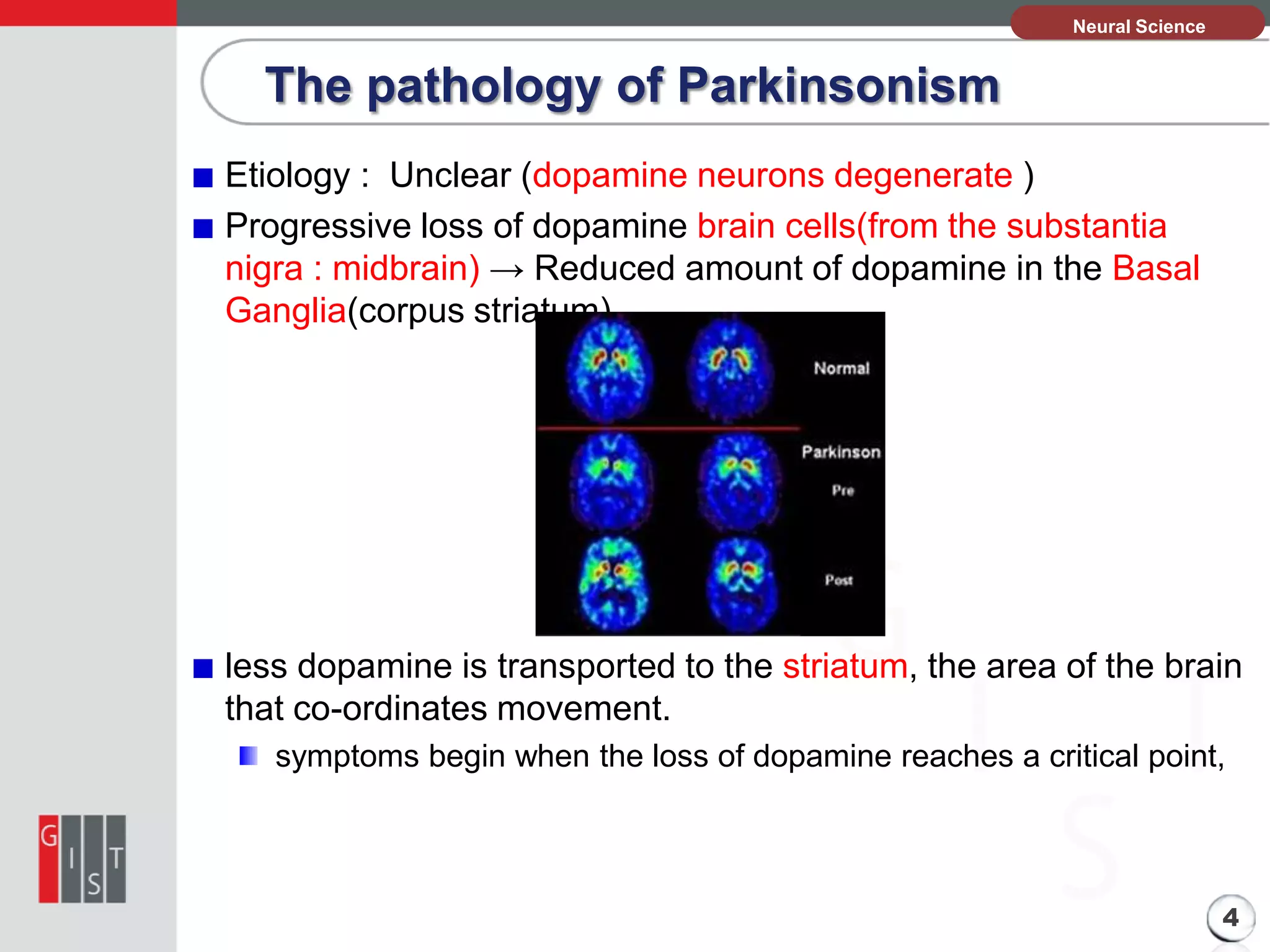
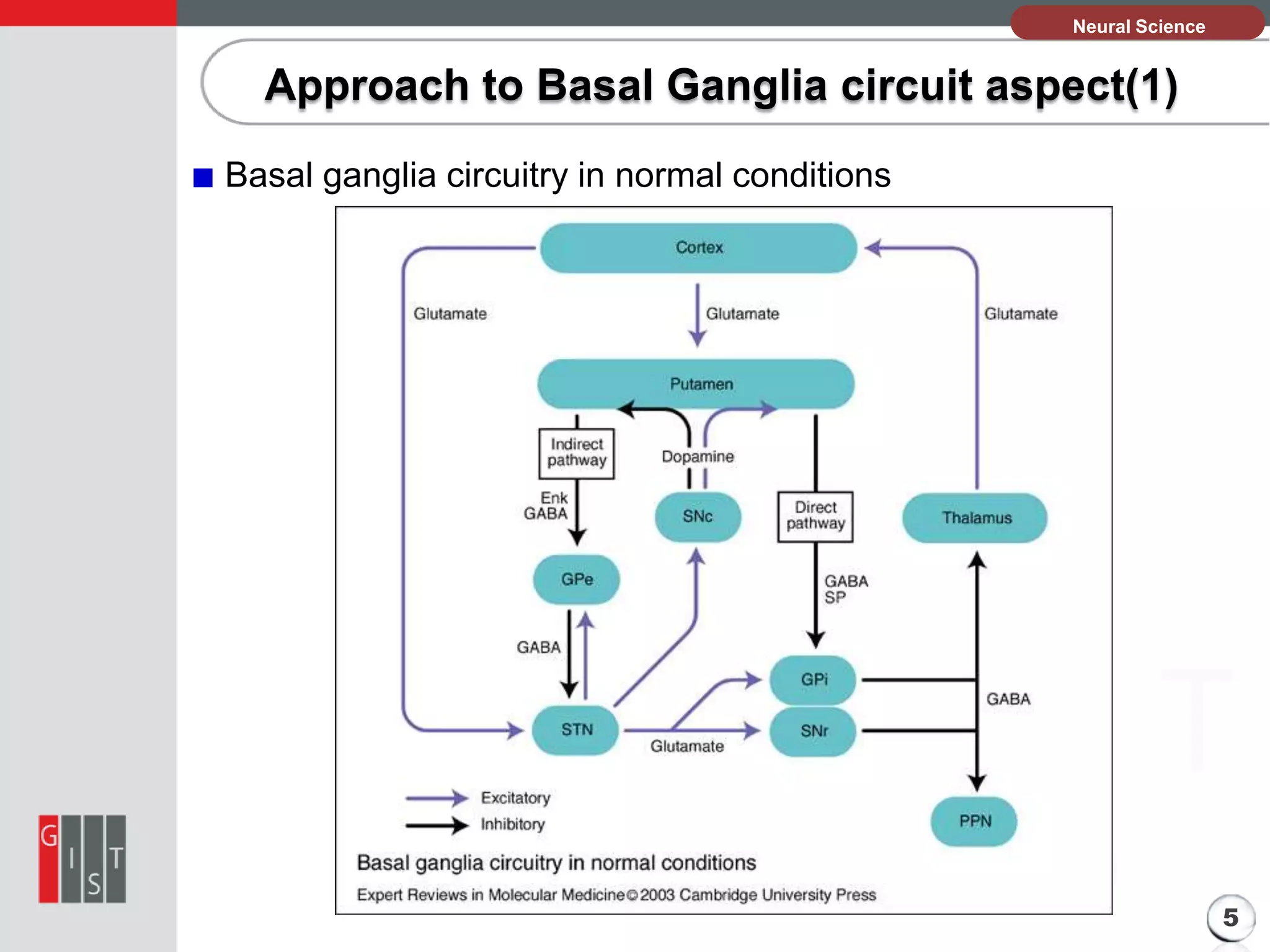
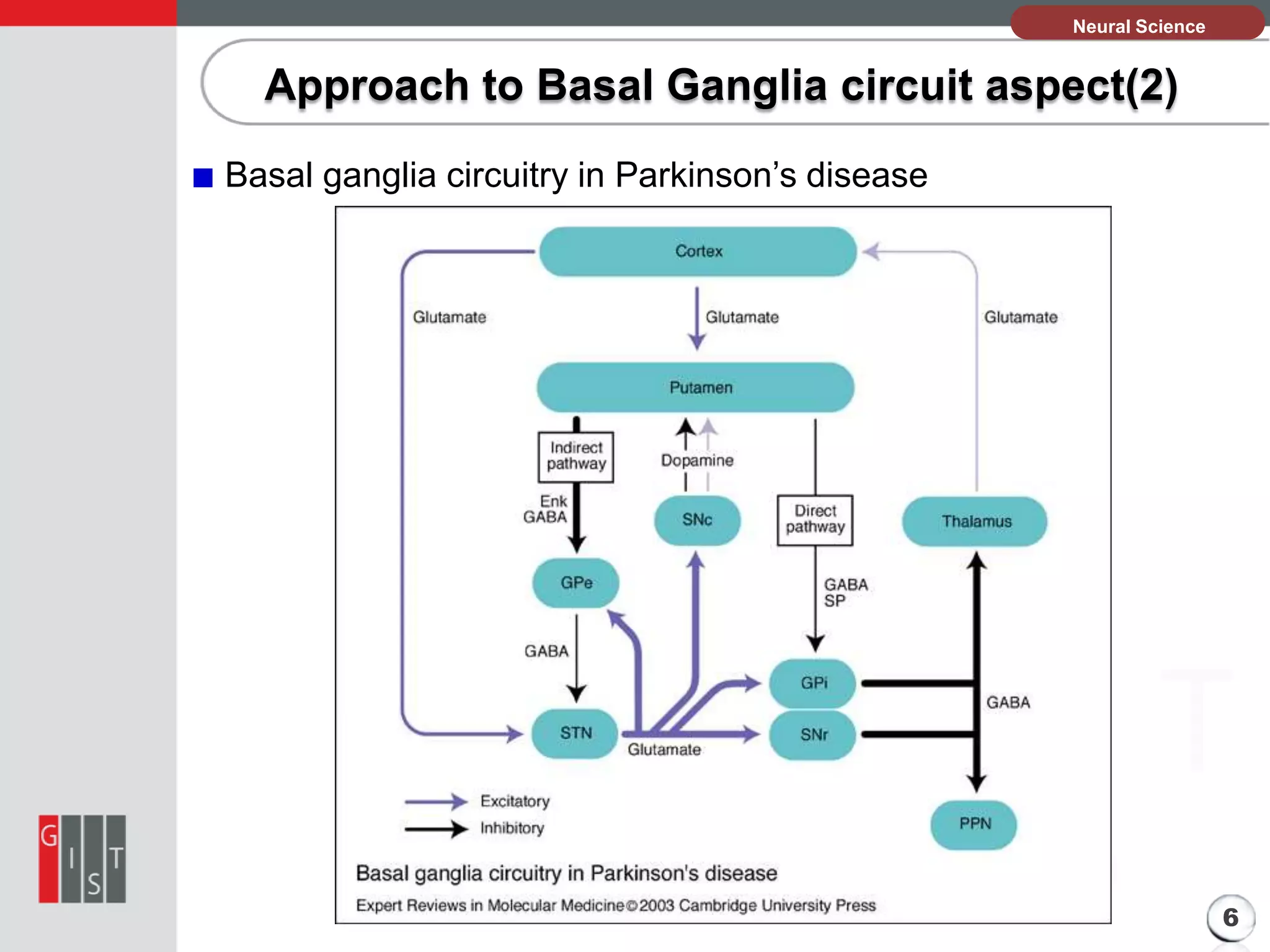
This document discusses Parkinsonism and the basal ganglia circuit approach. It begins with an introduction that defines Parkinsonism as a neurological syndrome characterized by tremors, hypokinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. It affects both motor and non-motor functions and generally impacts older populations. The pathology section explains that the cause is unclear but involves the progressive loss of dopamine-producing brain cells in the substantia nigra, which reduces dopamine in the basal ganglia. The approach to basal ganglia circuit aspect section looks at the normal basal ganglia circuitry and how it is impacted in Parkinson's disease.