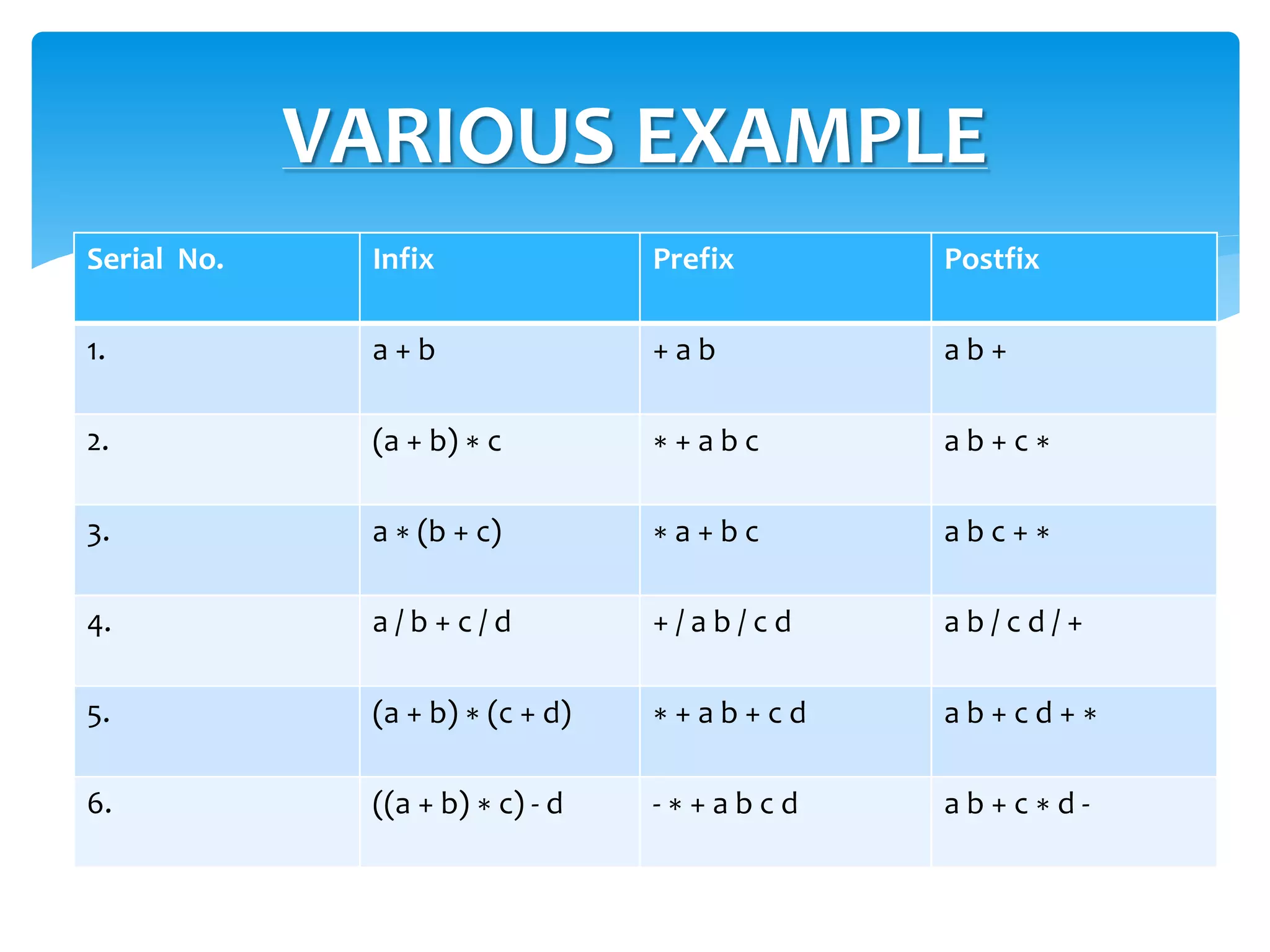
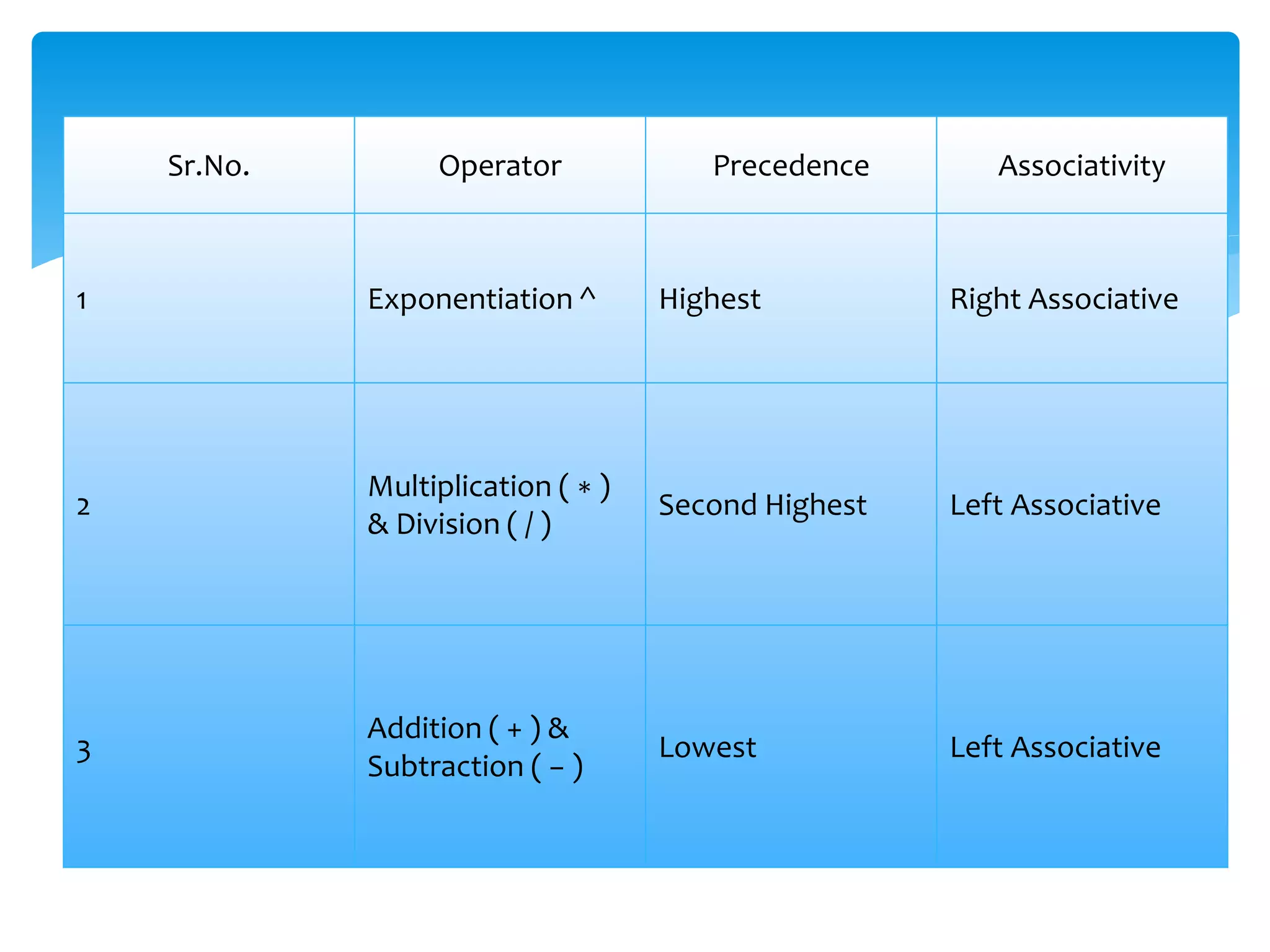
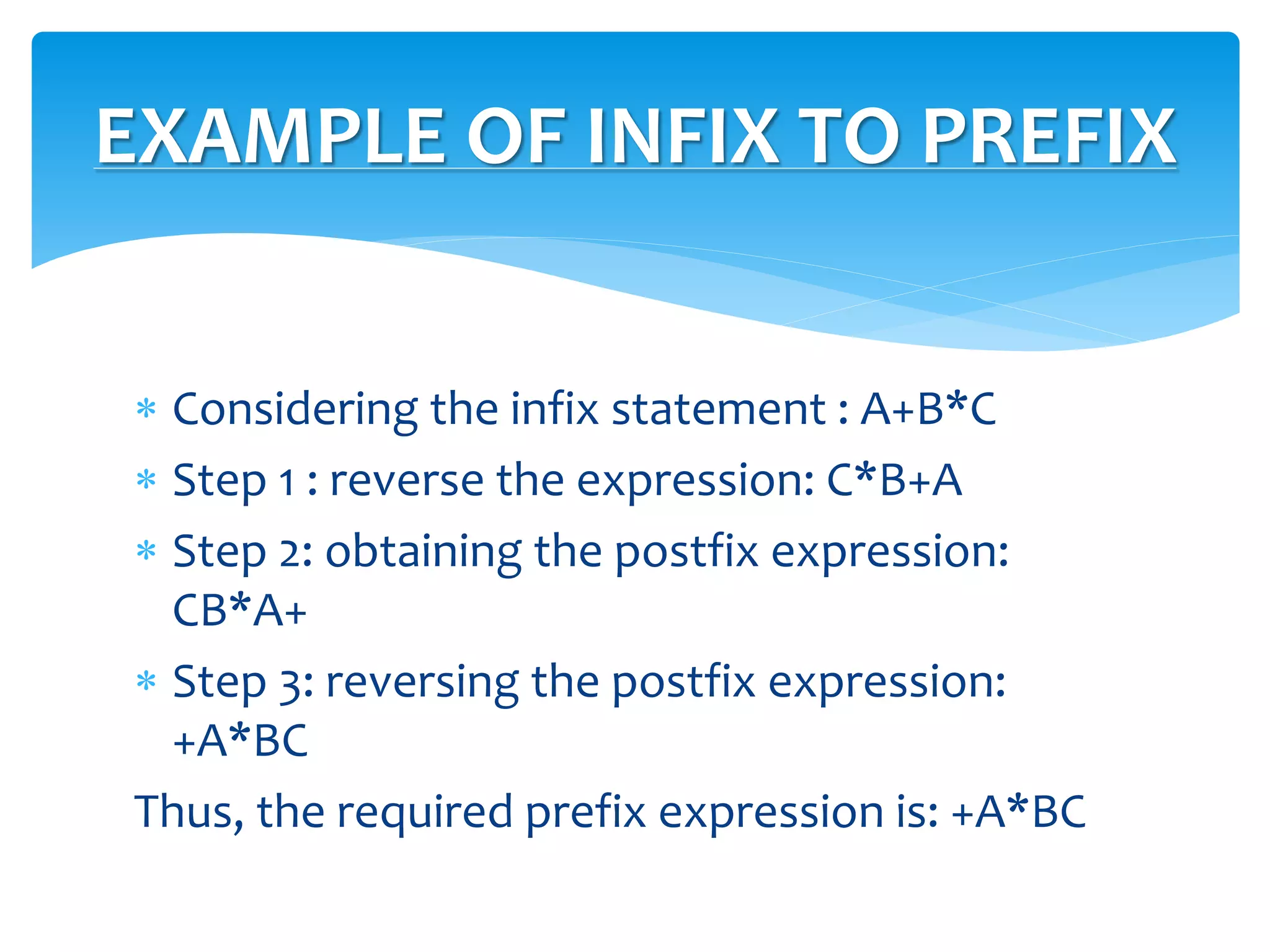
The document discusses different notation styles for representing arithmetic expressions, including infix, prefix, and postfix notations. It provides examples of converting expressions between these notations. Infix notation is the conventional style that humans use, but prefix and postfix notations are better suited for computer parsing. The document also covers parsing expressions, operator precedence, and the steps to convert between infix and prefix and infix and postfix notations.










