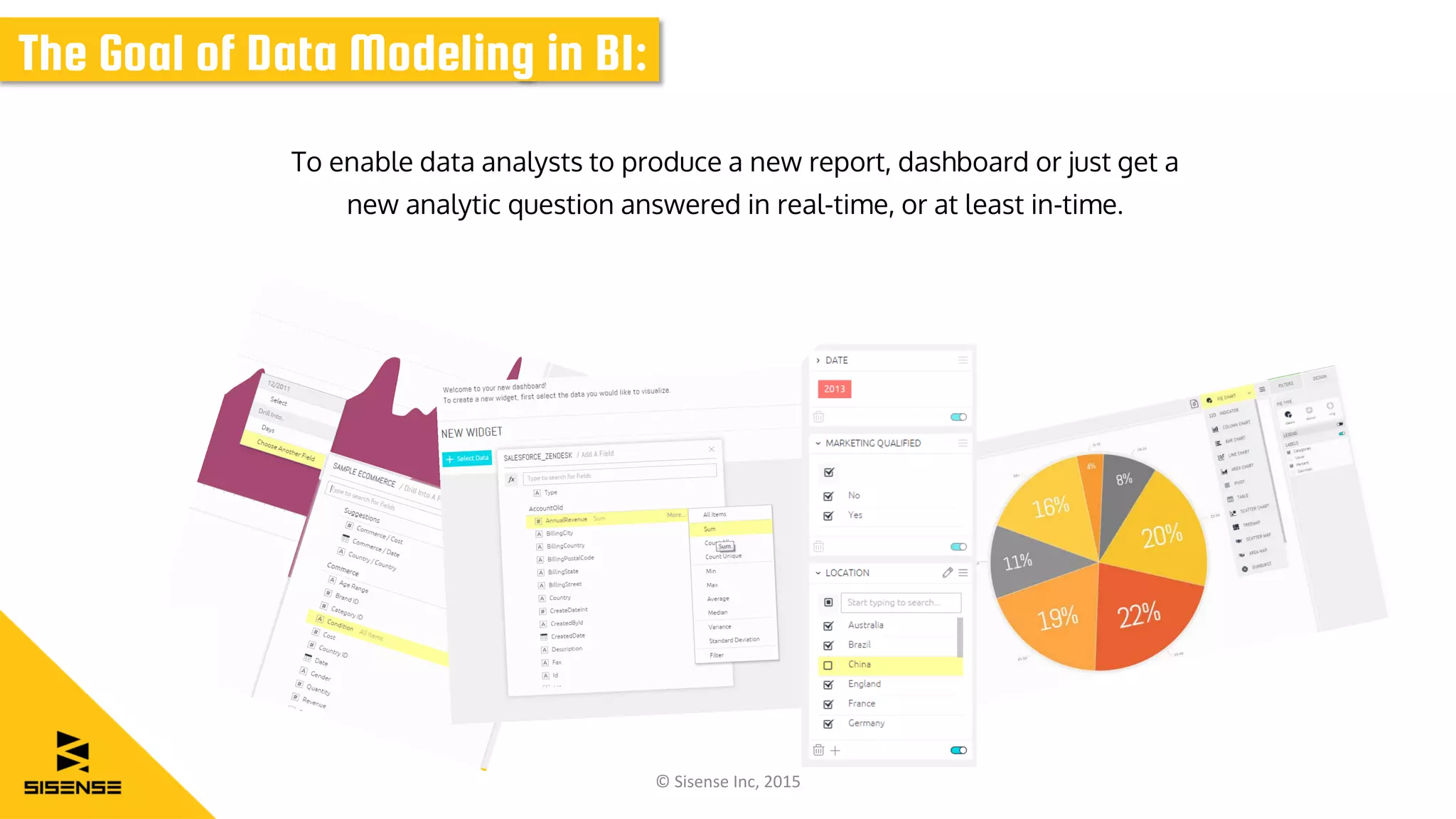
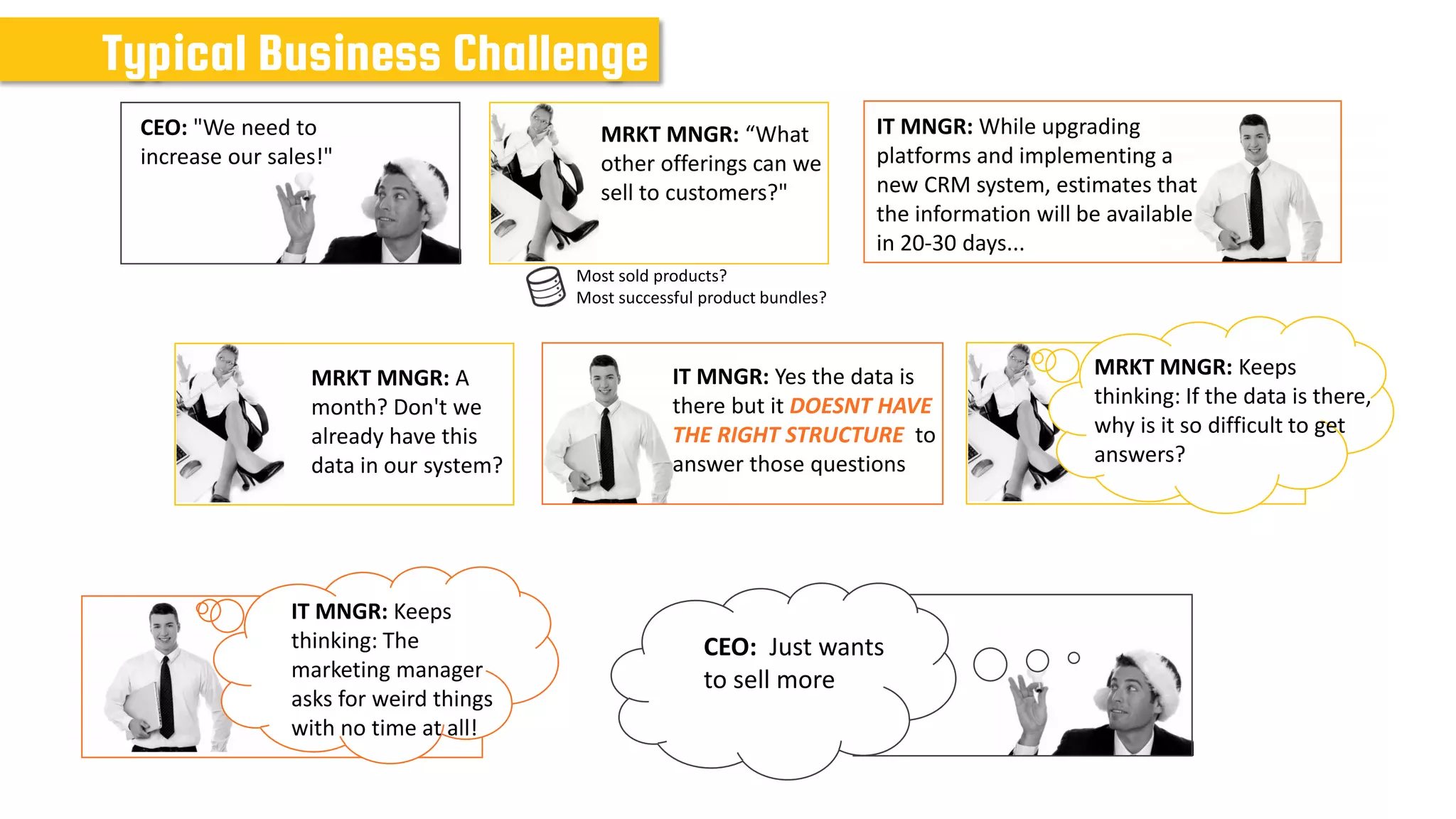
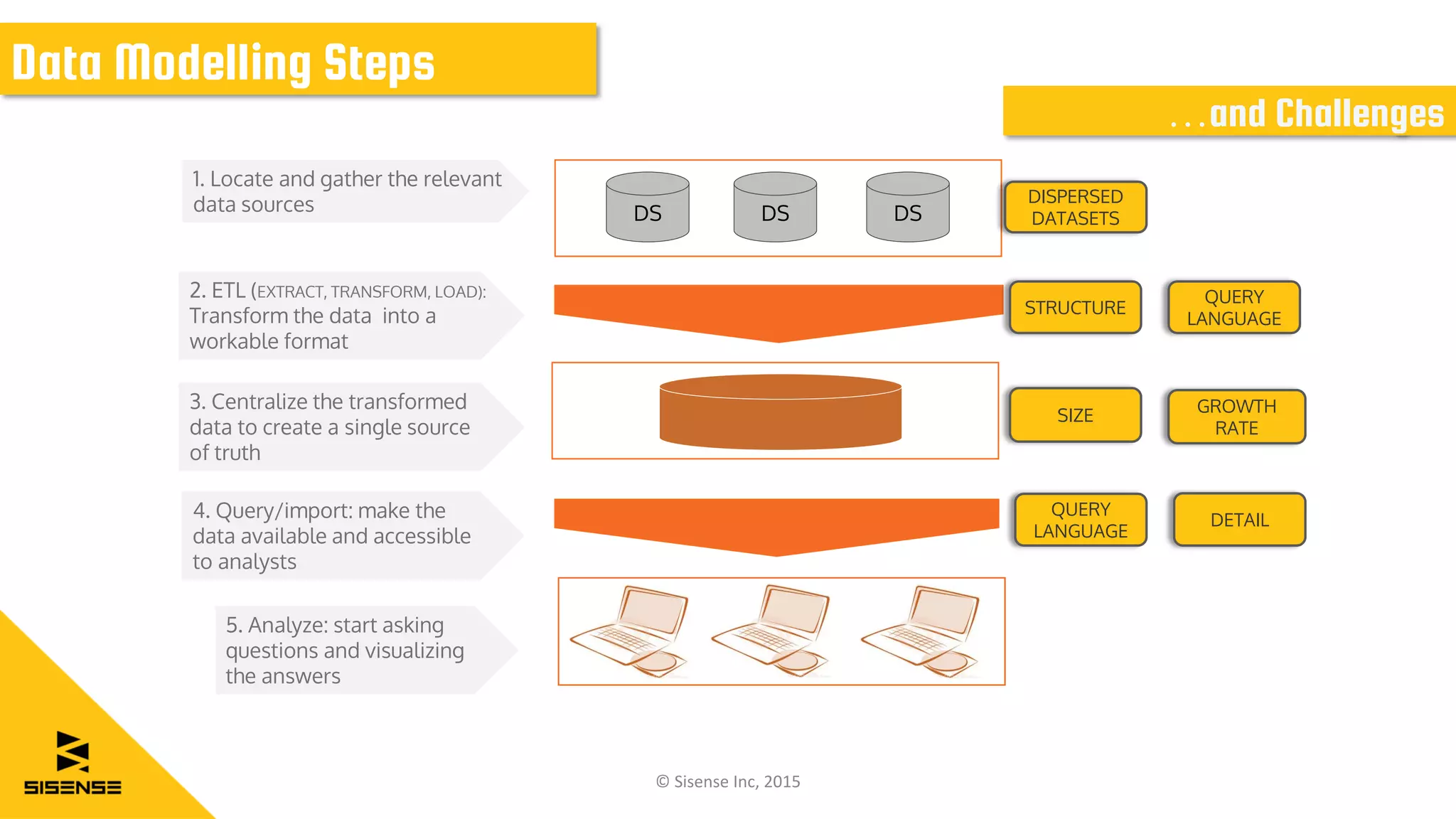
