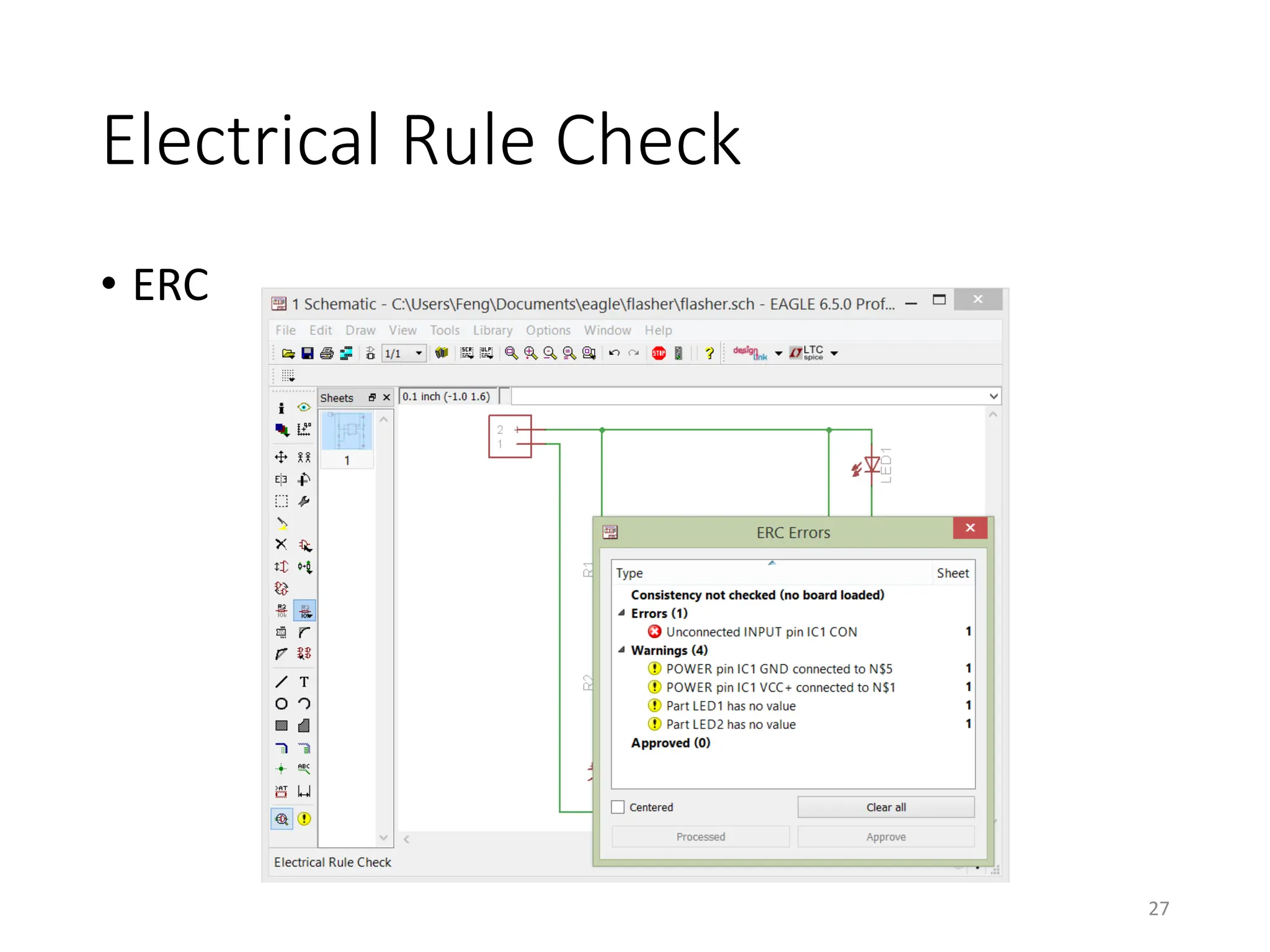
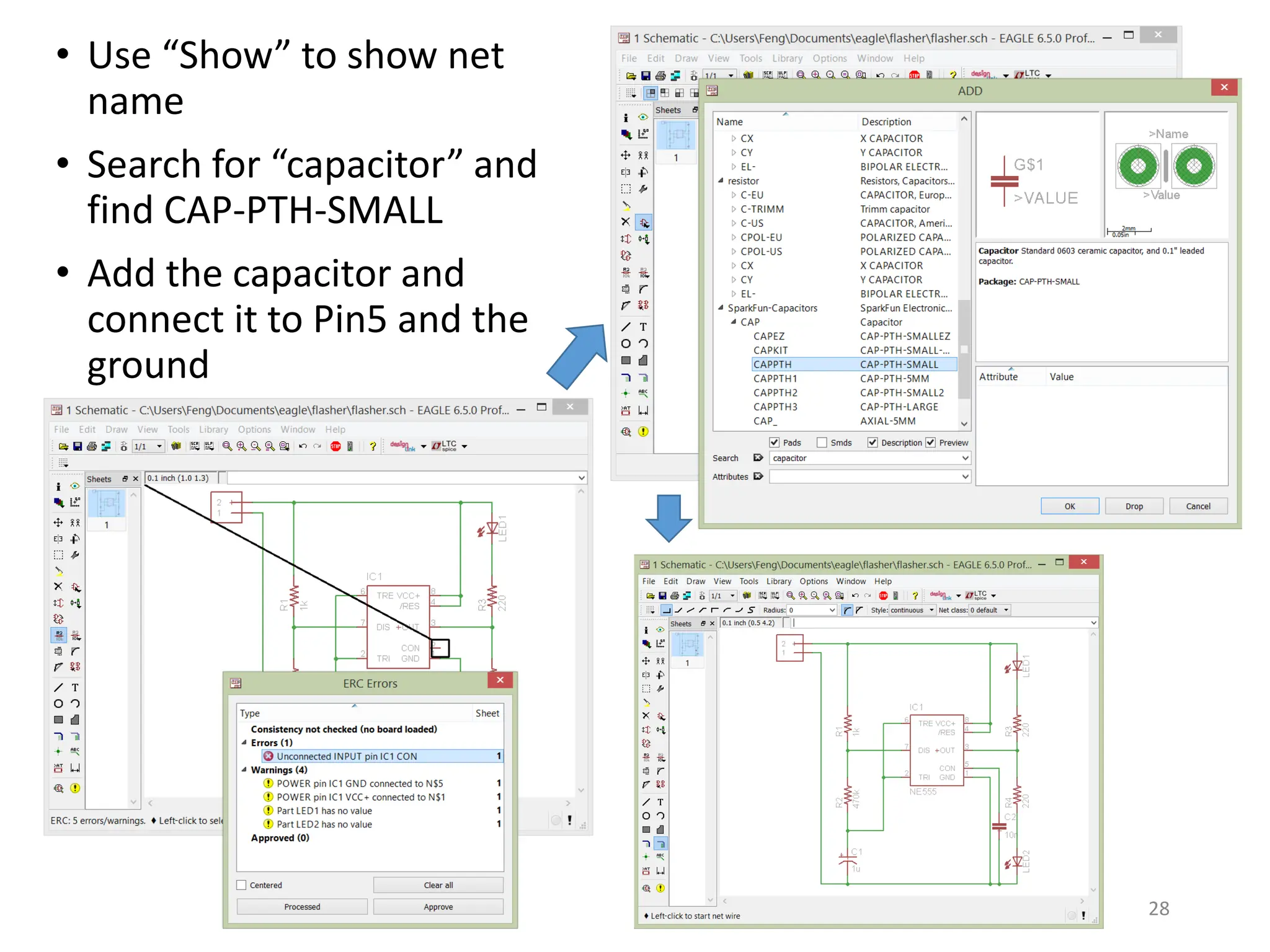
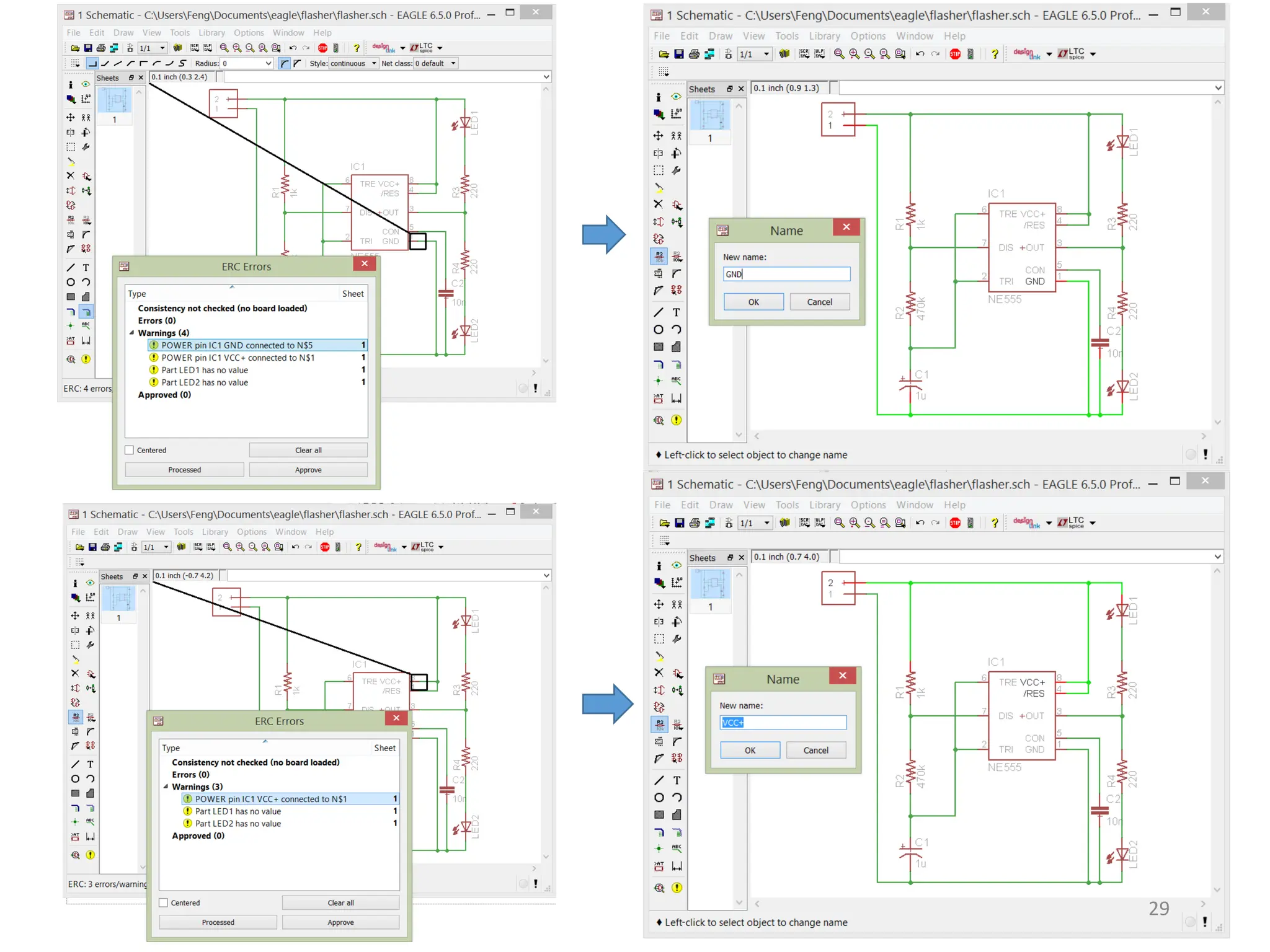
This document provides an overview of printed circuit board (PCB) design using EAGLE CAD software. It begins with introductions to PCBs and their components like pads, vias, and traces. Common packaging types for electronic components are described. The document then introduces the EAGLE software, covering its different versions, installation, libraries, and user interface. An example project of an LED flasher circuit using a 555 timer IC is presented to demonstrate the schematic capture and board layout processes in EAGLE. Key steps like adding components, routing traces, and running design rule checks are shown. The document concludes with explanations of generating output files like Gerber files needed for PCB fabrication.







