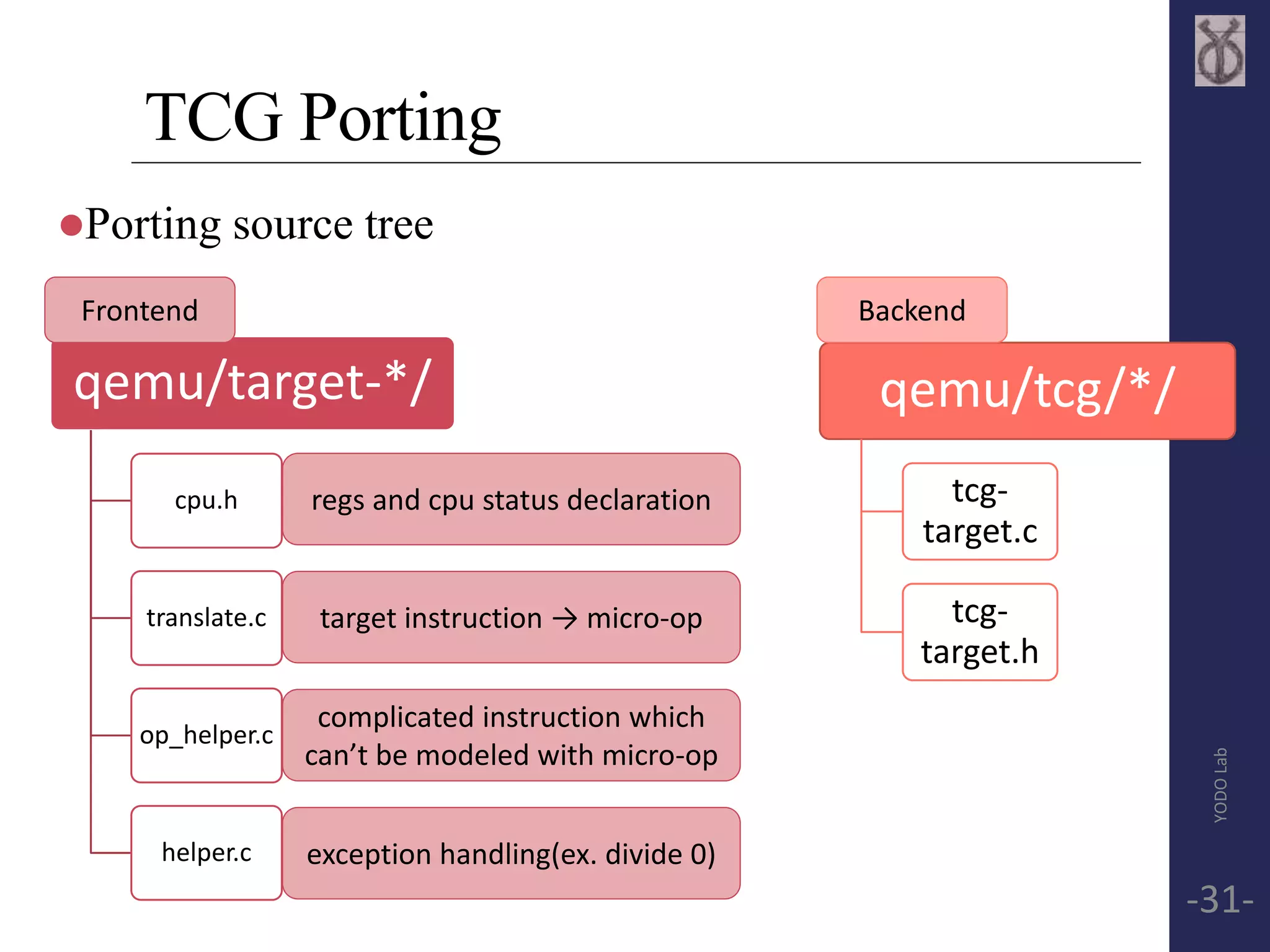
This document provides an overview of QEMU, including its use of dynamic translation and Tiny Code Generator (TCG) to emulate target CPUs on the host system. It discusses how QEMU translates target instructions into a RISC-like intermediate representation (TCG ops), optimizes and converts them