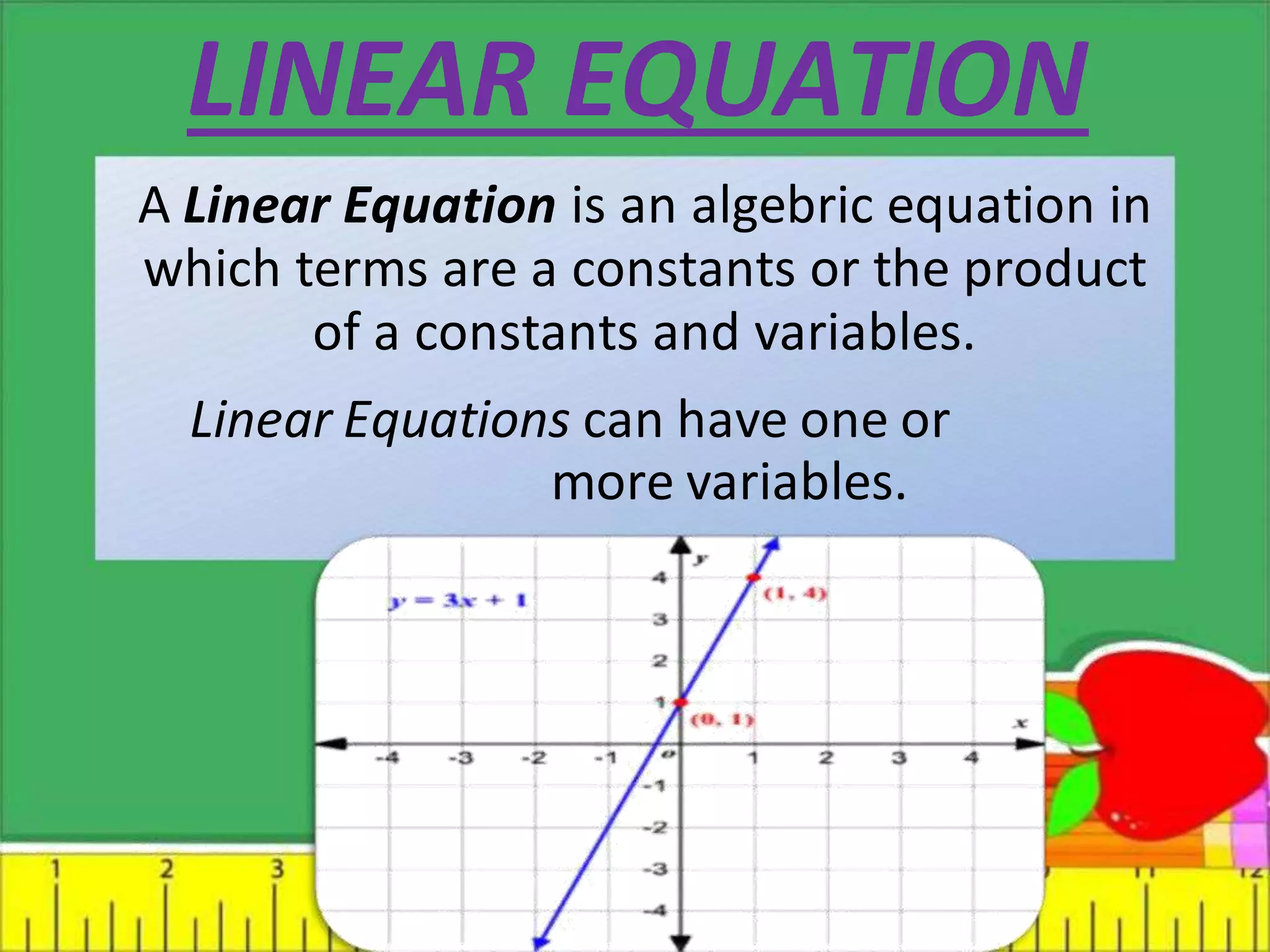
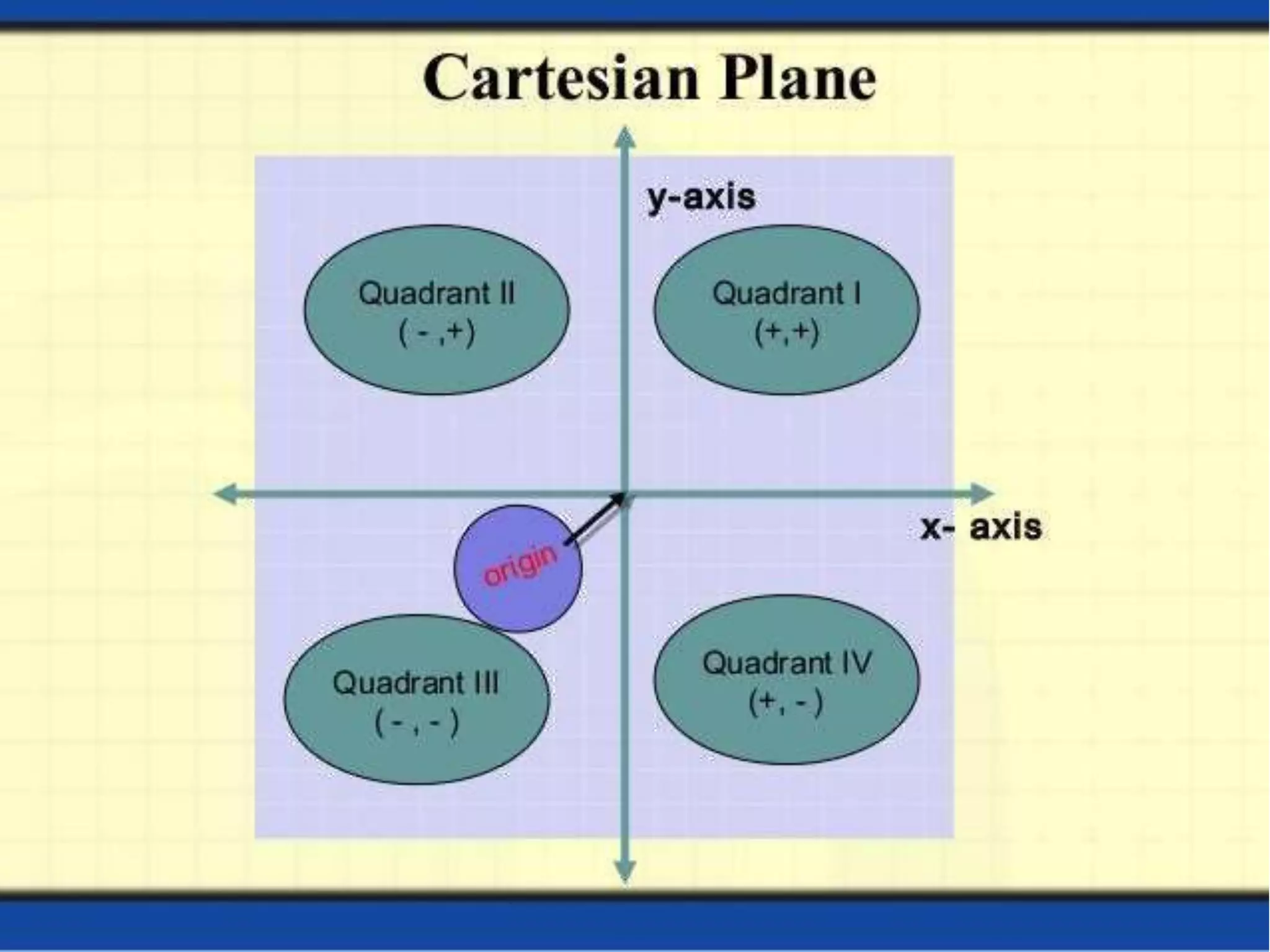
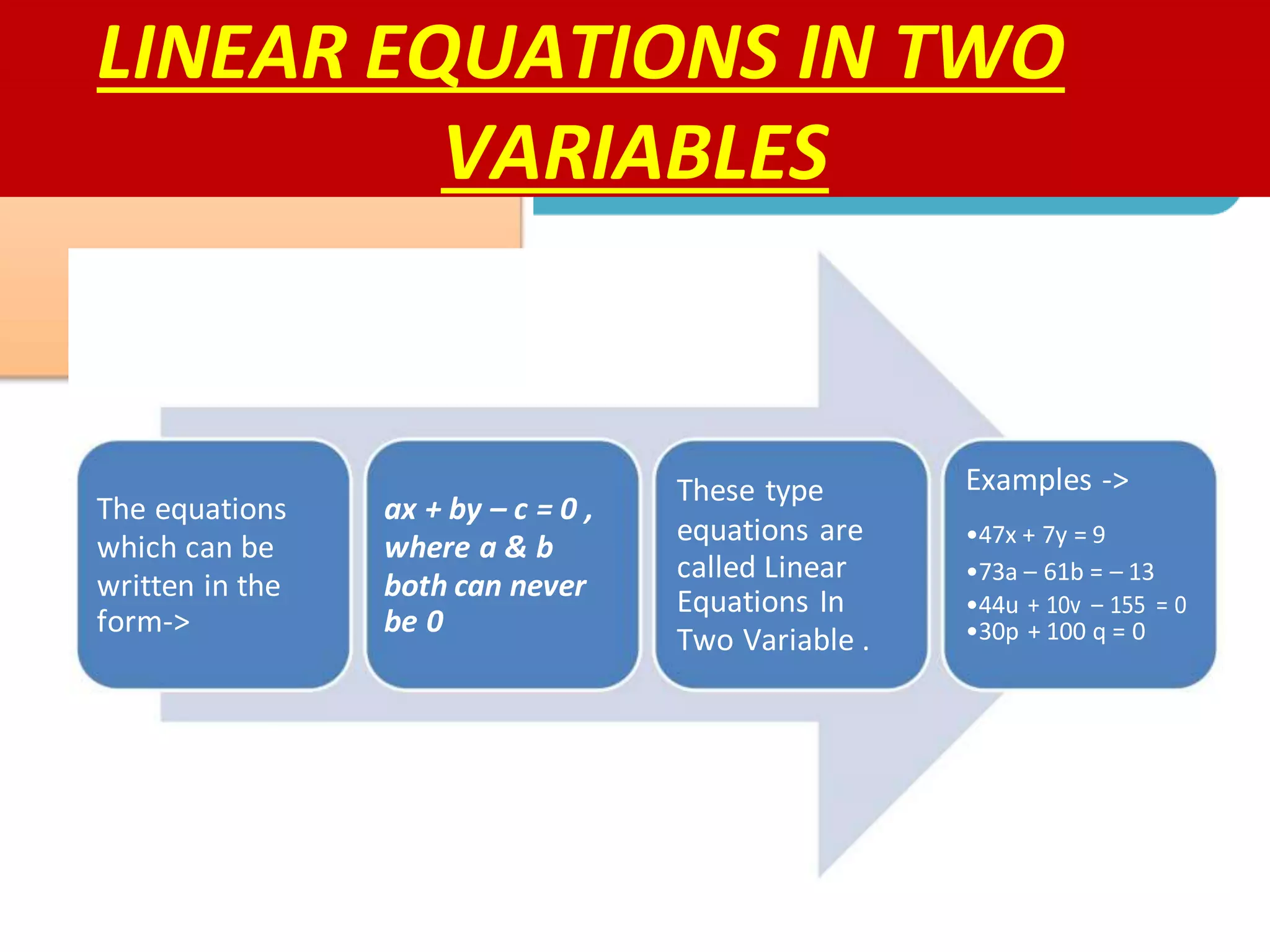
