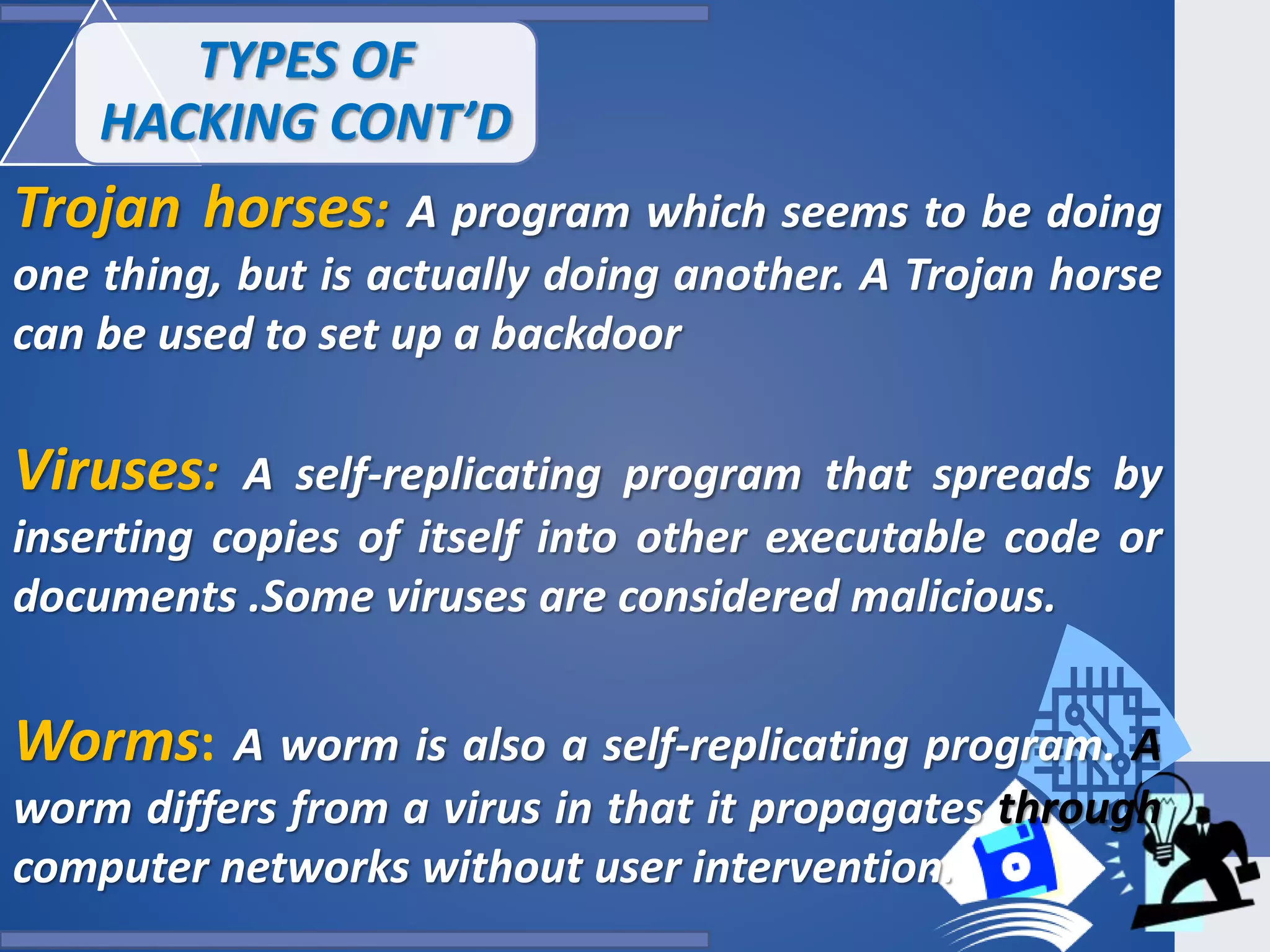
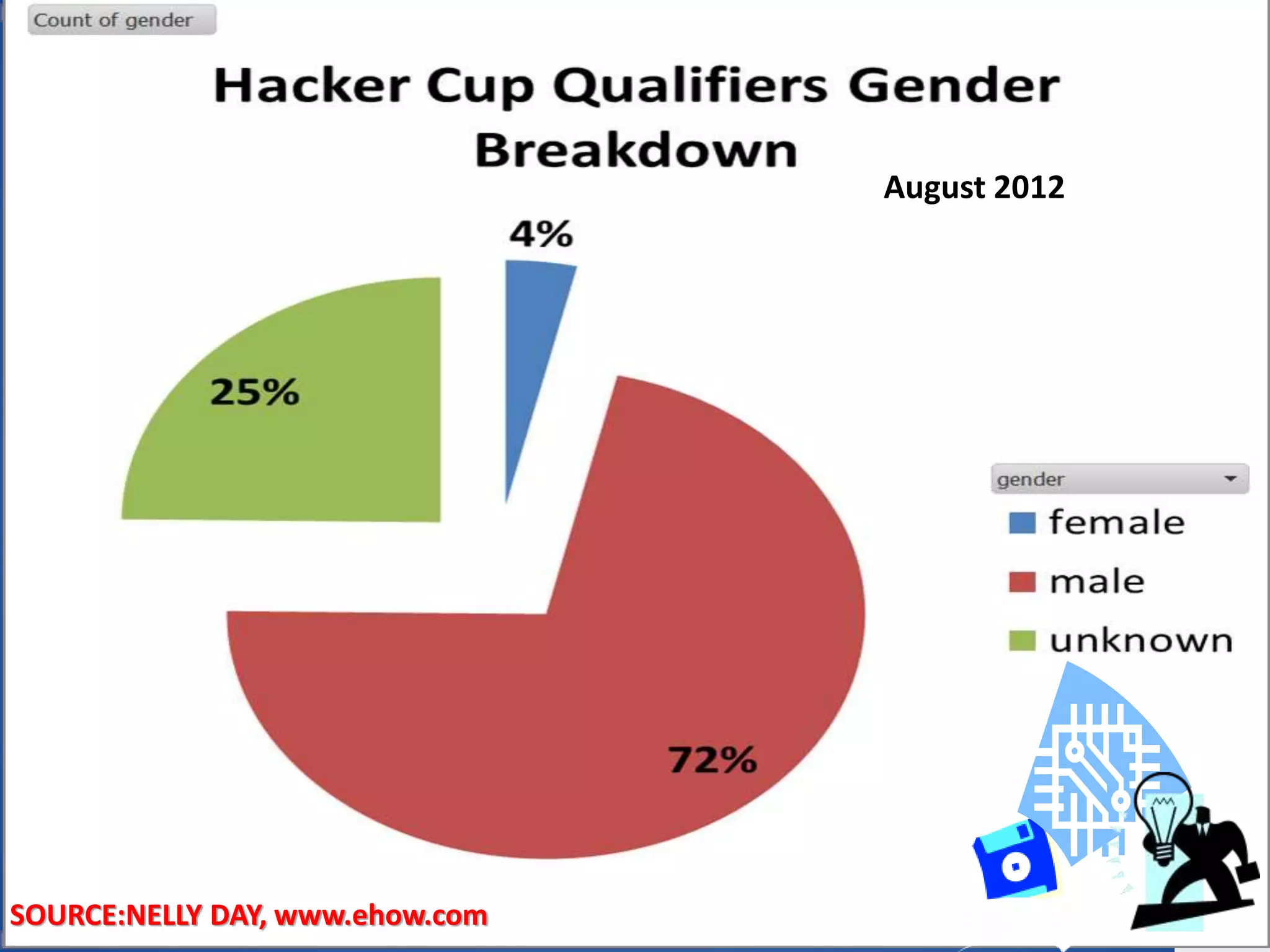
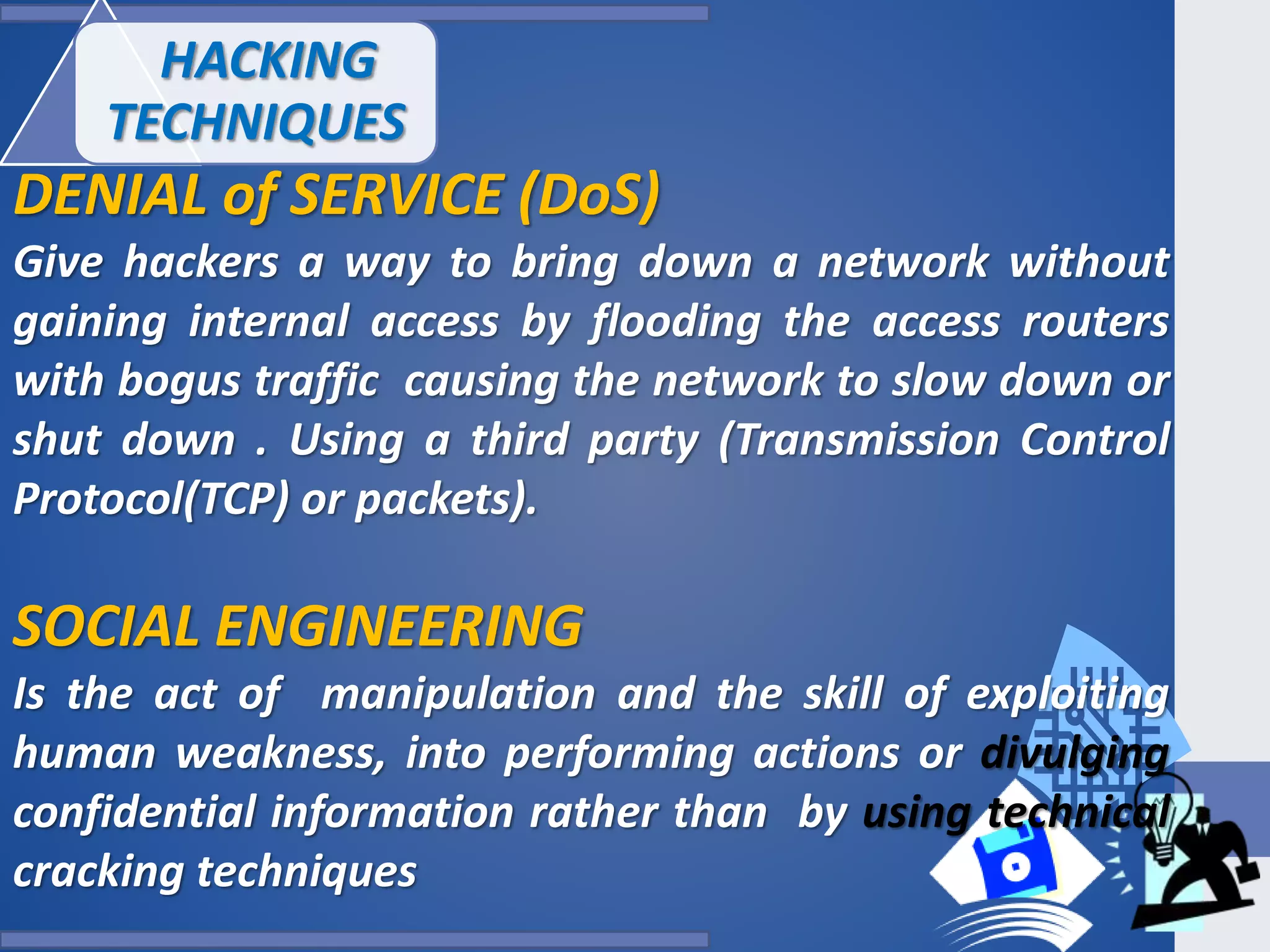
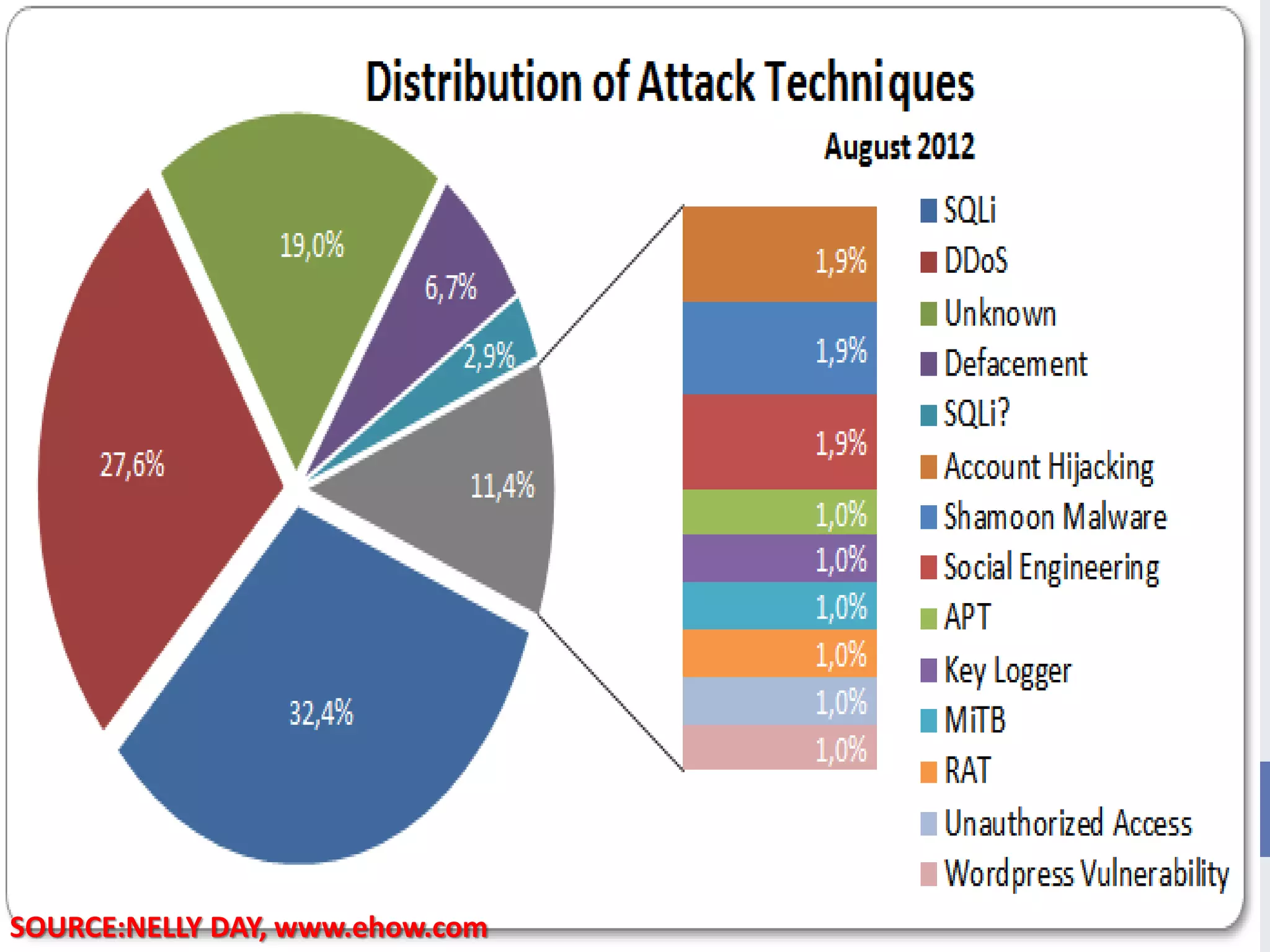
