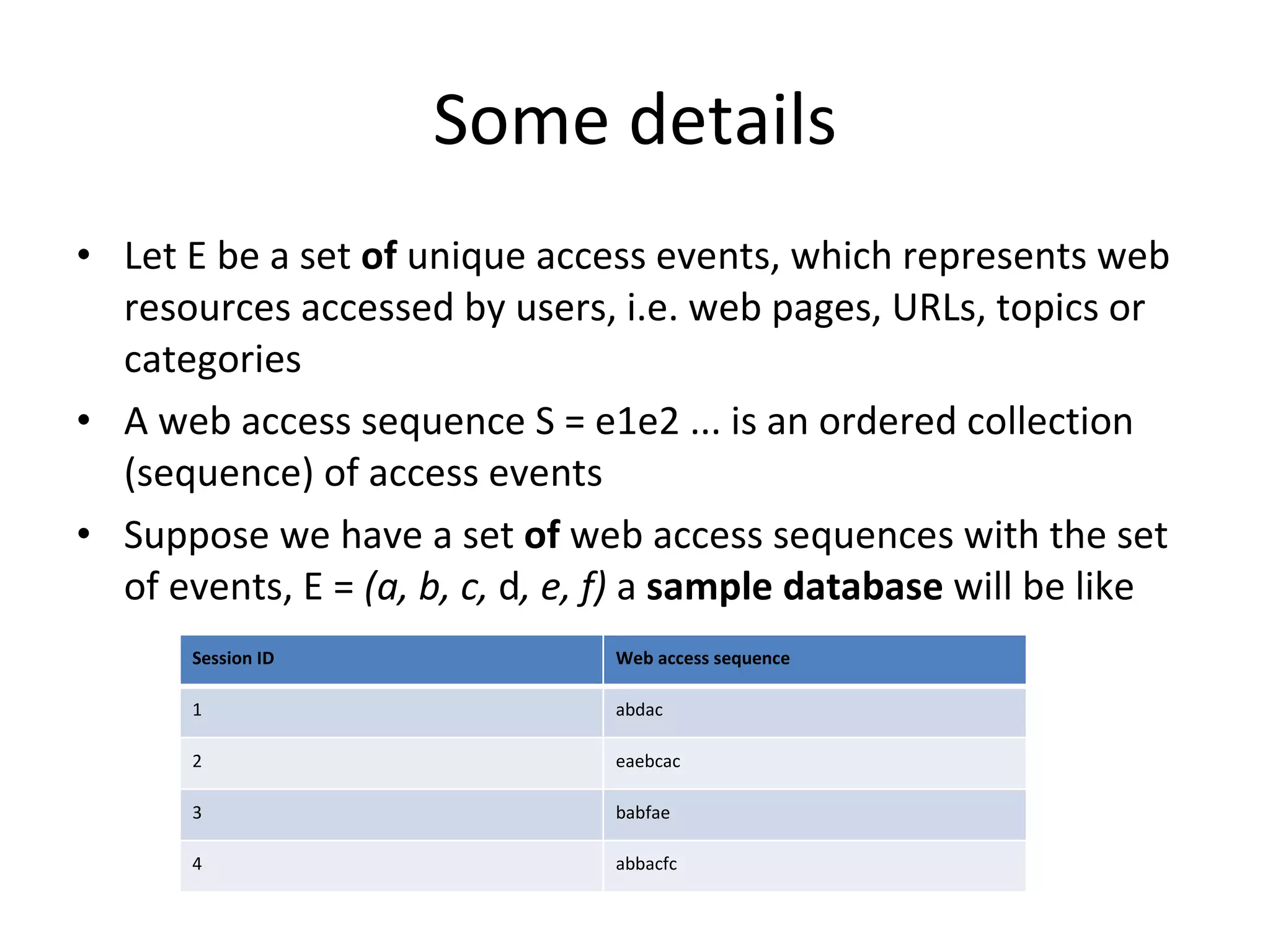
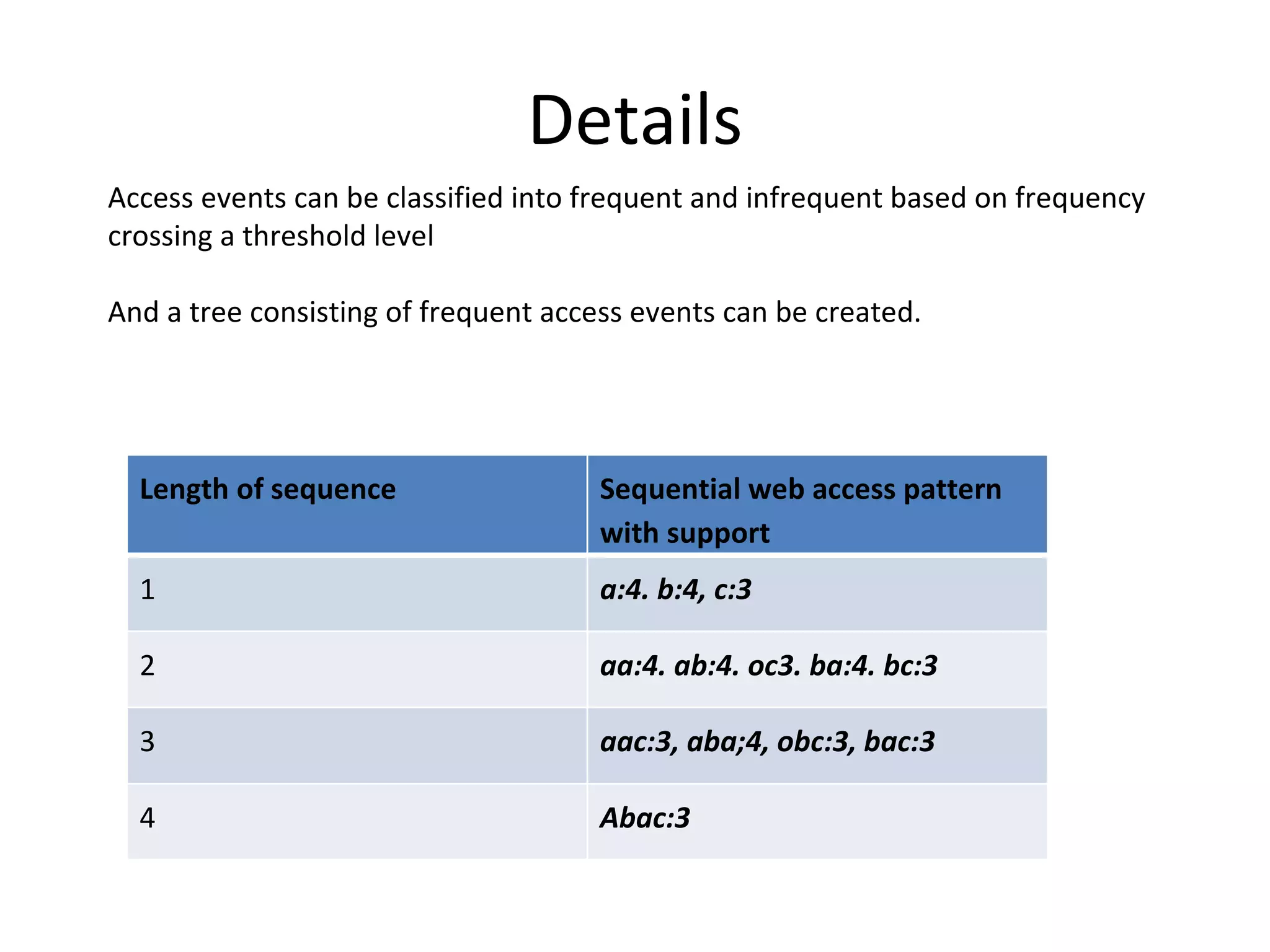
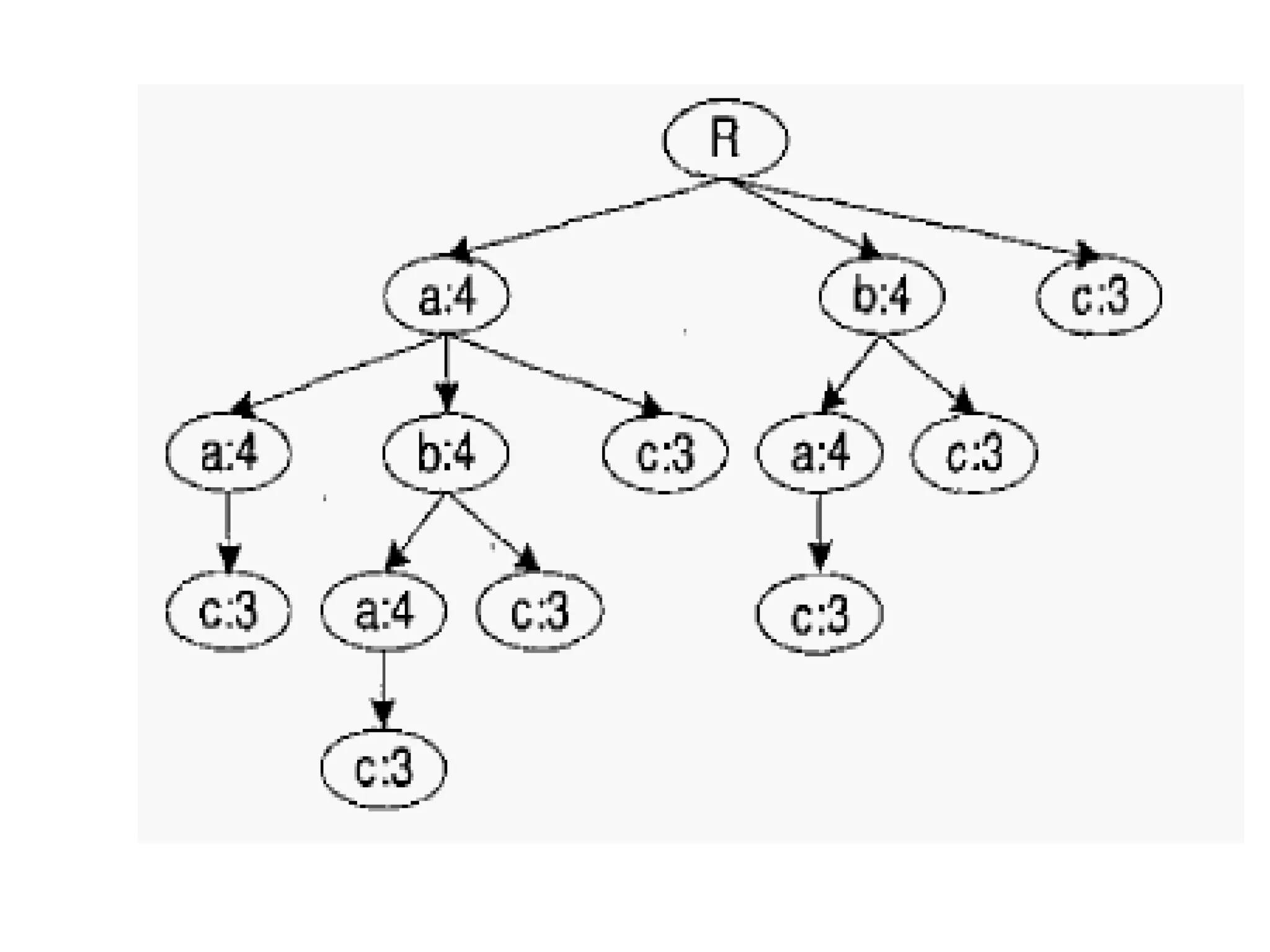
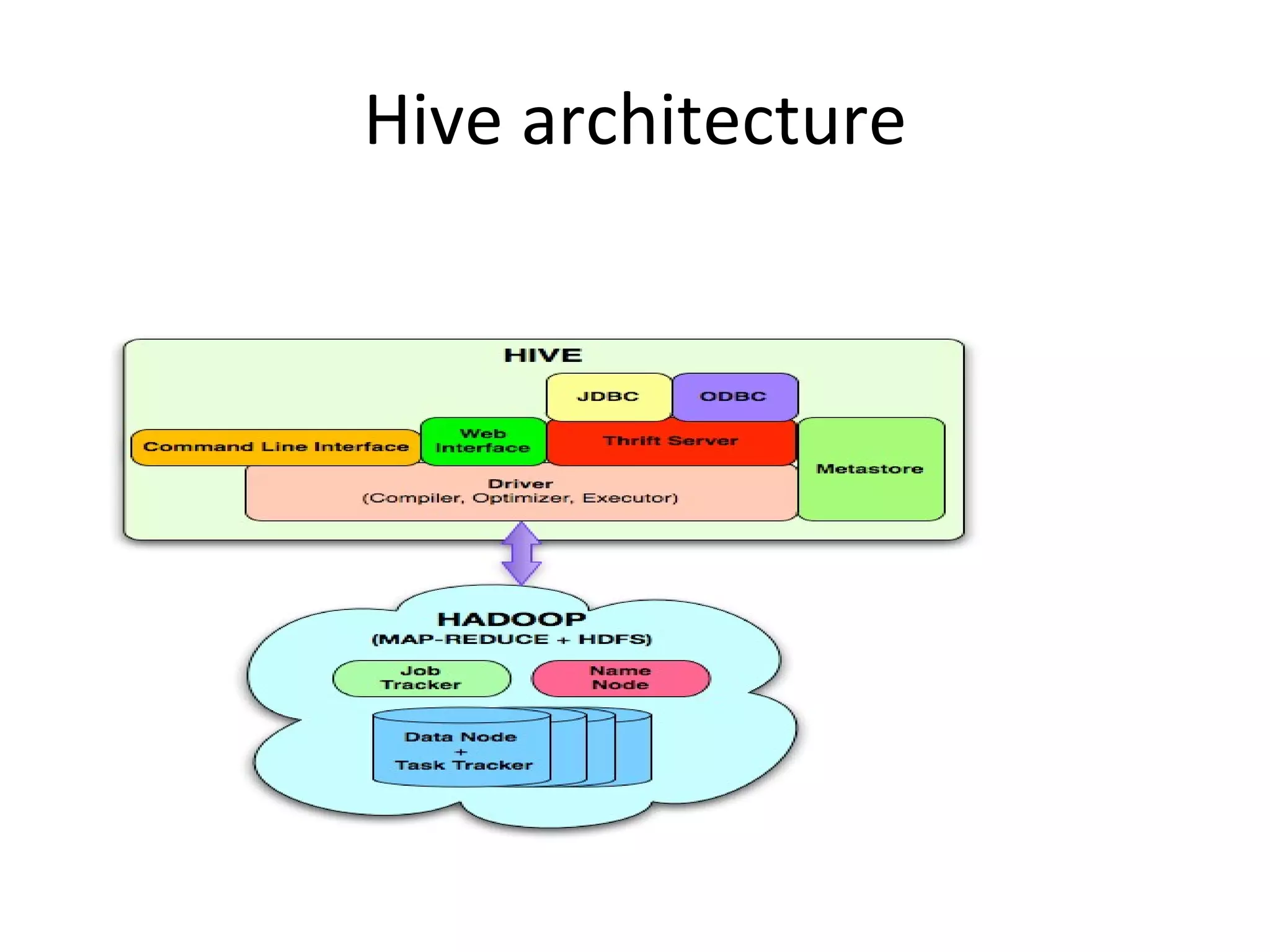
