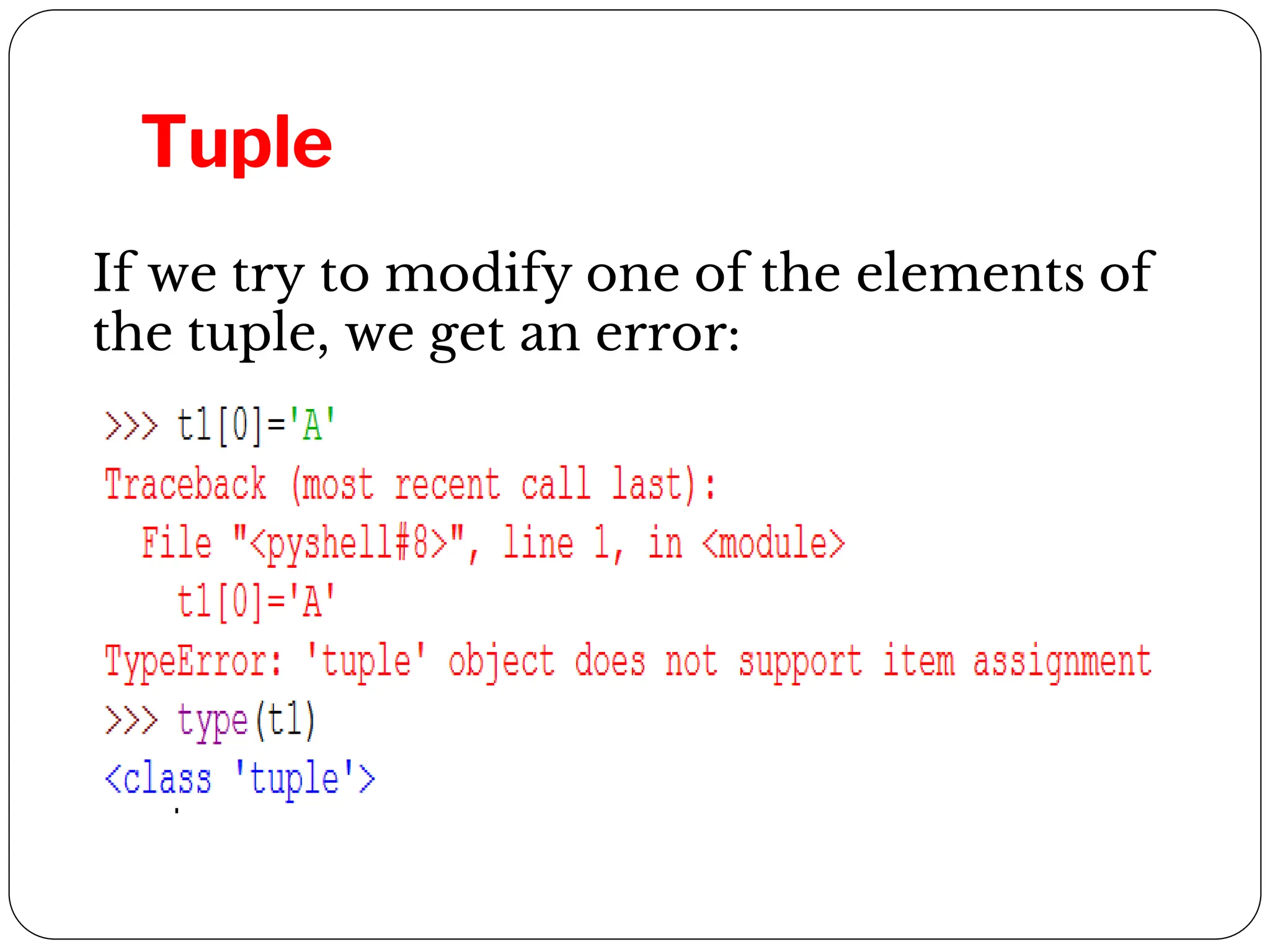
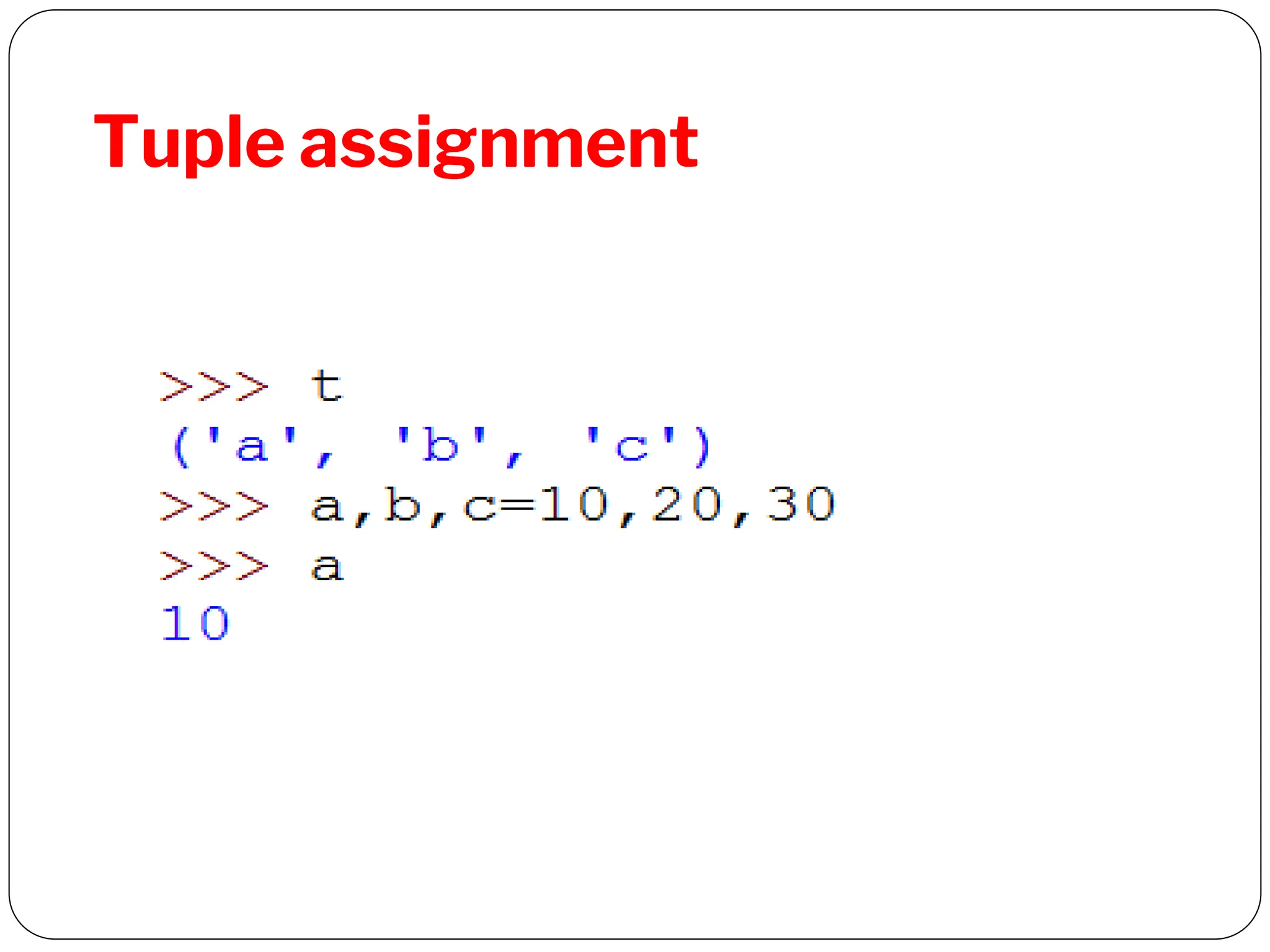
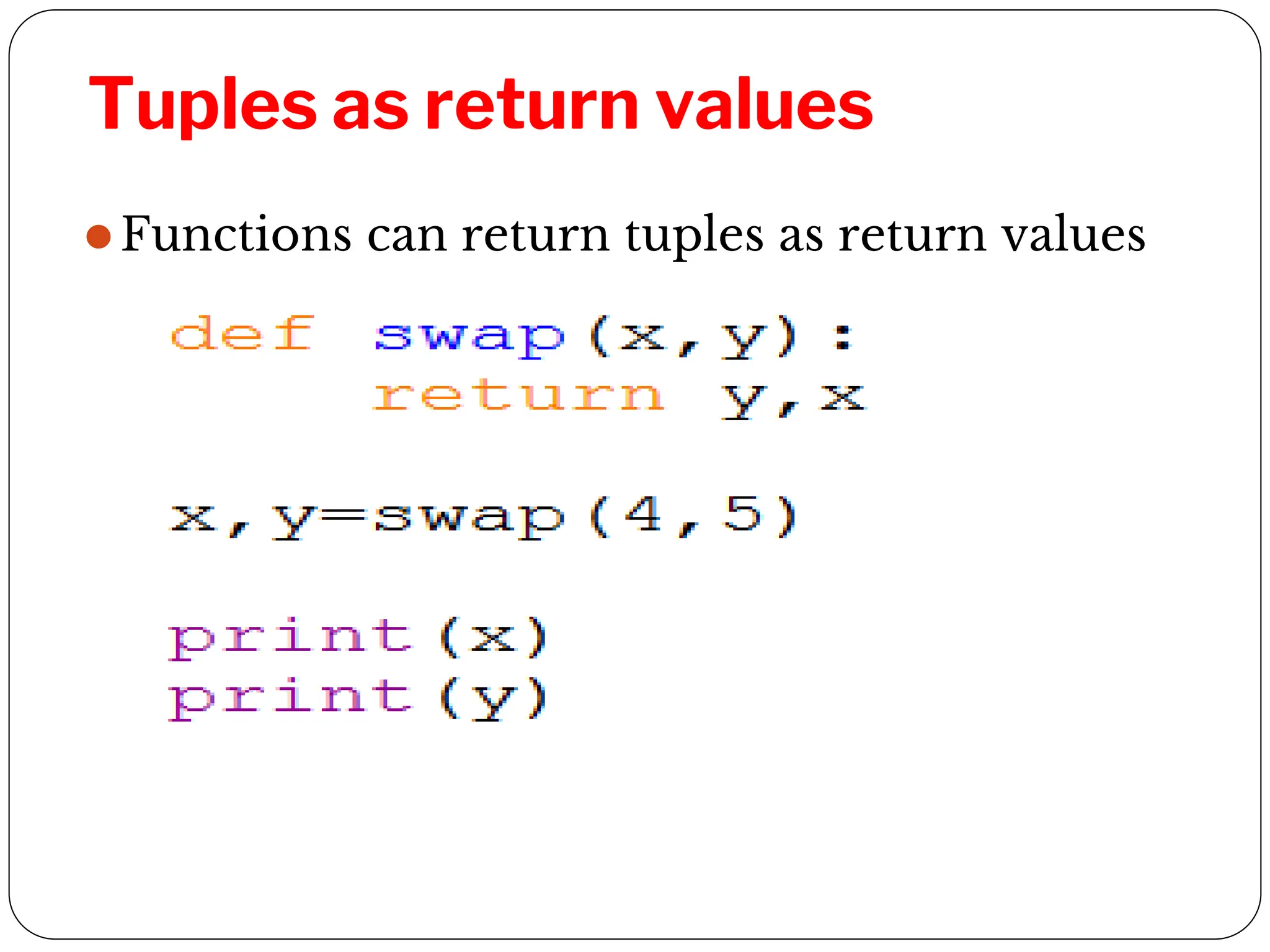
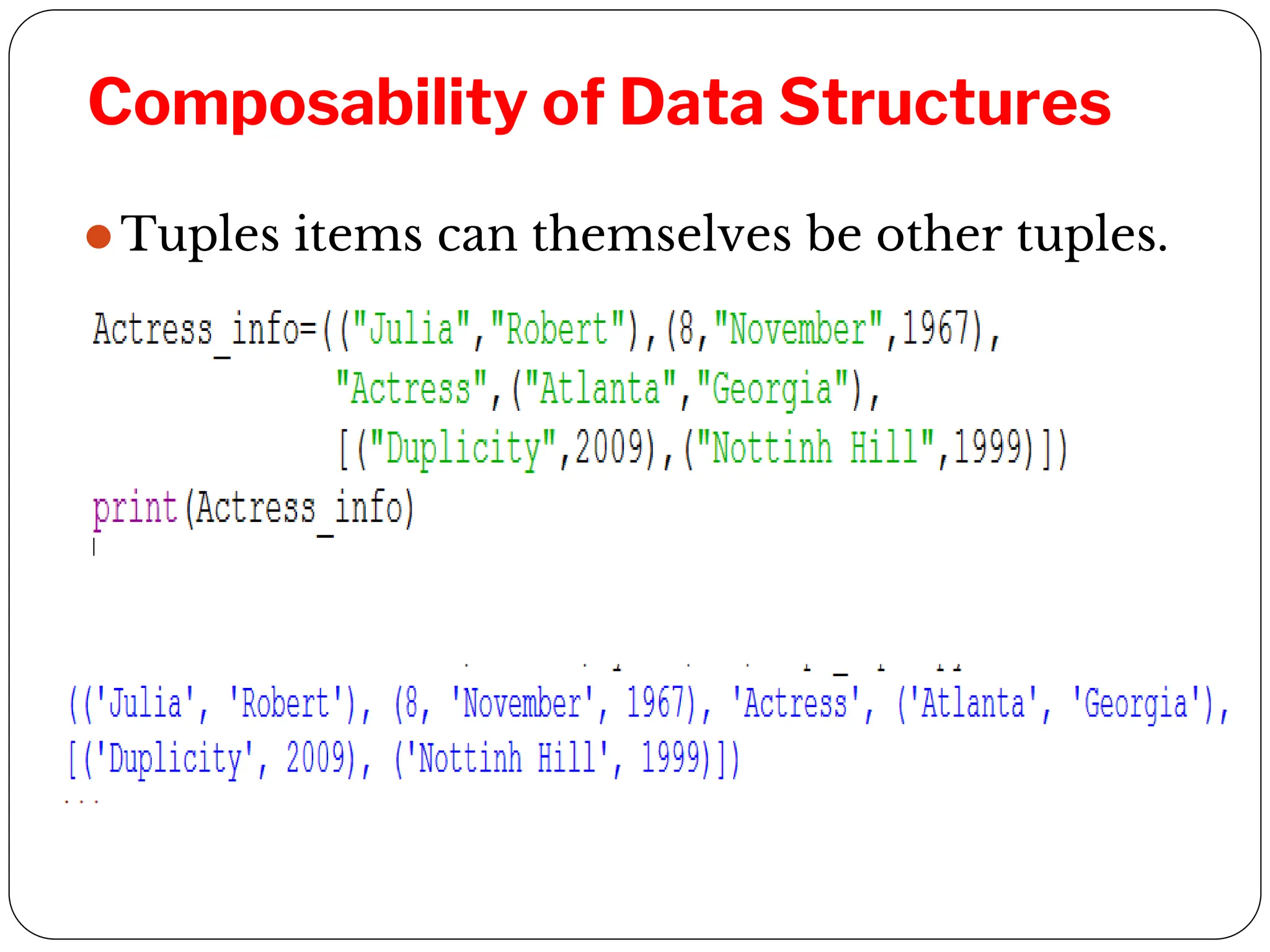
This document provides an introduction to Python programming unit 2 which covers lists, tuples, and dictionaries. Lists allow ordered sets of values accessed by index and can be modified. Tuples are similar to lists but immutable. Dictionaries store elements as key-value pairs that can be accessed by key. Common operations for each include accessing elements, determining length, membership testing, slicing, and built-in methods. Tuples can group data and be used as return values or in nested structures. Dictionaries allow creation and modification of elements through operations and methods.


