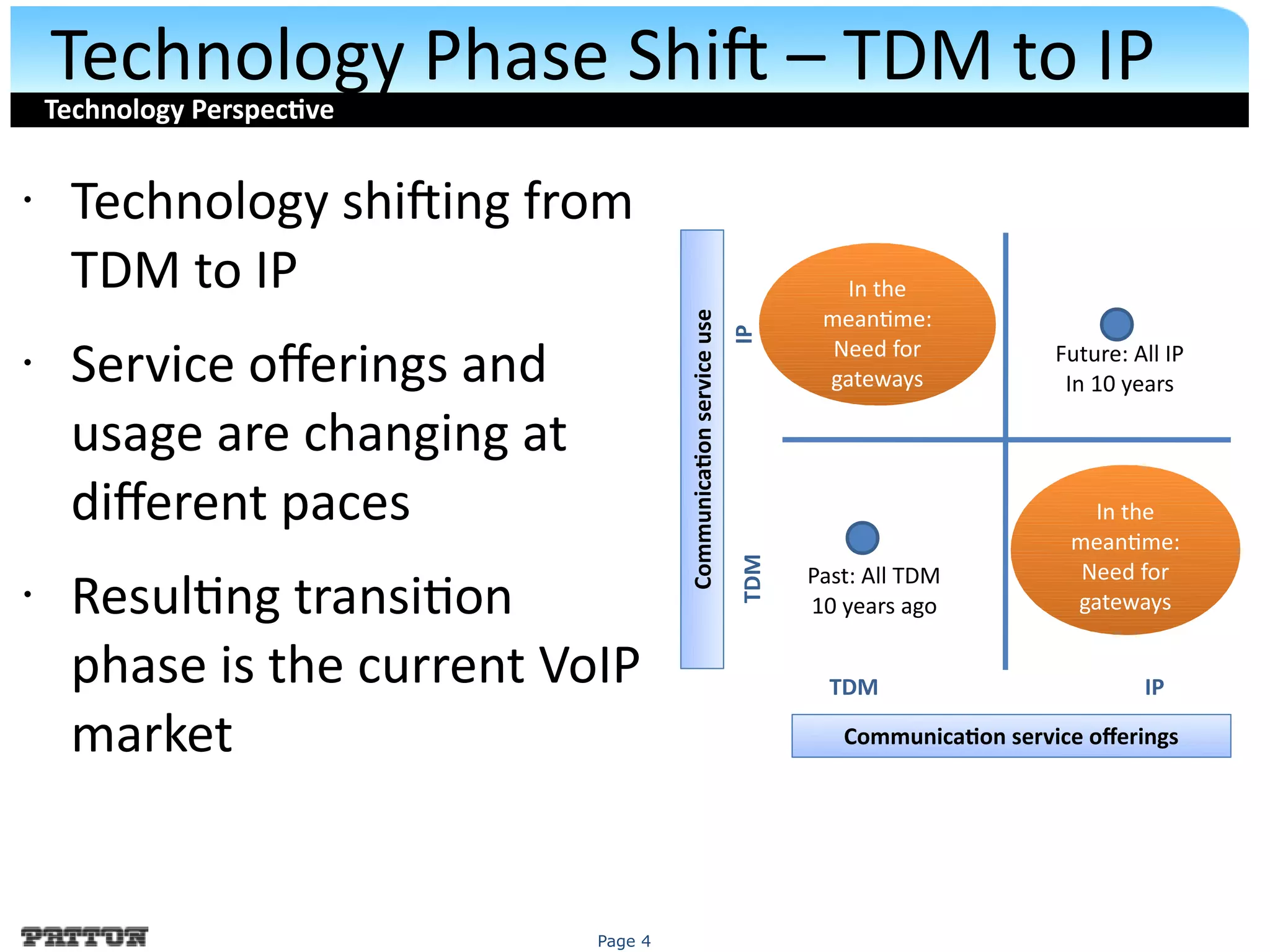
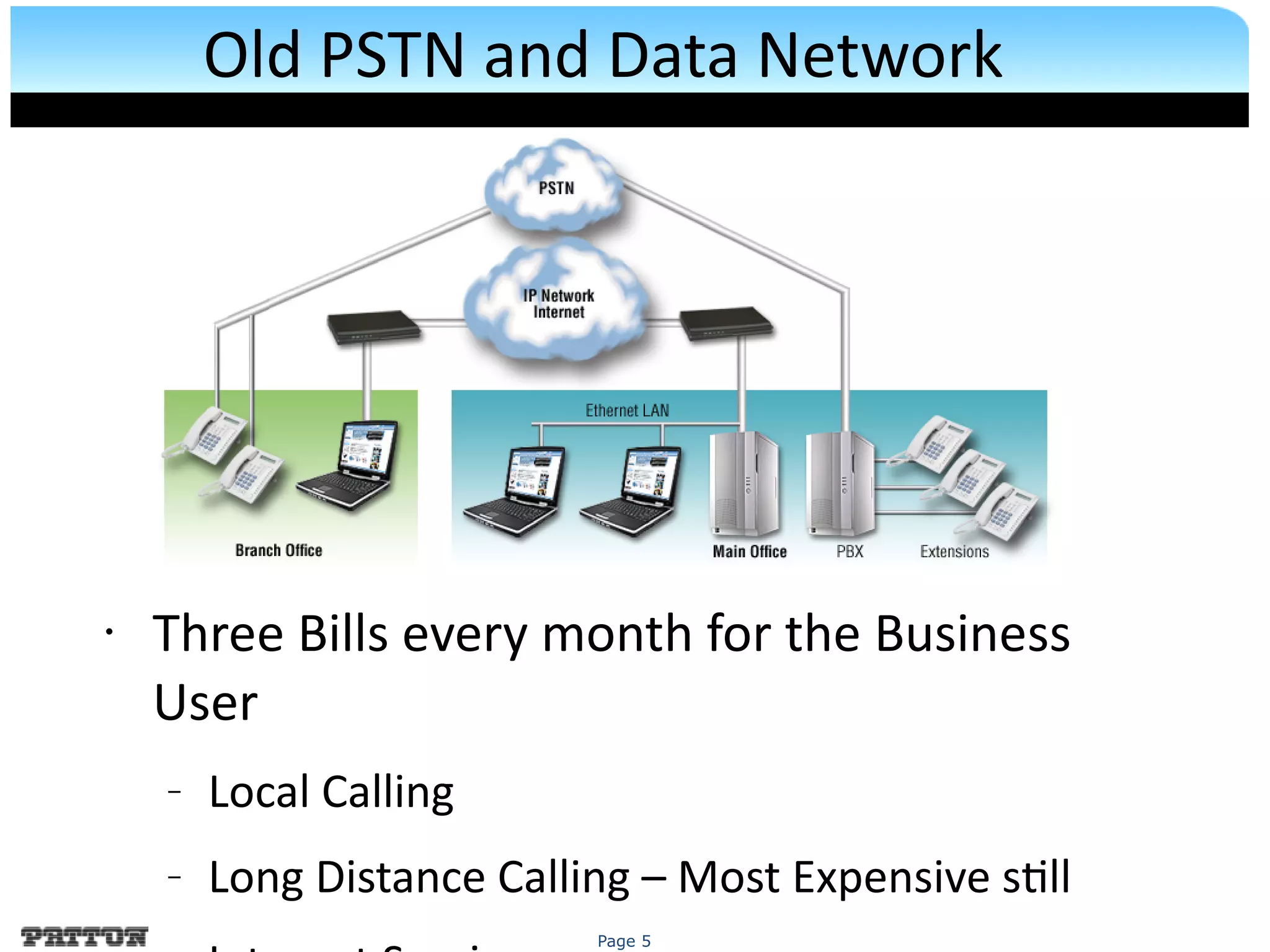
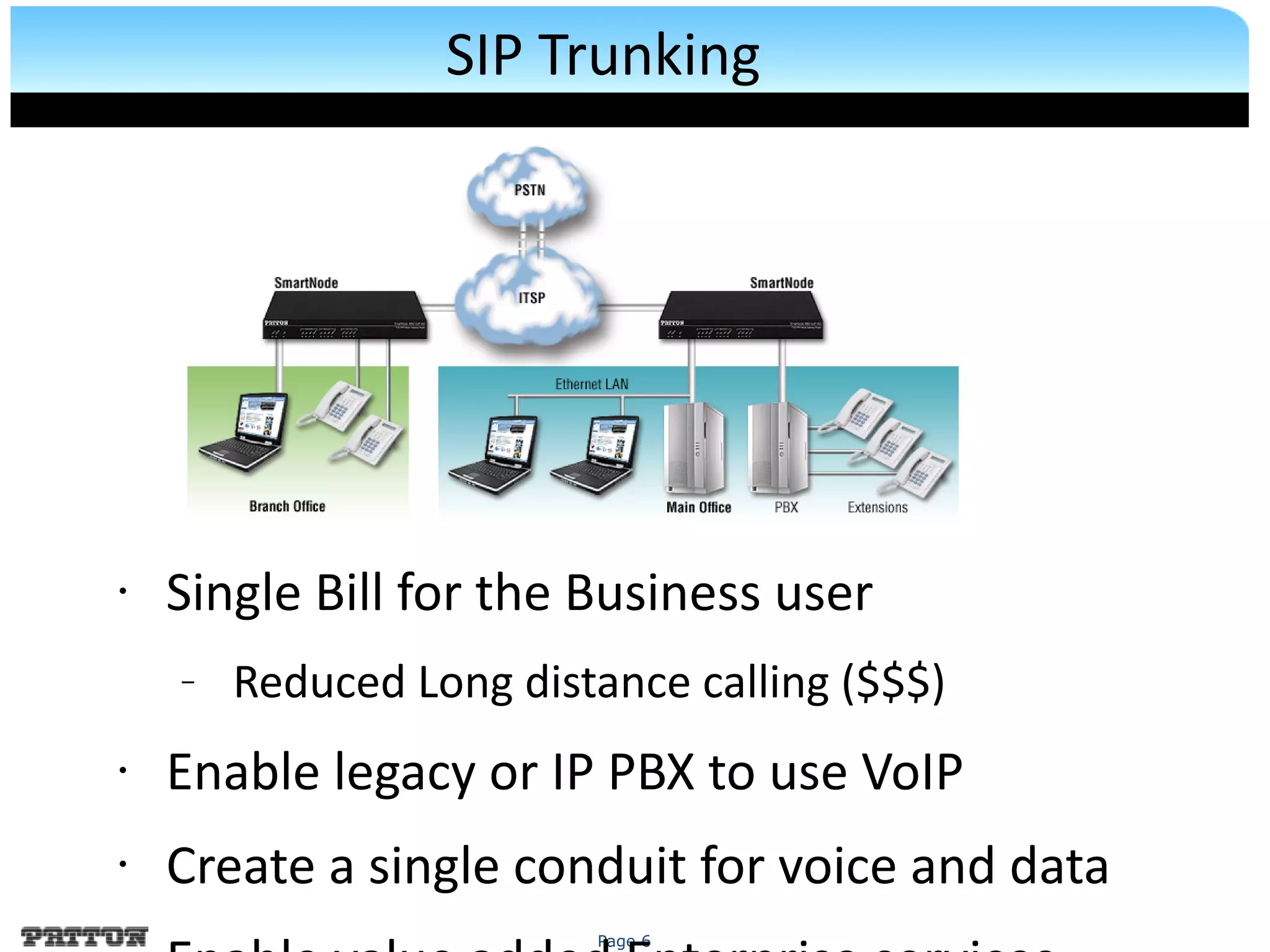
