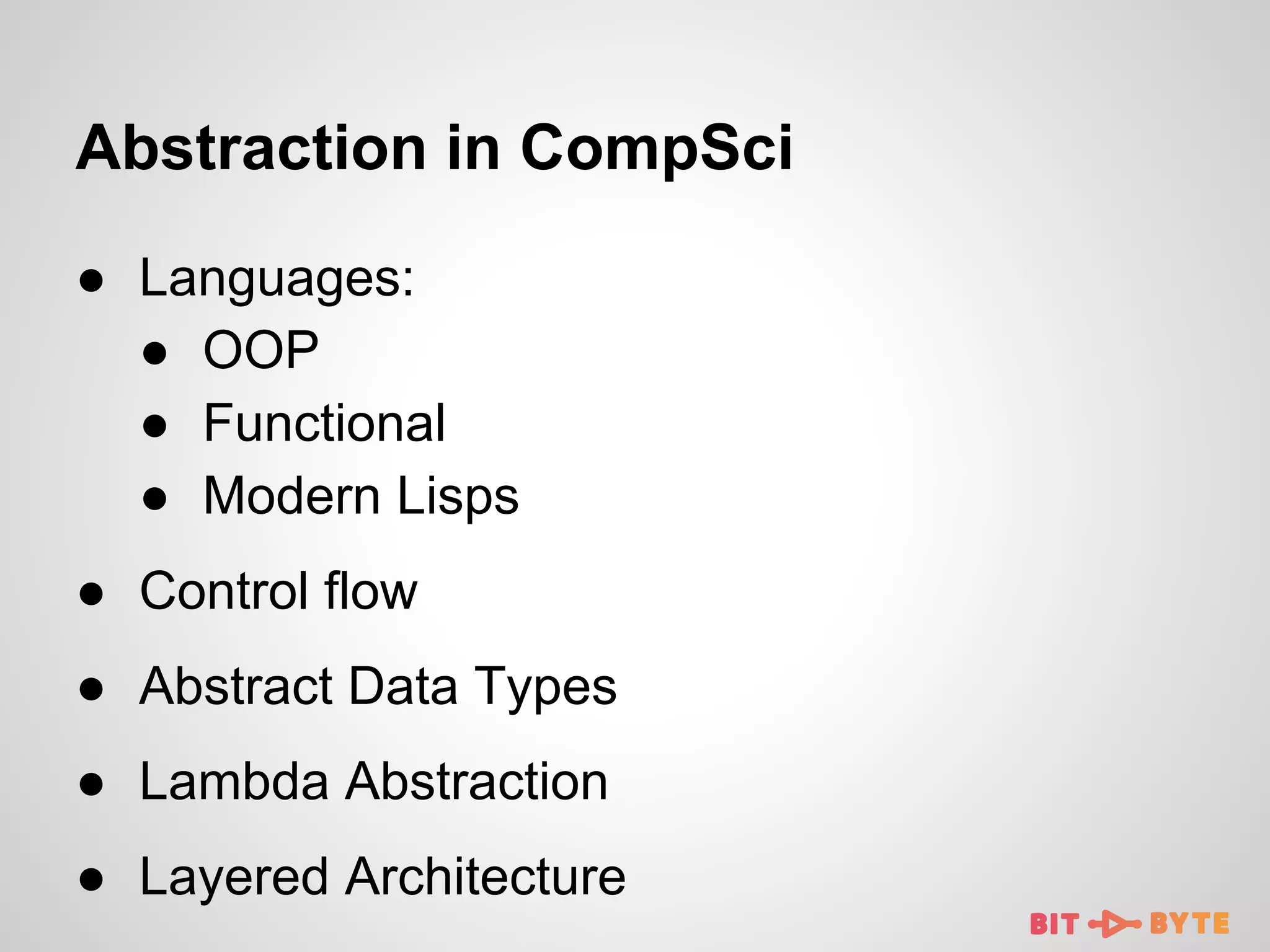
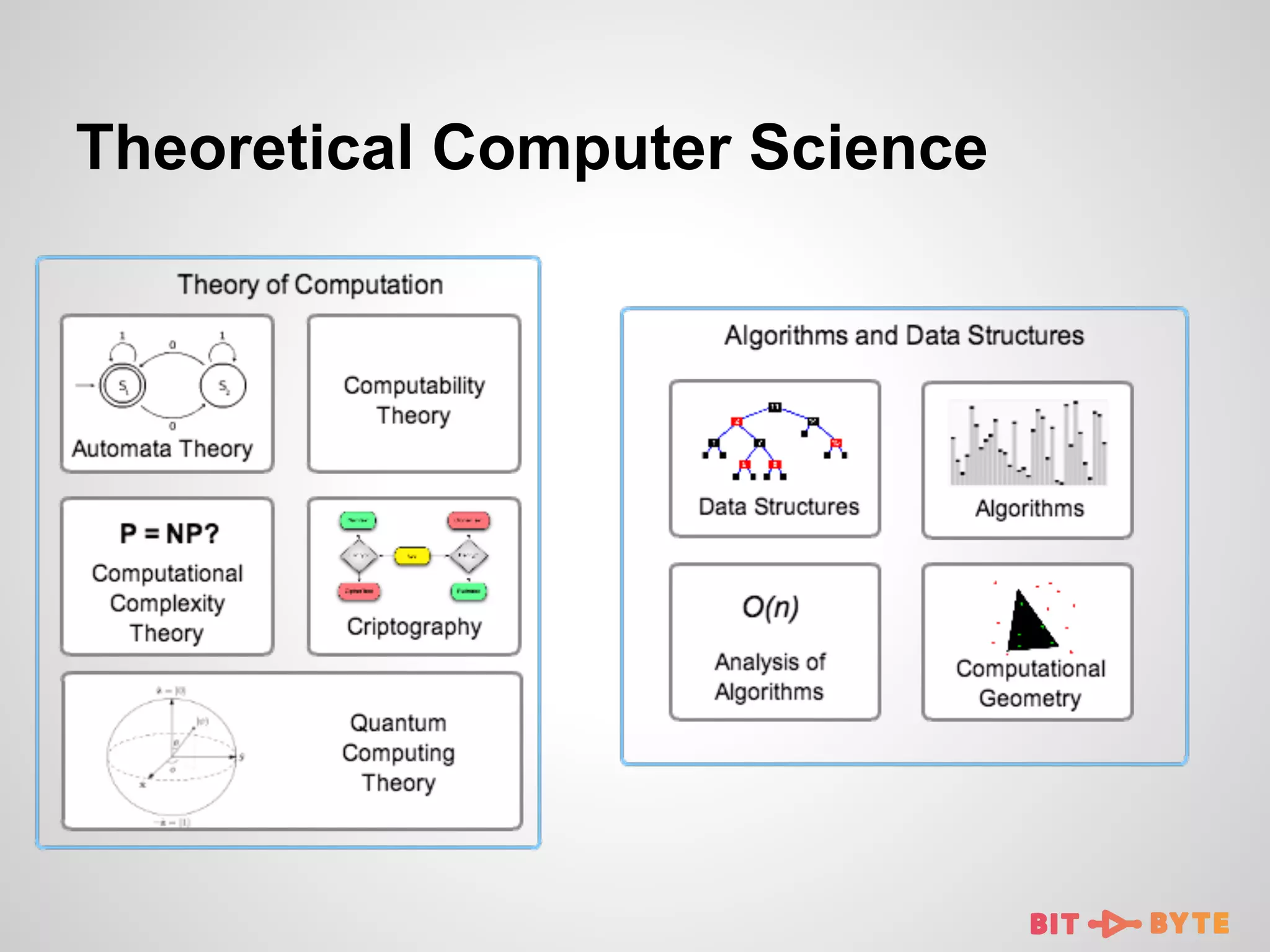
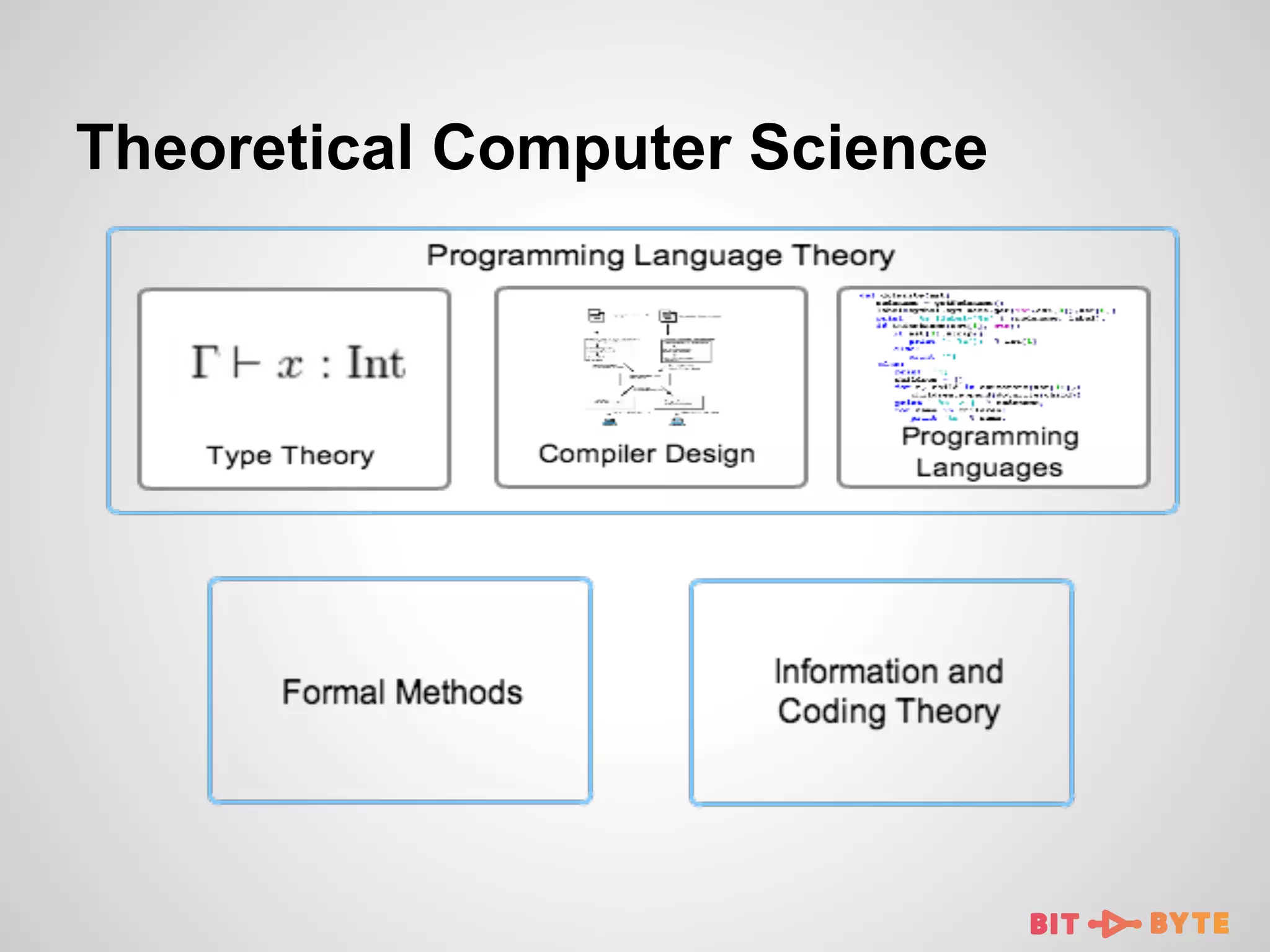
This document discusses being a professional software developer. It begins by introducing the author and agenda. It then defines a software developer and quotes perspectives on software engineering. Subsequent sections discuss the importance of skills like mathematics and abstraction. It provides examples of data structures and algorithms applications. Sections also cover programming languages, theoretical computer science, and applied computer science. The document emphasizes lifelong learning and enjoying the developer community.

























