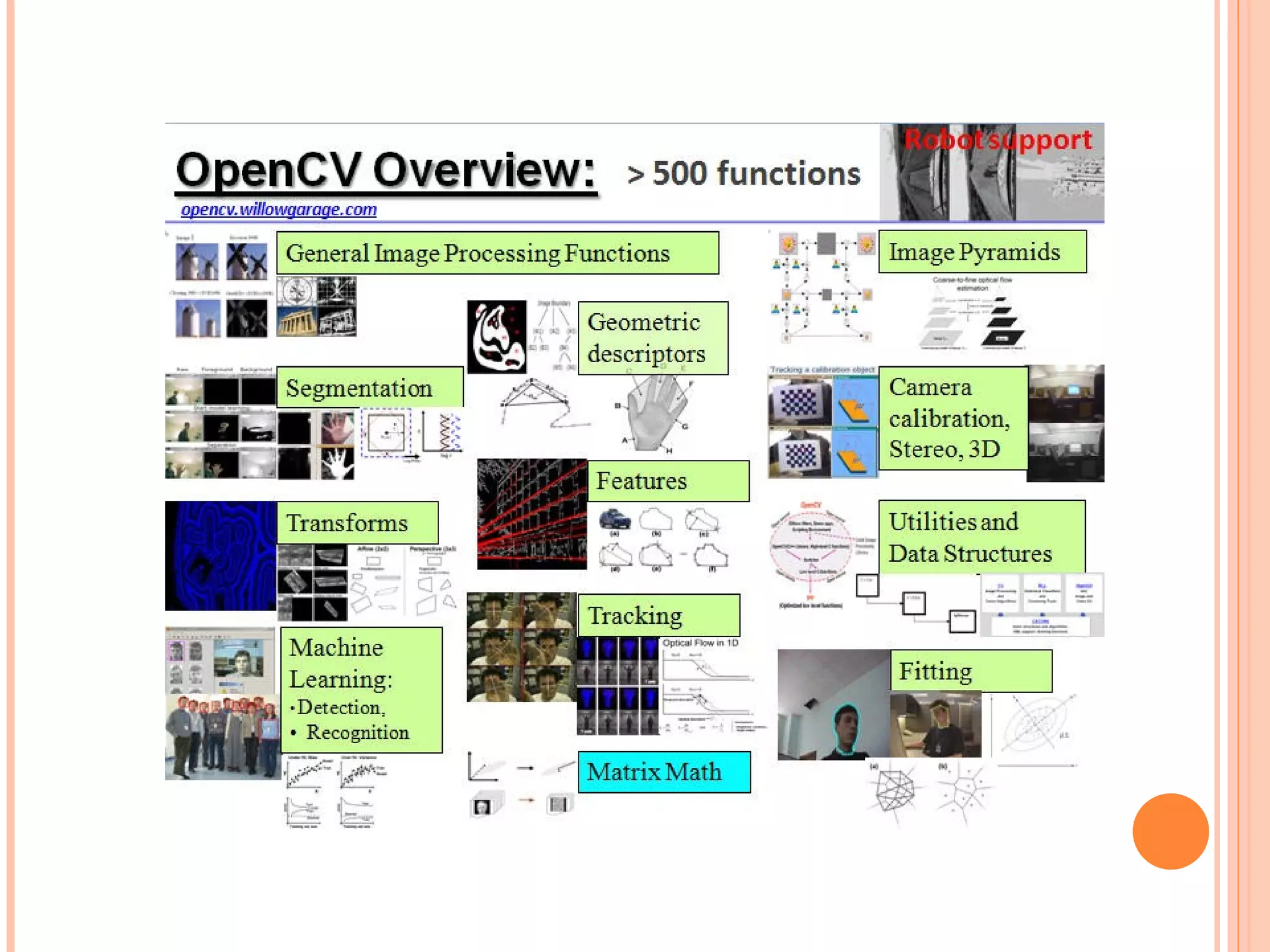
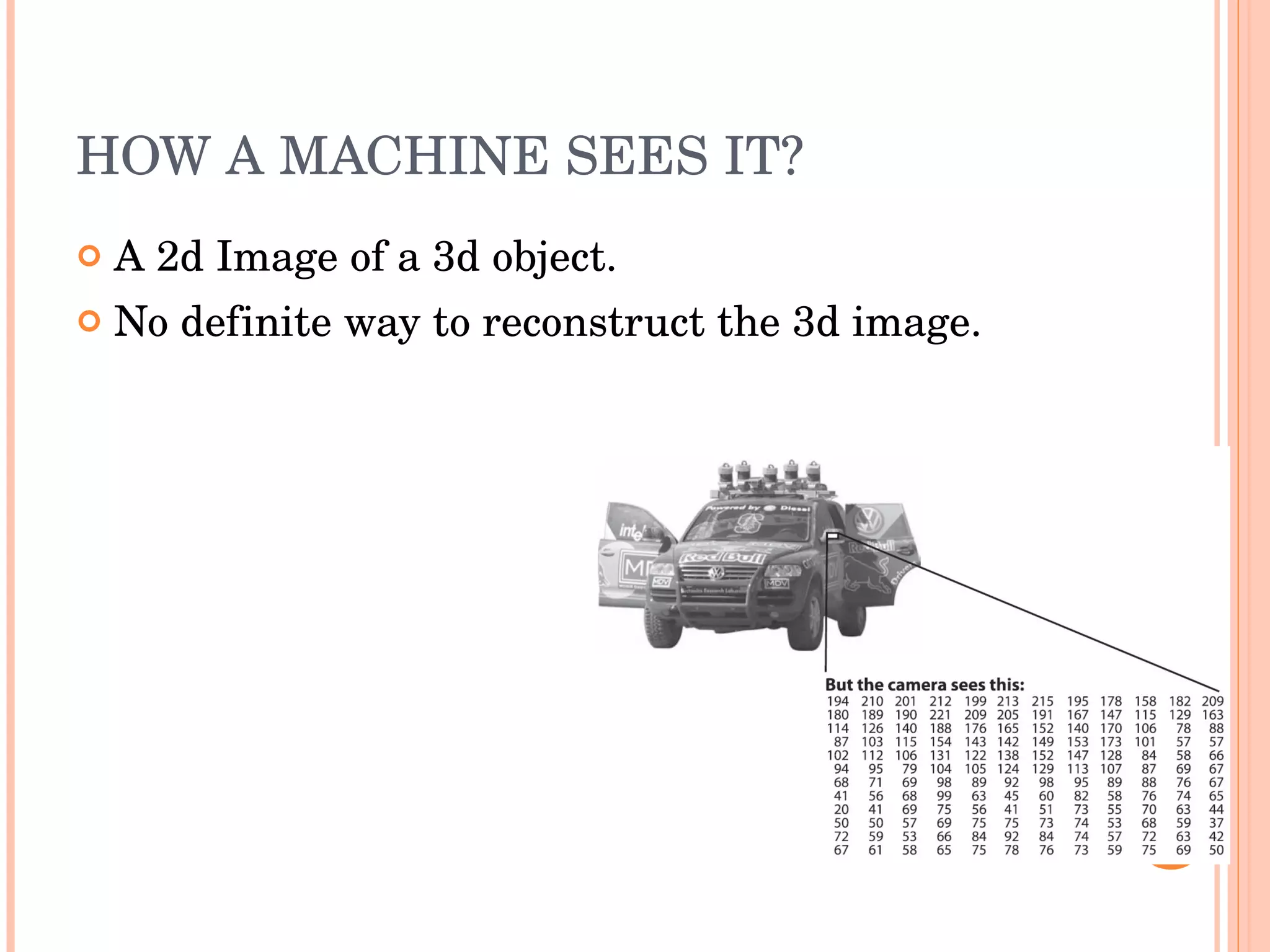
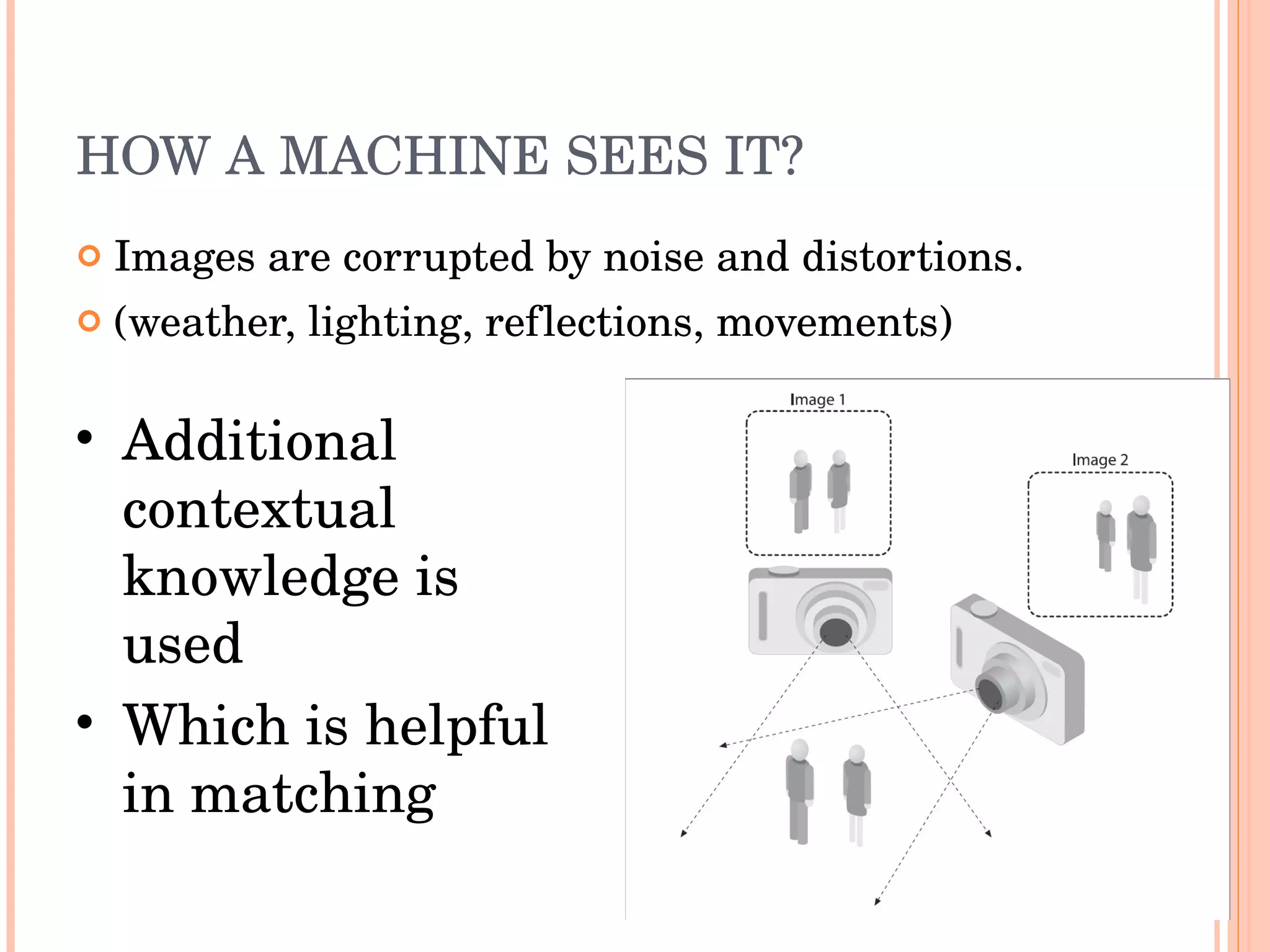