![LIST VALUES
⚫Ways to create a new list
⚫enclose the elements in square brackets [ ]:
Eg1 [10, 20, 30, 40]
Eg2 ["spam", "bungee", "swallow"]
Eg3 ["hello", 2.7, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-4-2048.jpg)
![LIST VALUES
⚫ Lists that contain consecutive integers:
⚫ Empty list it is denoted [].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-5-2048.jpg)


















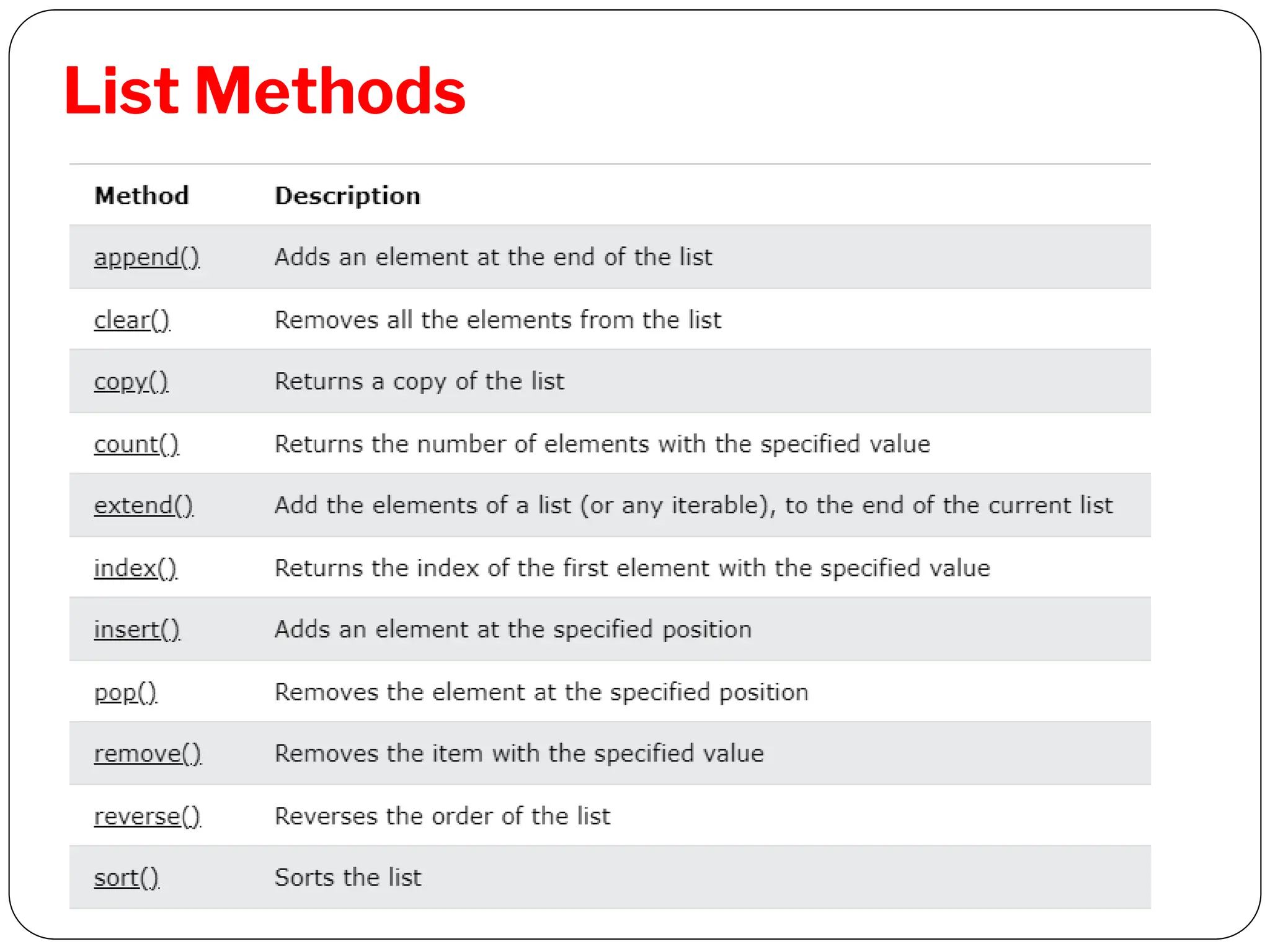
![List Methods
1. append()
syntax
list.append (element)
['Mathematics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000, 20544]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-30-2048.jpg)
![List Methods
insert()
syntax
list.insert(position, element)
['Mathematics', 'chemistry', 10087,