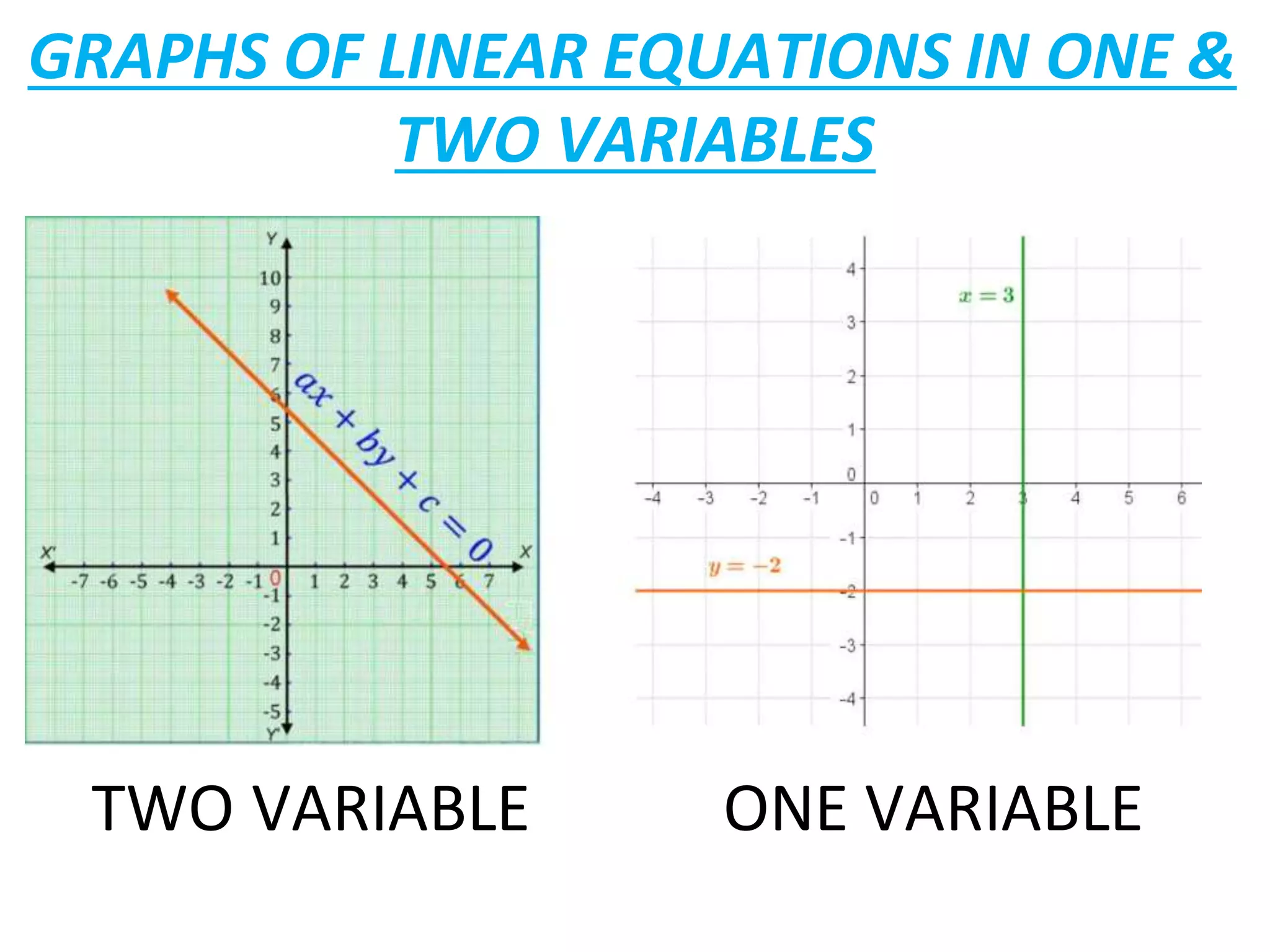
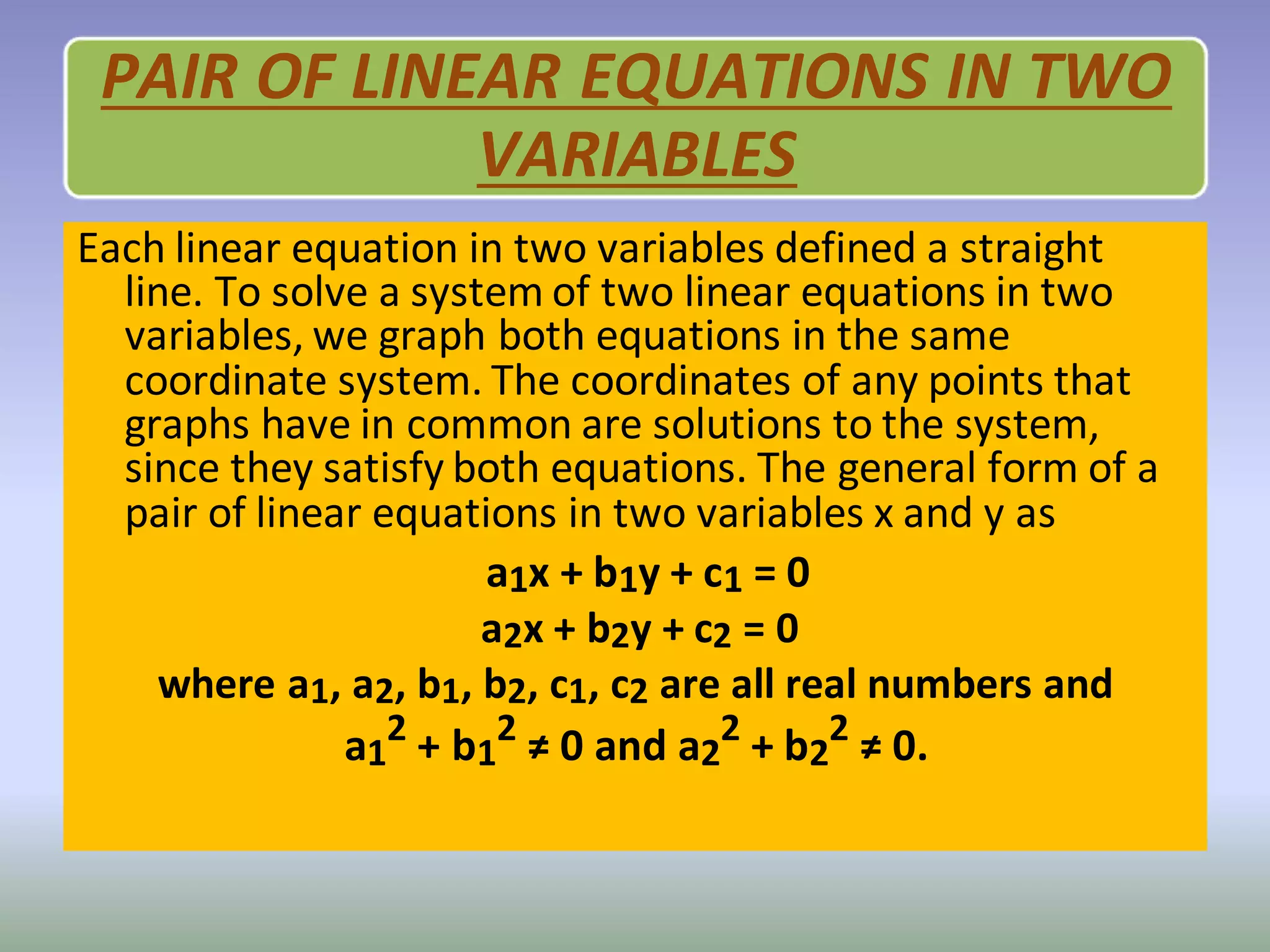
Linear equations are algebraic equations where terms are constants or products of constants and variables. There are two main types: equations with one variable and equations with two variables.