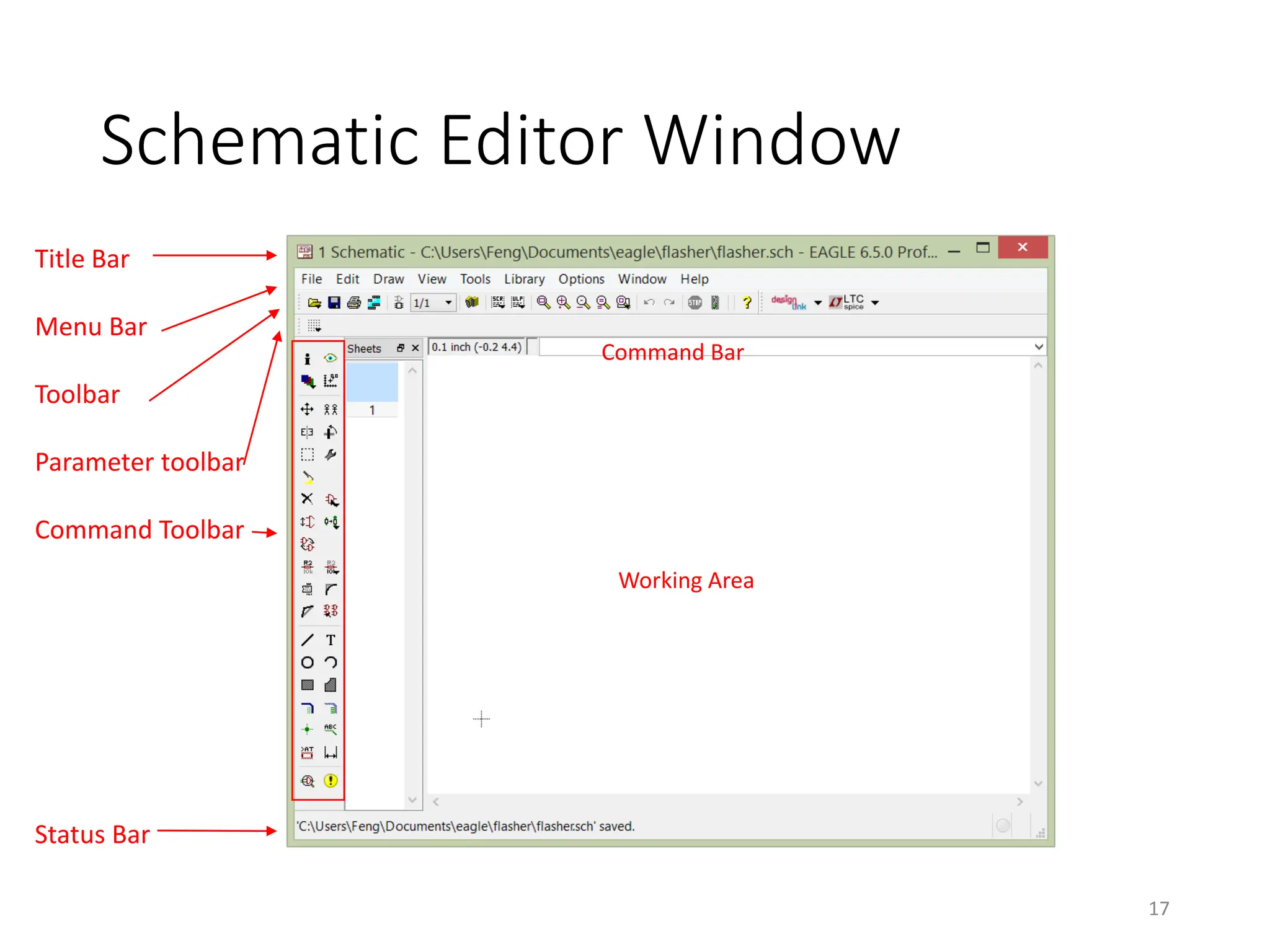
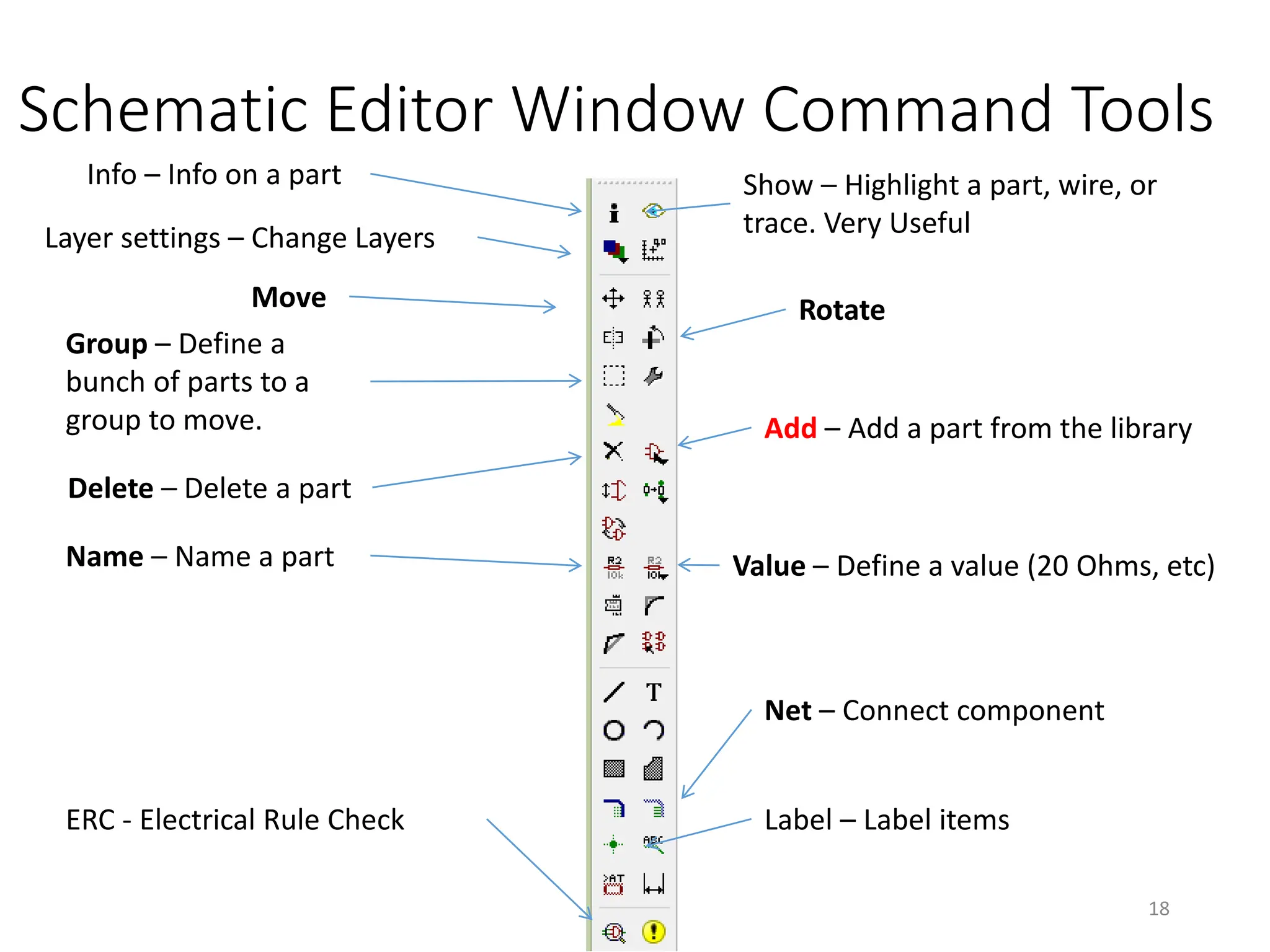
![Save and Rename of New Schematic
• [Schematic]File->Save as… (flasher.sch)
• Note: Do not create a
board file yet.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-16-2048.jpg)
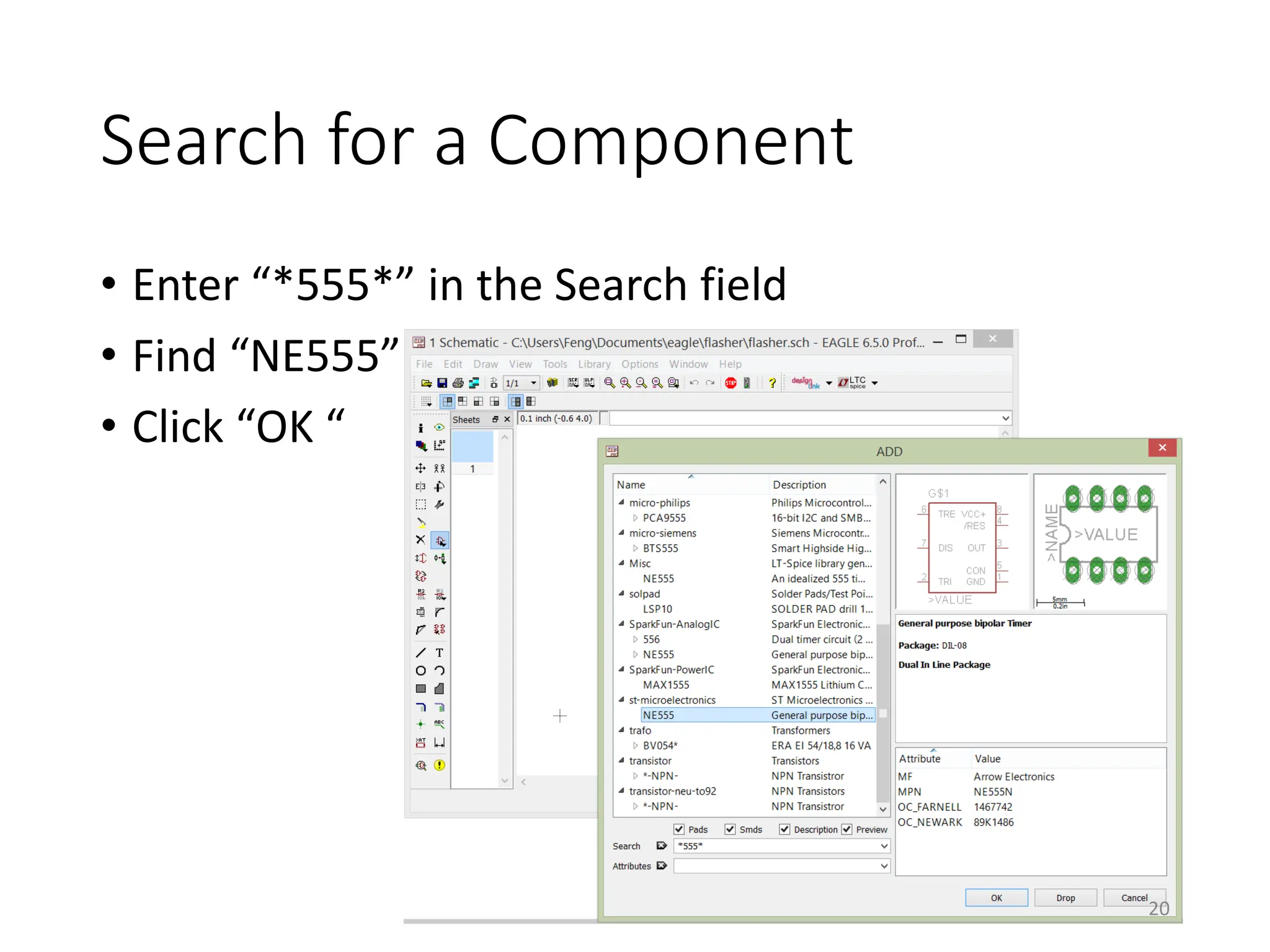
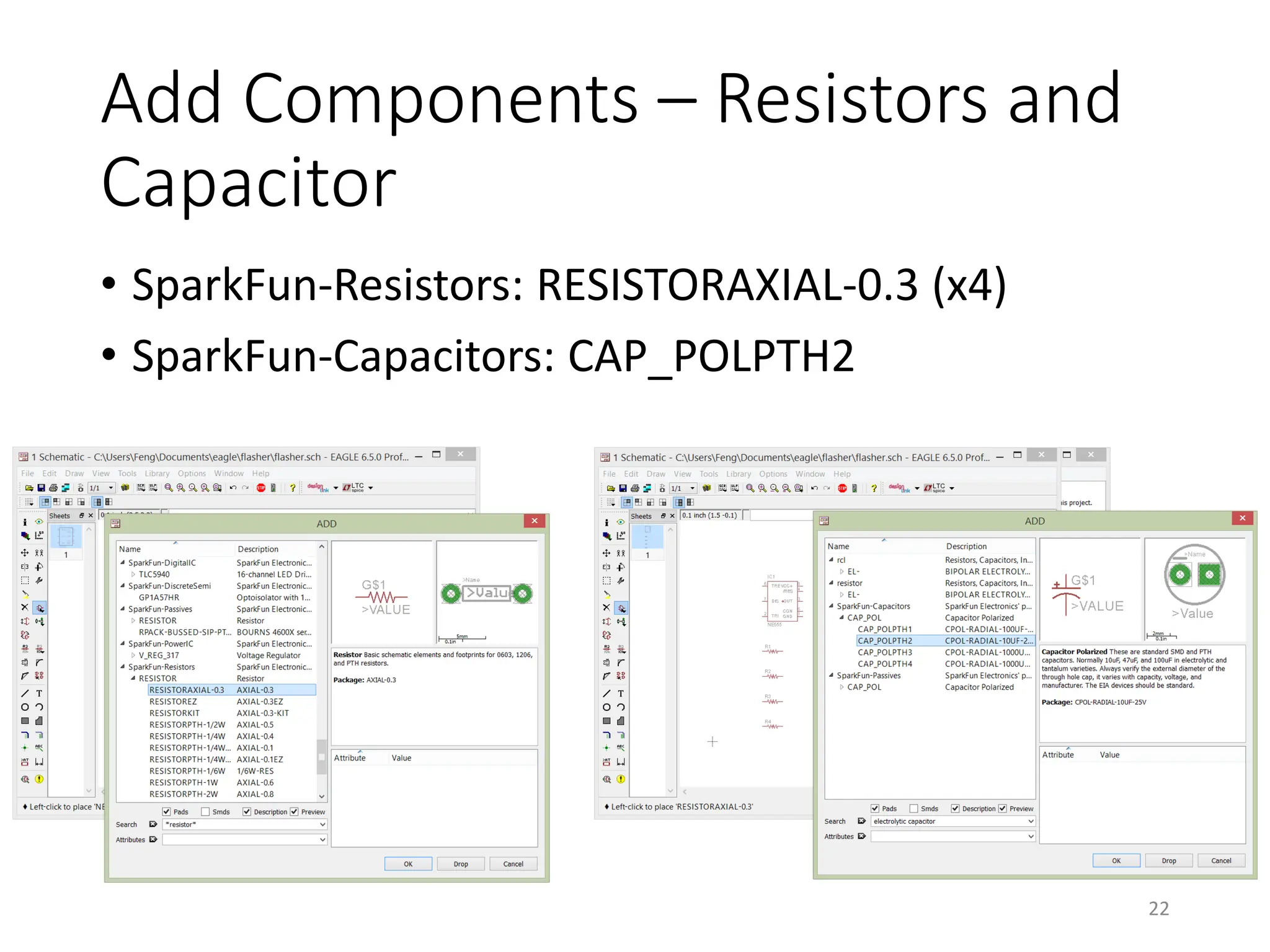
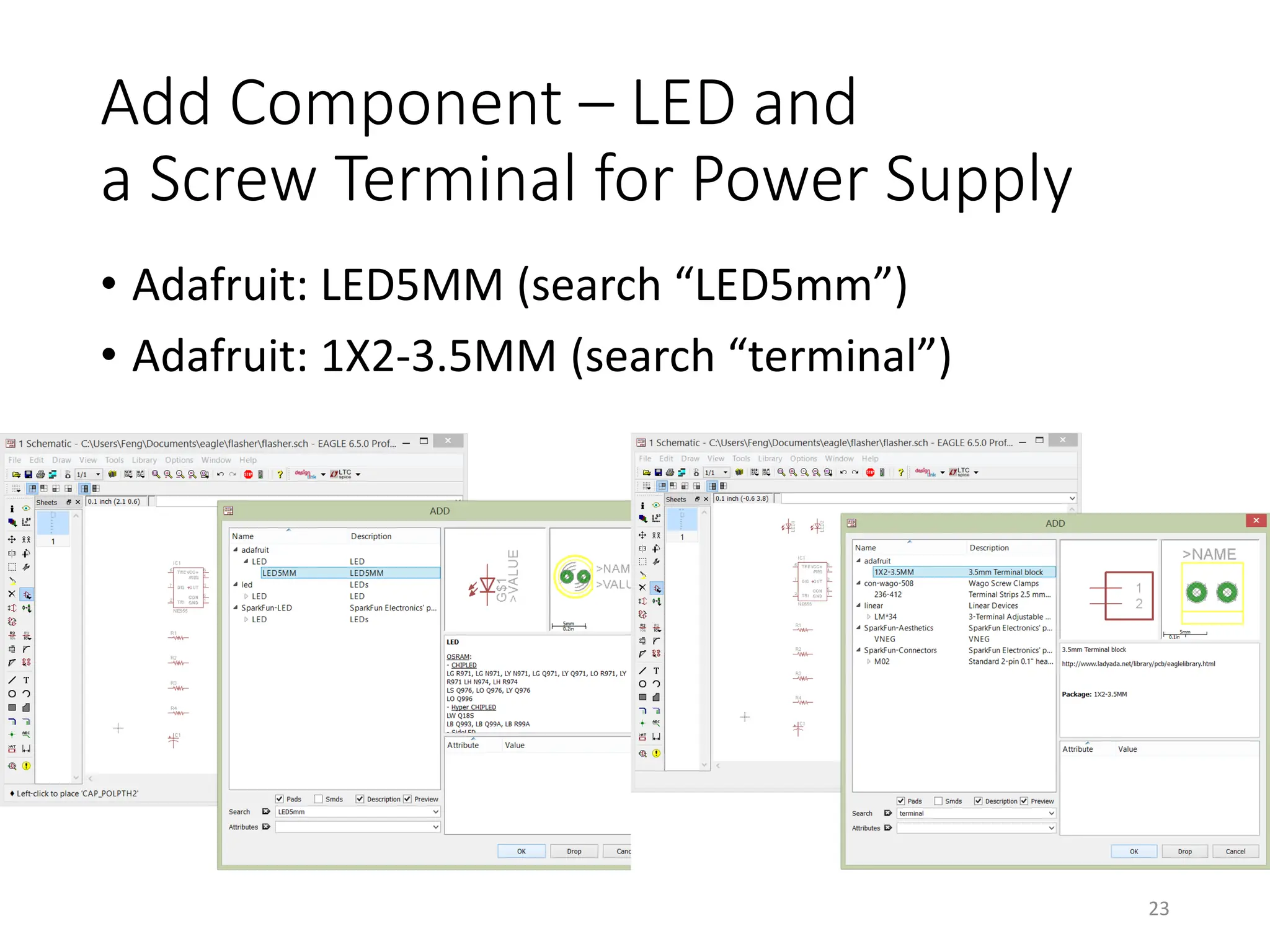
![Finding and Add a Component
• [Schematic] Add
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-19-2048.jpg)

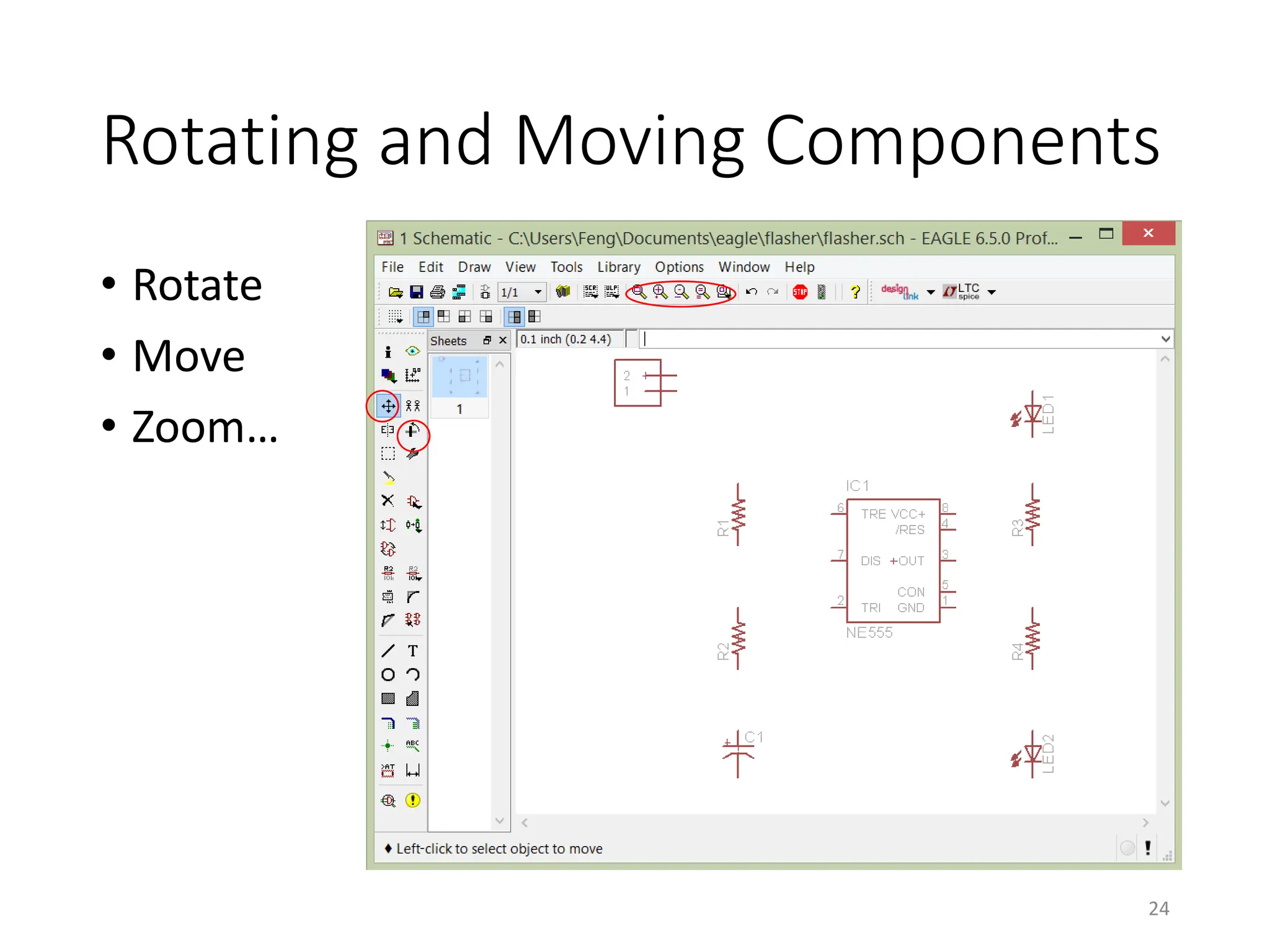