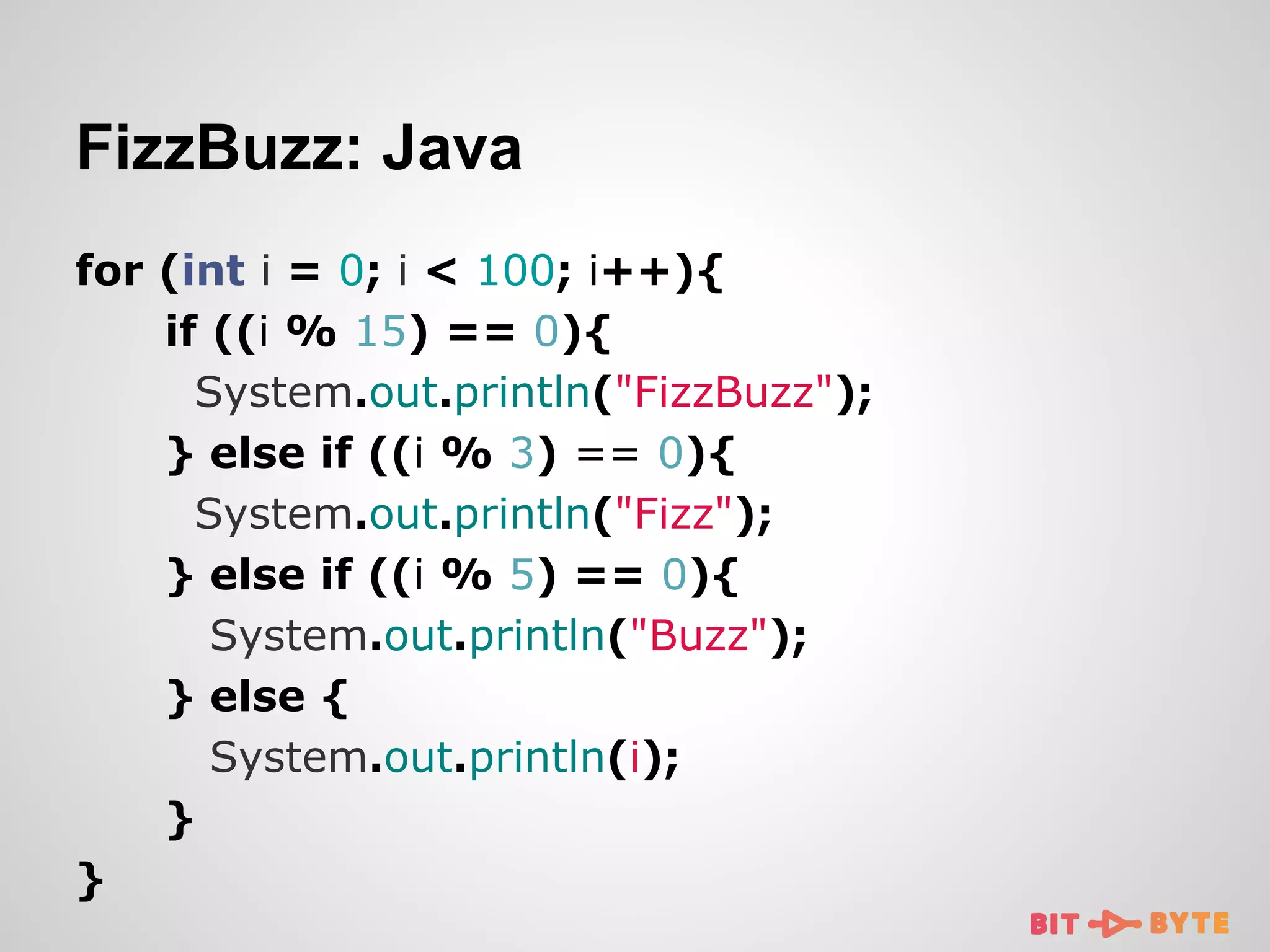
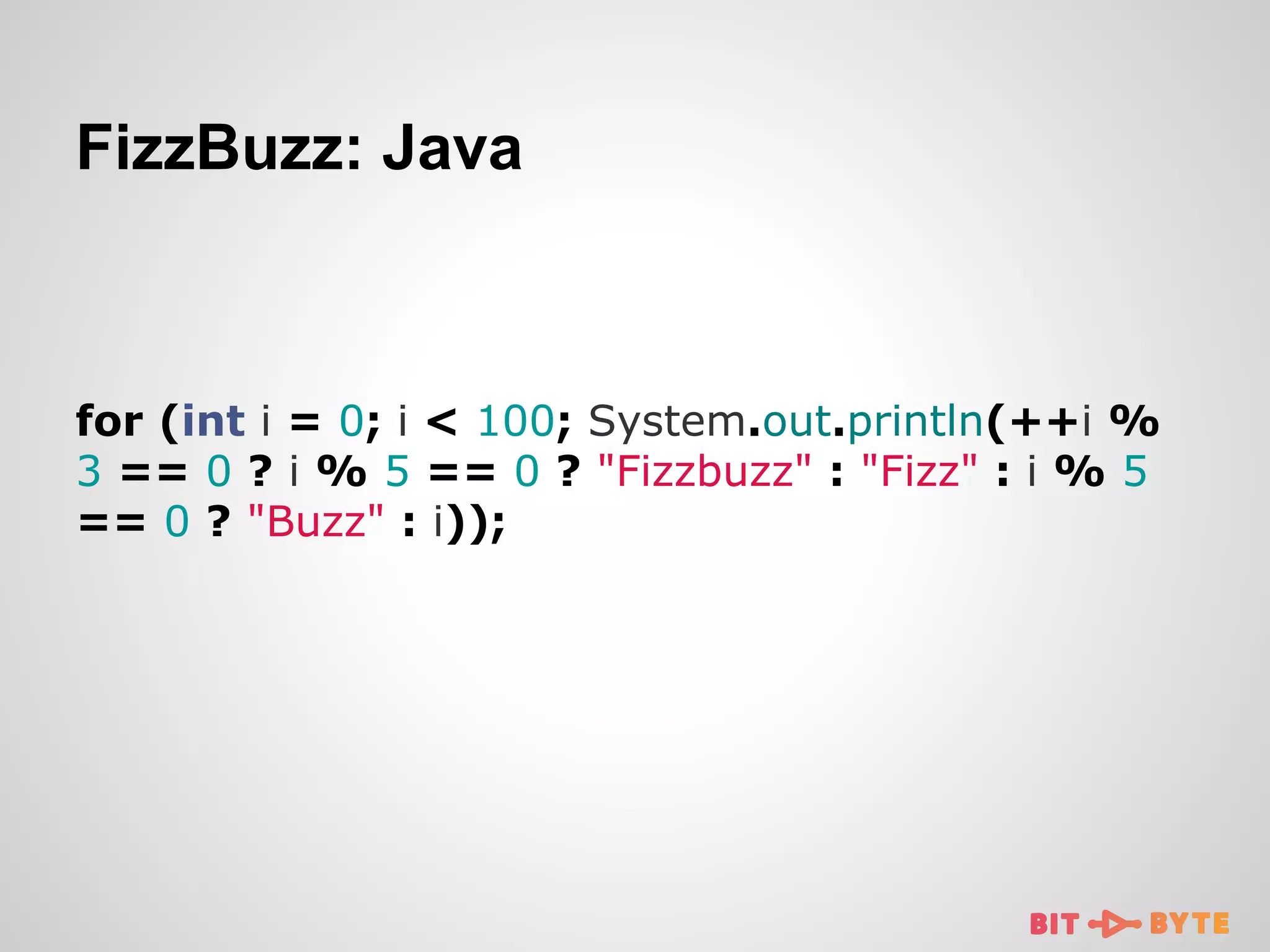
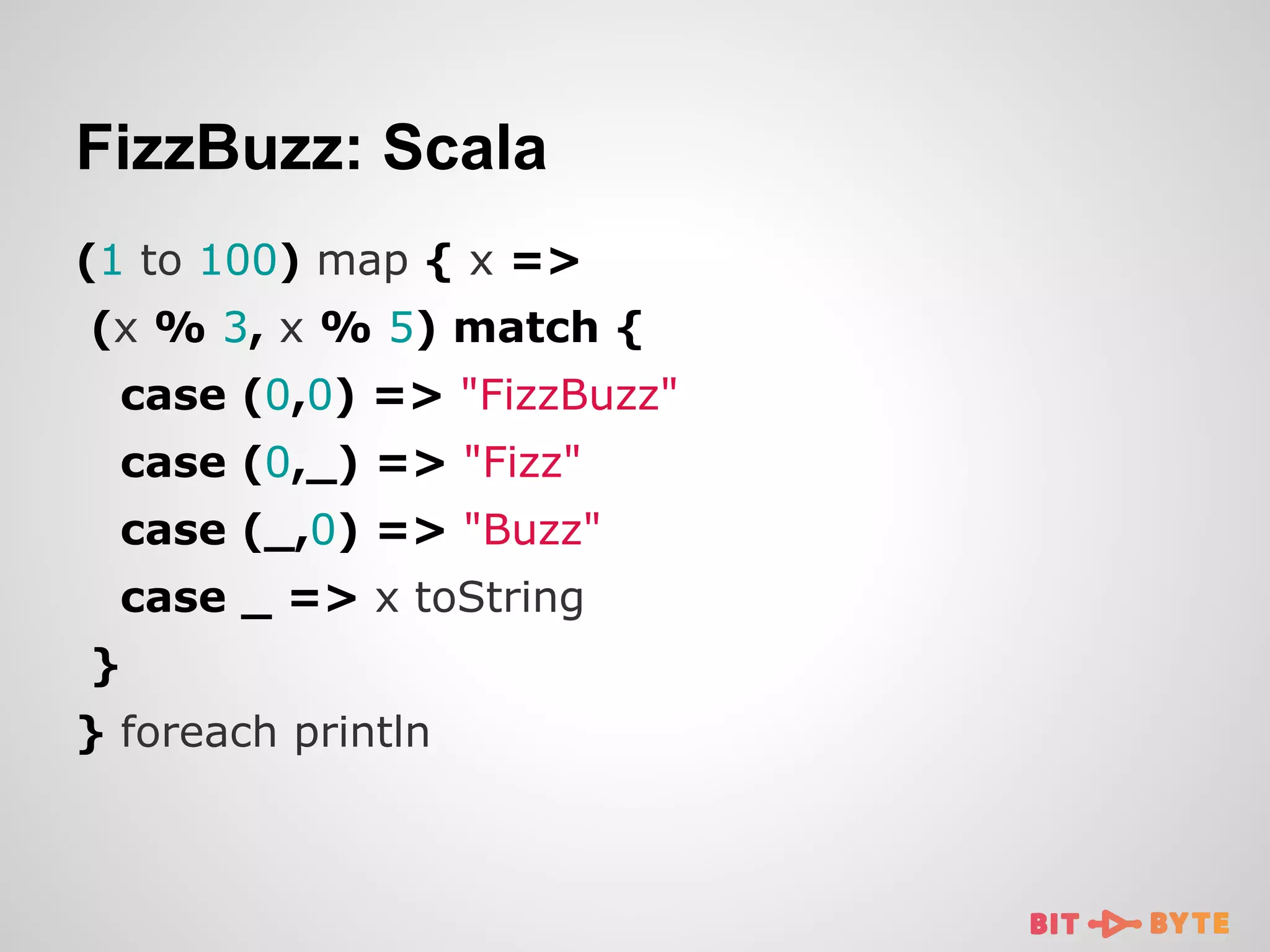