1997, 2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-31-2048.jpg)






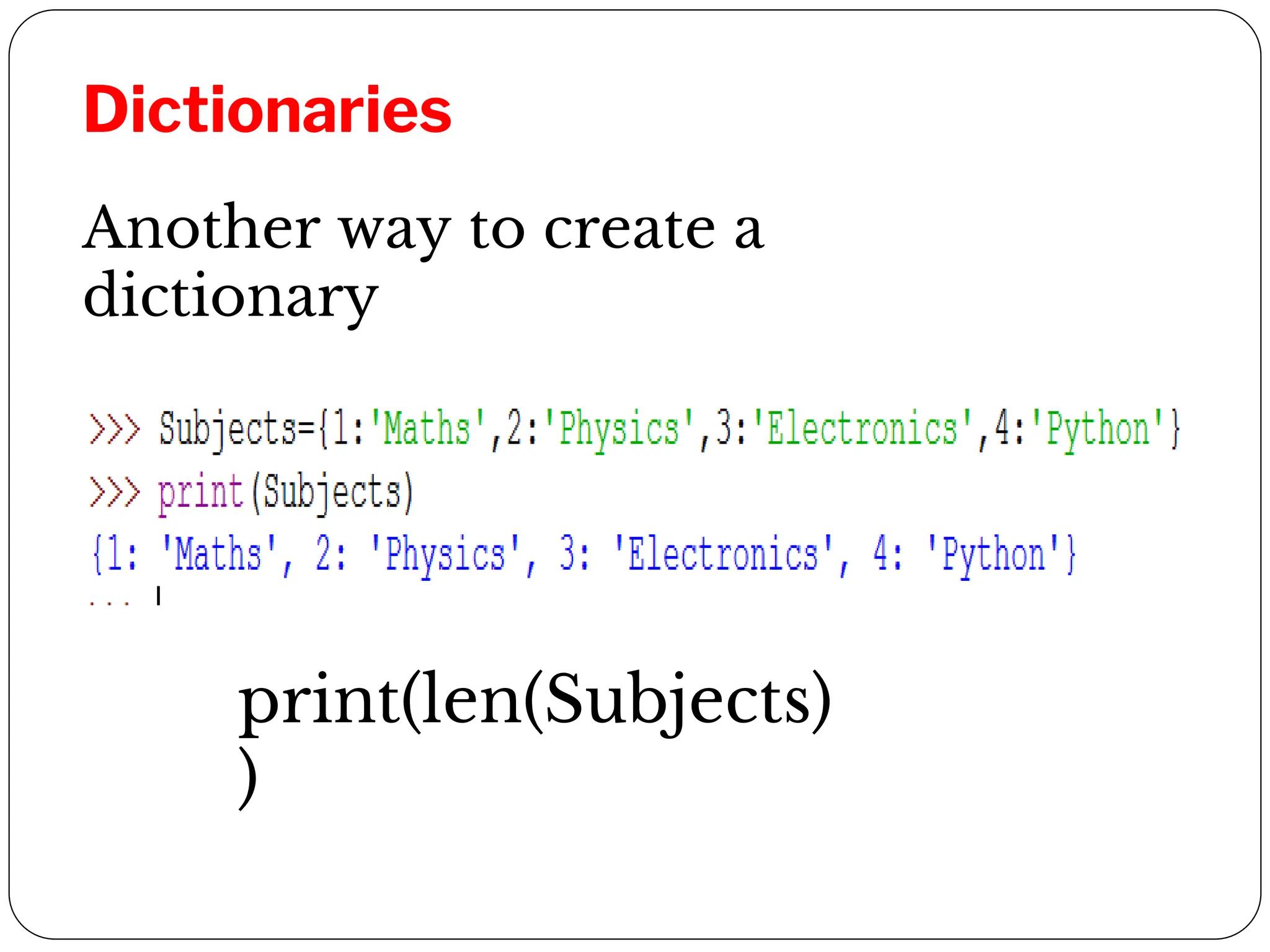

![Dictionary methods
▪ A method is similar to a function, it
takes arguments and returns a value
but the syntax is different.
▪ print(Subjects.keys())
dict_keys([2, 3, 4])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-50-2048.jpg)
![Dictionary methods
▪ The items method returns both, in the
form of a list of tuples—one for each
key-value pair:
print(Subjects.items())
dict_items([(2, 'Physics'), (3,
'Electronics'), (4, 'Python')])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-unit2-240105153652-b38caf59/75/Python-Ukllllllllllllllllllllllllllllnit-2-pdklllllllf-51-2048.jpg)