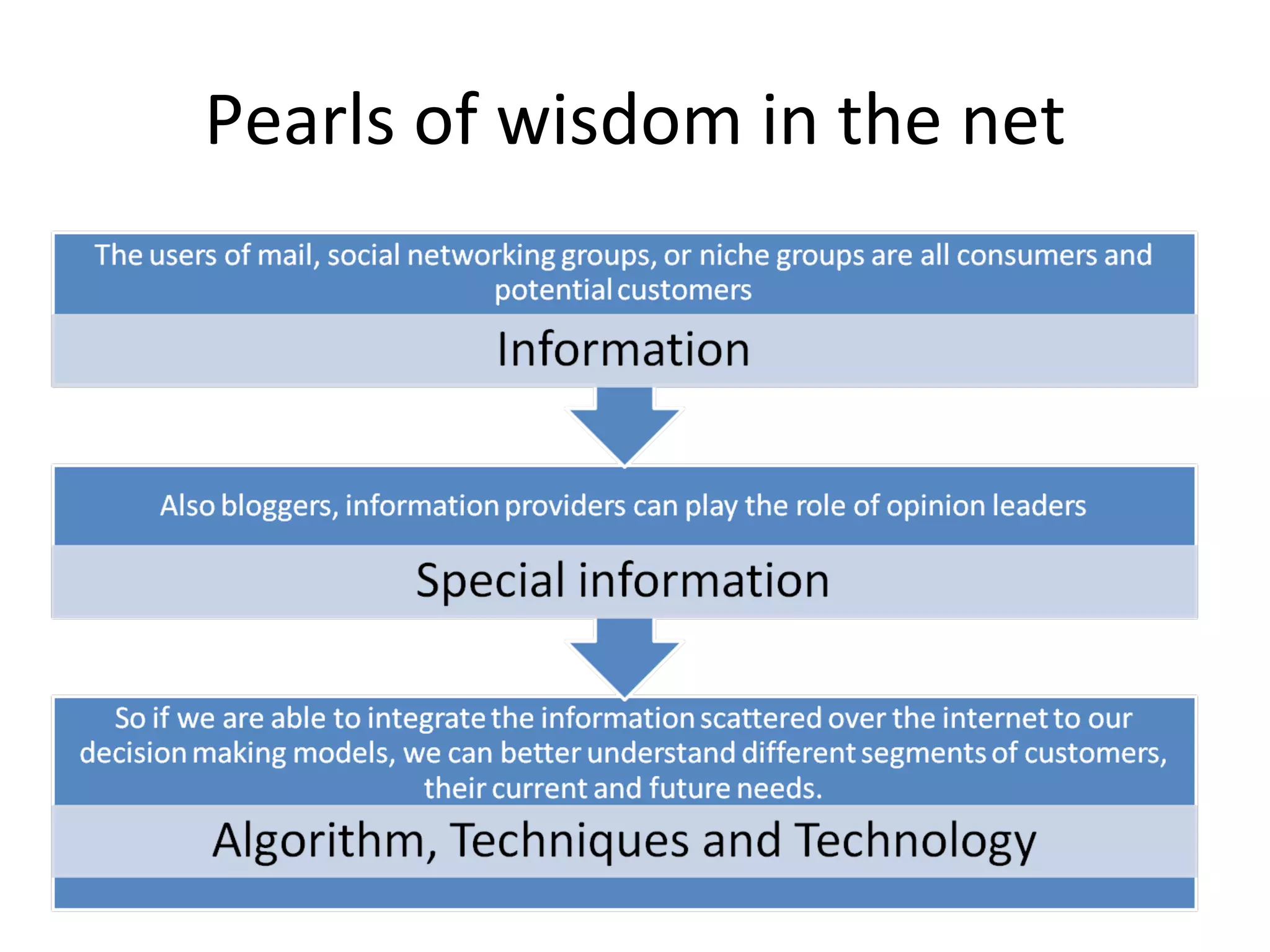
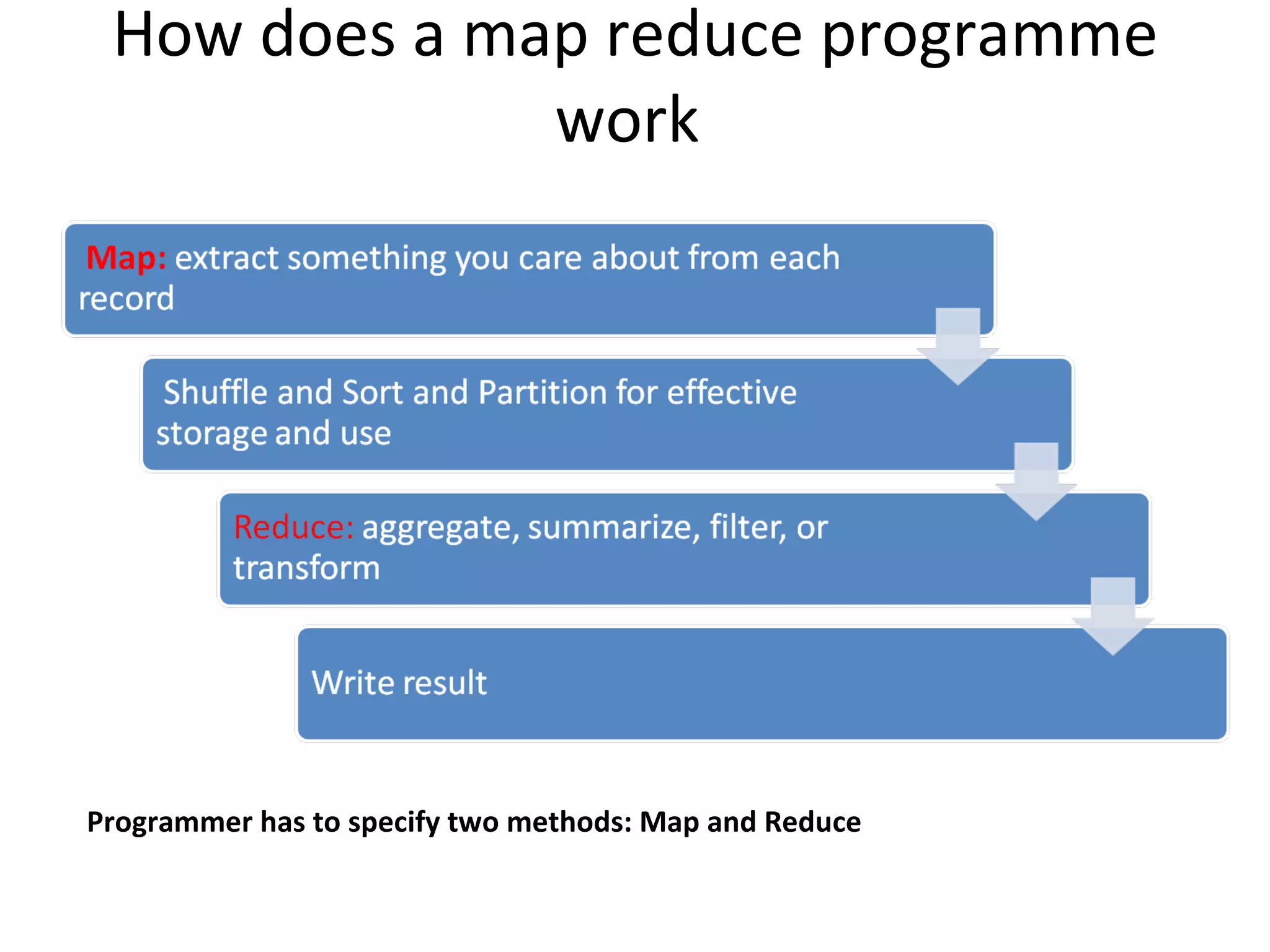
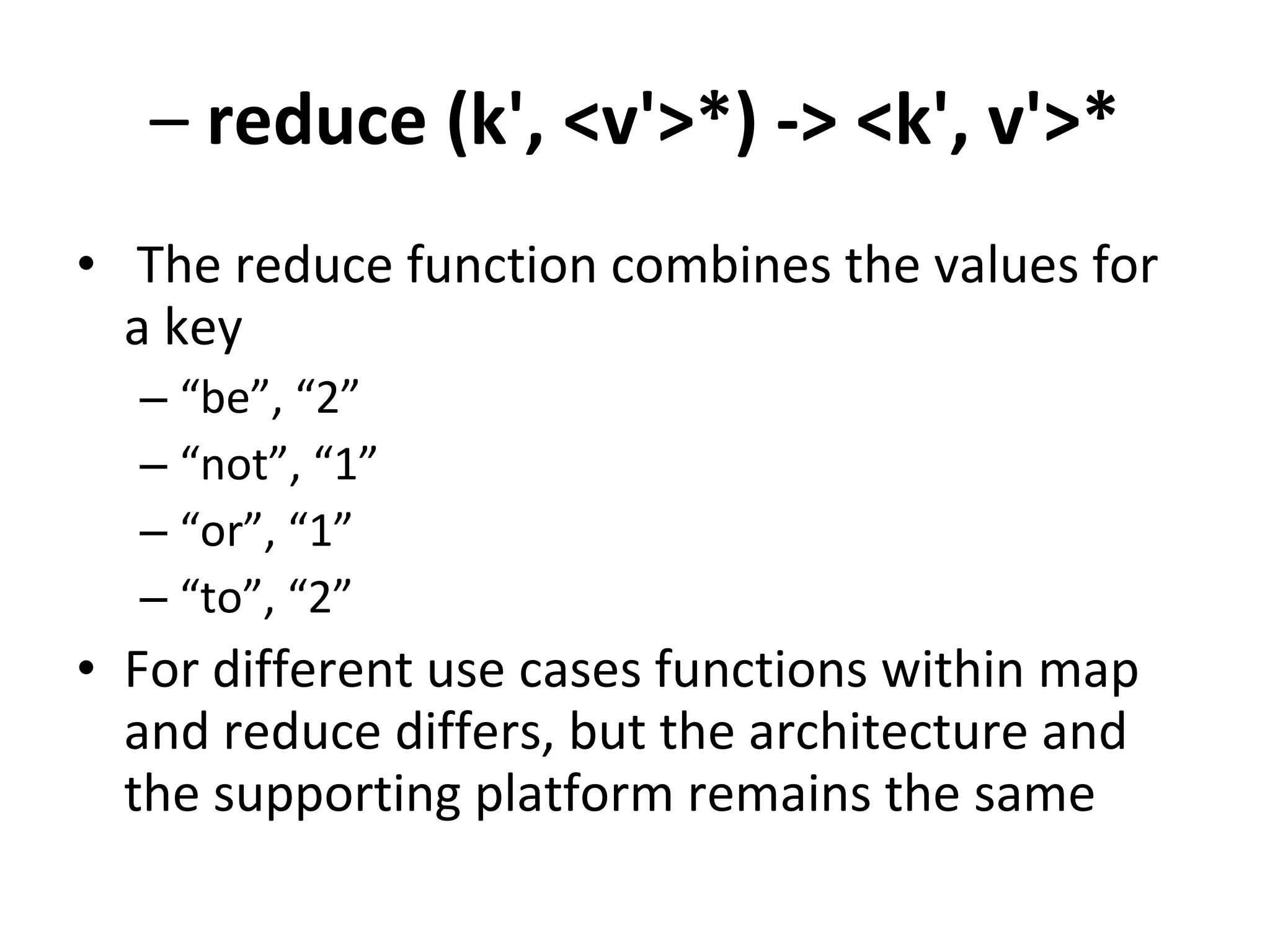
