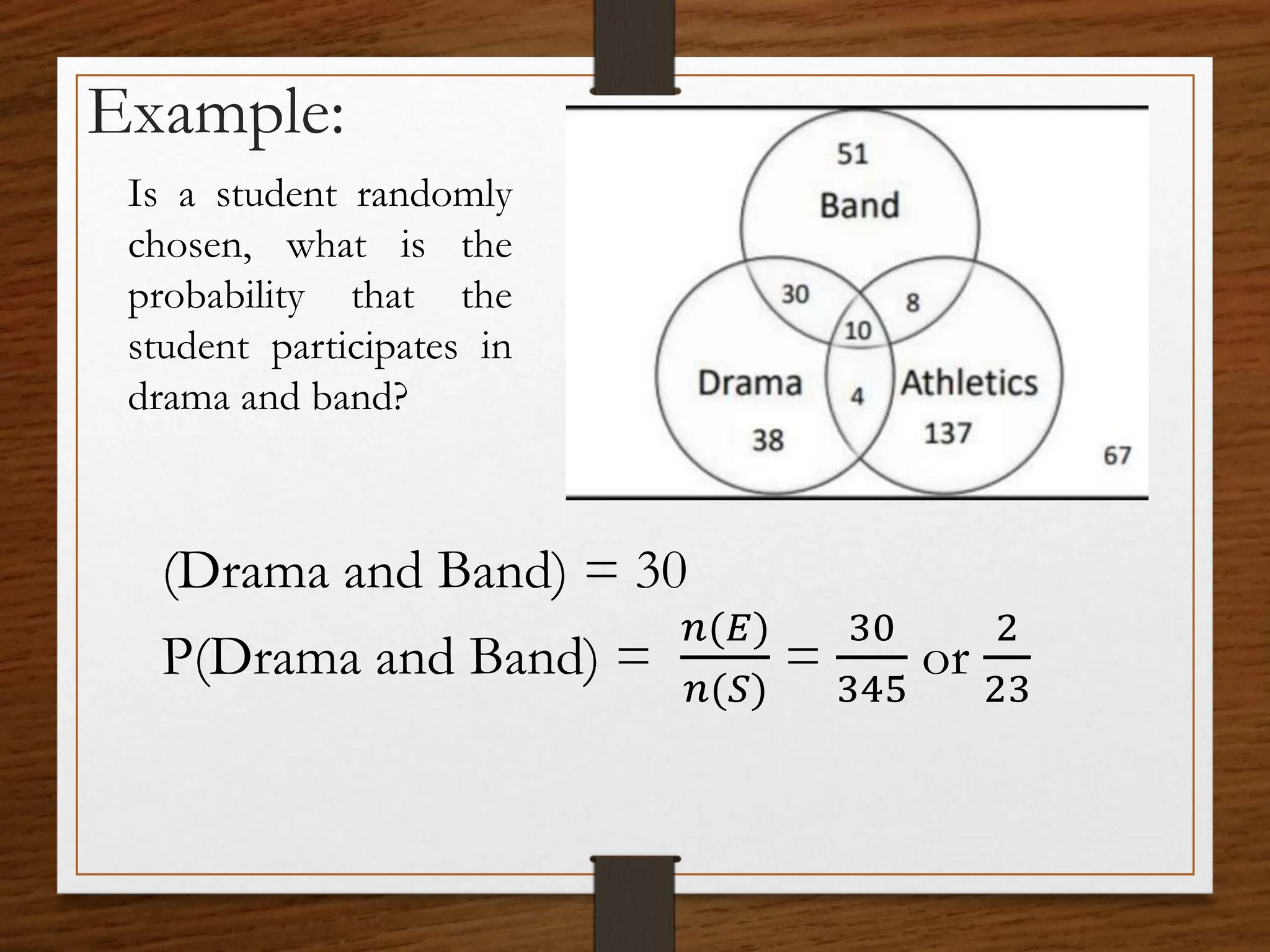
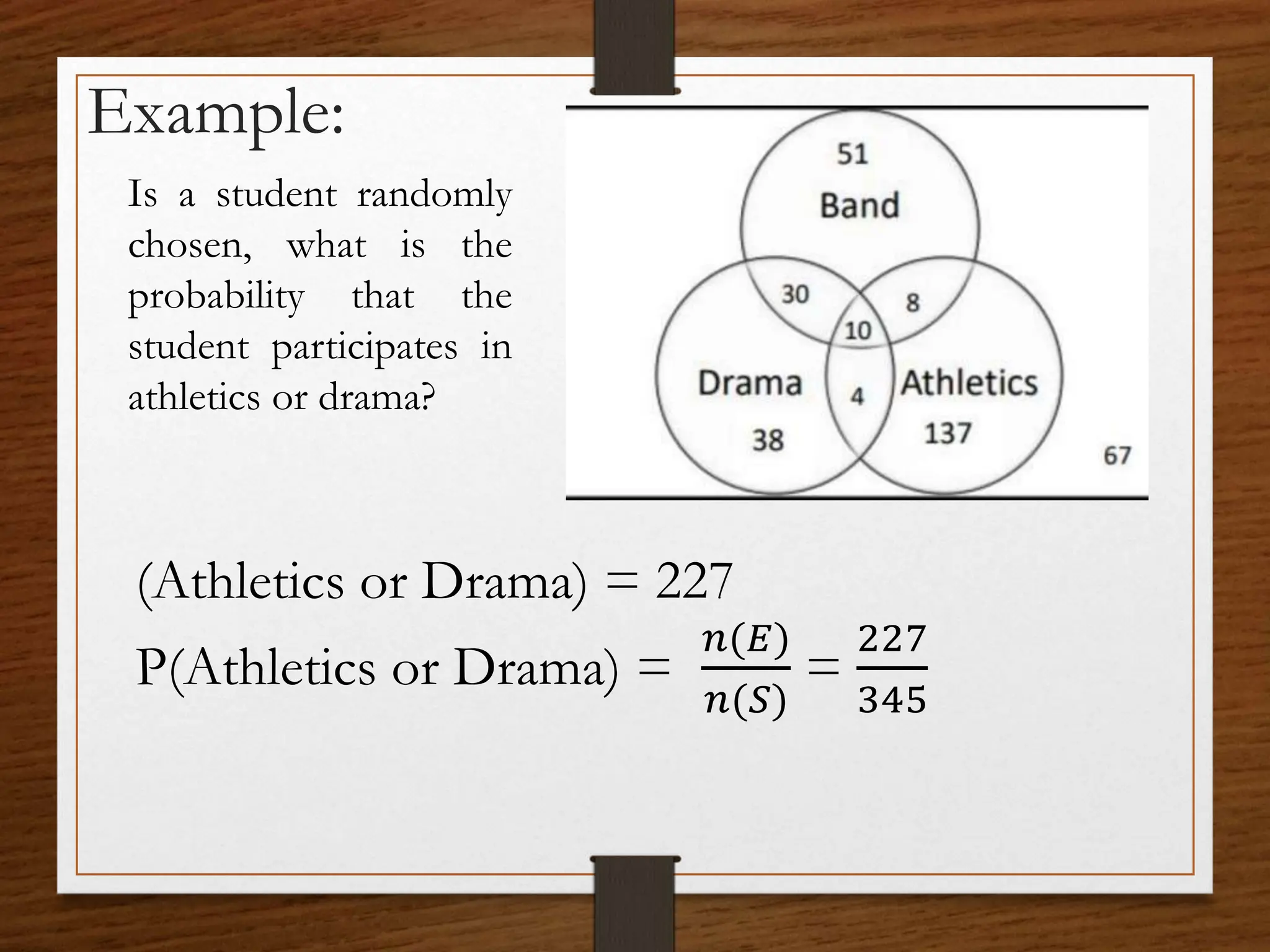
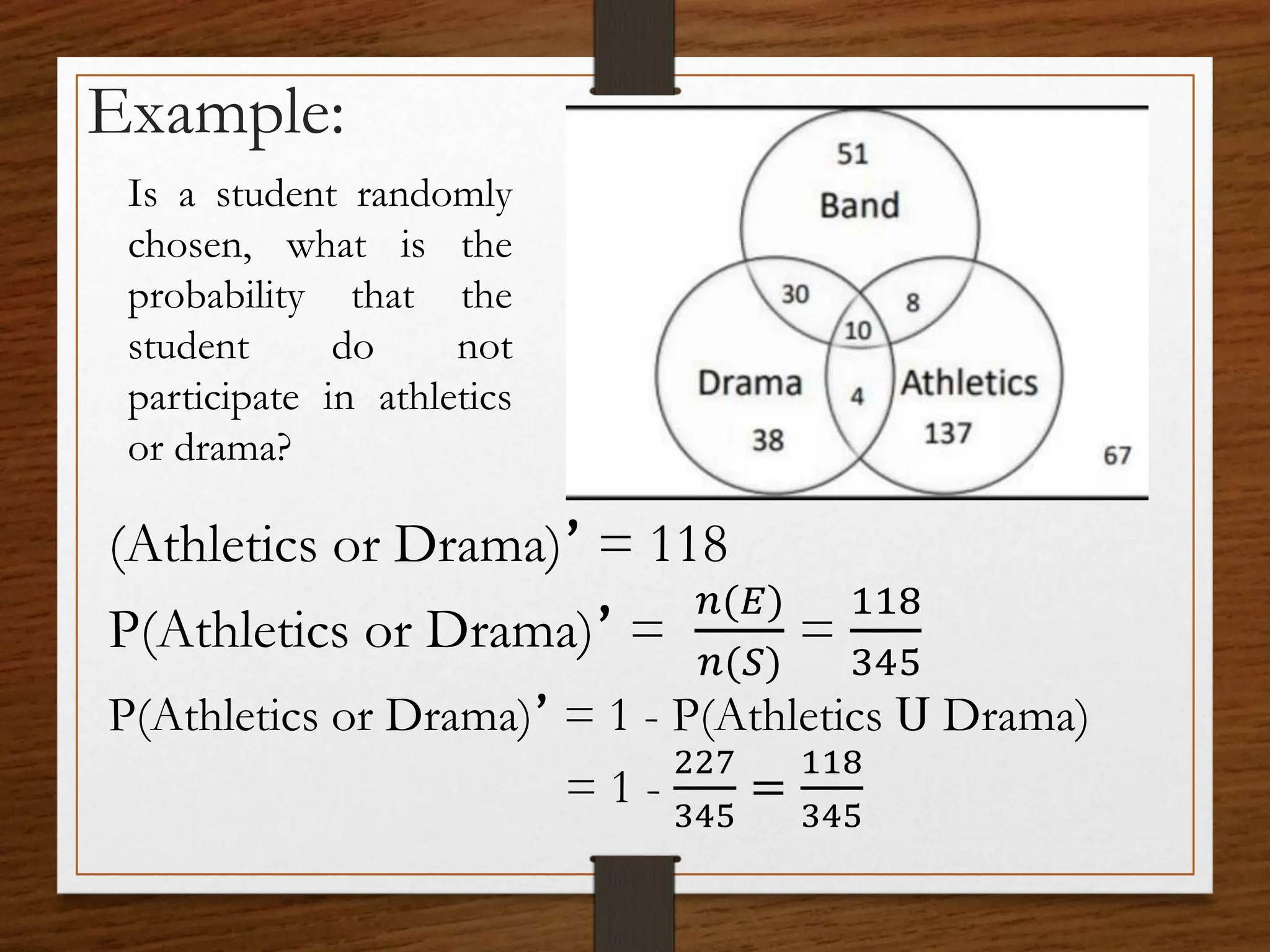