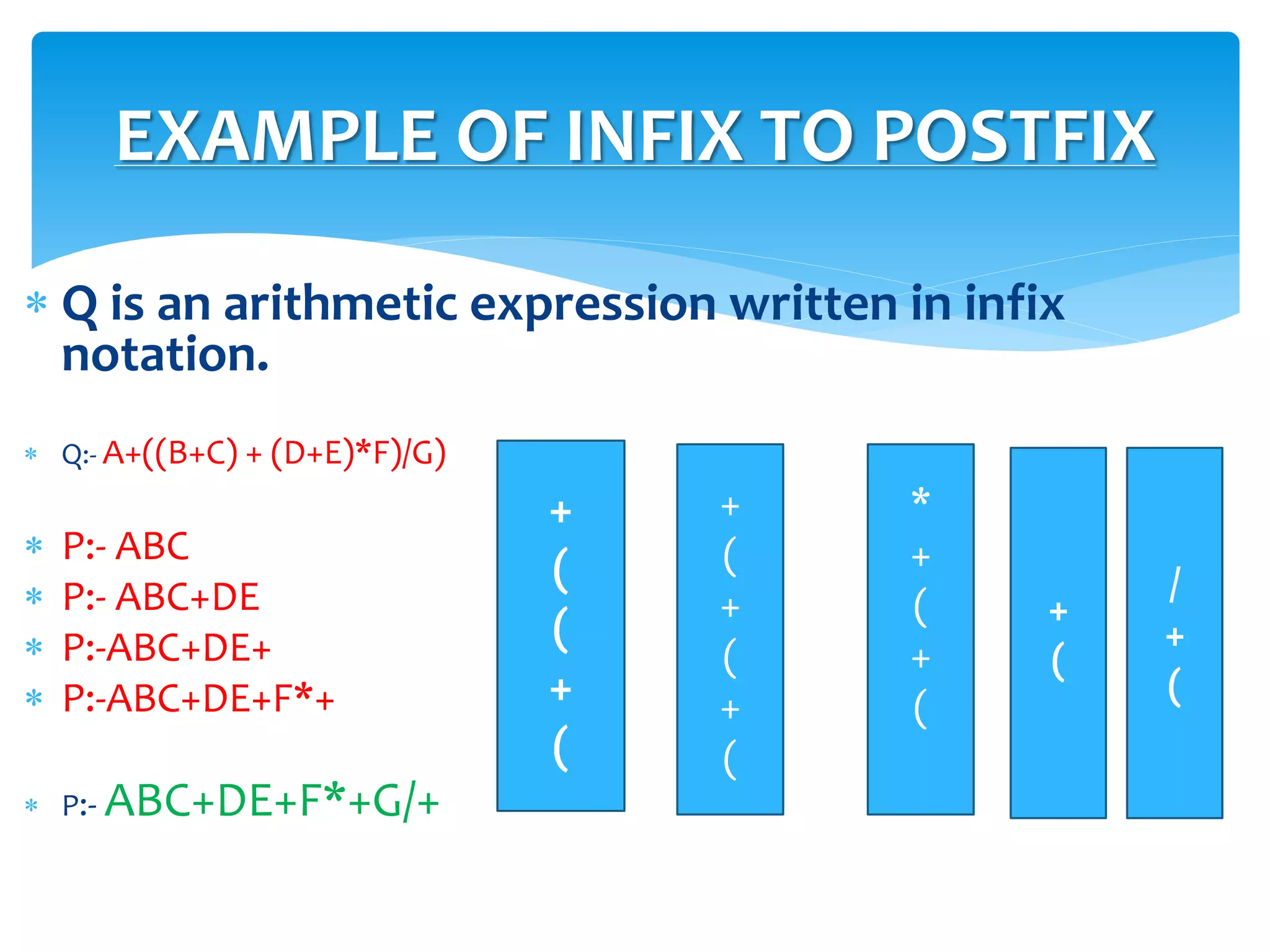
![ Q is an arithmetic expression written in infix
notation.
Q:- A+[(B+C) + (D+E)*F]/G)
P:- ABC
P:- ABC+DE
P:-ABC+DE+
P:-ABC+DE+F*+
P:- ABC+DE+F*+G/+
EXAMPLE OF INFIX TO POSTFIX](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05satyaprakashranjan-200413102917/75/Polish-Notation-In-Data-Structure-15-2048.jpg)