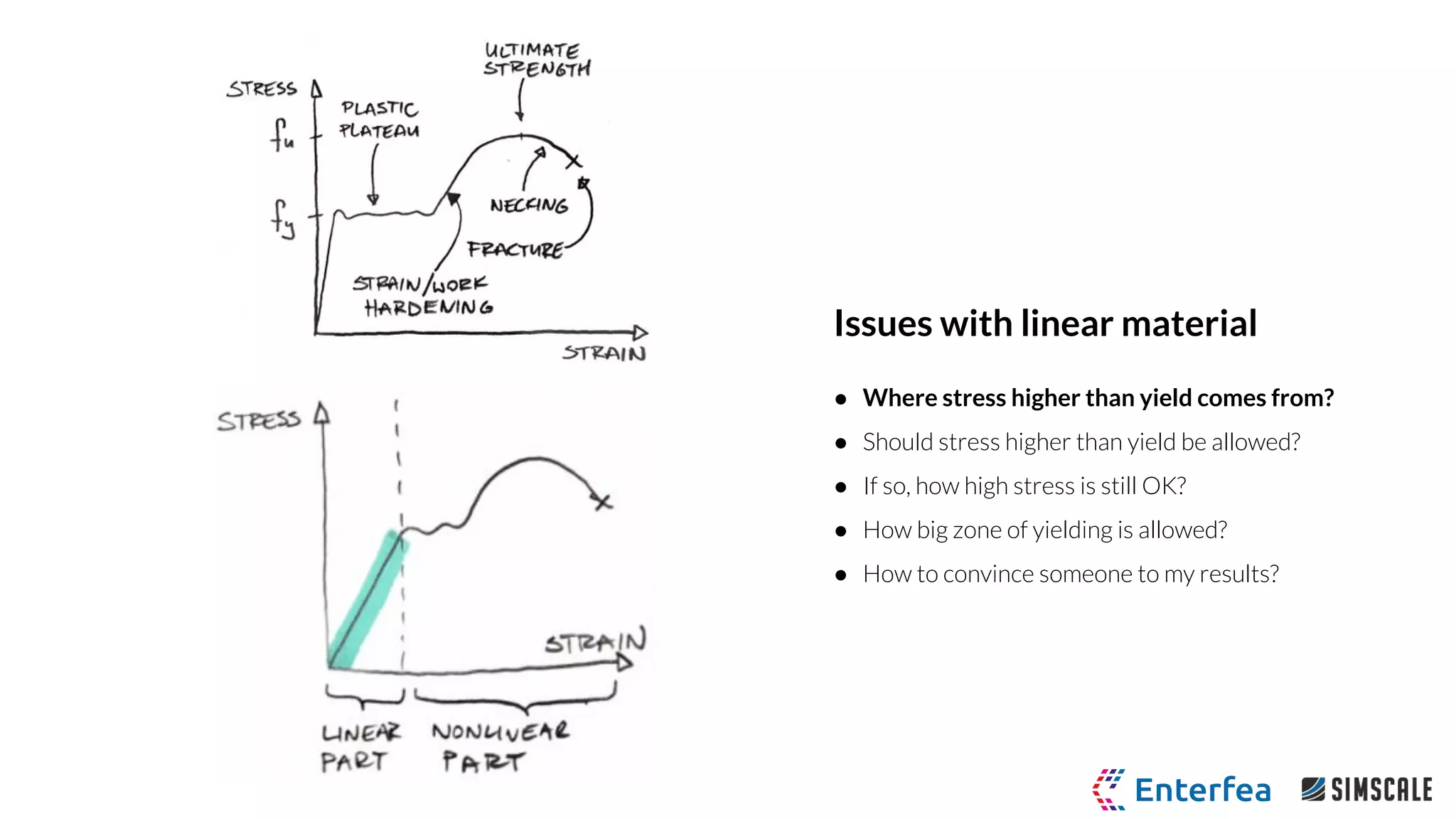
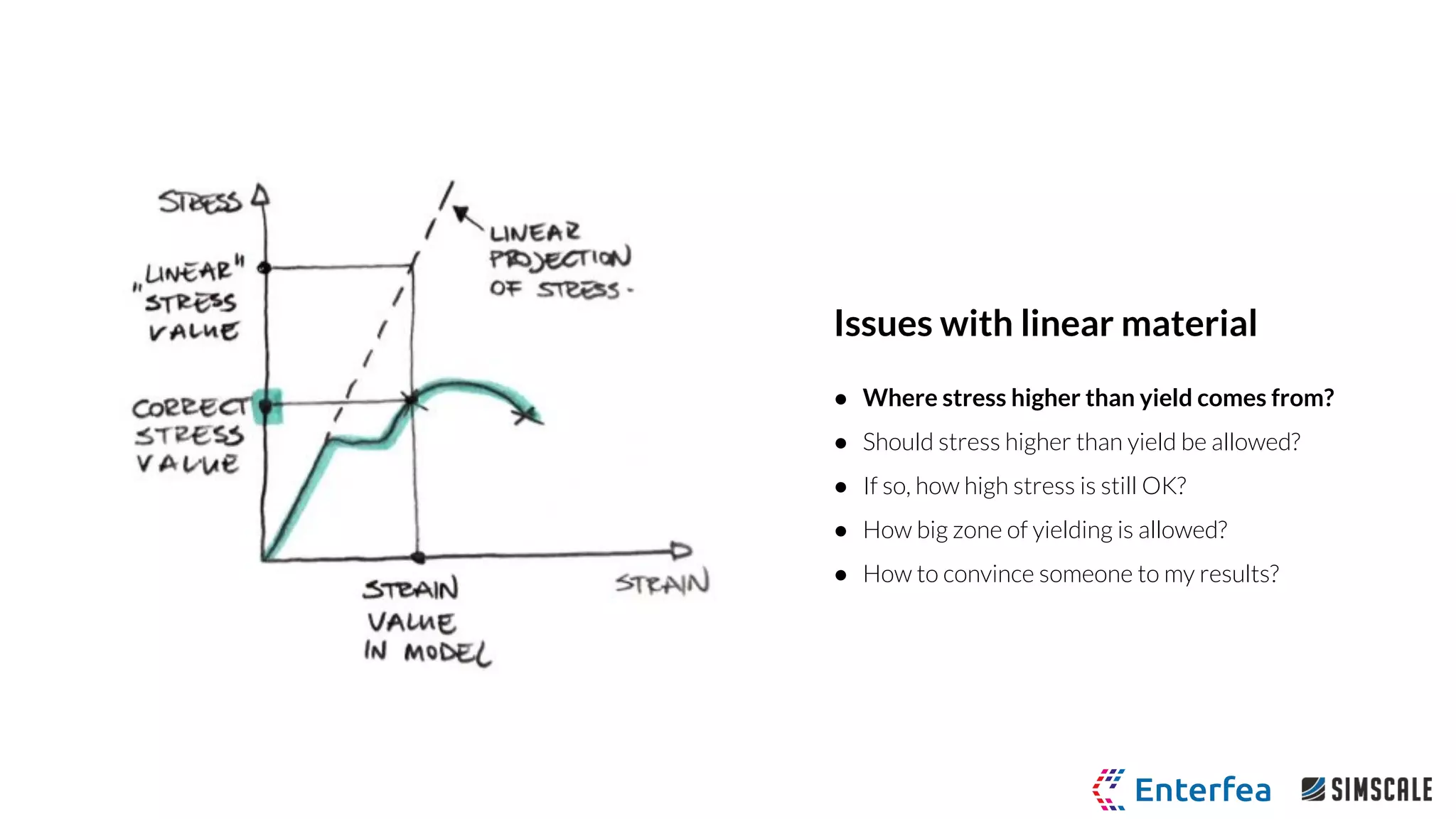
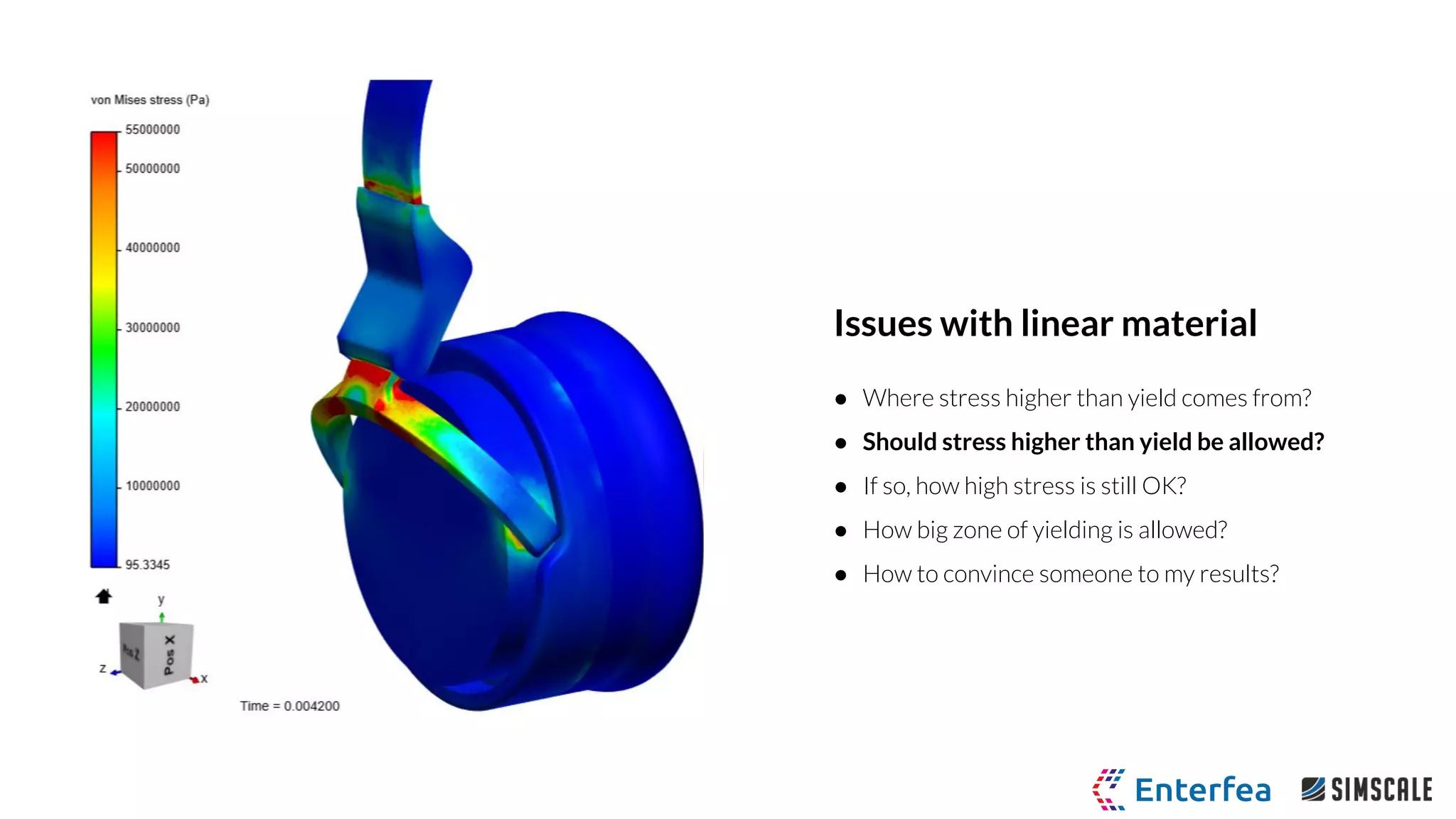
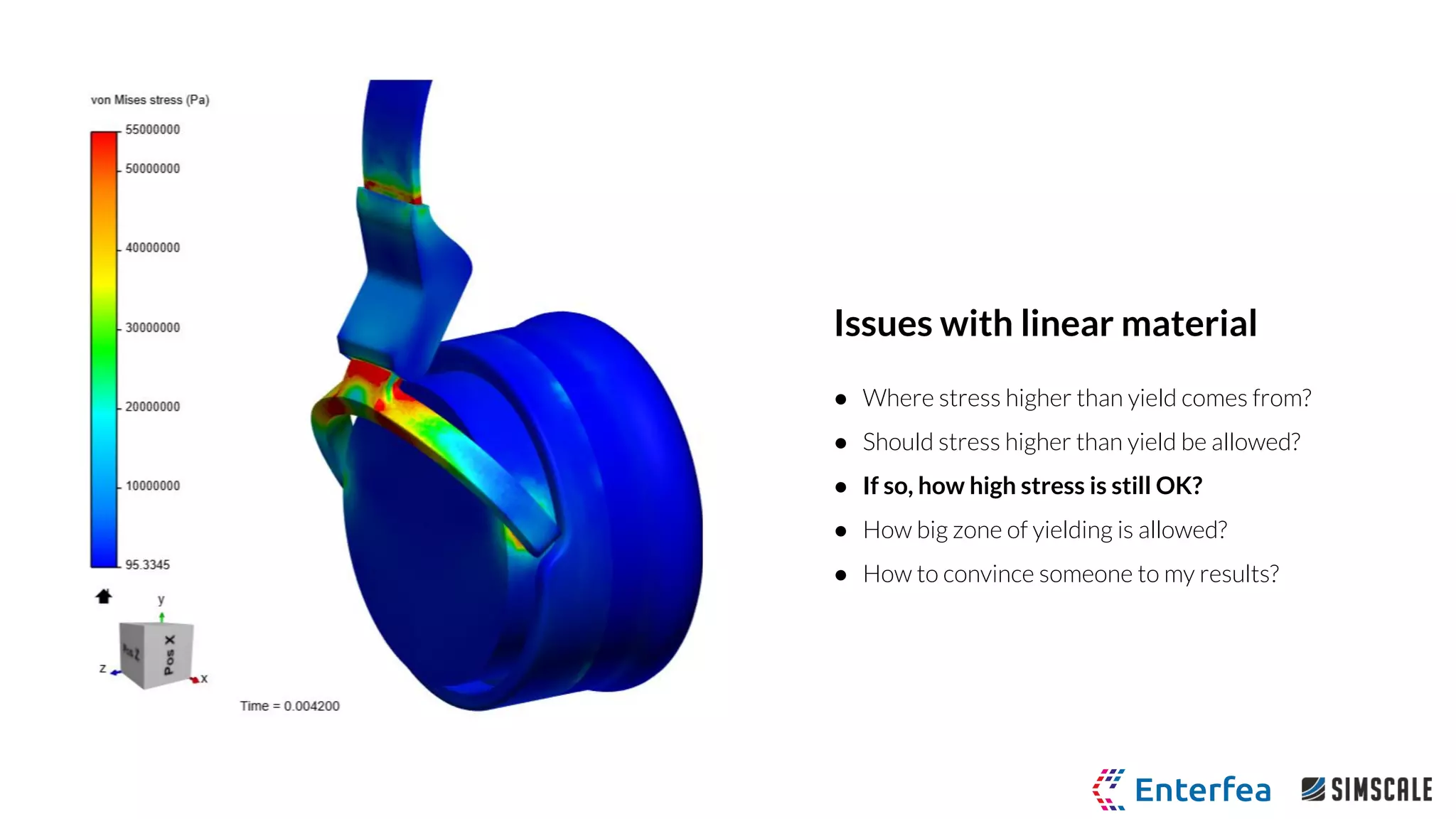
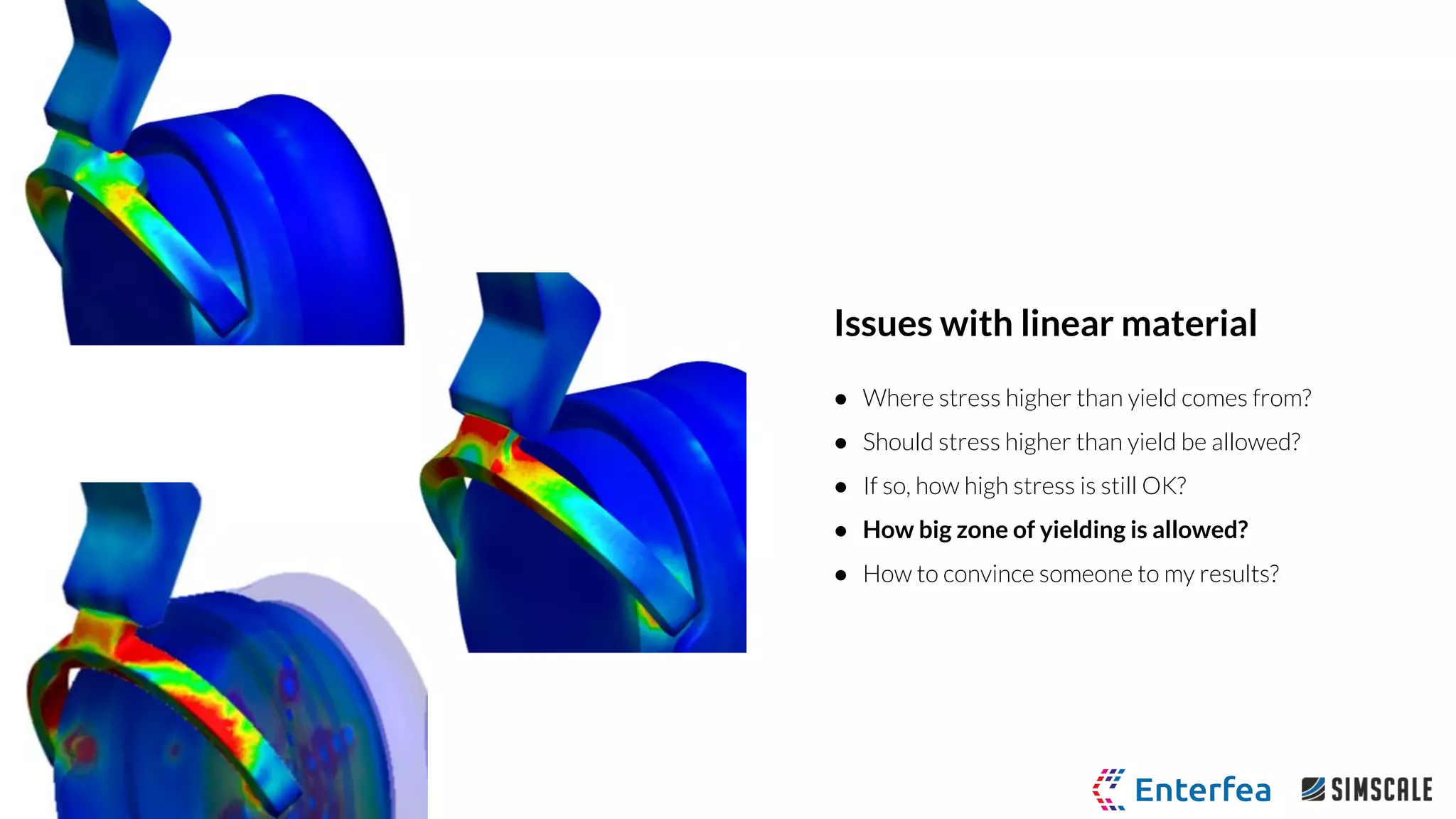