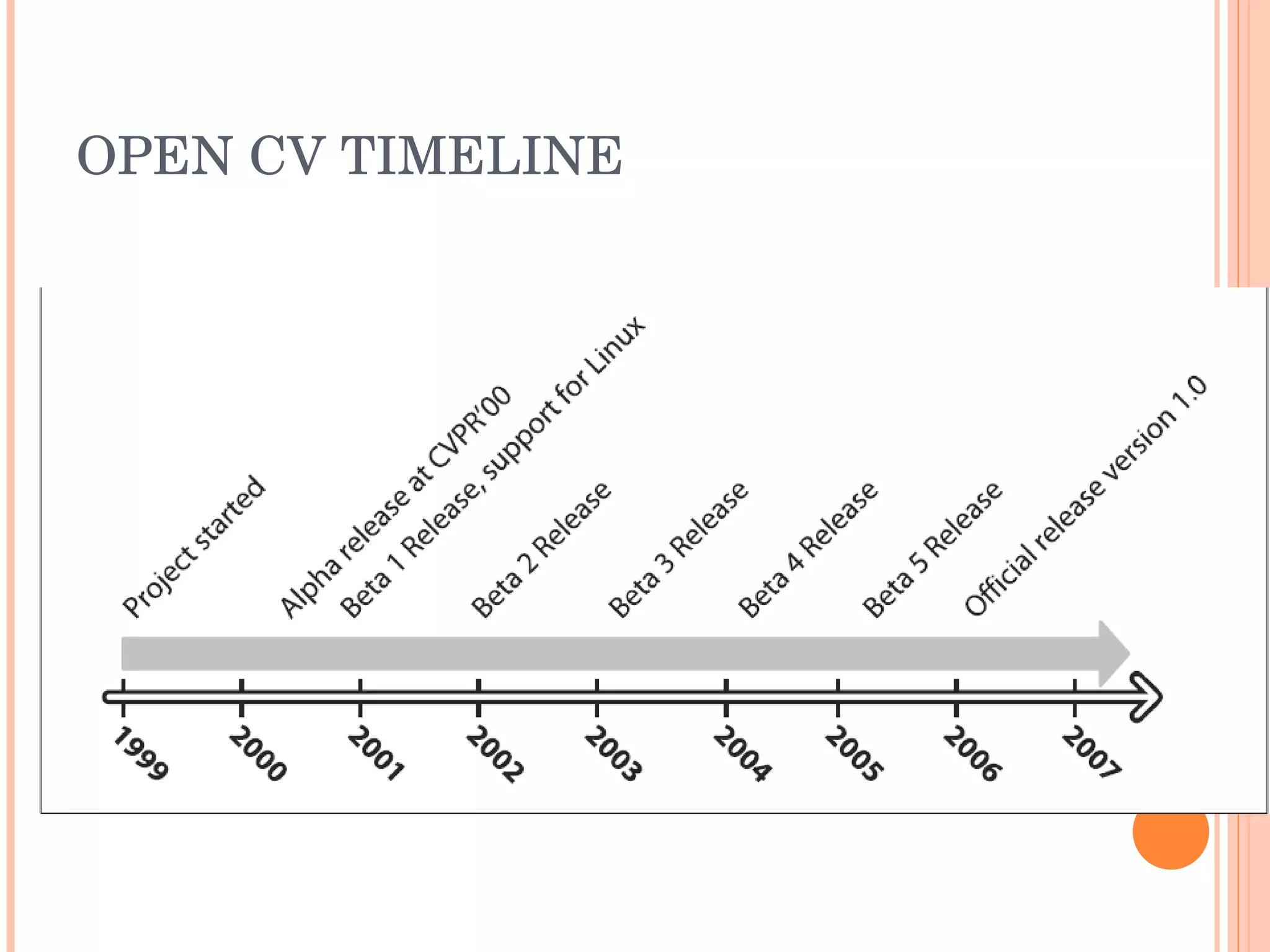
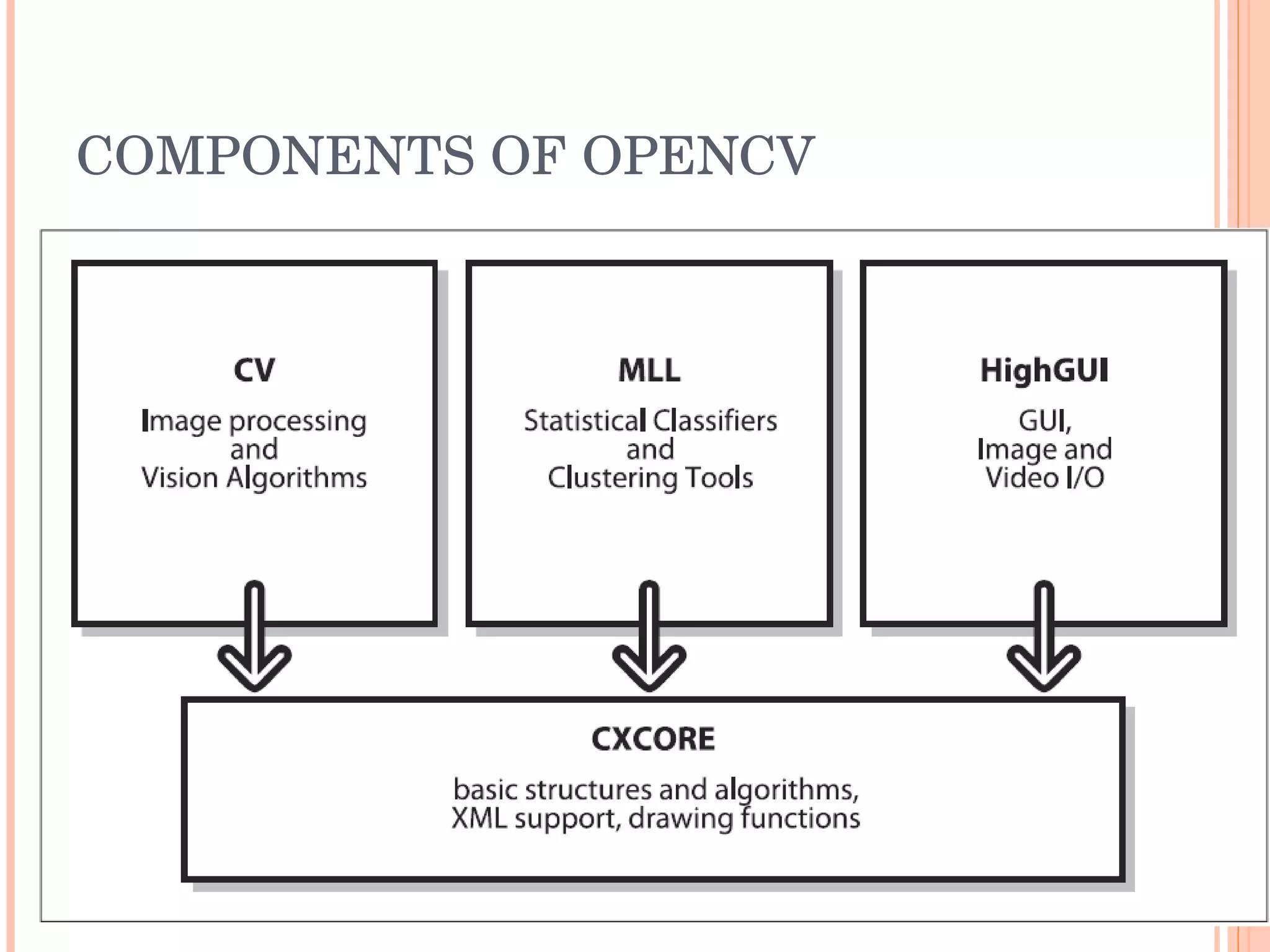
Open CV is an open source computer vision library that provides programming functions for real-time computer vision. It is cross-platform and can be used to build applications across operating systems. The library contains hundreds of functions for applications like factory product inspection, medical imaging, security, and robotics. It has a large user community including researchers and major tech companies and has been used in applications like surveillance, mapping, manufacturing inspection, and more.