Embed presentation






Multithreading allows multiple tasks to be performed simultaneously by executing independent threads. There are two methods for creating threads in C#: using the Thread class or the thread pool. Threads have a lifecycle that includes creation, execution, and termination. Synchronization is used to coordinate thread access to shared resources using locks, and threads can communicate through wait/pulse methods that pause execution until notified of state changes. Potential issues like deadlocks can occur if threads indefinitely wait for each other.
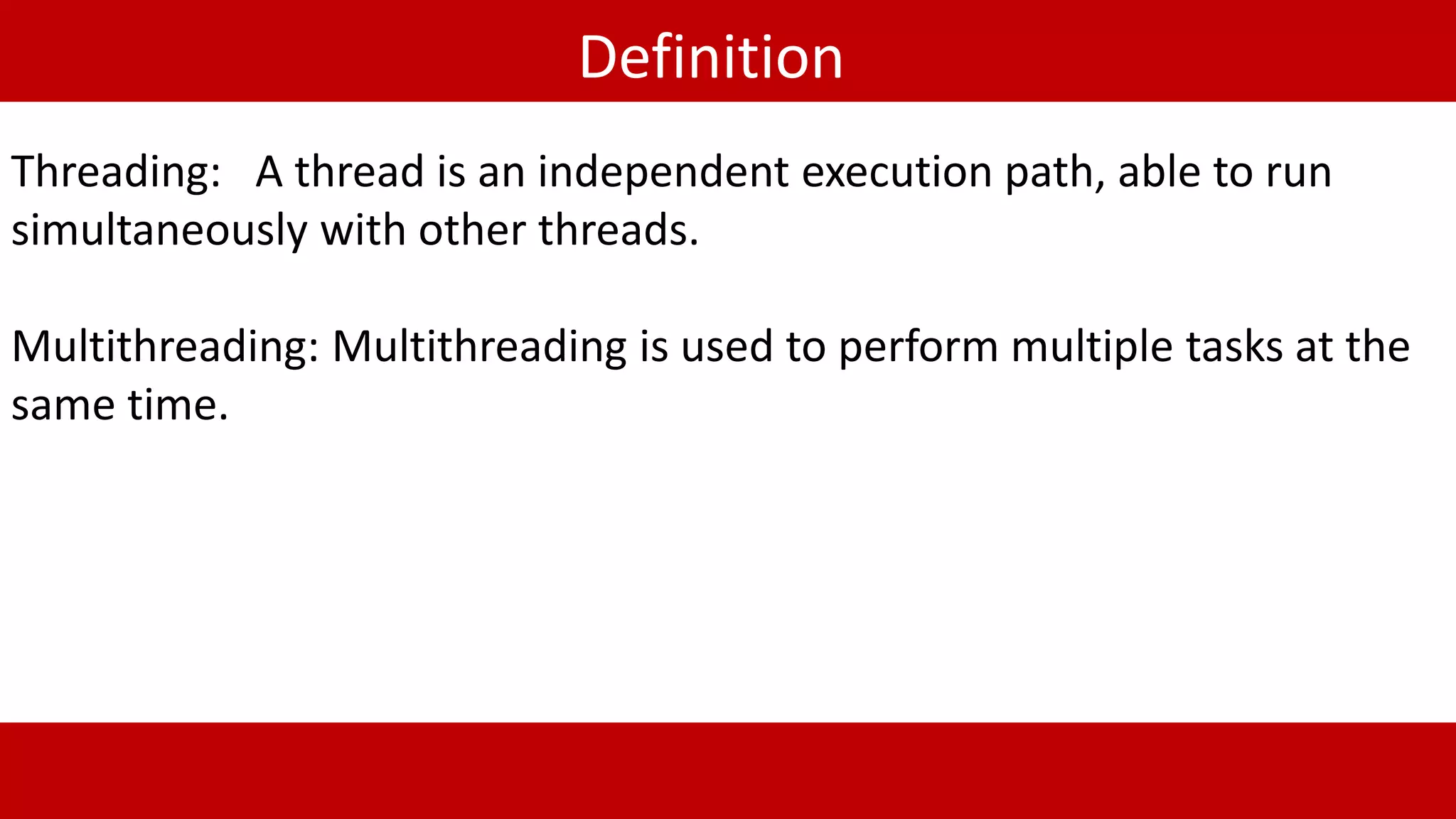
Introduction to multithreading and its definition. A thread runs concurrently, allowing multiple tasks.
