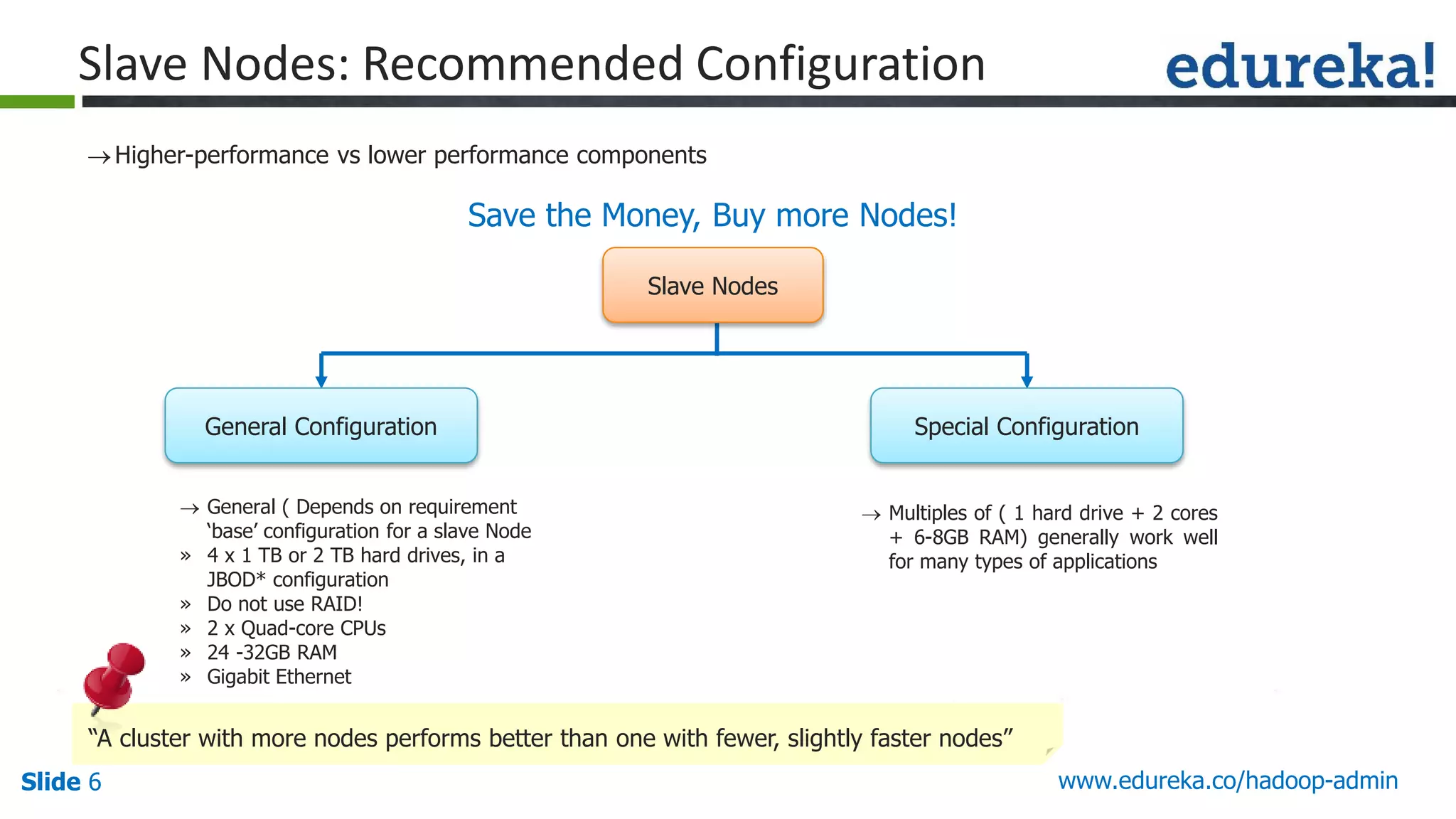
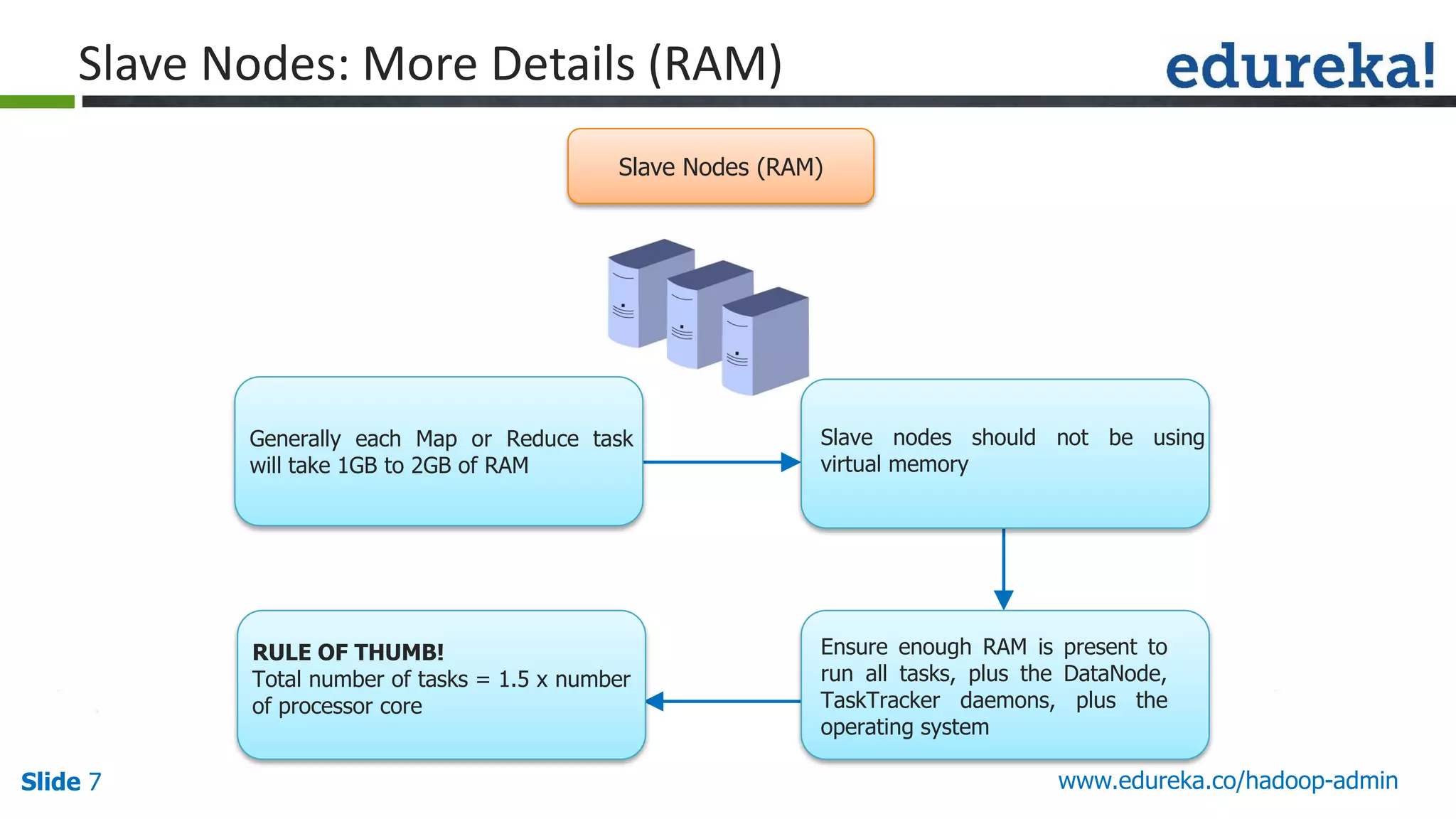
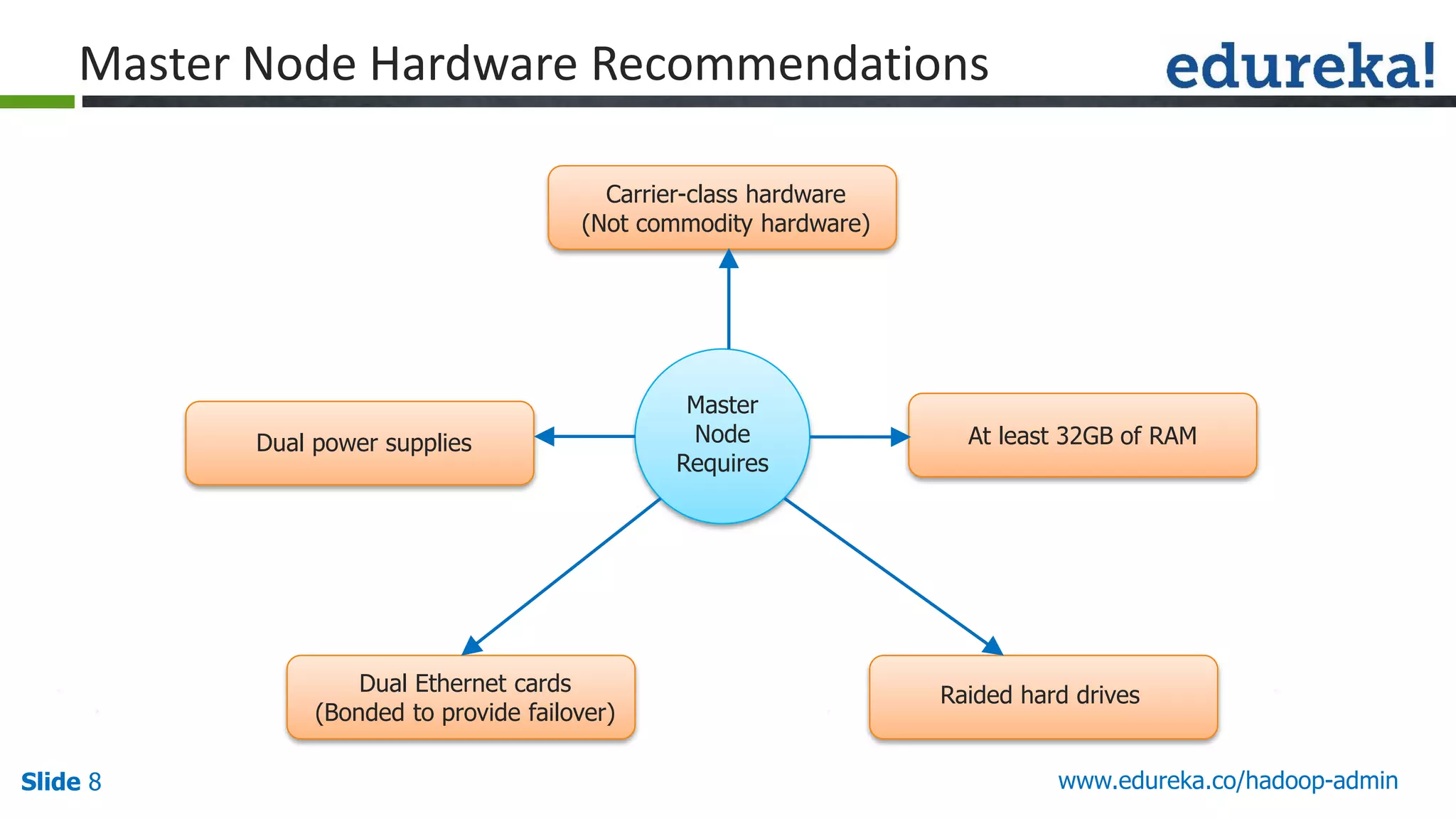
