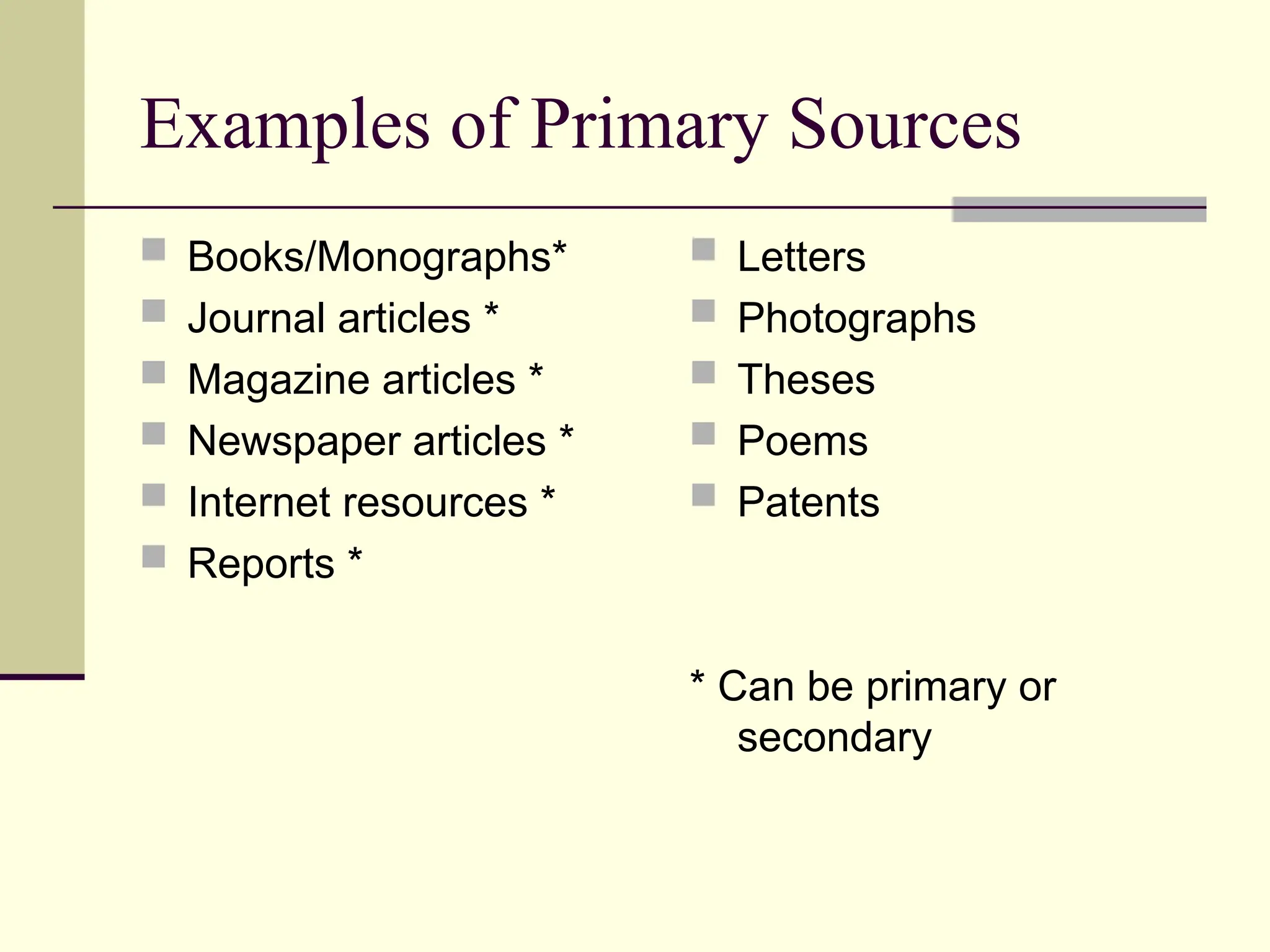
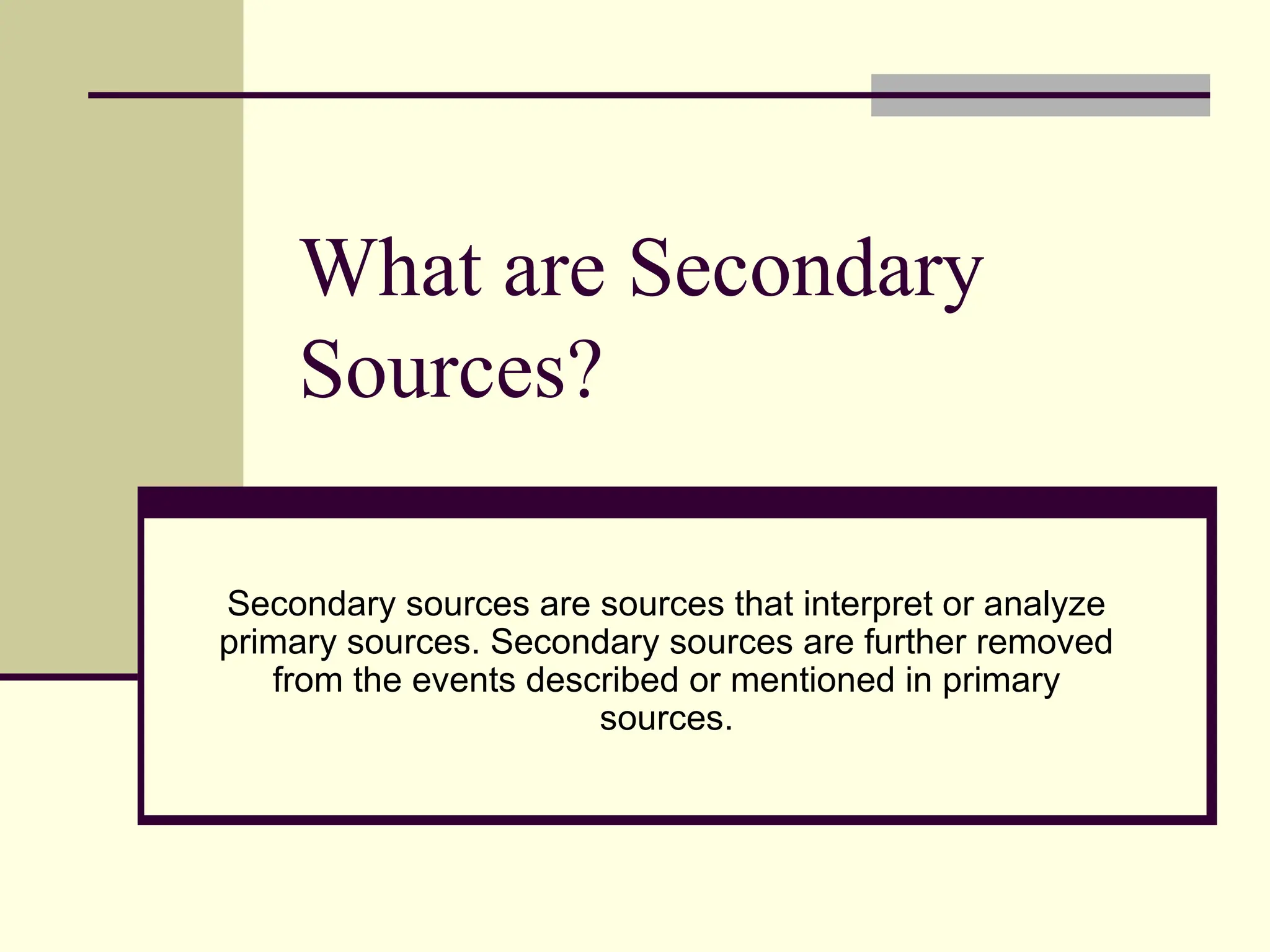
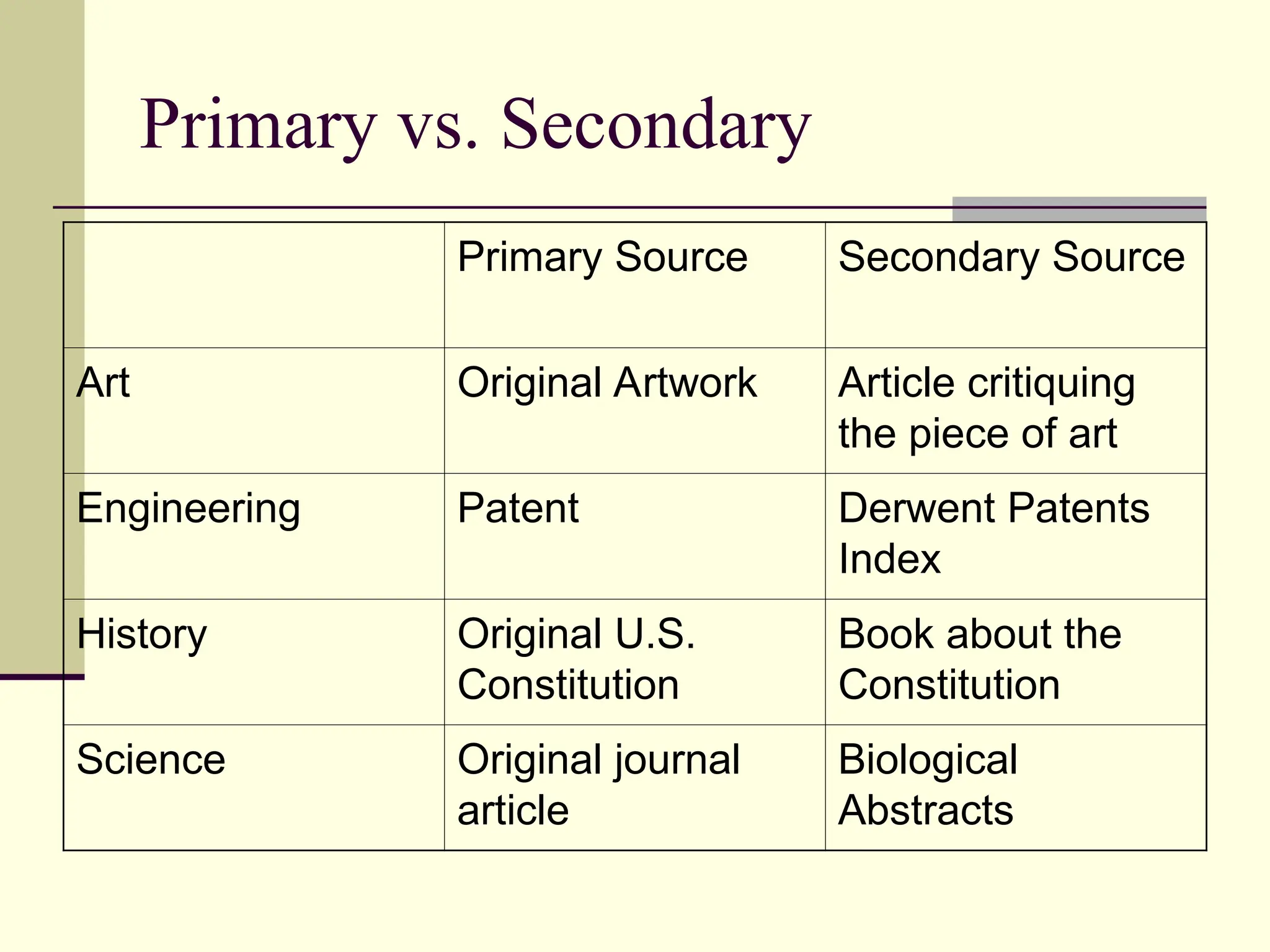
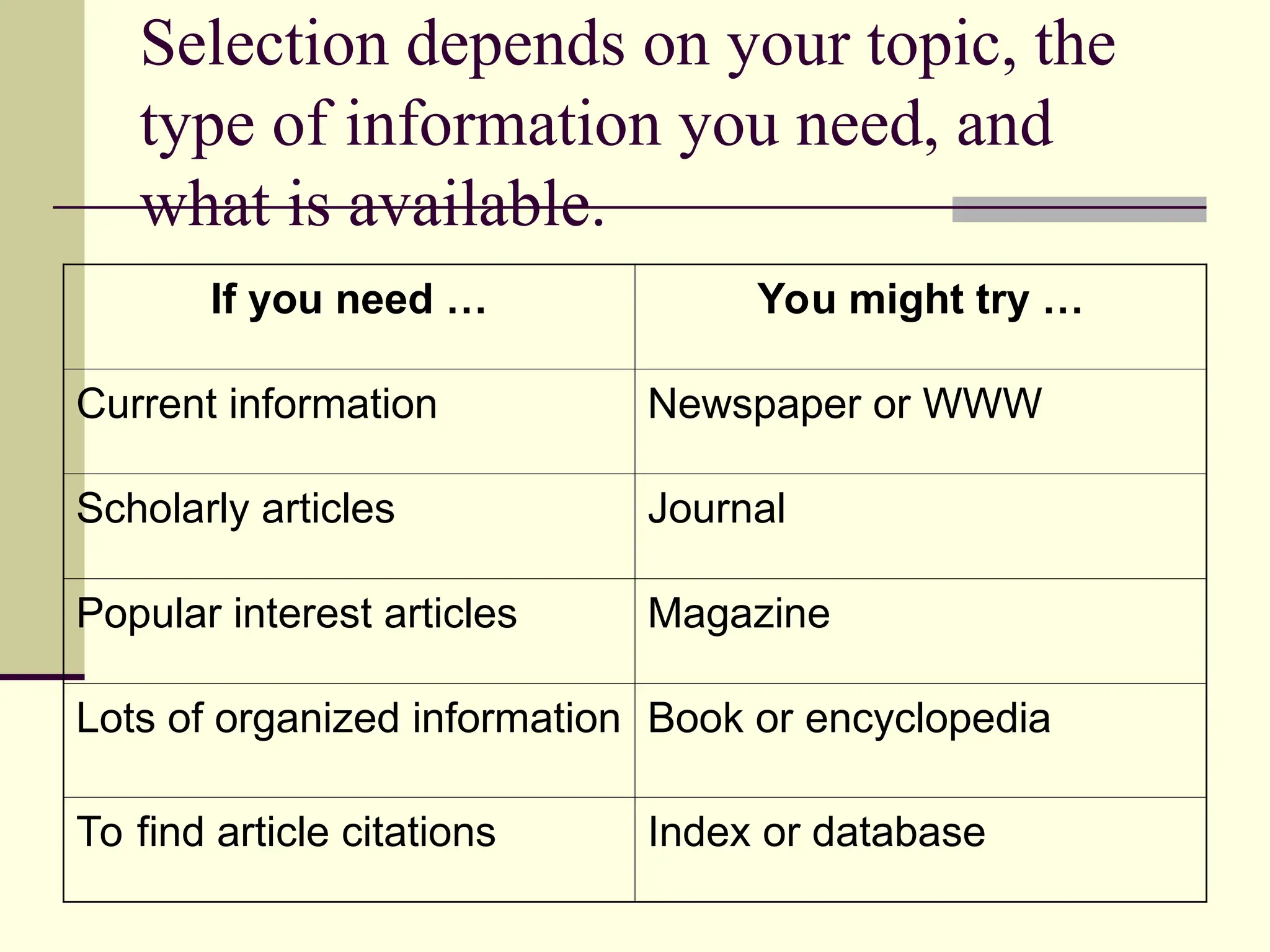
The document outlines the types of information sources available, categorizing them into primary sources, which are original documents created at the time of an event, and secondary sources that interpret or analyze primary sources. Examples include books, journal articles, and internet resources for primary sources, while secondary sources include biographies and encyclopedias. It also provides guidance on how to select the appropriate source based on the topic and the type of information needed.