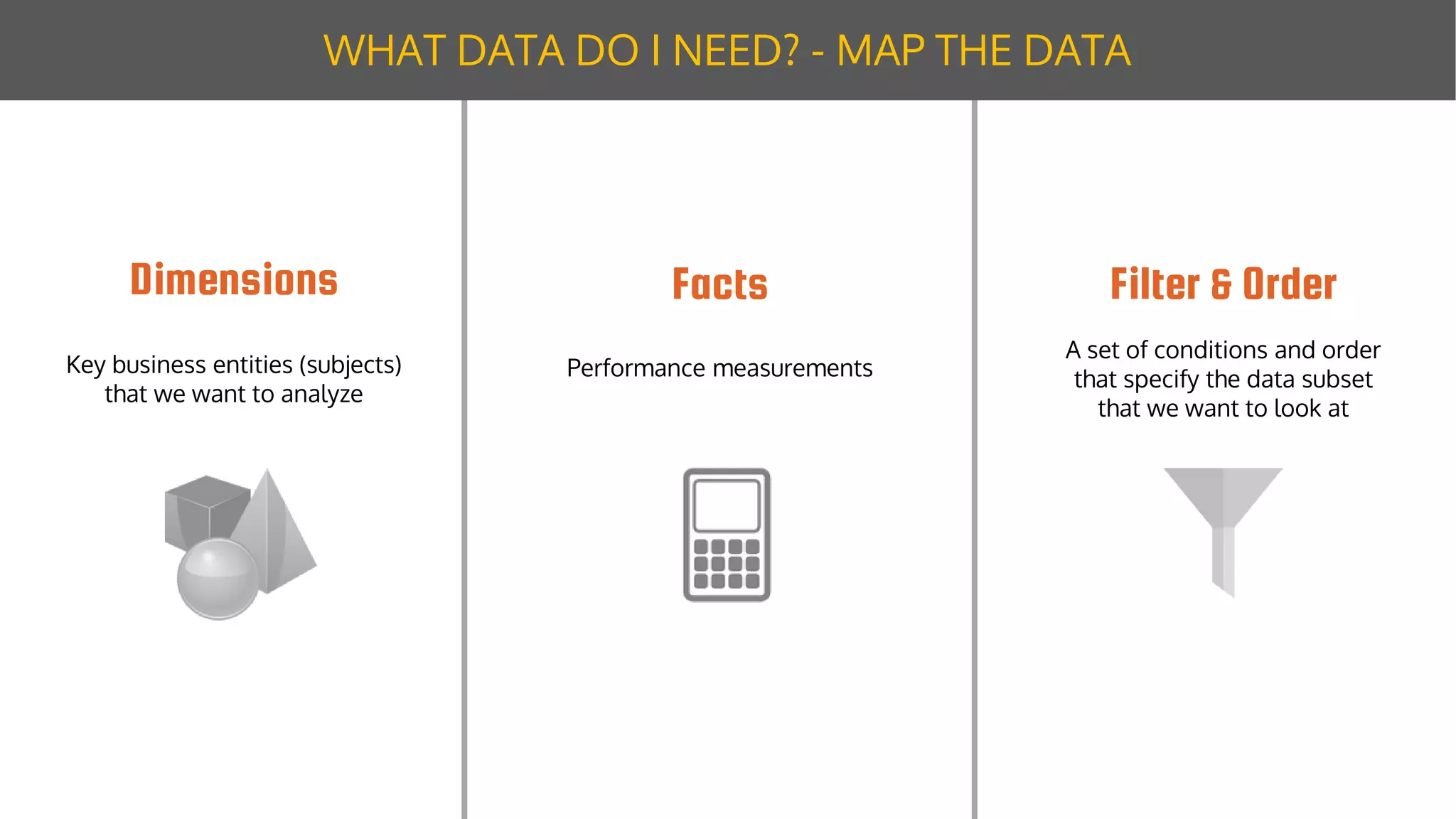
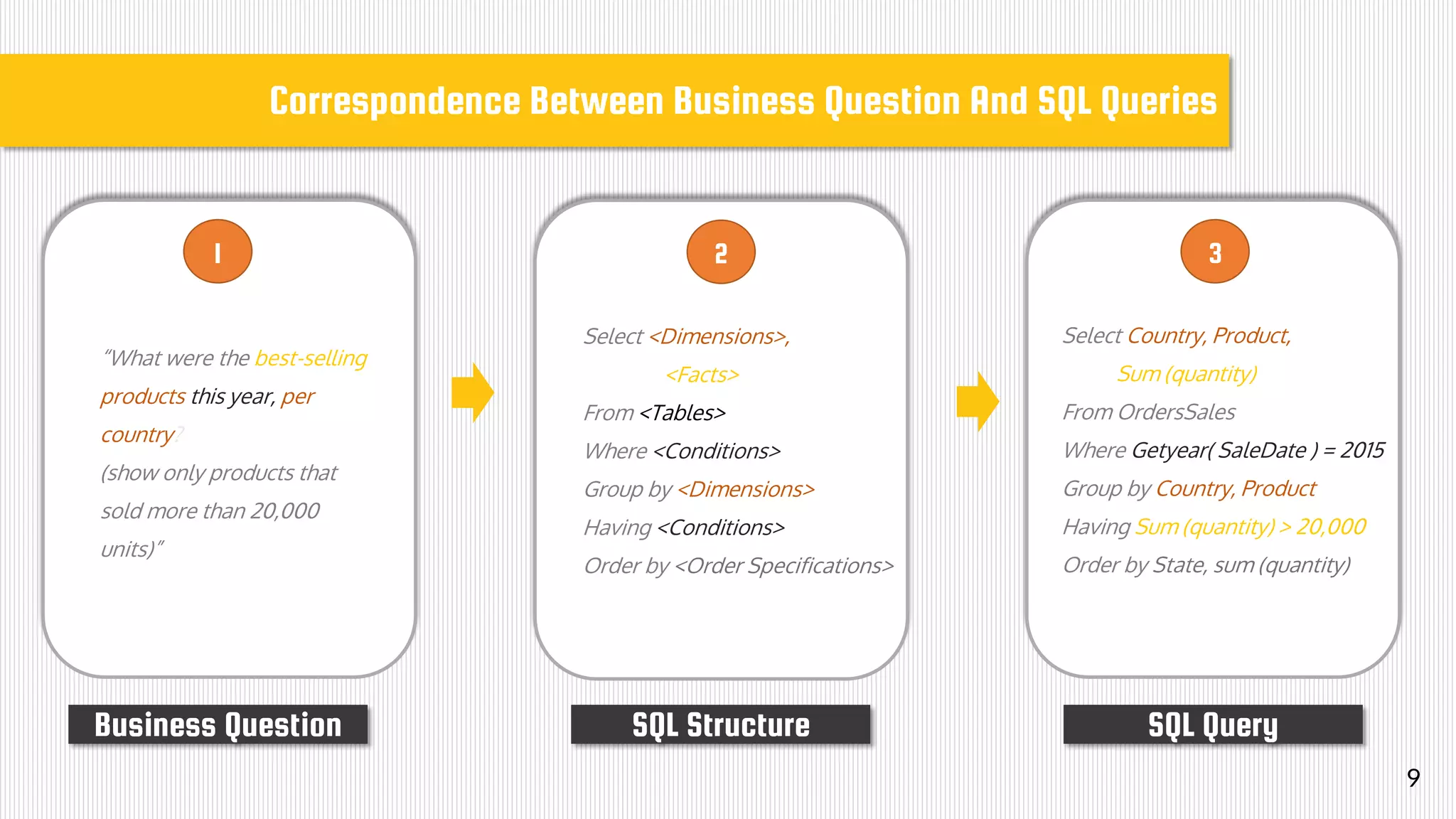
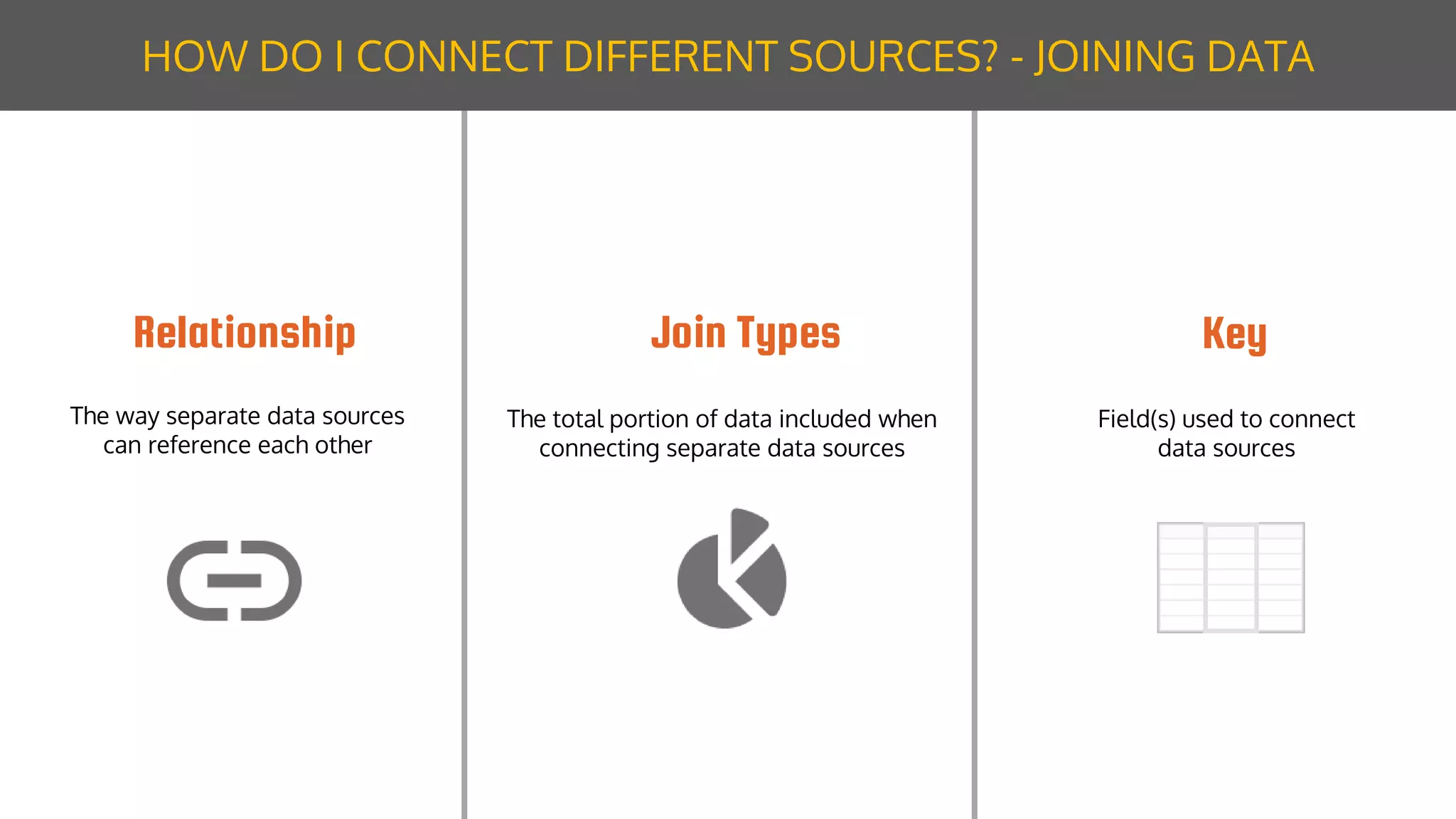
