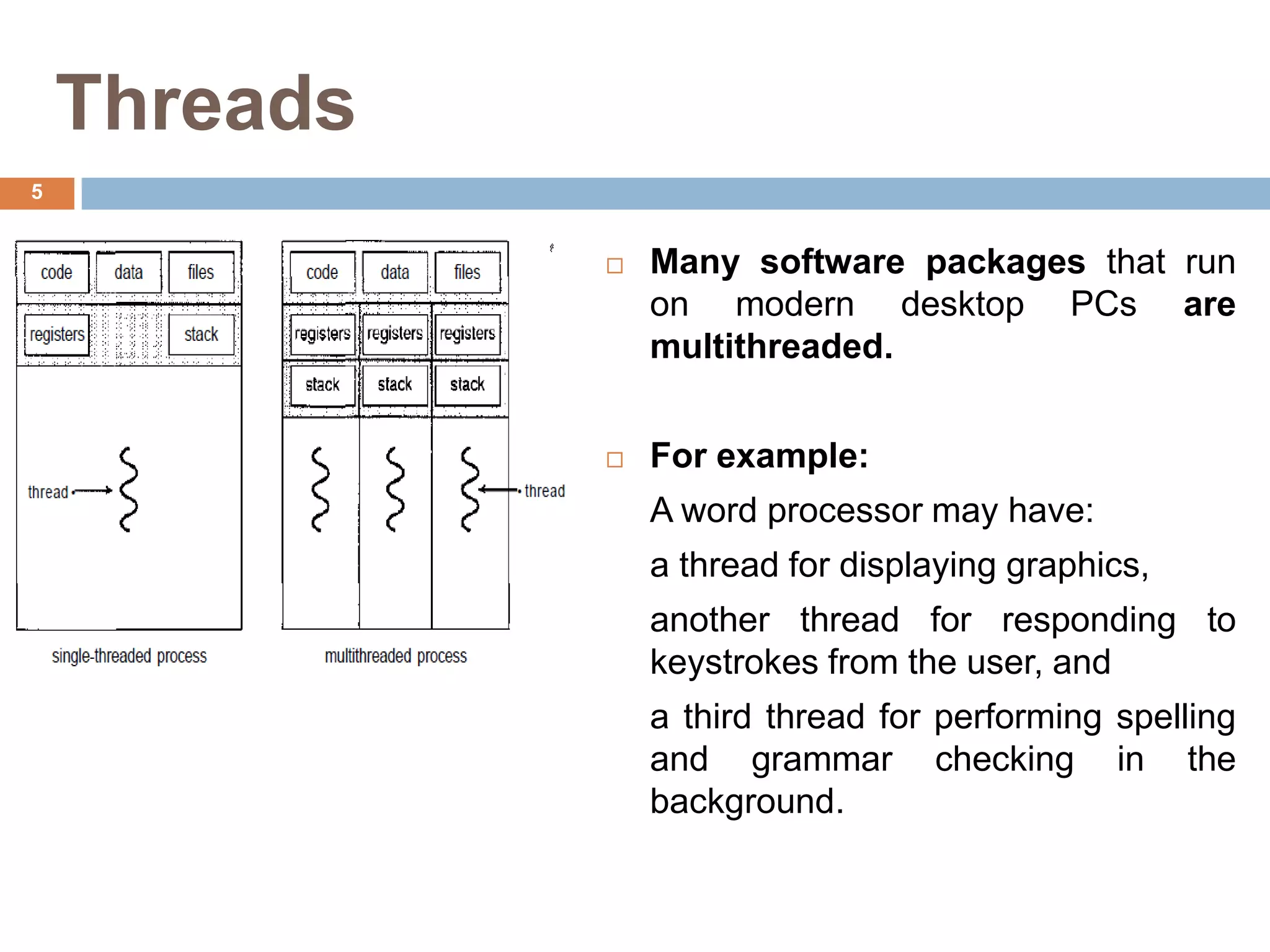
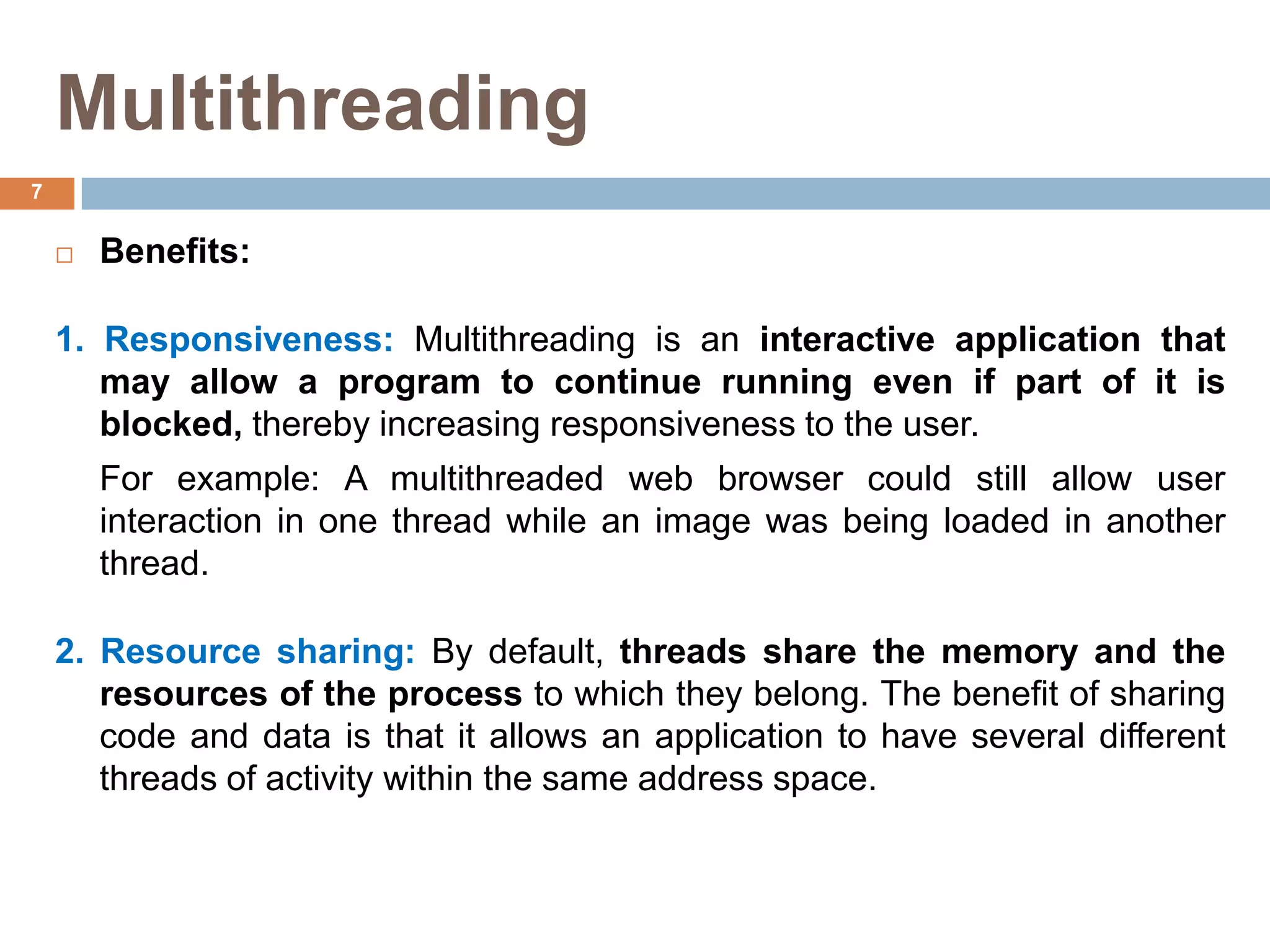
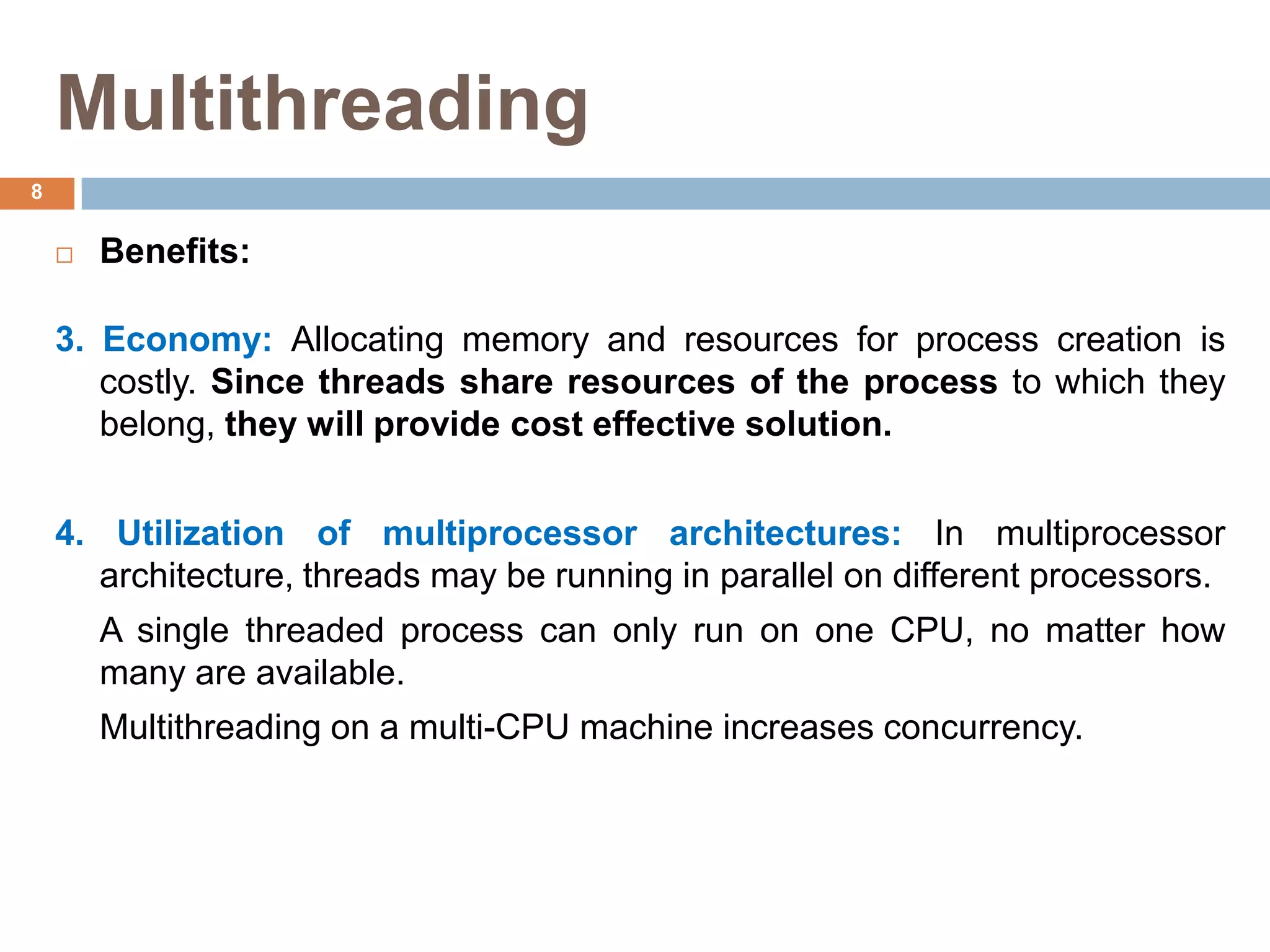