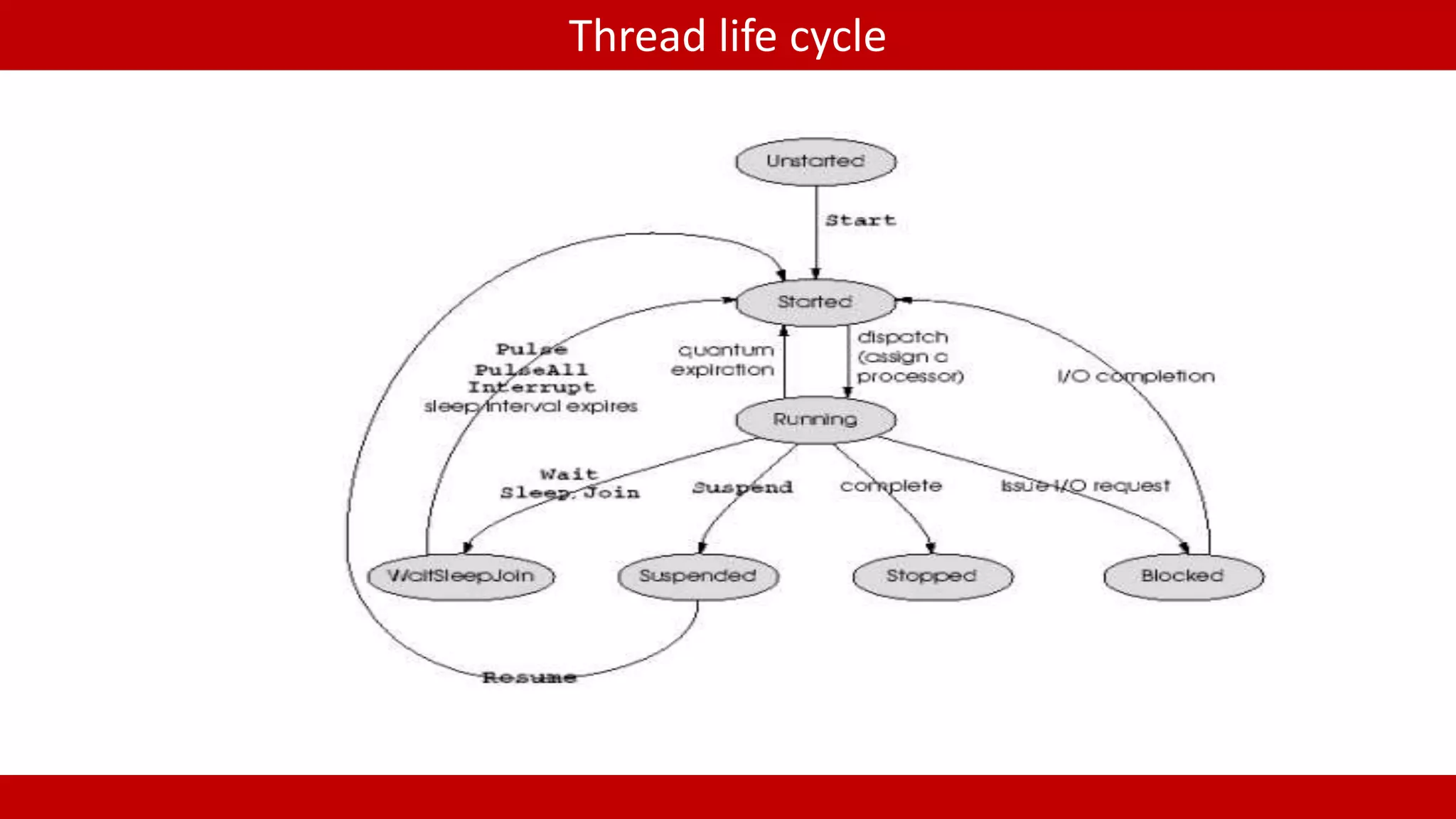
Overview of thread life cycle. C# methods for creating threads: Thread class and Thread pool.
