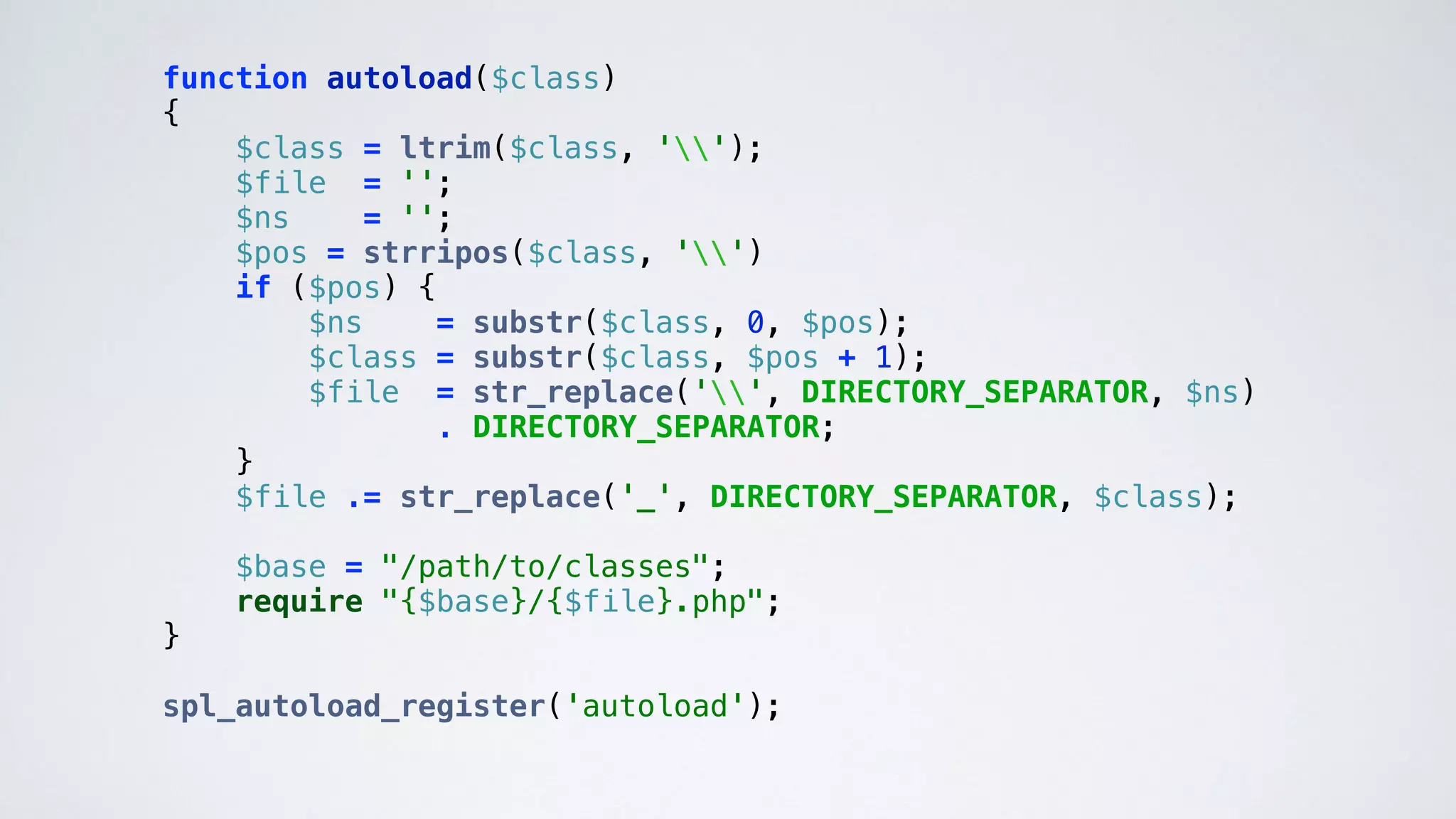
The document discusses the challenges and strategies for modernizing a messy legacy PHP codebase, emphasizing issues such as lack of structure, technical debt, and the need for refactoring. It outlines approaches including incremental improvements, autoloading, converting global variables to injected dependencies, and maintaining running applications during changes. The resulting benefits include improved organization, potential for unit testing, and overall better architecture for future development.