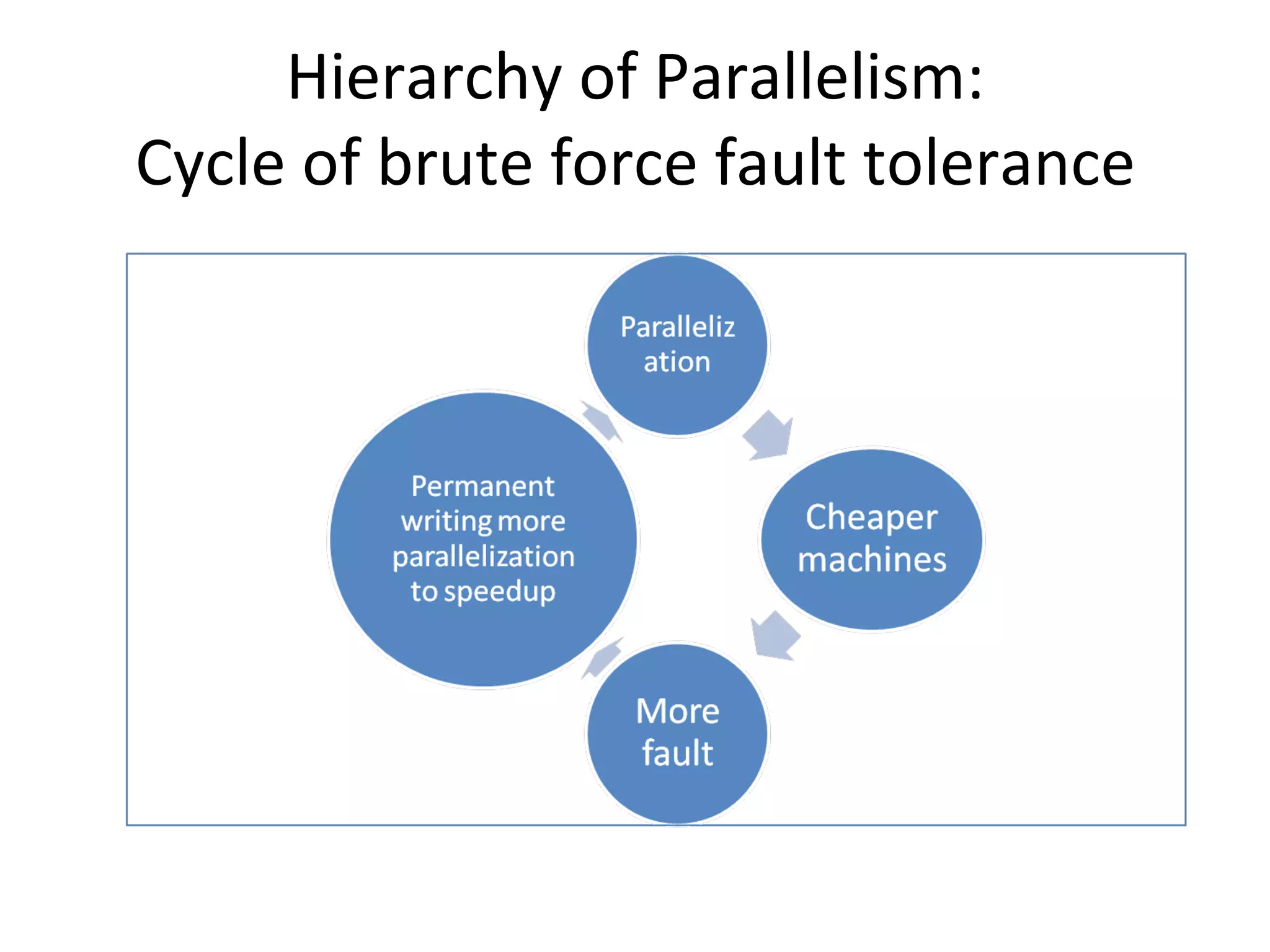
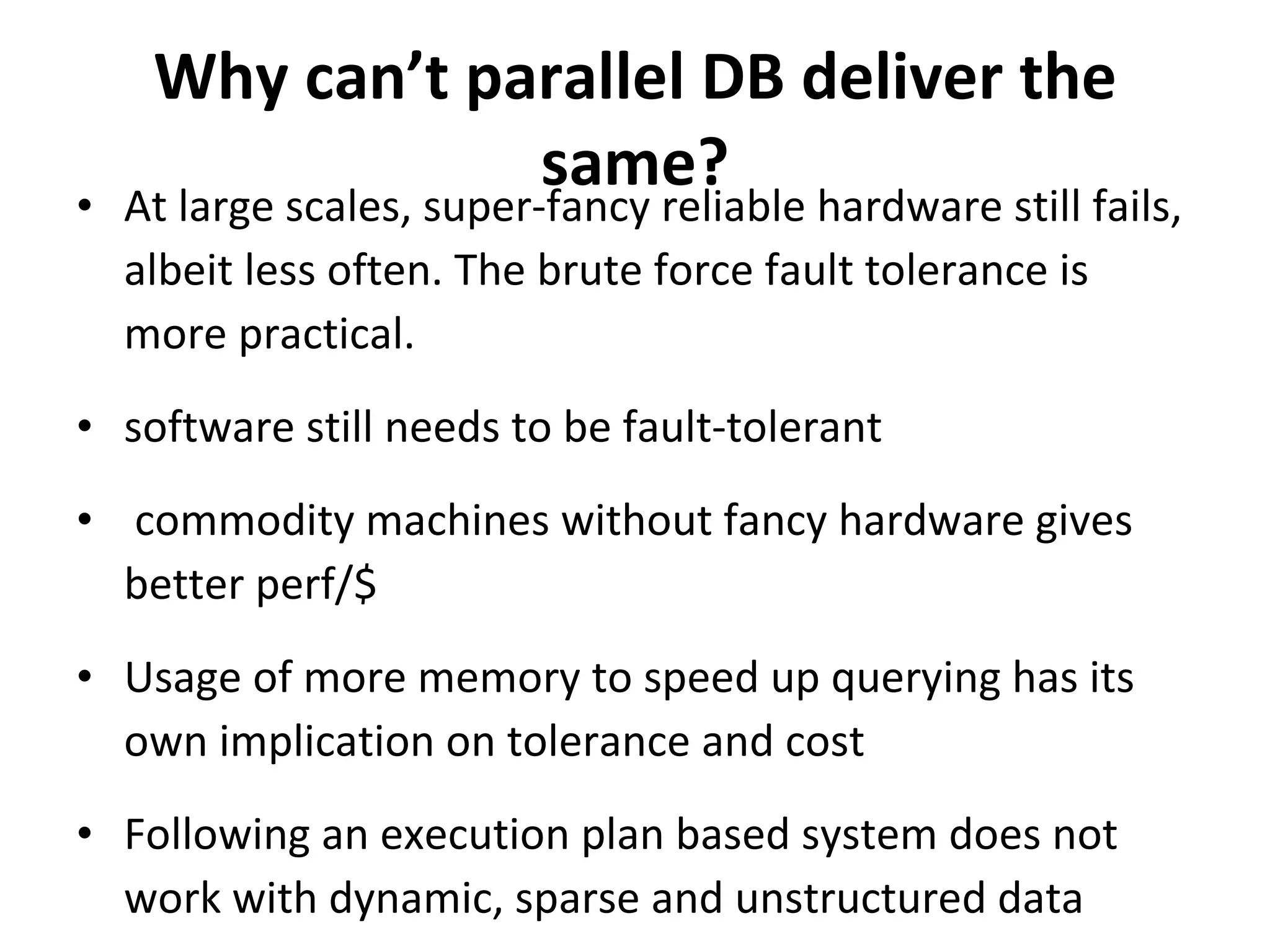
The document discusses map reduce and how it can be used for recommendation systems. It describes how map reduce works by mapping data into key-value pairs and then reducing them. This allows large amounts of sparse, unstructured data to be processed efficiently across many machines. It then gives an example of how map reduce could be used to build a sequential web access-based recommendation system by mapping log data into a pattern tree that is continuously updated and used to provide recommendations.





