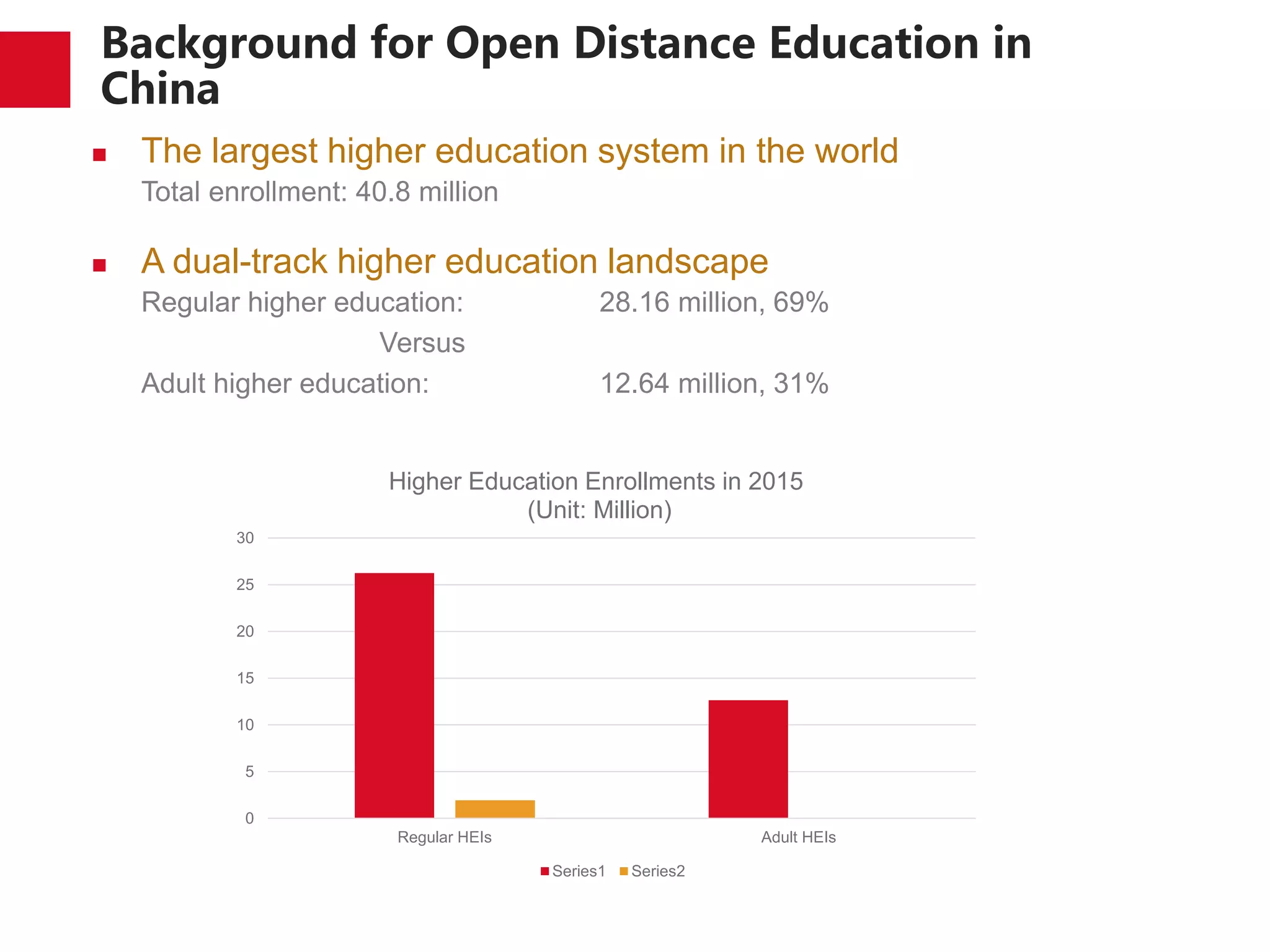
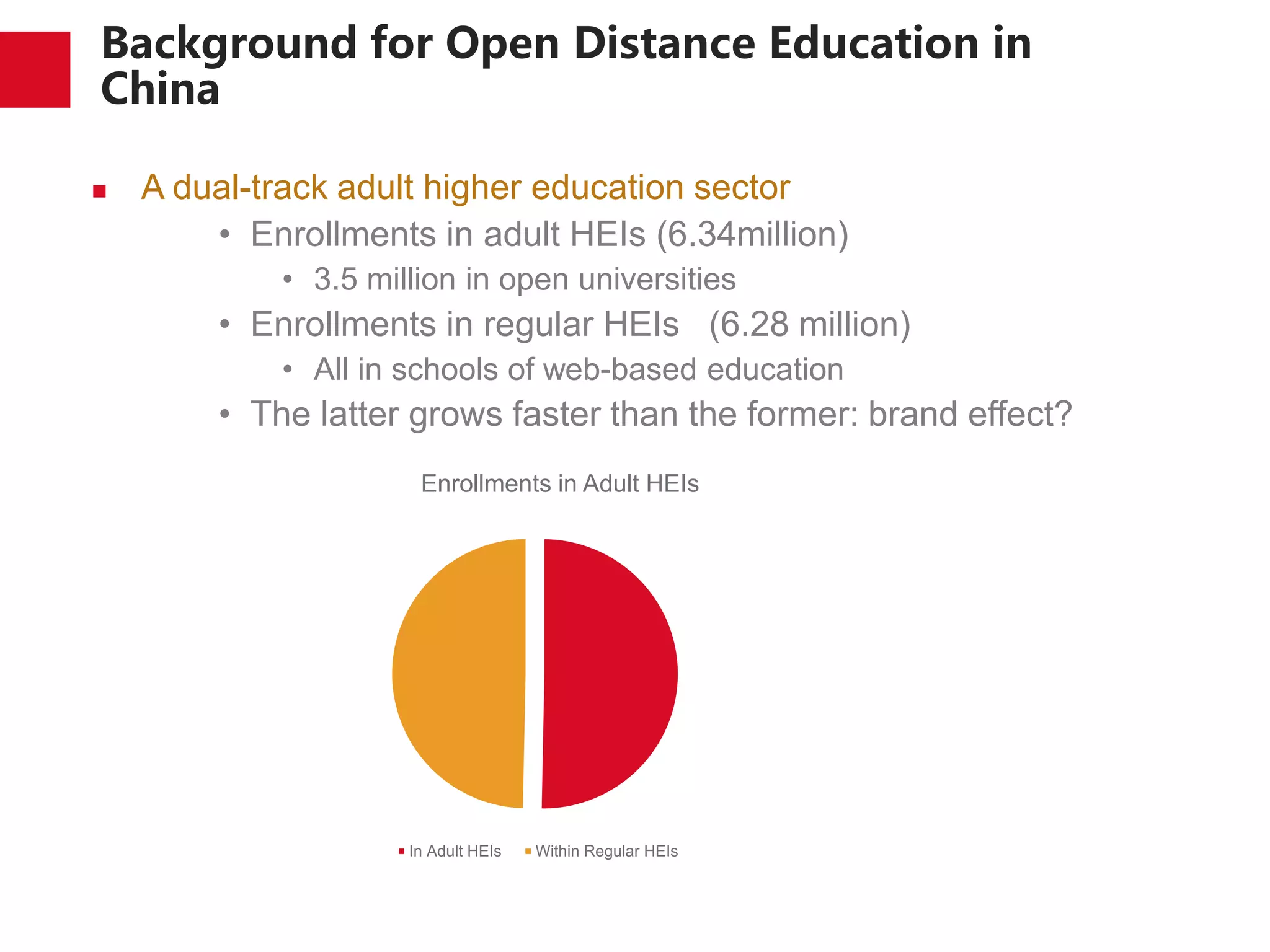