to host instructions. The document also mentions Linaro's work with QEMU and a QEMU monitor tool for debugging ARM systems emulated by QEMU.



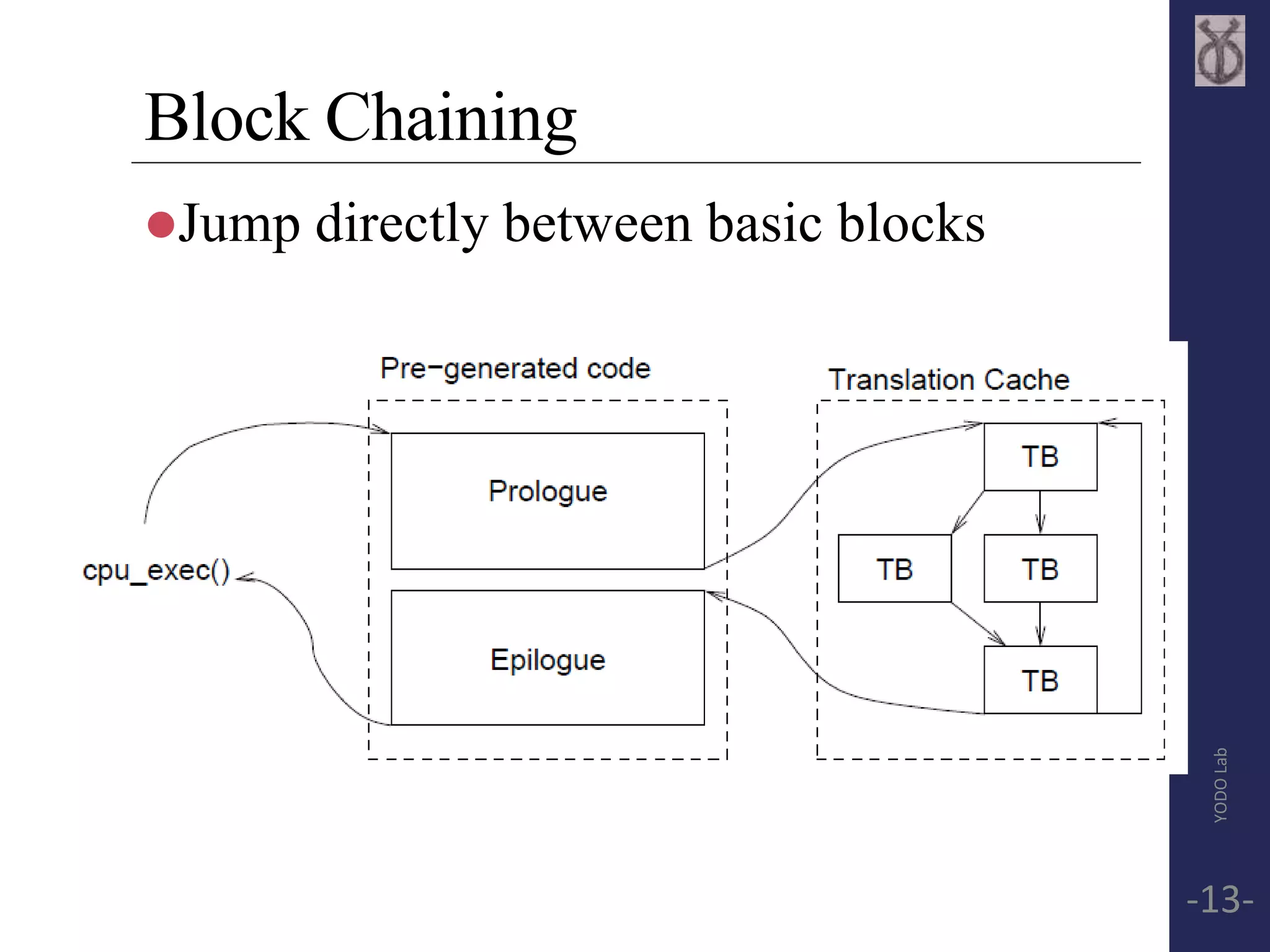
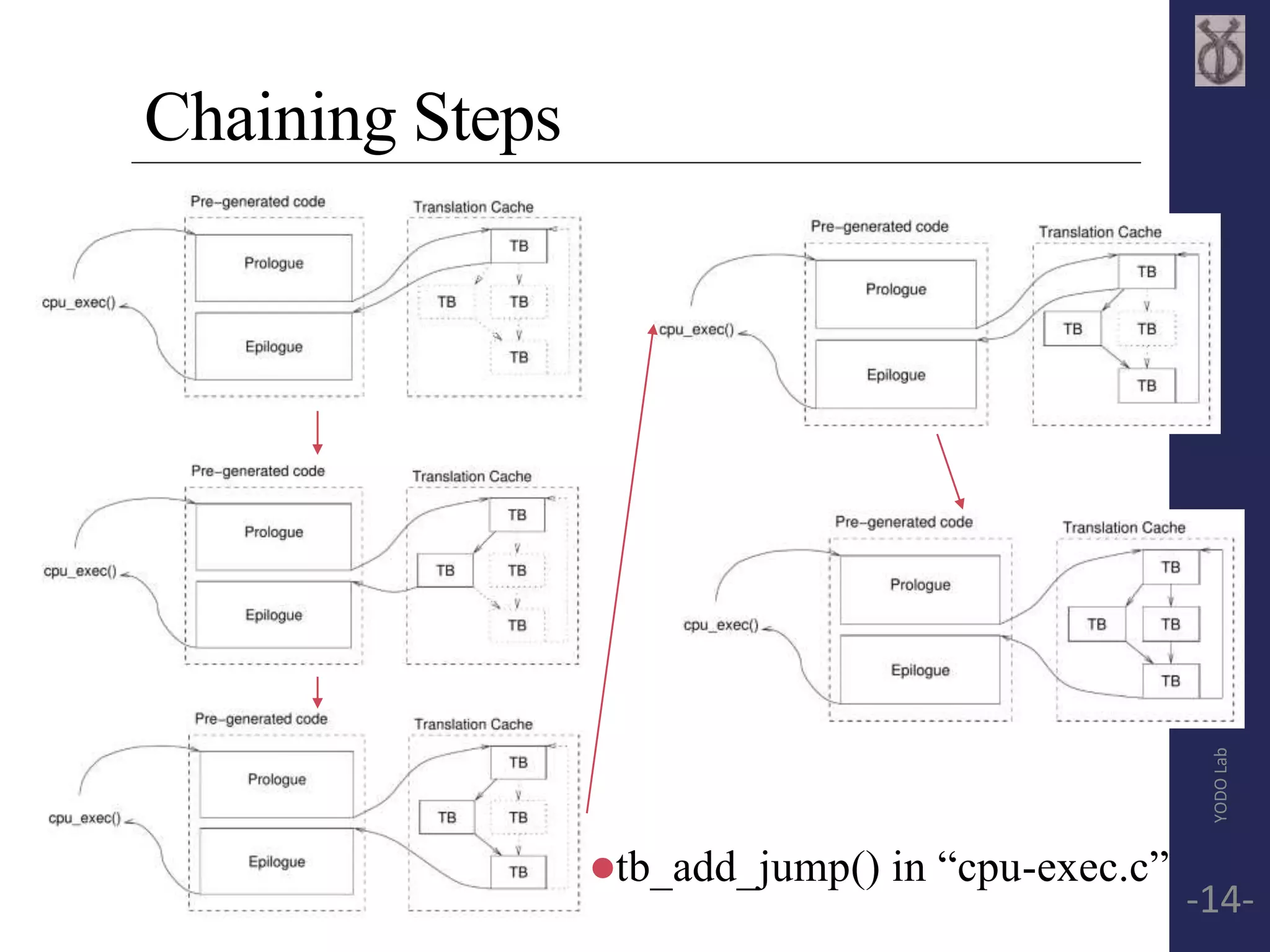
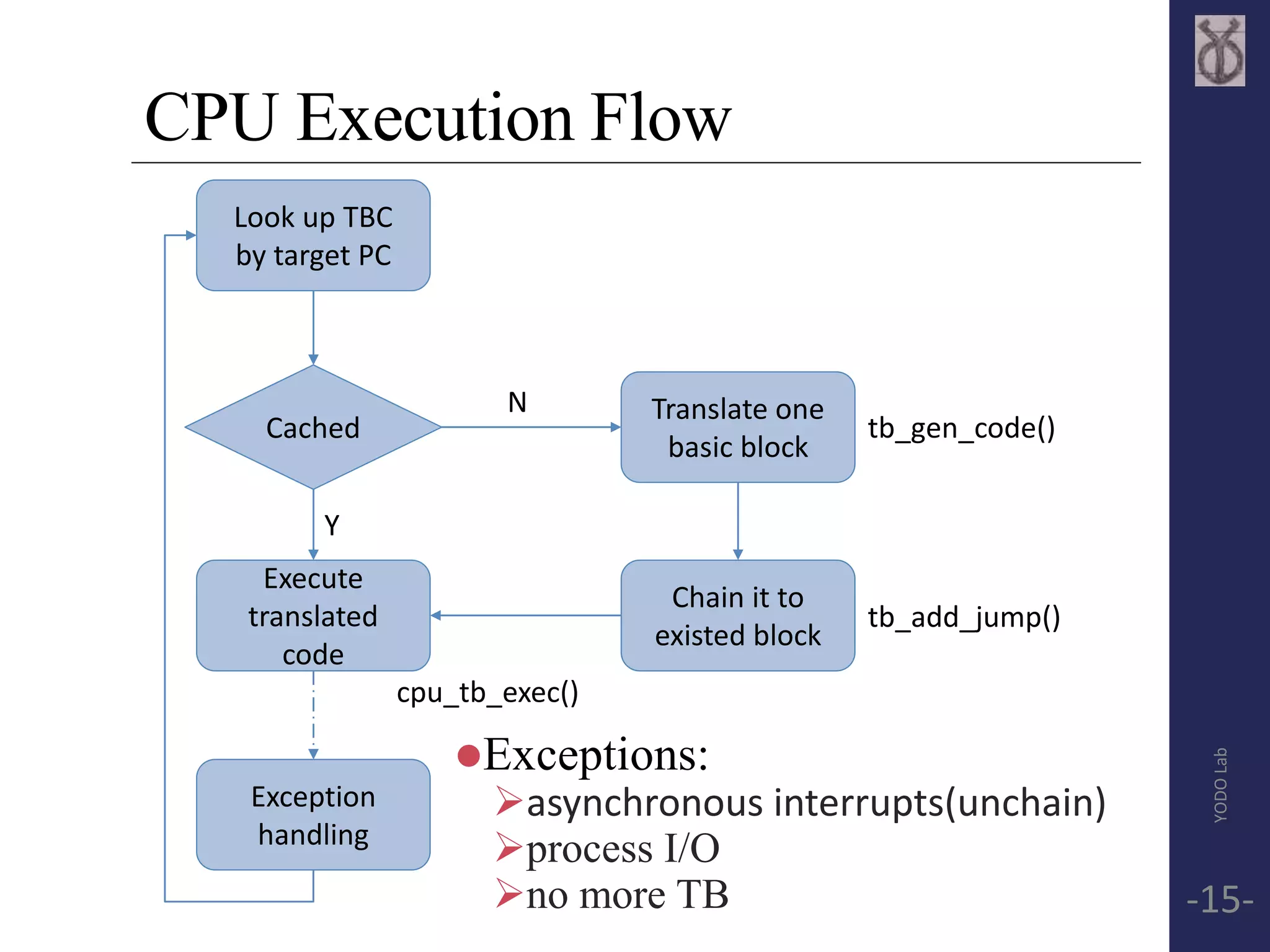
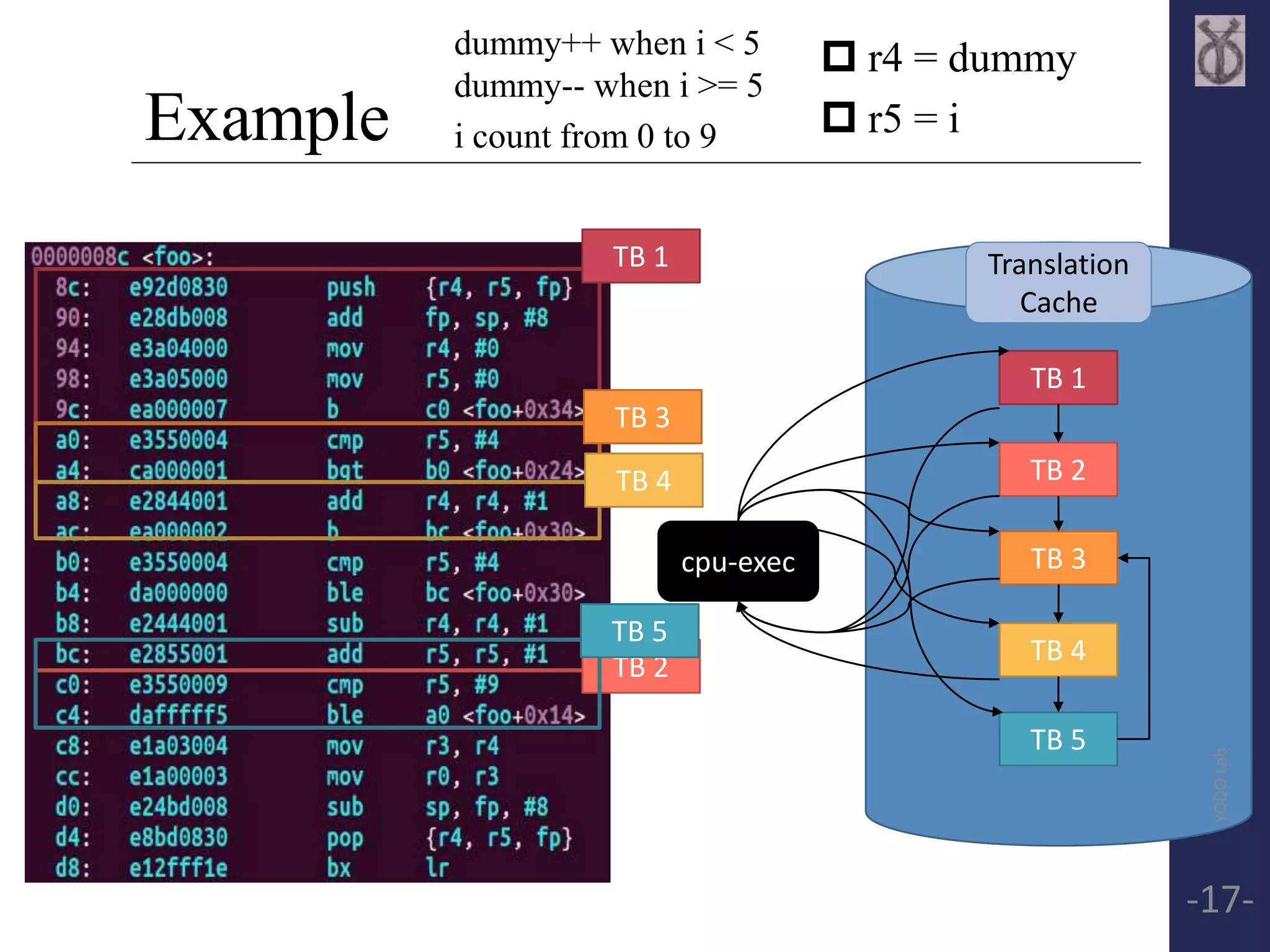
![Basic Block(Translated Block, TB)