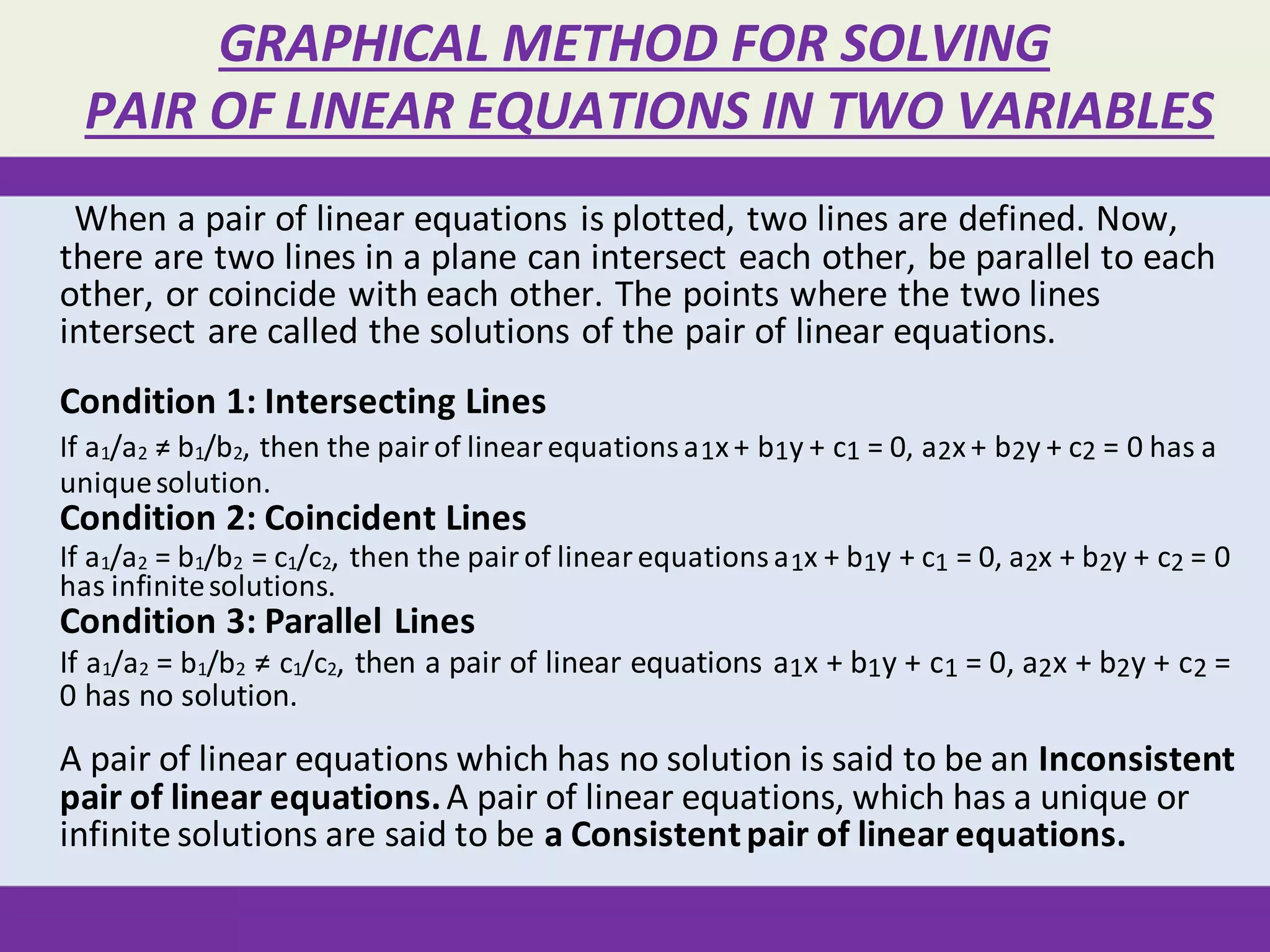
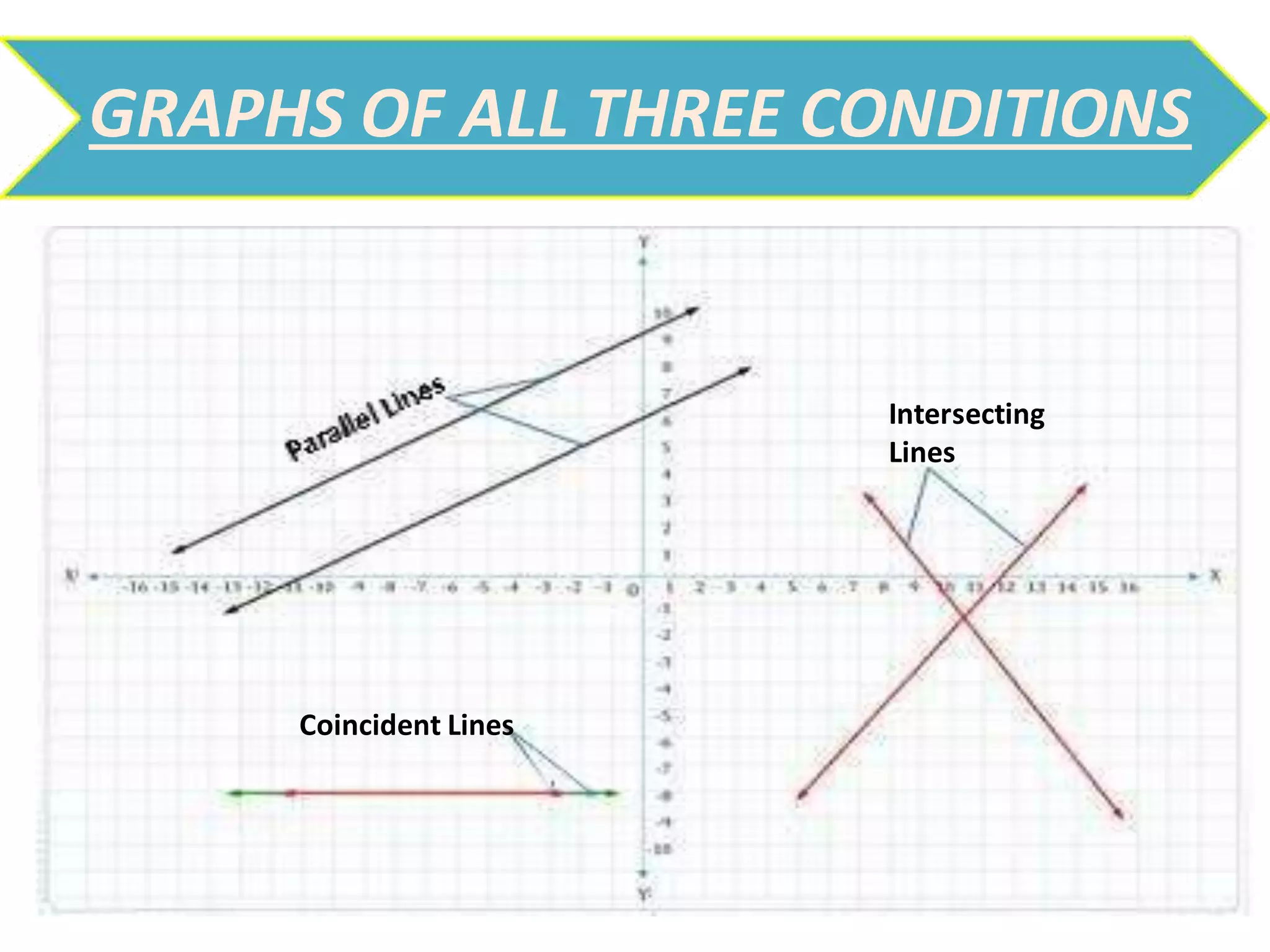
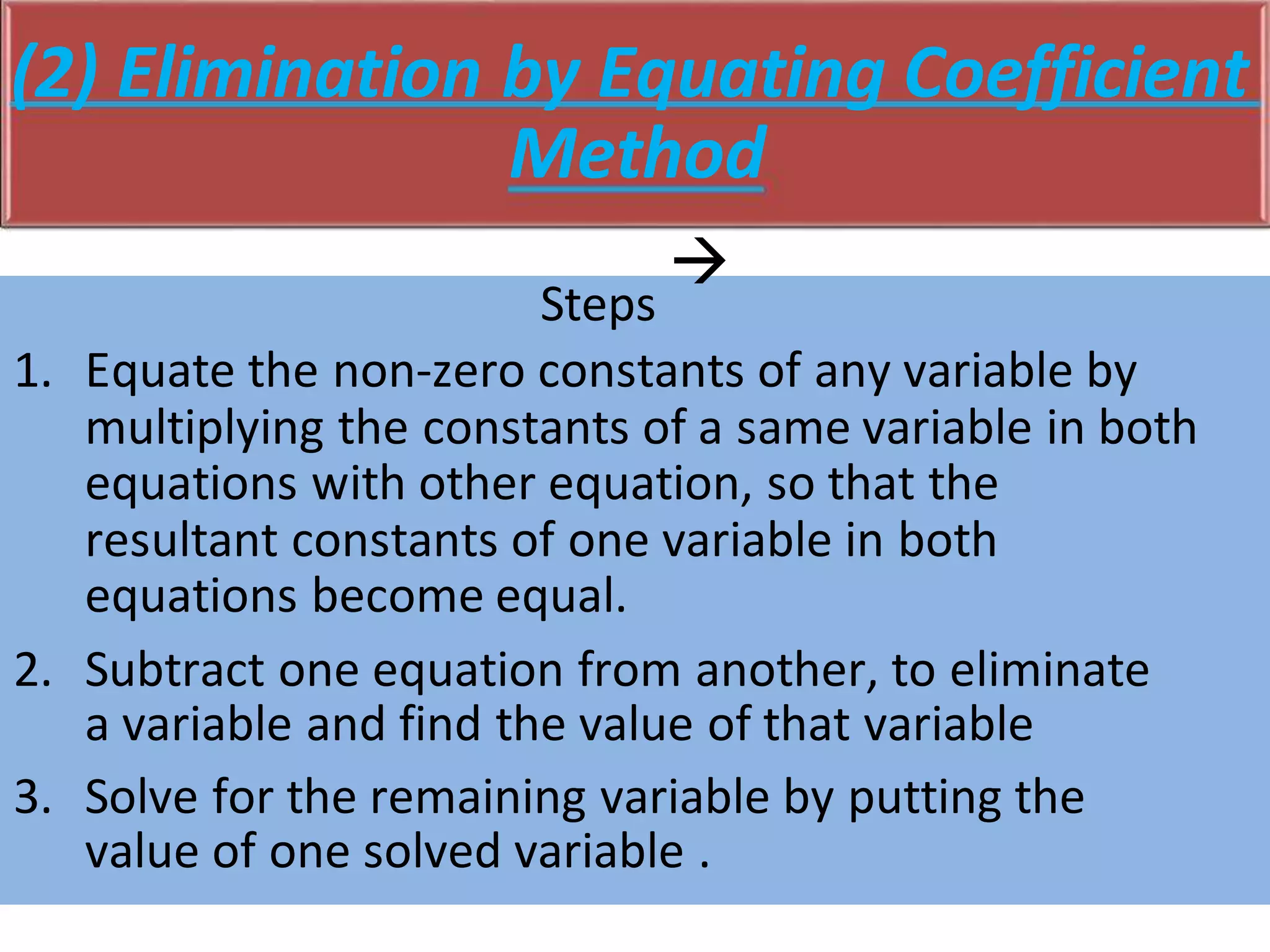
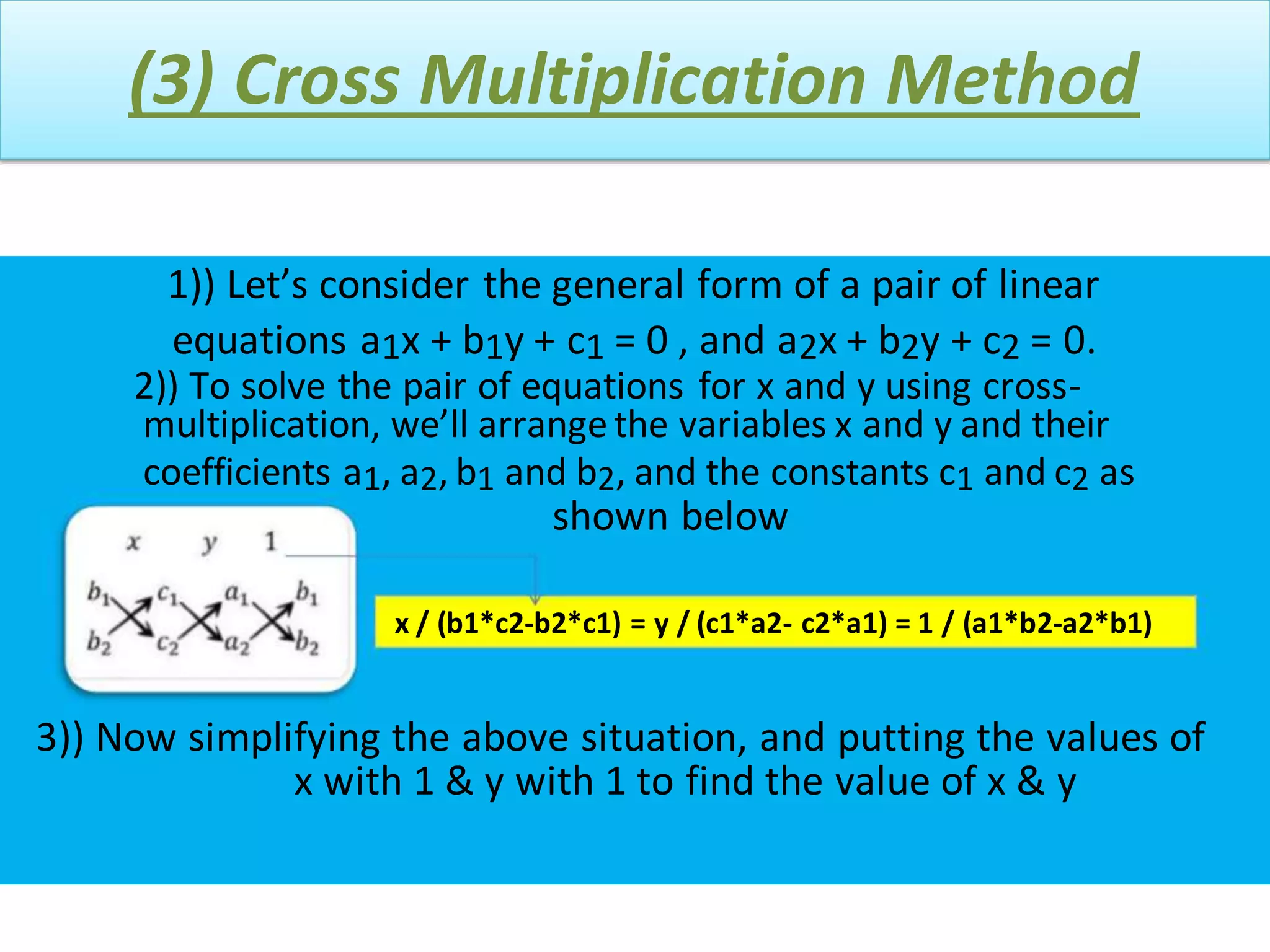
