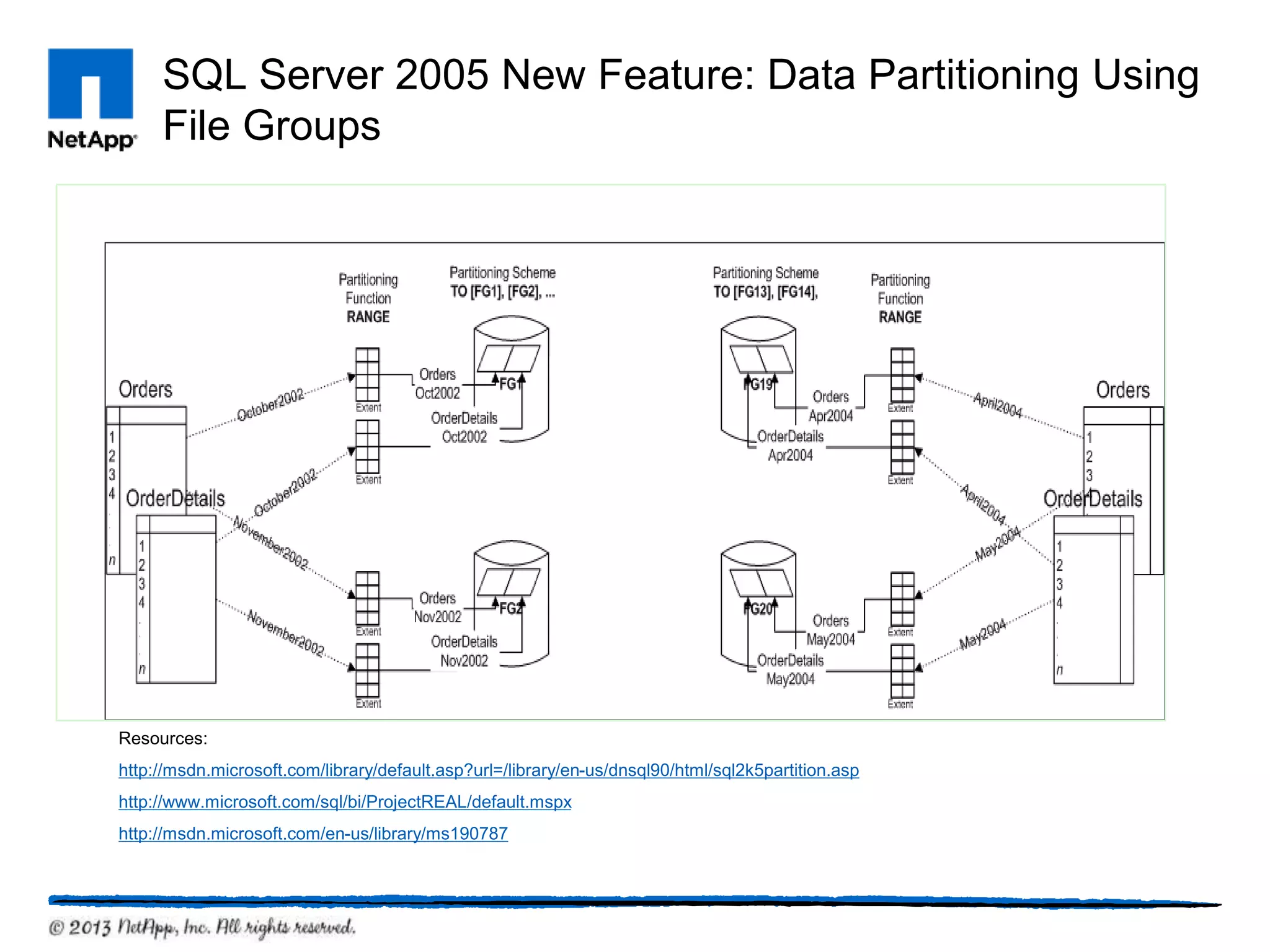
