that cannot be further reduced, and a recursive case that defines the object for larger inputs in terms of smaller ones until the base case is reached. Examples where recursion is commonly used include defining mathematical functions, number sequences, data structures, and language grammars. While recursion can elegantly solve problems, iterative algorithms are generally more efficient.