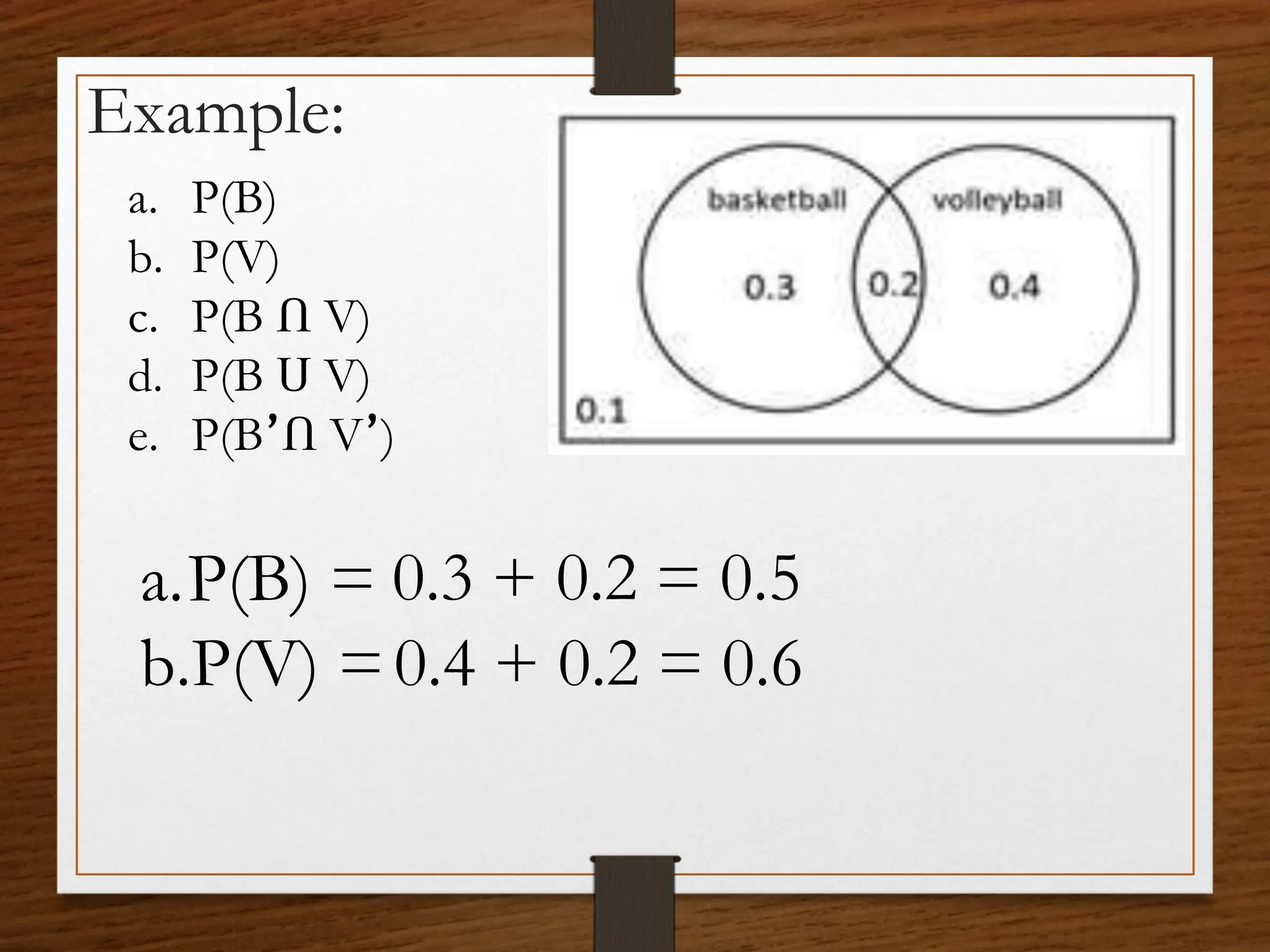
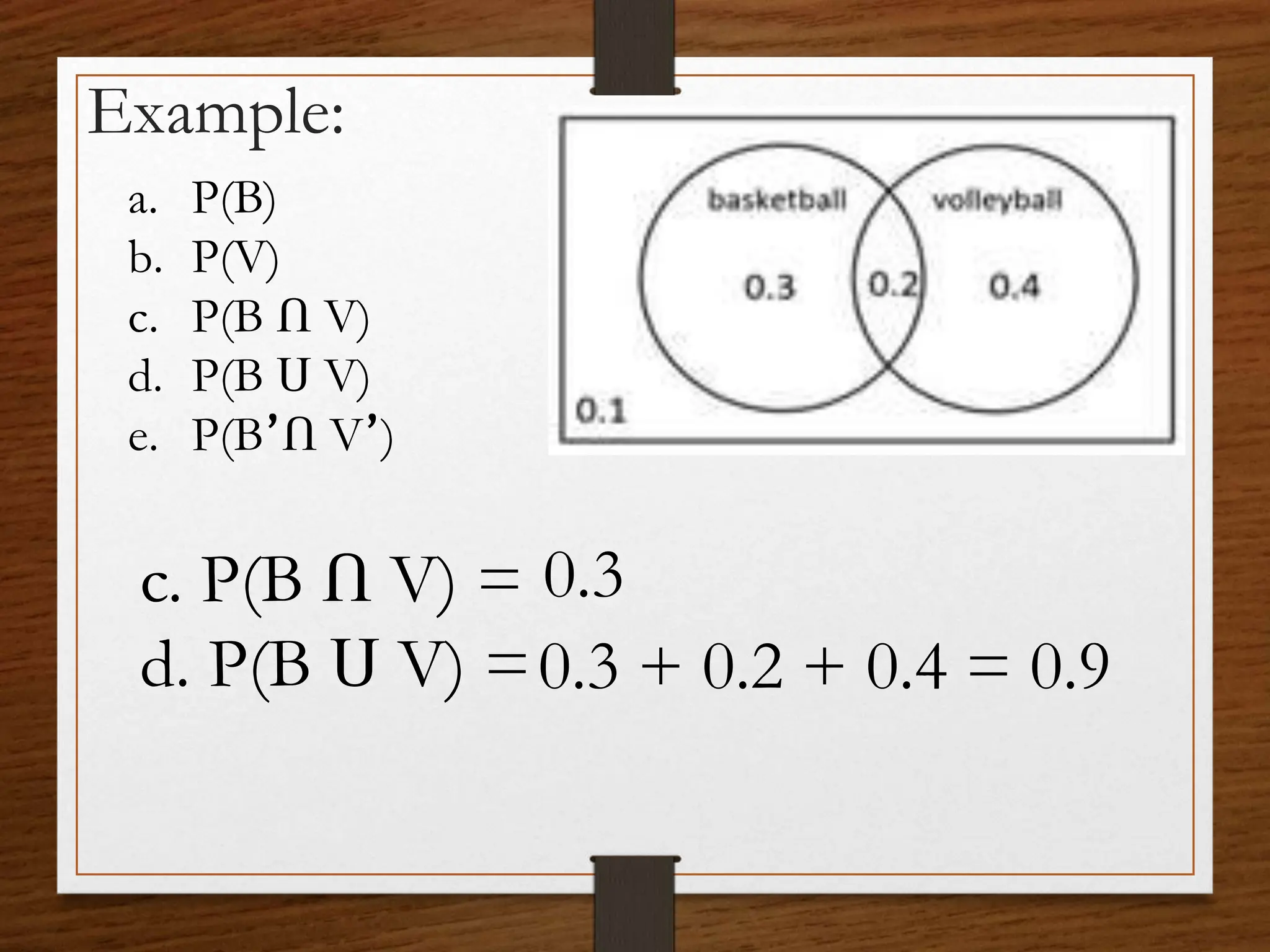
