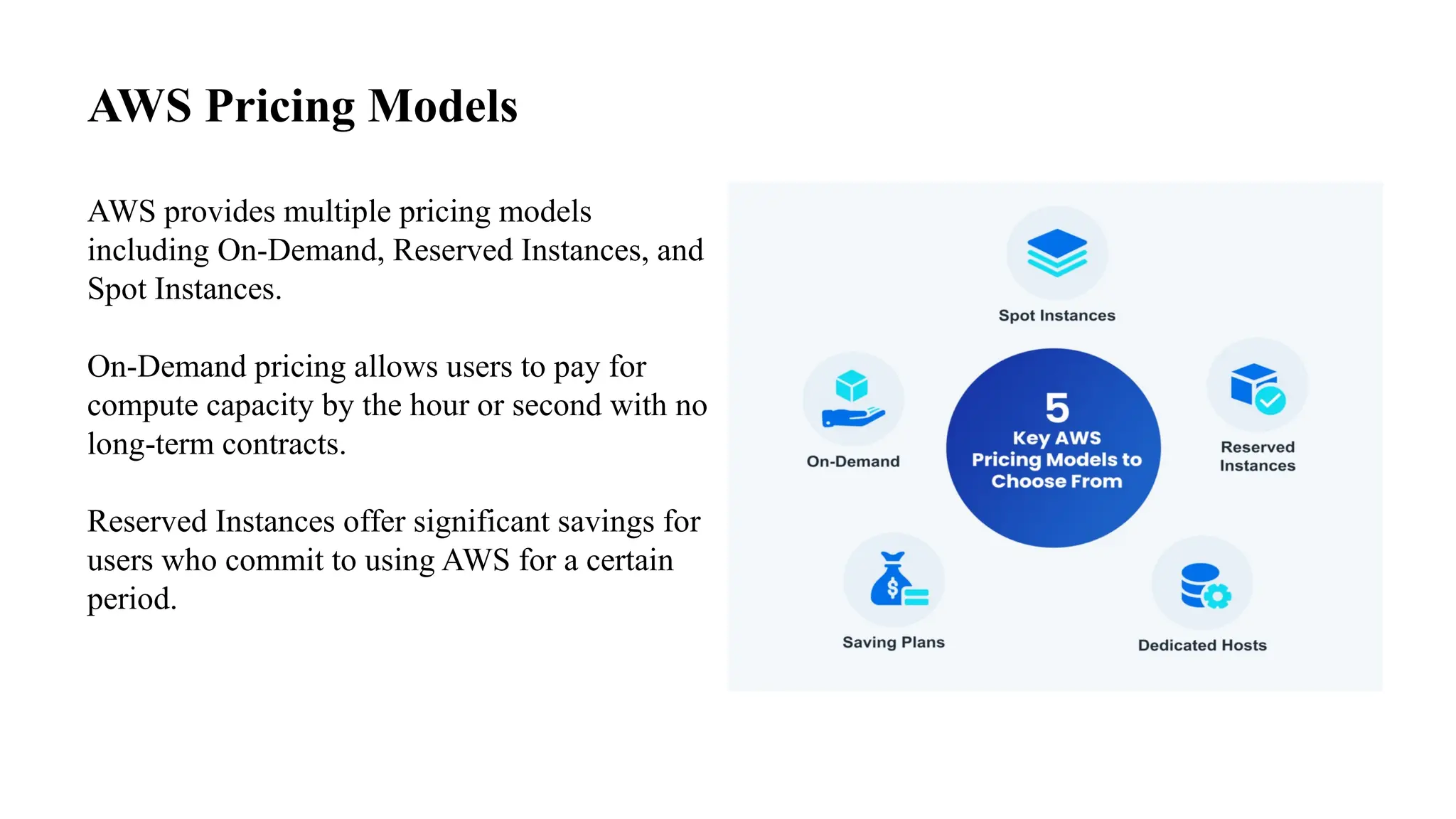
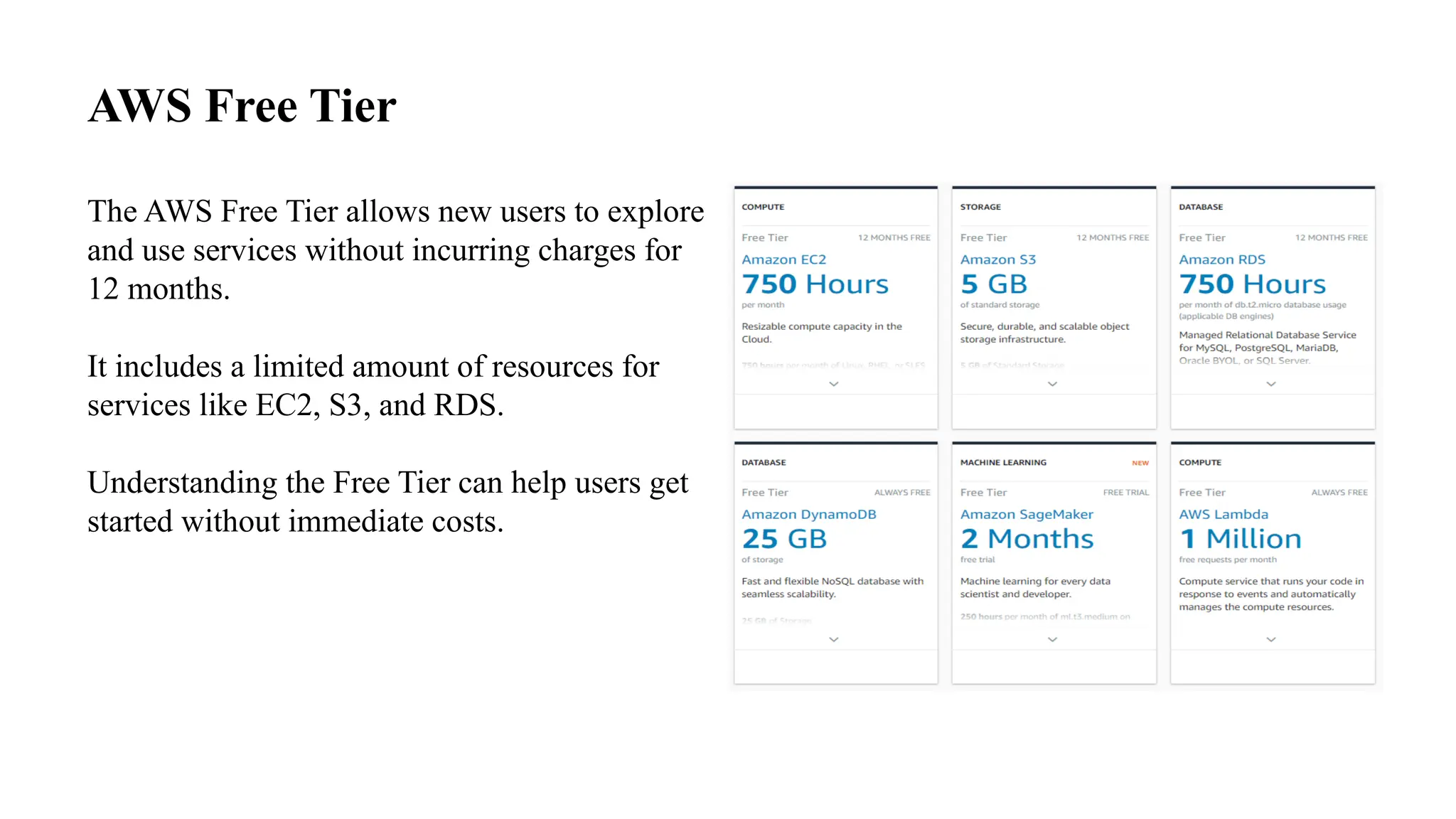
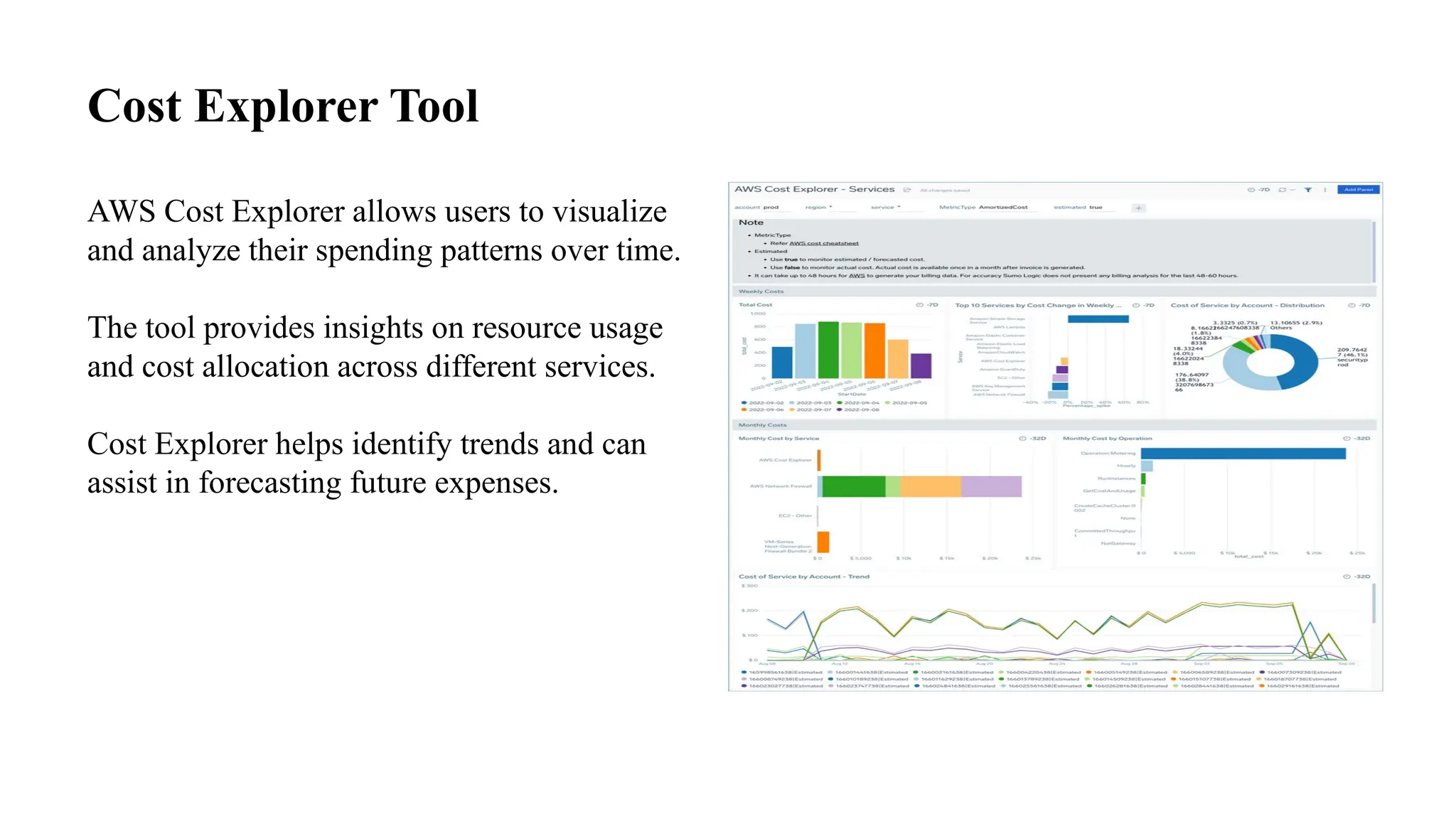