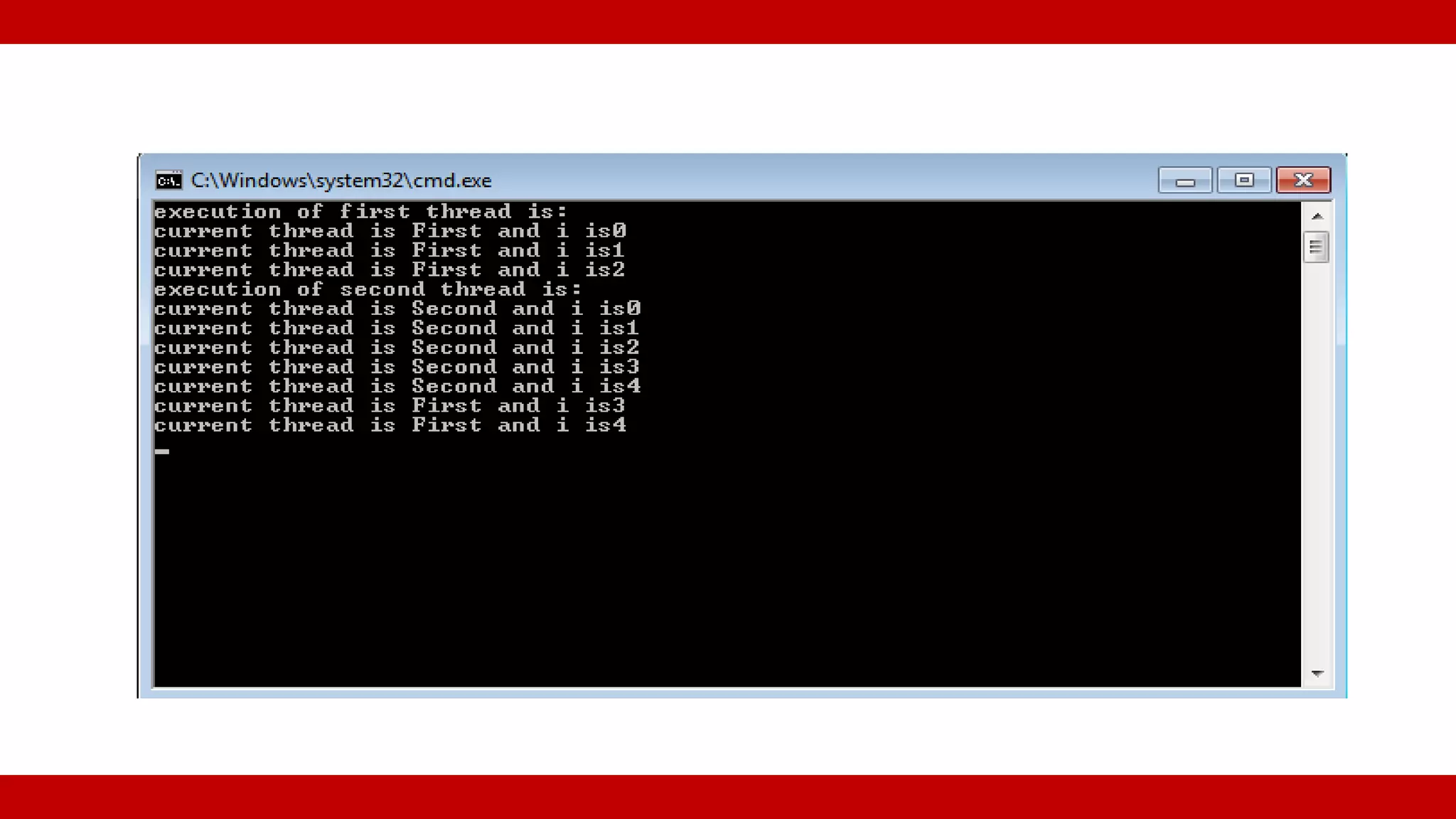
Example of creating and starting threads in C#. Demonstrates setting the name and priority of threads.
