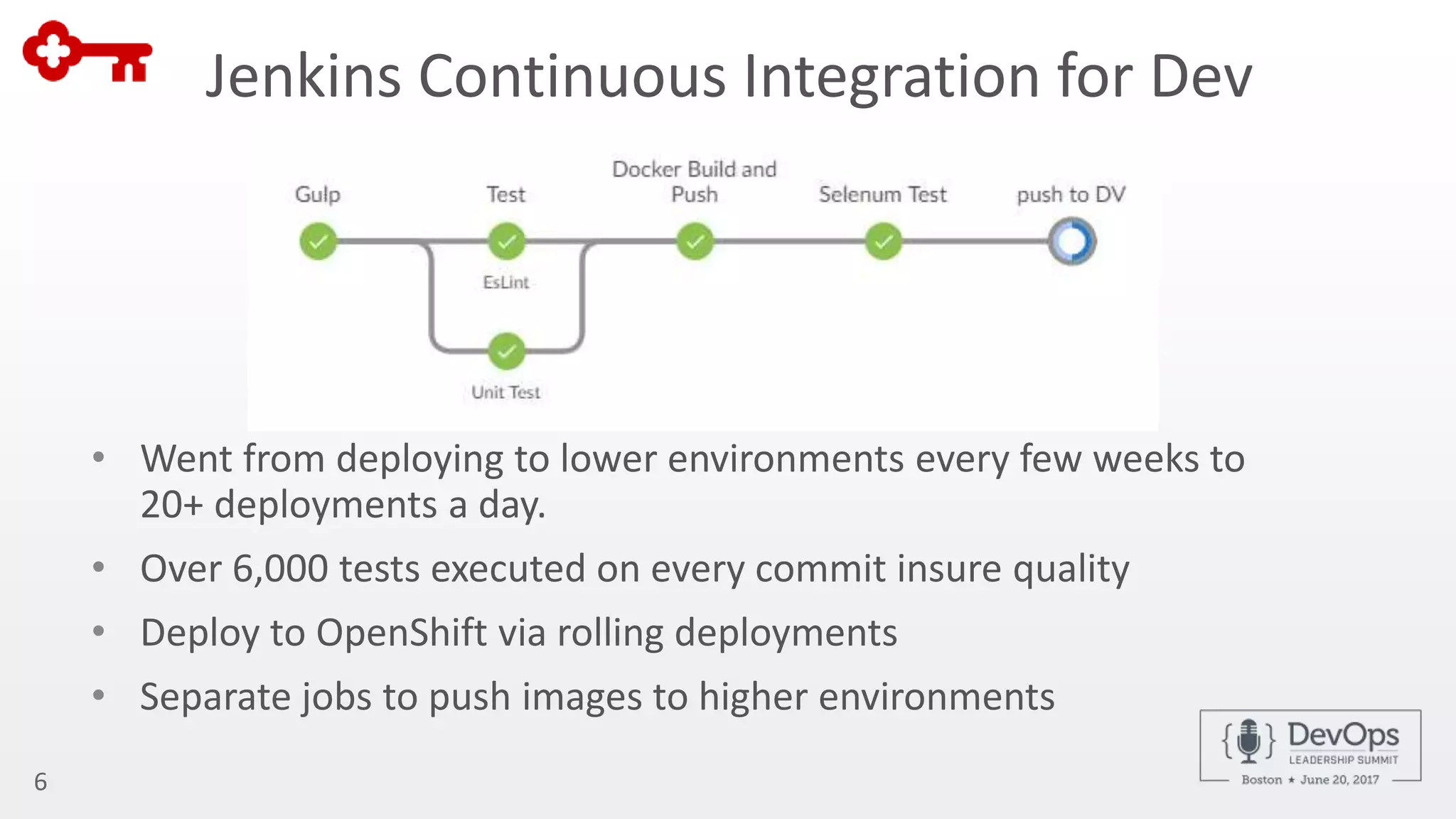
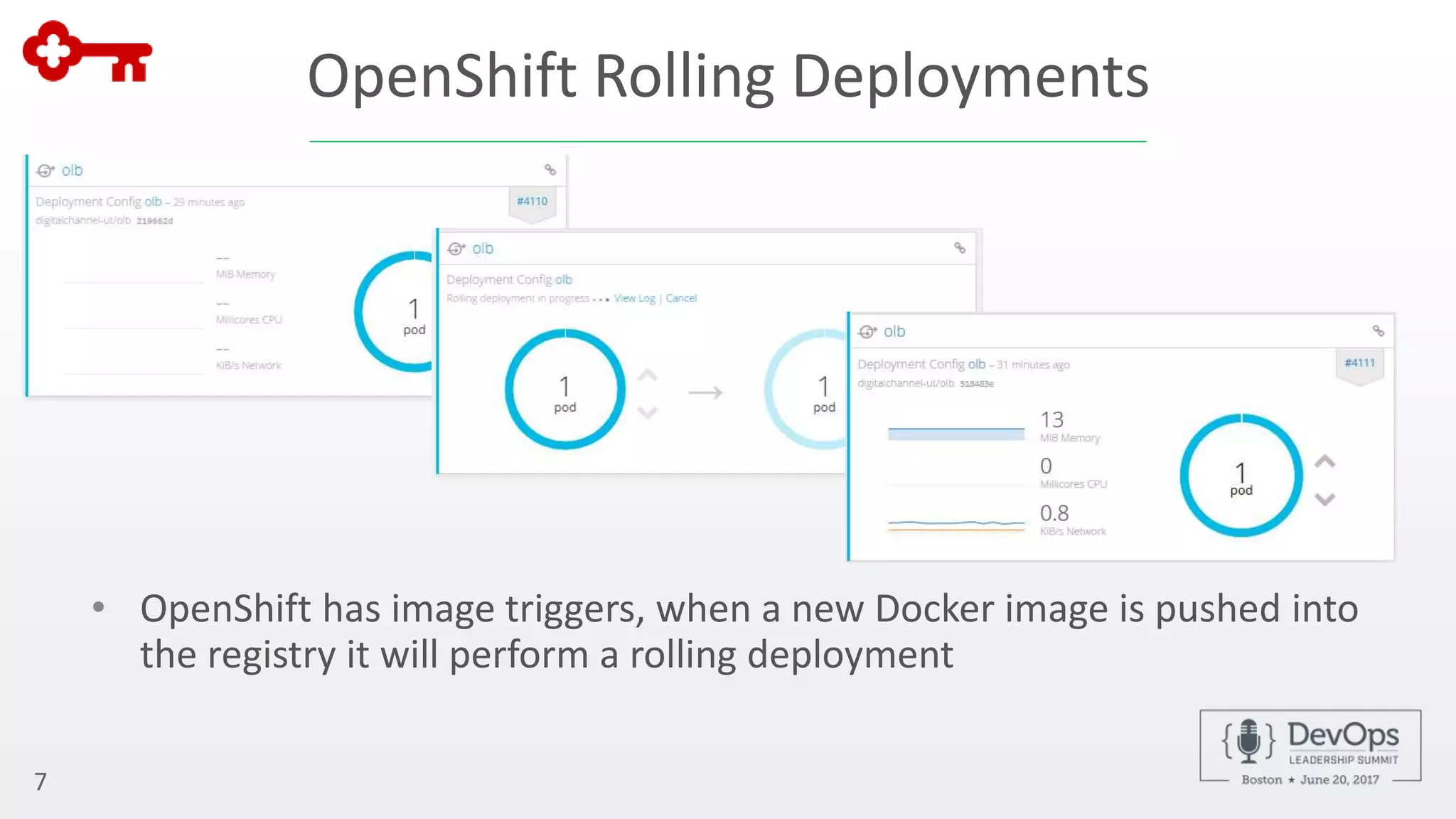
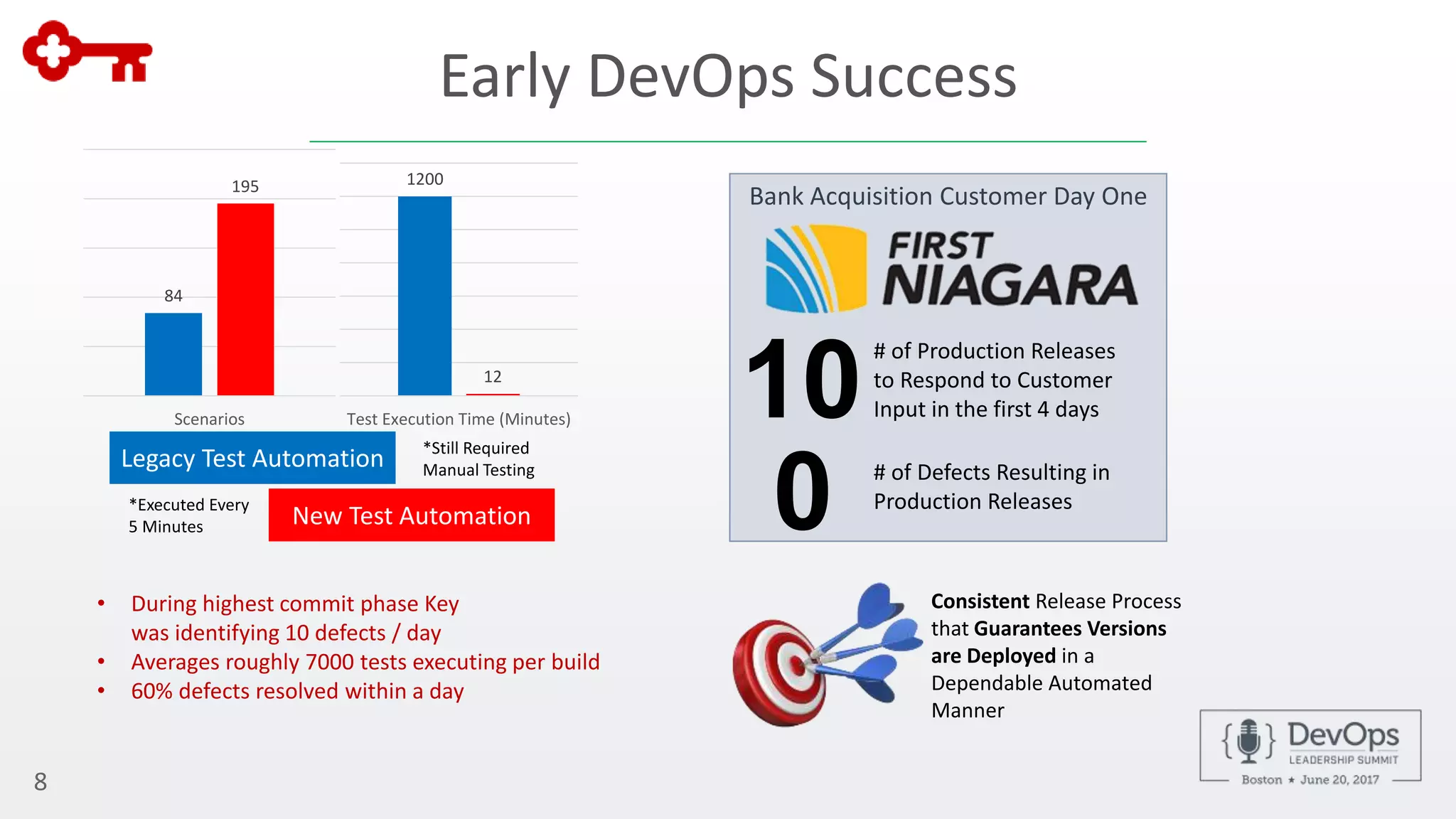