Block exit point:
encounter branch(modify PC)
reach page boundary
000081ac<abort>:
81ac: add $sp, $sp #-24
81b0: str $fp, [$sp+#20]
…
81c2: beq $lr
81c6: mov $sp, $fp
…
81d0: ret $lr
Branch
occur
Block 1
Block 2
YODO Lab
-12-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemu-binarytranslation-140930222818-phpapp02/75/QEMU-Binary-Translation-12-2048.jpg)

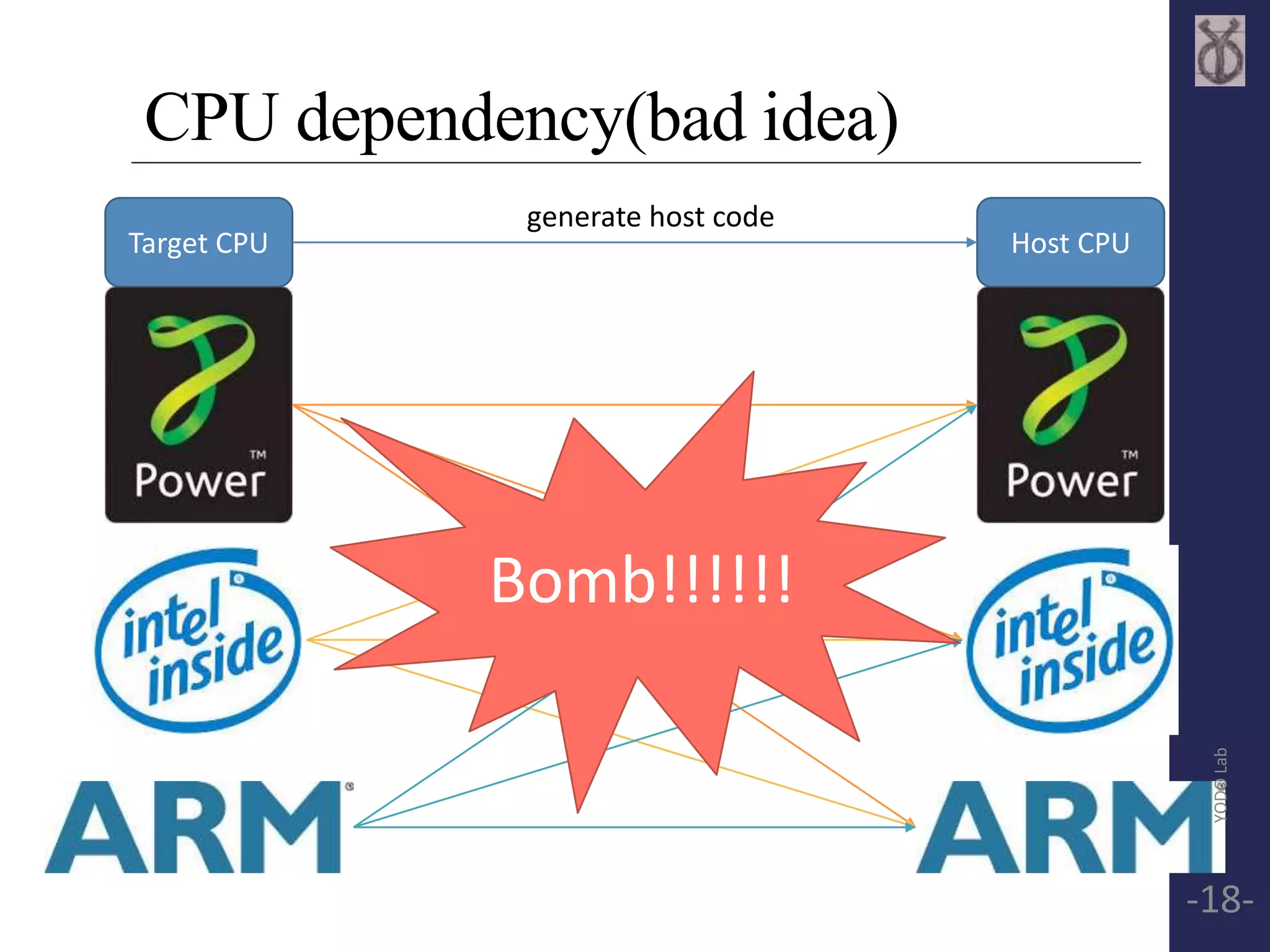
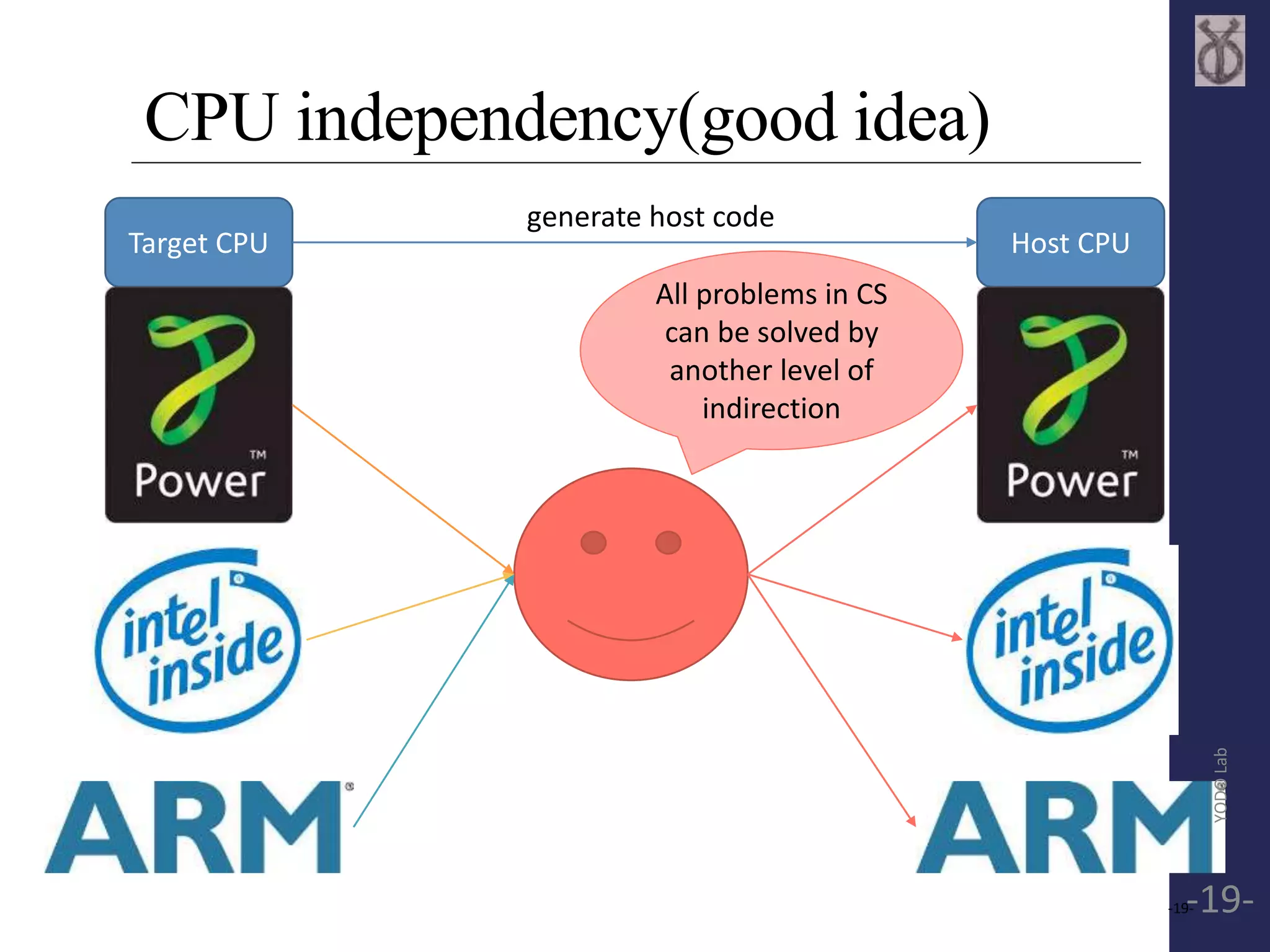
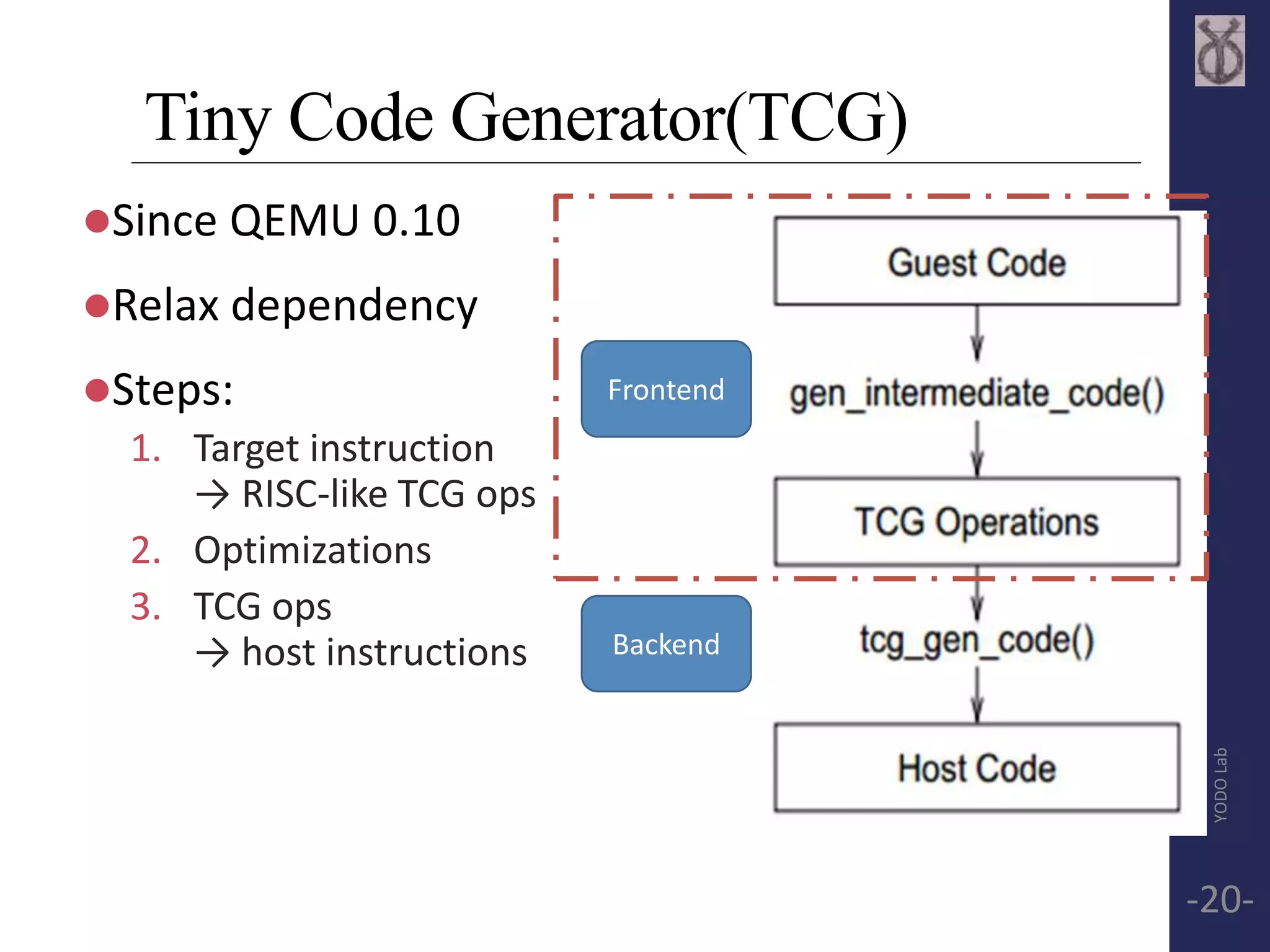
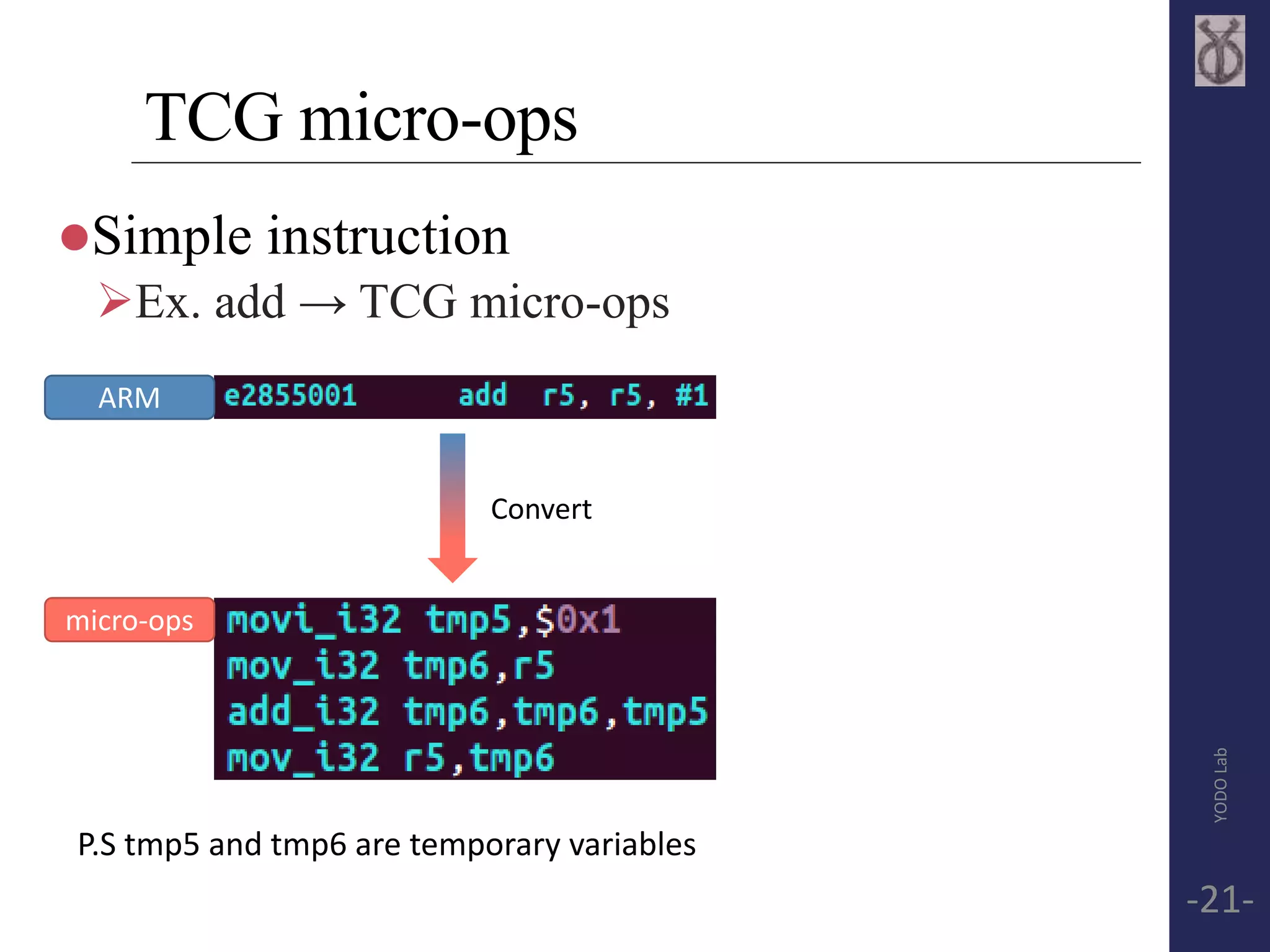
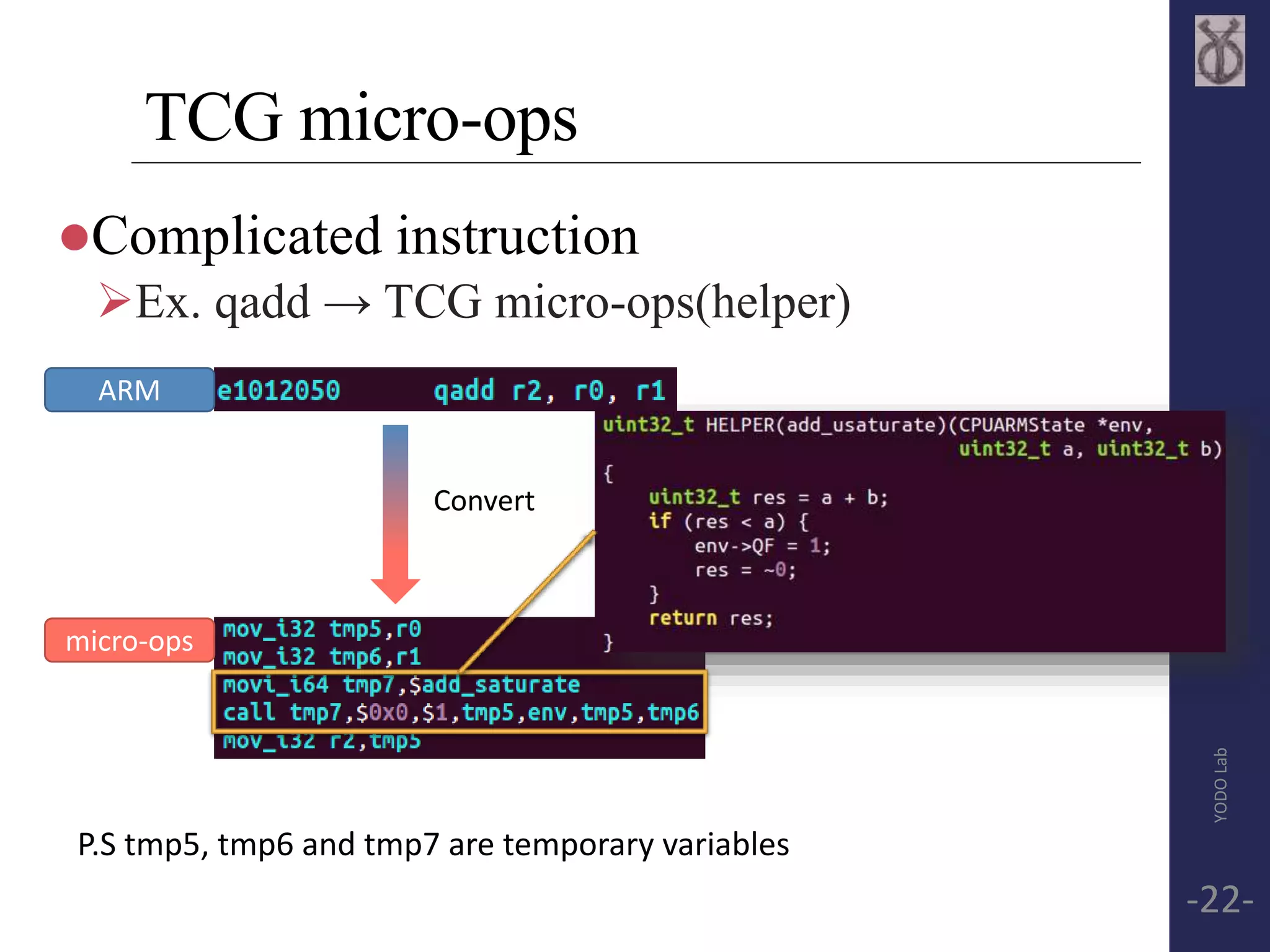

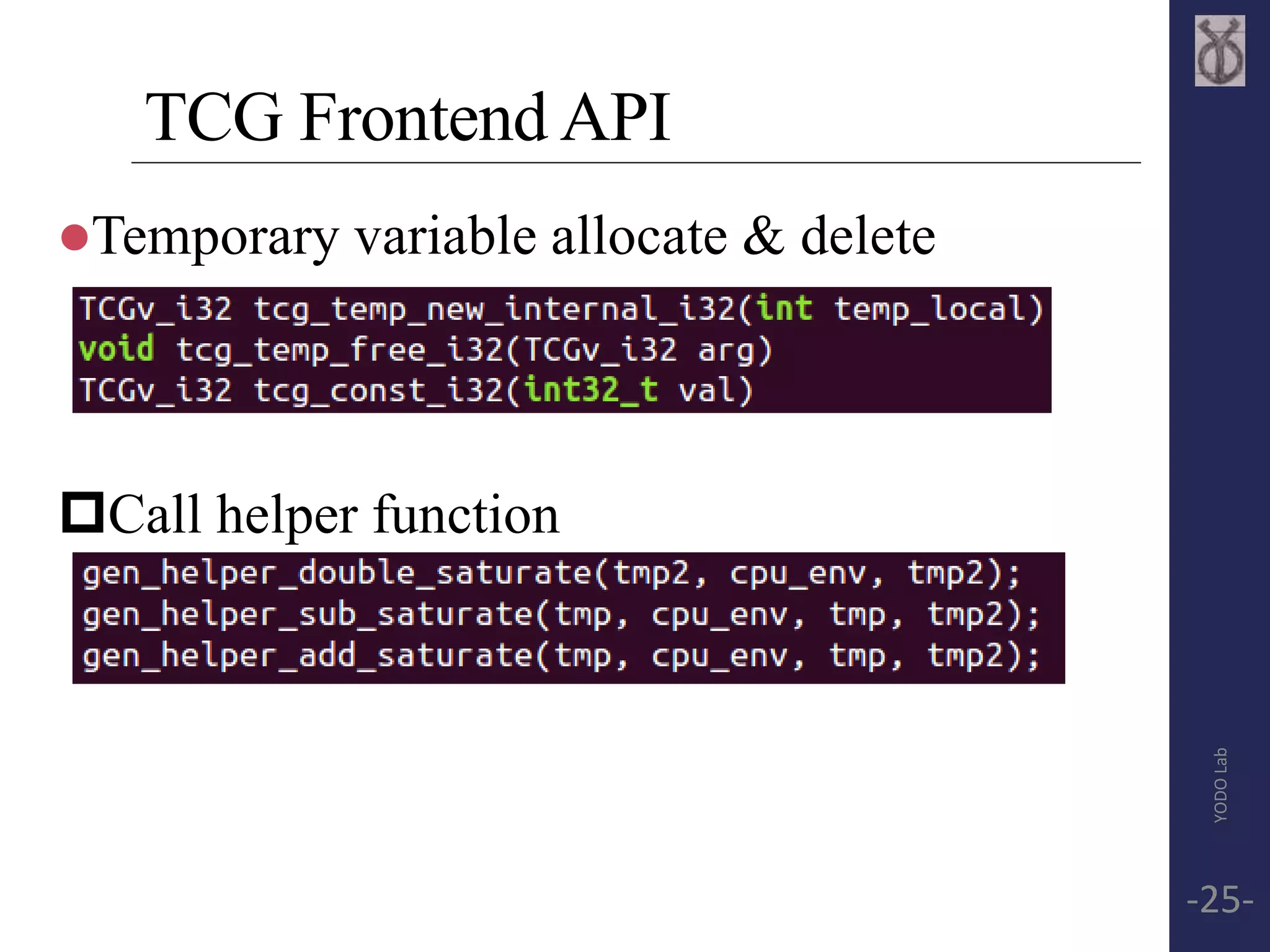
![TCG Frontend API
tcg_gen_<op>[i]_<reg_size>
<op> - operation
