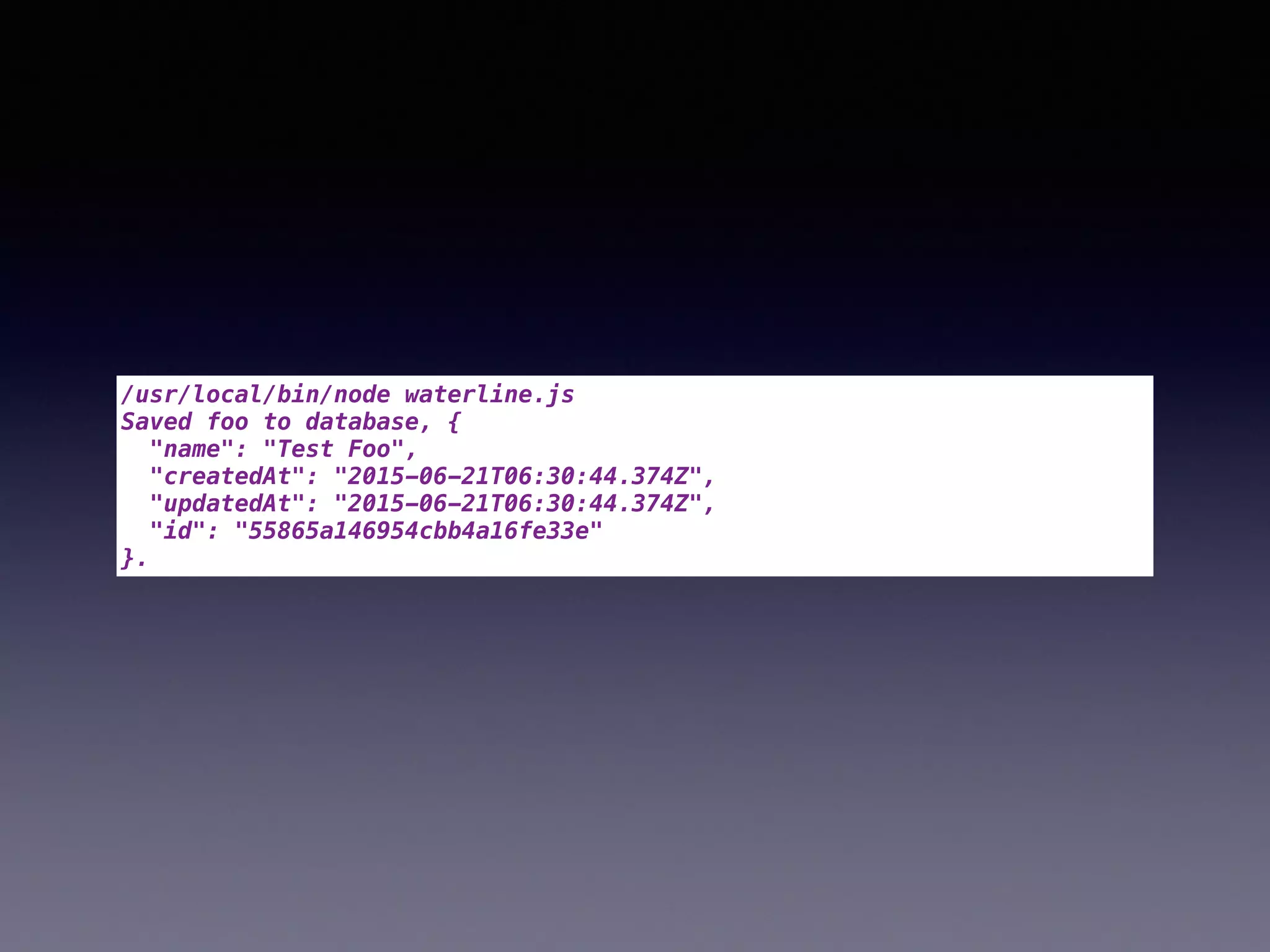
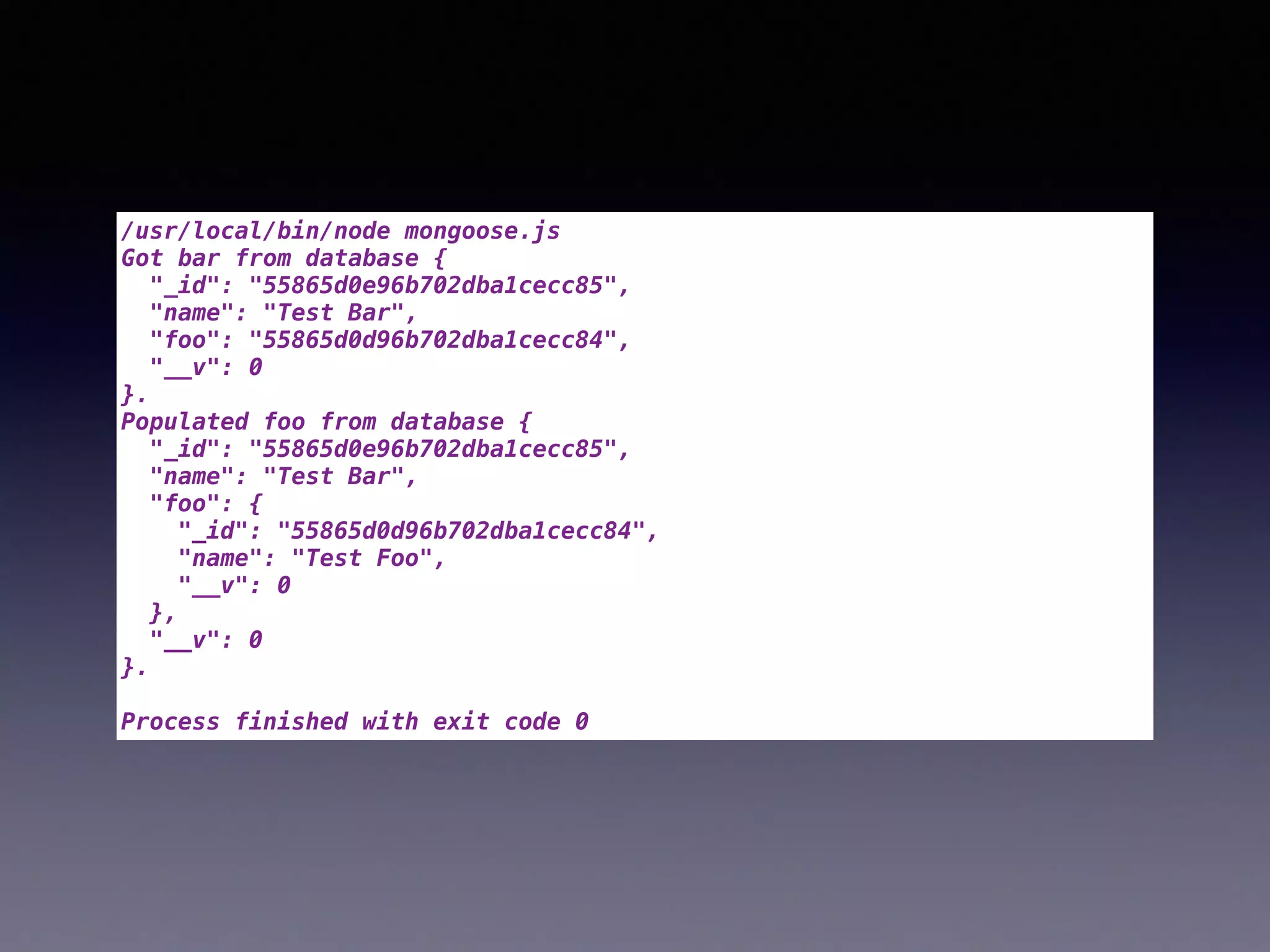
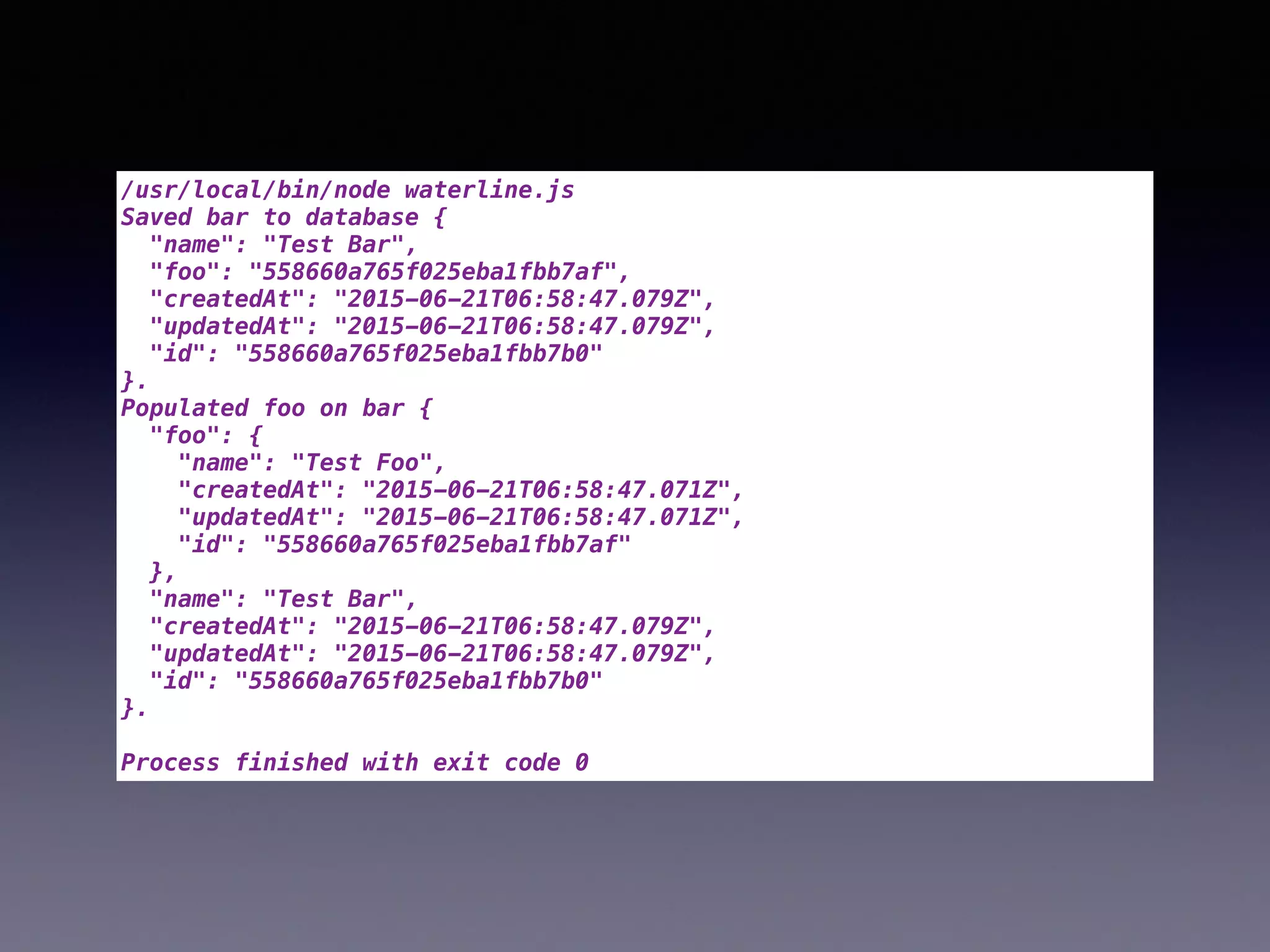
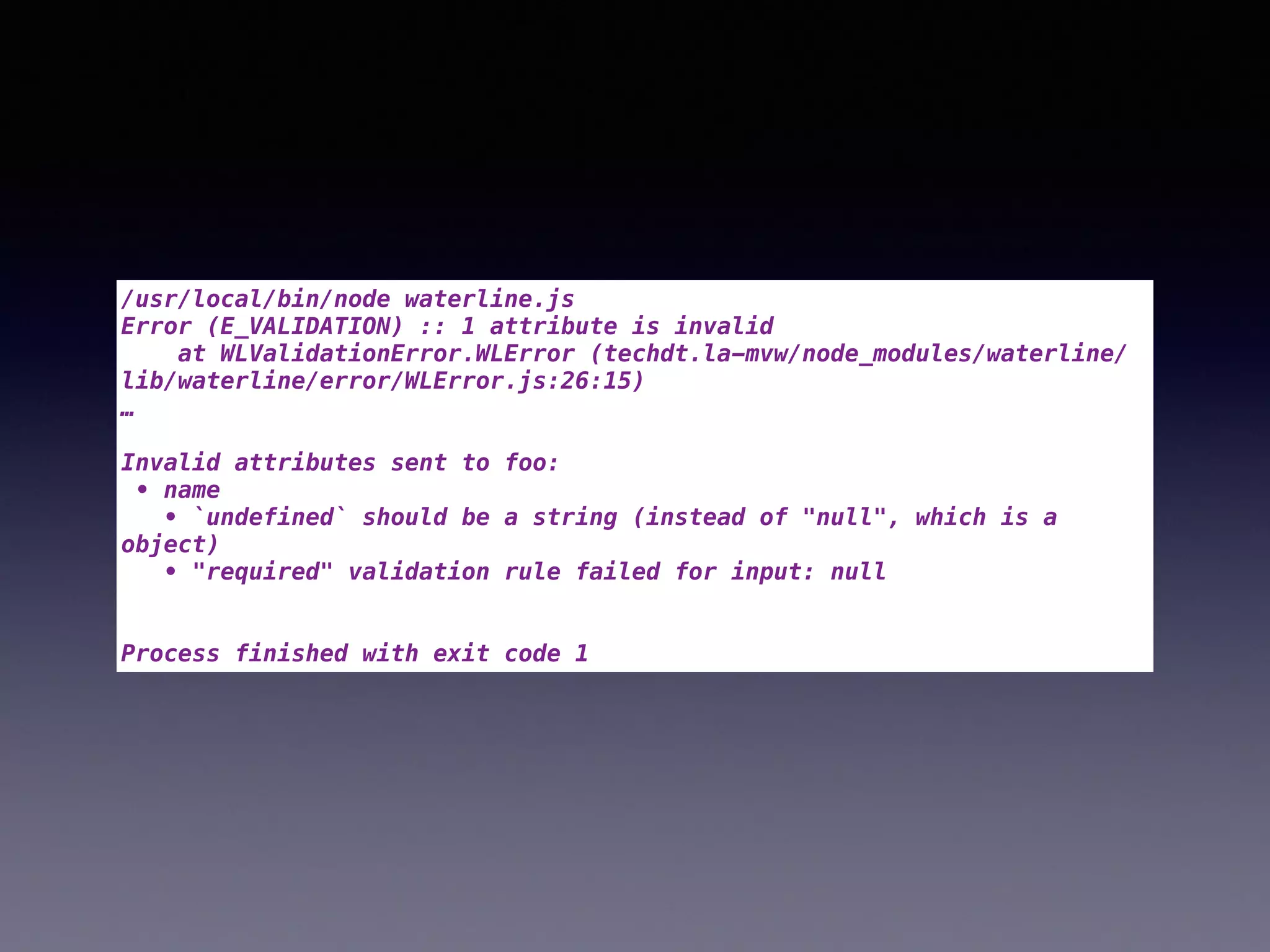
The document compares two JavaScript ORMs: Mongoose and Waterline, focusing on their setup, constraints, visibility, and associations. It outlines code examples demonstrating how both ORMs manage data, error handling, and property visibility. The conclusion highlights that Mongoose is better for concurrent updates, while Waterline offers a more modern framework with less complexity.








![/usr/local/bin/node mongoose.js
