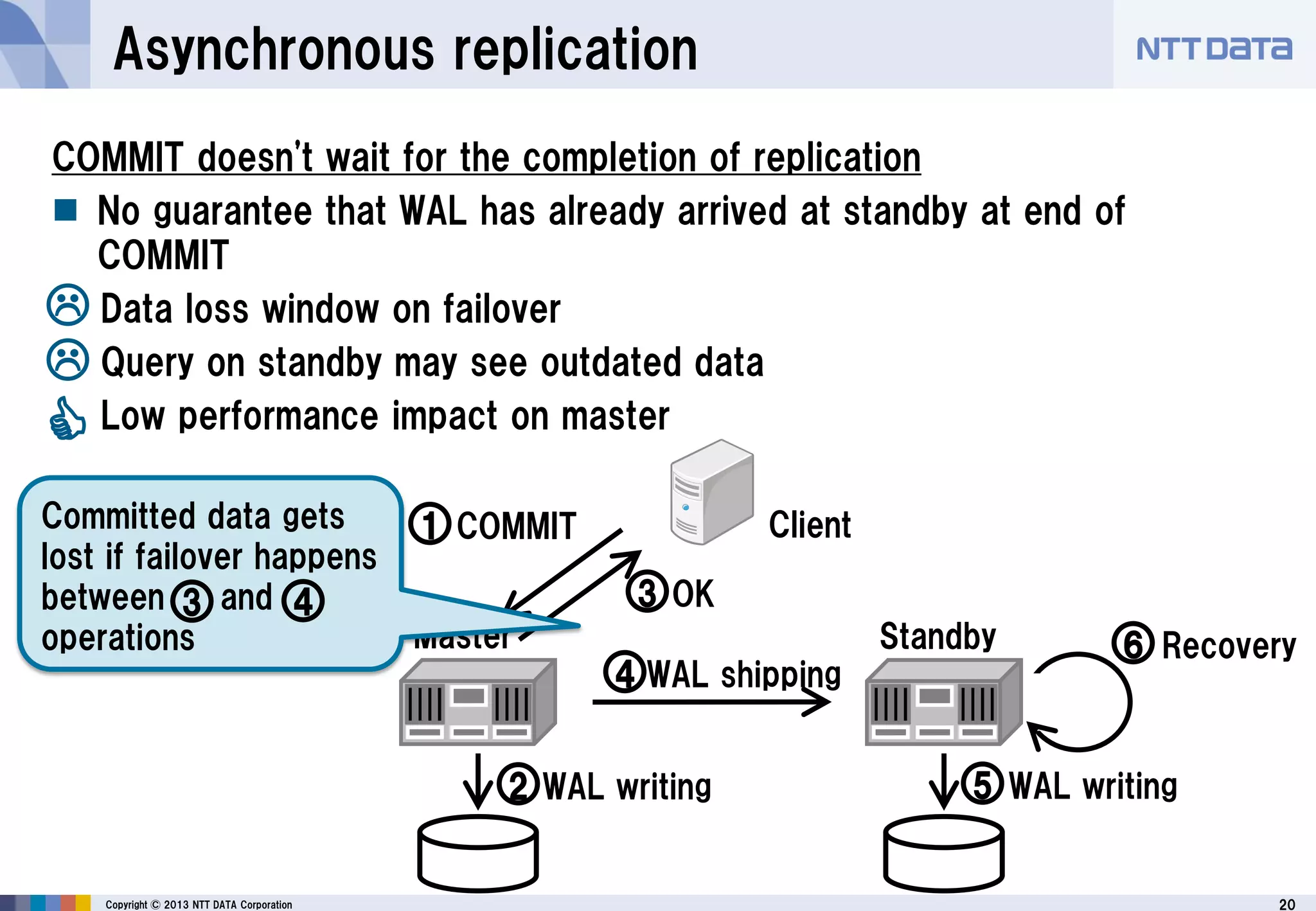
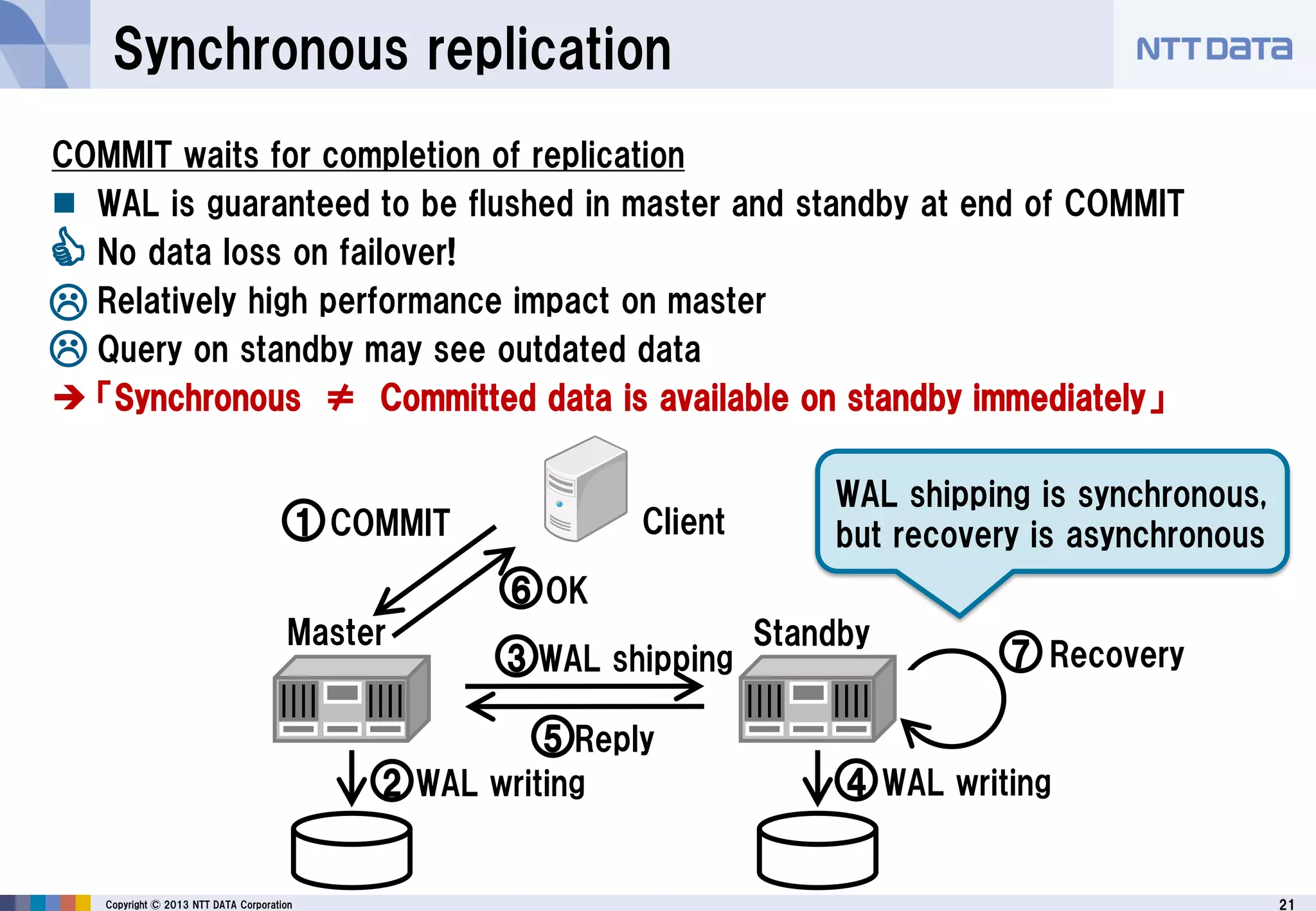
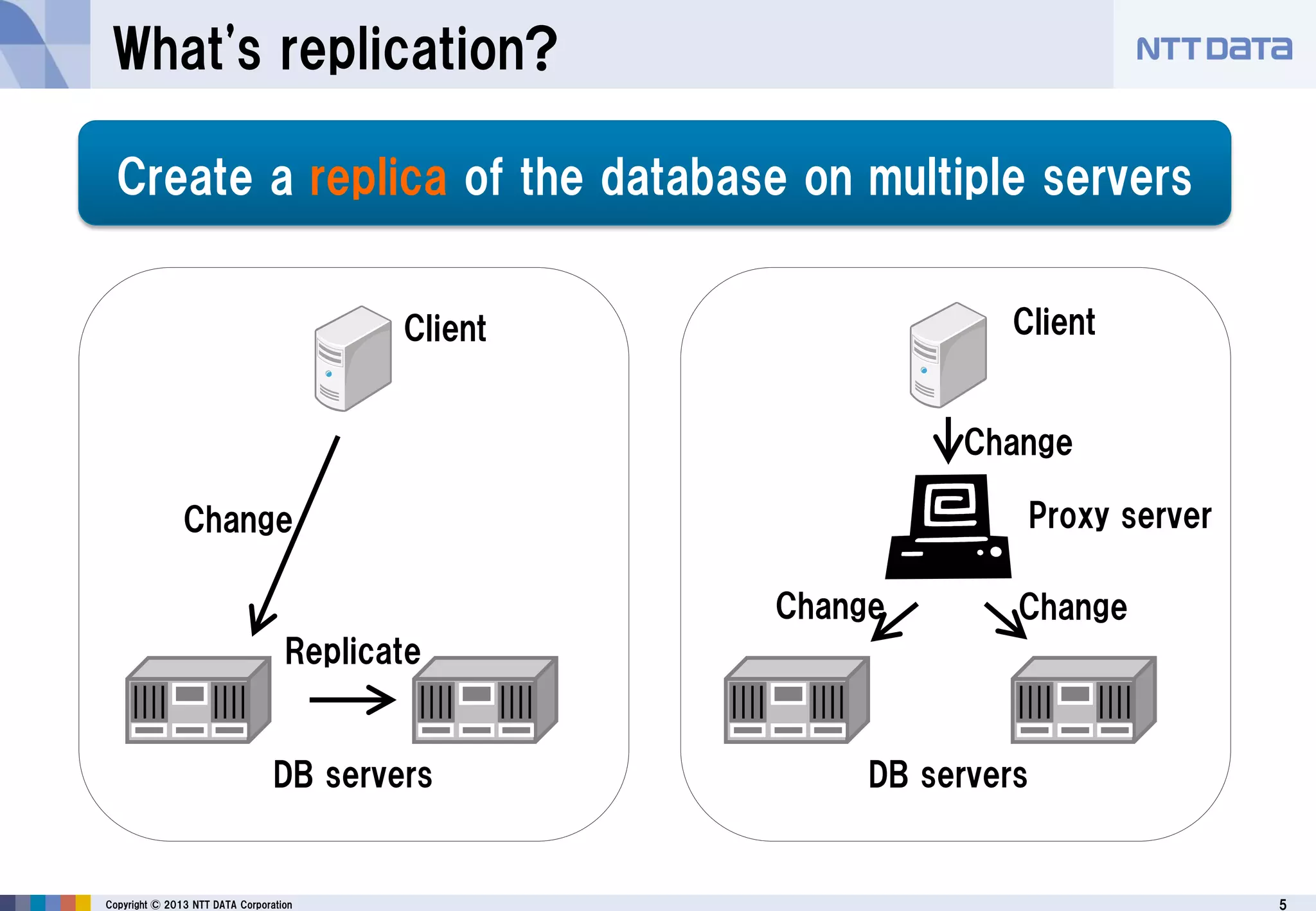
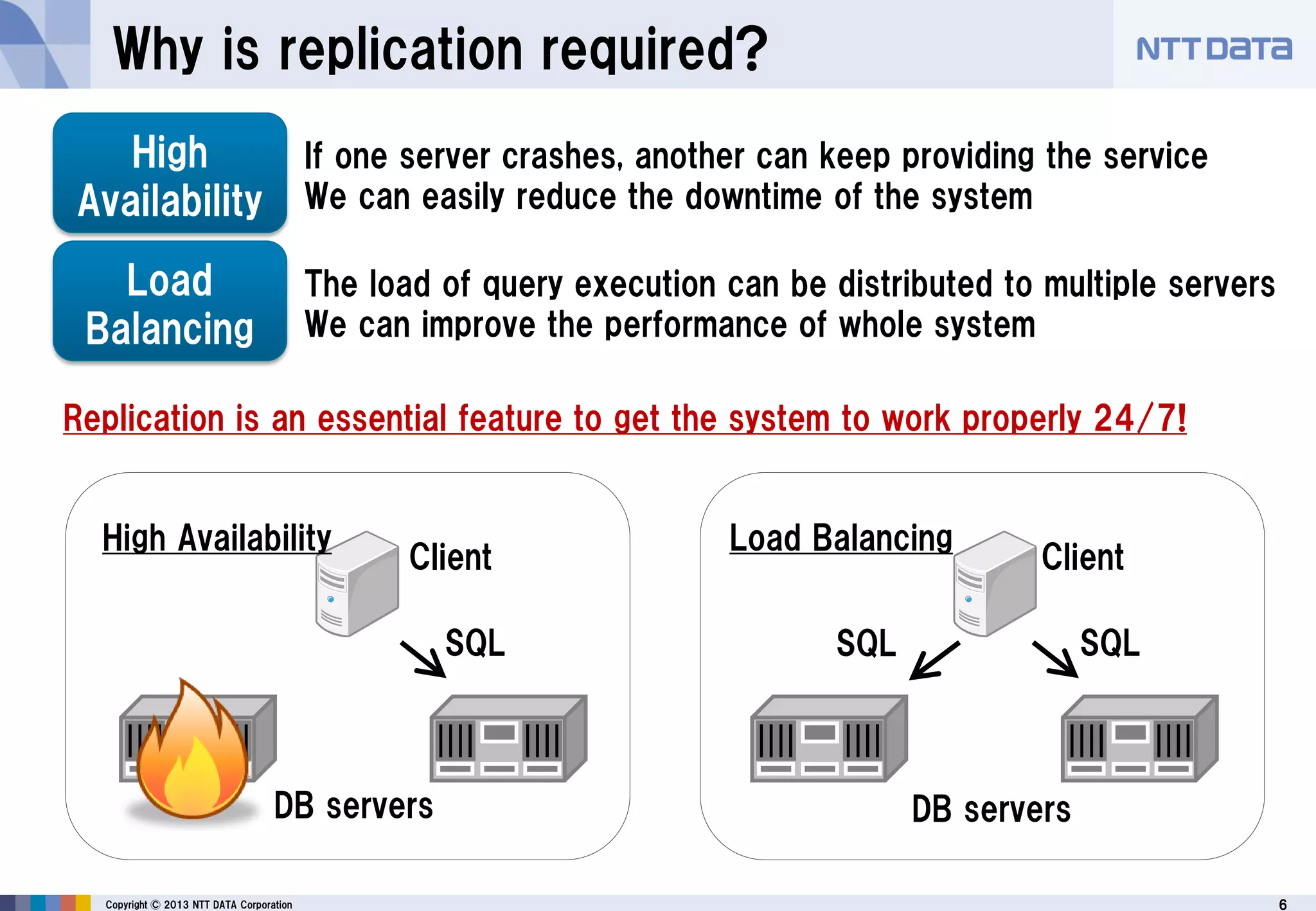
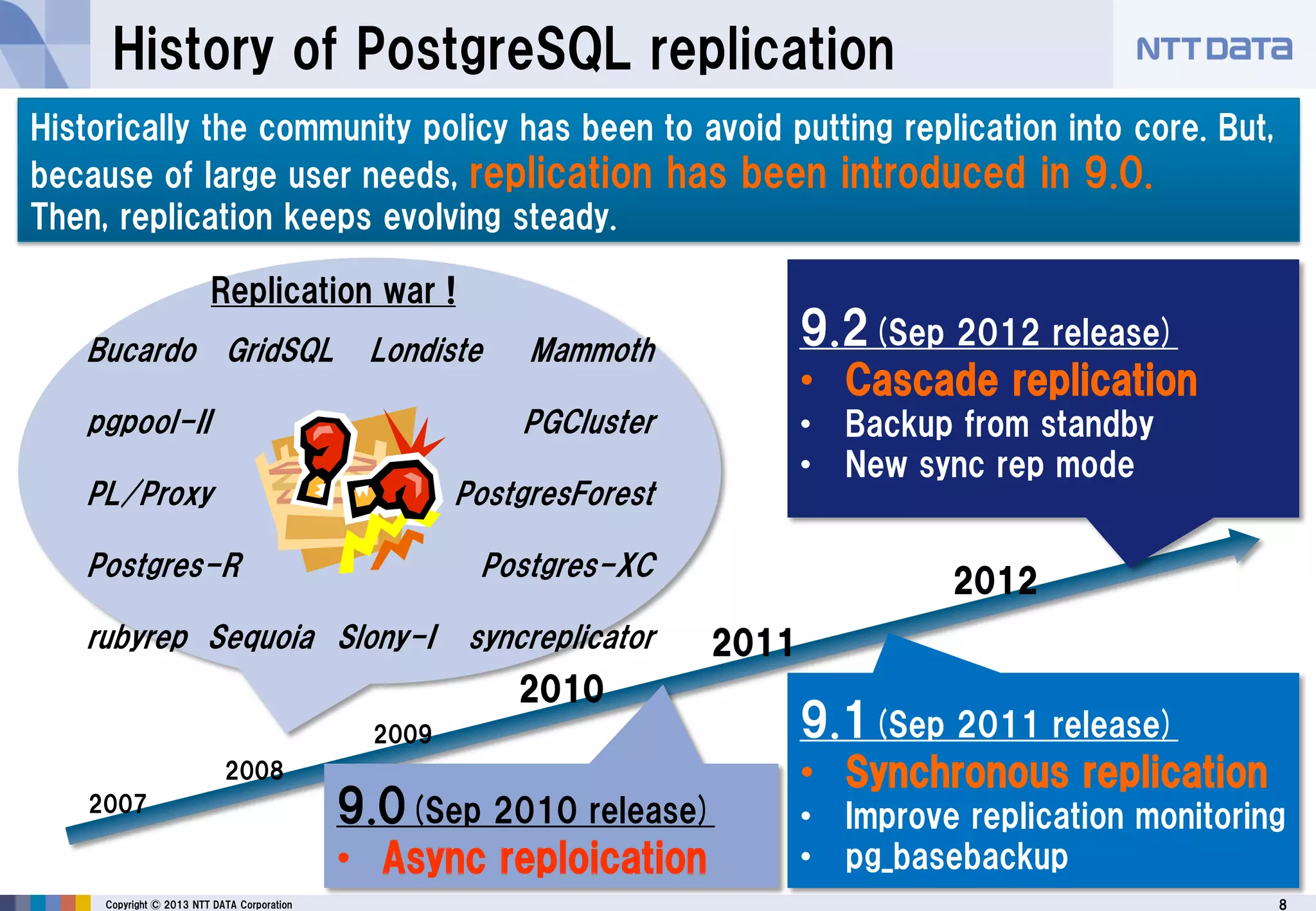