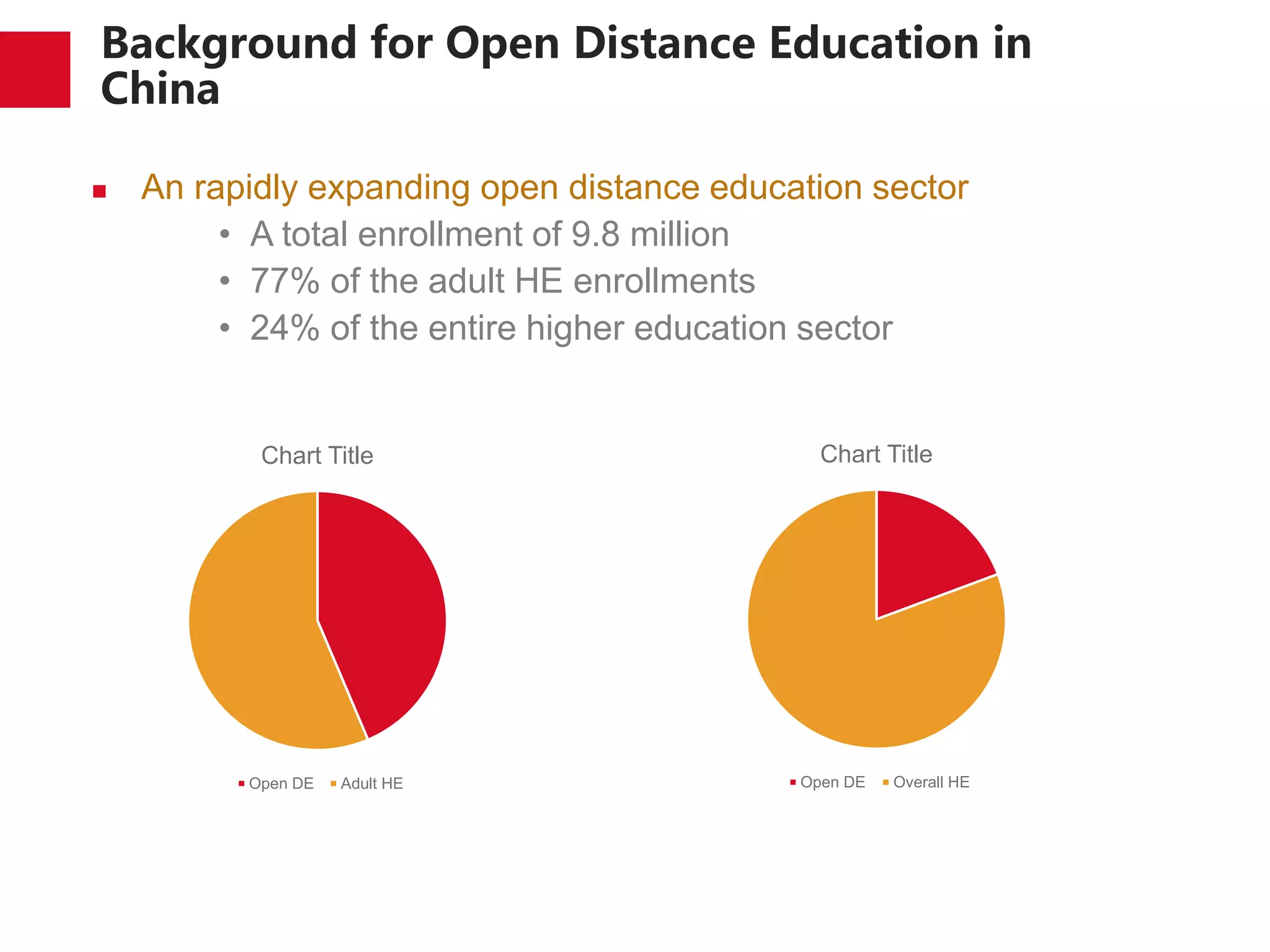
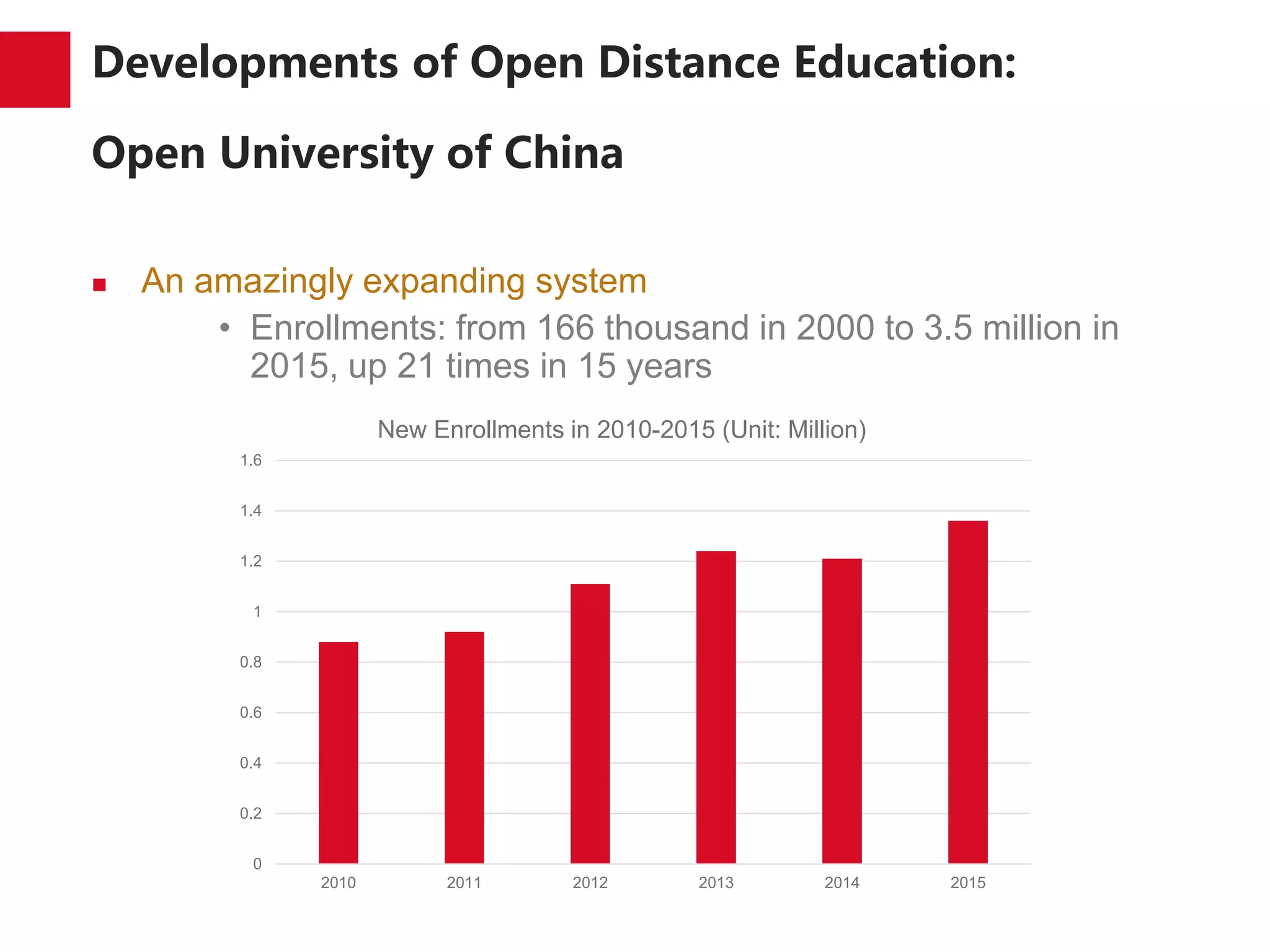
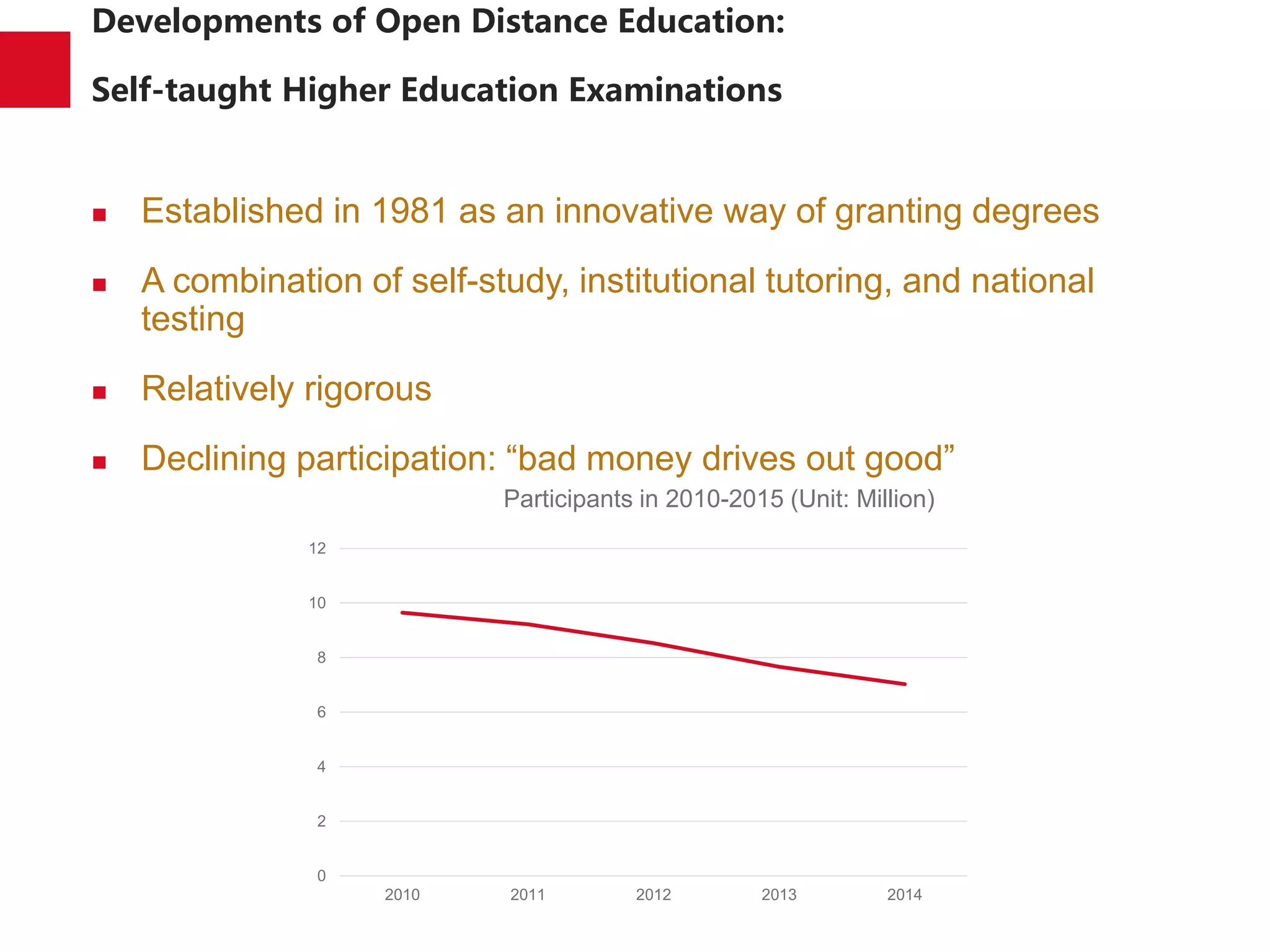