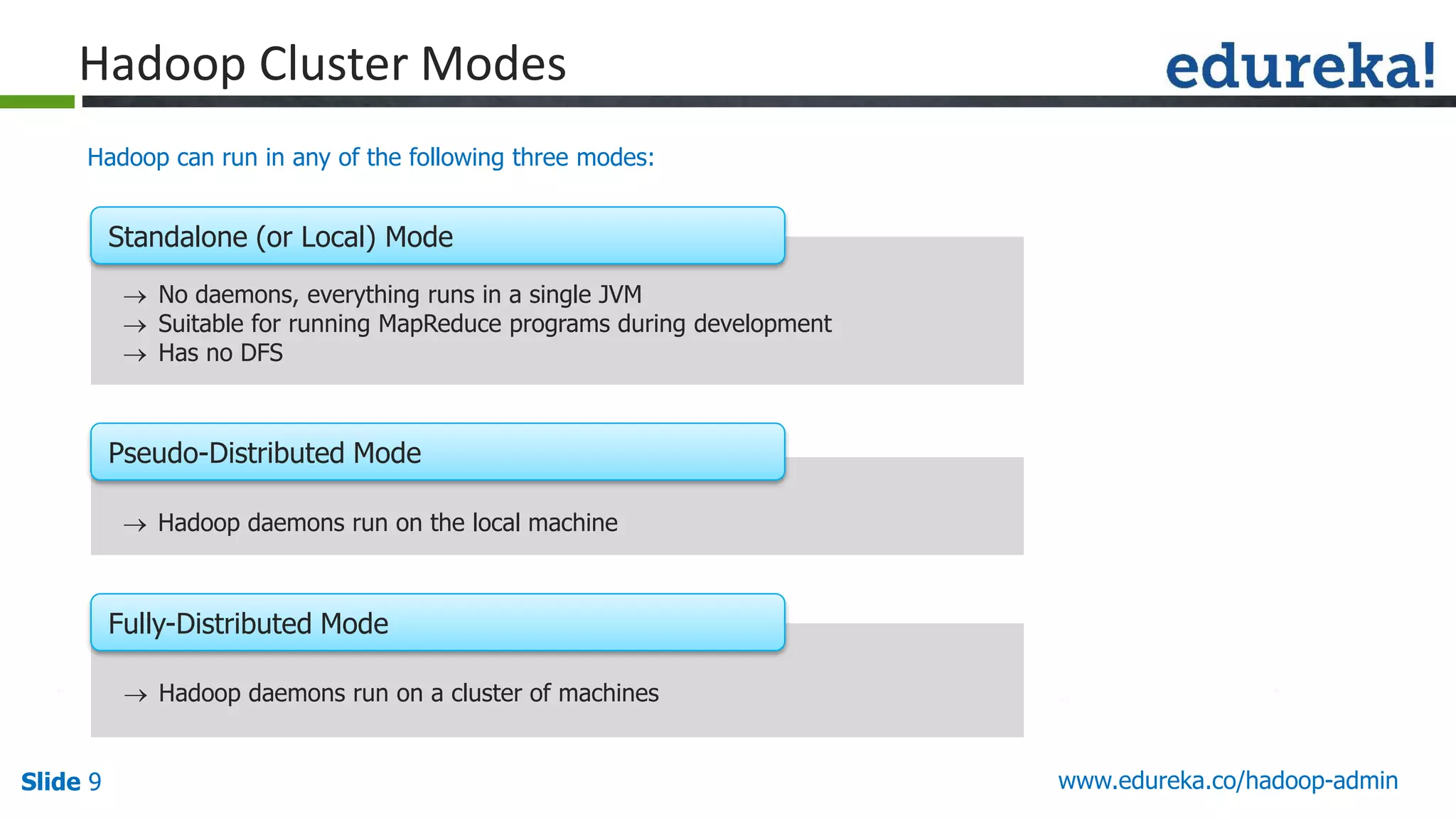
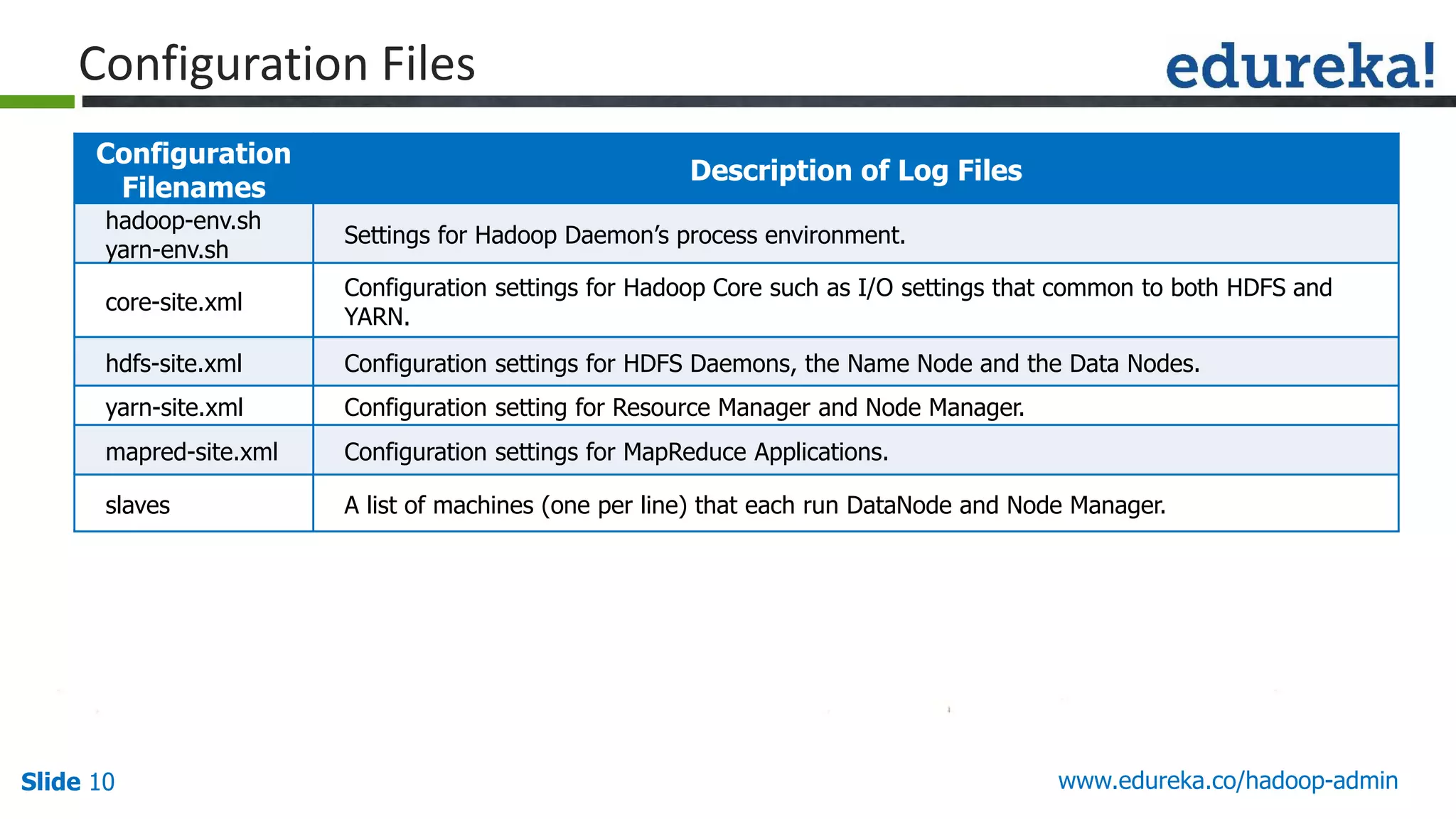
