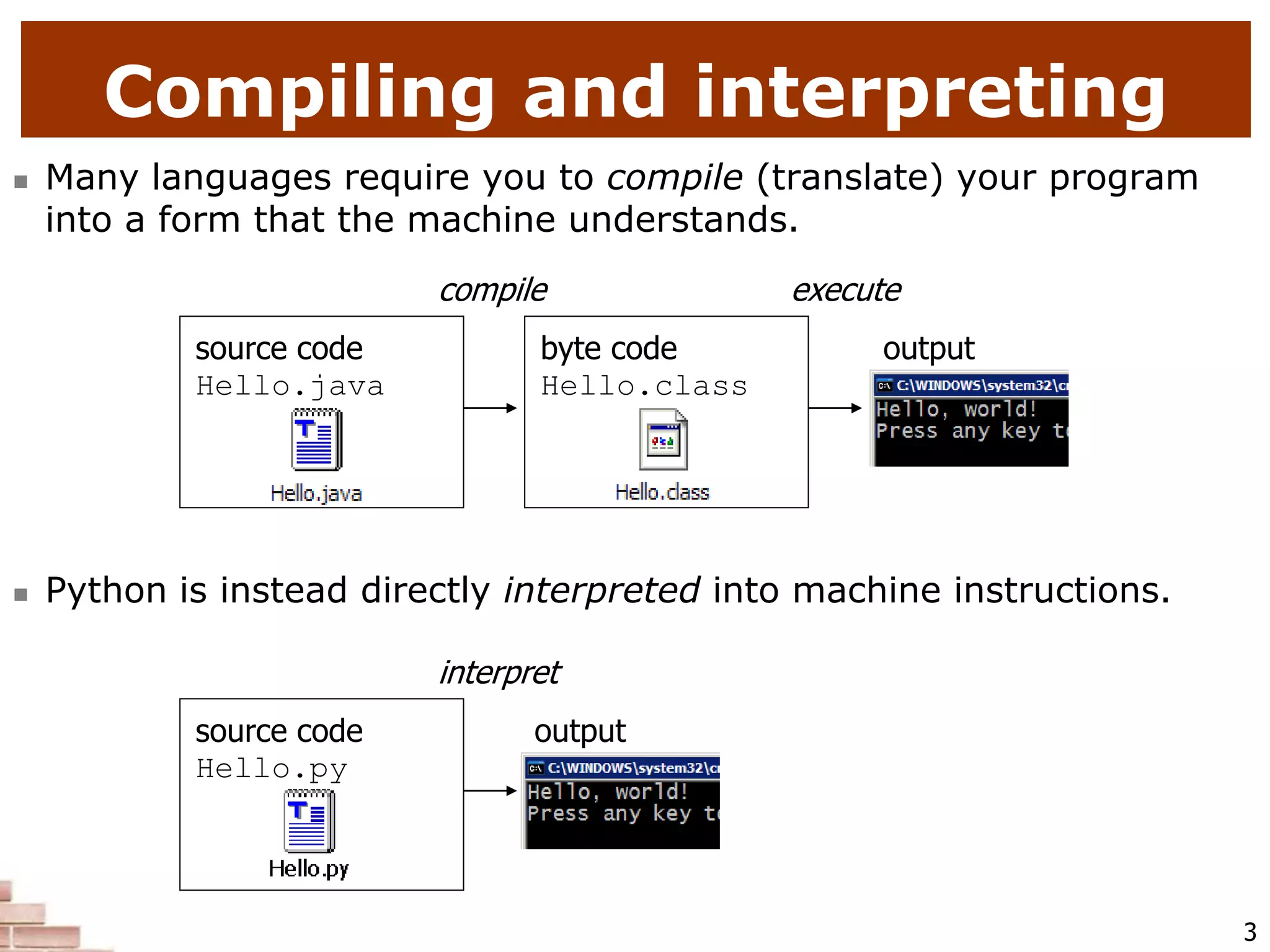
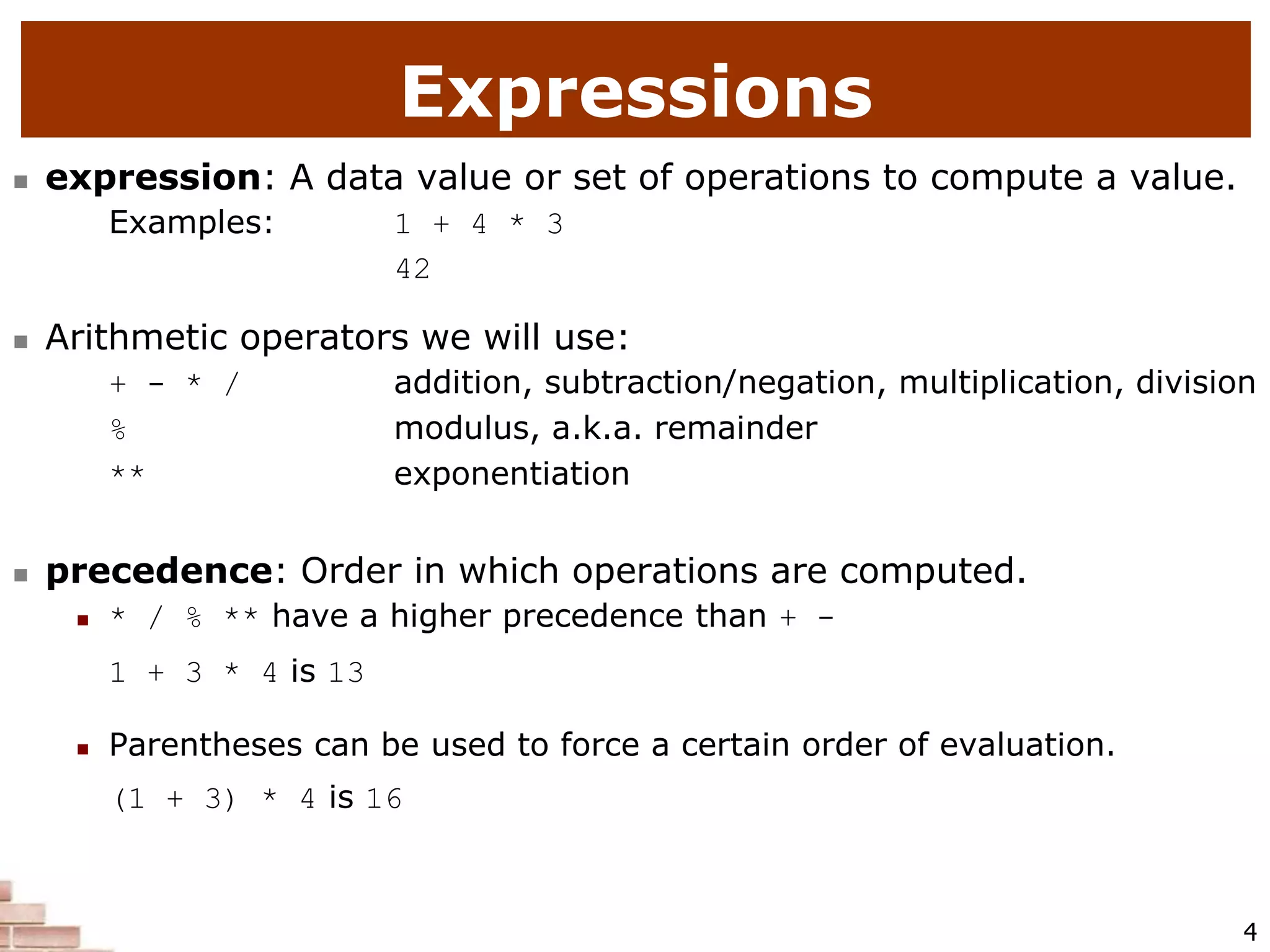
This document provides an introduction to programming with Python. It discusses several influential early programming languages like FORTRAN, COBOL, LISP, and BASIC. It also covers key Python concepts like expressions, variables, printing output, user input, repetition with for loops and while loops, conditional execution with if/else statements, string processing, and file I/O. The document is intended to teach basic Python syntax and structures to newcomers of the language.









