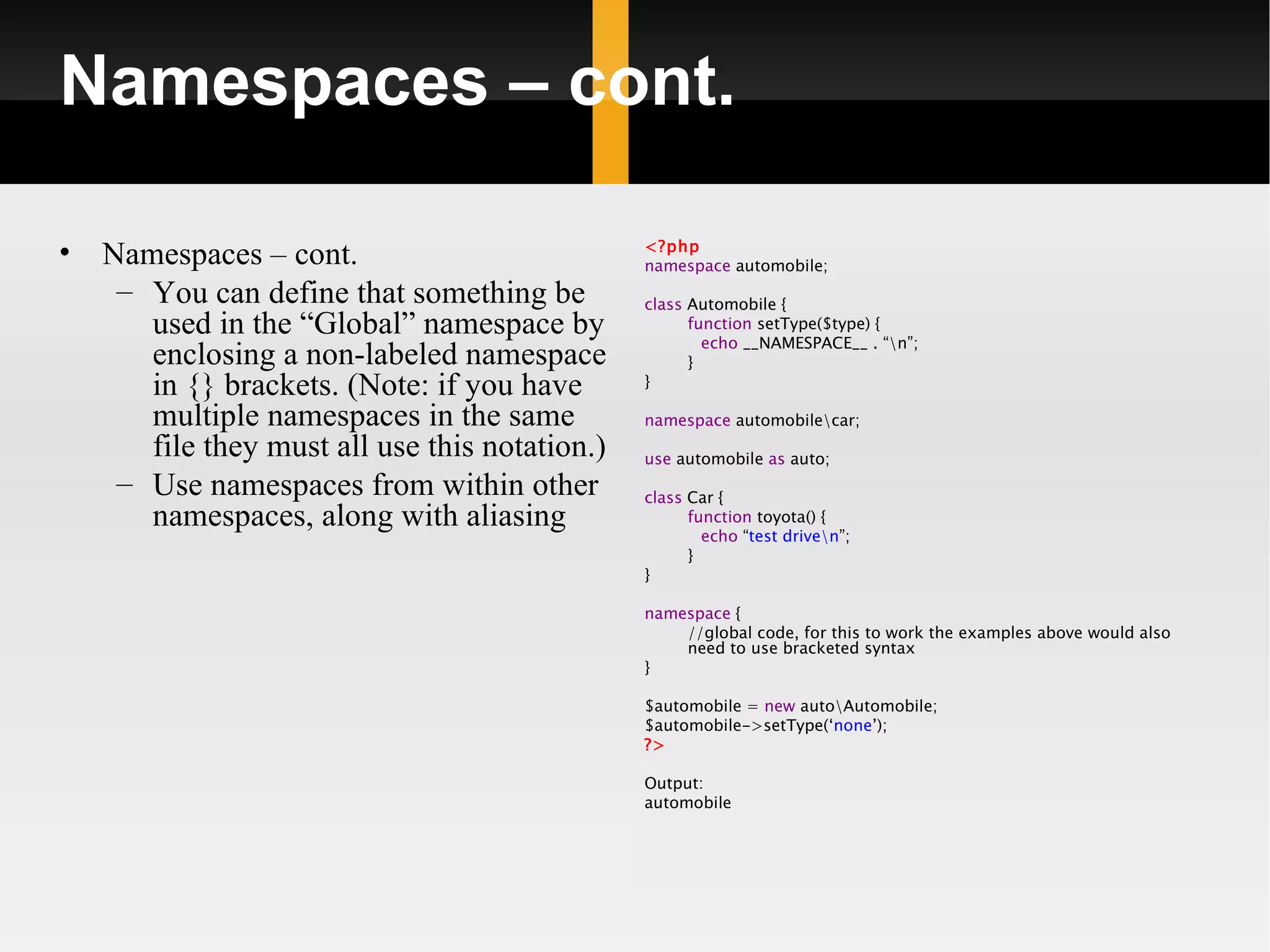
The document discusses the evolution of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in PHP from version 4 to 5.3, highlighting key features and improvements, such as visibility, abstraction, interfaces, and exception handling. It covers new functionalities introduced in PHP 5.0 and 5.3, including namespaces, late static bindings, closures, and magic methods. The presentation aims to provide a high-level overview for the South Florida PHP Users Group without delving into excessive detail.