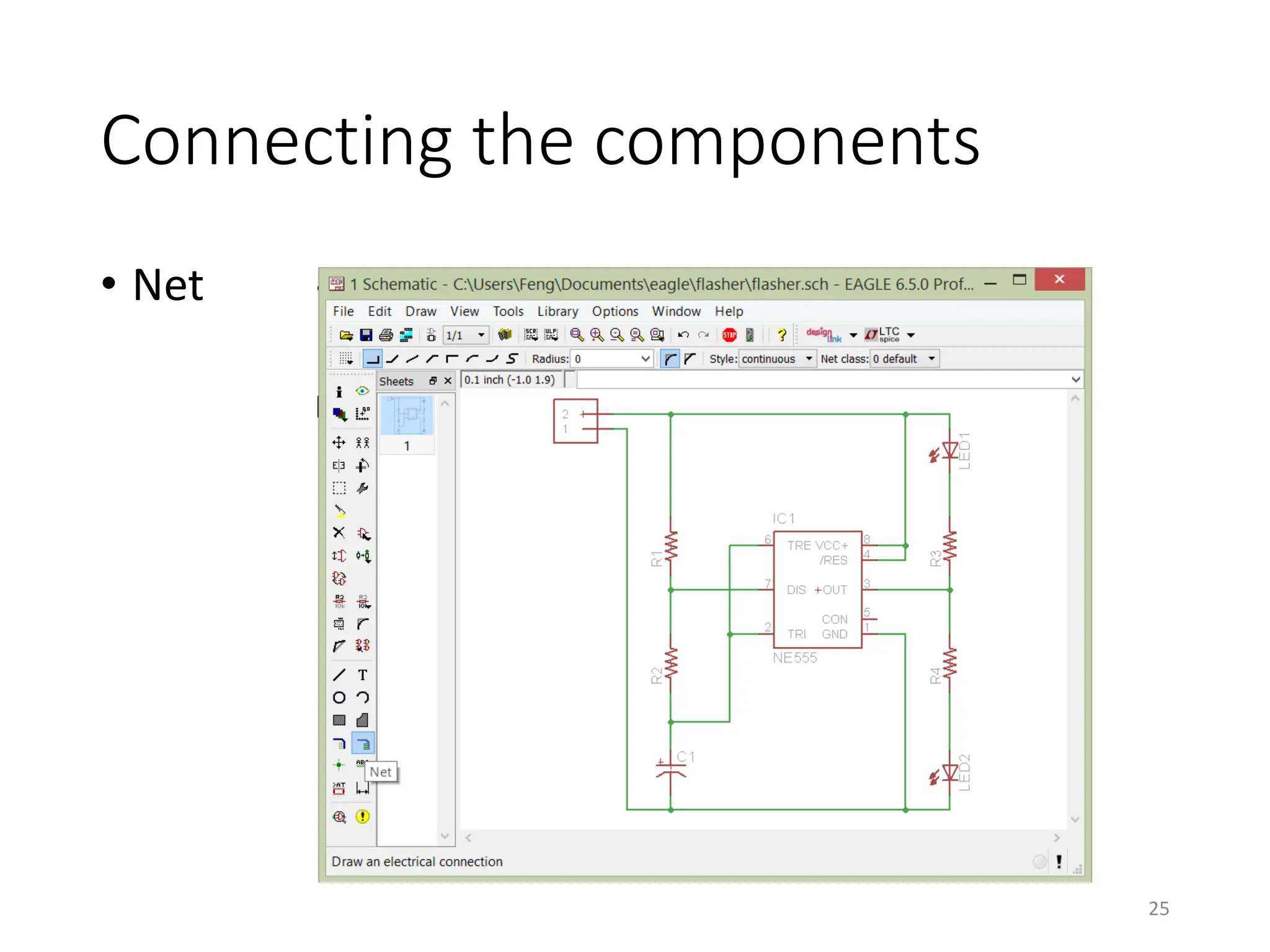
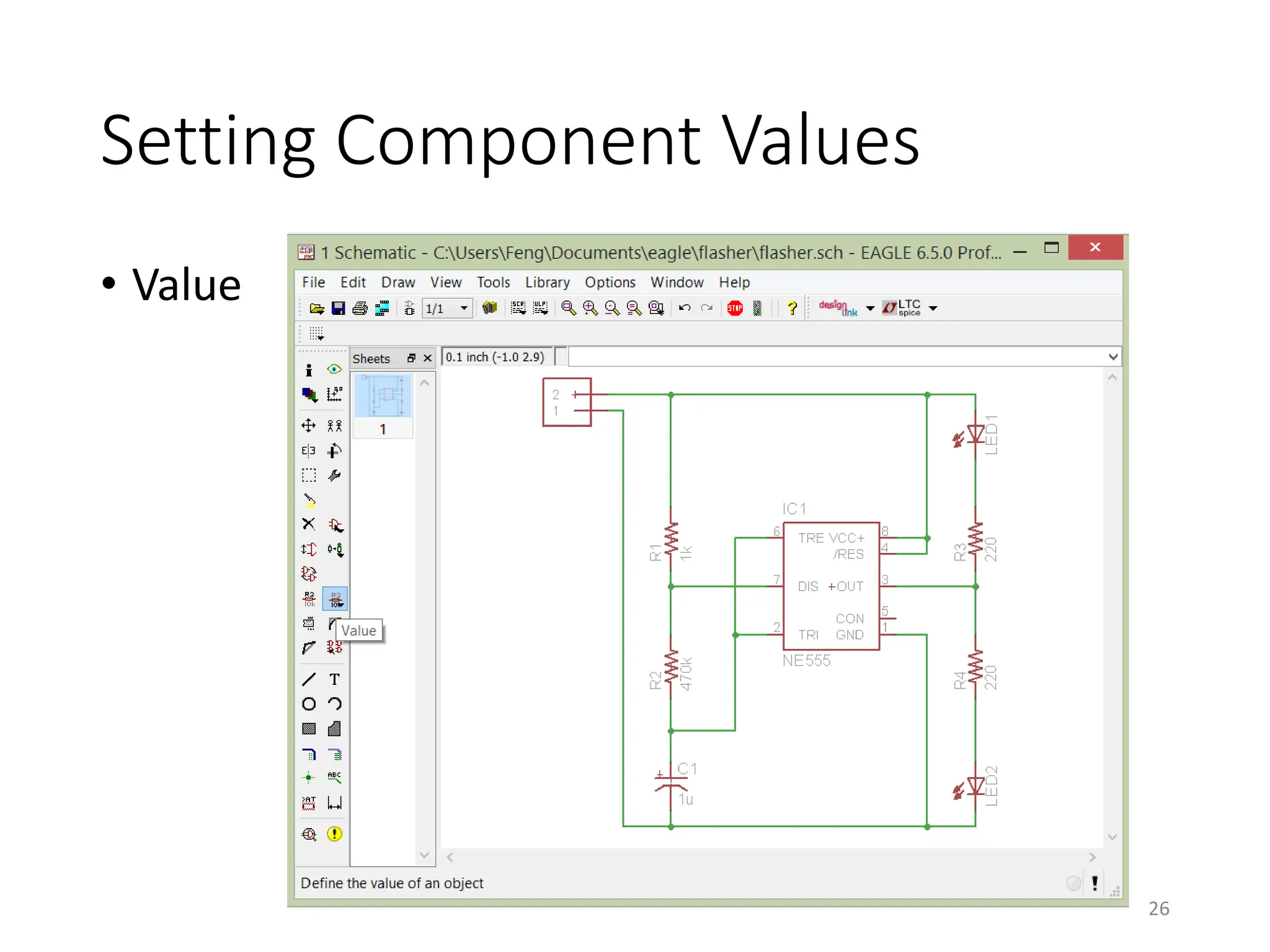
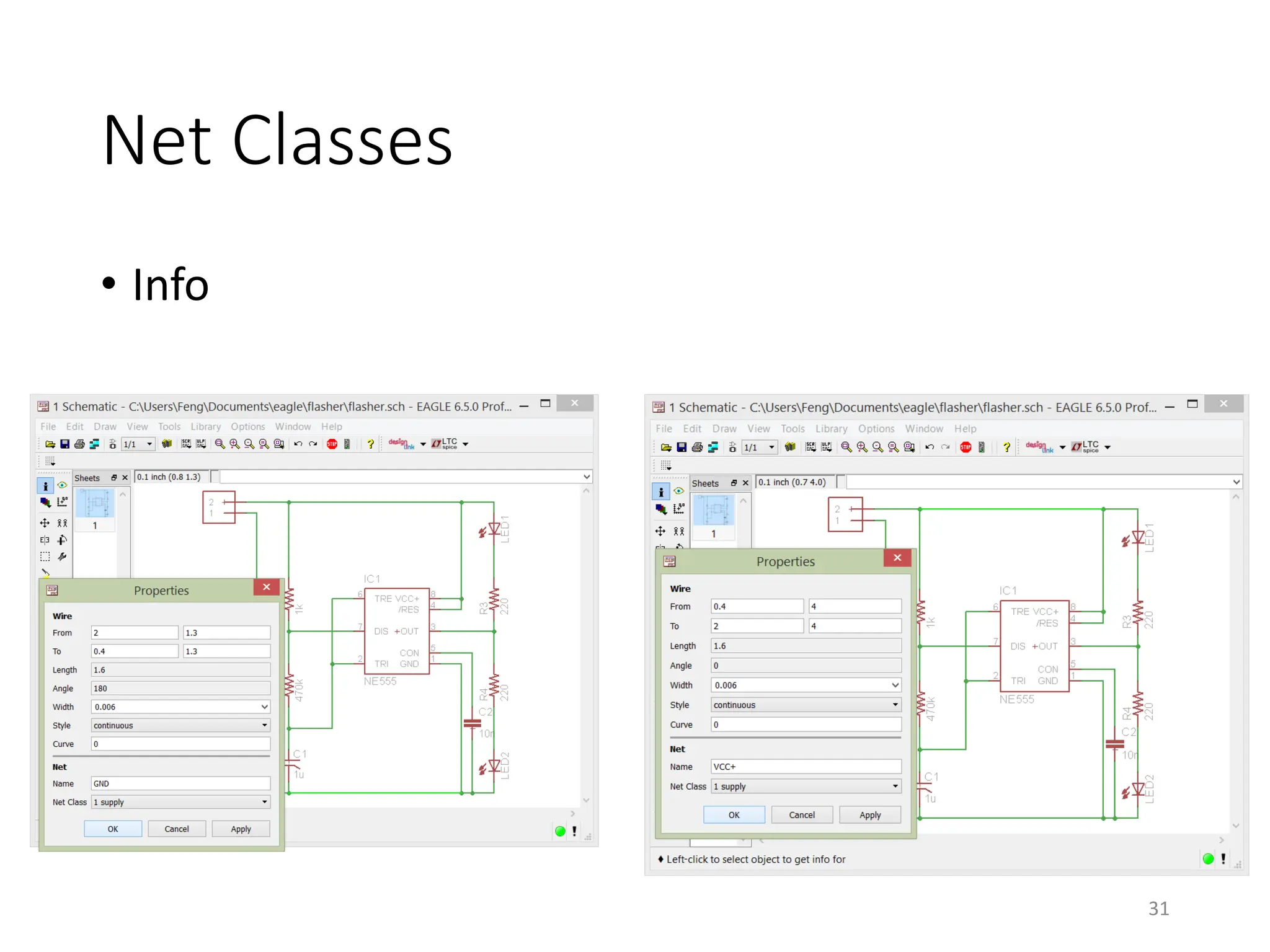
![Net classes
• [Schematic]Edit->Net classes
• Can also be done in Layout Editor later
30
1mil = 0.001inch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-30-2048.jpg)
![Laying Out the Board
• [Schematic]File->Switch to board
• “This is no board, so would like to create one from
the schematic?” – “Yes”
• Yellow lines: airwires-connections that will have to
be converted into tracks
• Rectangle: borders
32
Note: 1. Do NOT close either
schematic or board window.
