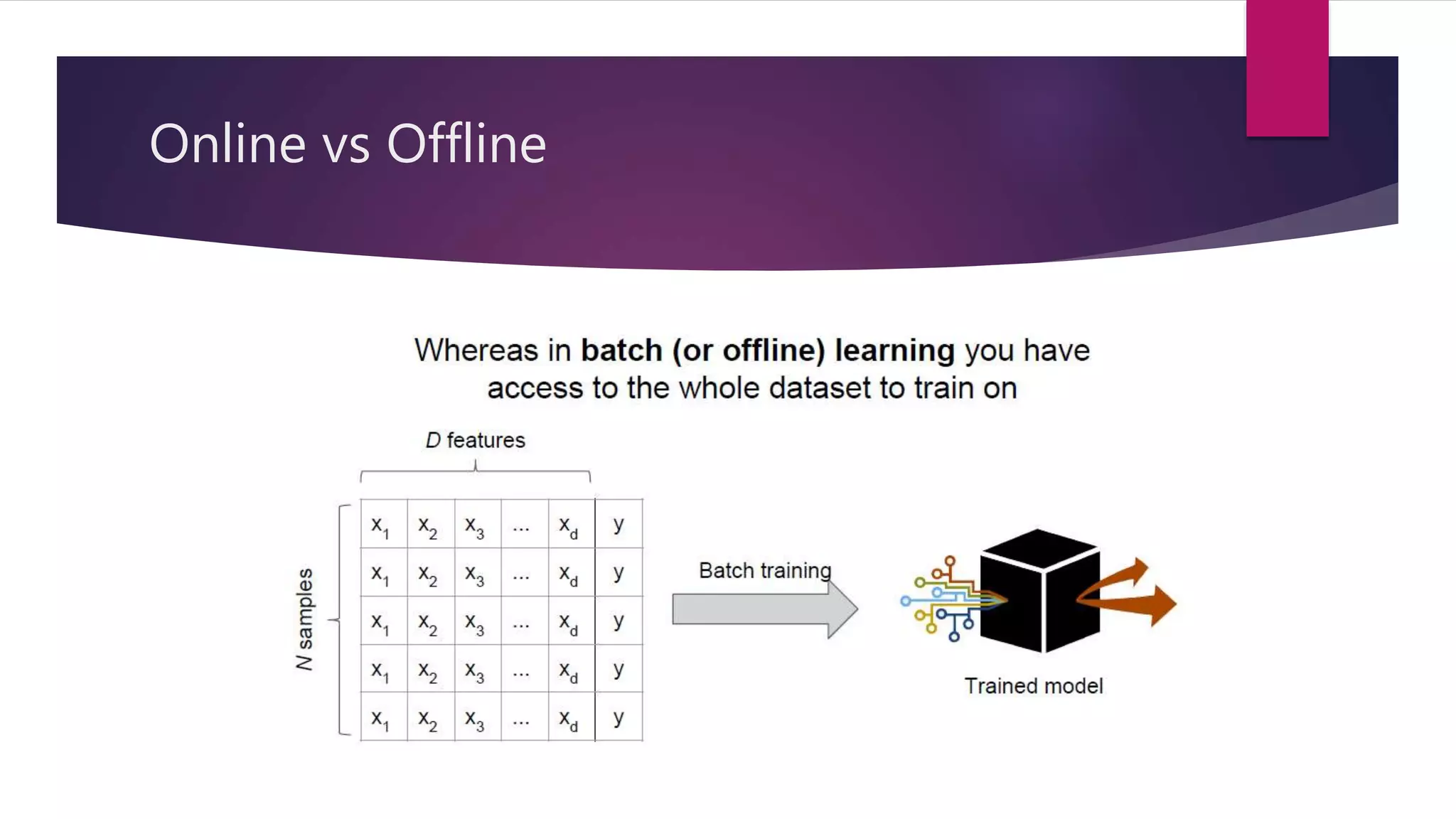
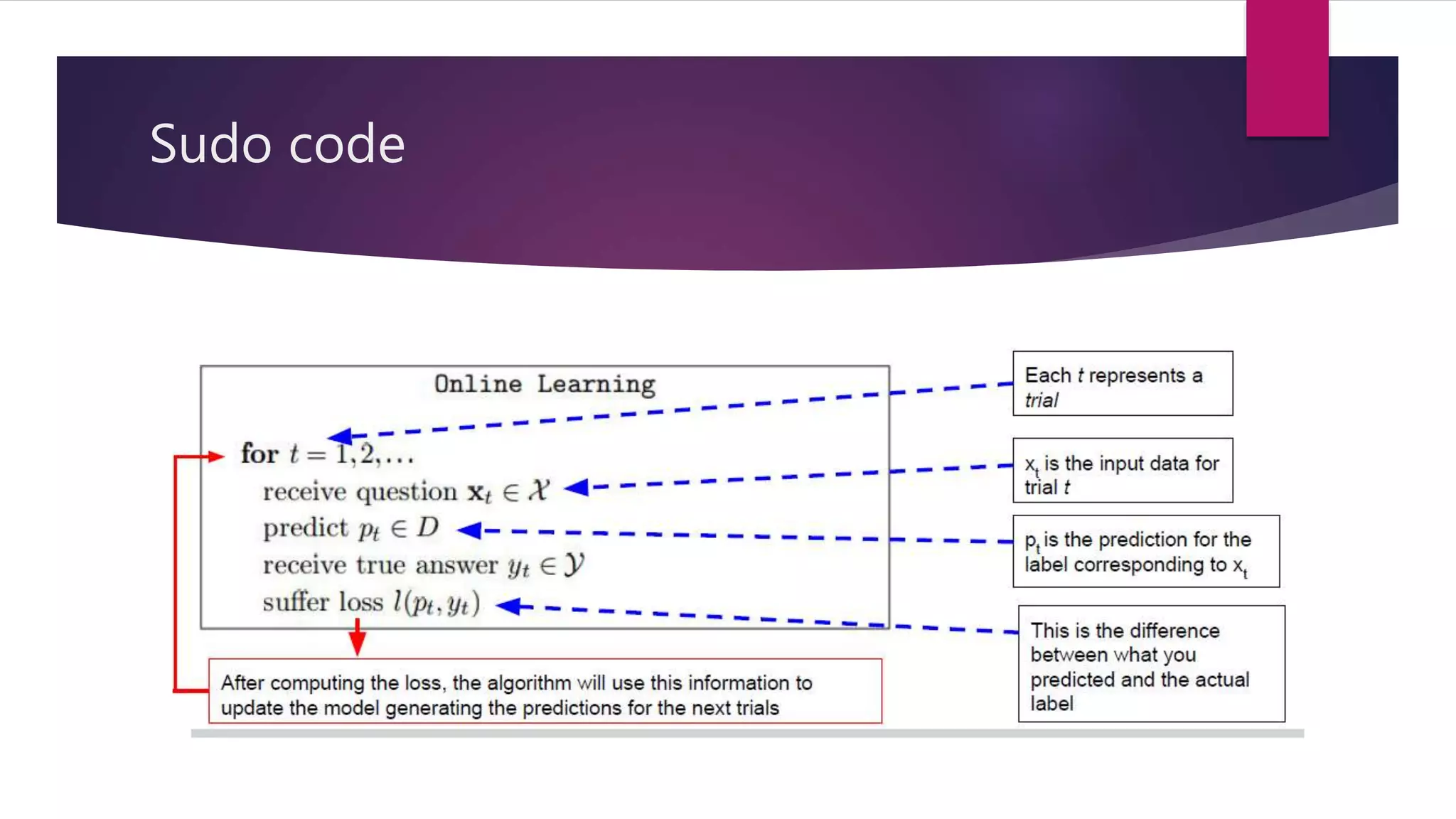
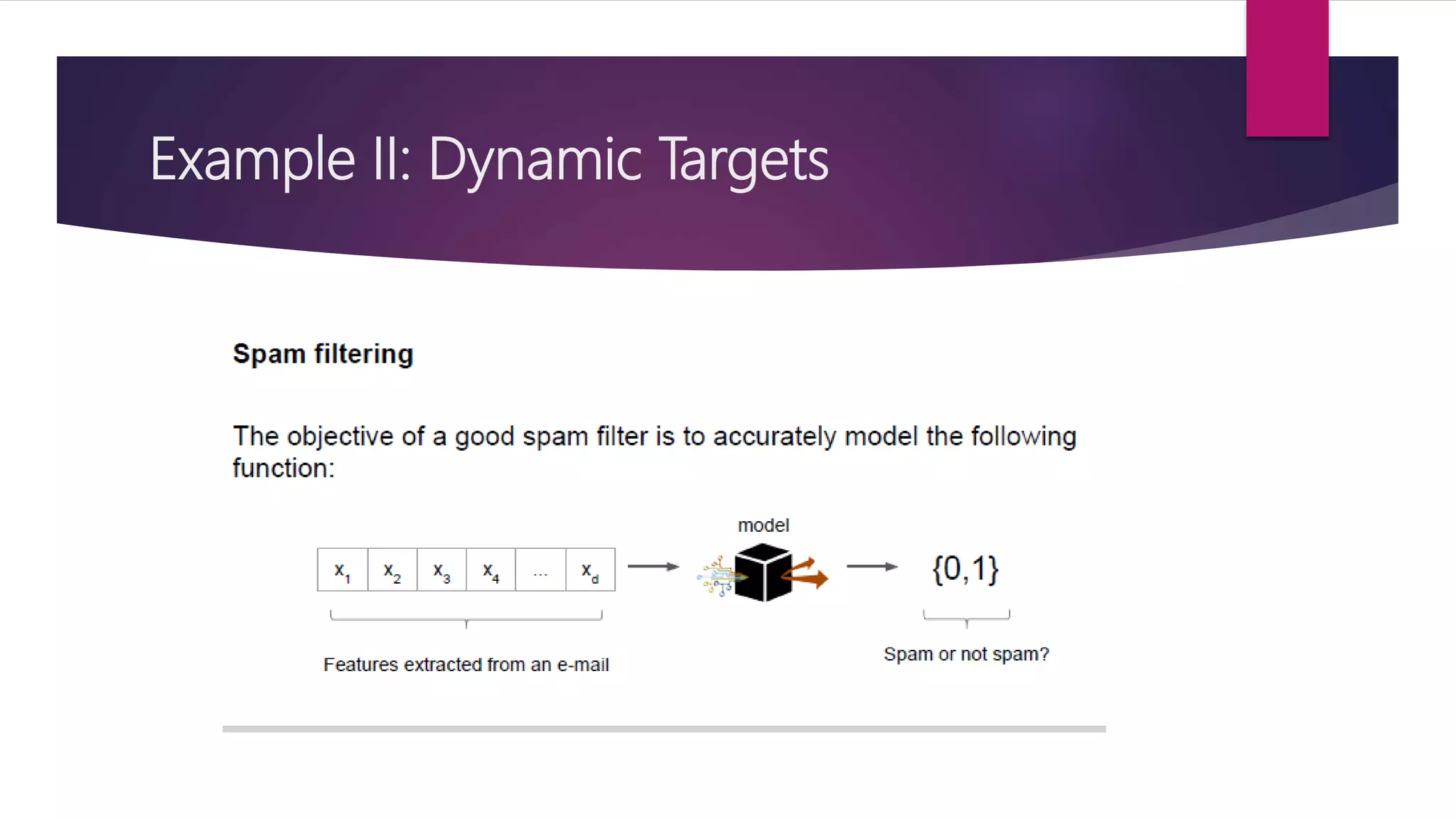
The document discusses online learning and adaptive game playing. It defines online learning as processing data sequentially in a streaming fashion to train machine learning models. This allows learning from large datasets that cannot fit in memory or when data is continuously generated. Common applications include recommendations, fraud detection, and portfolio management. The document also discusses how reinforcement learning differs from online learning in having a goal of optimizing rewards through a sequence of actions rather than predicting single outputs. It describes early implementations of adaptive game playing using algorithms like naive Bayes, Markov decision processes, and n-grams on the game of rock-paper-scissors before discussing a more complex fighting game implementation.