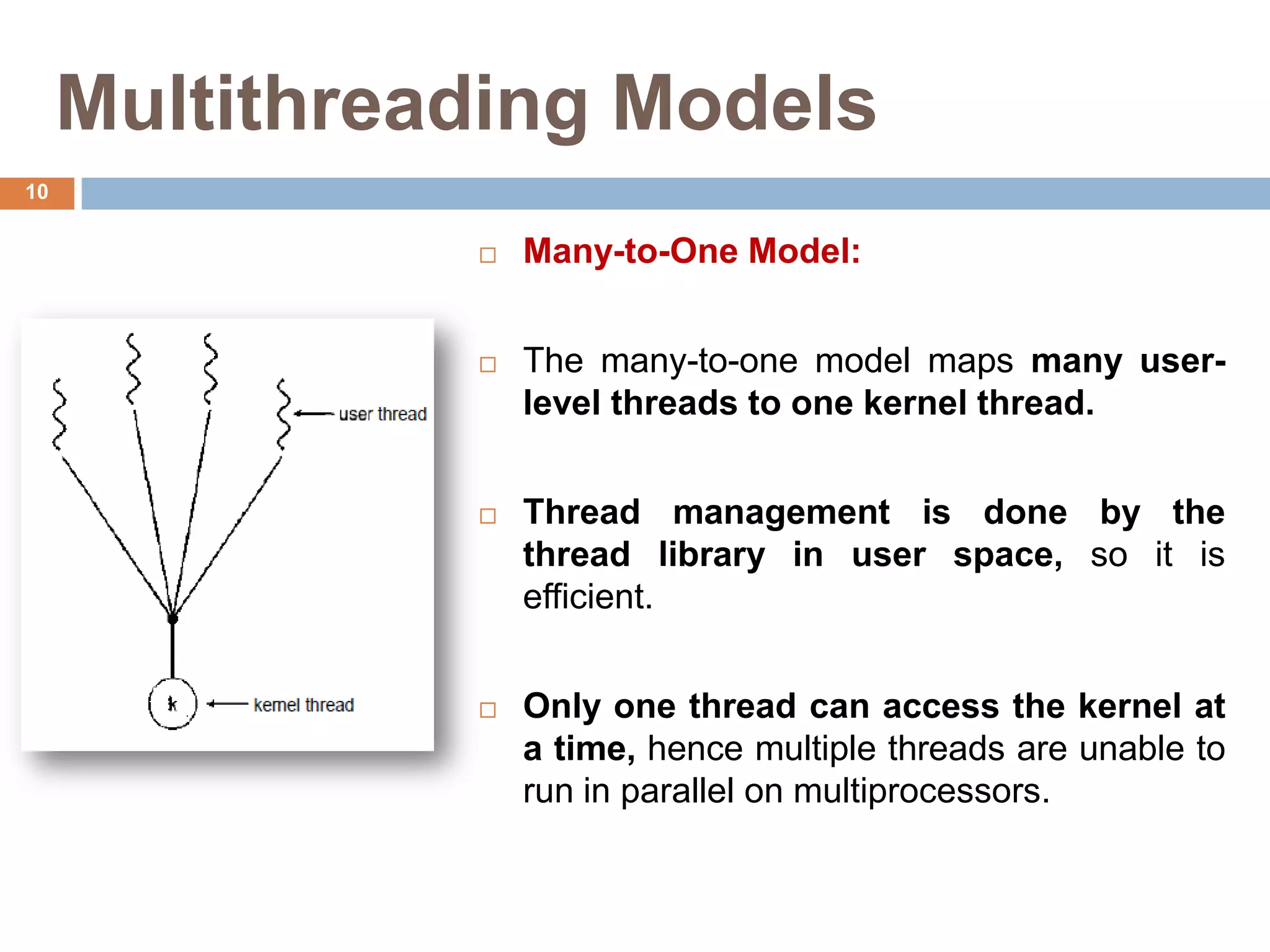
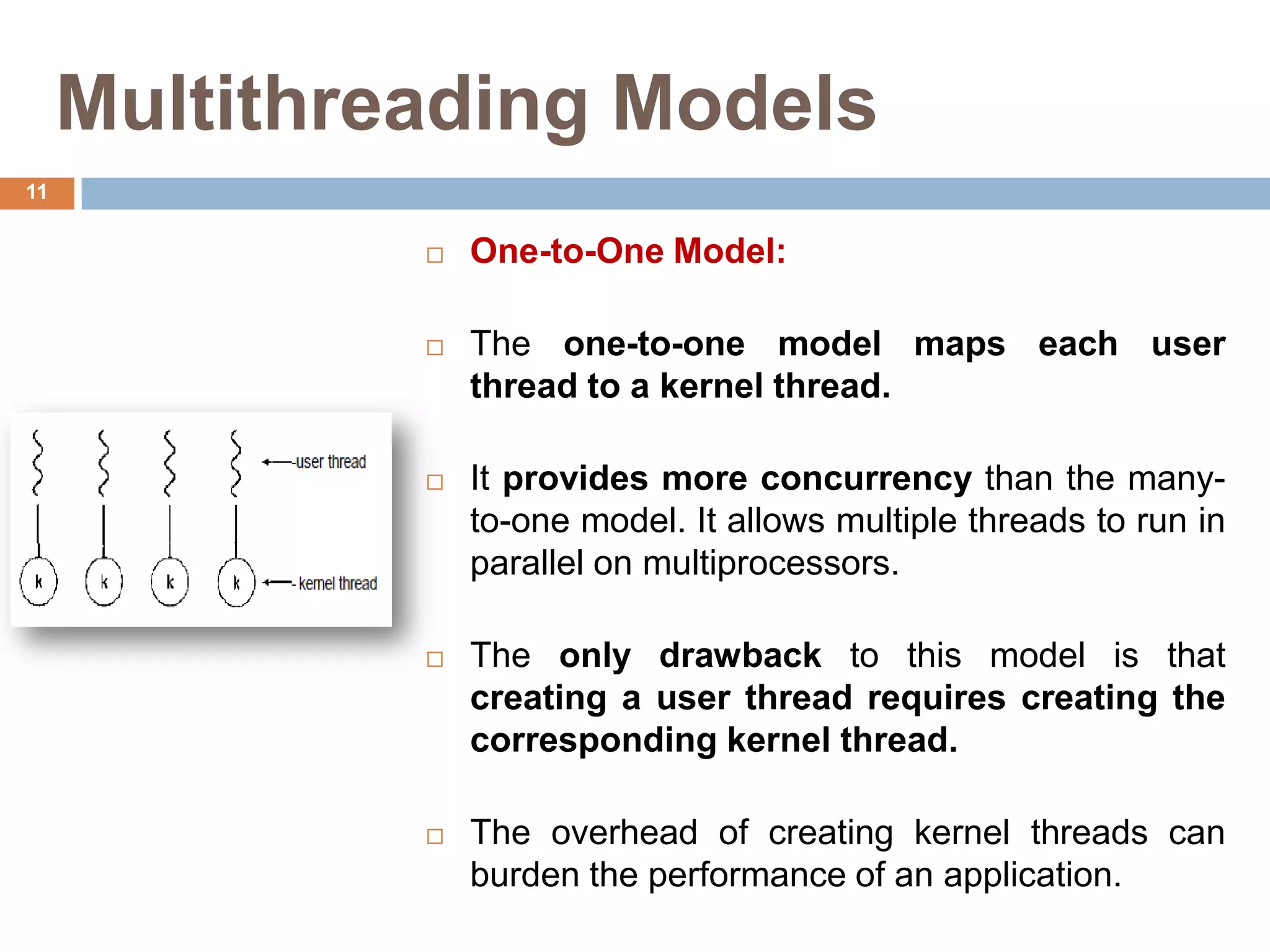
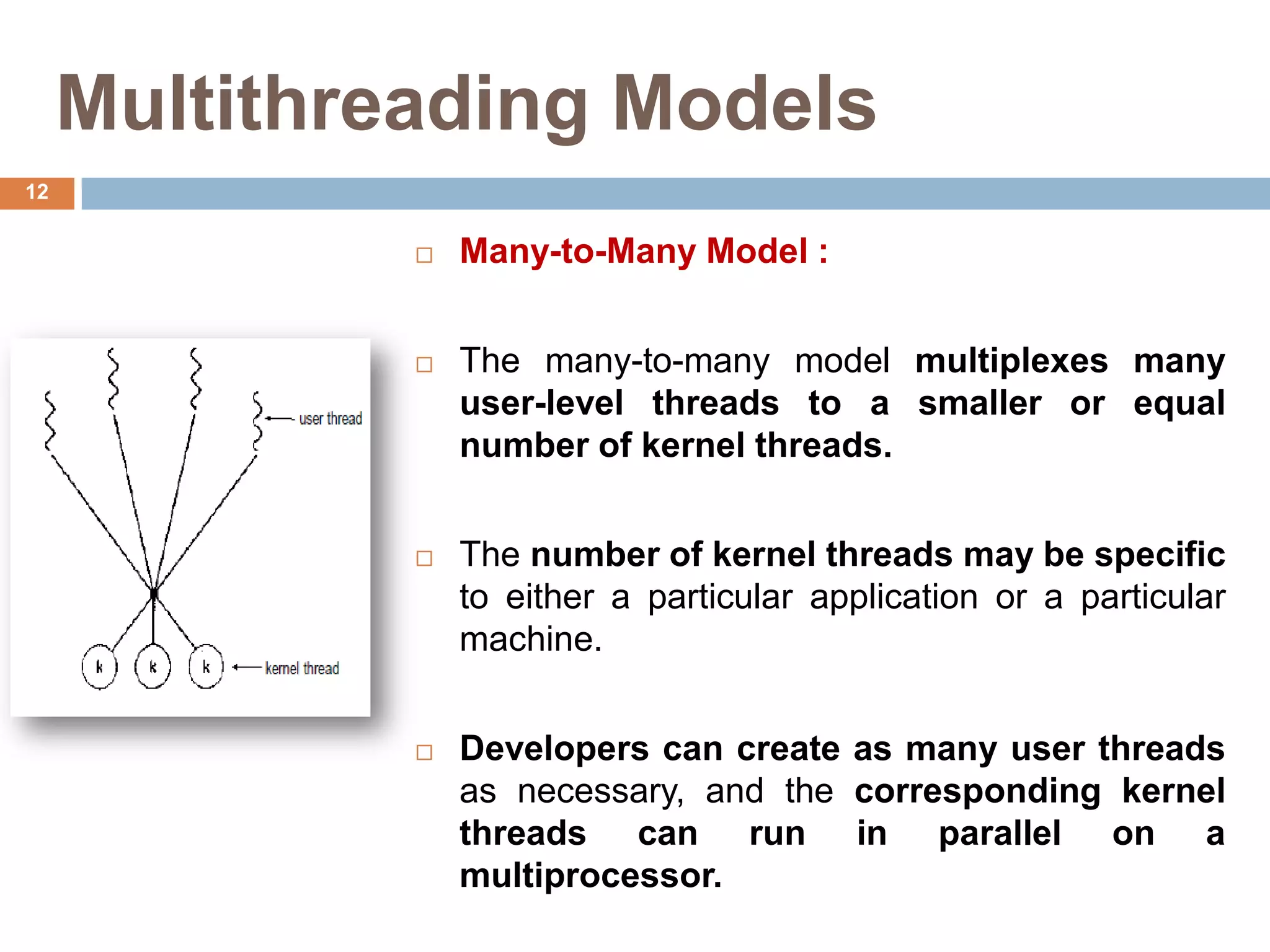
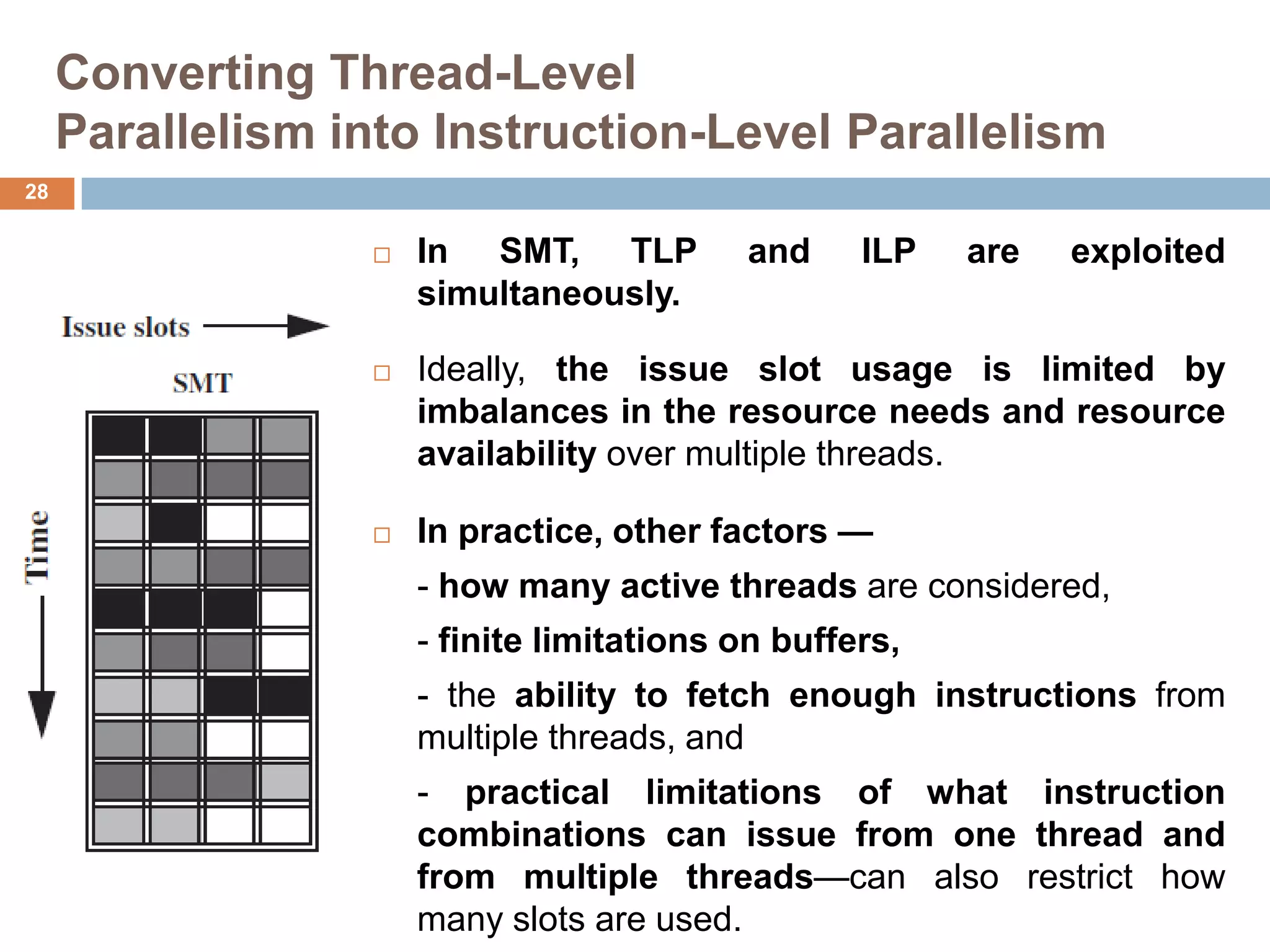
The document discusses multithreading and how it can be used to exploit thread-level parallelism (TLP) in processors designed for instruction-level parallelism (ILP). There are two main approaches for multithreading - fine-grained and coarse-grained. Fine-grained switches threads every instruction while coarse-grained switches on long stalls. Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) allows a processor to issue instructions from multiple threads in the same cycle by treating instructions from different threads as independent. This converts TLP into additional ILP to better utilize the resources of superscalar and multicore processors.