They must both remain open
while working. Change in on
editor window will lead to
change in the other window.
2. Change background color:
[Board]Options->User
interface…->Background->White](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-32-2048.jpg)
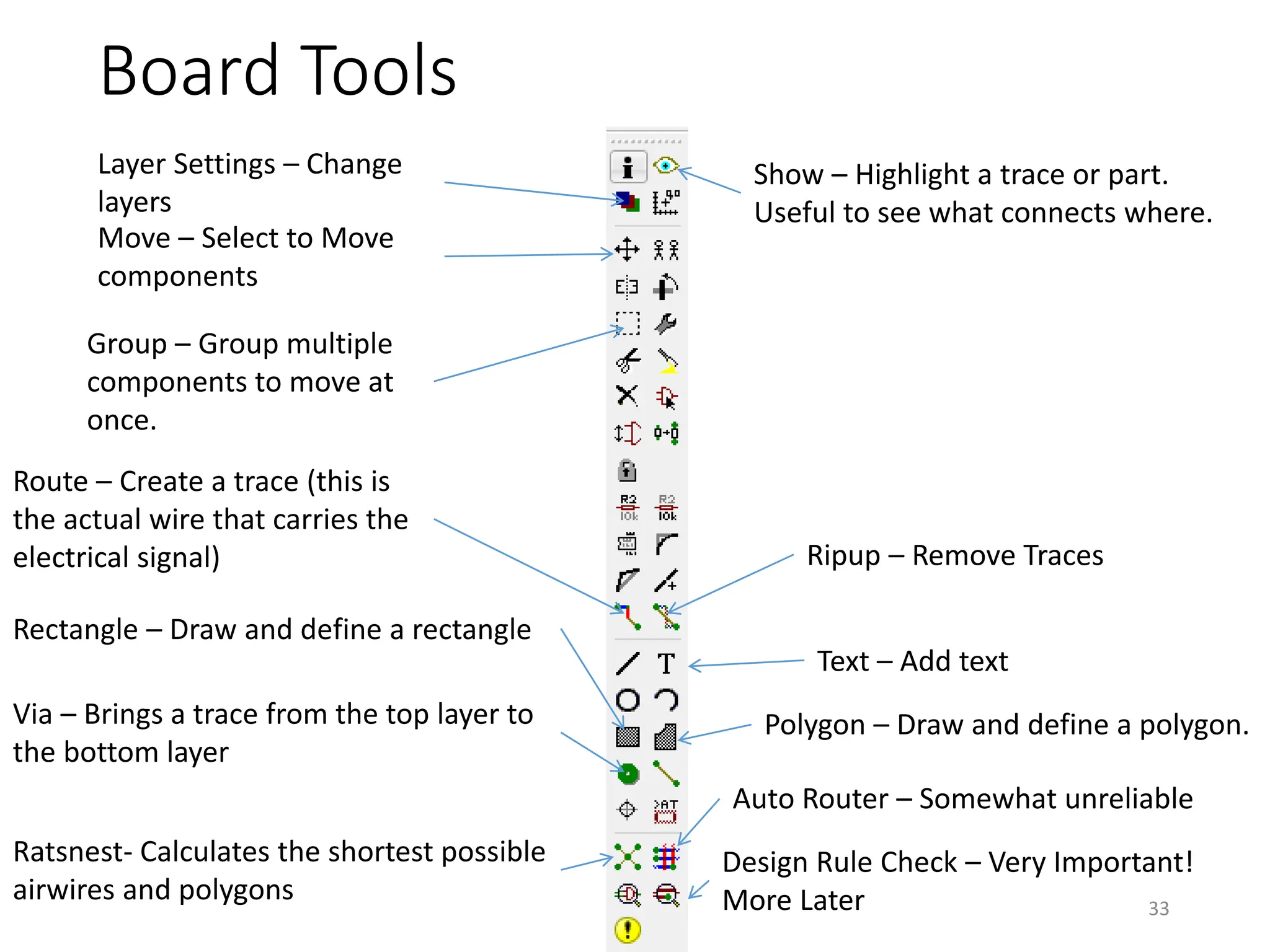
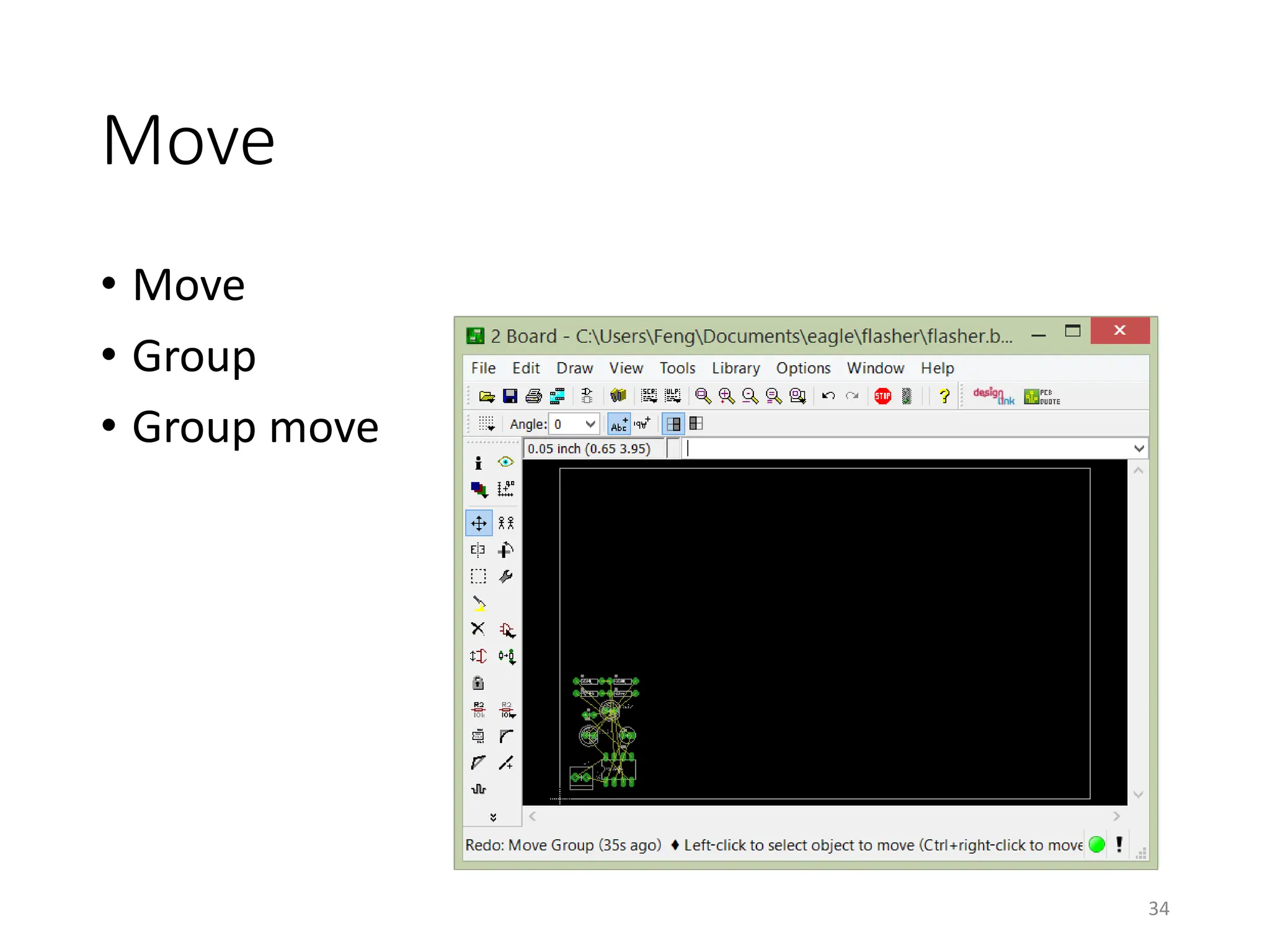
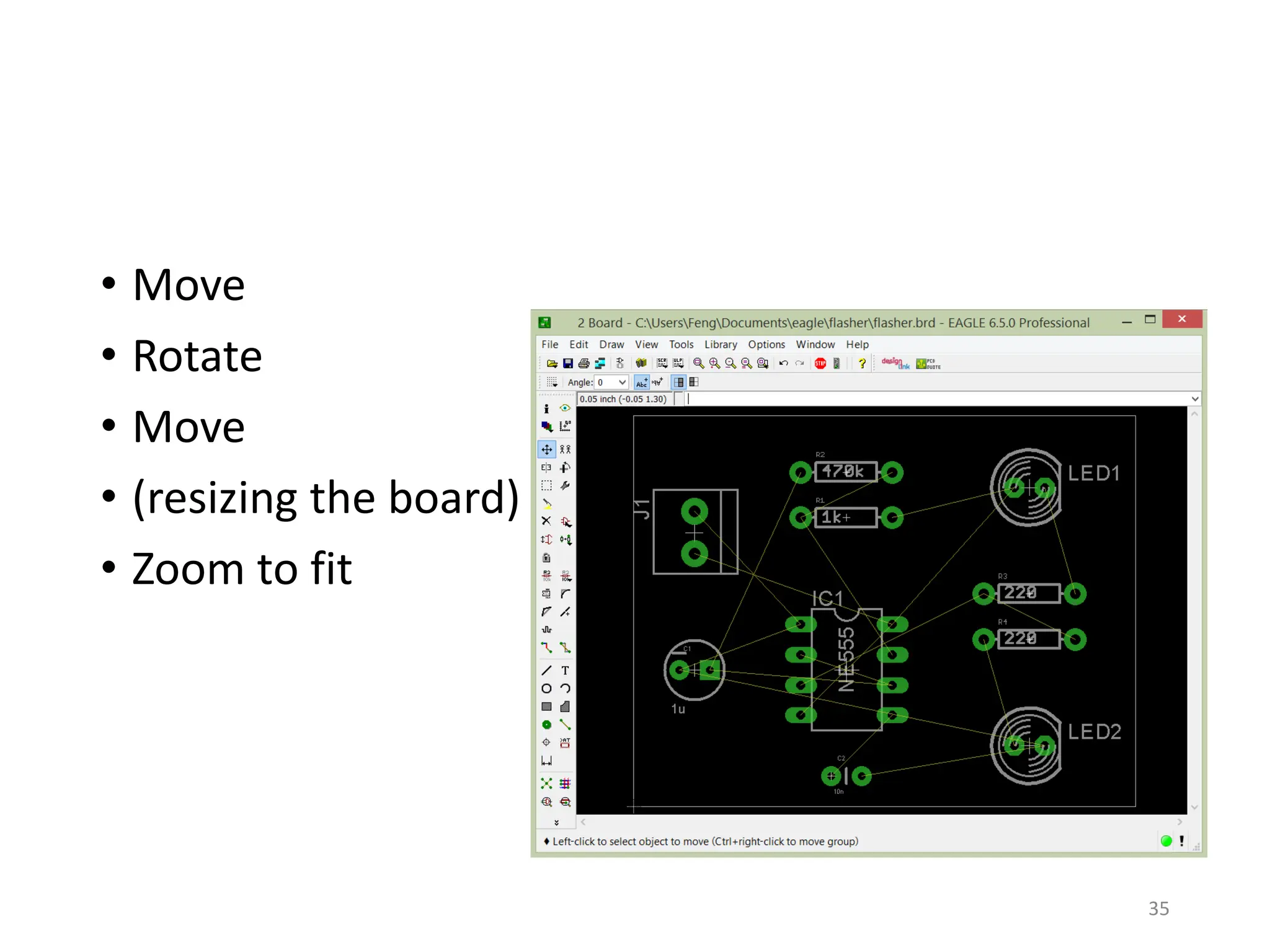