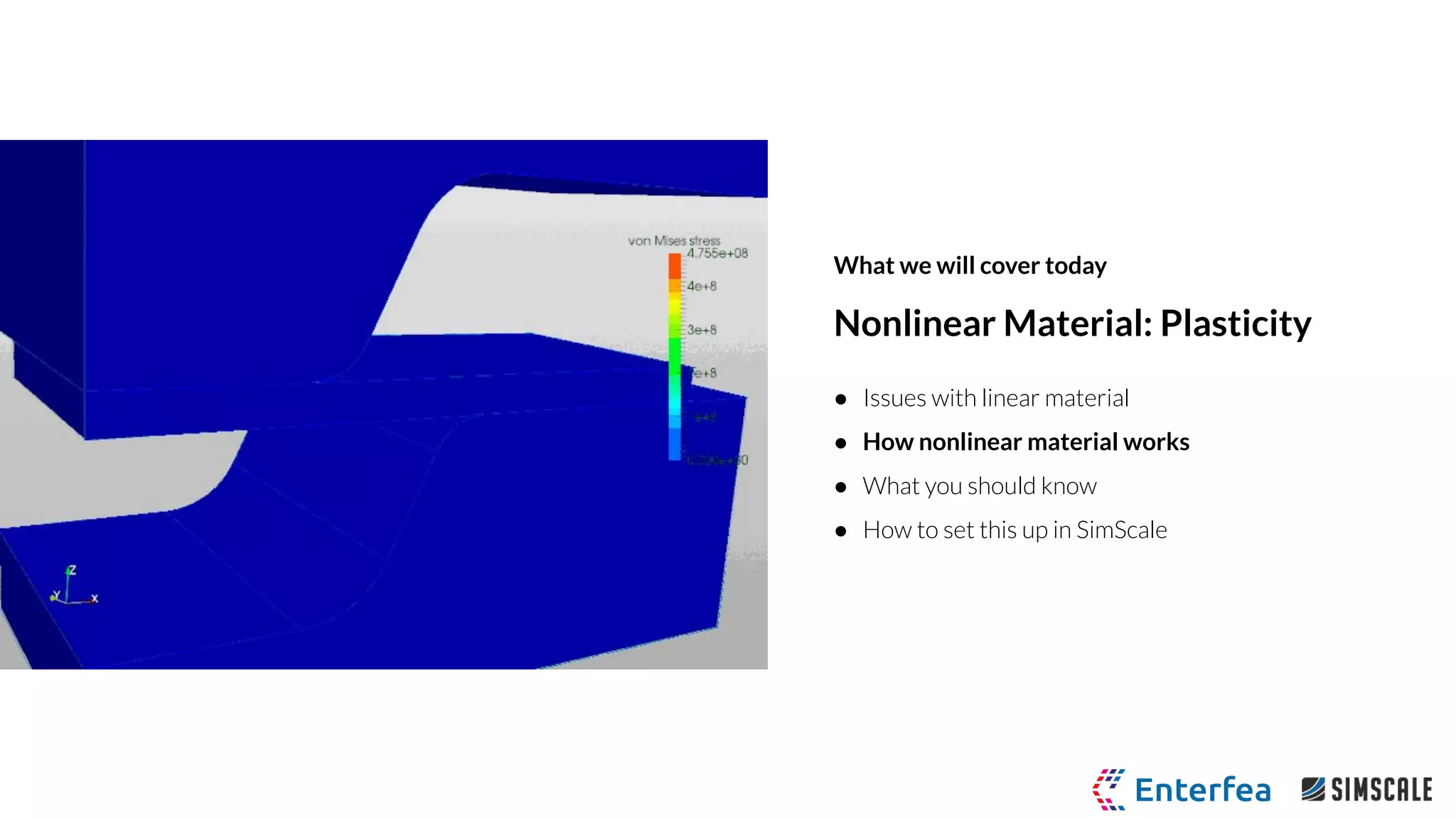
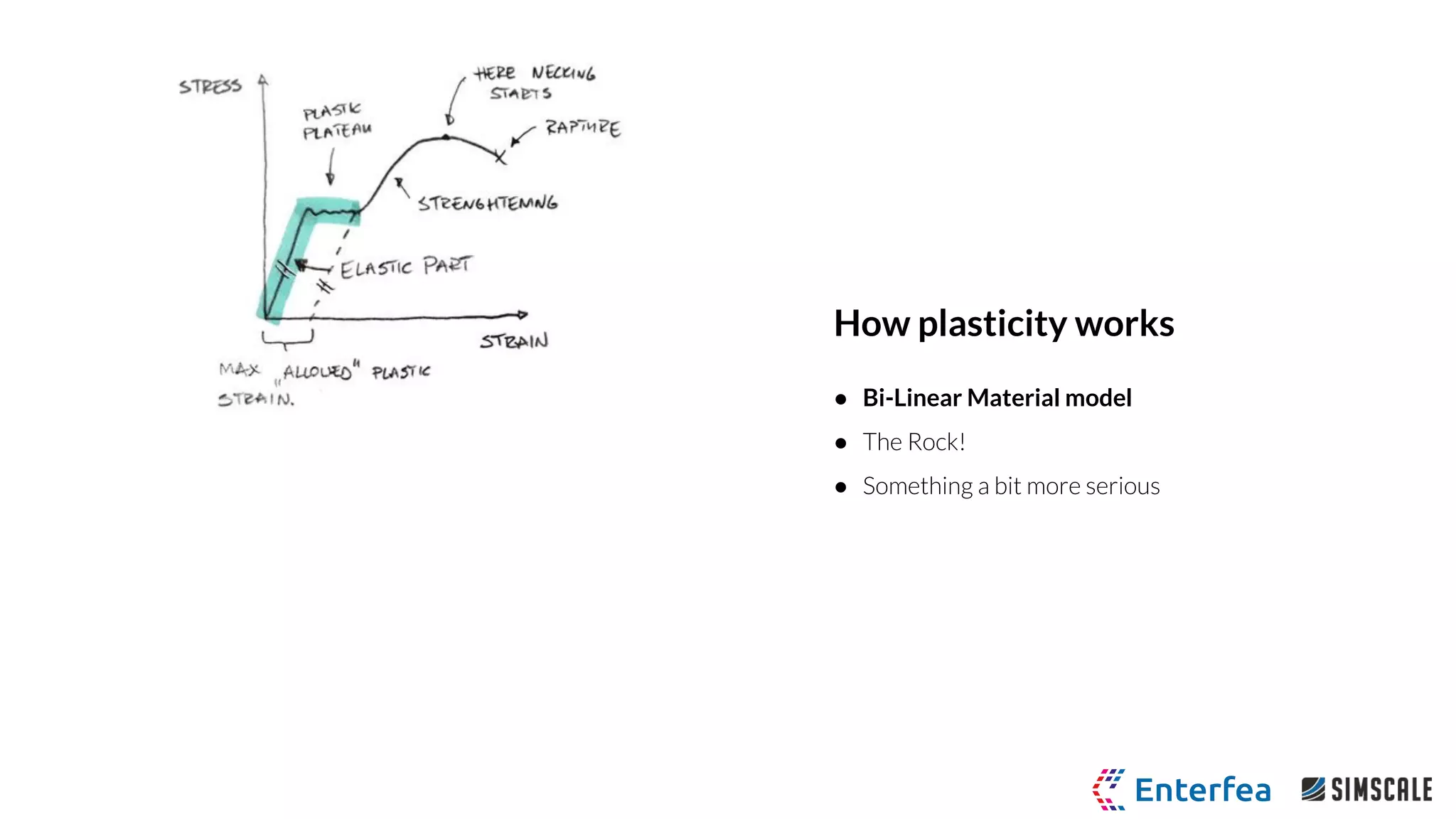
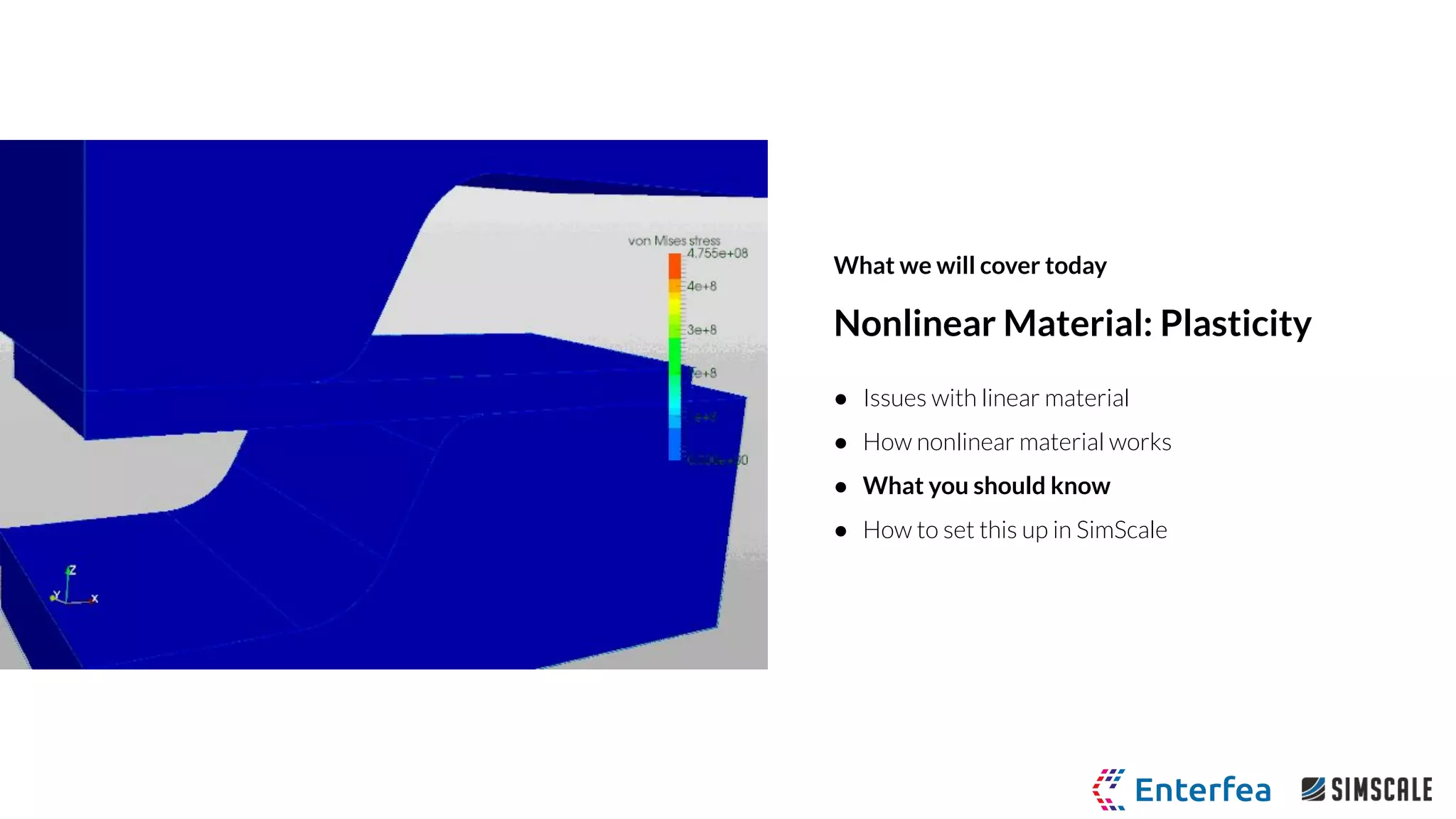
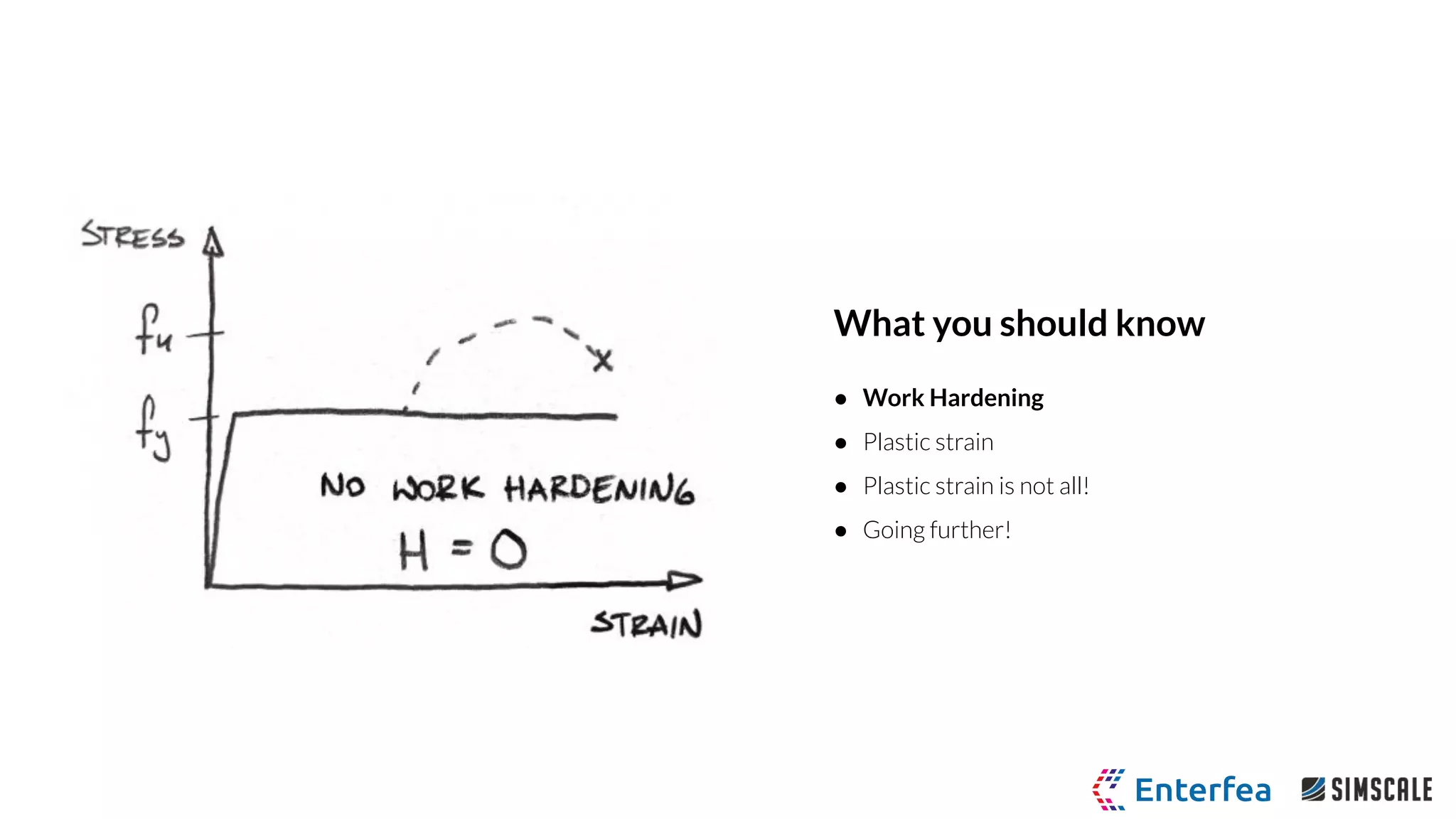
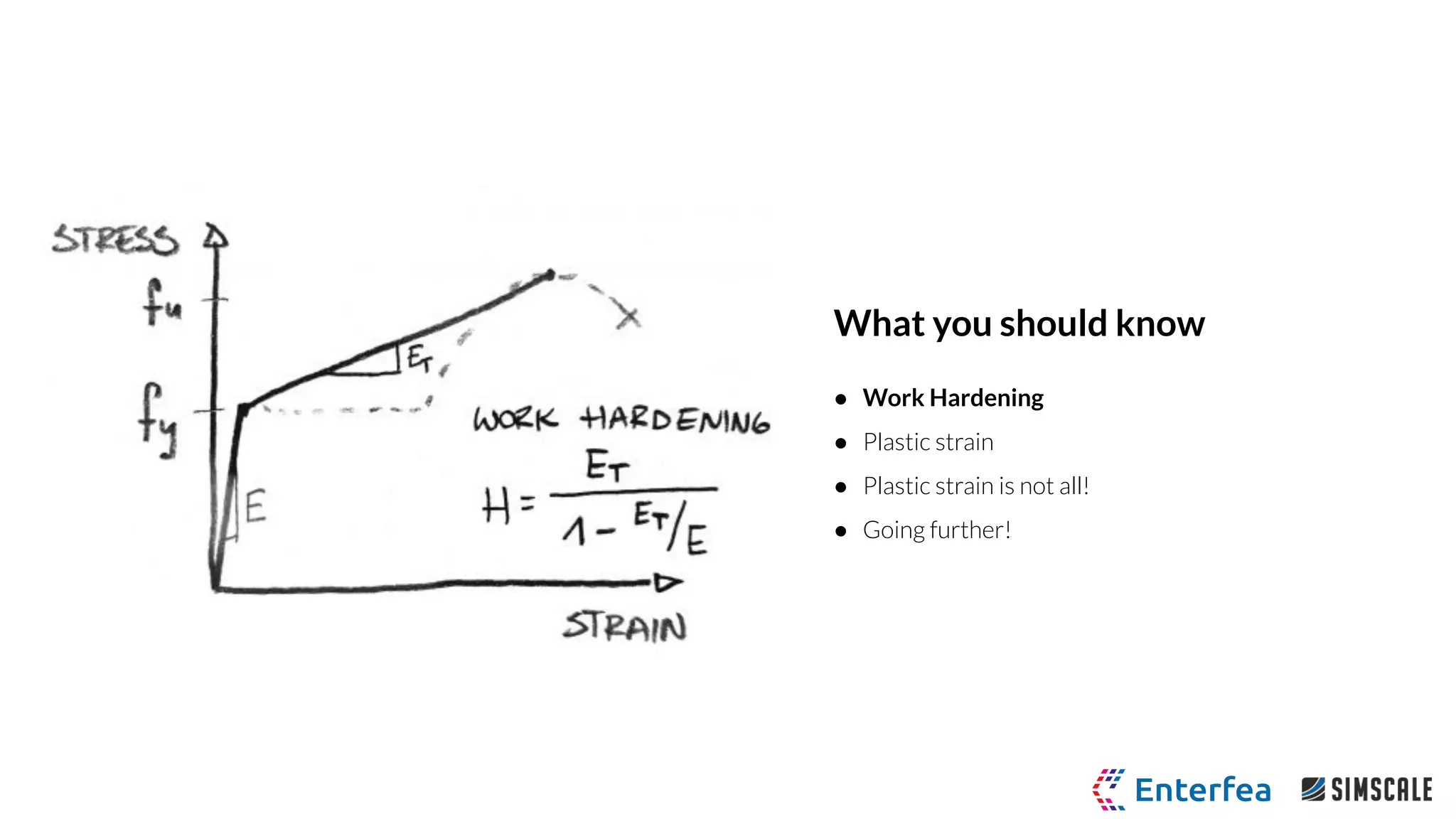