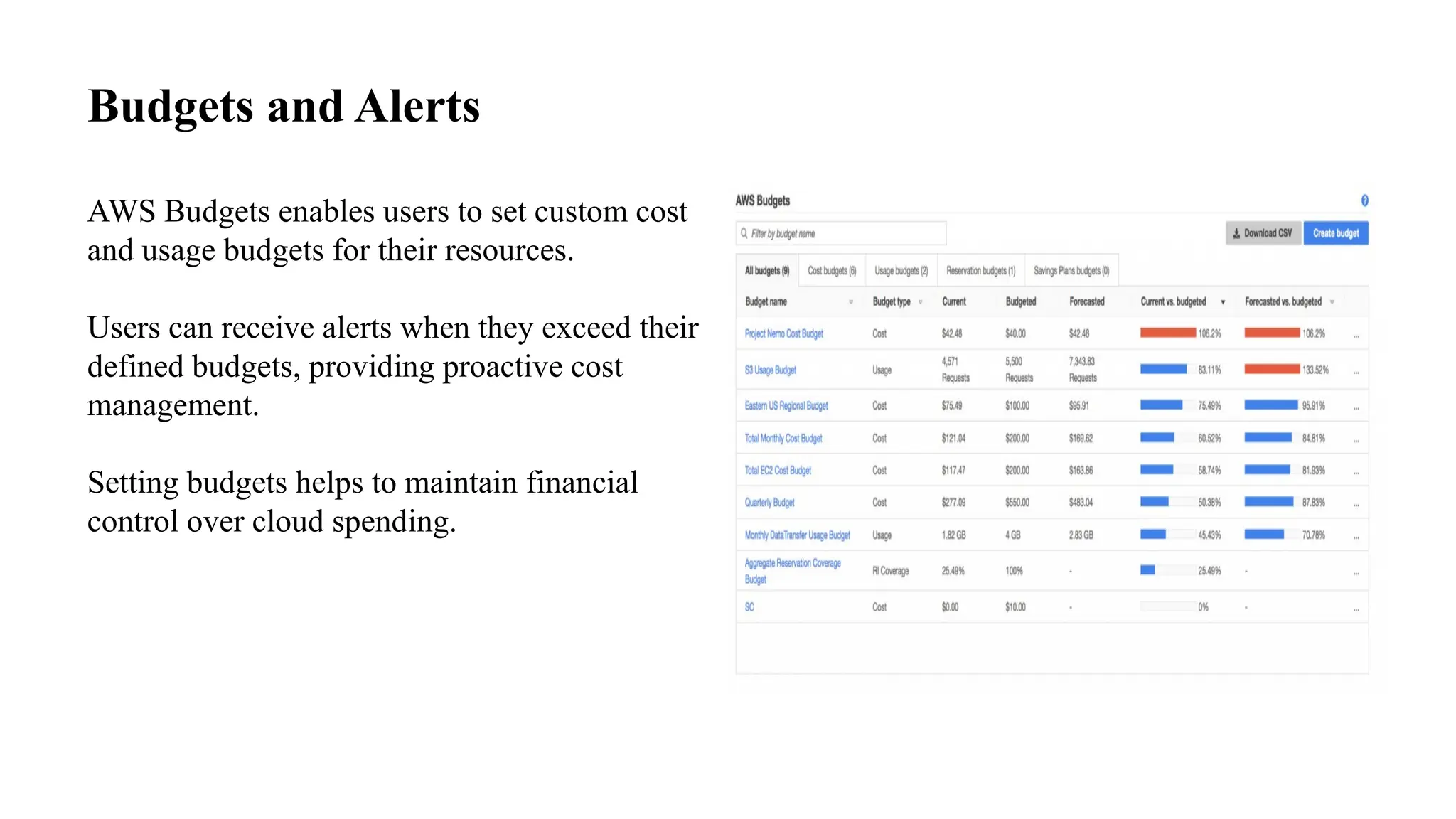
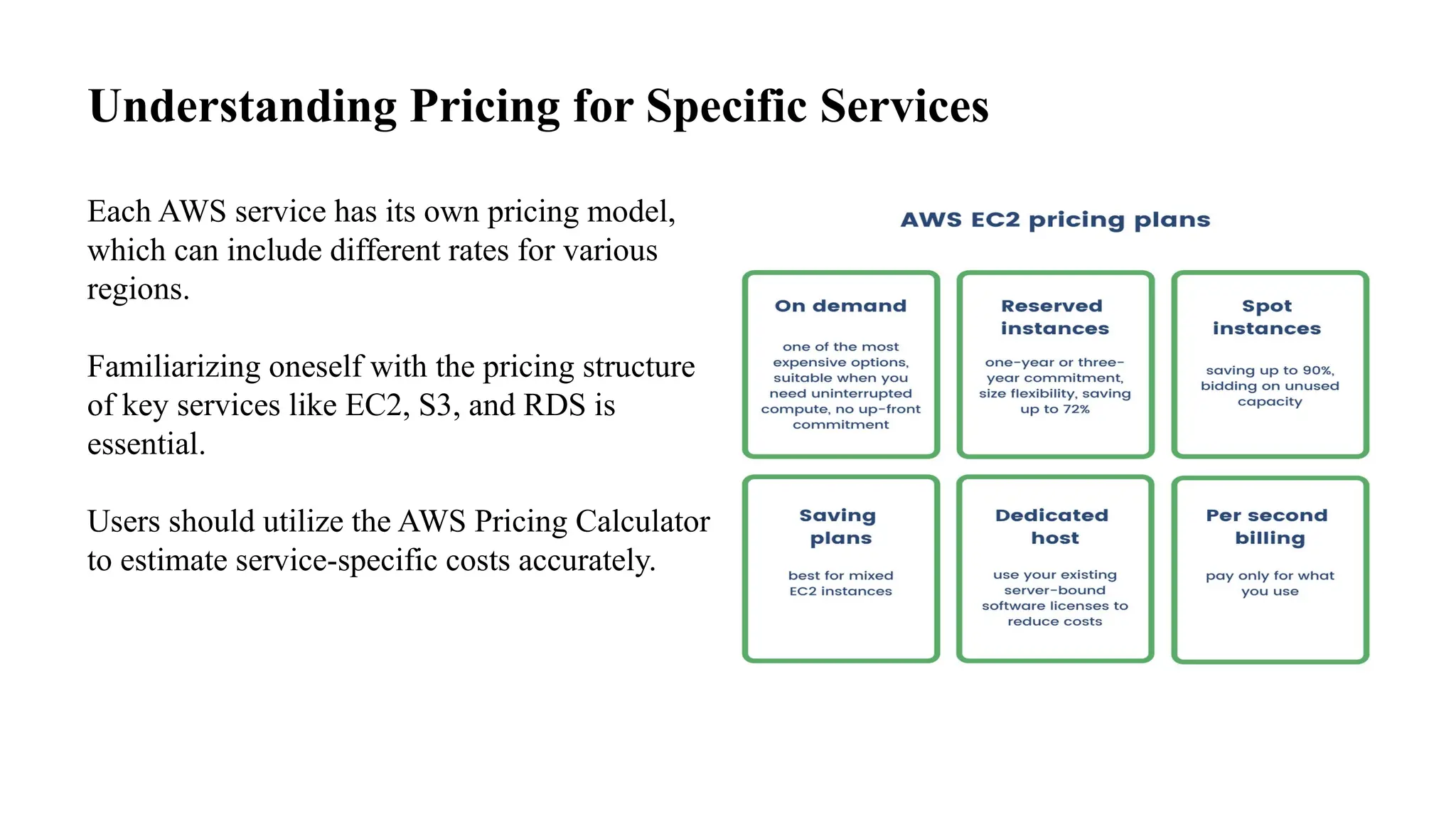
This document provides an overview of AWS pricing and cost management strategies essential for effective budgeting. It covers various pricing models such as on-demand, reserved instances, and spot instances, as well as the AWS free tier and tools like the AWS Pricing Calculator and Cost Explorer. Best practices for cost optimization, monitoring, and utilizing third-party tools are also discussed to help organizations manage their AWS expenditures efficiently.