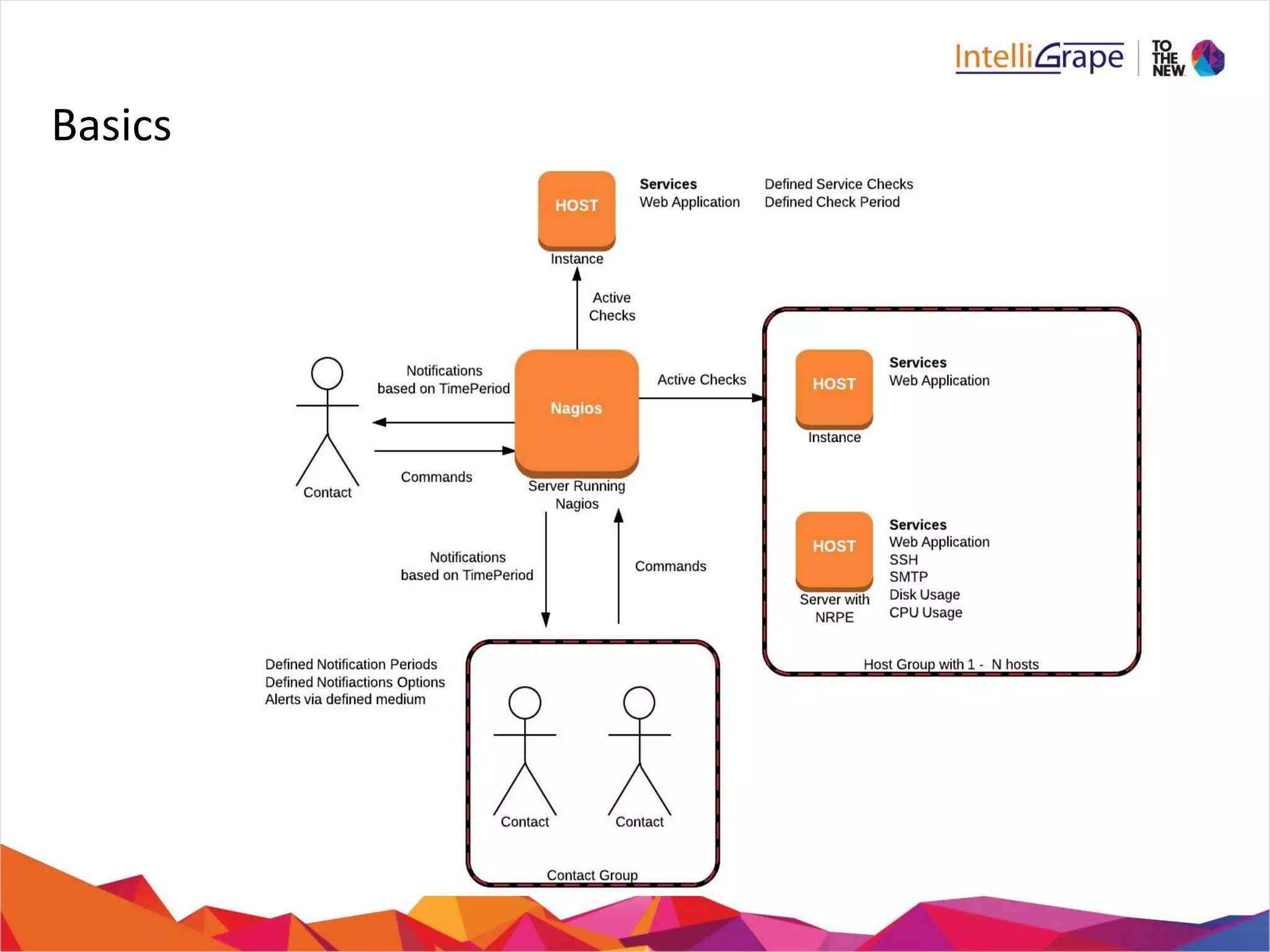
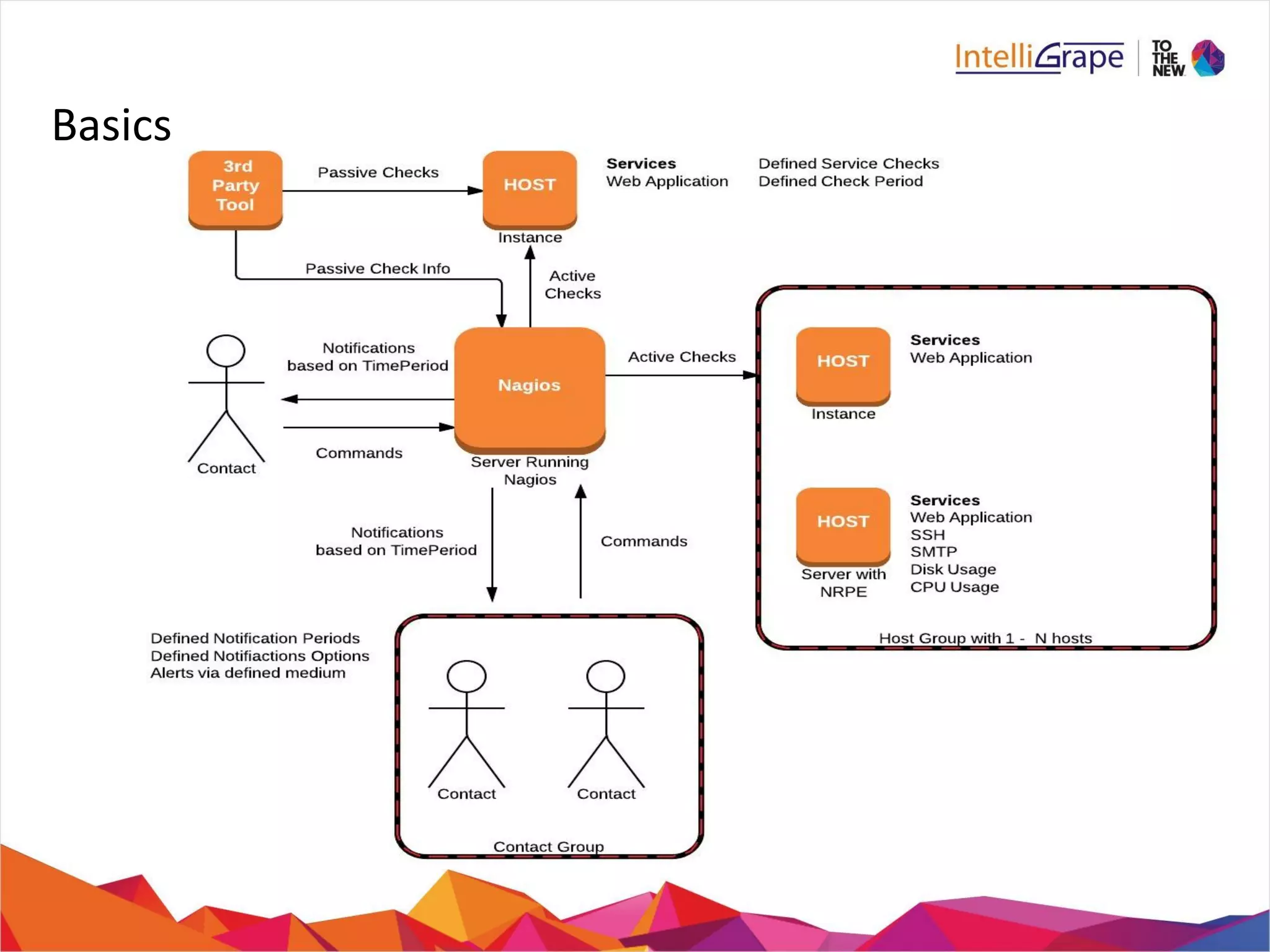
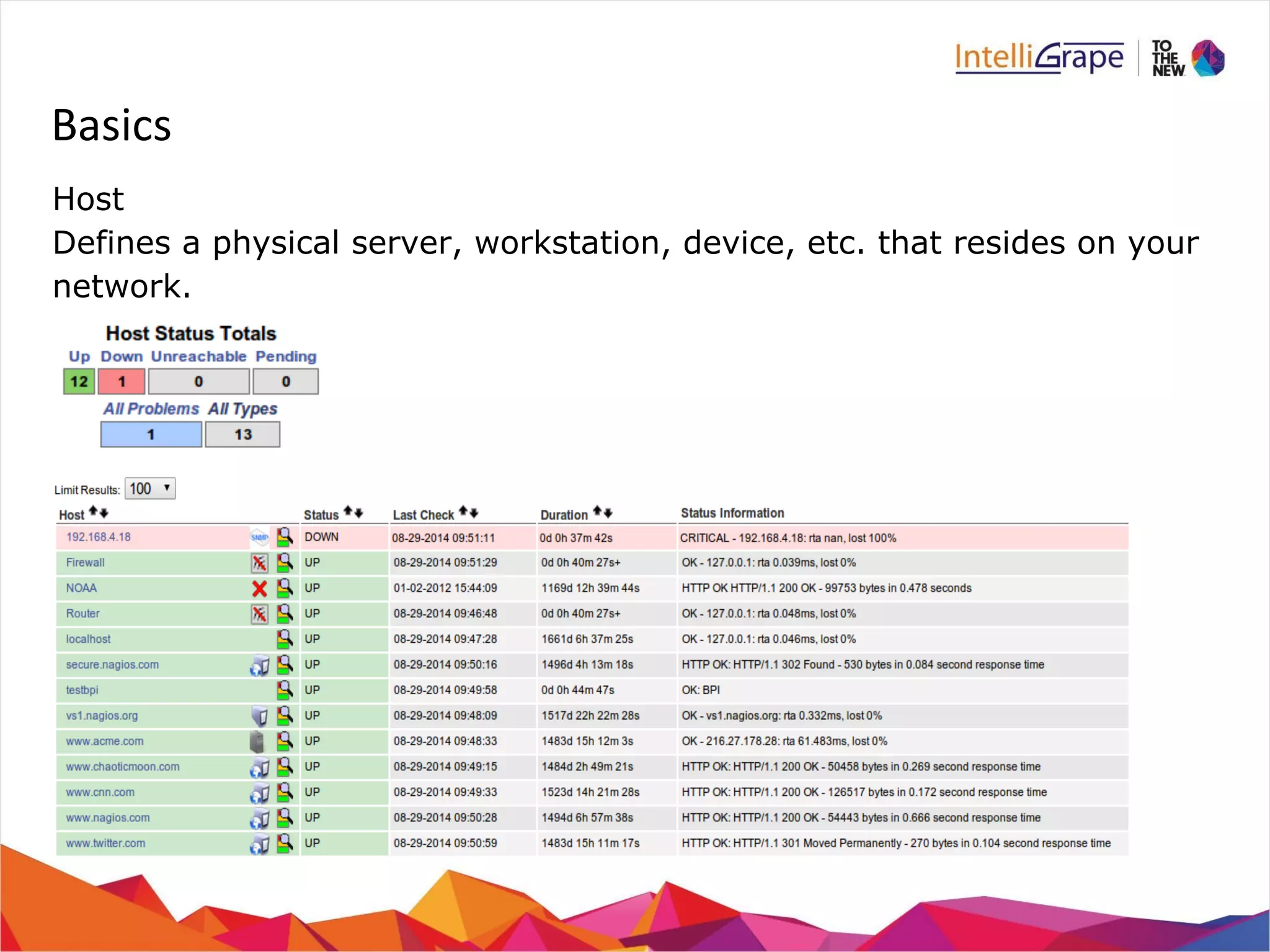
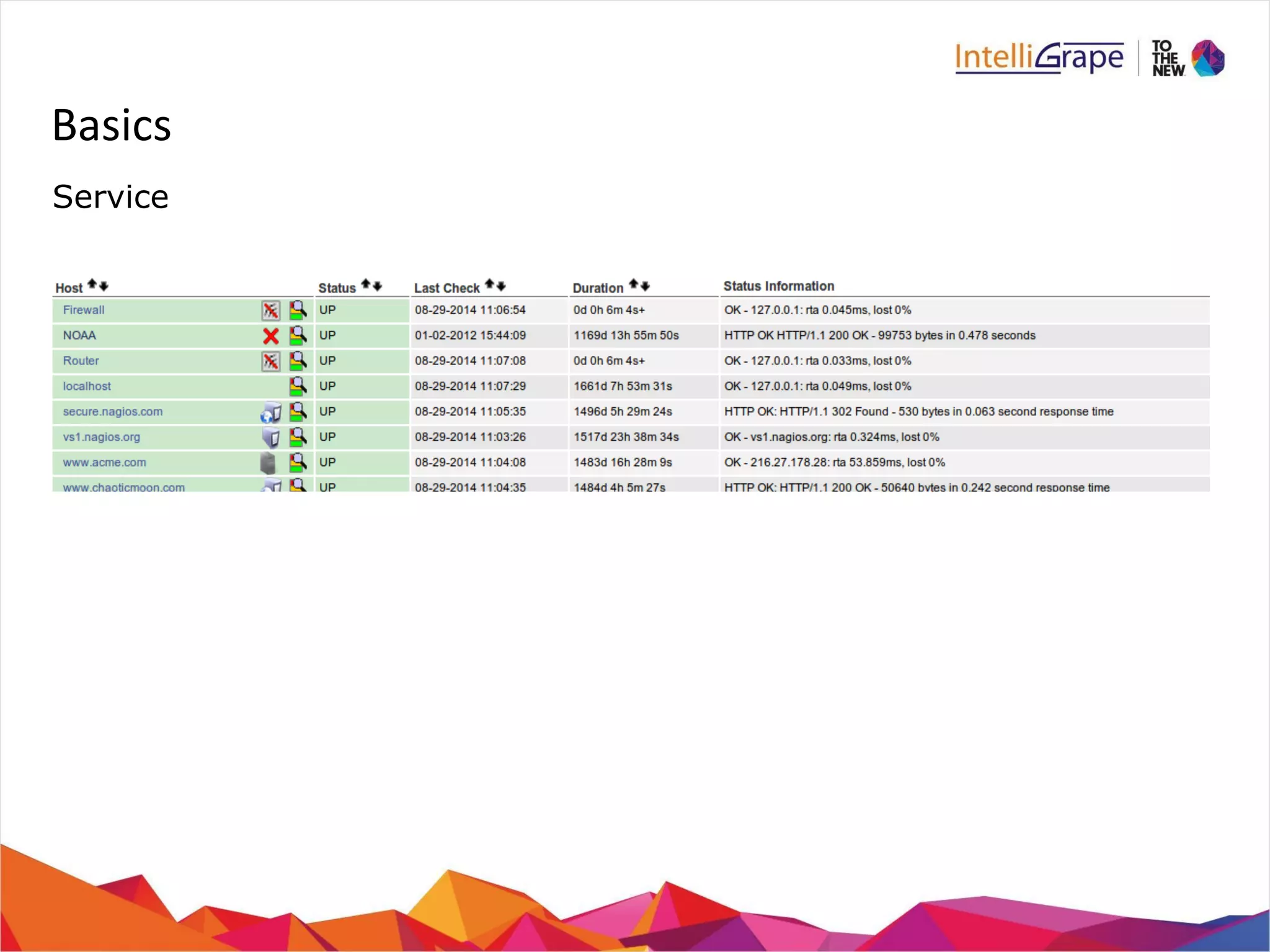
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Nagios, an open-source IT infrastructure monitoring tool, outlining its features, architecture, and monitoring capabilities for both public and private services. Key functionalities include active and passive checks, event handlers, notification systems, and reporting mechanisms to enhance proactive problem detection and resolution. It also offers guidance for beginners, training options, and resources for effective utilization of the software.














