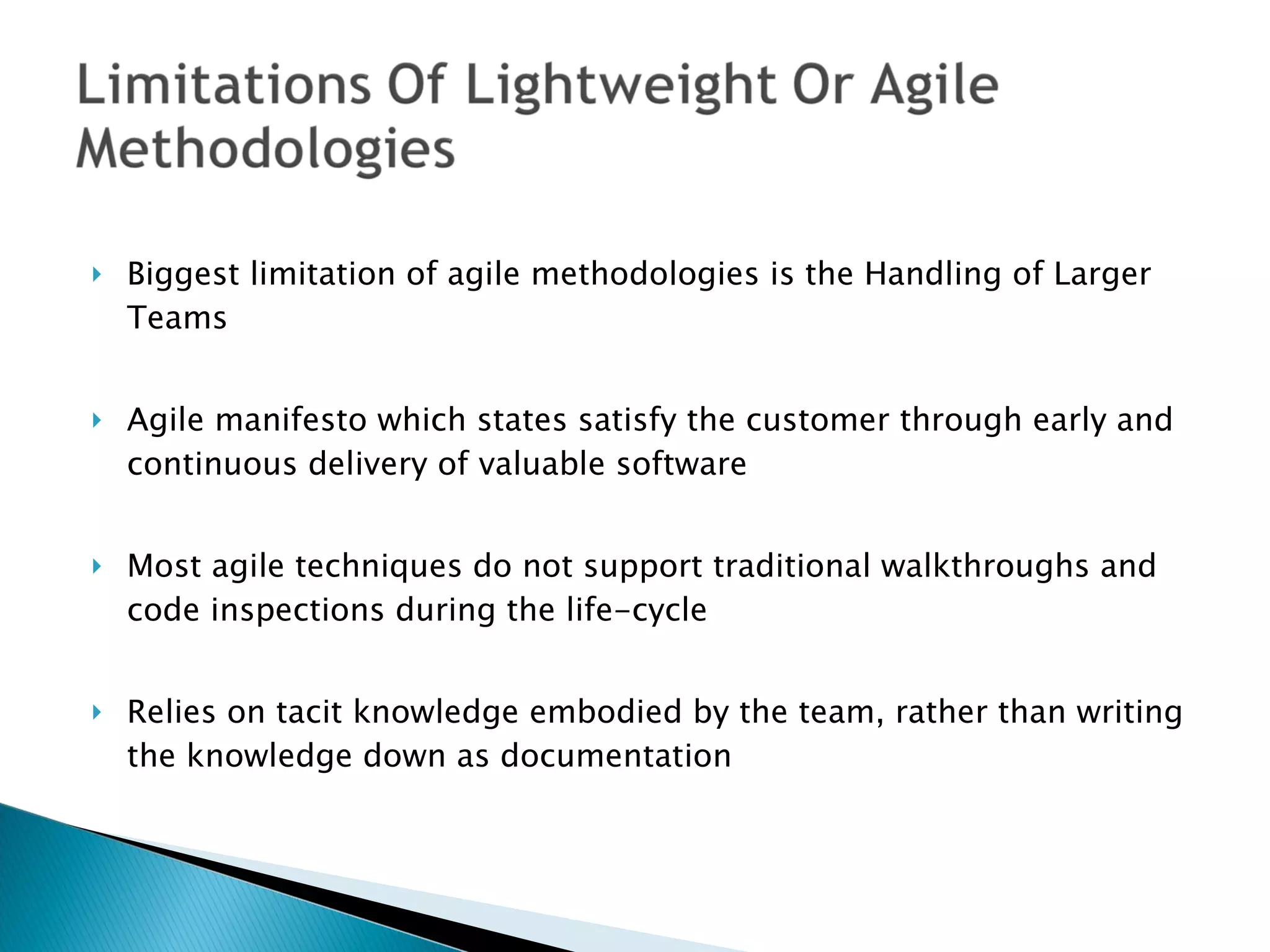
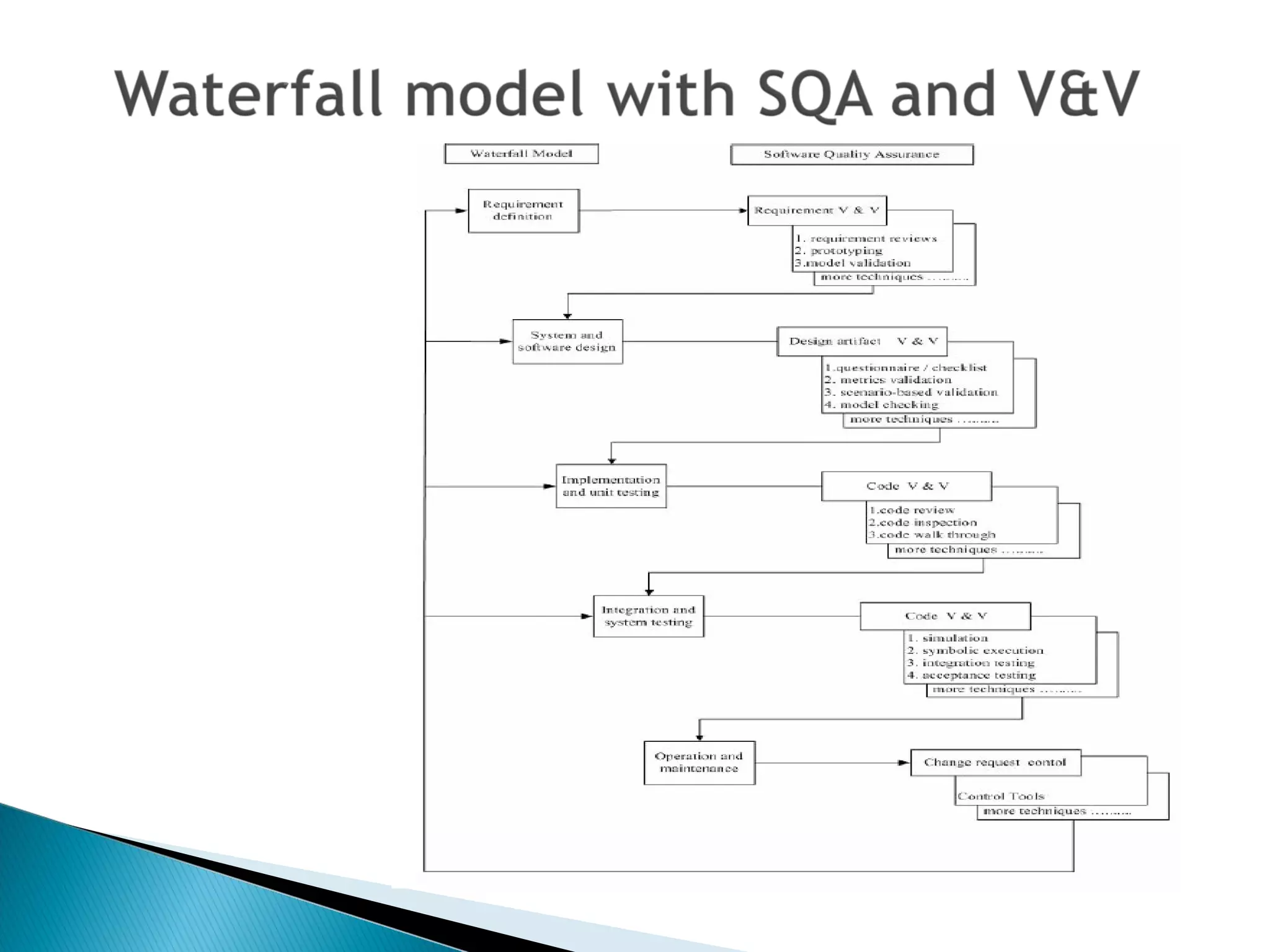
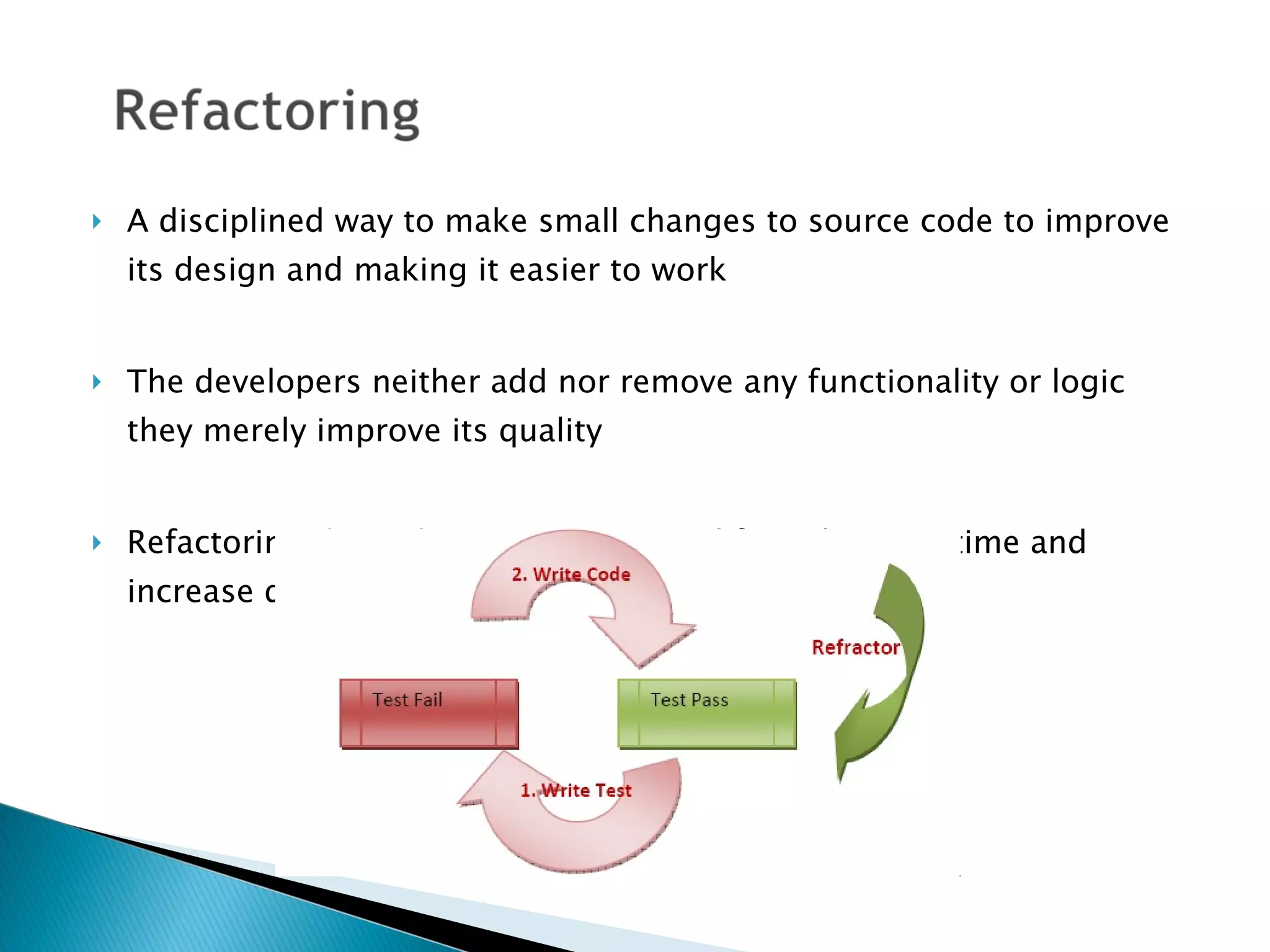
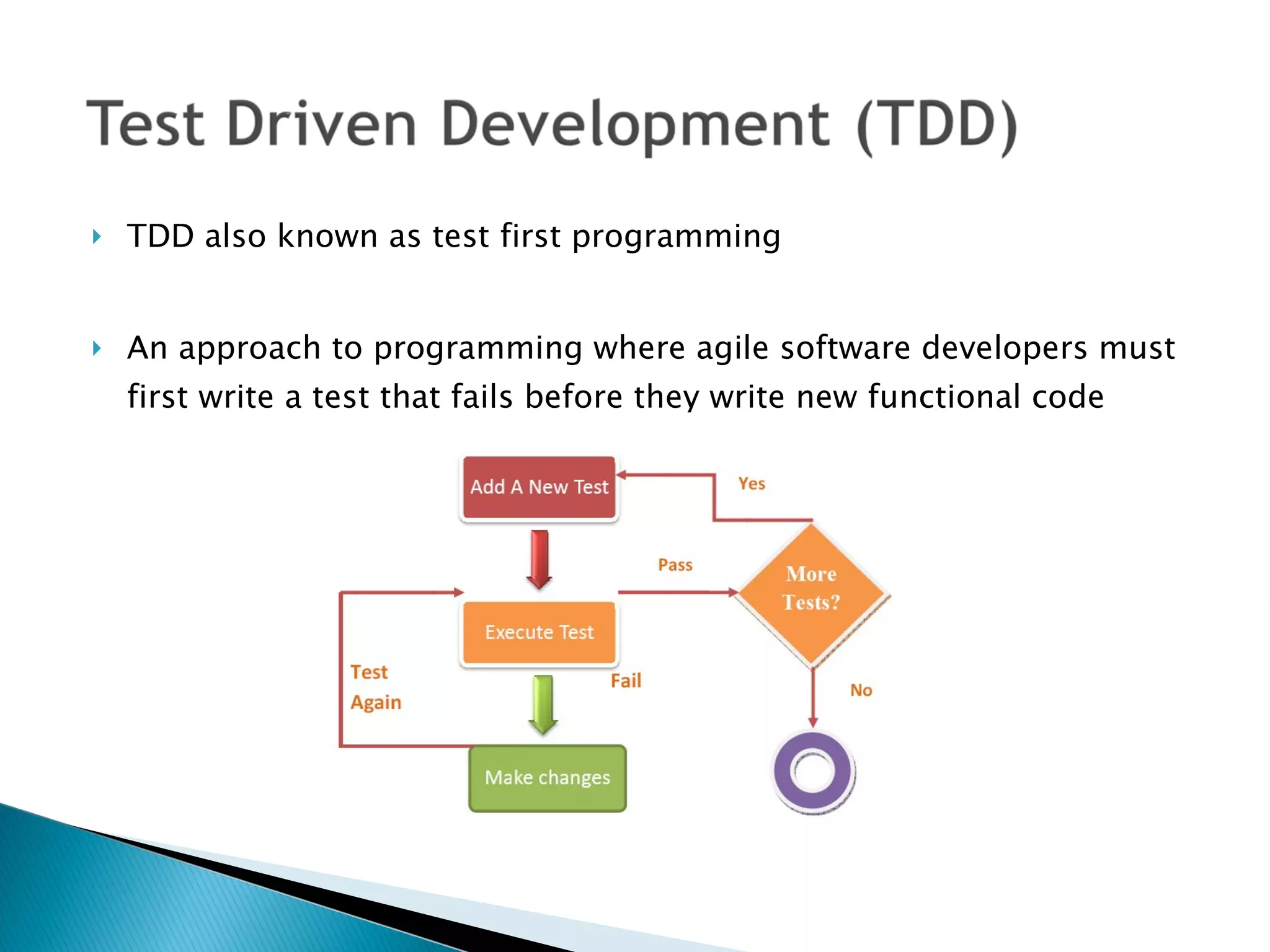