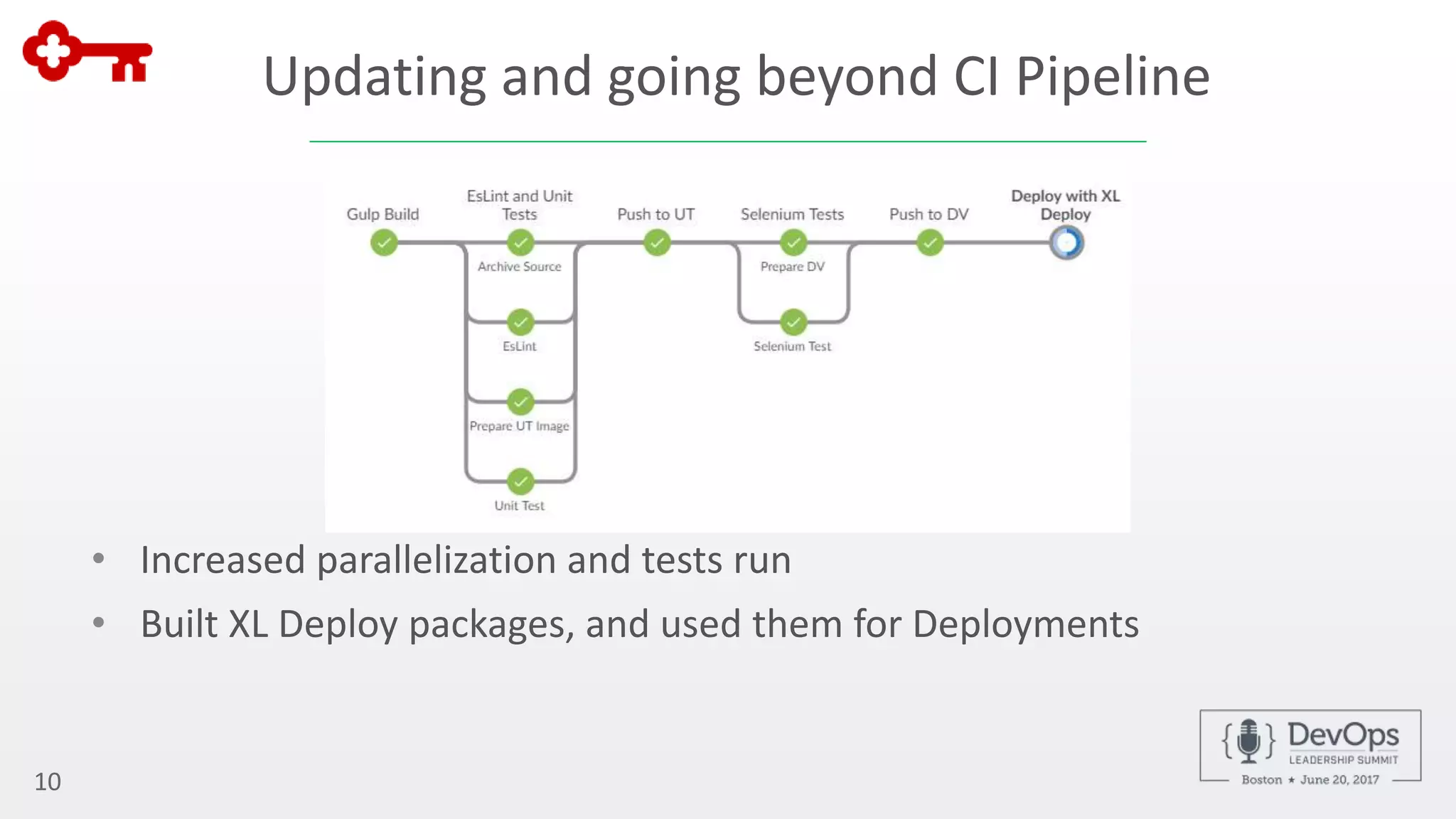
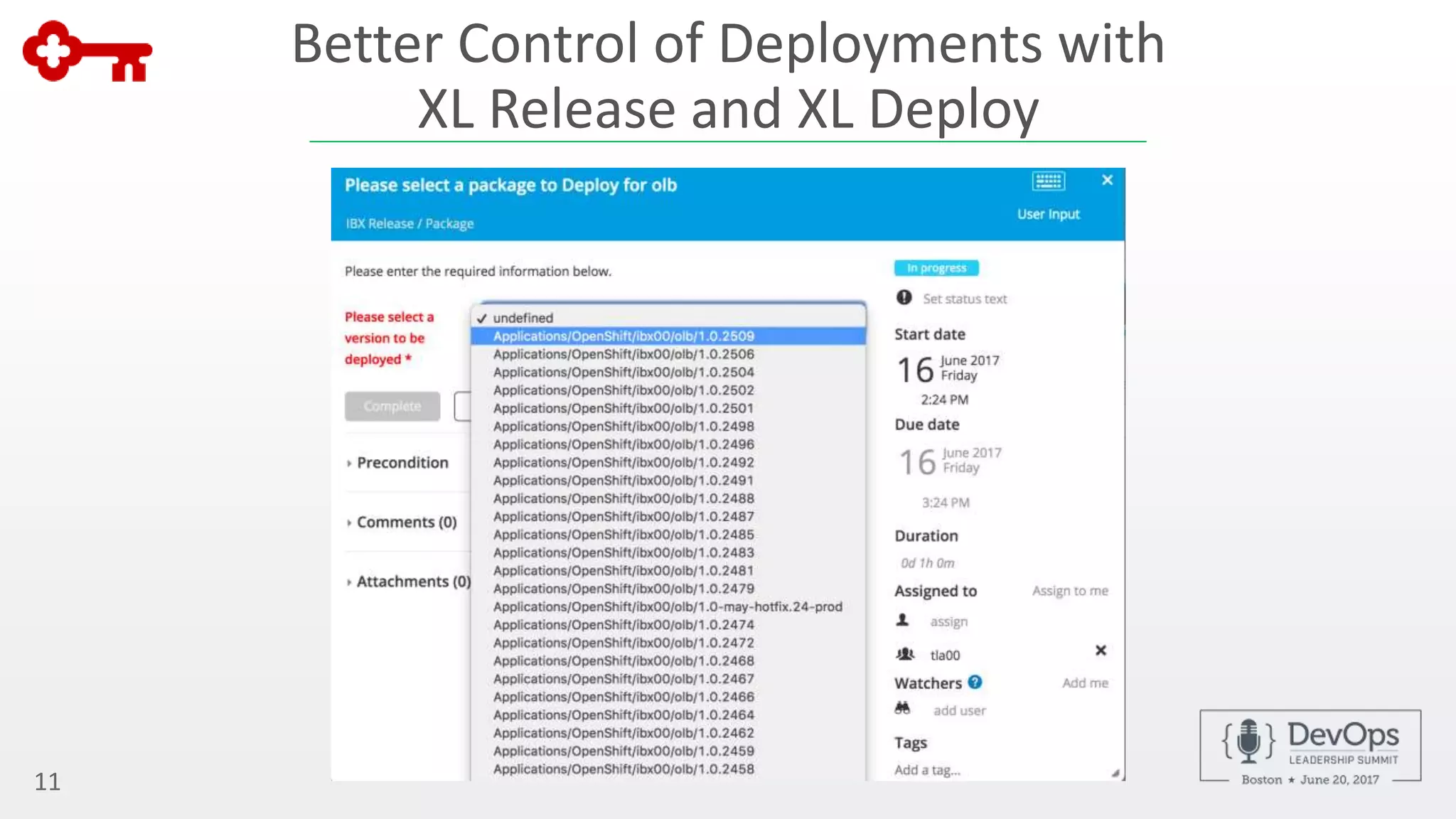