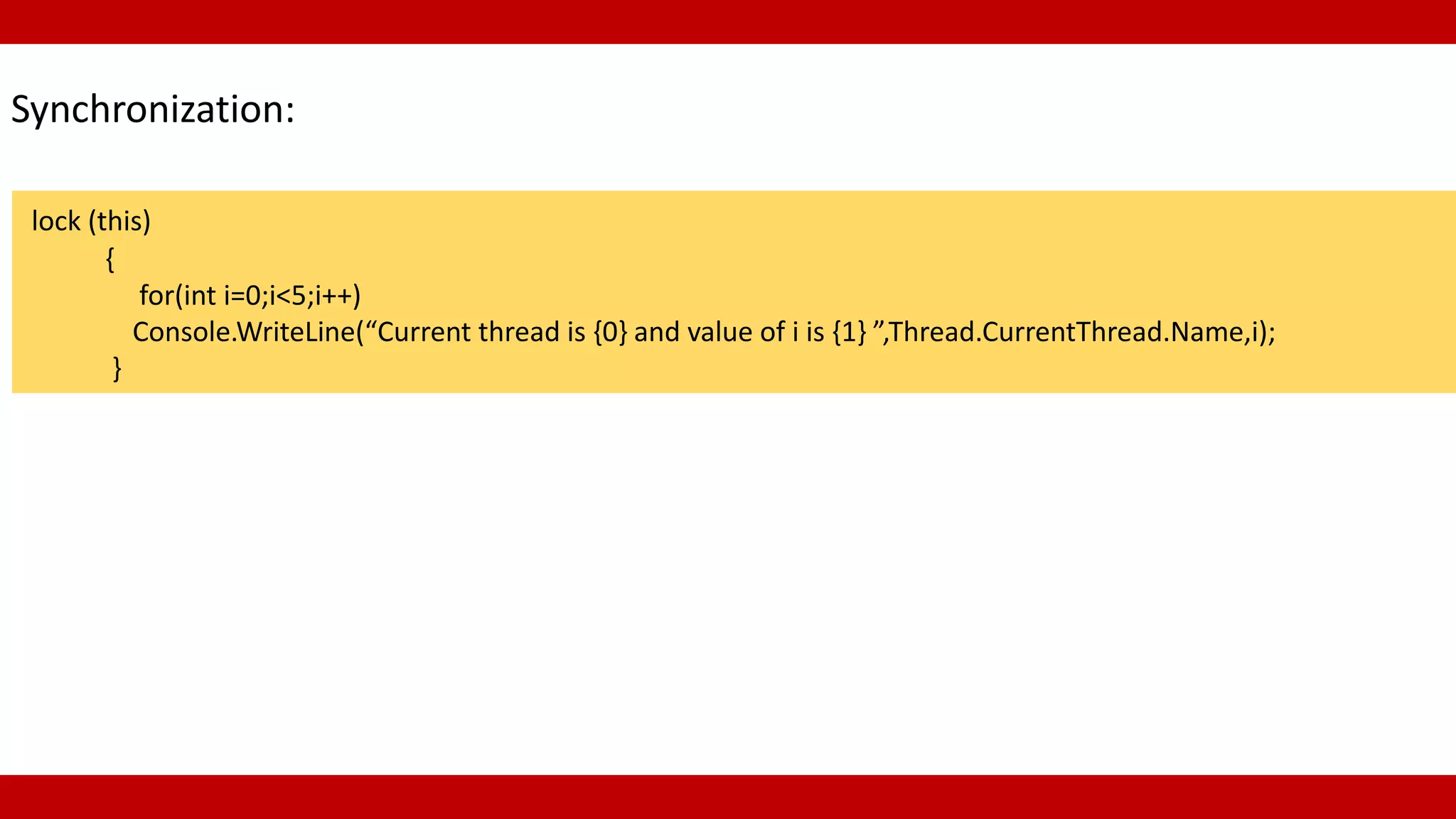
Synchronization in multithreading using lock statements to ensure thread safety during execution.