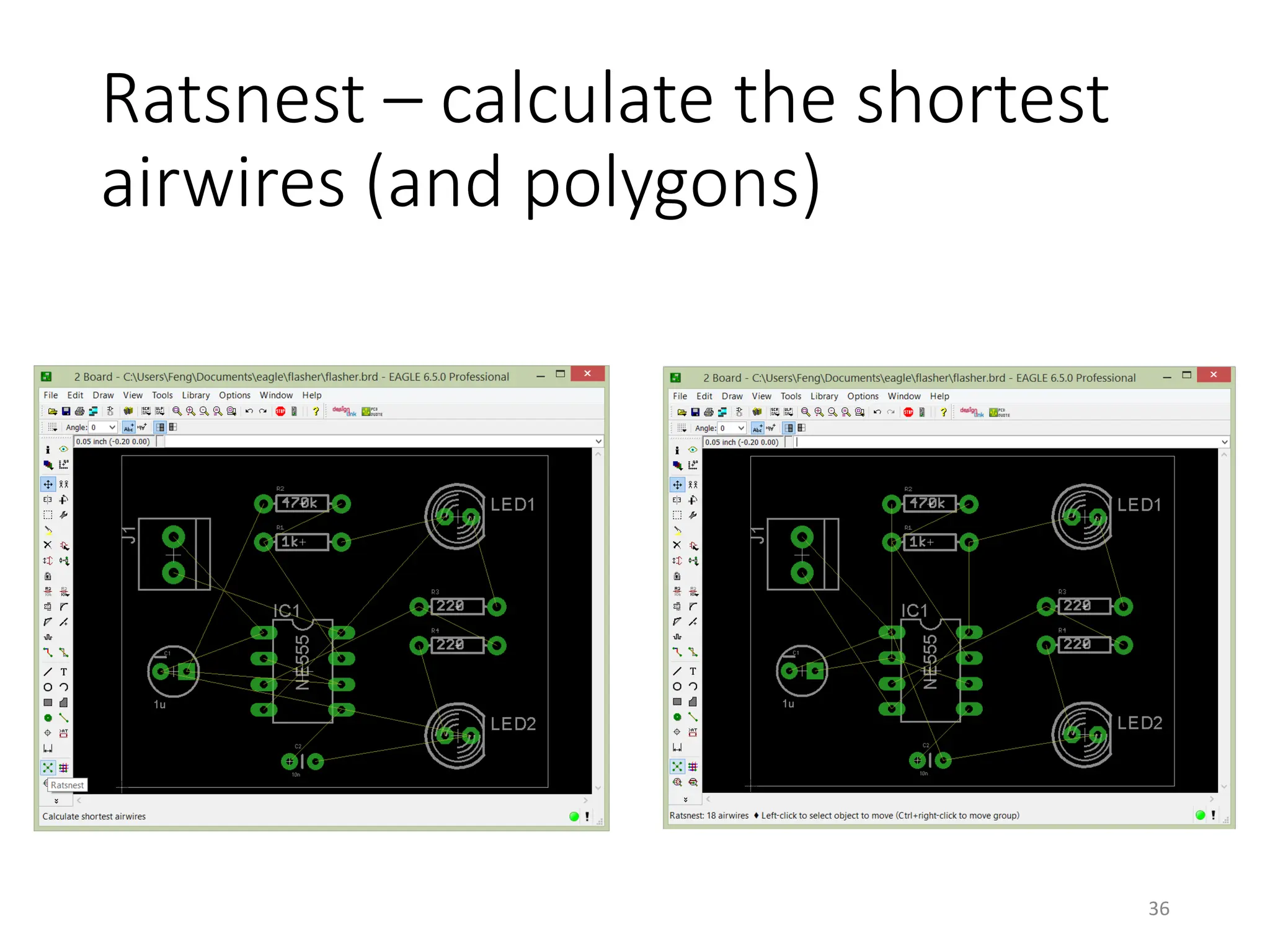
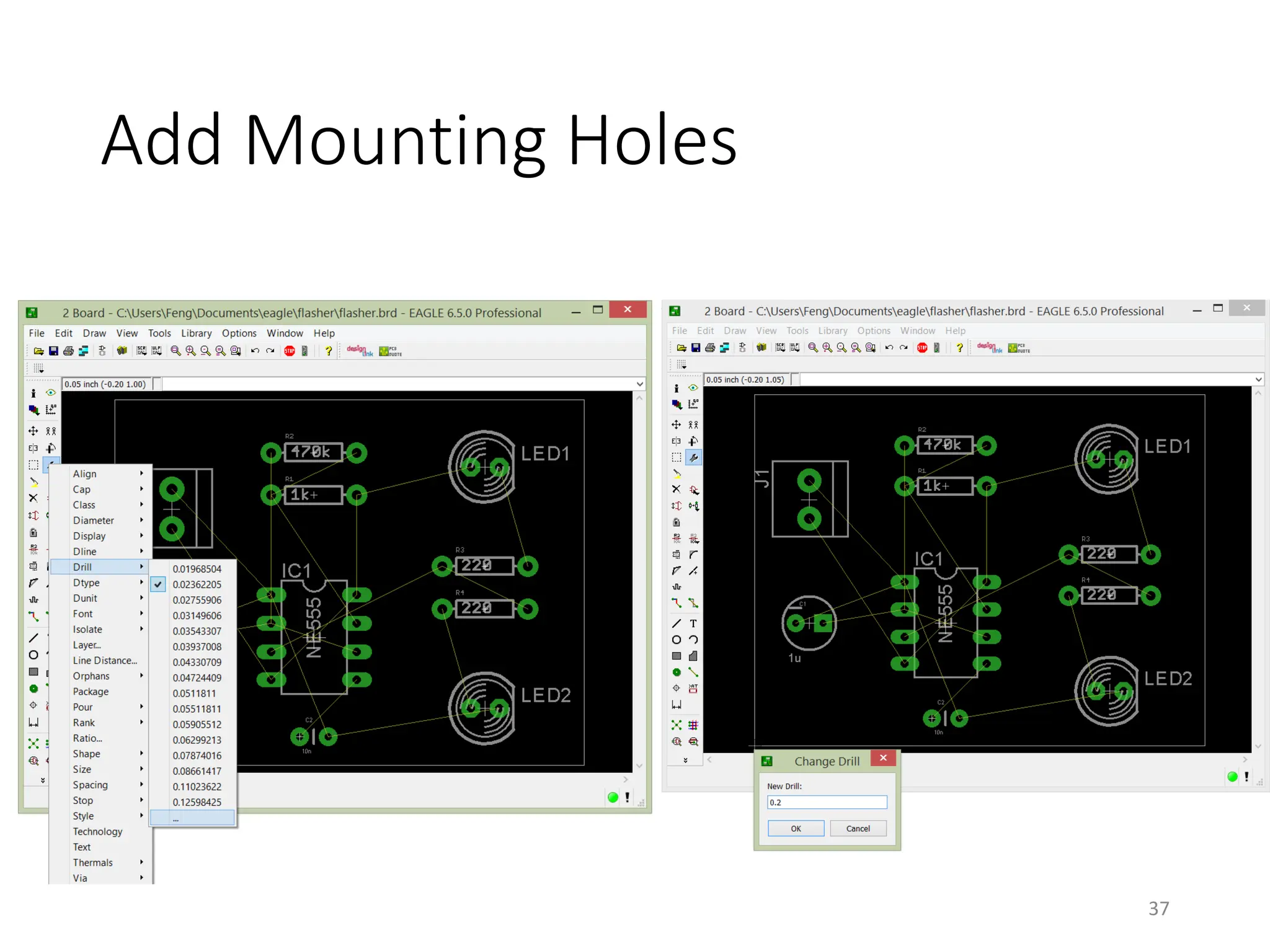
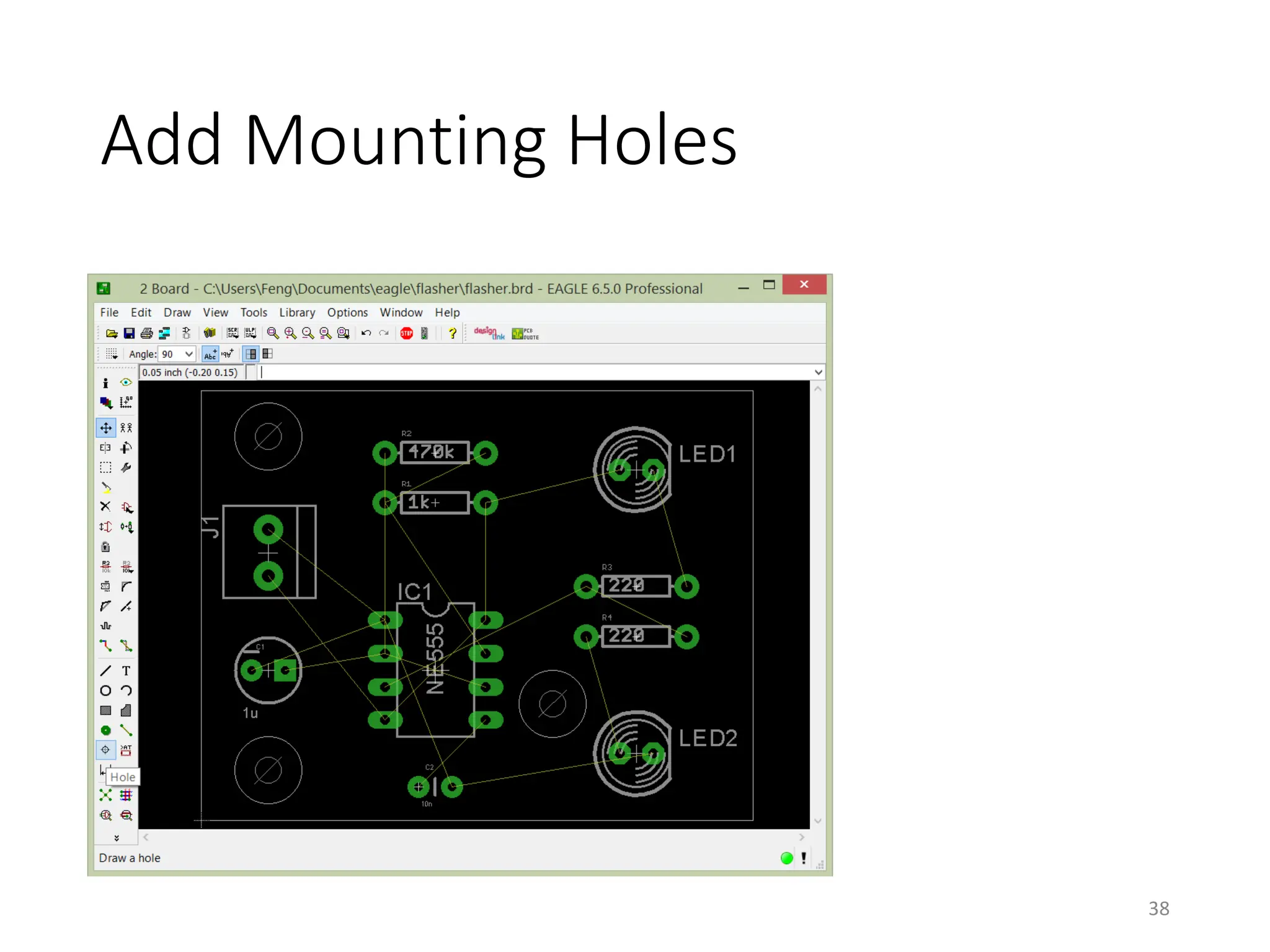
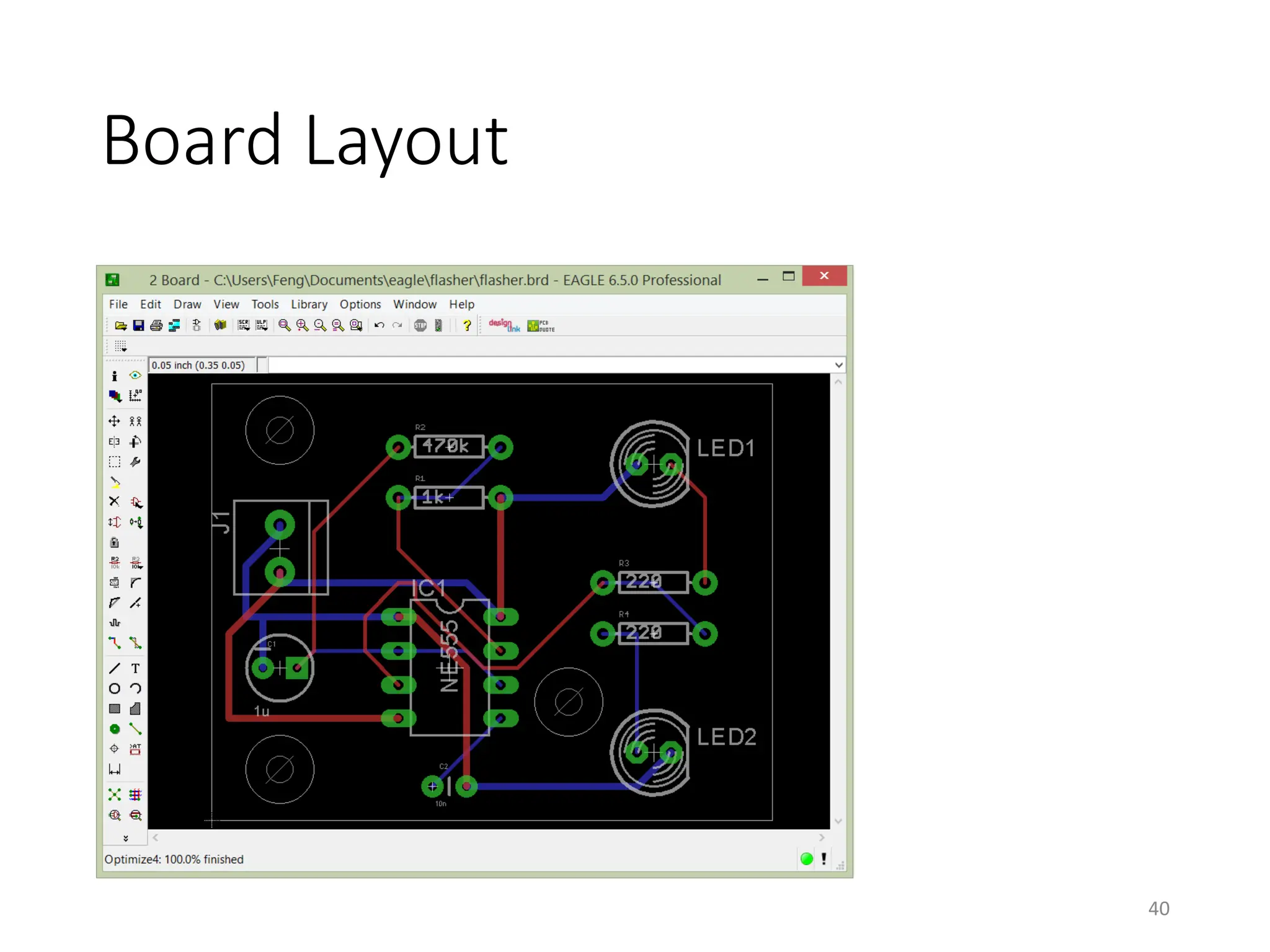
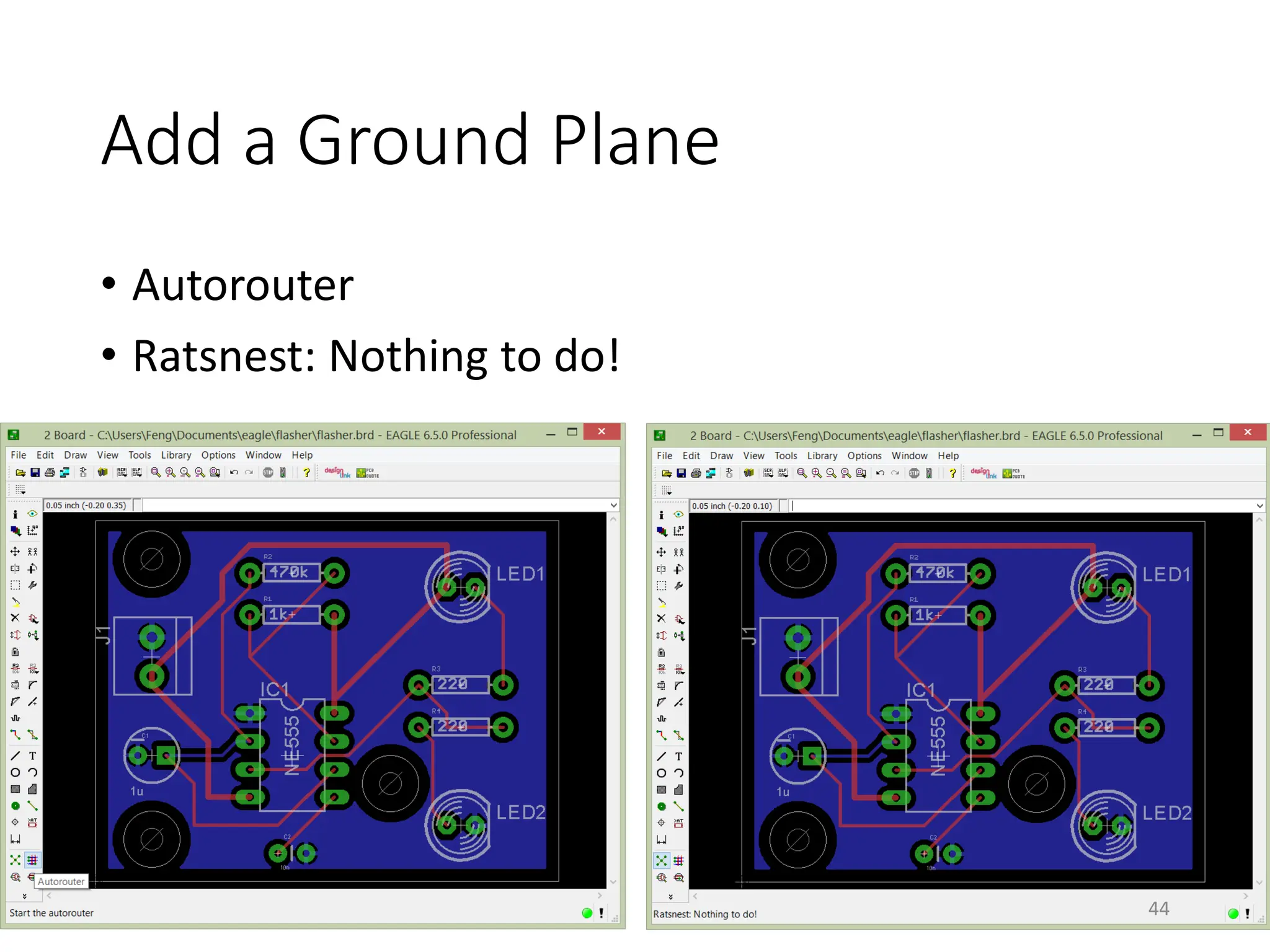
![Autorouter
• [Board] Autorouter
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-39-2048.jpg)
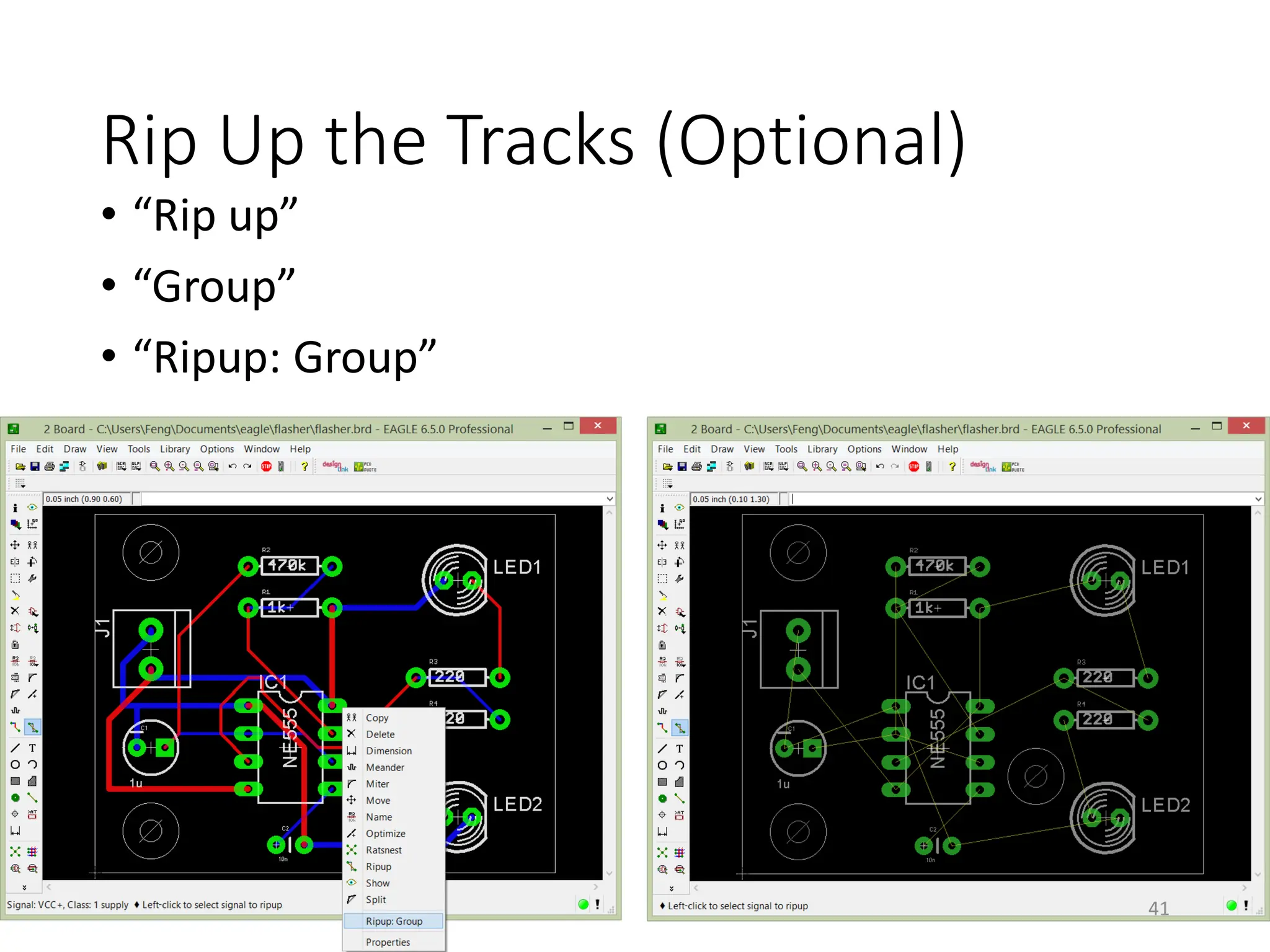
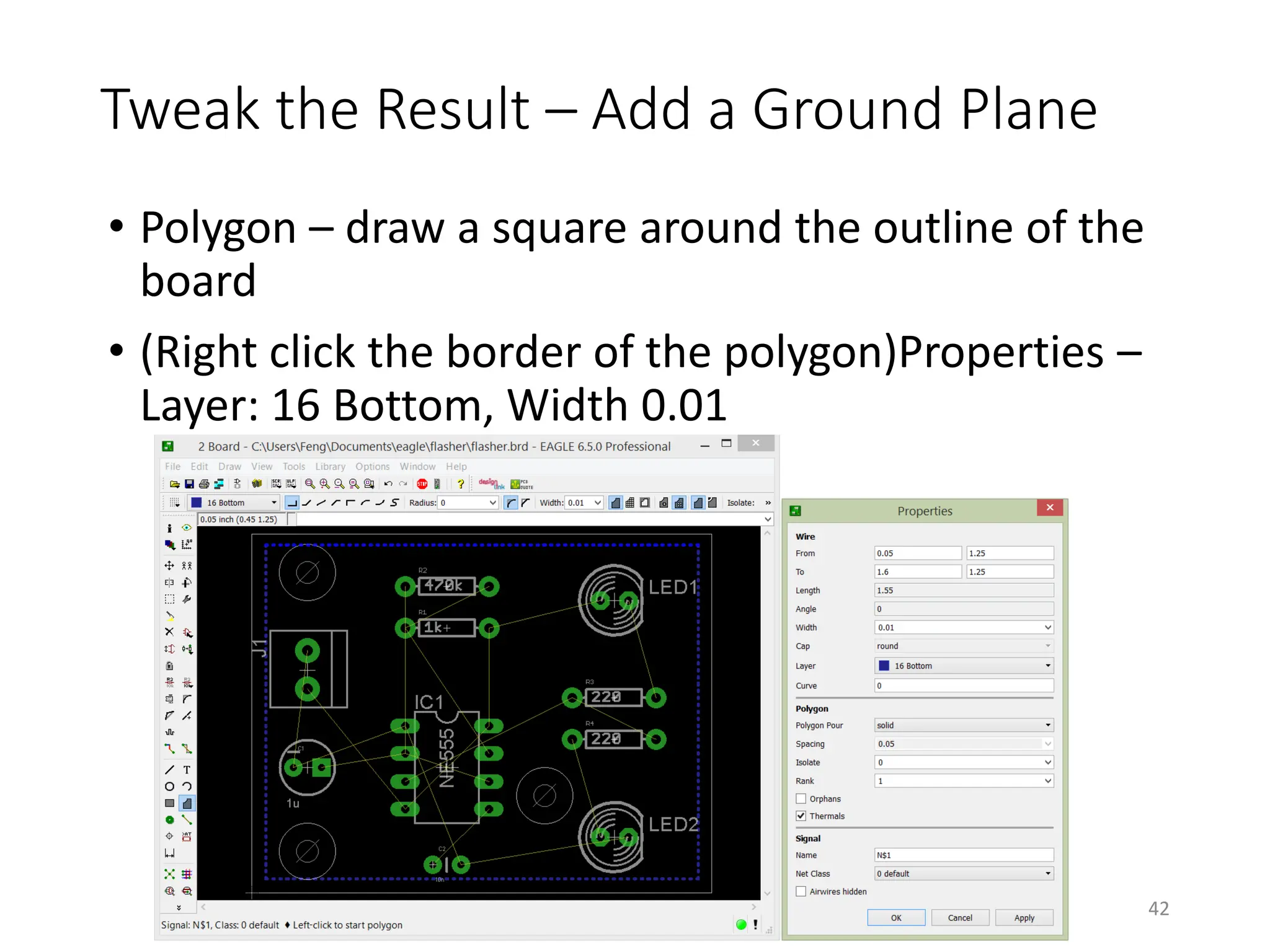

![Design Rule Checker