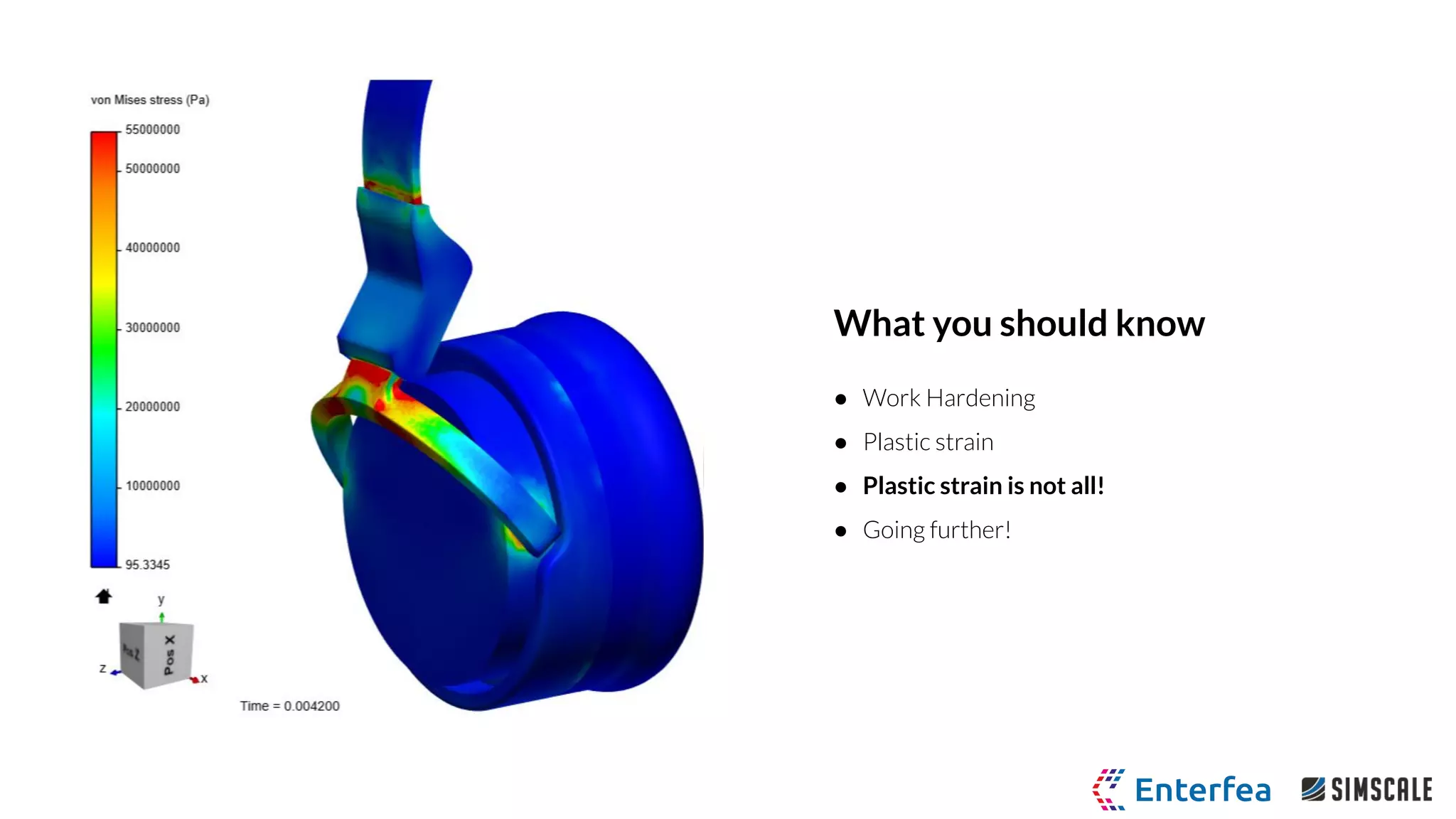
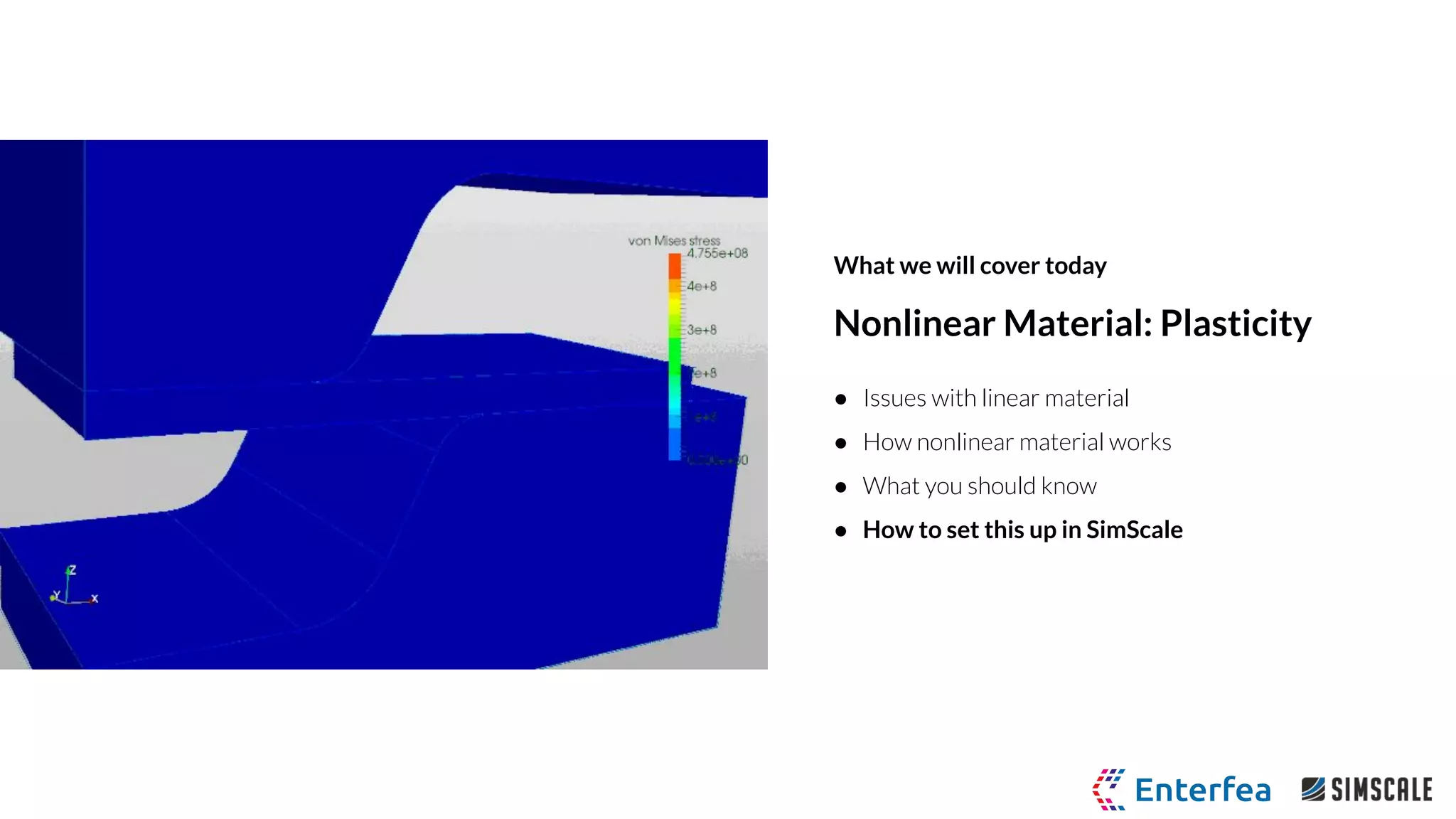
The webinar by Richard Szöke-Schuller and Łukasz Skotny focuses on the use of nonlinear materials and plasticity in finite element analysis (FEA), discussing the limitations of linear materials and how to set up simulations in SimScale. Key topics include understanding the behavior of nonlinear materials, work hardening, and practical case studies involving I-beams under pressure load. The session aims to provide insights for structural design and optimization through hands-on training.