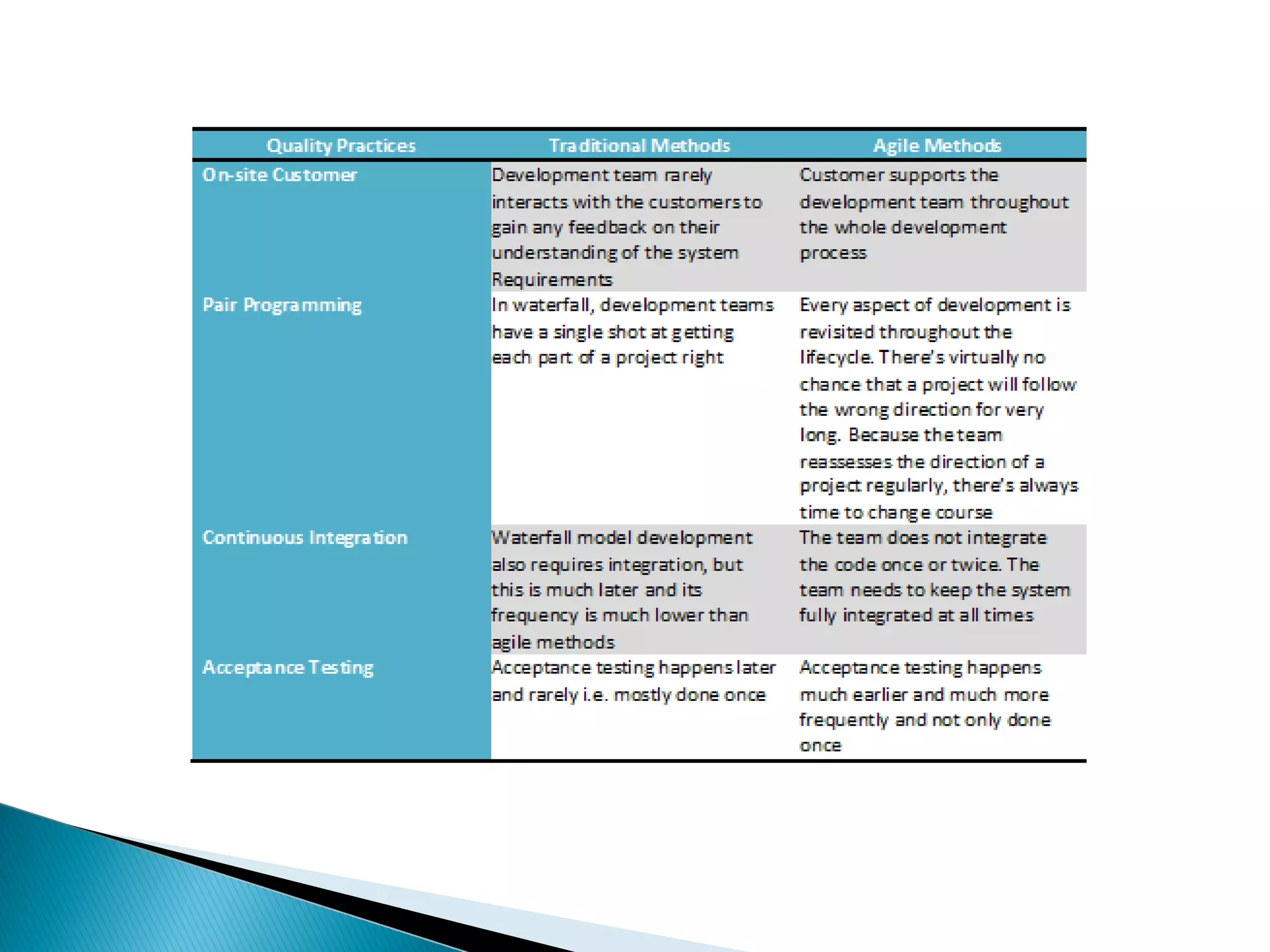
This document compares quality assurance techniques between traditional and agile software development methodologies. It discusses the limitations of traditional waterfall models and agile methods. Traditional methods emphasize well-defined requirements and documentation, while agile prioritizes working software through short iterations with frequent customer feedback. Both approaches aim to ensure quality, but agile relies more on practices like refactoring, test-driven development, and continuous integration throughout the development cycle. In conclusion, agile may better facilitate quality by starting testing earlier and more frequently integrating customer input.