{ [ValidationError: Foo validation failed]
message: 'Foo validation failed',
name: 'ValidationError',
errors:
{ name:
{ [ValidatorError: Path `name` is required.]
properties: [Object],
message: 'Path `name` is required.',
name: 'ValidatorError',
kind: 'required',
path: 'name',
value: undefined } } }
Process finished with exit code 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e80jkaadrk2ratketi5s-signature-565c82d08d36faba5e7c1e32b0cc8cfe7cb36cf212b43e8d9af67a3c2001ff7d-poli-150724040549-lva1-app6892/75/Big-Data-Day-LA-2015-Mongoose-v-s-Waterline-Battle-of-the-ORM-by-Tim-Fulmer-of-HopSkipDrive-9-2048.jpg)


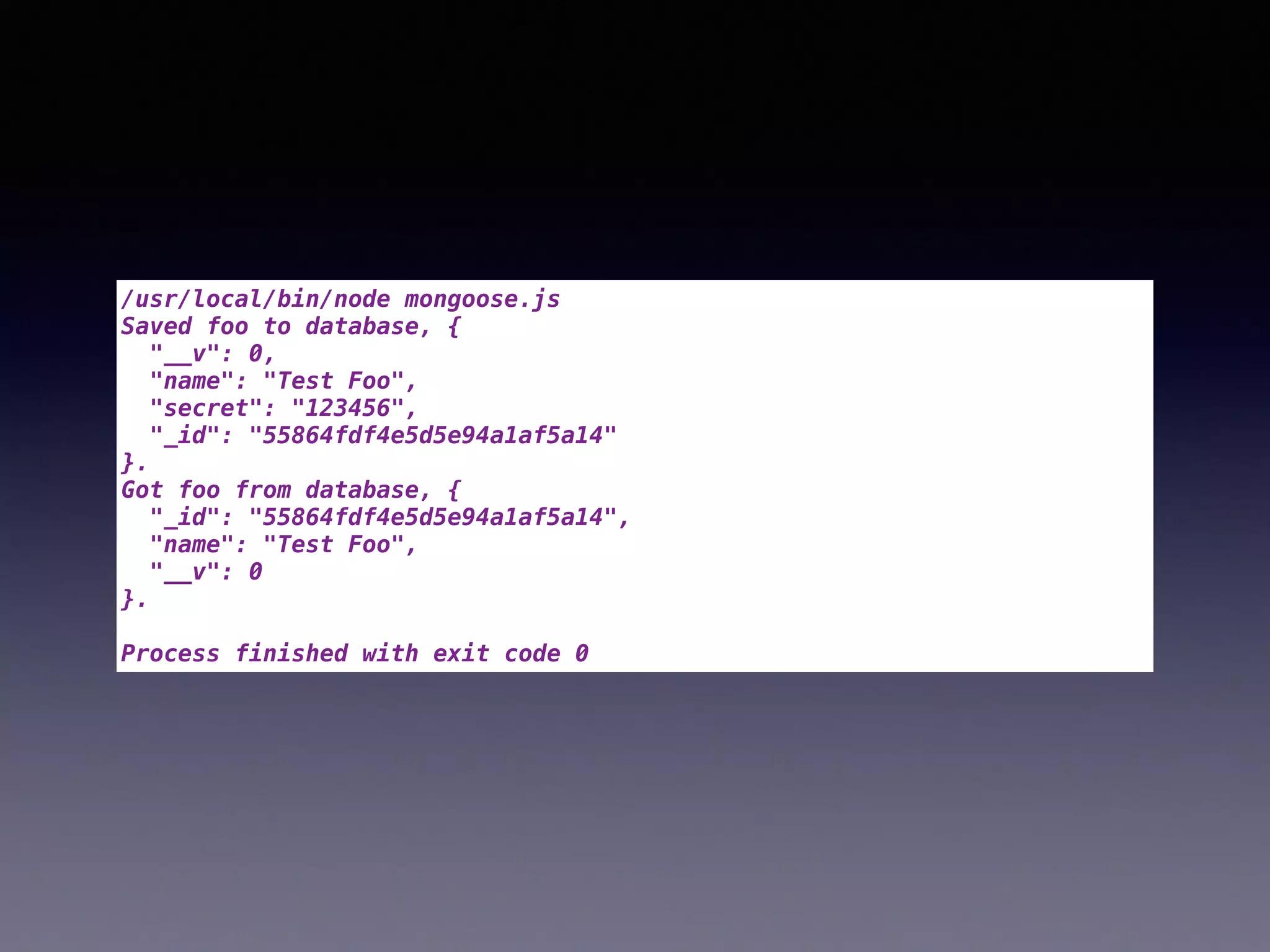
![Mongoose Visibility [1]
Foo=mongoose.model('Foo',{
name:{type:String,required:true},
secret:{type:String,select:false}
});
…
function testSecret(){
var foo=new Foo({name:'Test Foo',secret:'123456'});
foo.save(function(err,foo){
if(err) return console.log(err);
console.log(
'Saved foo to database, %s.',JSON.stringify(foo,null,2));
Foo.findOne({_id:foo._id})
.exec(function(err,foo){
if(err) return console.log(err);
if(!foo) console.log(
'Mongoose returns undefined when findOne returns nothing.');