![Event Handlers
Event handlers are executed when a service or host:
• Is in a SOFT problem state
• Initially goes into a HARD problem state
• Initially recovers from a SOFT or HARD problem state
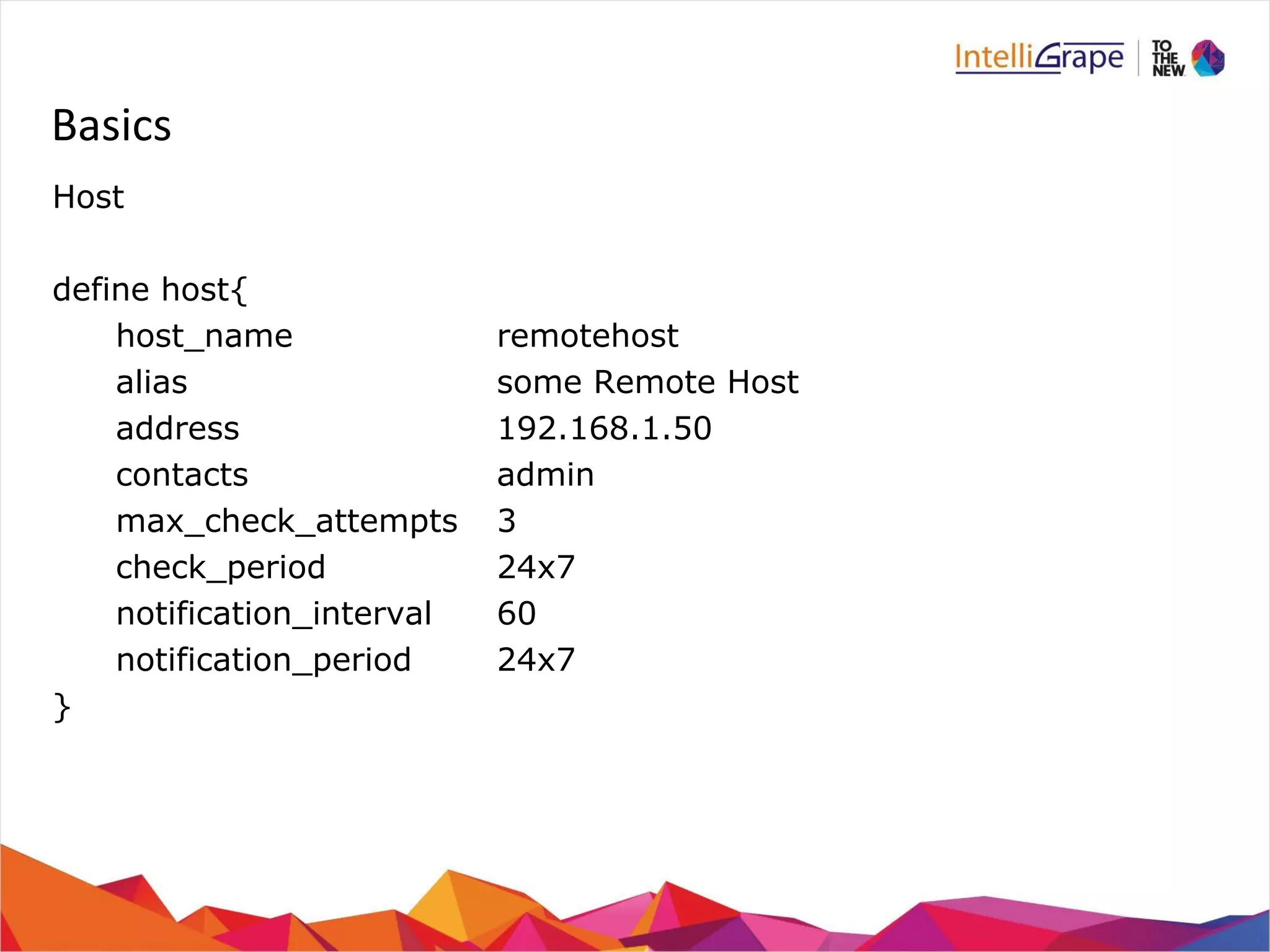
define service {
..
event_handler command_name
event_handler_enabled [0/1]
..
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nagios-140911144441-phpapp02/75/Nagios-Getting-Started-24-2048.jpg)