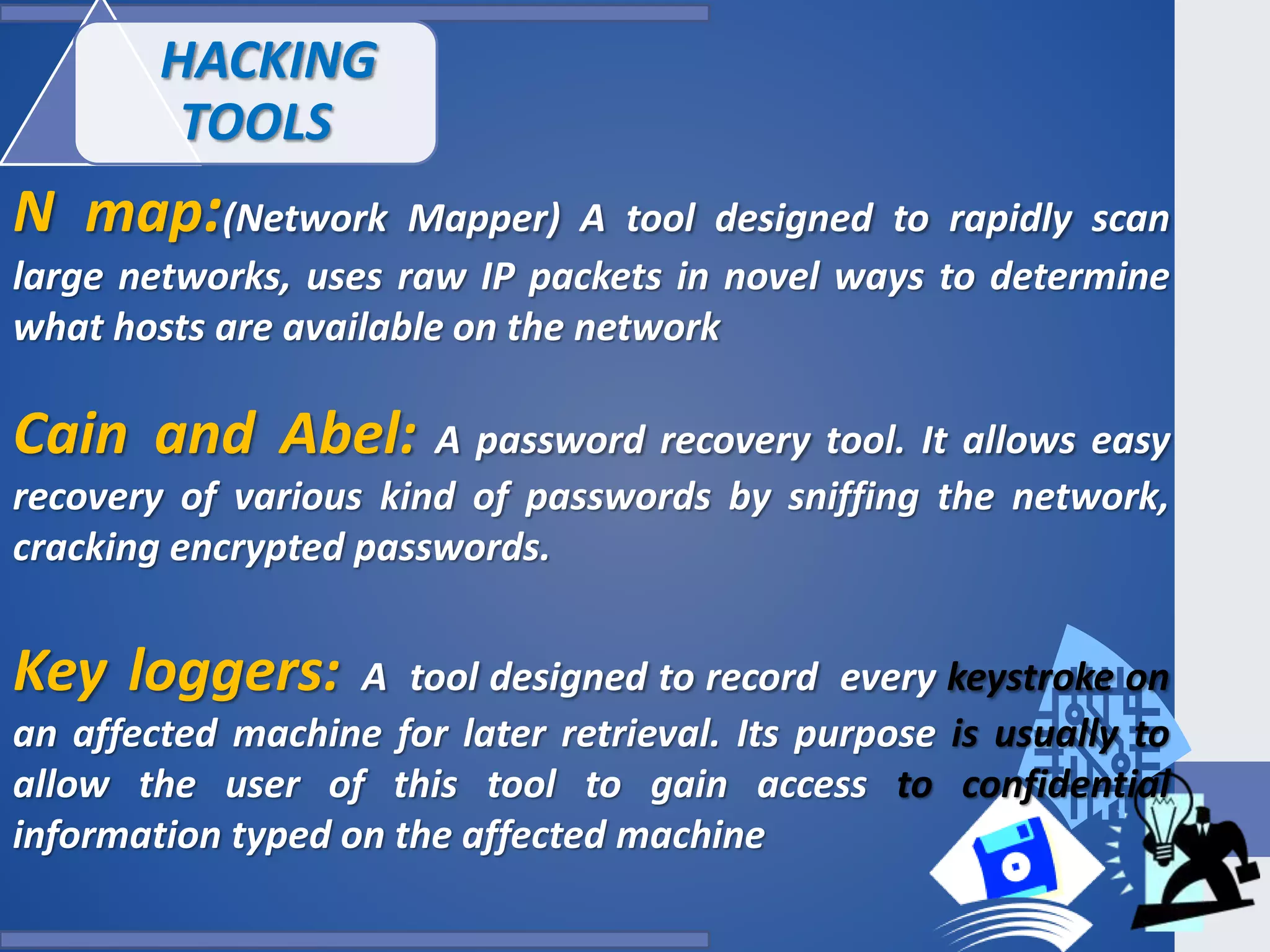
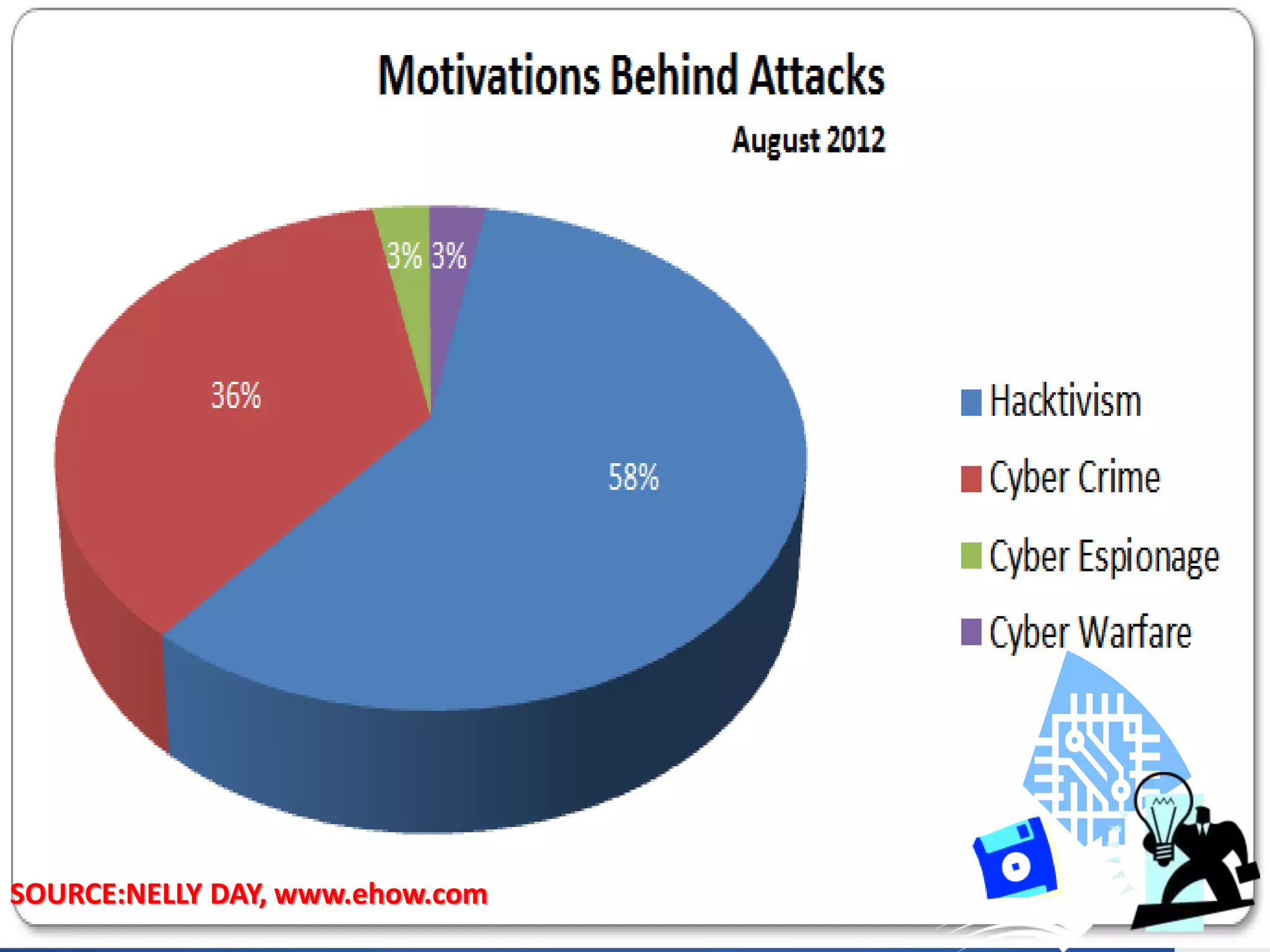
This document provides an outline for a presentation on hacking. It begins with definitions of hacking and different types of hackers. The history and evolution of hacking is discussed. Various types of hacking techniques like denial of service attacks, password cracking, and social engineering are described. Common hacking tools such as Nmap, Cain and Abel, and keyloggers are listed. The document outlines how hacking attacks work and their potential effects. It discusses certifications in ethical hacking and concludes that while hacking can be a crime, proper security measures and computer ethics can help prevent and detect hacking activities.