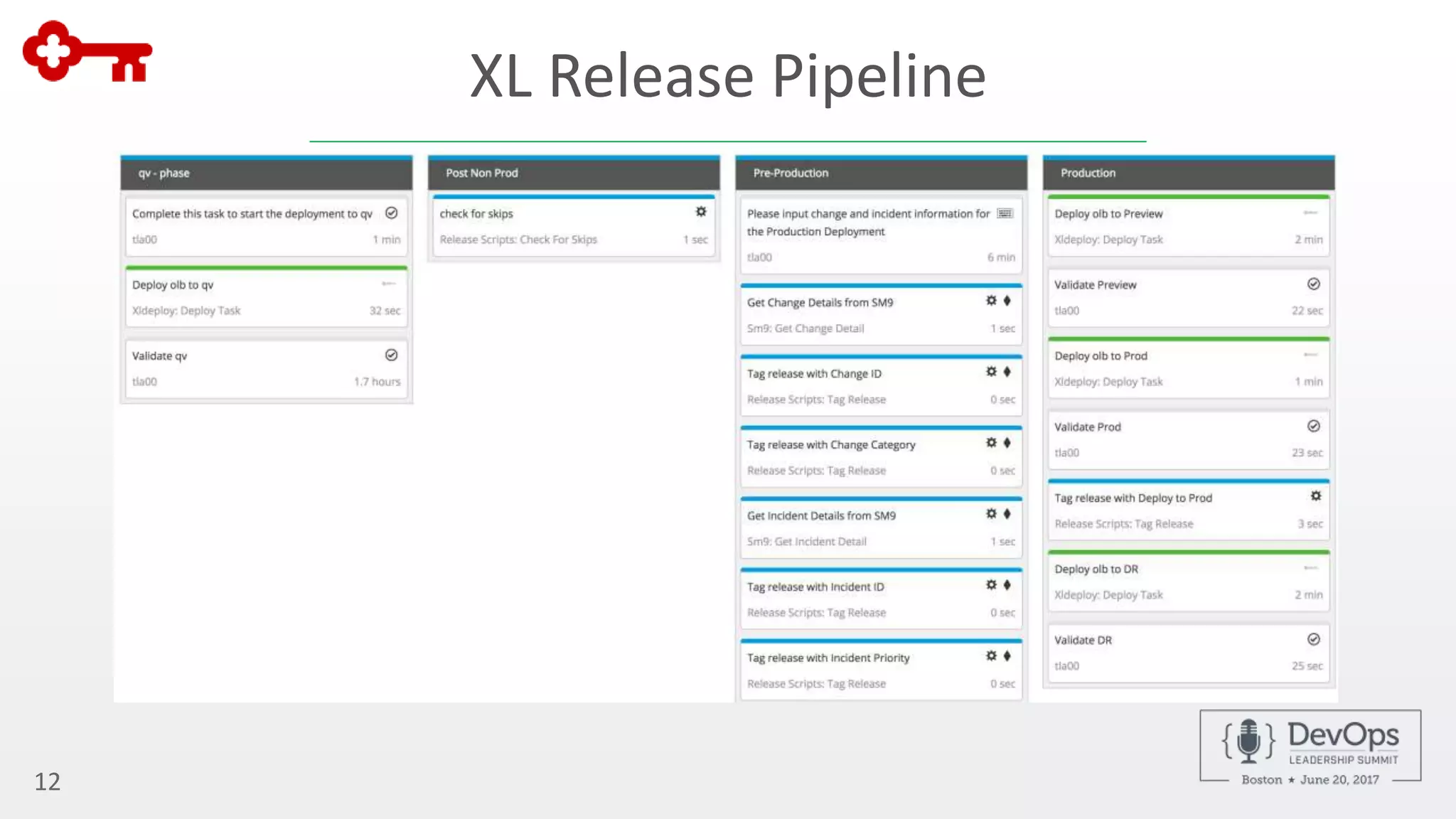
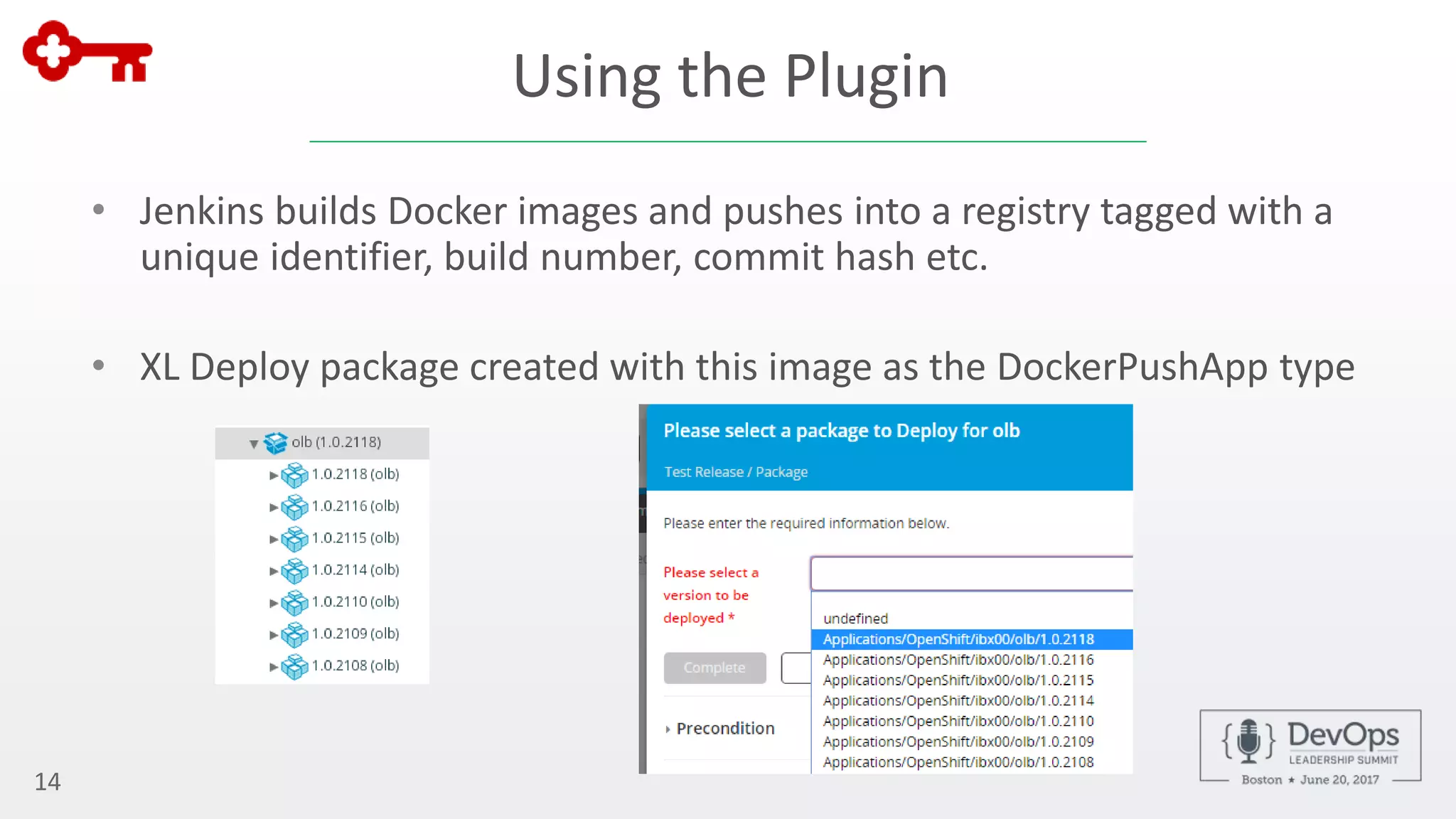
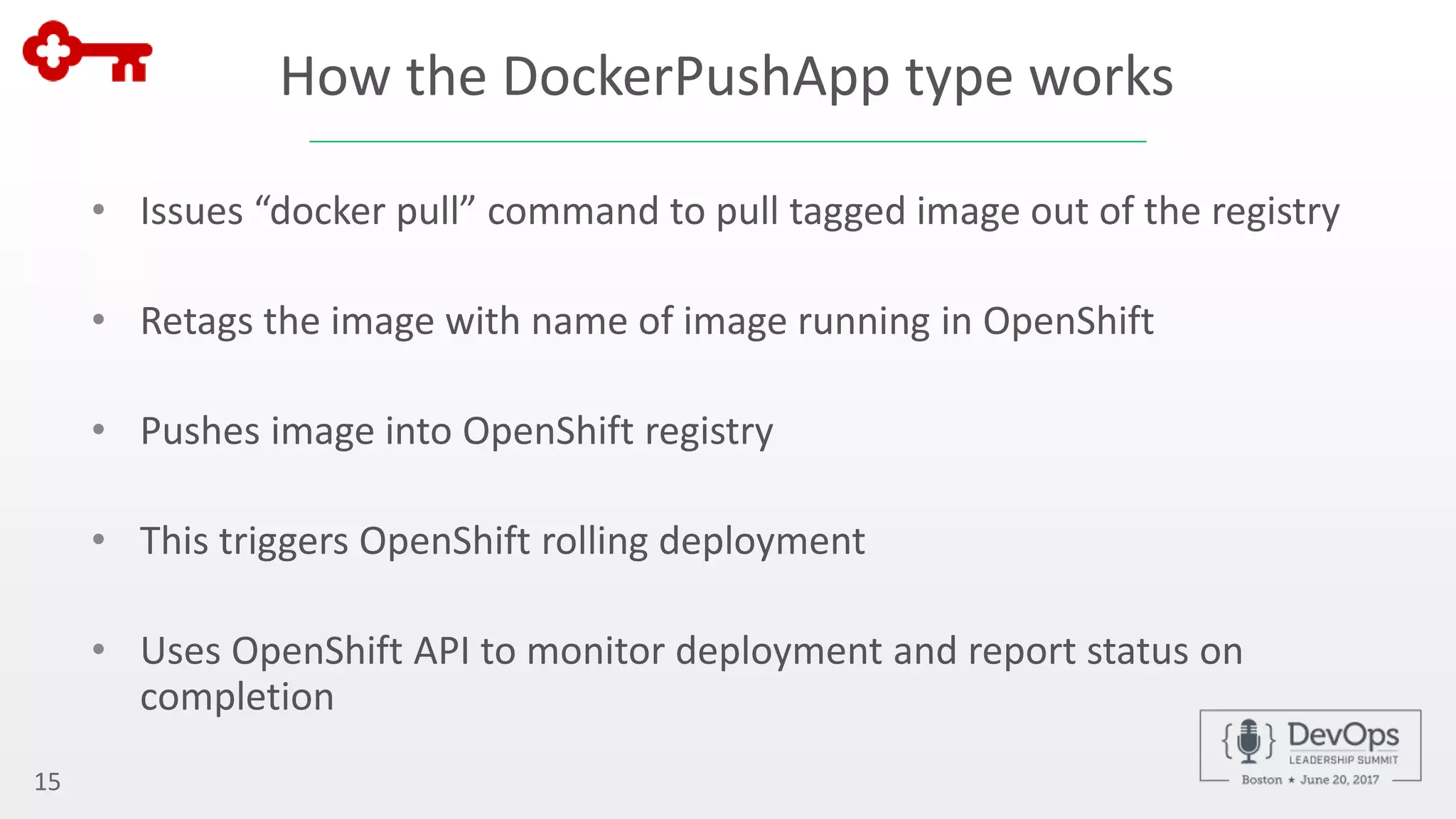
The document outlines the automation of private cloud deployment at KeyBank using XebiaLabs and OpenShift in response to operational challenges. It details the transition to Docker containers, Jenkins for continuous integration, and the implementation of a robust deployment pipeline which improved efficiency significantly. Key metrics include increasing deployment frequency to over 20 times a day and executing thousands of tests per build, all aimed at enhancing performance and reliability in banking operations.