[i] - immediate or register
<reg_size> - size of register
YODO Lab
-24-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemu-binarytranslation-140930222818-phpapp02/75/QEMU-Binary-Translation-24-2048.jpg)
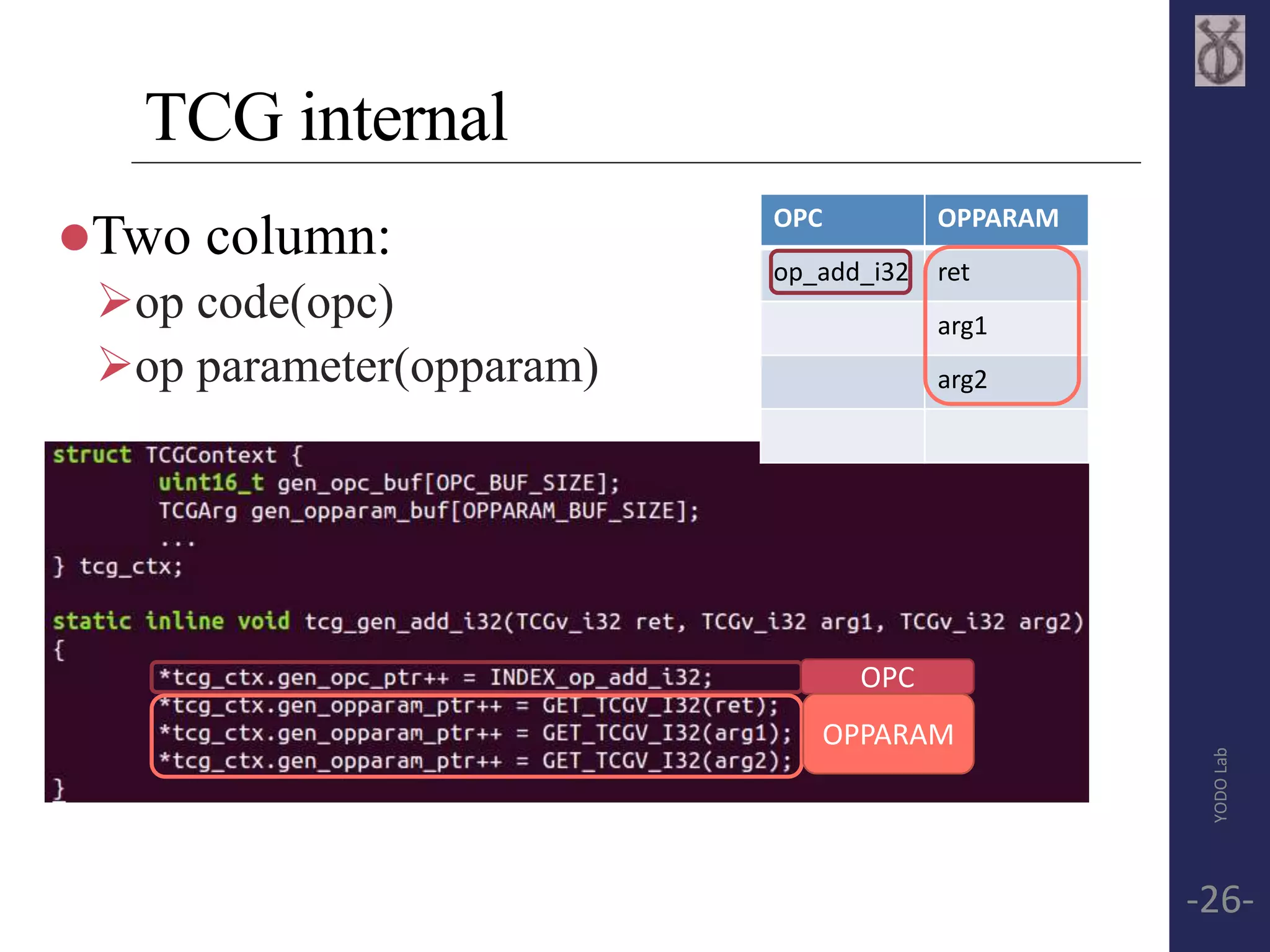
![ARM Convert micro-ops
OPC OPPARAM
op_movi_i32
op_mov_i32
op_add_i32
op_mov_i32