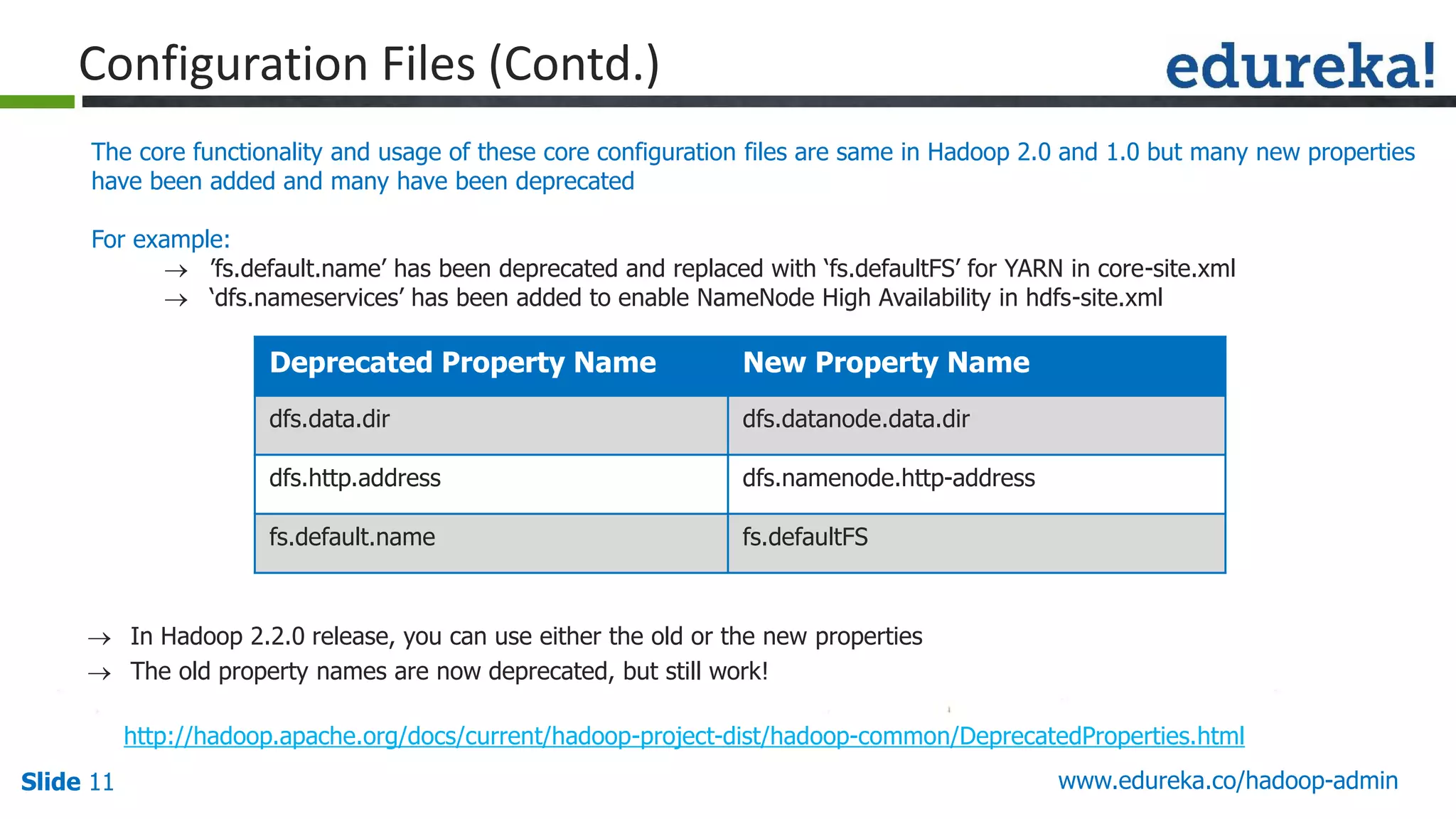
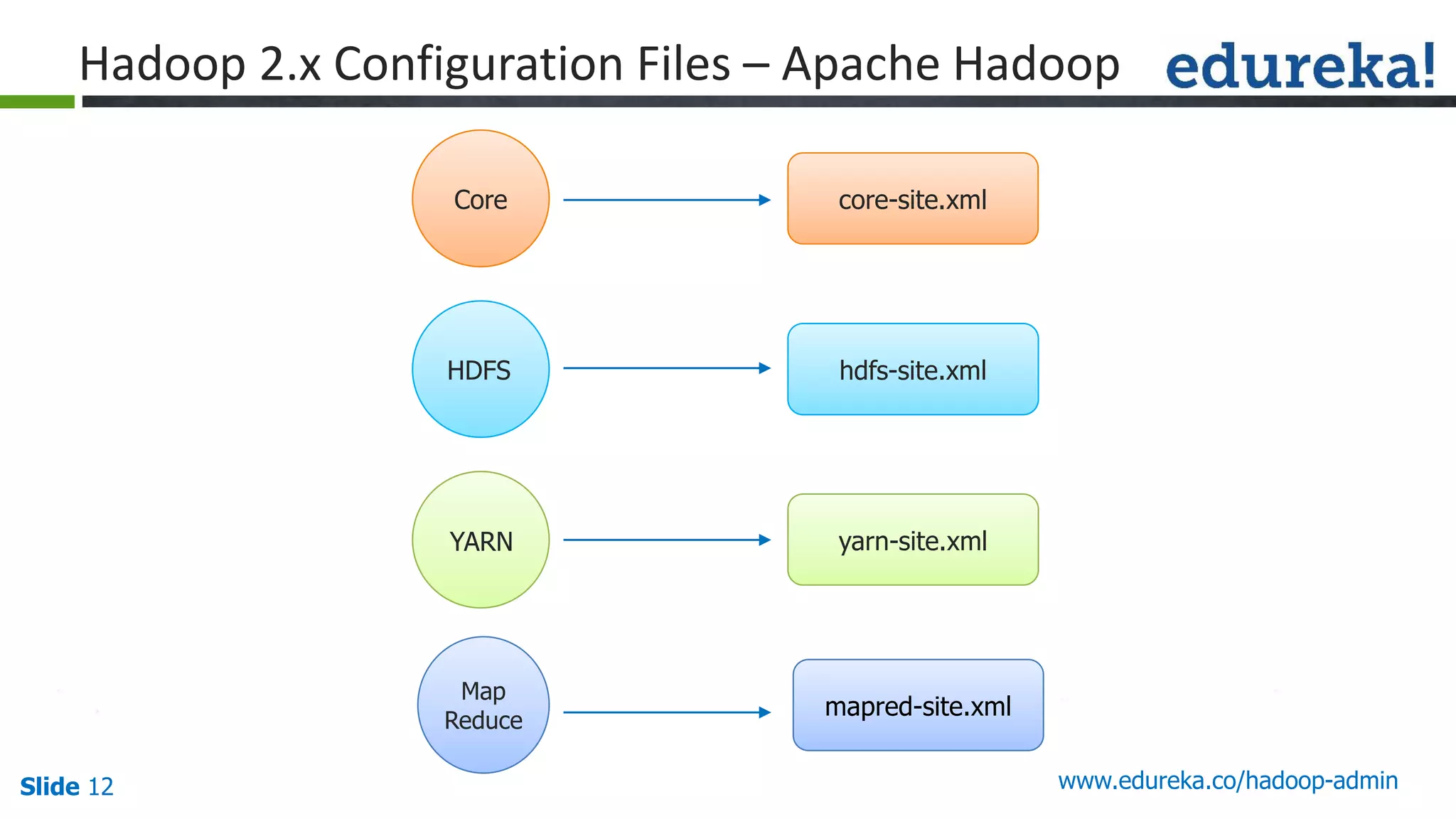
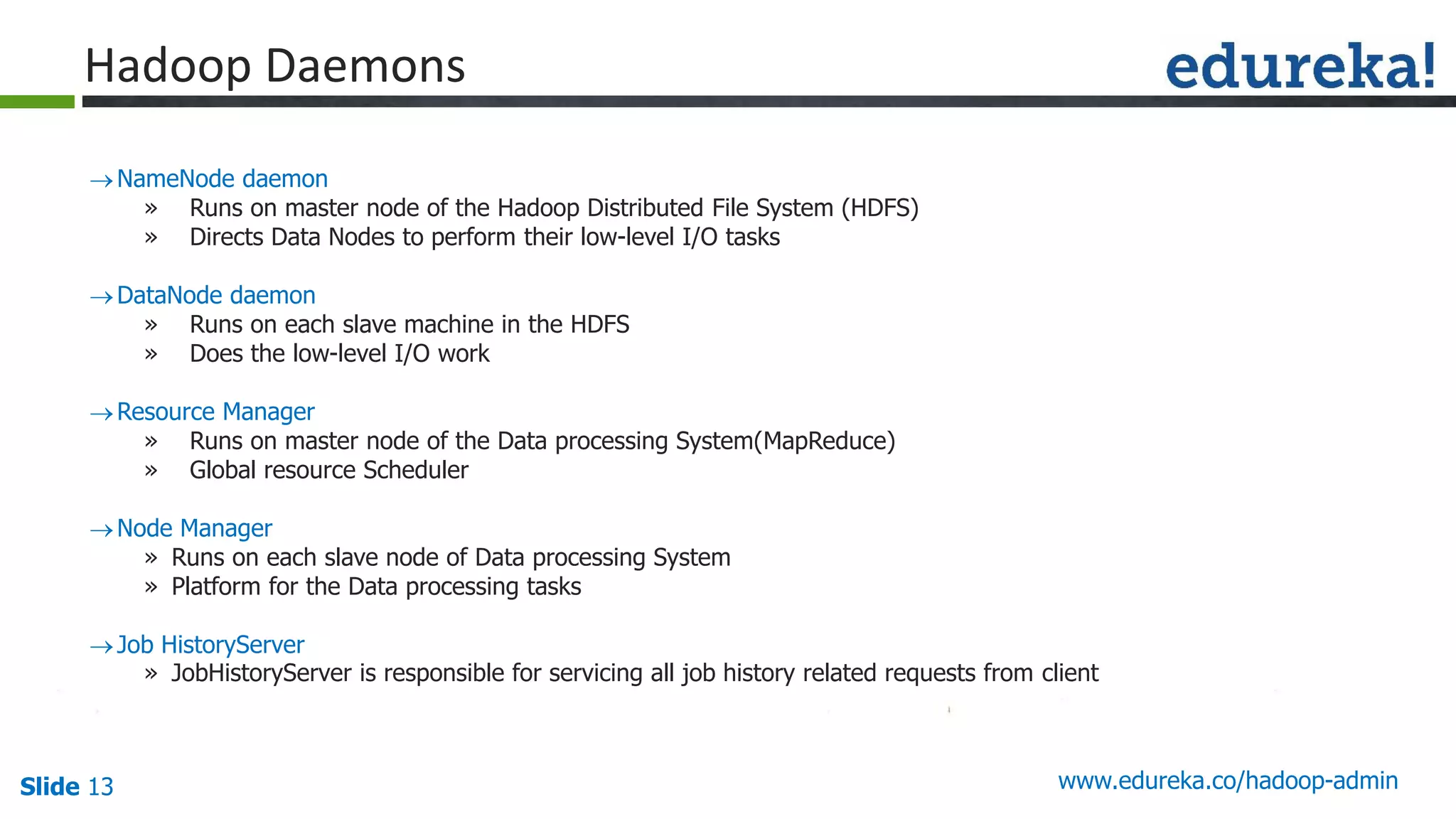
