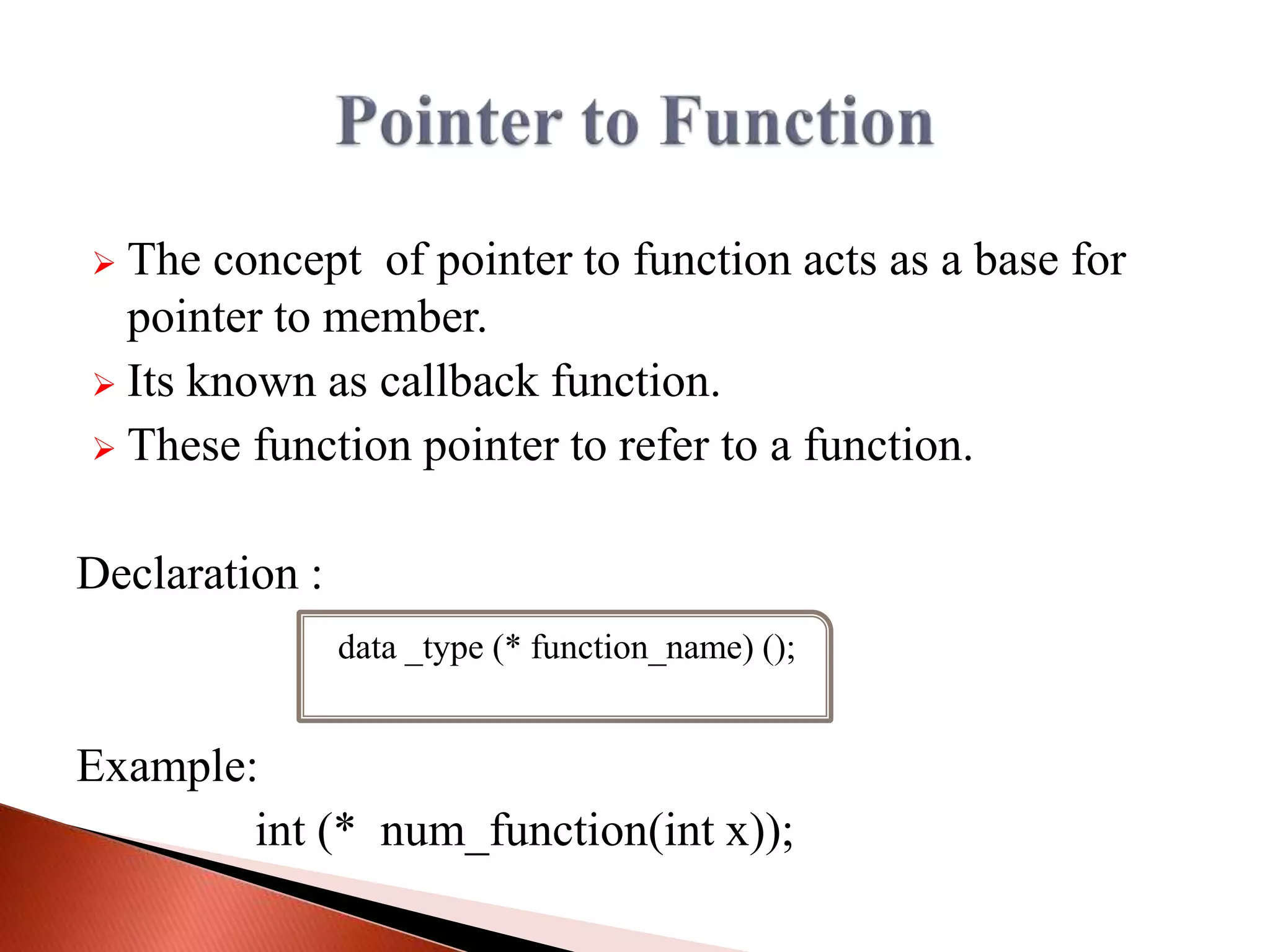
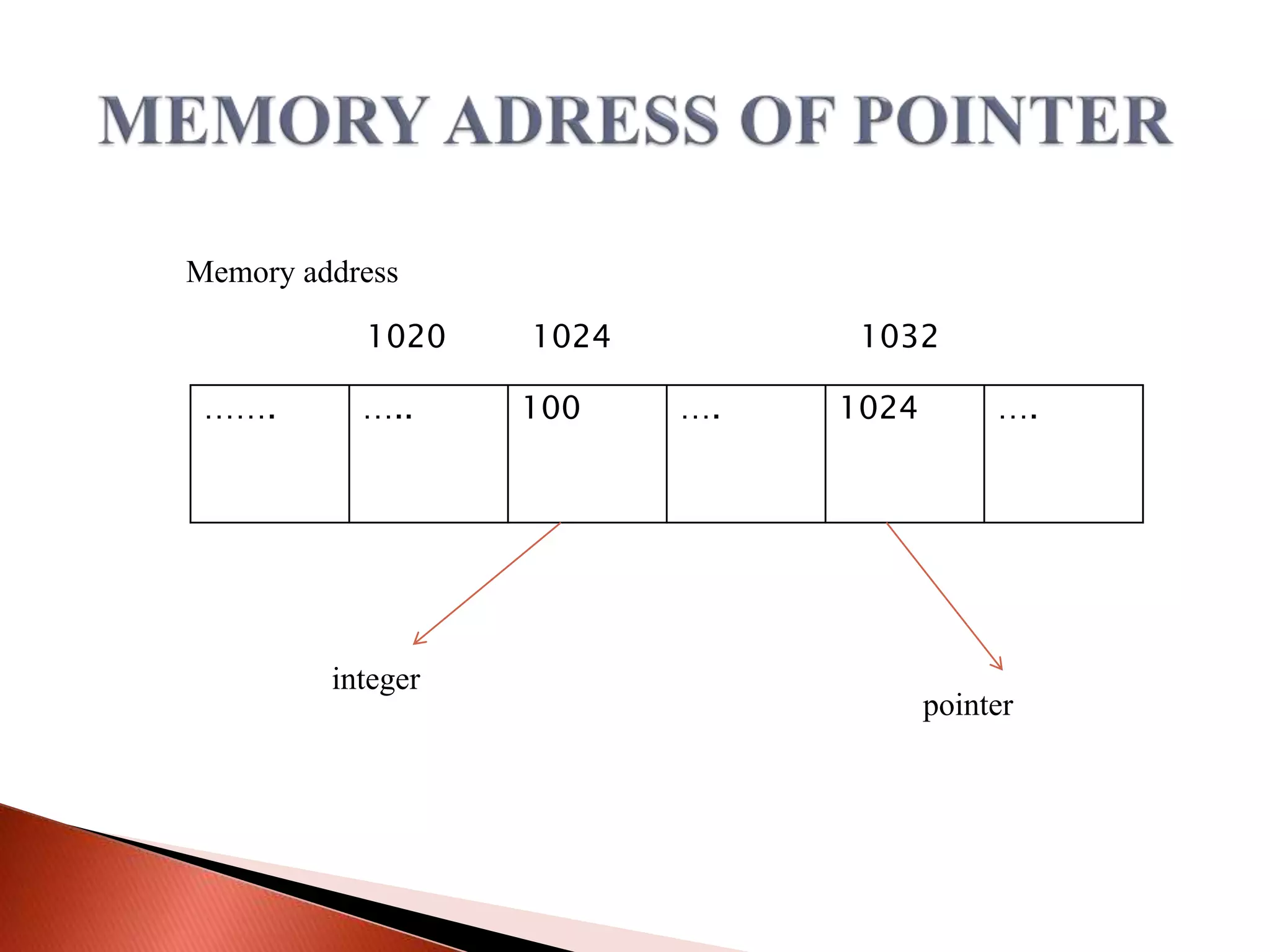
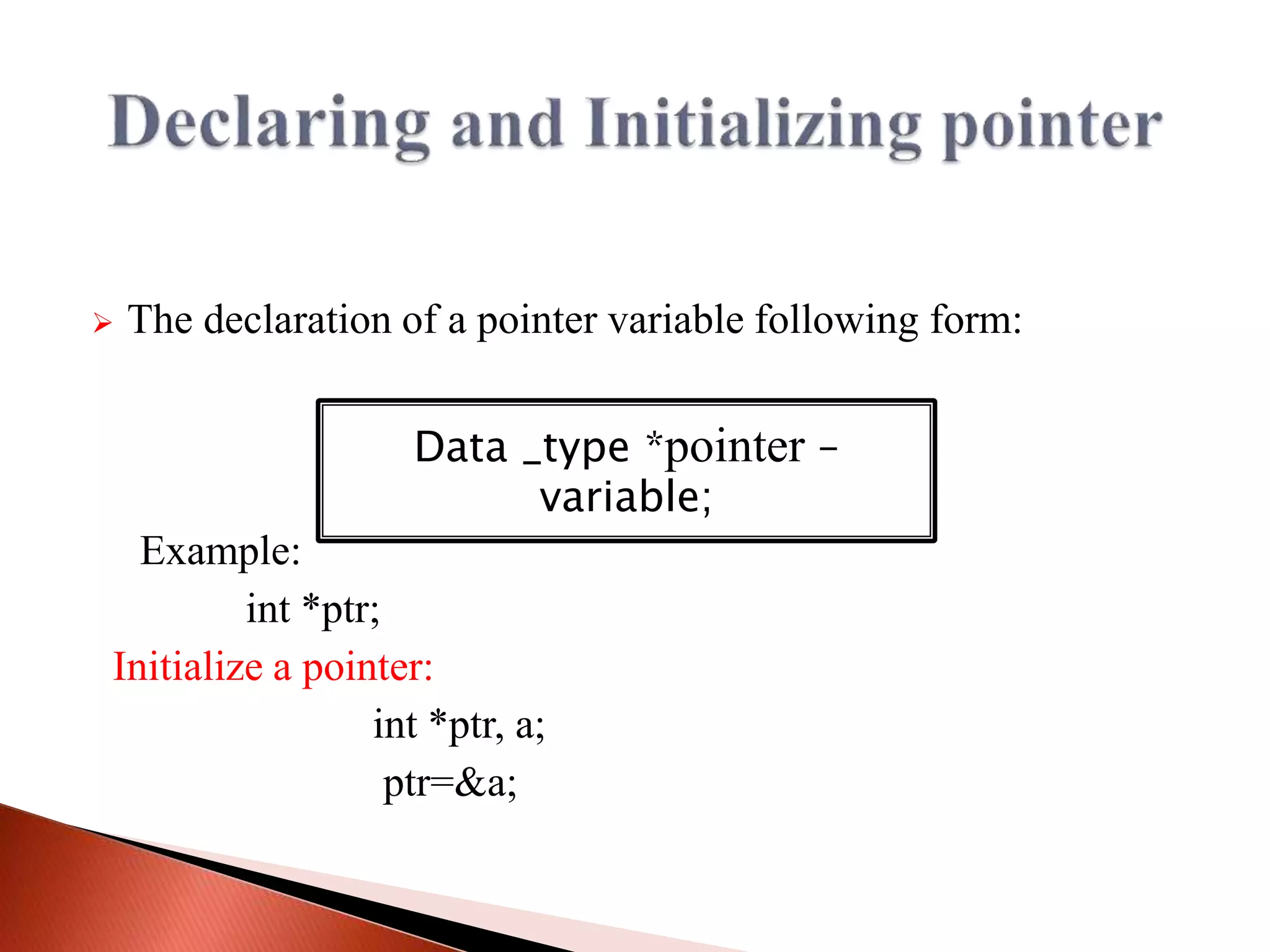
The document discusses different types of polymorphism in C++ including function overloading, operator overloading, and virtual functions. It also covers key concepts related to pointers in C++ like pointer declaration syntax, dereferencing pointers, pointer arithmetic, arrays of pointers, pointers to functions, pointers to class members, and pointers to derived class objects.





![C++ allows pointers to perform the following arithmetic
operation:
1) A pointer can be incremented (++) or decremented (--).
2) Any integer can be added to subtracted from a pointer.
3) One pointer can be subtracted from another.
Example:
Int *aptr;
Ptr=&a[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerandpolymorphism-181001065353/75/Pointer-and-polymorphism-8-2048.jpg)
![The array of pointer represents a collection of
address.
An array of pointer point to an array of data
items.
Example:
int *in array[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerandpolymorphism-181001065353/75/Pointer-and-polymorphism-9-2048.jpg)
![A[2]
A[1]
A[1]
A[3]
A[4]
1000
1004
1008
1012
1016
a
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerandpolymorphism-181001065353/75/Pointer-and-polymorphism-10-2048.jpg)
![The usage of pointer with one dimensional
array element.
A string is one dimensional array of character.
Example:
char num[]=“one”;
const char *numptr=“one”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pointerandpolymorphism-181001065353/75/Pointer-and-polymorphism-11-2048.jpg)