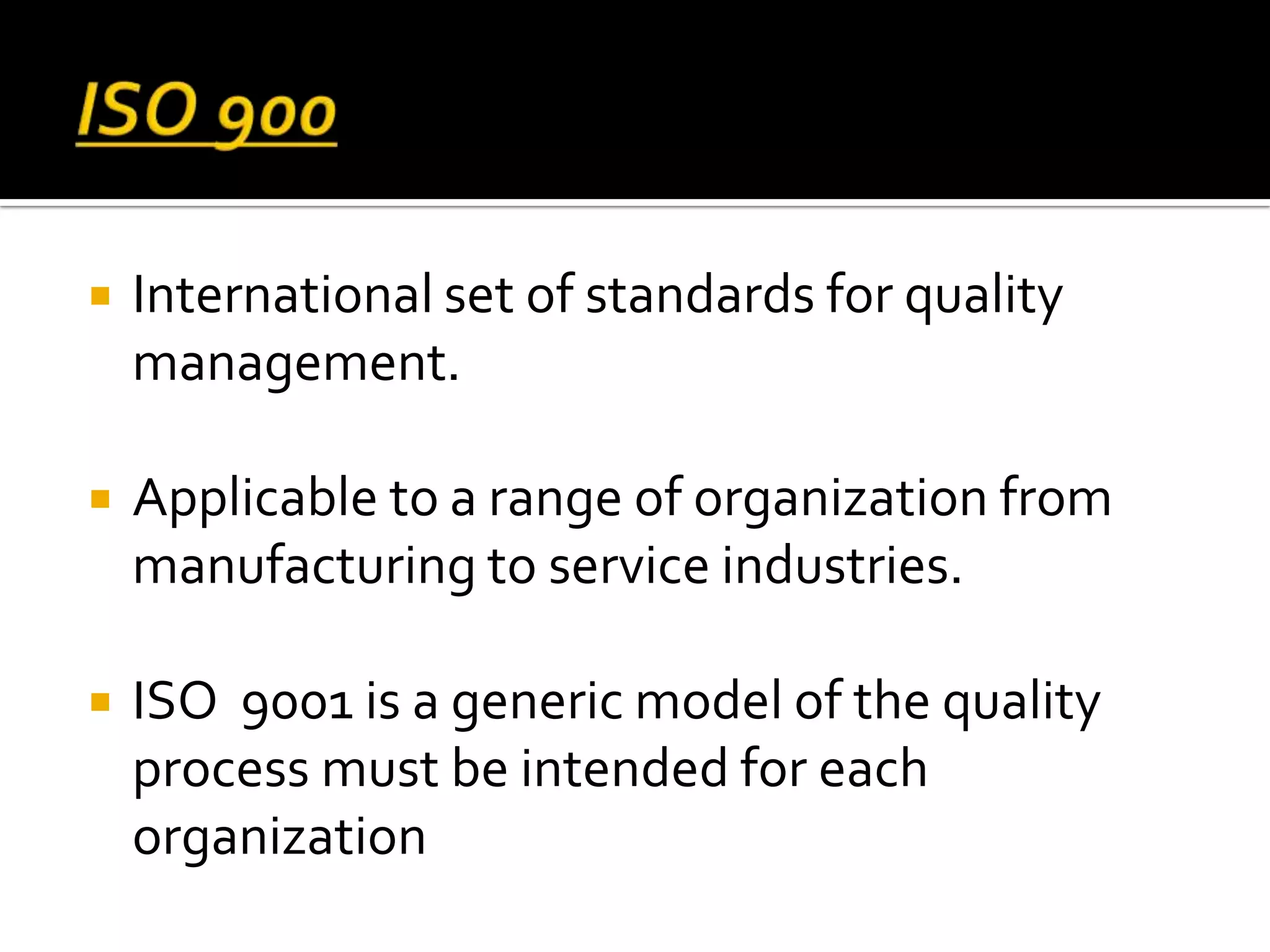
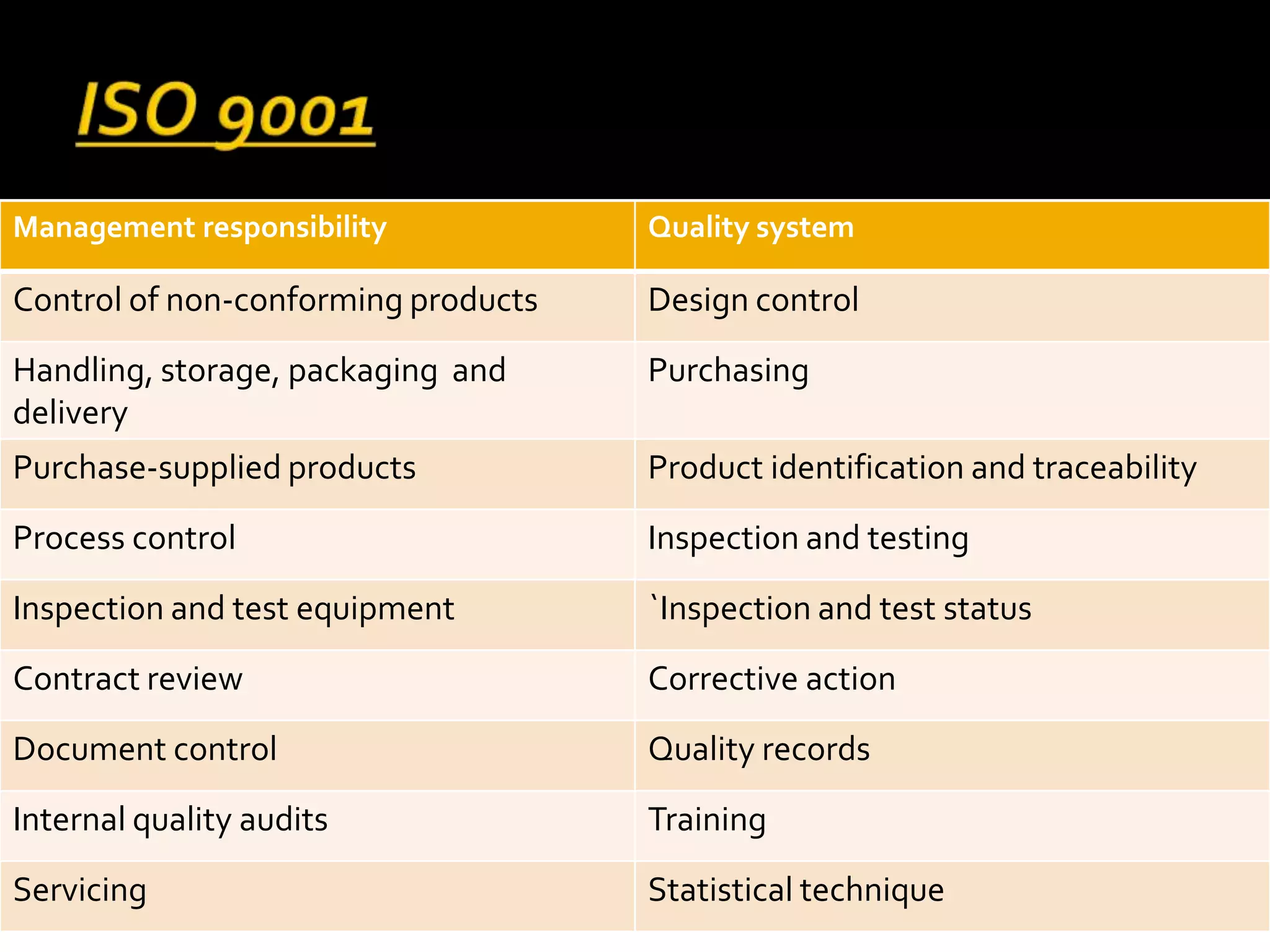
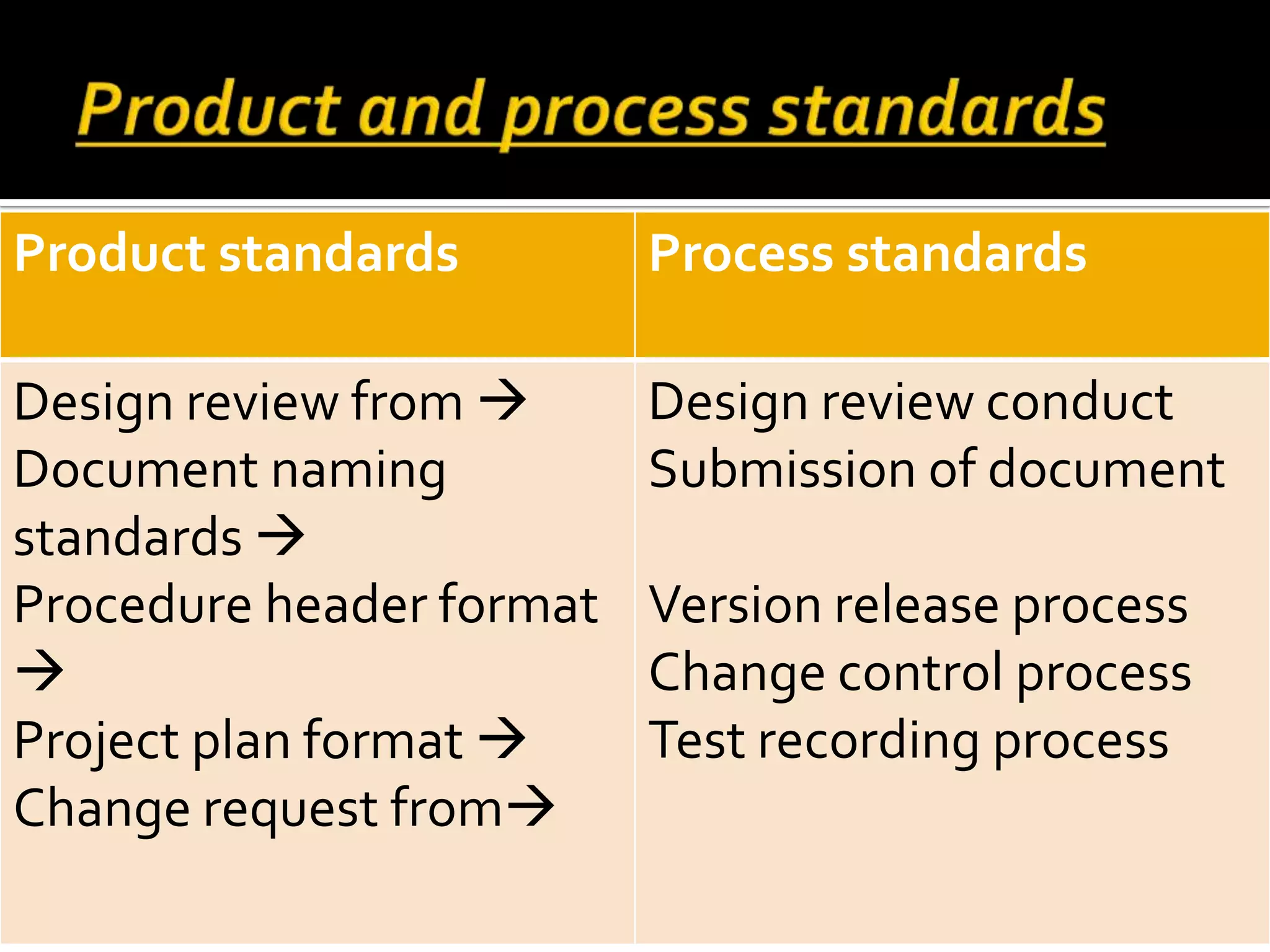
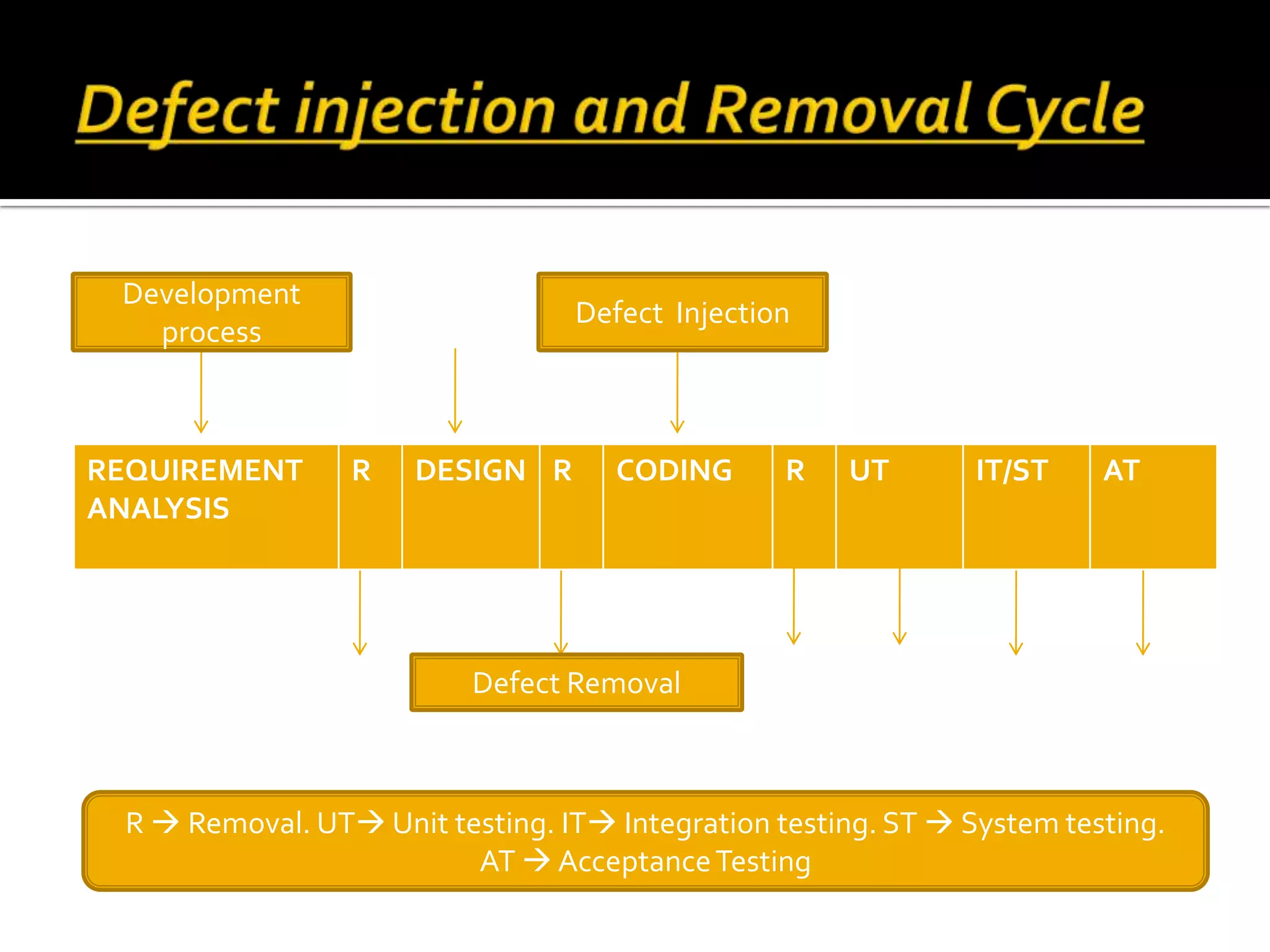
This document discusses software quality management. It introduces key quality management activities like quality assurance, planning, and control. Standards play an important role in quality management. Quality management aims to develop a quality culture and ensure software meets requirements, though requirements can be imperfect. Quality management involves procedures like reviews, testing, and measurements to improve quality despite specification issues.