• [Board]DRC
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-45-2048.jpg)
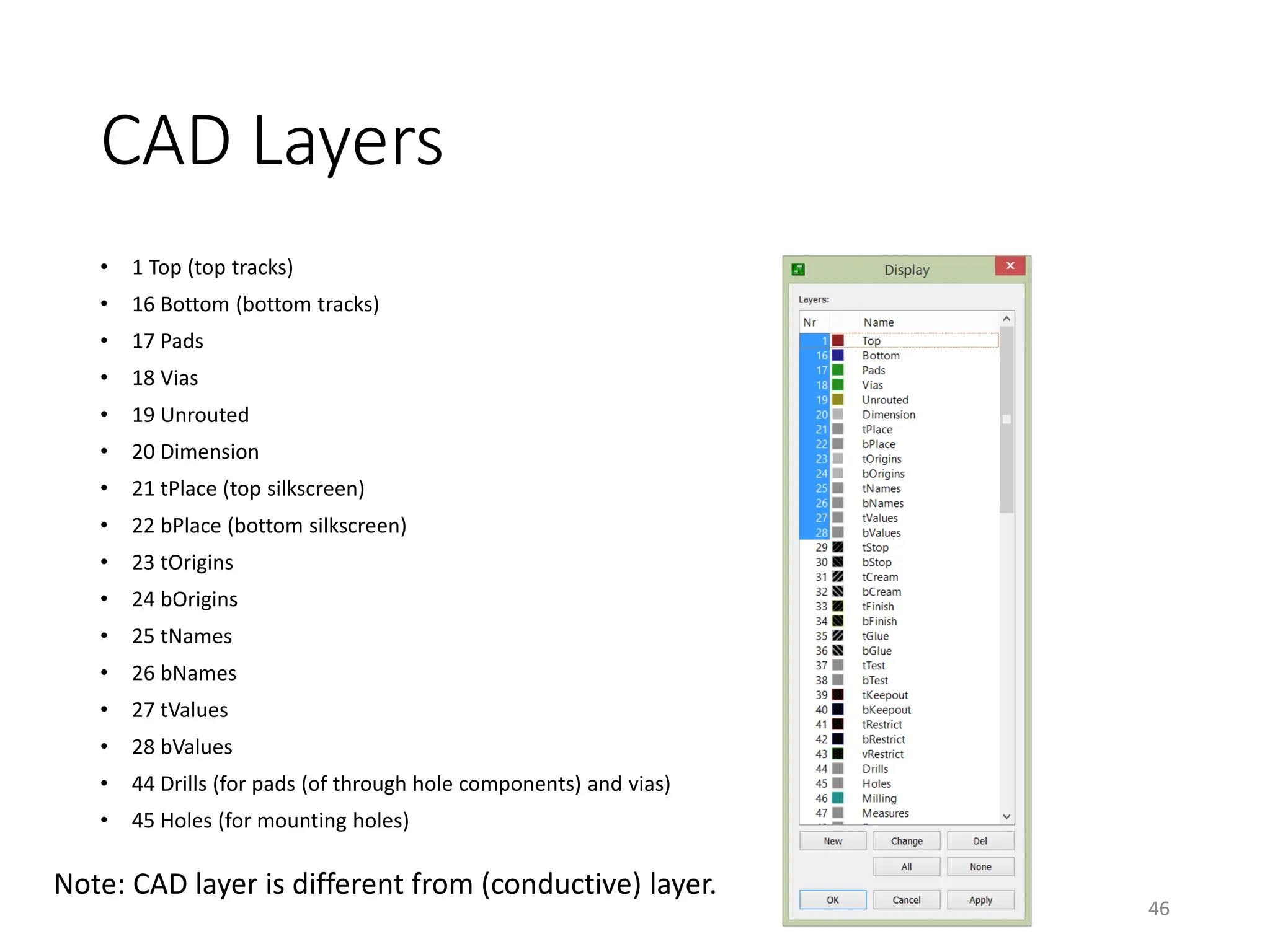
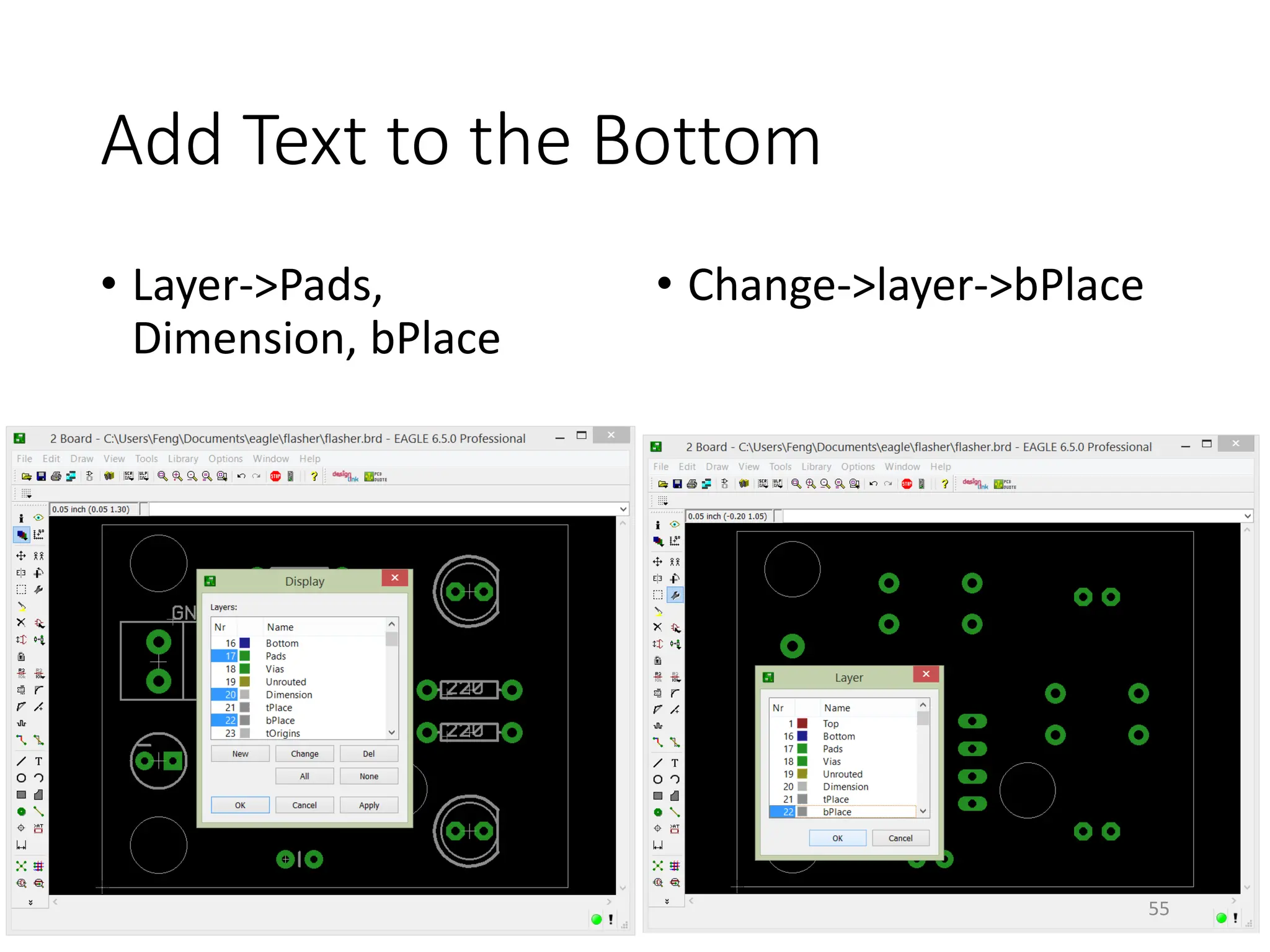
![Add Text on the Top (Silkscreen)
• [Board]Layers – Pads, Dimension, tPlace, tOrigins,
tNames, tValues
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-47-2048.jpg)
![Smash – Separate the Text From Devices
• [Board]Smash
• Group