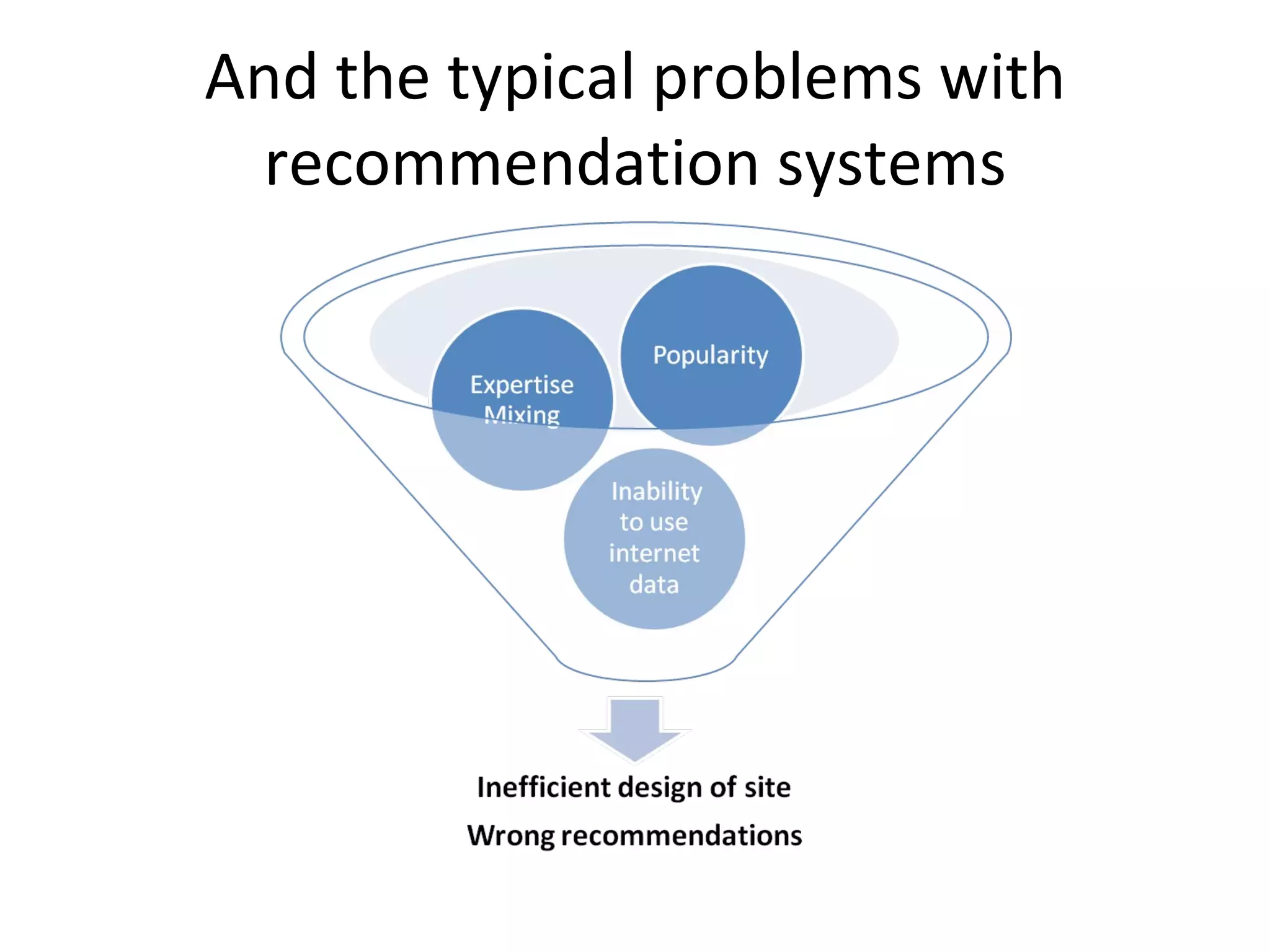









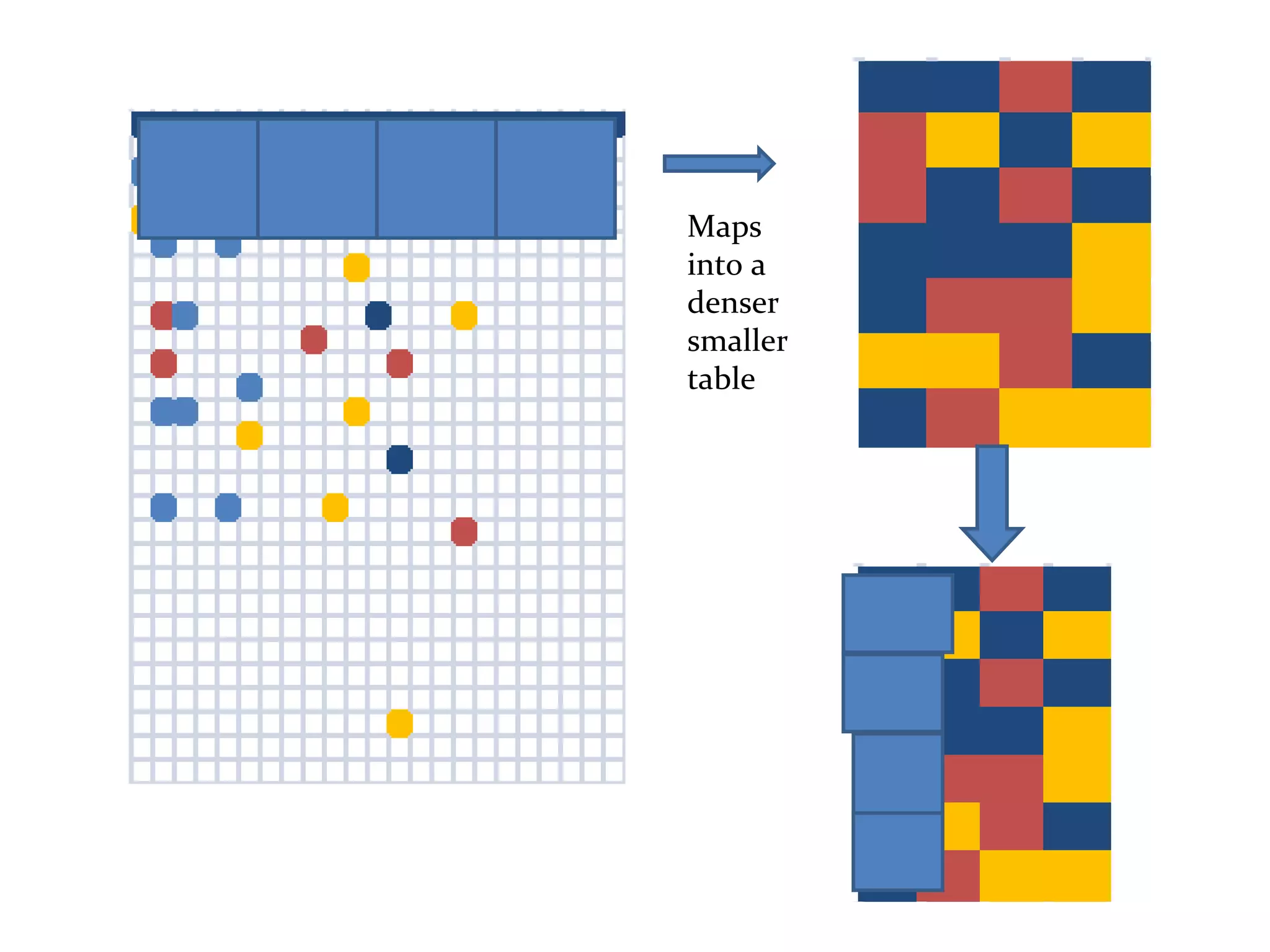


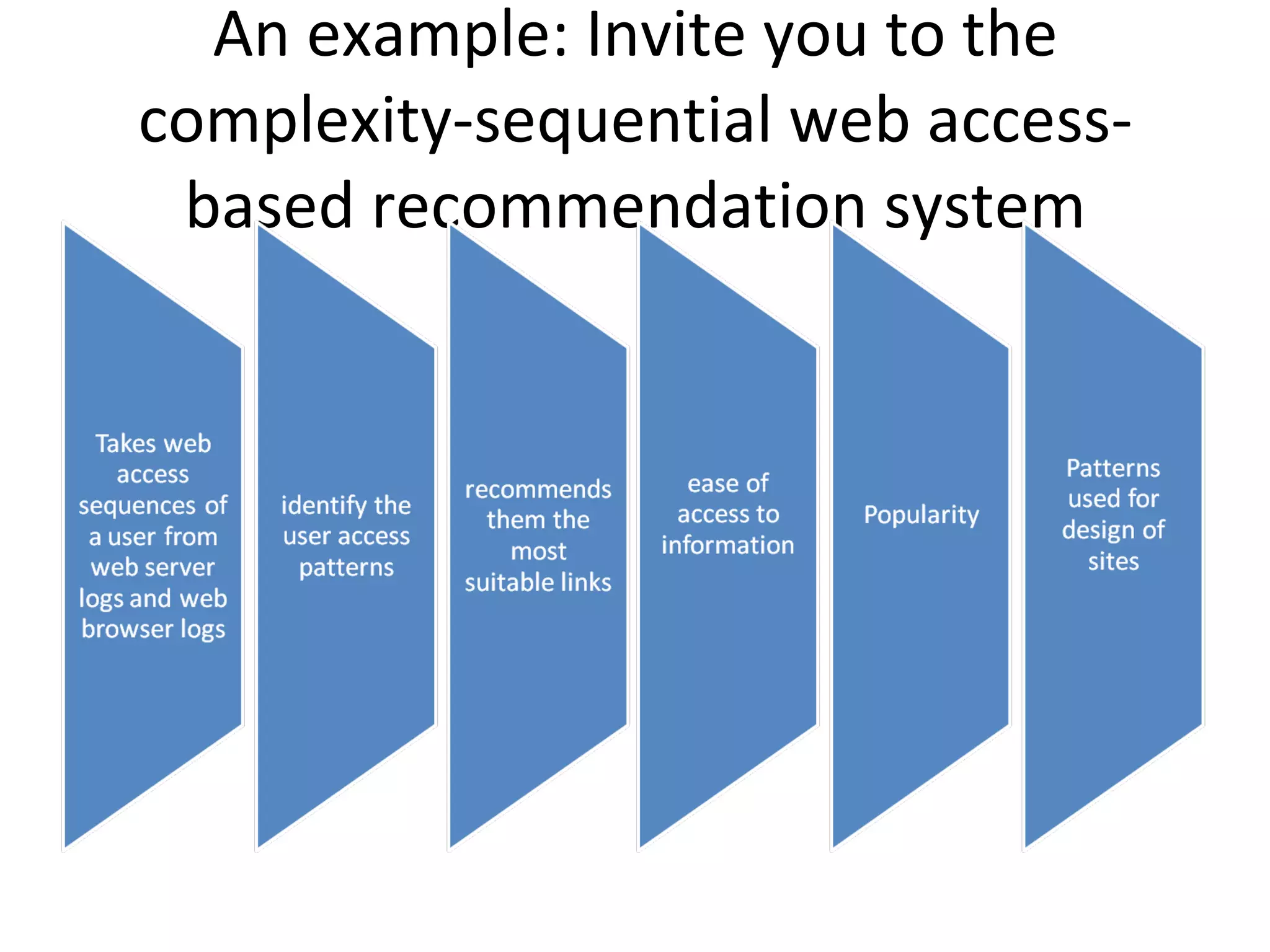
![sequential web access-based recommendation system It goes through web server logs, mines the pattern in the sequence and then creates a pattern tree. And the pattern tree is continuously modified taking the data from different servers.[Zhou et al]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrbiamrp-110503090207-phpapp02/75/Mr-bi-amrp-30-2048.jpg)