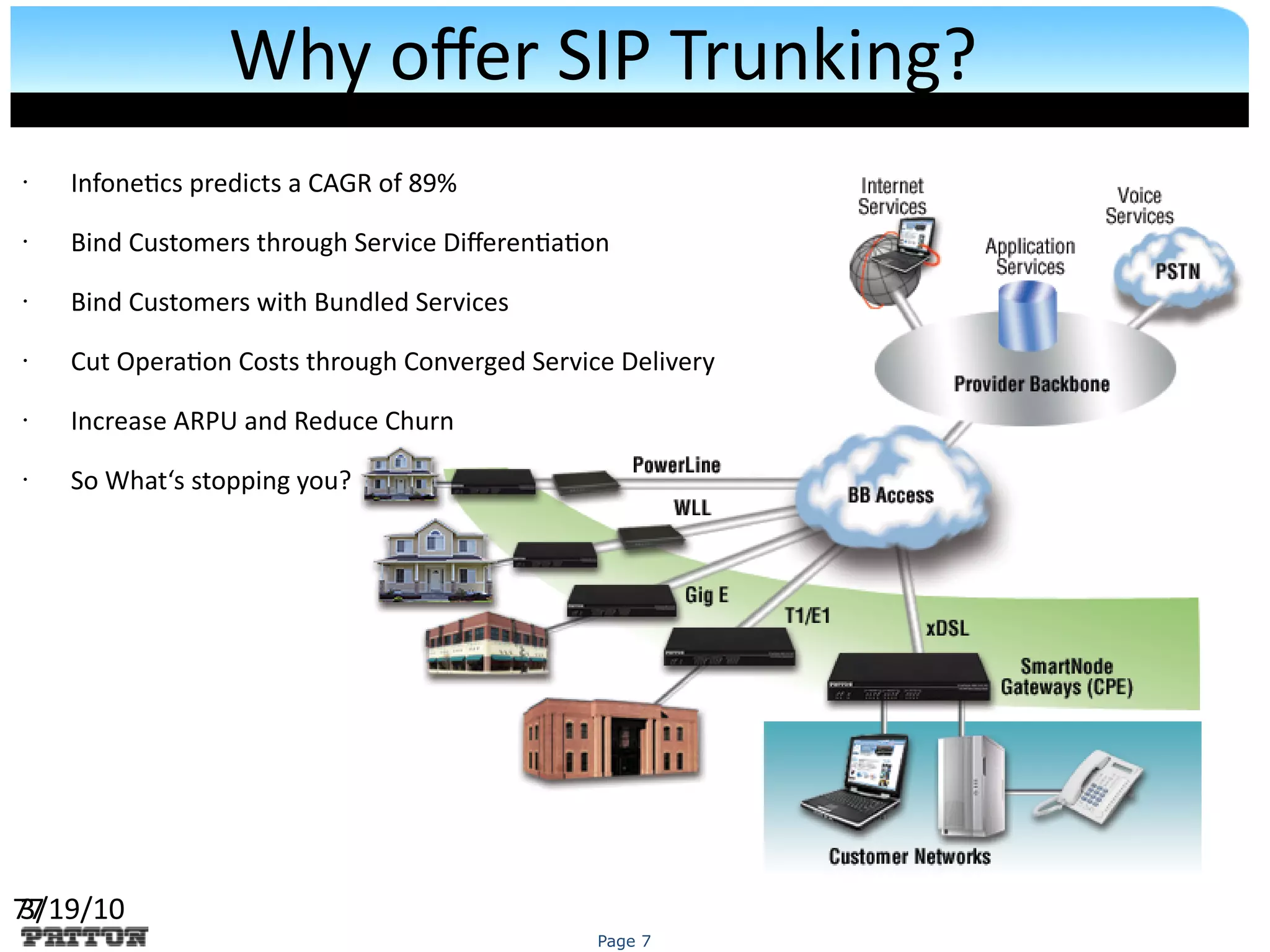
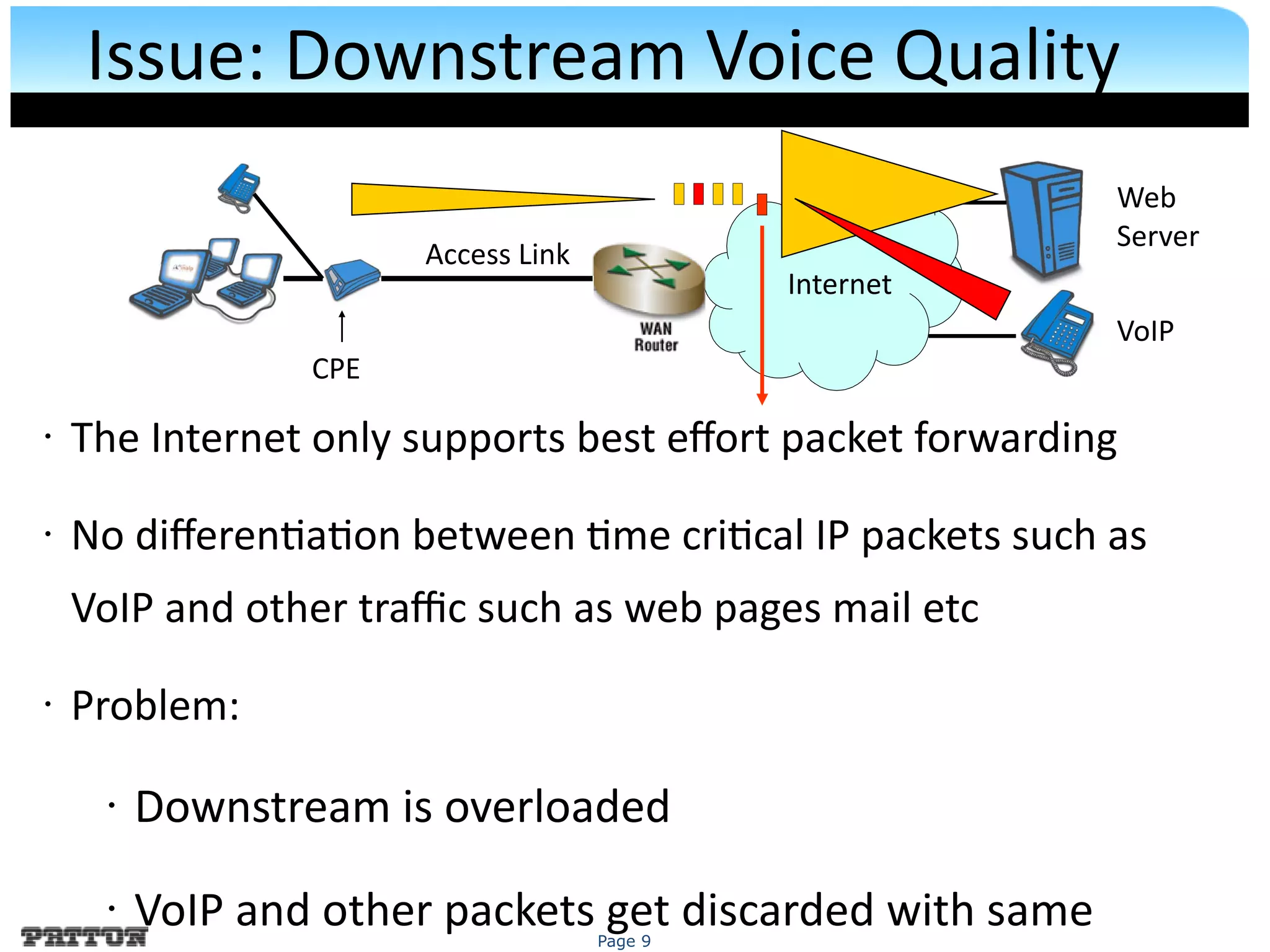