![Example case:
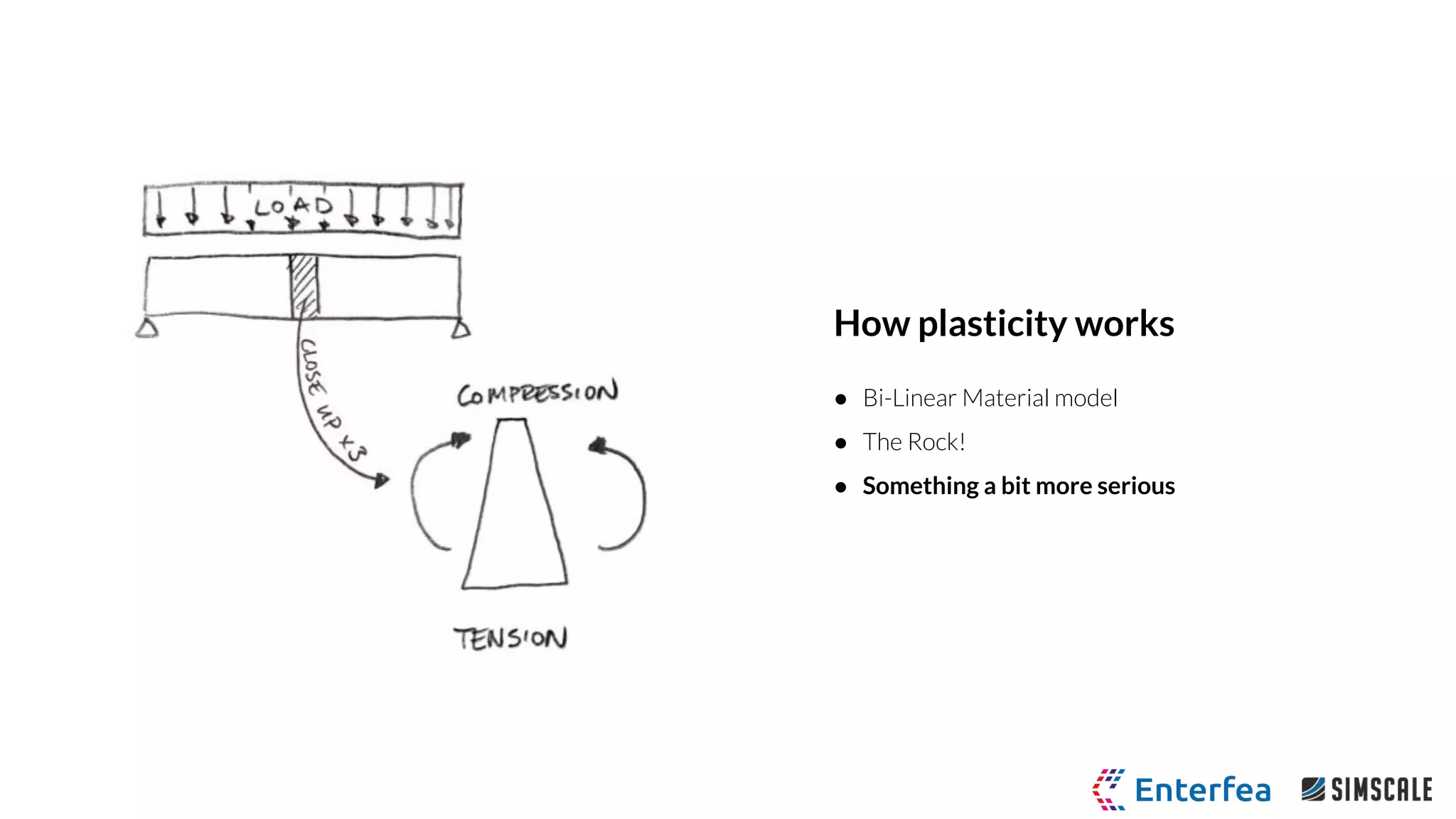
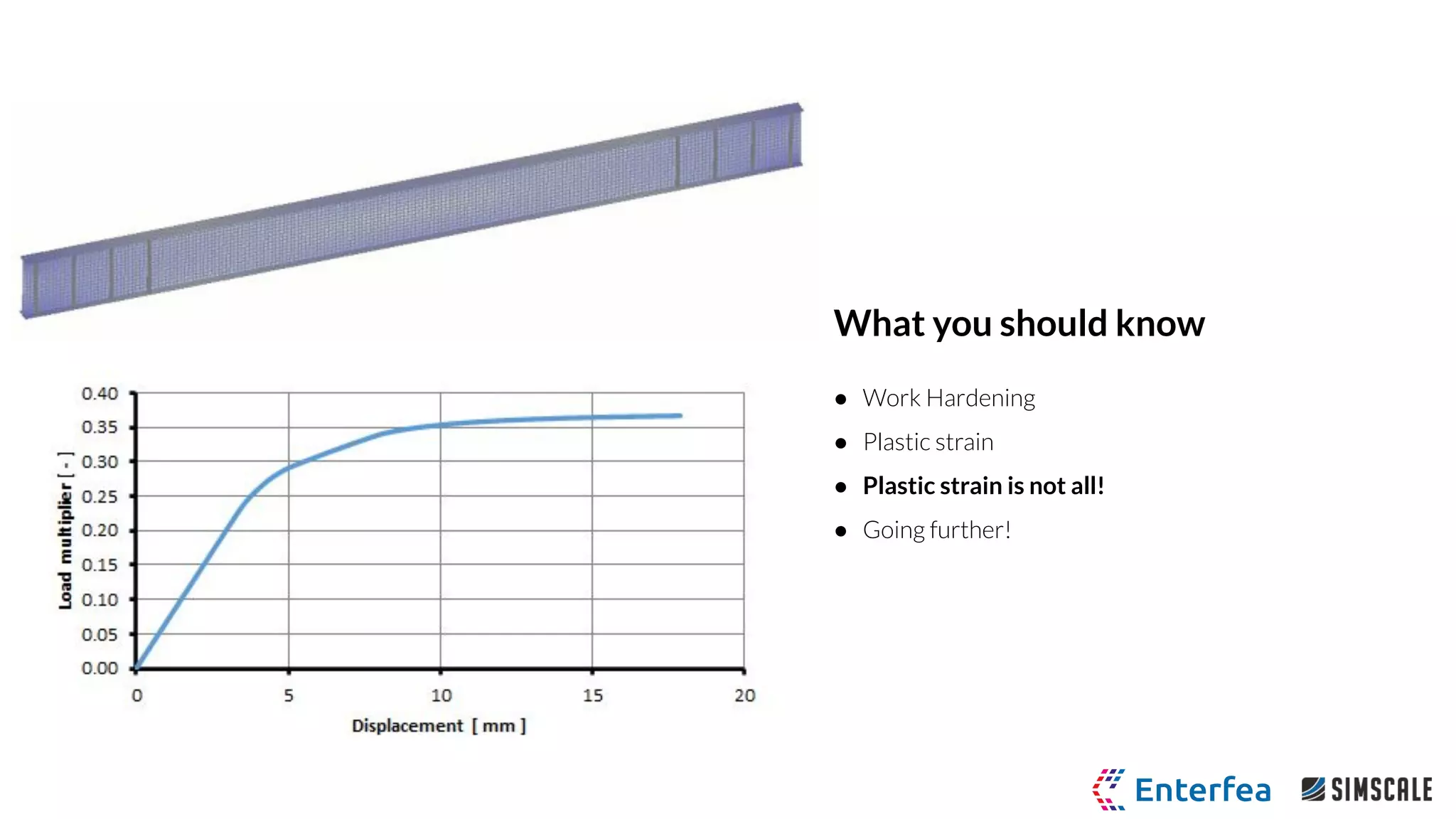
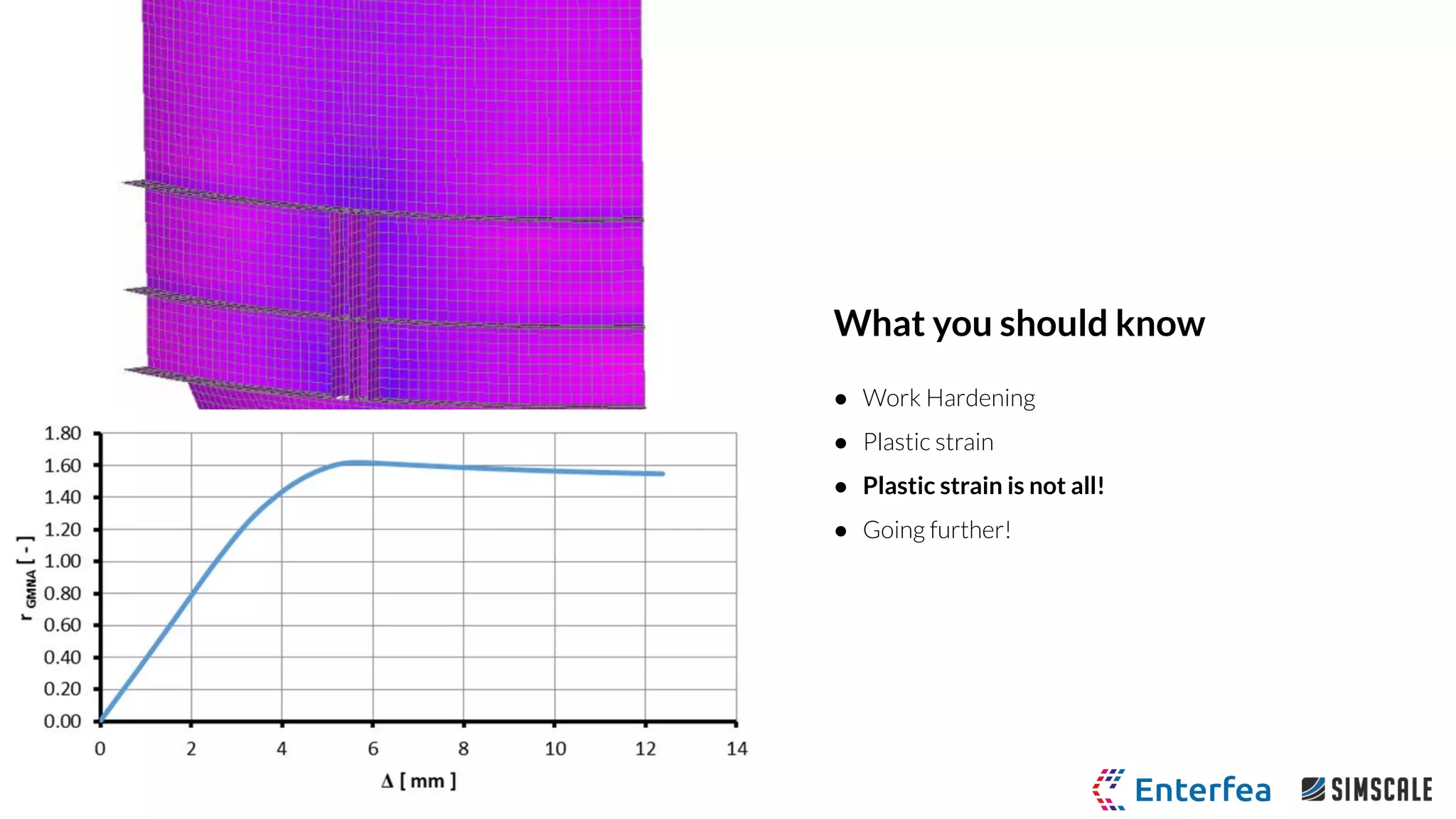
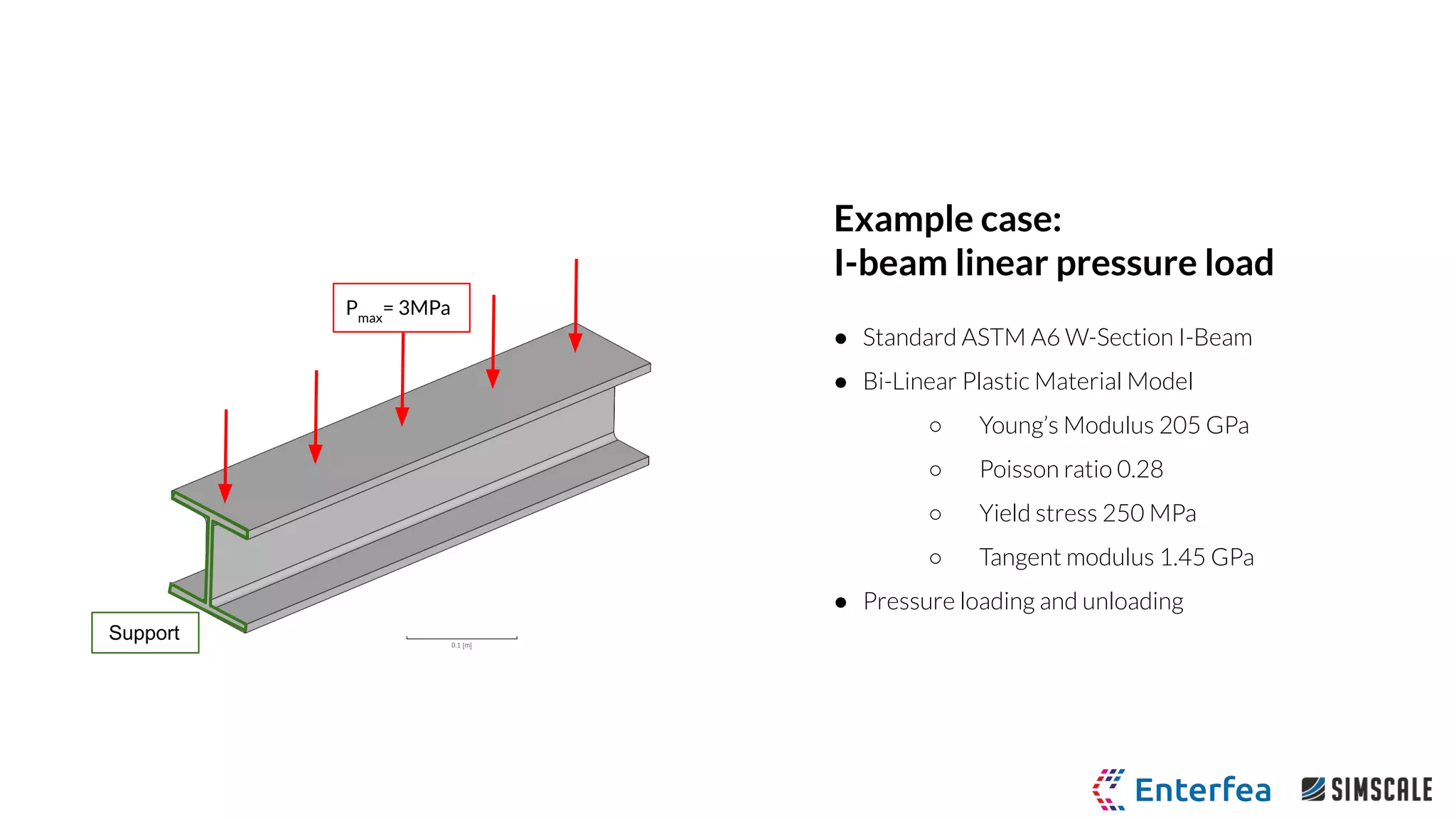
I-beam linear pressure load
● Standard ASTM A6 W-Section I-Beam
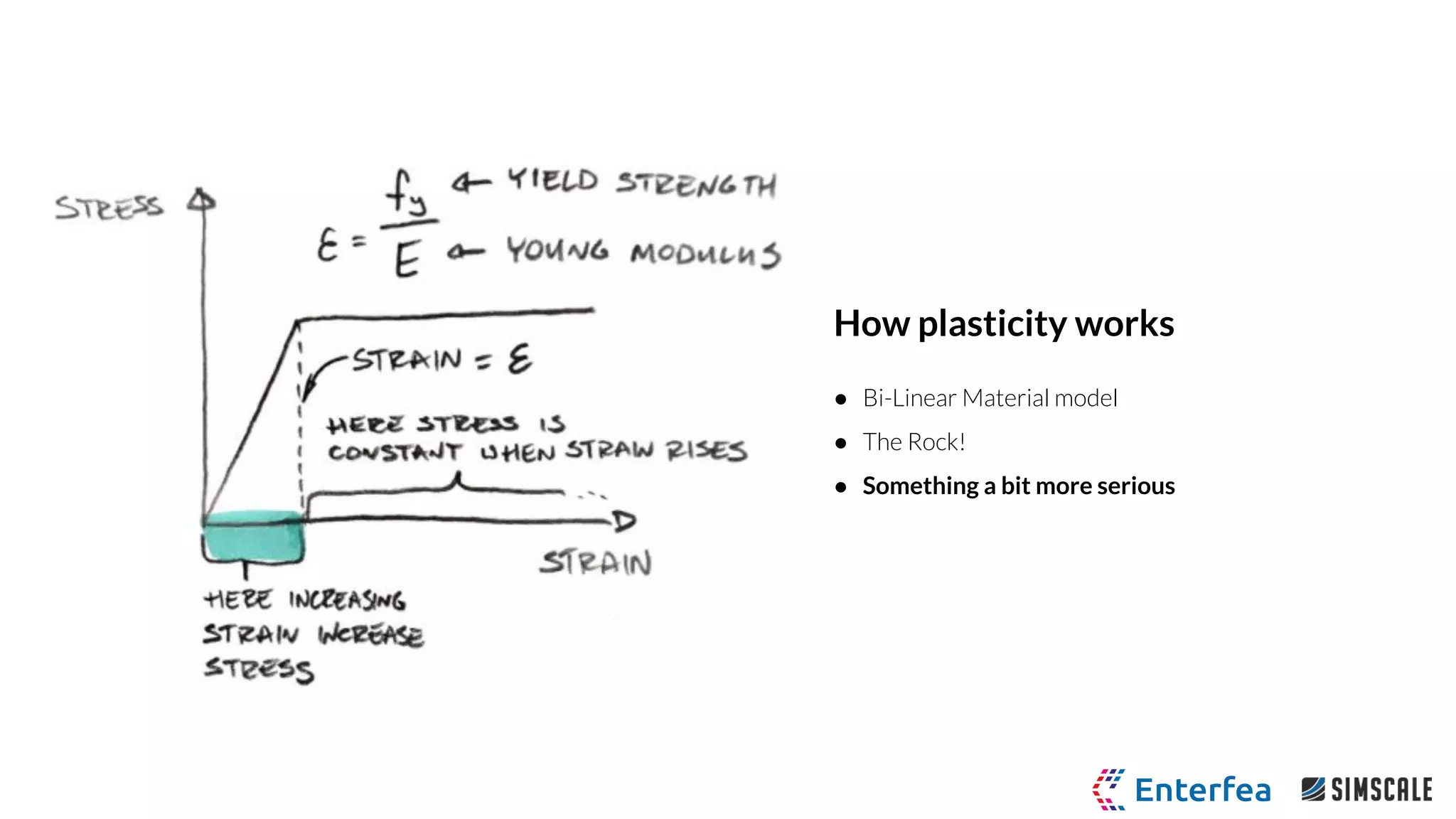
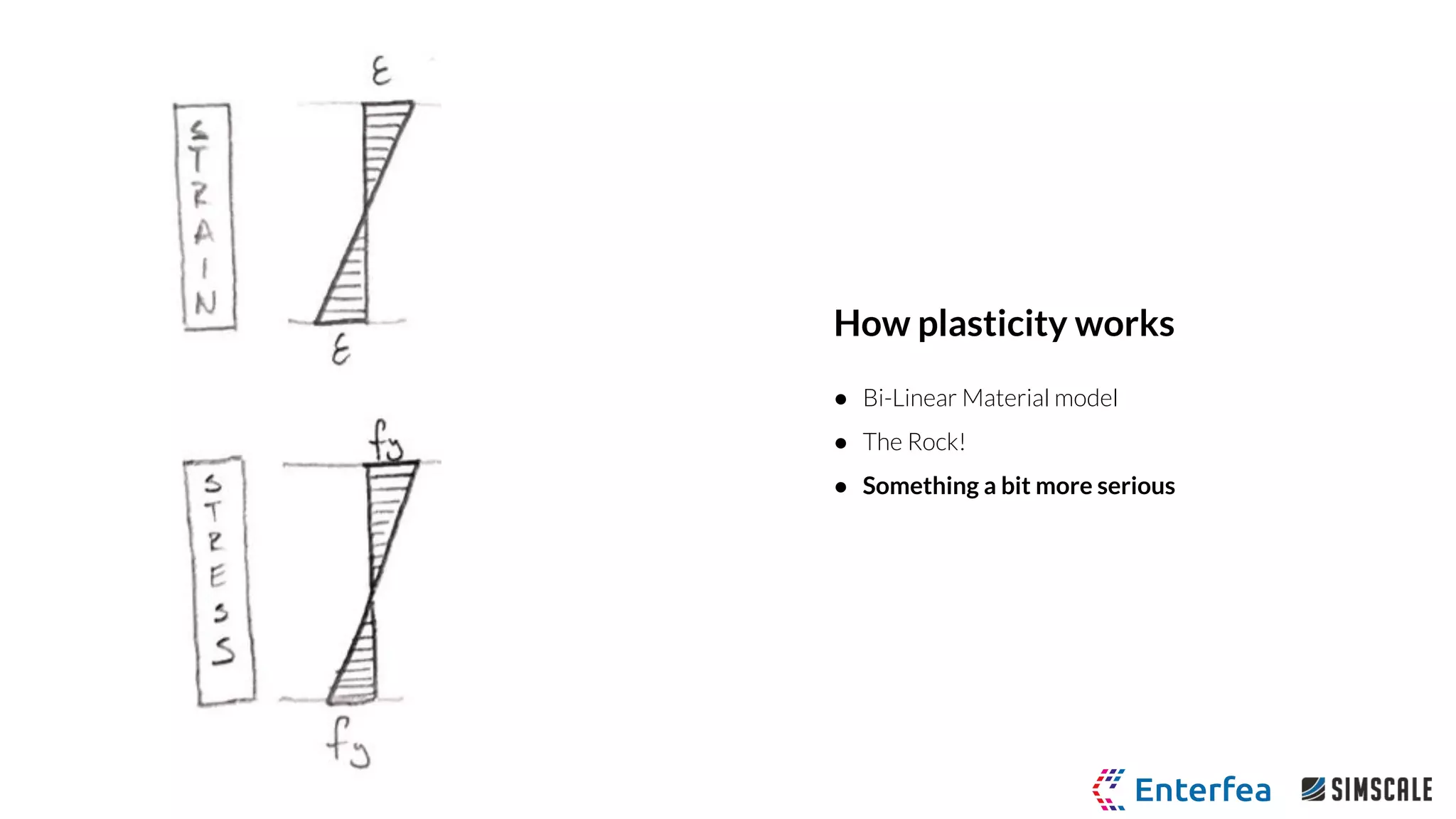
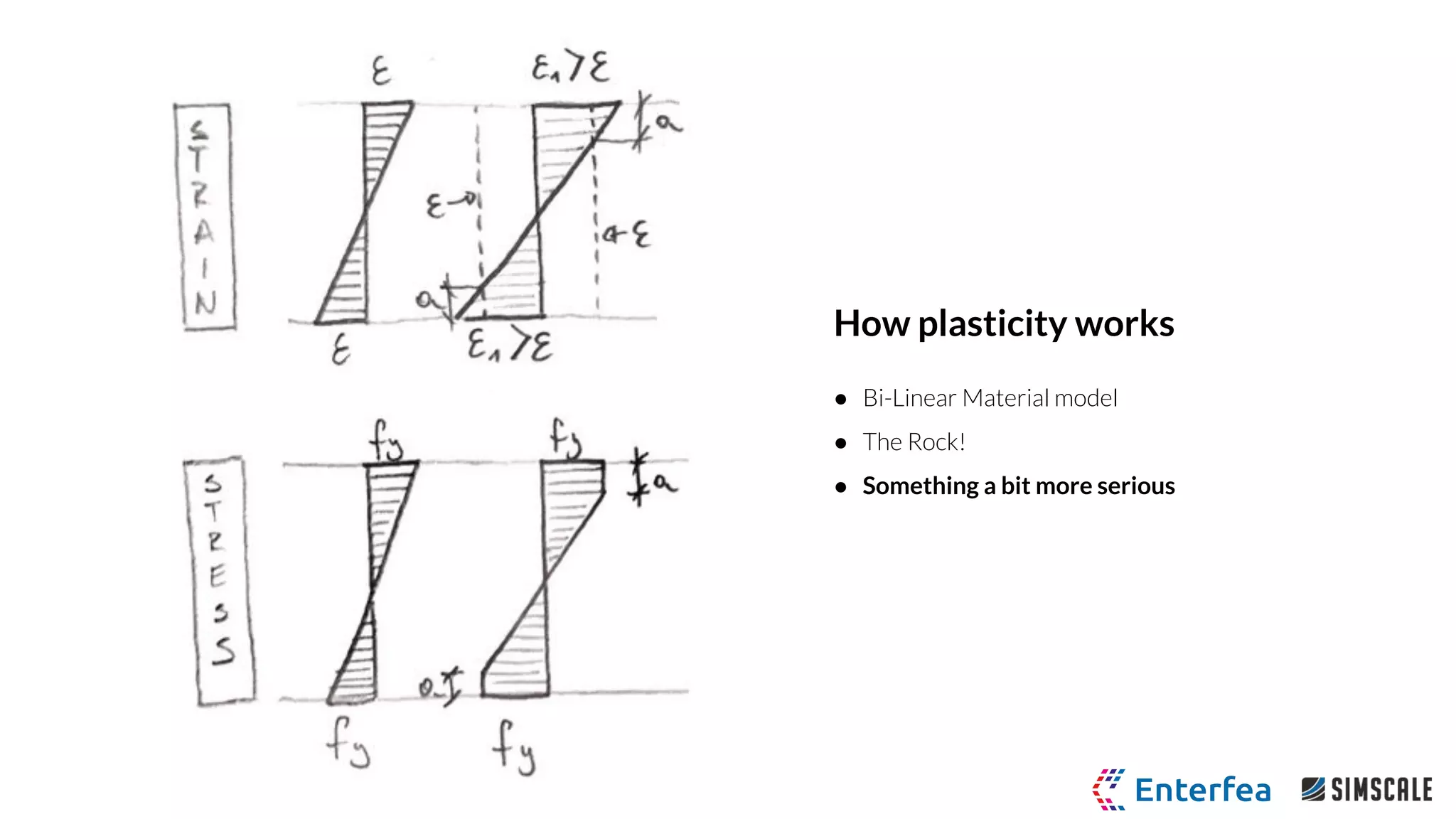
● Bi-Linear Plastic Material Model
○ Young’s Modulus 205 GPa
○ Poisson ratio 0.28
○ Yield stress 250 MPa
○ Tangent modulus 1.45 GPa
● Pressure loading and unloading
Displacement at max load
● Top: Linear 3.35 [mm] !
● Bottom: Plastic 102 [mm]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plasticityandnonlinearmaterials-191205130102/75/Plasticity-and-Nonlinear-Materials-in-FEA-32-2048.jpg)
![Example case:
I-beam linear pressure load
● Standard ASTM A6 W-Section I-Beam
● Bi-Linear Plastic Material Model
○ Young’s Modulus 205 GPa
○ Poisson ratio 0.28
○ Yield stress 250 MPa
○ Tangent modulus 1.45 GPa
● Pressure loading and unloading
Displacement at max load
● Top: Linear 3.35 [mm] !
● Bottom: Plastic 102 [mm]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plasticityandnonlinearmaterials-191205130102/75/Plasticity-and-Nonlinear-Materials-in-FEA-33-2048.jpg)