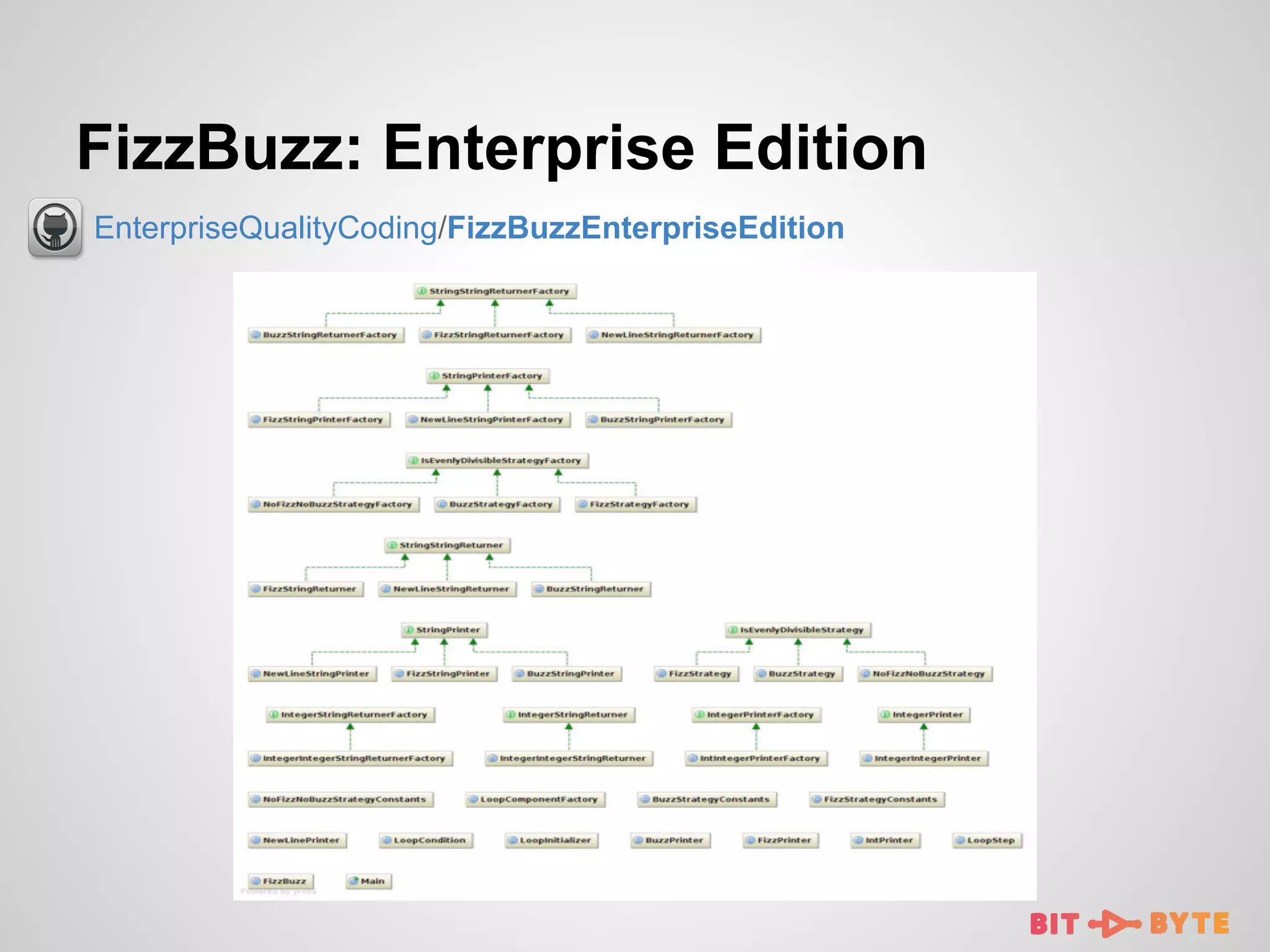
![FizzBuzz: Clojure
(use '[match.core :only (match)])
(doseq [n (range 1 101)]
(println (match [(mod n 3) (mod n 5)]
[0 0] "FizzBuzz"
[0 _] "Fizz"
[_ 0] "Buzz"
:else n)))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onbeingaprofessionalsoftwaredeveloper-131016061053-phpapp02/75/On-being-a-professional-software-developer-36-2048.jpg)