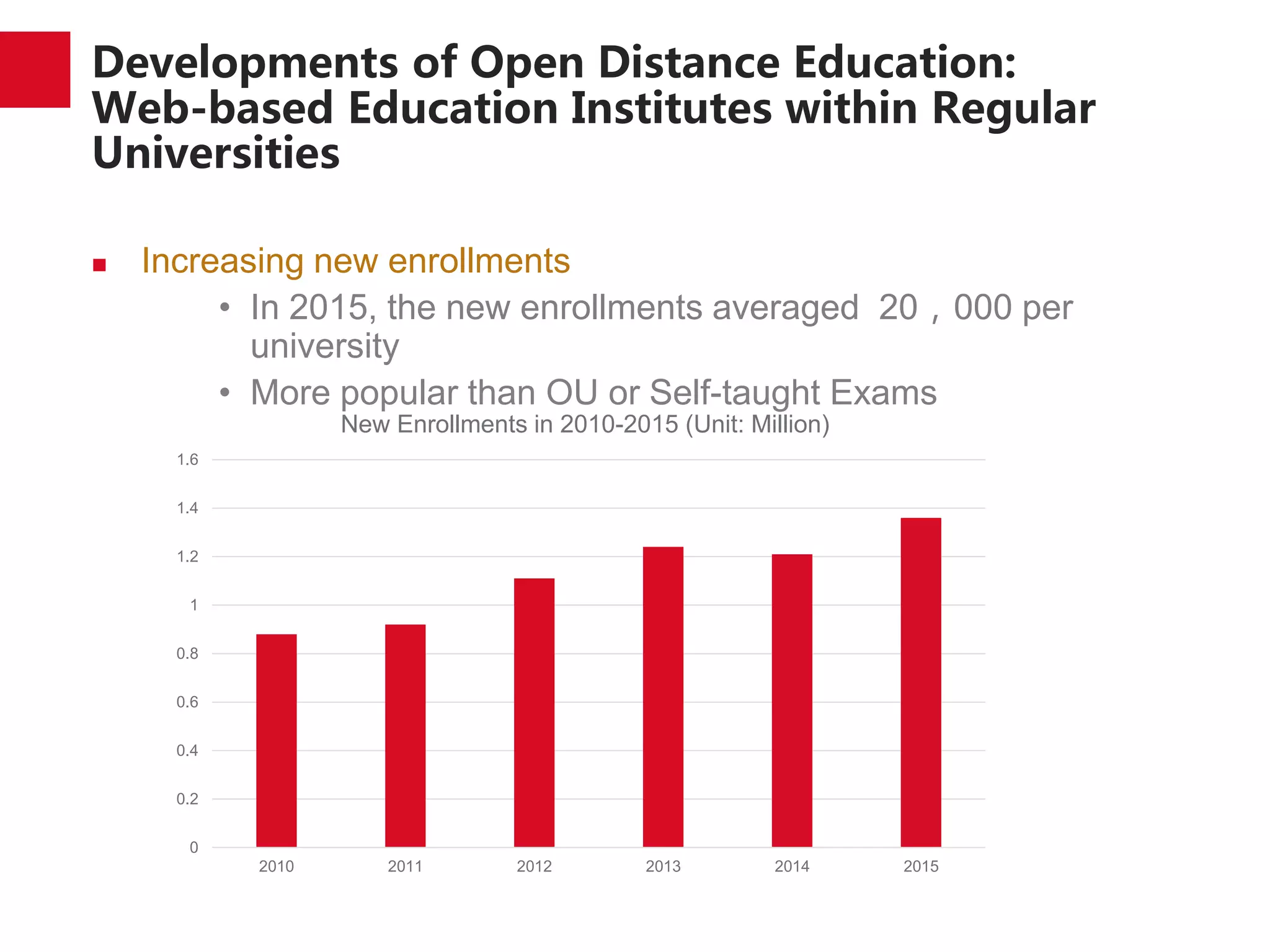
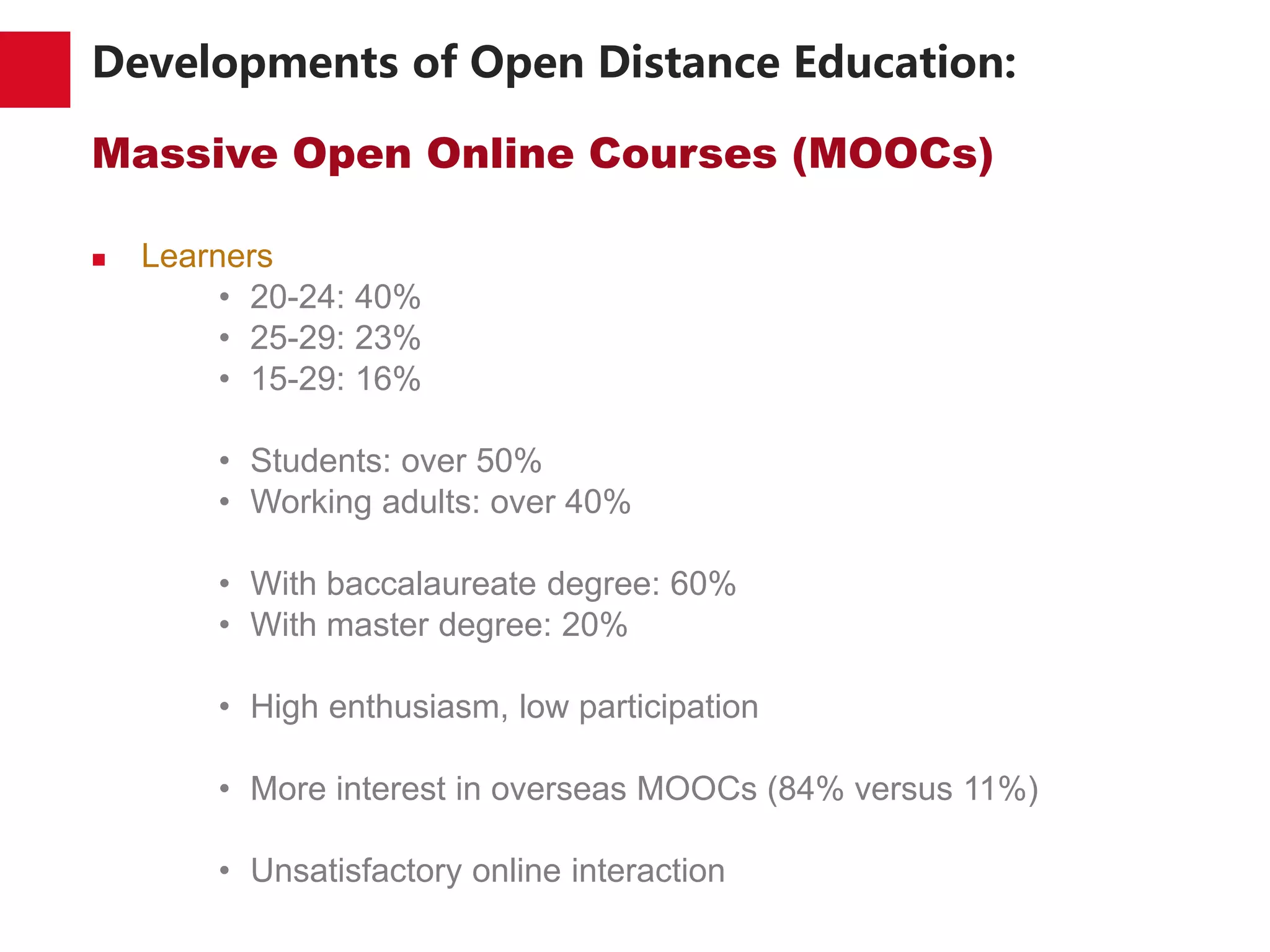