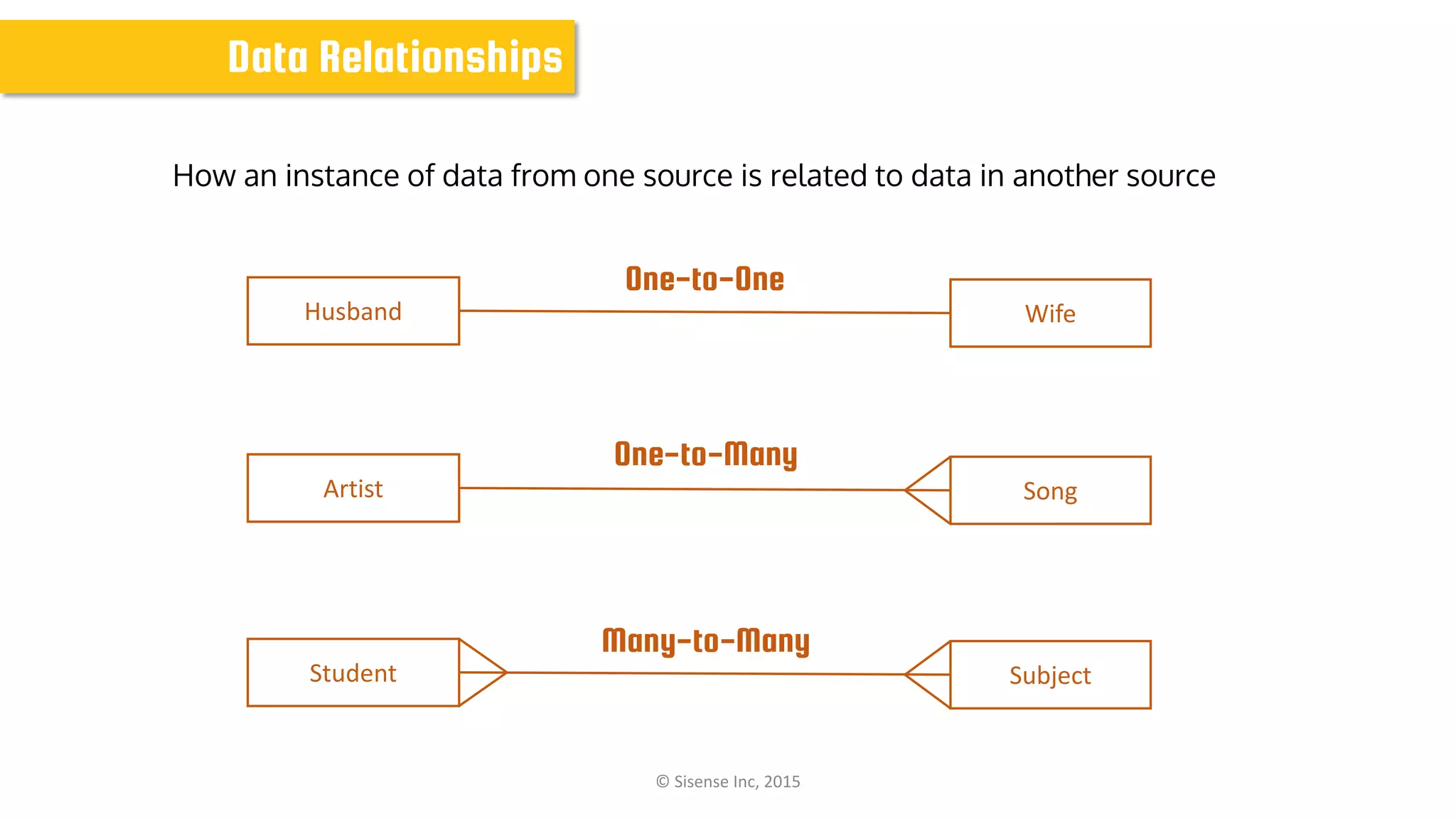
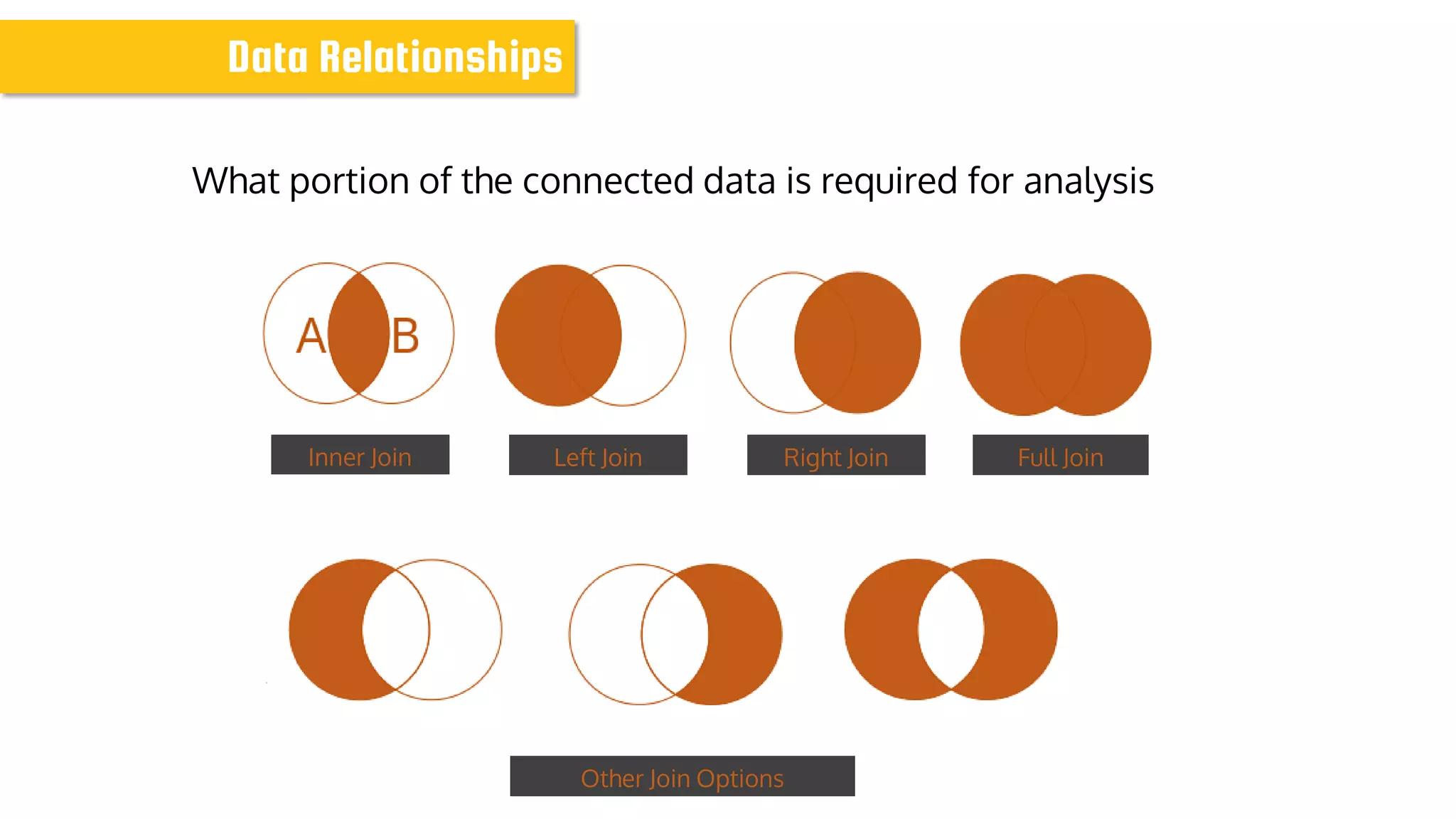