t0
arg2
t1
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
t1
t0
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
YODO Lab
-27-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemu-binarytranslation-140930222818-phpapp02/75/QEMU-Binary-Translation-27-2048.jpg)
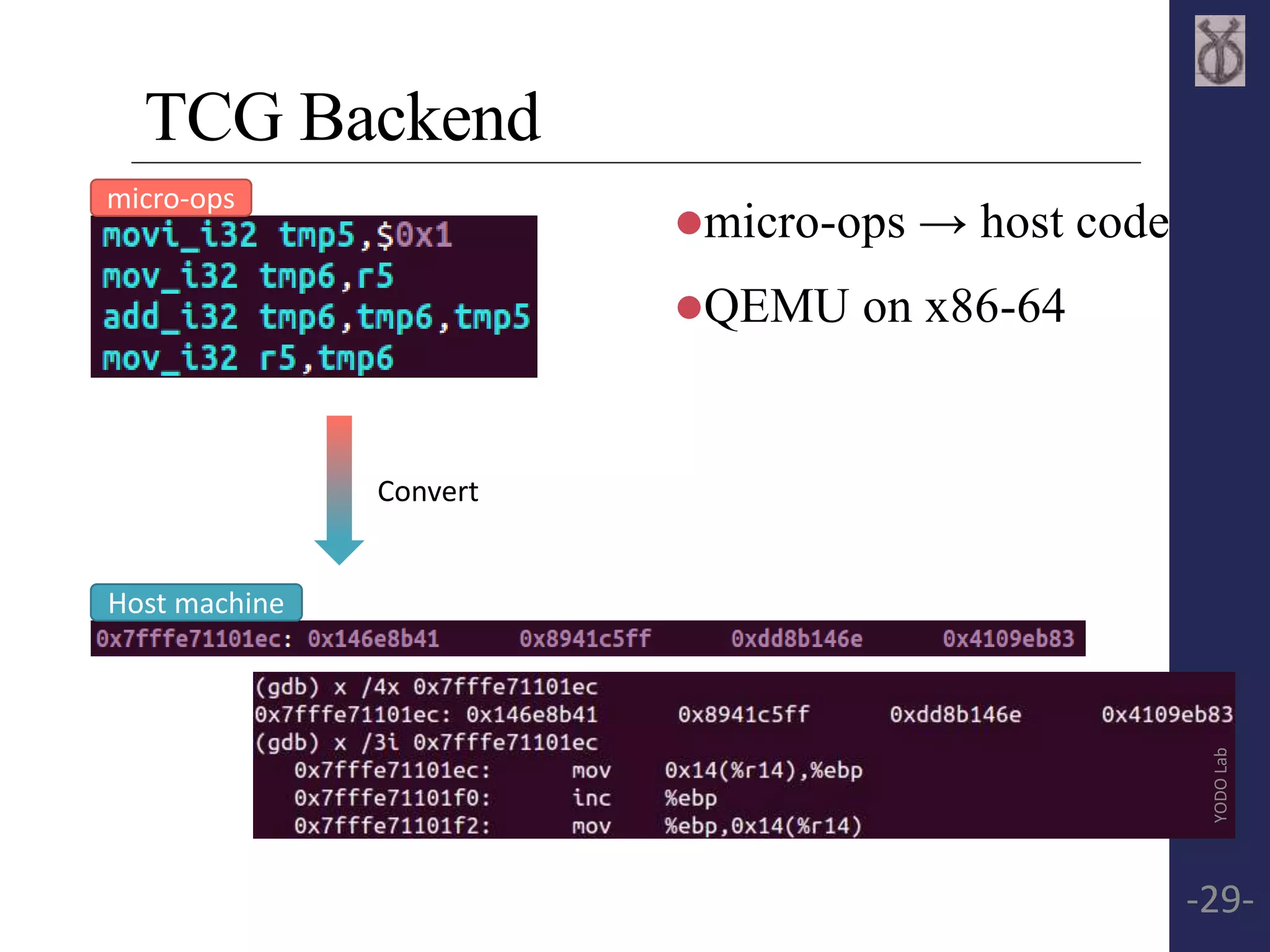
![TCG Backend
Frontend
Backend
OPC OPPARAM
op_movi_i32
op_mov_i32
op_add_i32
op_mov_i32
t0
arg2
t1
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
t1
t0
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
YODO Lab
-28-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemu-binarytranslation-140930222818-phpapp02/75/QEMU-Binary-Translation-28-2048.jpg)
![TCG Backend
x86-64 backend example
OPC OPPARAM
op_movi_i32
op_mov_i32
op_add_i32
op_mov_i32
t0
arg2
t1
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
t1
t0
cpu_R[arg1]
t1
YODO Lab
-30-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemu-binarytranslation-140930222818-phpapp02/75/QEMU-Binary-Translation-30-2048.jpg)