console.log(
'Got foo from database, %s.',JSON.stringify(foo,null,2));
process.exit(0);
});
})
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e80jkaadrk2ratketi5s-signature-565c82d08d36faba5e7c1e32b0cc8cfe7cb36cf212b43e8d9af67a3c2001ff7d-poli-150724040549-lva1-app6892/75/Big-Data-Day-LA-2015-Mongoose-v-s-Waterline-Battle-of-the-ORM-by-Tim-Fulmer-of-HopSkipDrive-13-2048.jpg)
![Mongoose Visibility [2]
FooSchema=new mongoose.Schema({
name:{type:String,required:true},
secret:{type:String,select:false}
},{toJSON:{transform: function (doc,ret) {delete ret.secret;}}}
),
Foo=mongoose.model('Foo',FooSchema);
/usr/local/bin/node mongoose.js
Saved foo to database, {
"__v": 0,
"name": "Test Foo",
"_id": "558654d2945f15a1a1a2d840"
}.
Got foo from database, {
"_id": "558654d2945f15a1a1a2d840",
"name": "Test Foo",
"__v": 0
}.
Process finished with exit code 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e80jkaadrk2ratketi5s-signature-565c82d08d36faba5e7c1e32b0cc8cfe7cb36cf212b43e8d9af67a3c2001ff7d-poli-150724040549-lva1-app6892/75/Big-Data-Day-LA-2015-Mongoose-v-s-Waterline-Battle-of-the-ORM-by-Tim-Fulmer-of-HopSkipDrive-15-2048.jpg)