• Smash: Group
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-48-2048.jpg)
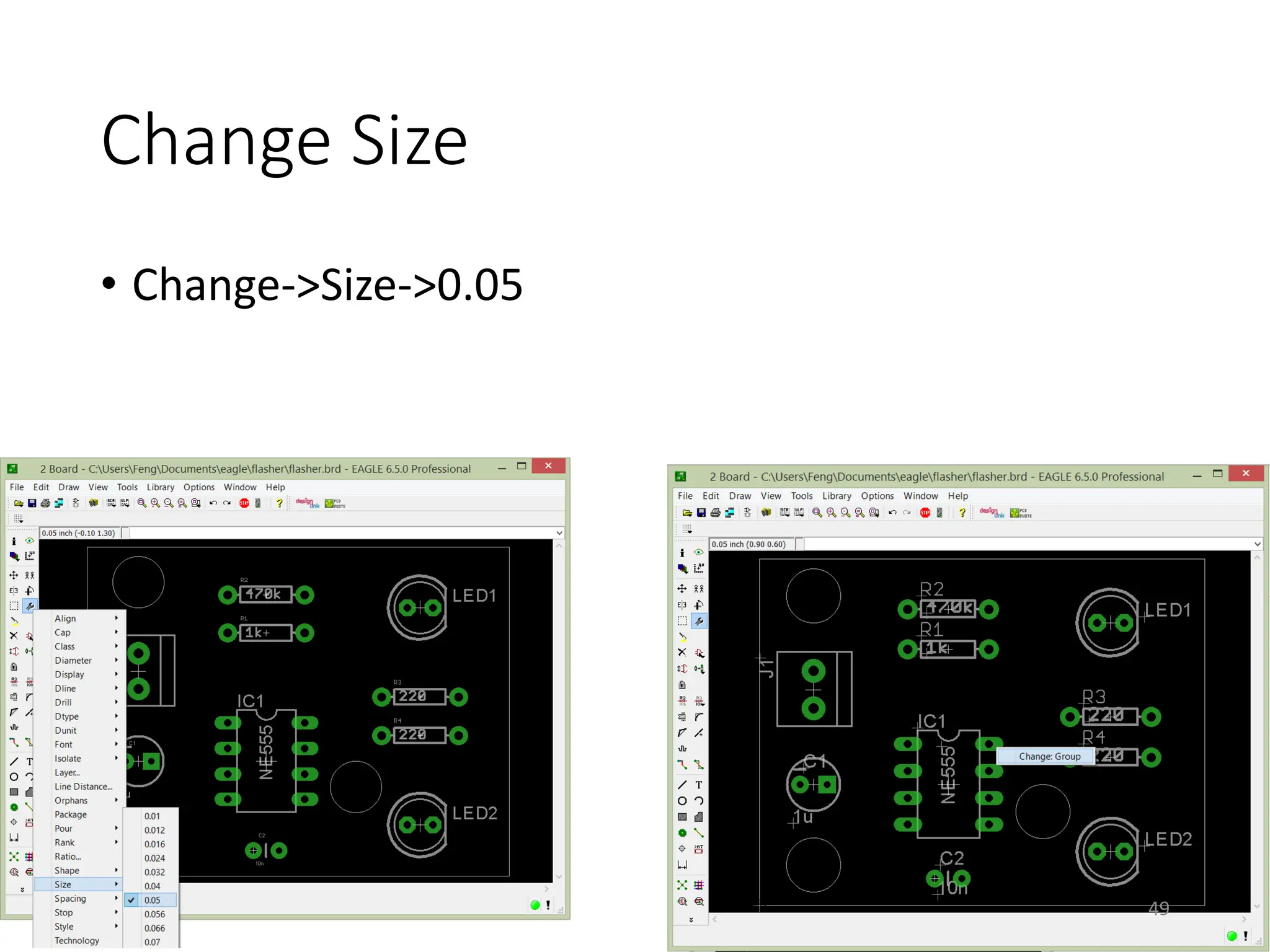
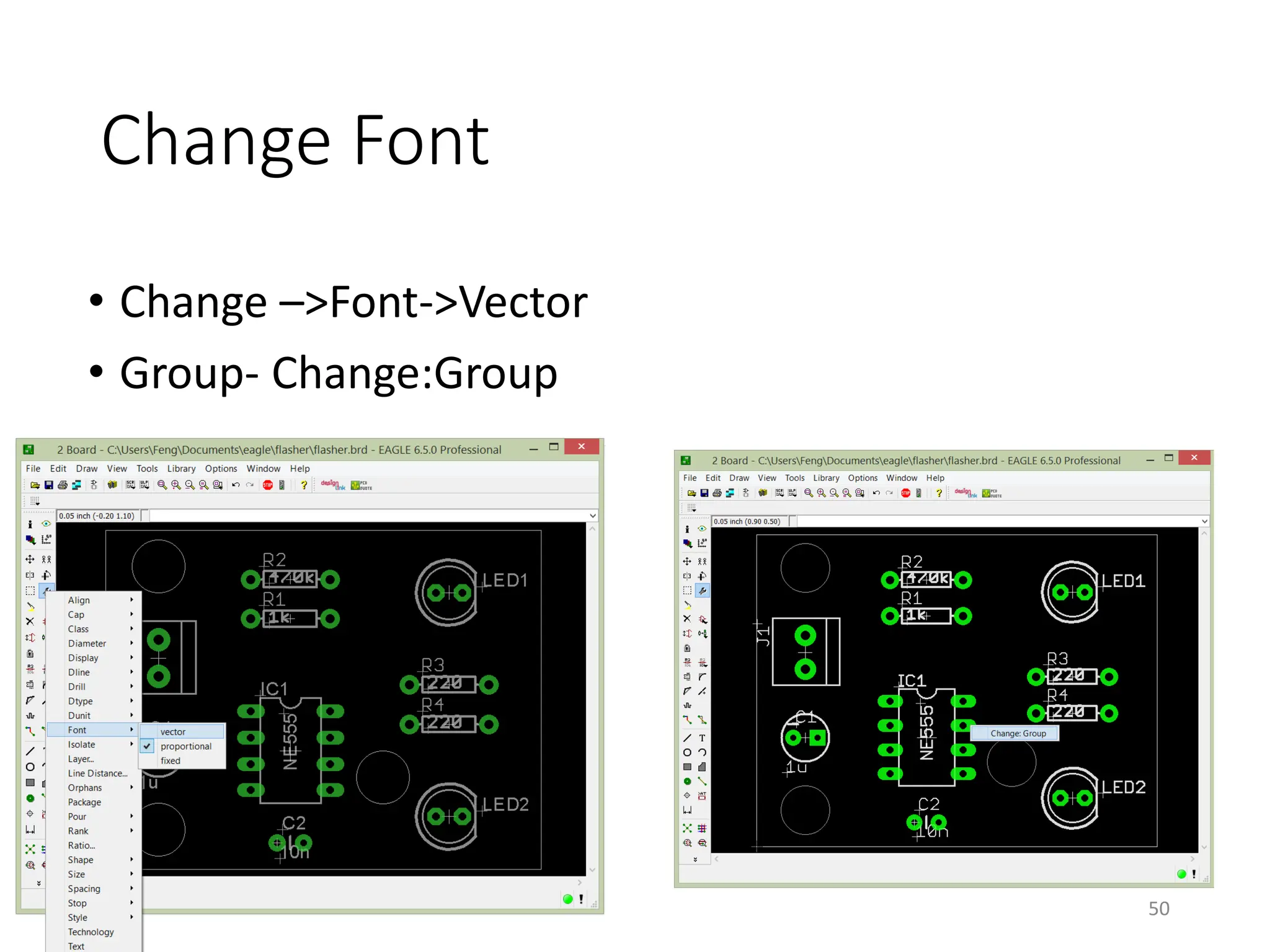
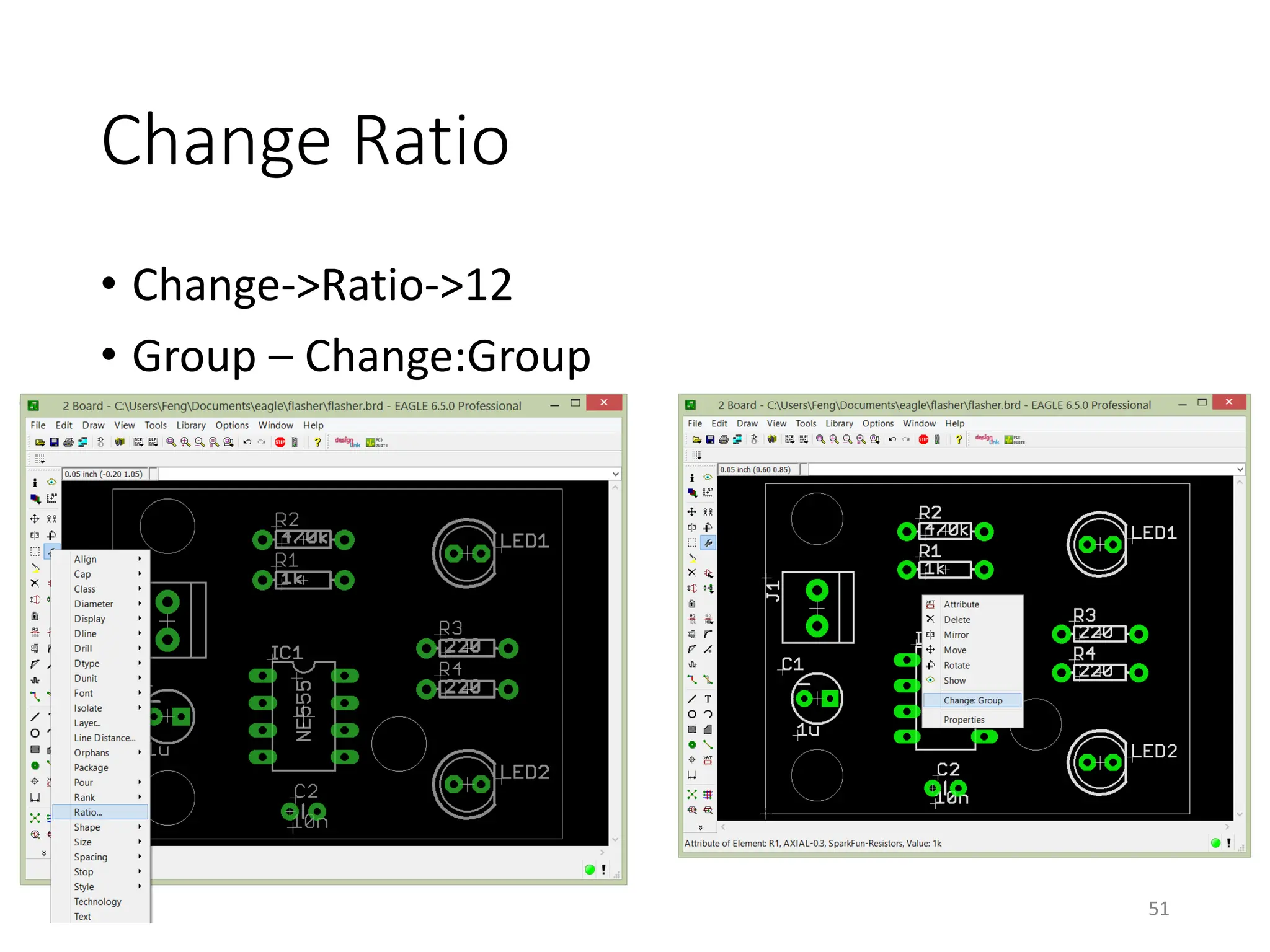
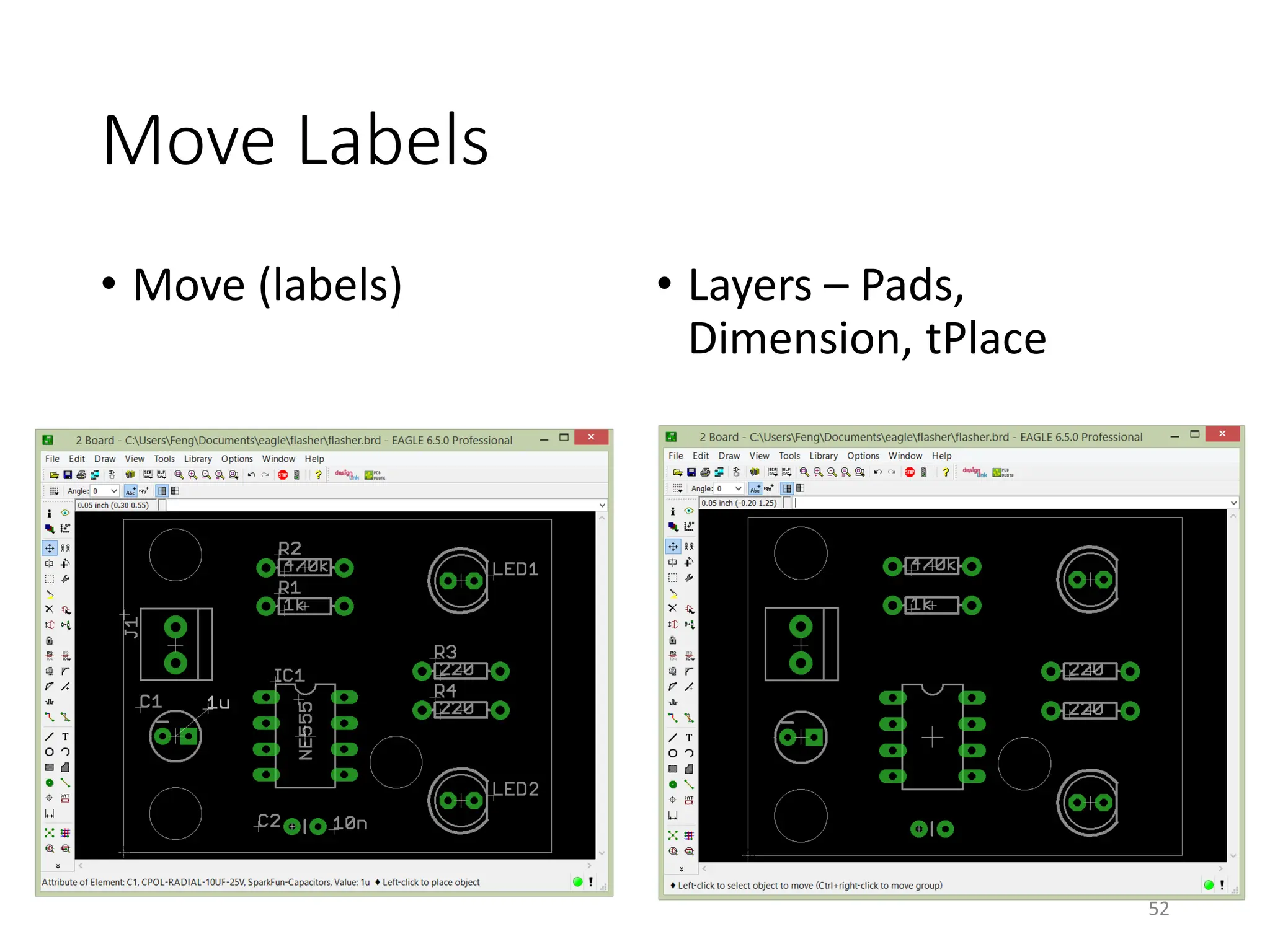
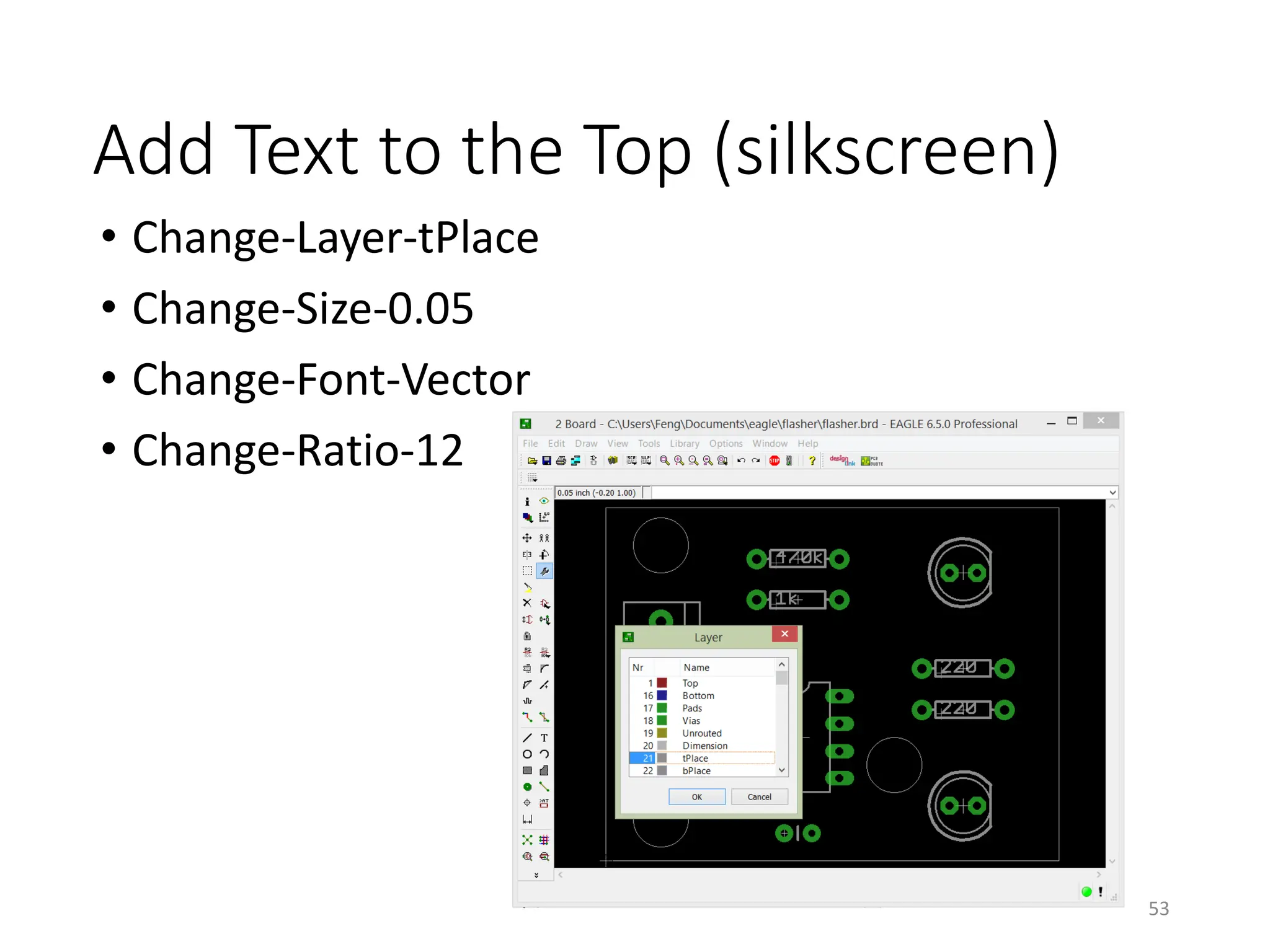


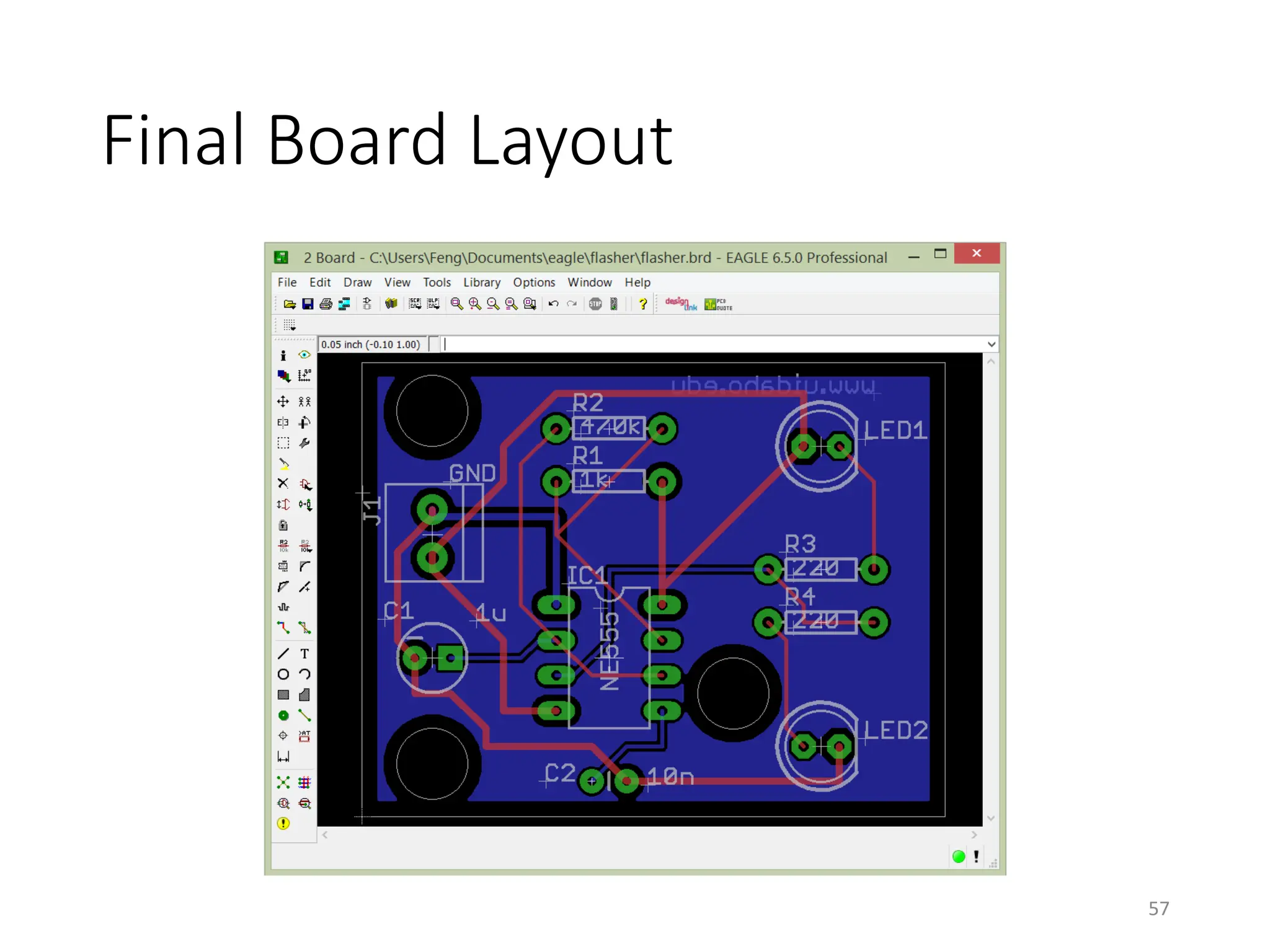
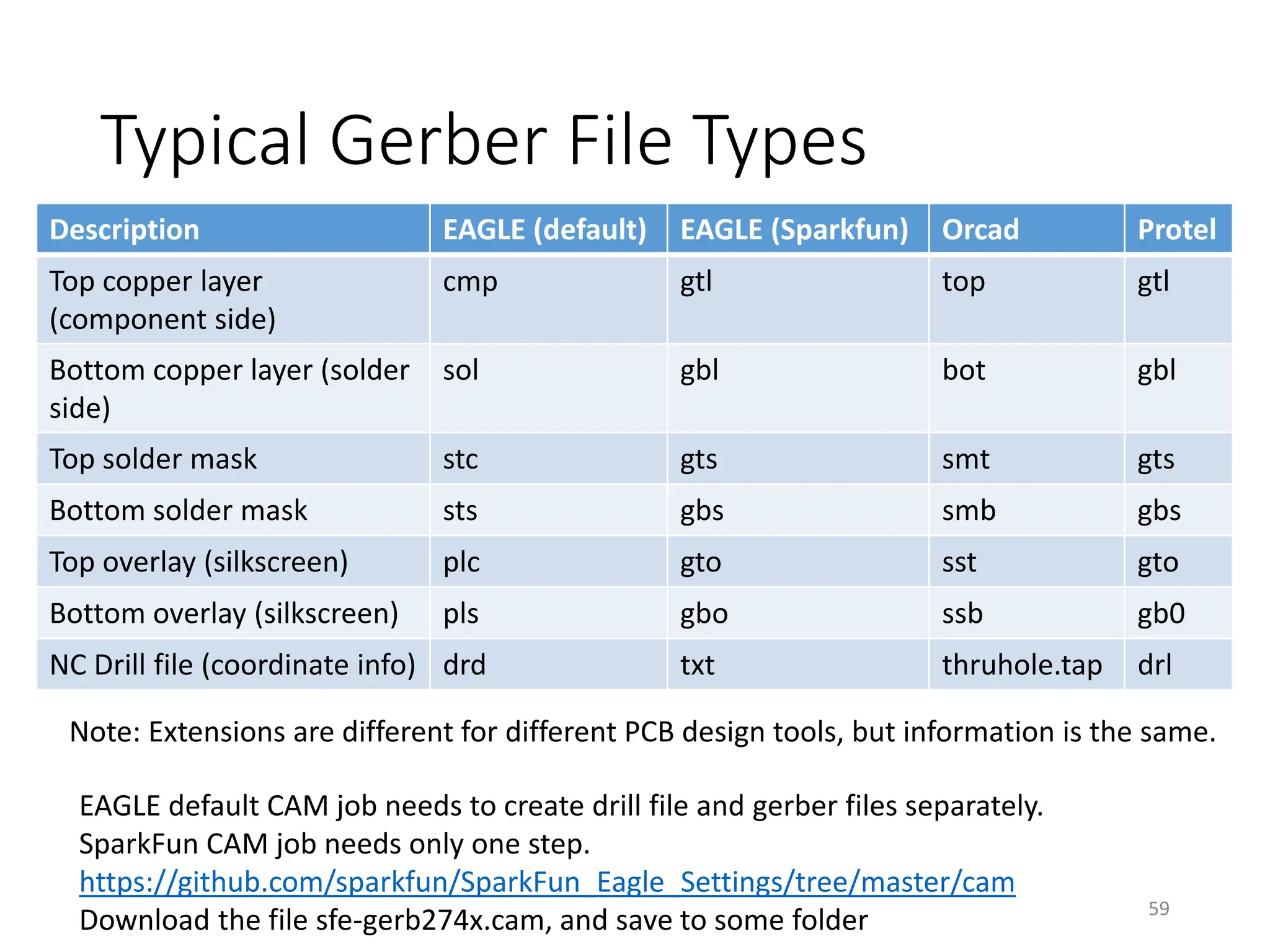
![Gerber File Generation – CAM
Processor
• [Board] File->CAM Processor
• [CAM Processor] File->Open->Job->sfe-
gerb274x.cam
60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-60-2048.jpg)
![Gerber File Generation – CAM
Processor
• [CAM Processor] Process Job
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcbdesignwitheagle-240412005901-52f183a1/75/PCB-Design-with-EAGLE-software-interactions-PDF-61-2048.jpg)