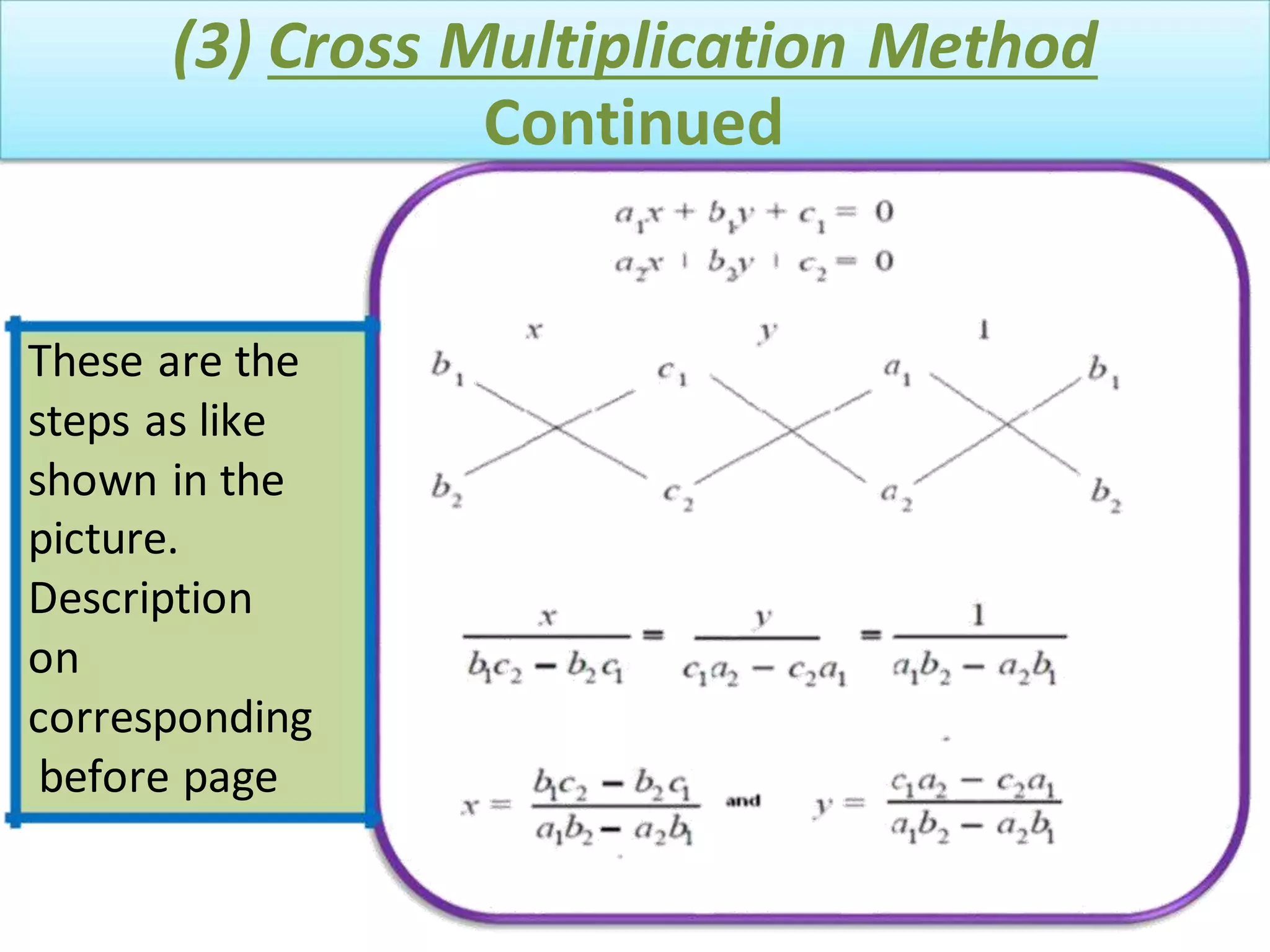
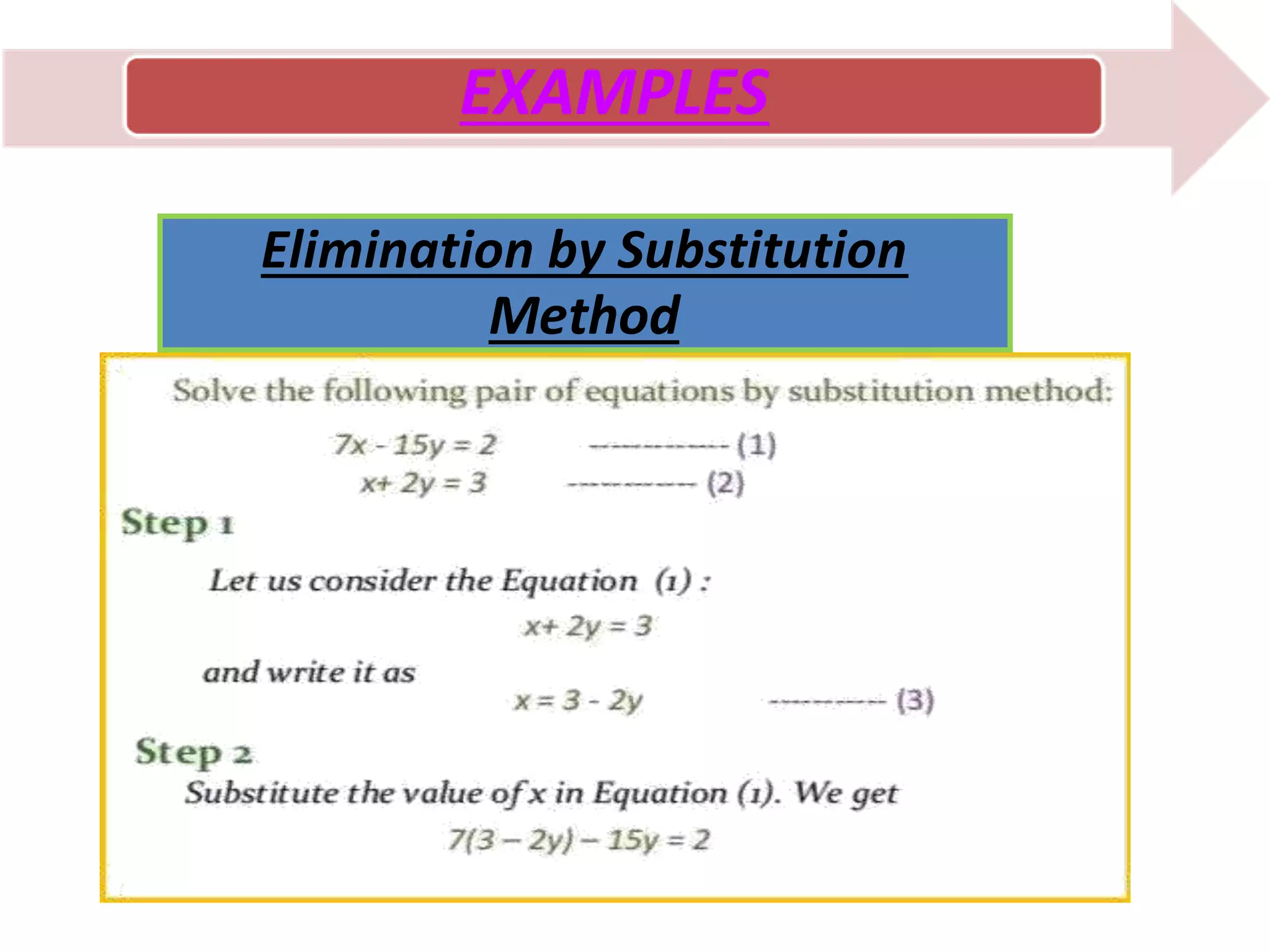
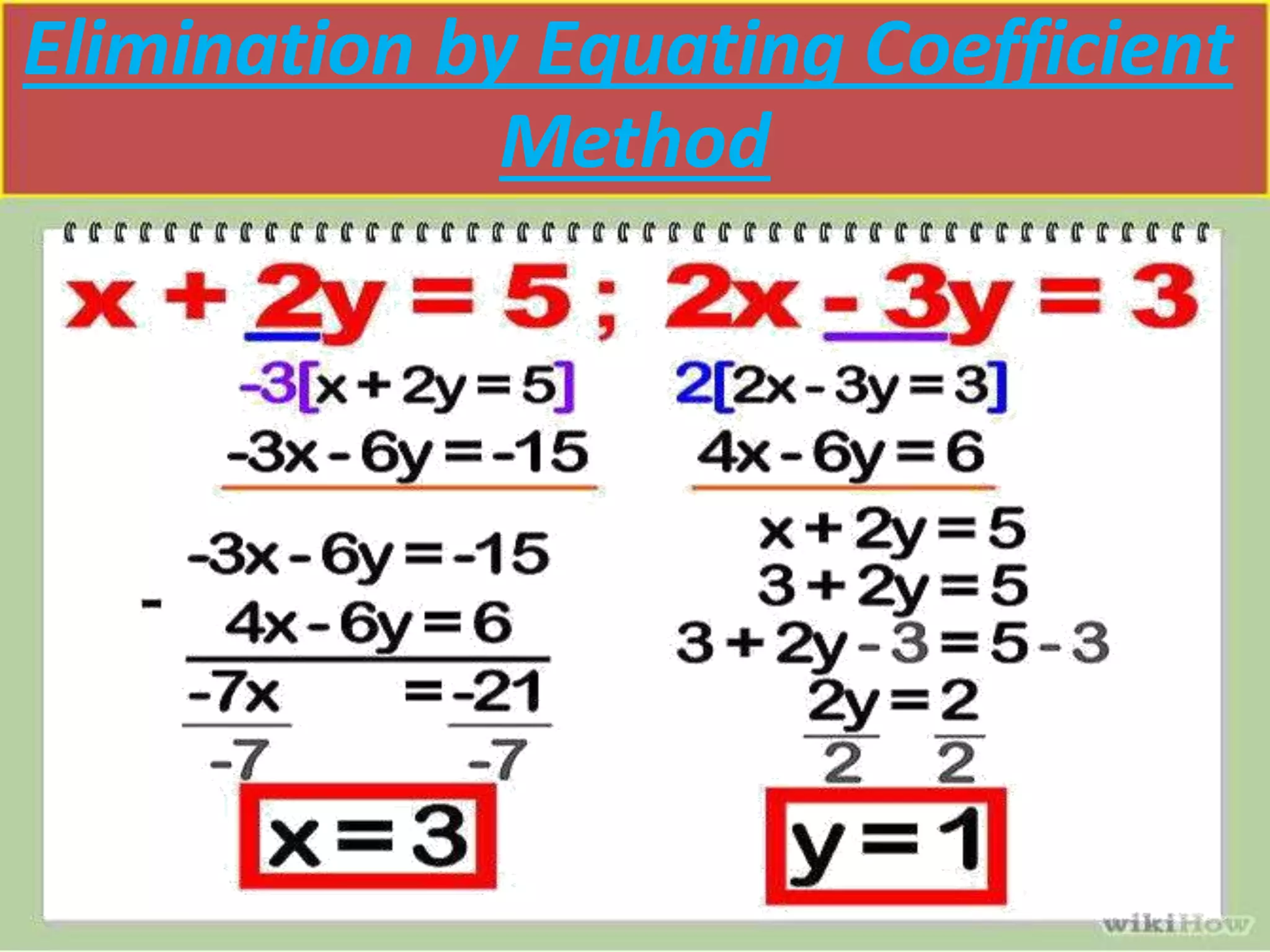
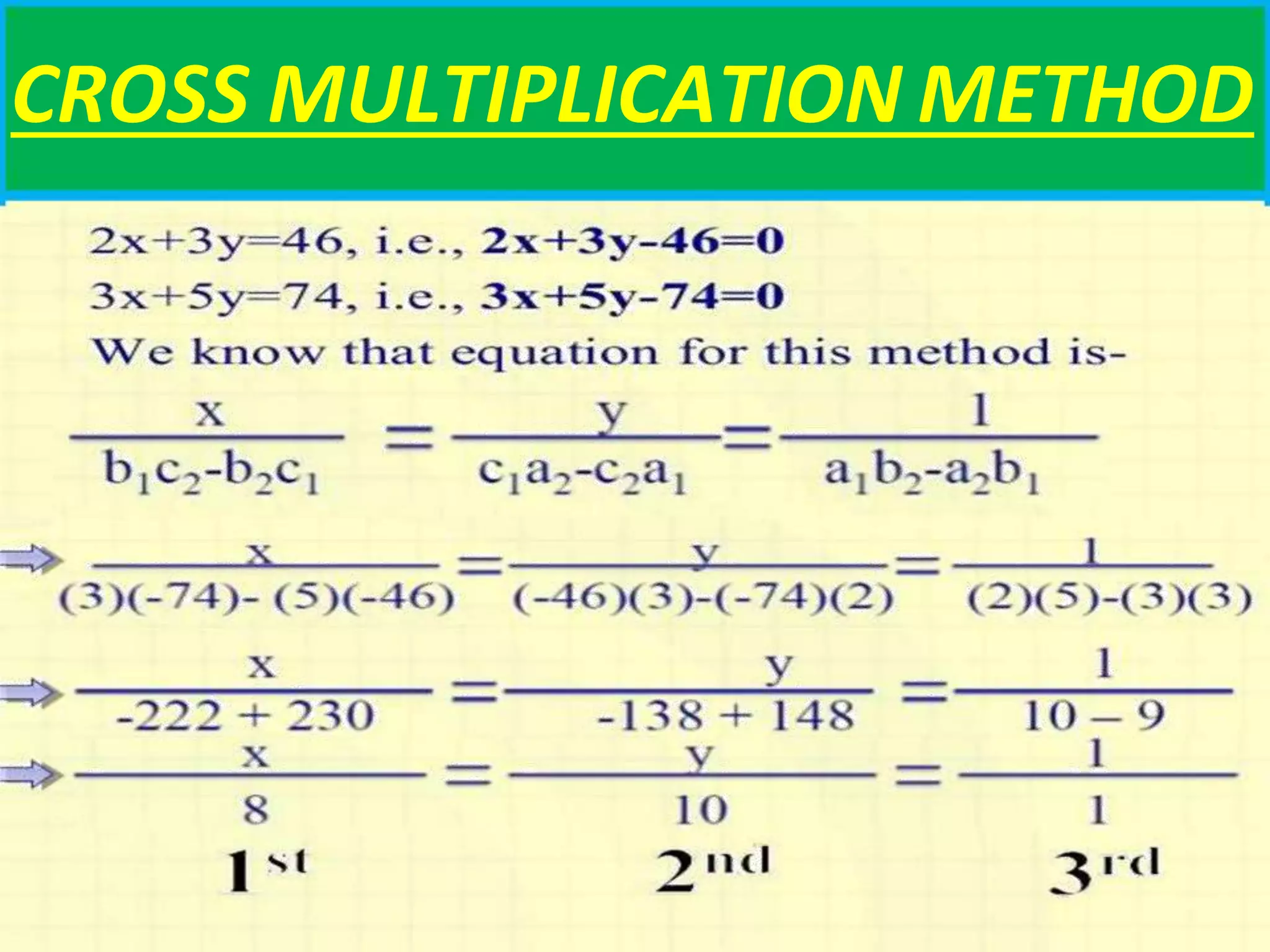
There are three main methods to solve a pair of linear equations with two variables: 1) the graphical method involves plotting the lines defined by each equation and finding their point(s) of intersection, 2) the algebraic elimination method involves manipulating the equations to eliminate one variable, and 3) the cross-multiplication method sets up the equations in a fraction format and cross-multiplies the variables and coefficients. Examples are shown for each solving method.