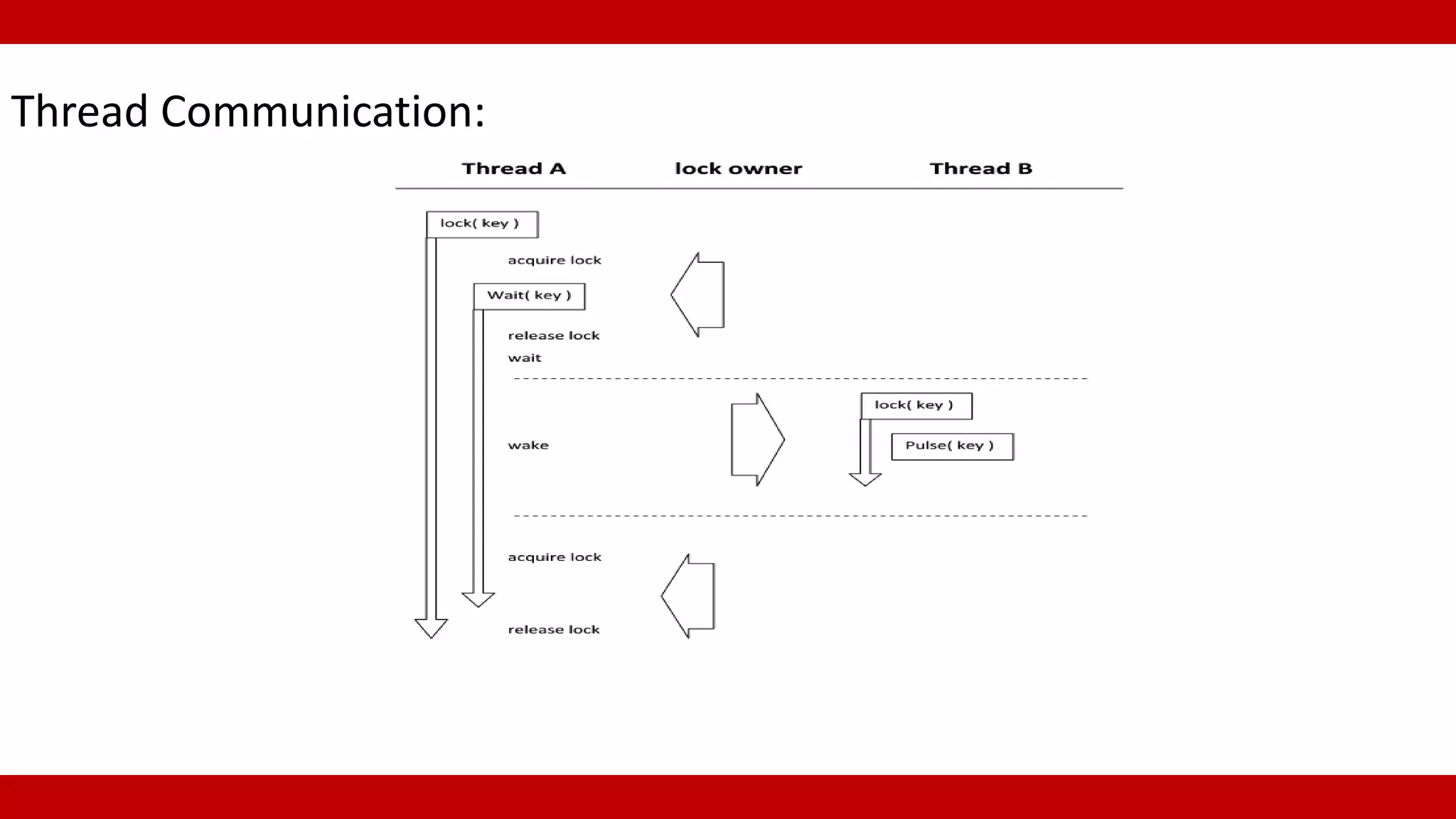
Methods for thread communication: Wait() to block a thread and Pulse() to notify state changes.
Explanation of deadlocks in multithreading, where processes get stuck waiting on each other.