![Procedural? Really?
• PHP was started as a procedural <?php
function vehicle($wheels, $color, $hp) {
tool to perform quick tasks. // build a car using info provided
Large adoption brought more $car = array(
users who wanted OOP, so here ‘wheels’ => $wheels,
‘color’ => $color,
we are. ‘hp’ => $hp);
– Everything went fairly sequential return $car;
– Took a fair amount of labor within }
code to change values afterward $car = vehicle(4, ‘red’, 240);
– Procedural does make sense for // now continue with code that uses $car
simple tasks, such as CRON jobs to If ($car[‘color’] == ‘red’) {
perform quick tasks. echo ‘Your car is red’;
}
?>
Output:
Your car is red
Possible usage:
Here is the car: <?php print_r($car); ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-02-08oopandphp5-3intro-120606122543-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-OOP-and-new-features-in-PHP-5-3-2-2048.jpg)
![OOP the basics
• PHP 4 brought the introduction <?php
Interface mobility {
function setColor($color);
of oop to PHP. }
function setHorsepower($hp);
– Application builds an object class Vehicle implements mobility {
– Helps with DRY (Don’t repeat public $color;
public $horsepower;
yourself) function setColor($color) {
– Simplifies structure, code still can }
$this->color = $color;
be sequential but is more ‘modular’ function setHorsepower($hp) {
– Helps keep code more readable }
$this->horsepower = $hp;
}
– Object can be manipulated easier
prior to use of the object Class Car extends Vehicle {
public $wheel;
– We instantiate the class by creating function addWheel($n) {
a “new” object, then manipulate the }
$this->wheel += $n;
object by calling the different }
“methods” within the class. $myCar = new Car();
$myCar->setColor(‘red’);
$myCar->setHorsepower(250);
$myCar->addWheel(3);
$myCar->addWheel(1);
print_r($myCar);
?>
Output:
Car Object([wheel]=>4[color]=>red[horsepower]=>250)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-02-08oopandphp5-3intro-120606122543-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-OOP-and-new-features-in-PHP-5-3-3-2048.jpg)









![Closures (Anonymous functions)
• Closures (Anonymous functions) <?php
class Cart {
– Allows the creation of functions protected $products = array();
const PRICE_SHIRT = 20.00;
which have no specific name. const PRICE_SCARF = 4.00;
– Most useful as the value of callback public function order() {
$this->products[‘shirt’] = 2;
parameters. $this->products[‘scarf’] = 3;
}
– Can be used as the value of a
variable. public function getTotal($tax) {
$total = 0.00;
– Can inherit variables from the $callback = function ($quantity, $product) use ($tax, &$total) {
parent scope. (Not the same as $pricePerItem =
constant(__CLASS__ . “::PRICE_” . strtoupper($product));
using global variables)
$total += ($pricePerItem * $quantity) * ($tax +1.0);
};
array_walk($this->products, $callback);
return round($total, 2);
}
}
?>
Output:
55.64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-02-08oopandphp5-3intro-120606122543-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-OOP-and-new-features-in-PHP-5-3-14-2048.jpg)


![Nowdoc
• Nowdoc <?php
– nowdoc is similar to heredoc, but echo <<<‘EOT’
no parsing is done inside a nowdoc. My $foo->foo.
name is “$name”. I am printing some
• Ideal for code snippets or large Now, I am printing some {$foo->bar[1]}.
blocks of text without the need for This should not print a capital ‘A’: /x41
escaping. EOT;
• Best used with static content. ?>
– Uses the same <<< sequence, but
the following identifier is encosed
in single quotes.
Output:
My name is “$name”. I am printing some
$foo->foo.
Now, I am printing some {$foo->bar[1]}.
This should not print a capital ‘A’: /x41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-02-08oopandphp5-3intro-120606122543-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-OOP-and-new-features-in-PHP-5-3-17-2048.jpg)