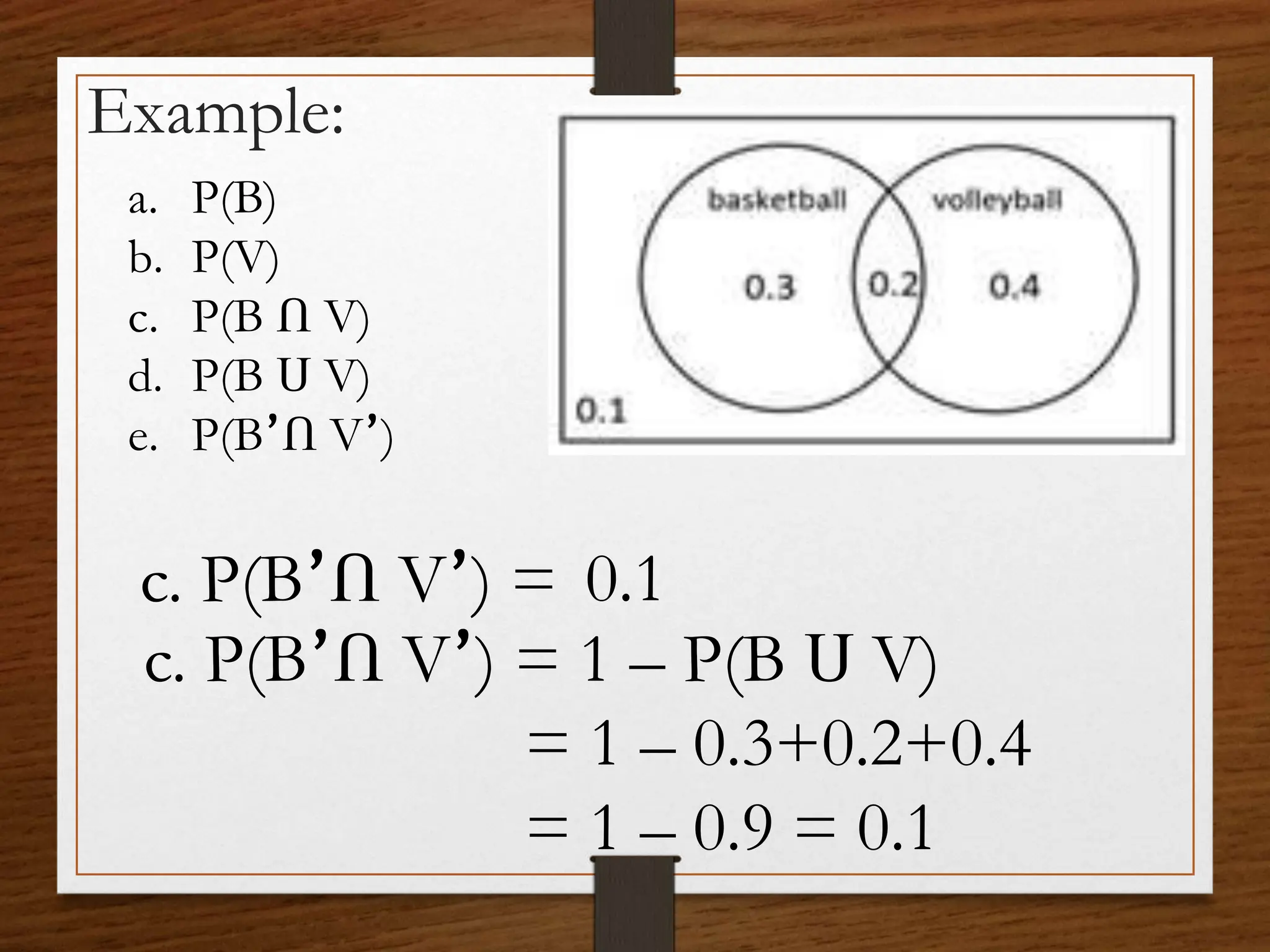
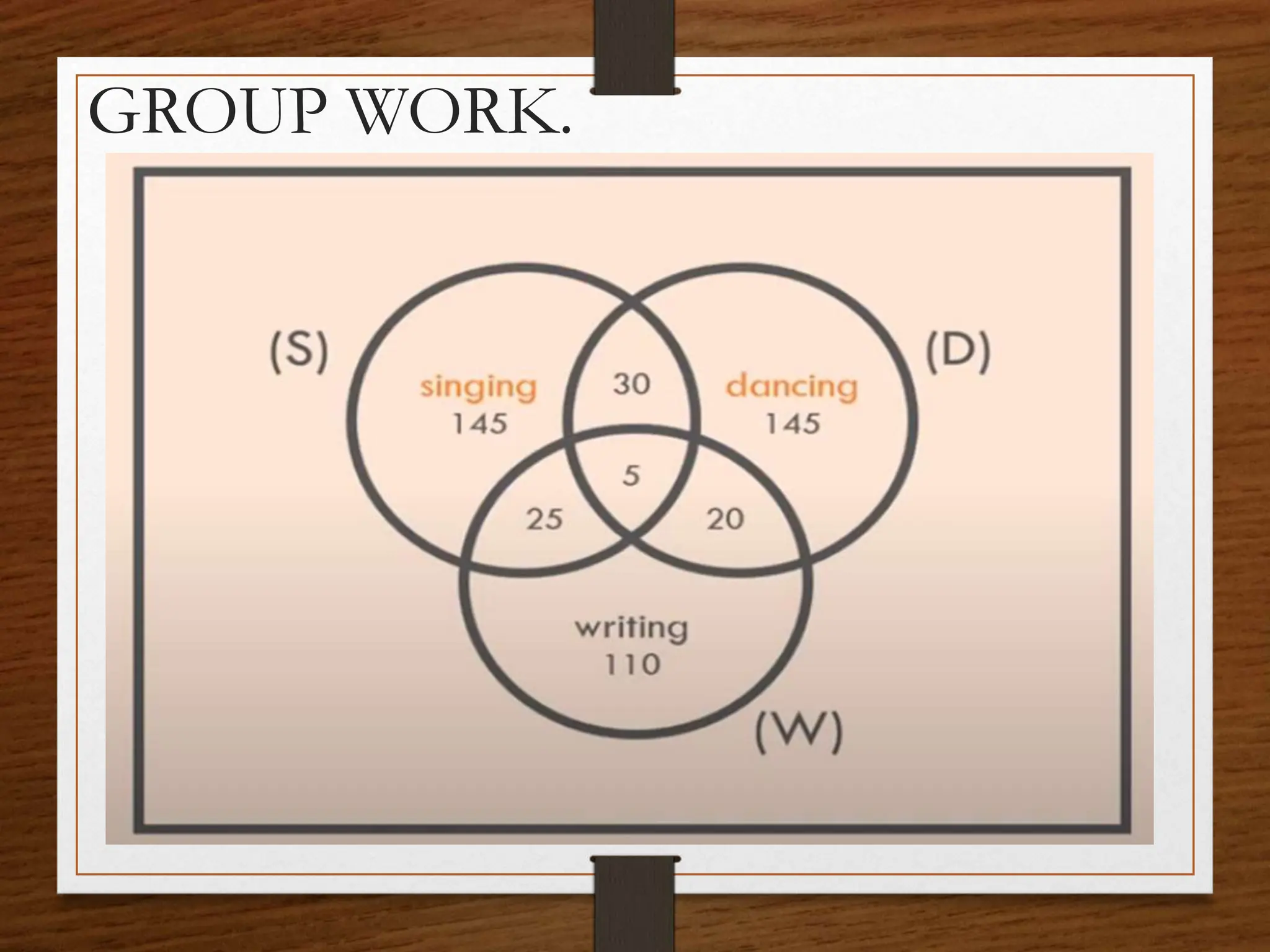
This document discusses probability concepts including intersection, union, and complement of events. It provides examples to illustrate finding the probability of intersection (P(A ∩ B)), union (P(A ∪ B)), and complement (P(A')) of events. One example calculates the probabilities of: P(B), P(V), P(B ∩ V), P(B ∪ V), and P(B' ∩ V') given P(B)=0.3, P(V)=0.2. It also asks students to practice calculating these probabilities in groups for events with given probabilities.