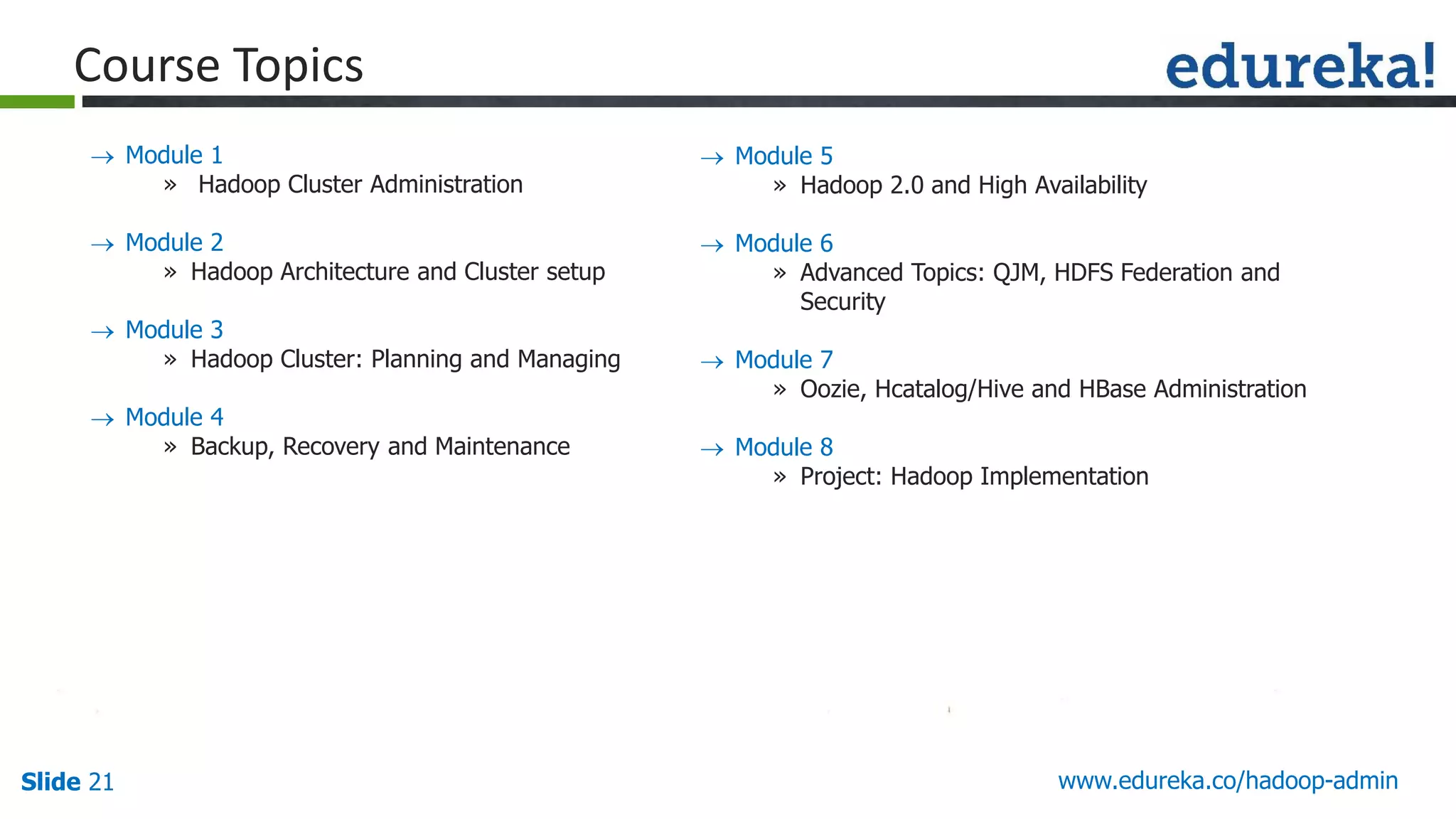
The document outlines a Hadoop administration course offered by Edureka, detailing the objectives, core components, recommended configurations, and operational modes of a Hadoop cluster. It emphasizes the importance of proper hardware setup and cluster management responsibilities, along with integration on cloud platforms like AWS for dynamic resource allocation. Additionally, it highlights various modules of the course covering advanced topics and practical project work.