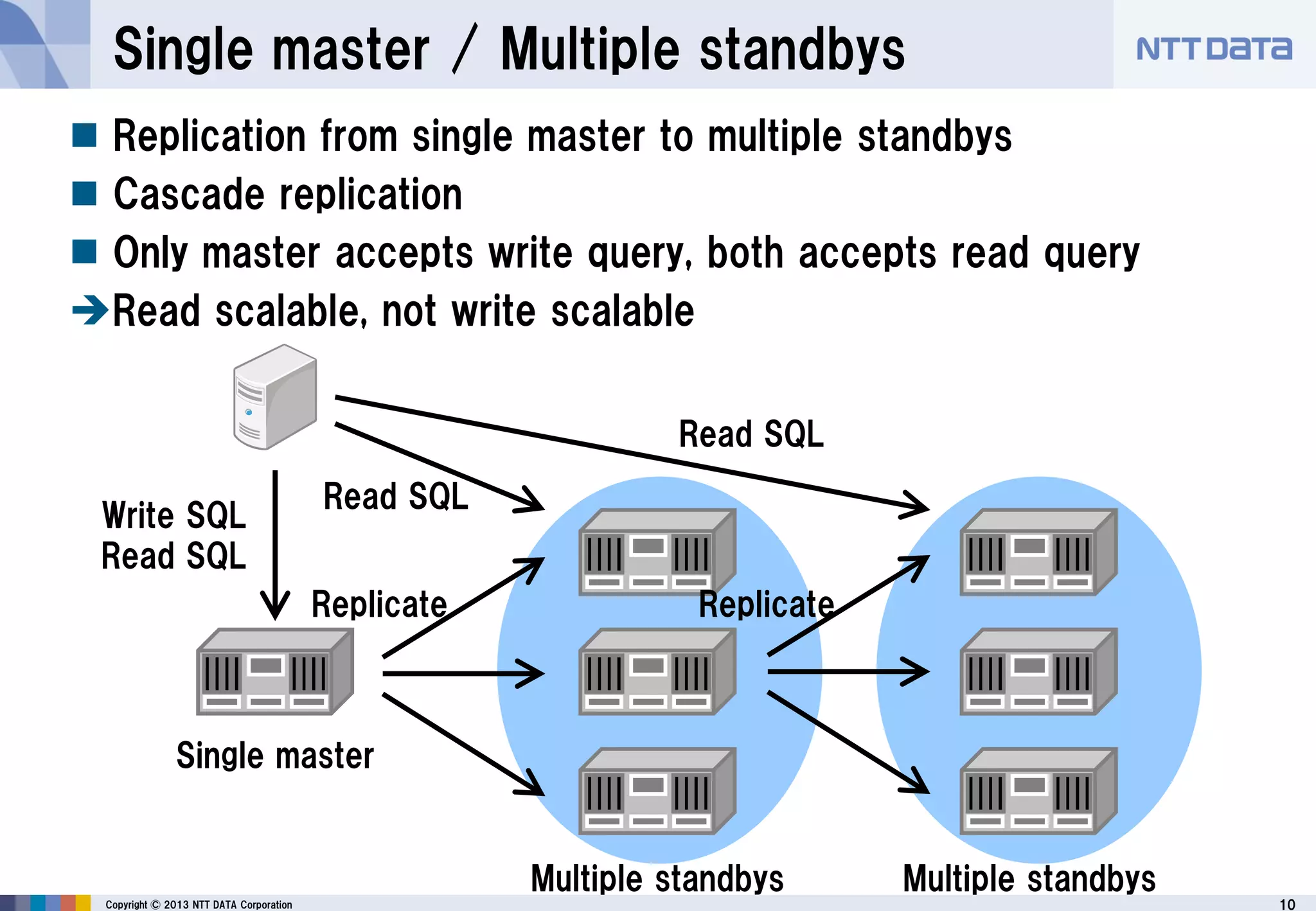
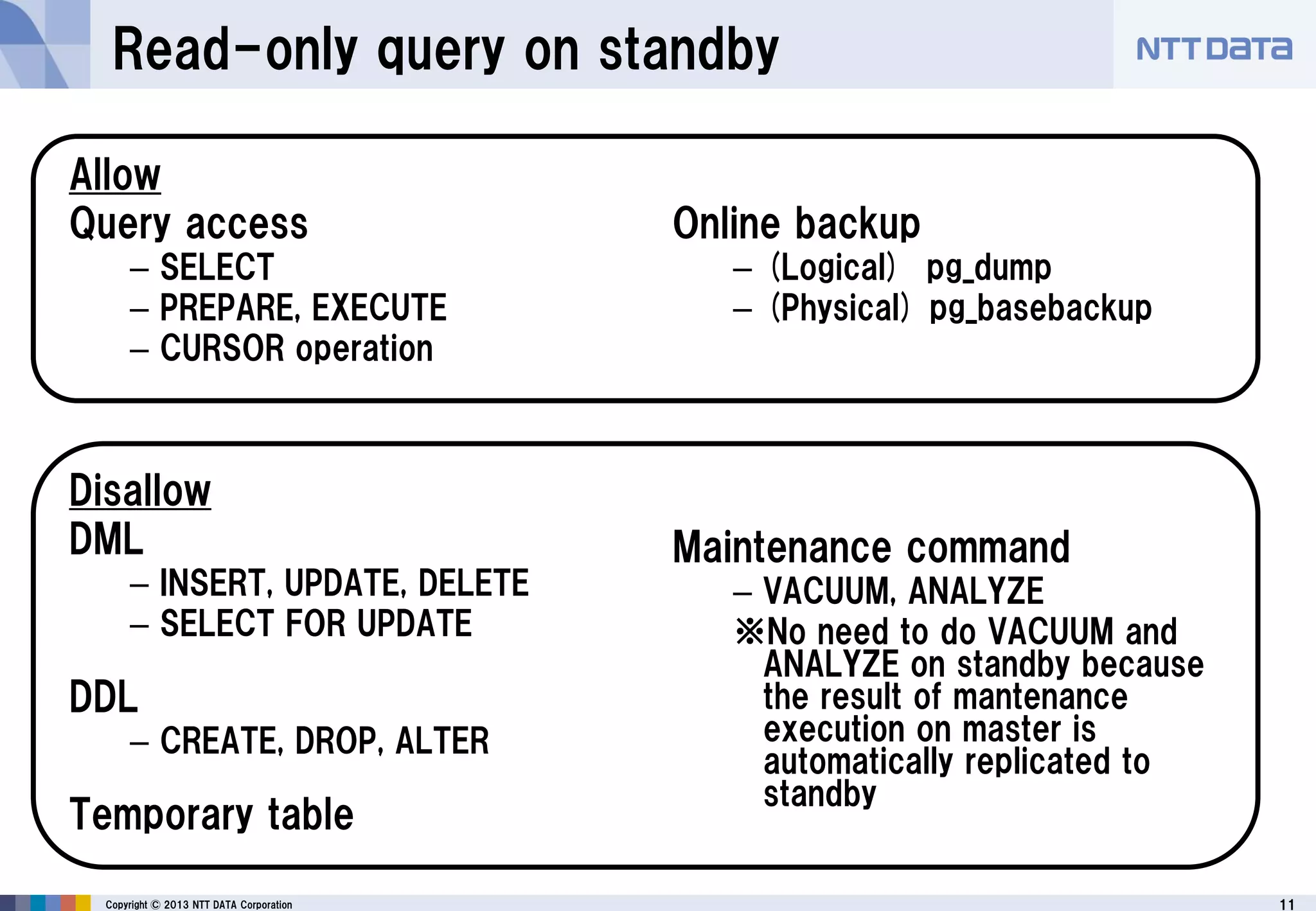
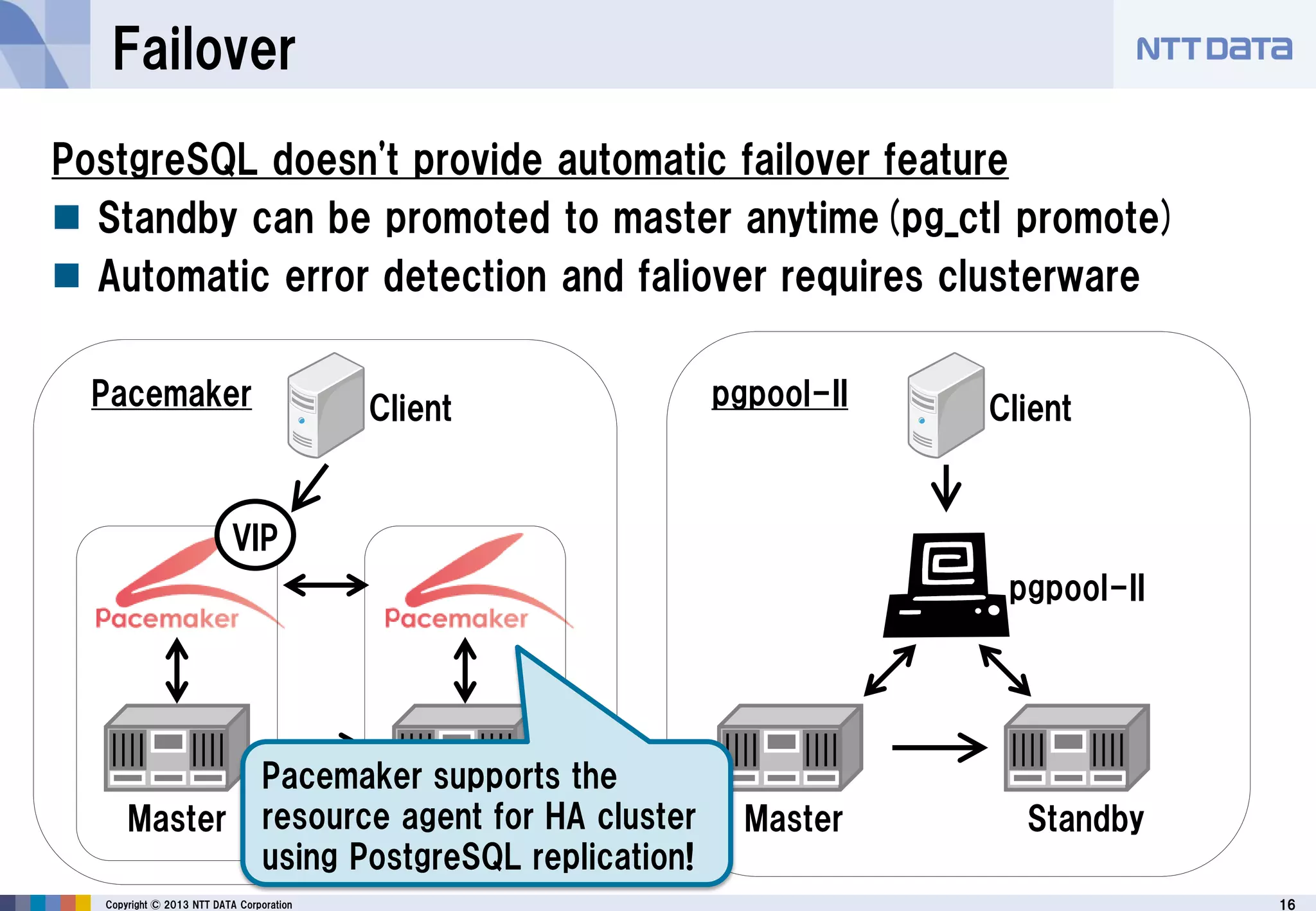
The document discusses PostgreSQL replication, detailing its features, historical evolution, and operational modes. It highlights replication's importance for high availability, load balancing, and reducing downtime, along with the distinctions between asynchronous and synchronous replication. Additionally, it addresses limitations, failover mechanisms, and monitoring capabilities within PostgreSQL's replication framework.





![17Copyright © 2013 NTT DATA Corporation
Monitoring
=# SELECT * FROM pg_stat_replication;
-[ RECORD 1 ]----+------------------------------
procpid | 26531
usesysid | 10
usename | postgres
application_name | tokyo
client_addr | 192.168.1.2
client_hostname |
client_port | 39654
backend_start | 2012-02-01 18:54:49.429459+09
state | streaming
sent_location | 0/406E7CC
write_location | 0/406E7CC
flush_location | 0/406E7CC
replay_location | 0/406E1B0
sync_priority | 1
sync_state | sync
Replication progress
How far has master sent WAL?
How far has standby written, flushed or
replayed WAL?
Replication connection information
Standby IP address, Port number,
ROLE for replication、
Replication start time, etc
Replication status
Current synchronous mode,
Standby has already caught up with master?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgresqlreplication-130430071355-phpapp02/75/PostgreSQL-replication-17-2048.jpg)