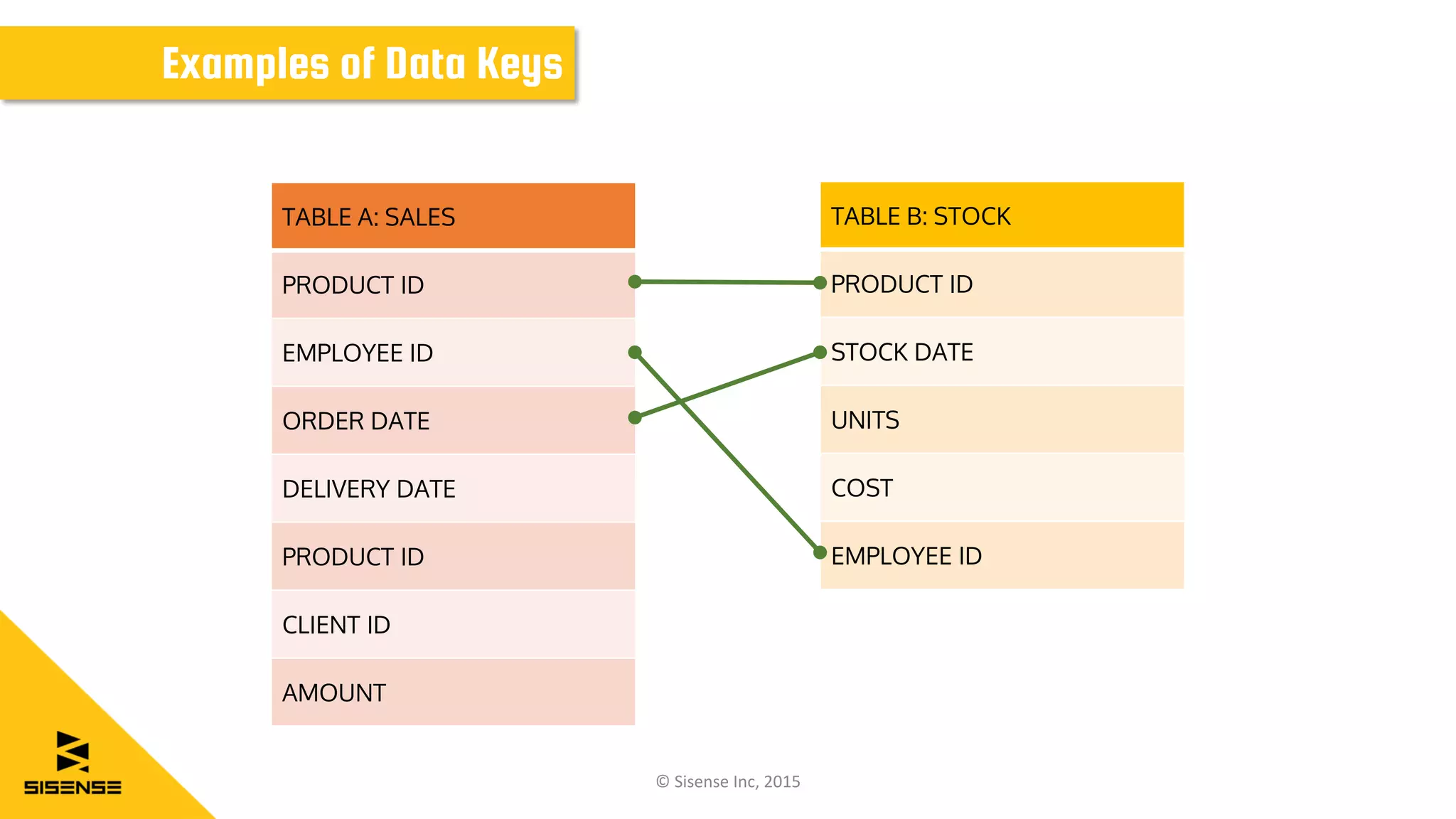
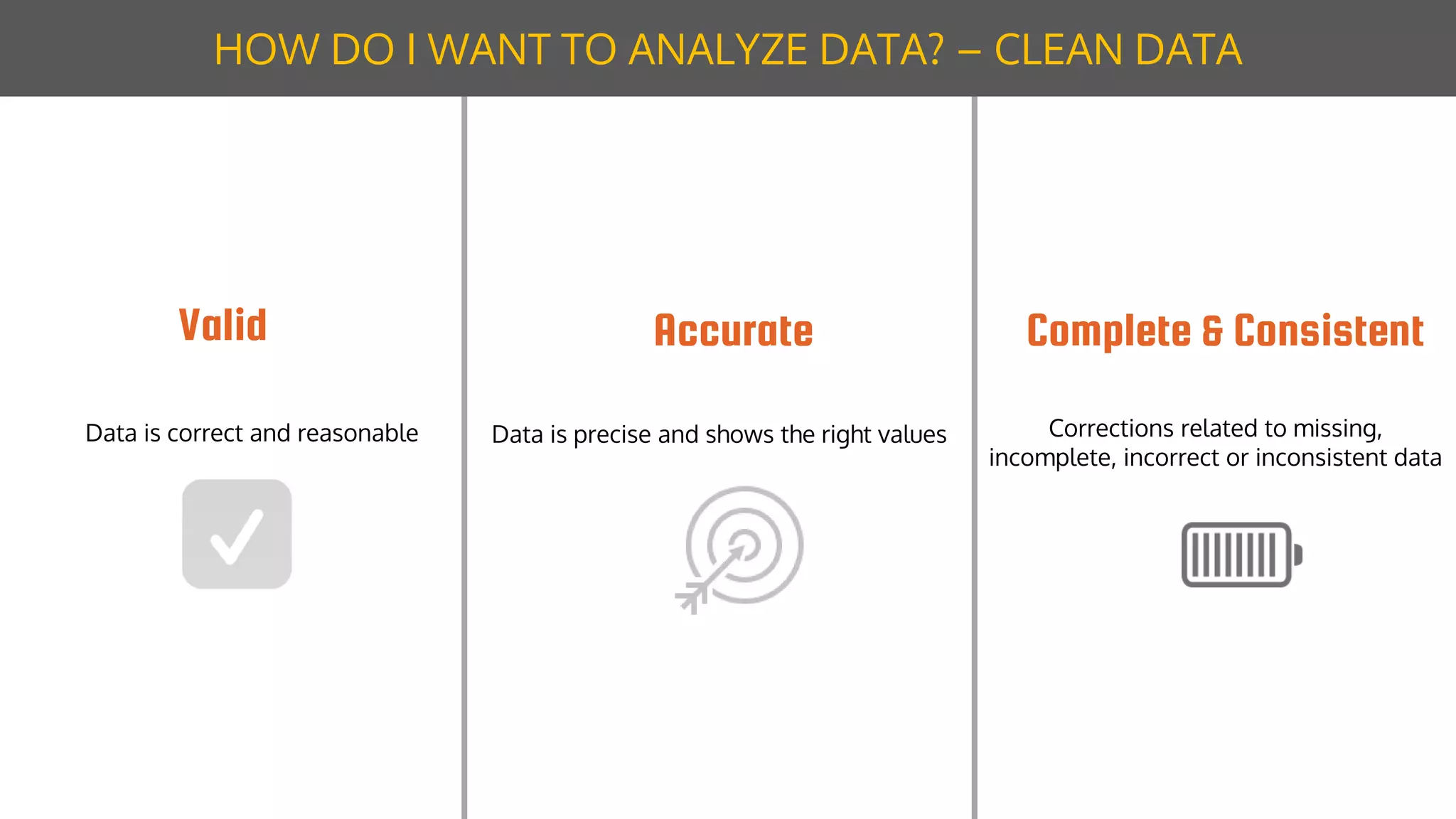
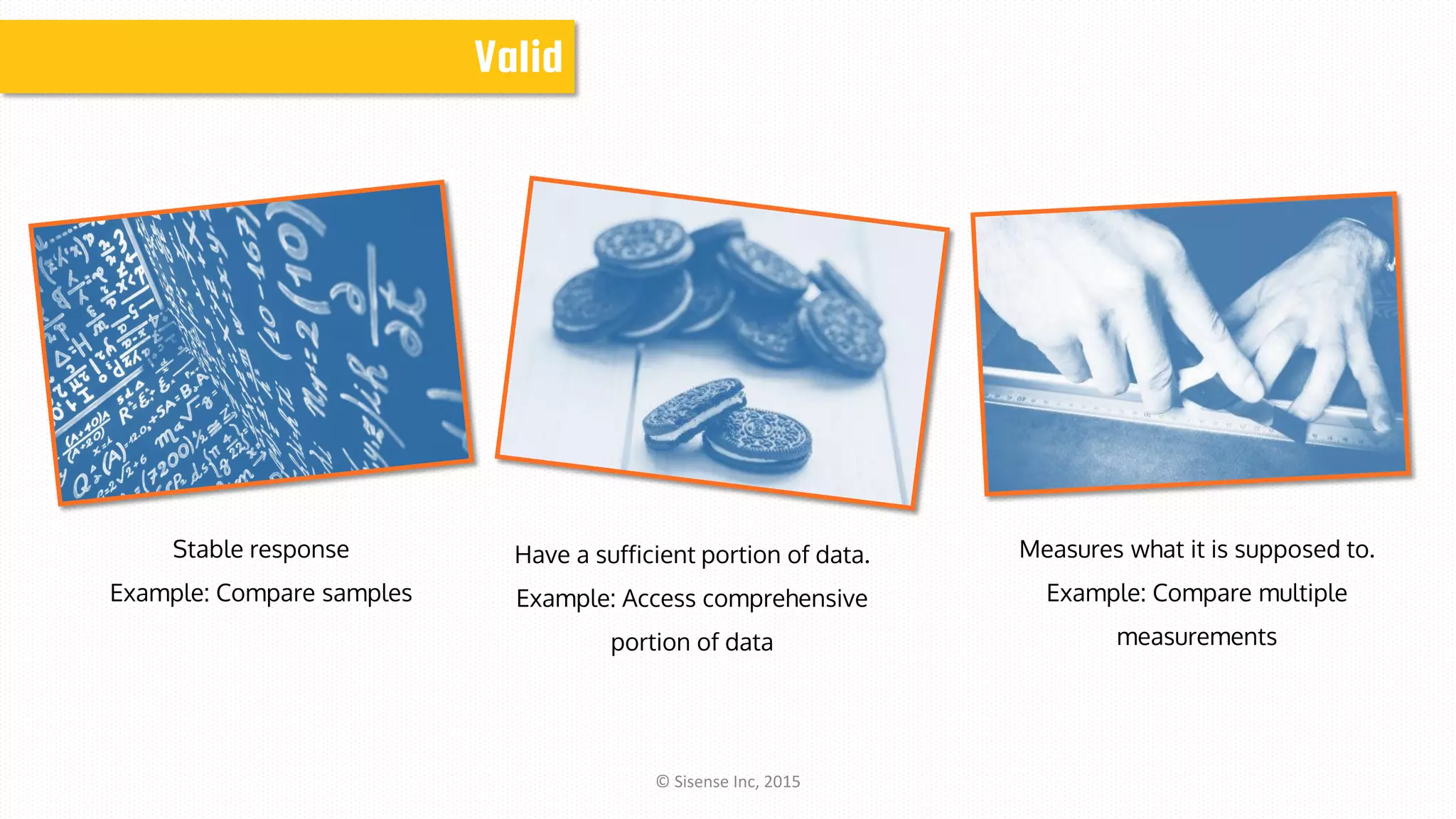
The document discusses data modeling for business intelligence, emphasizing the importance of accurate, up-to-date, and structured data for analytics. It outlines key steps in data modeling, including ETL processes, data centralization, and the relationship between business questions and SQL queries. Additionally, it highlights the significance of clean and consistent data for effective analysis and mentions Sisense as a tool for facilitating these processes.