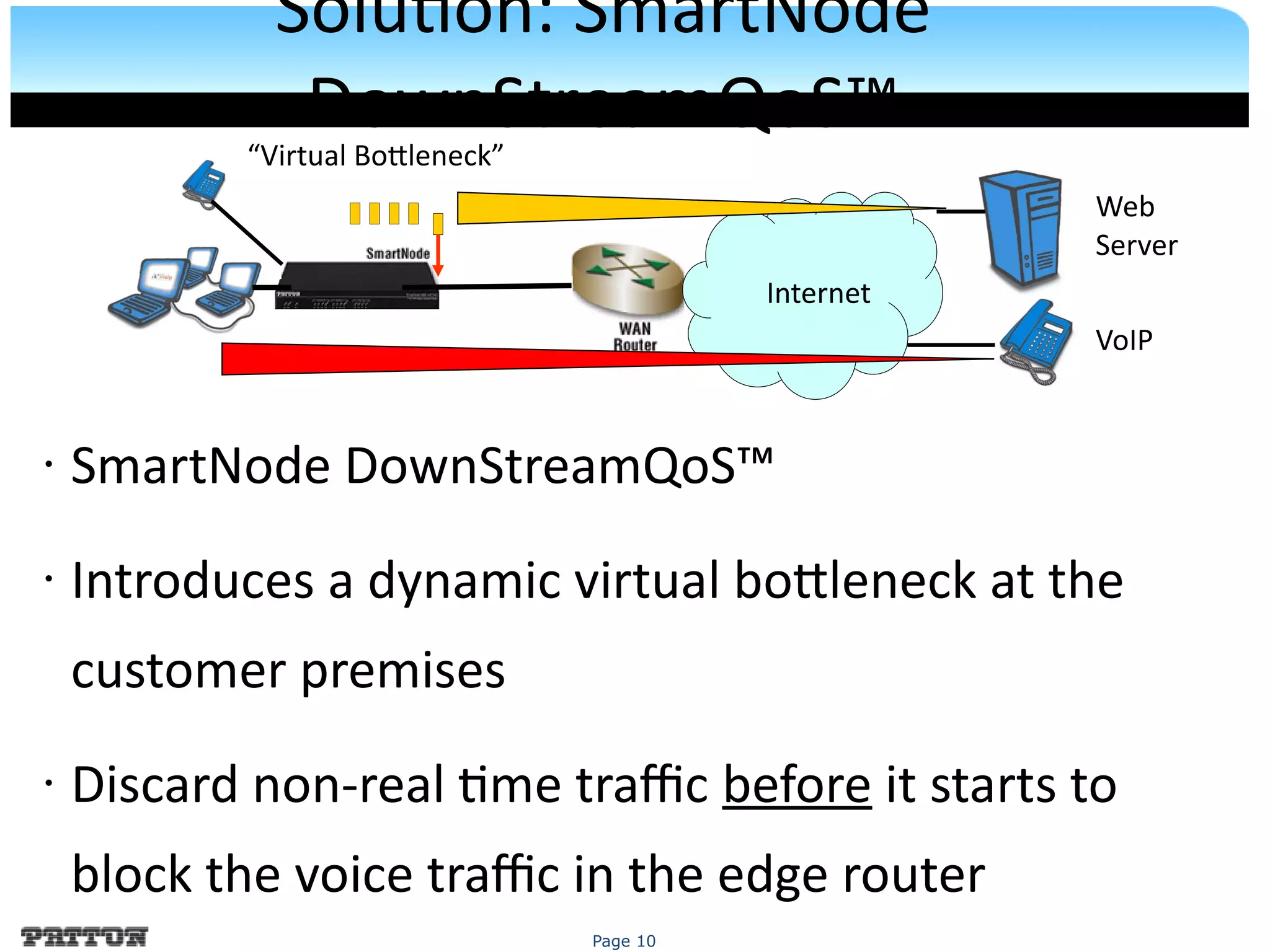
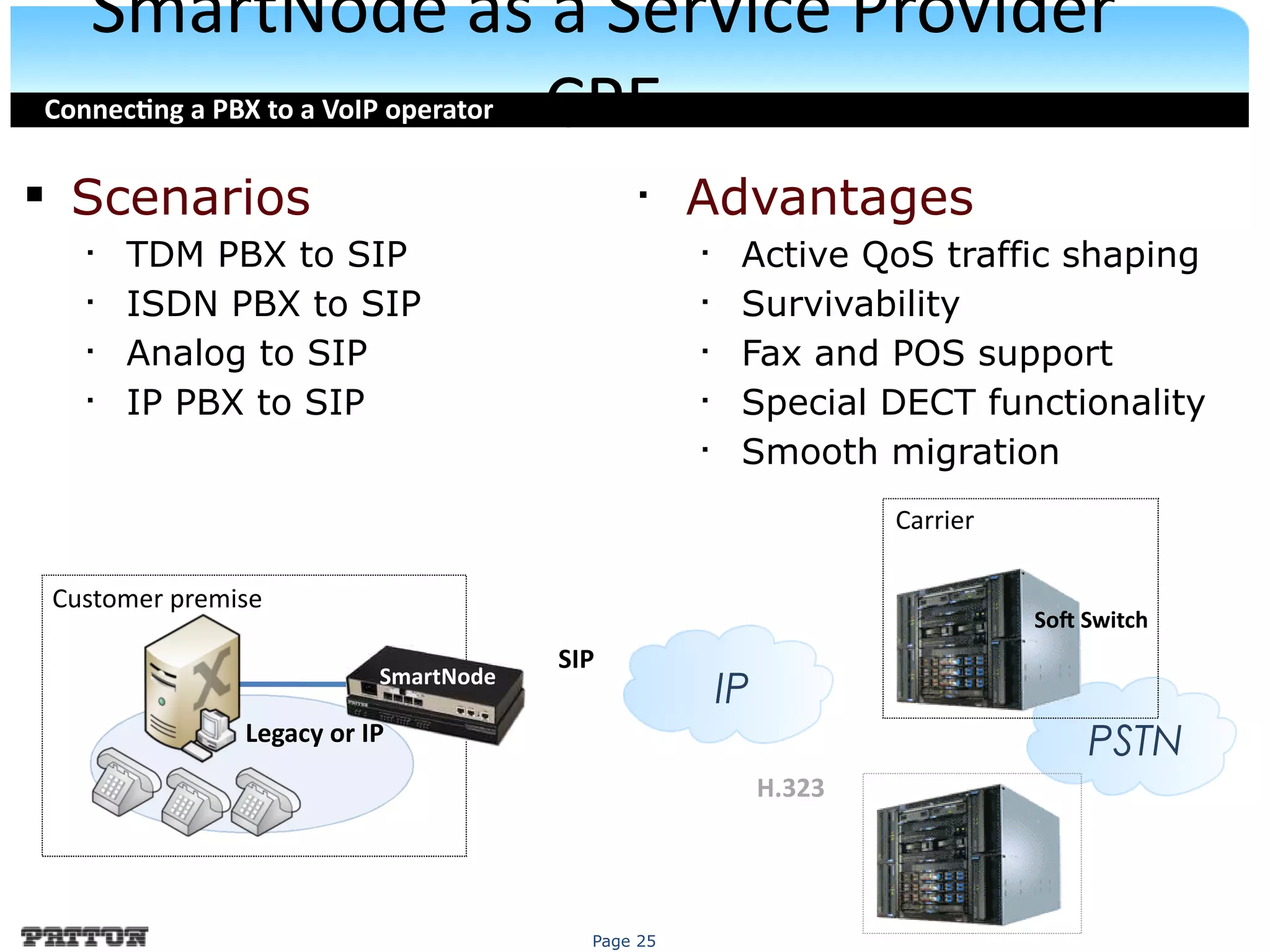
The document discusses SIP trunking and issues related to its implementation. It describes SIP trunking technology, issues around quality of service, survivability, network management, integration with legacy PBXs, and IP PBX interoperability. Solutions discussed include the SmartNode DownStreamQoS, auto-provisioning, and the SmartNode SN4960 gateway and SN5200 session border controller to address these issues and provide SIP trunking capabilities to different PBX environments.