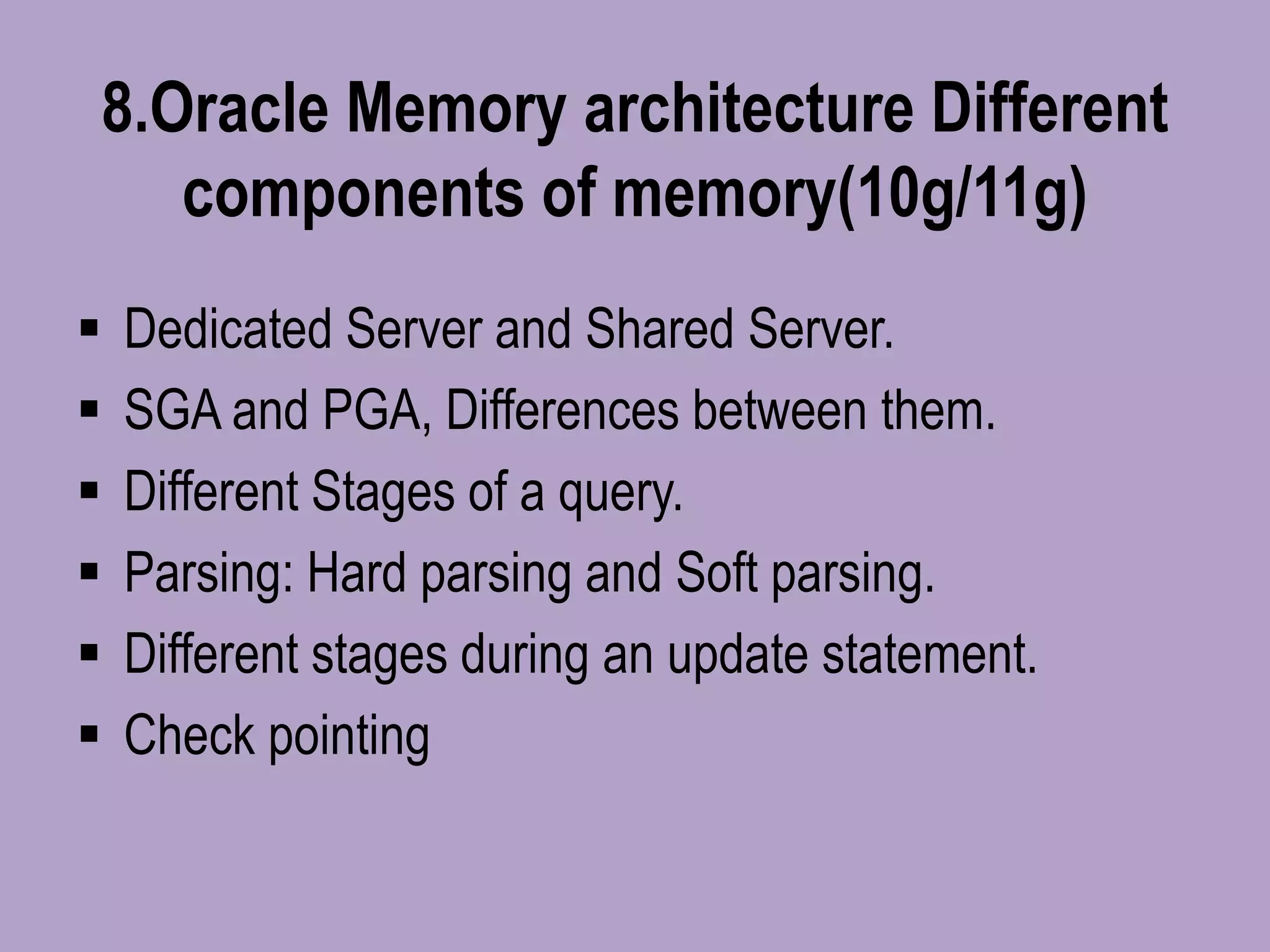
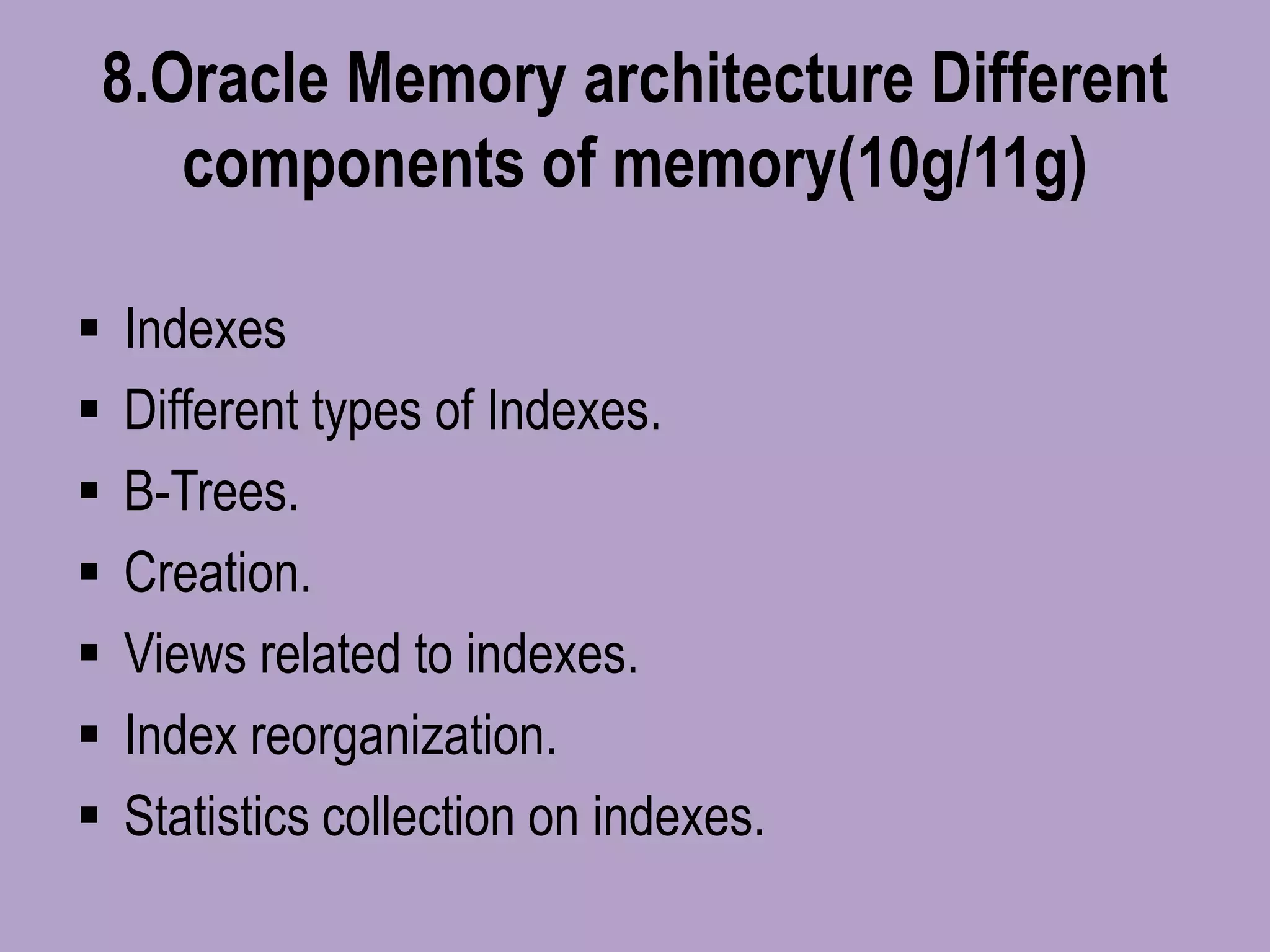
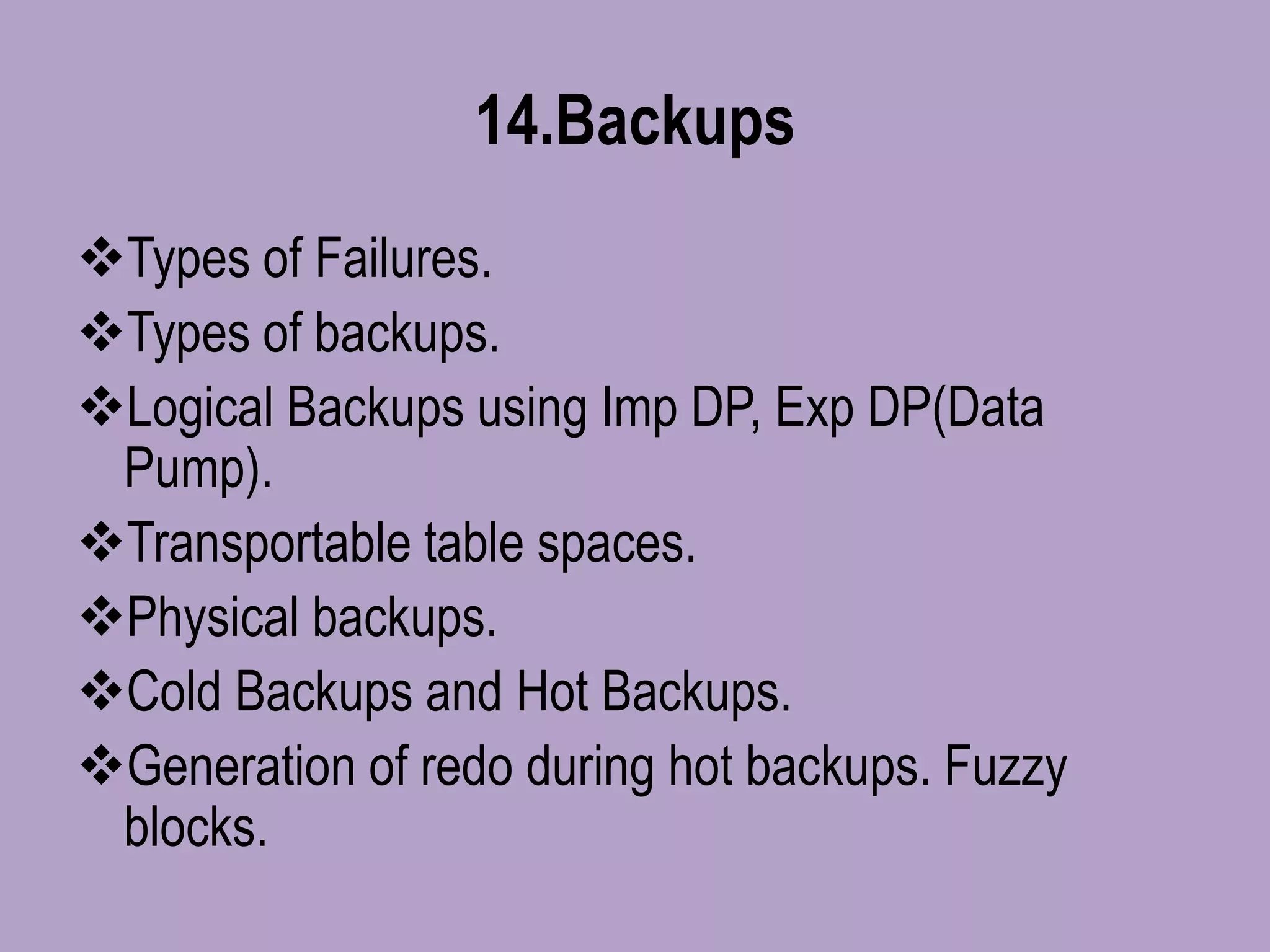
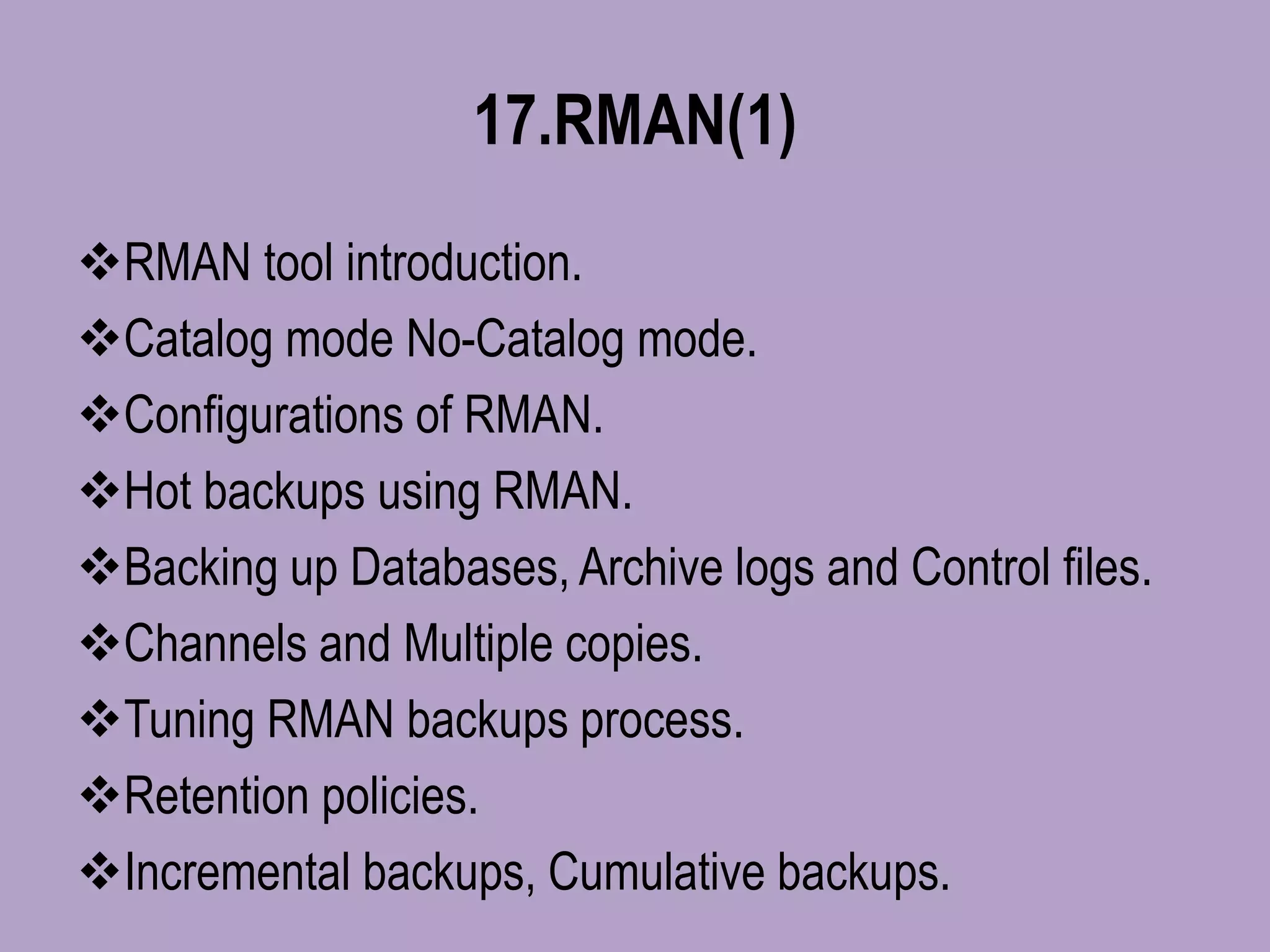
The document outlines a comprehensive Oracle Core DBA online training program covering essential topics such as database types, installation processes, database creation, memory architecture, backups, recovery methods, and performance tuning. It also includes details on user management, security, RMAN backup and restoration, as well as advanced concepts like Data Guard and Automatic Storage Management (ASM). Contact information for queries and demo requests is provided at the end.