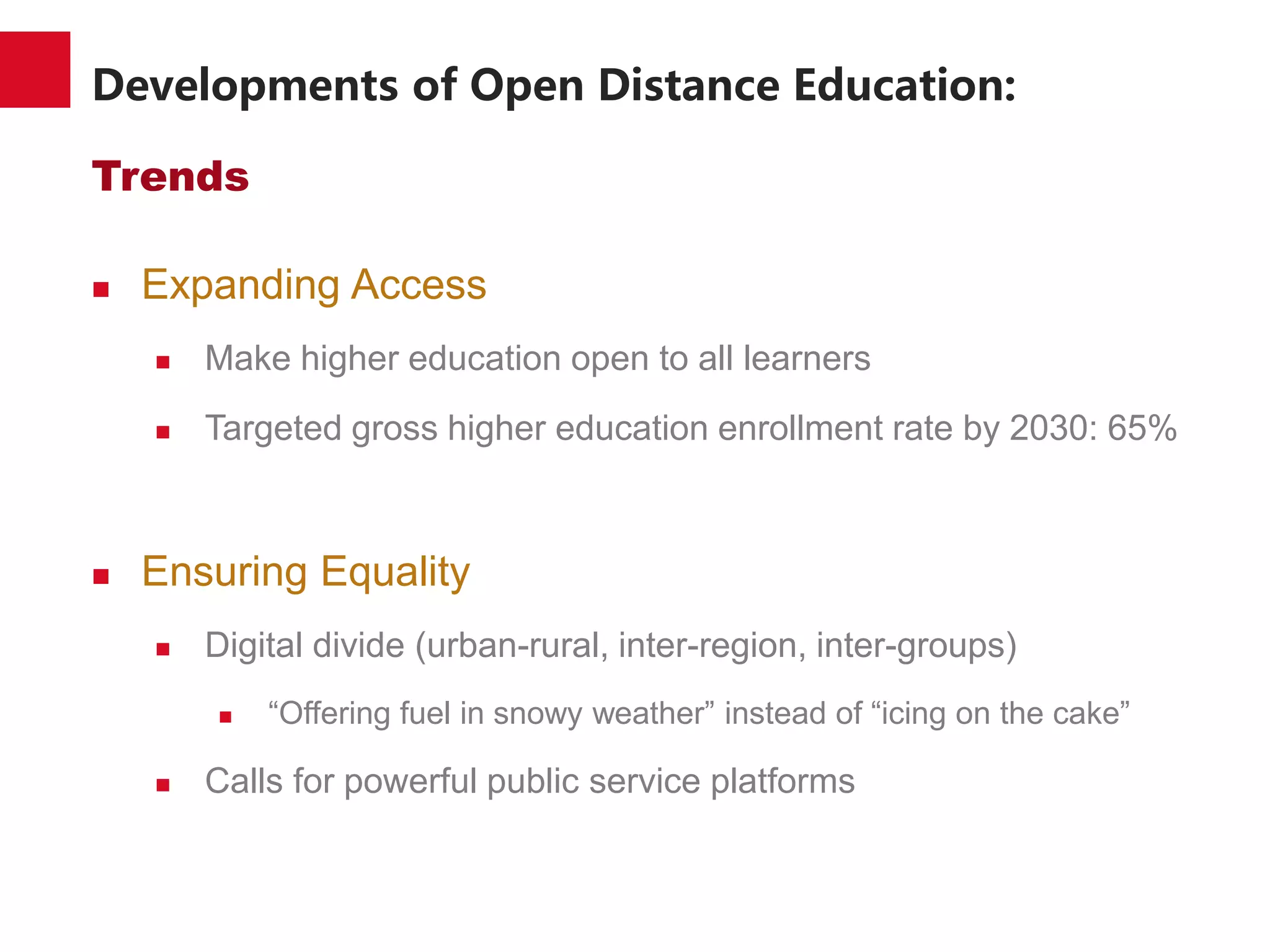
The document discusses the trends and developments of open distance education in China, highlighting its rapid growth and the dual-track higher education system. It outlines the expansion of open universities, web-based education, and MOOCs, as well as the challenges faced in infrastructure, quality assurance, and student engagement. Future trends indicate a focus on expanding access, improving quality, and addressing the digital divide in higher education.