![17
Indexes
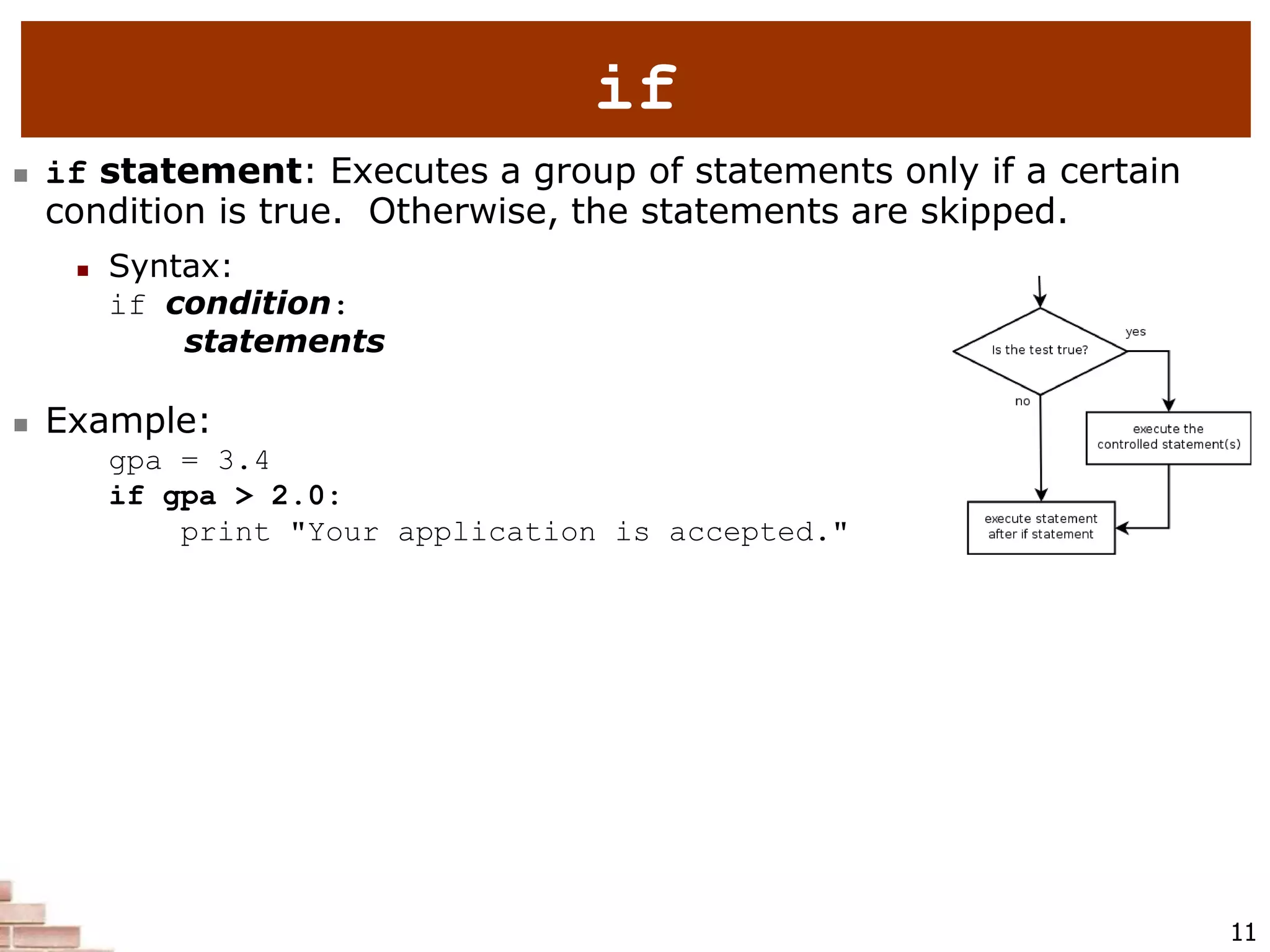
Characters in a string are numbered with indexes starting at 0:
Example:
name = "P. Diddy"
Accessing an individual character of a string:
variableName [ index ]
Example:
print name, "starts with", name[0]
Output:
P. Diddy starts with P
index 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
character P . D i d d y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-200504143126/75/Python-17-2048.jpg)