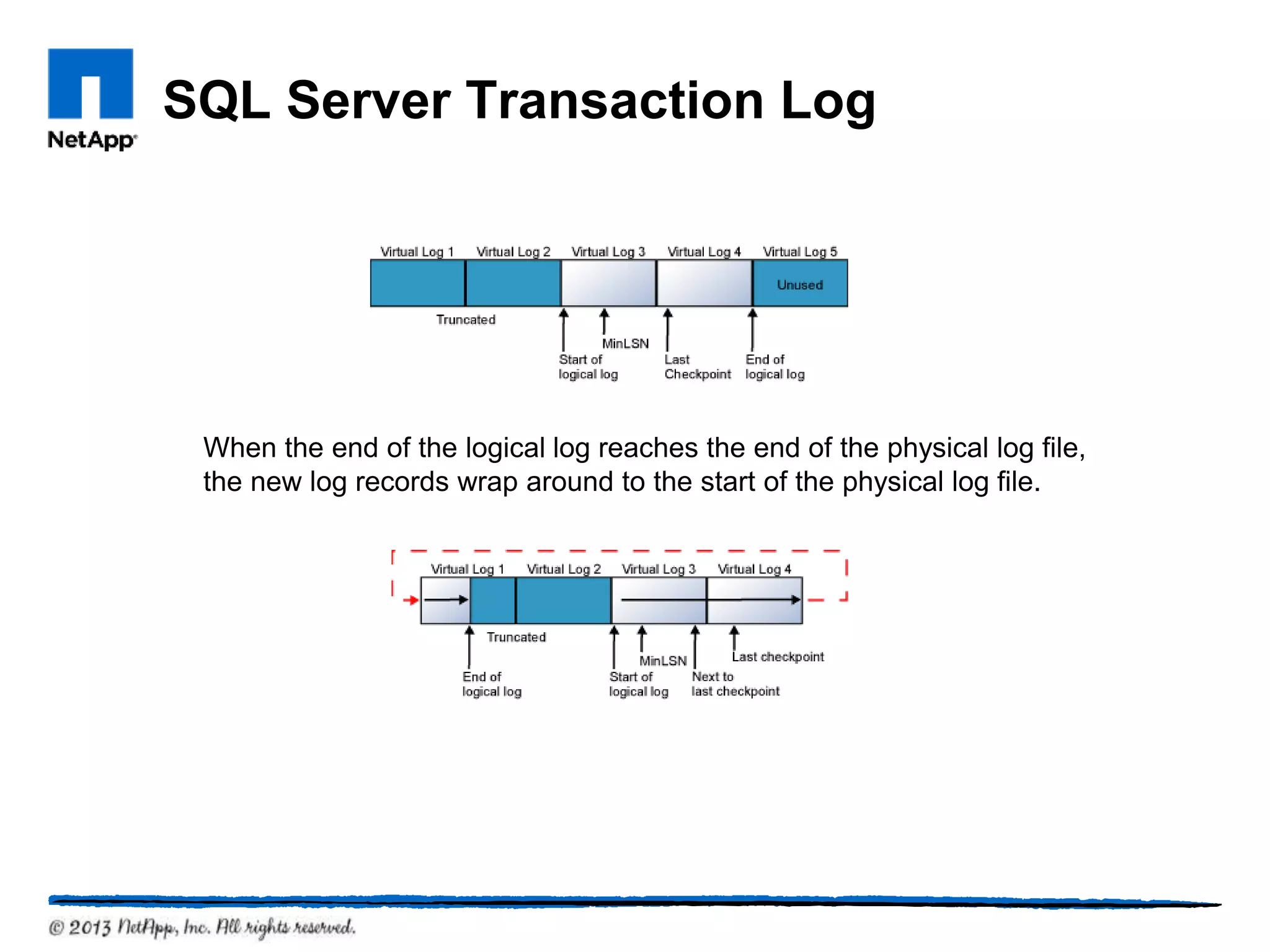
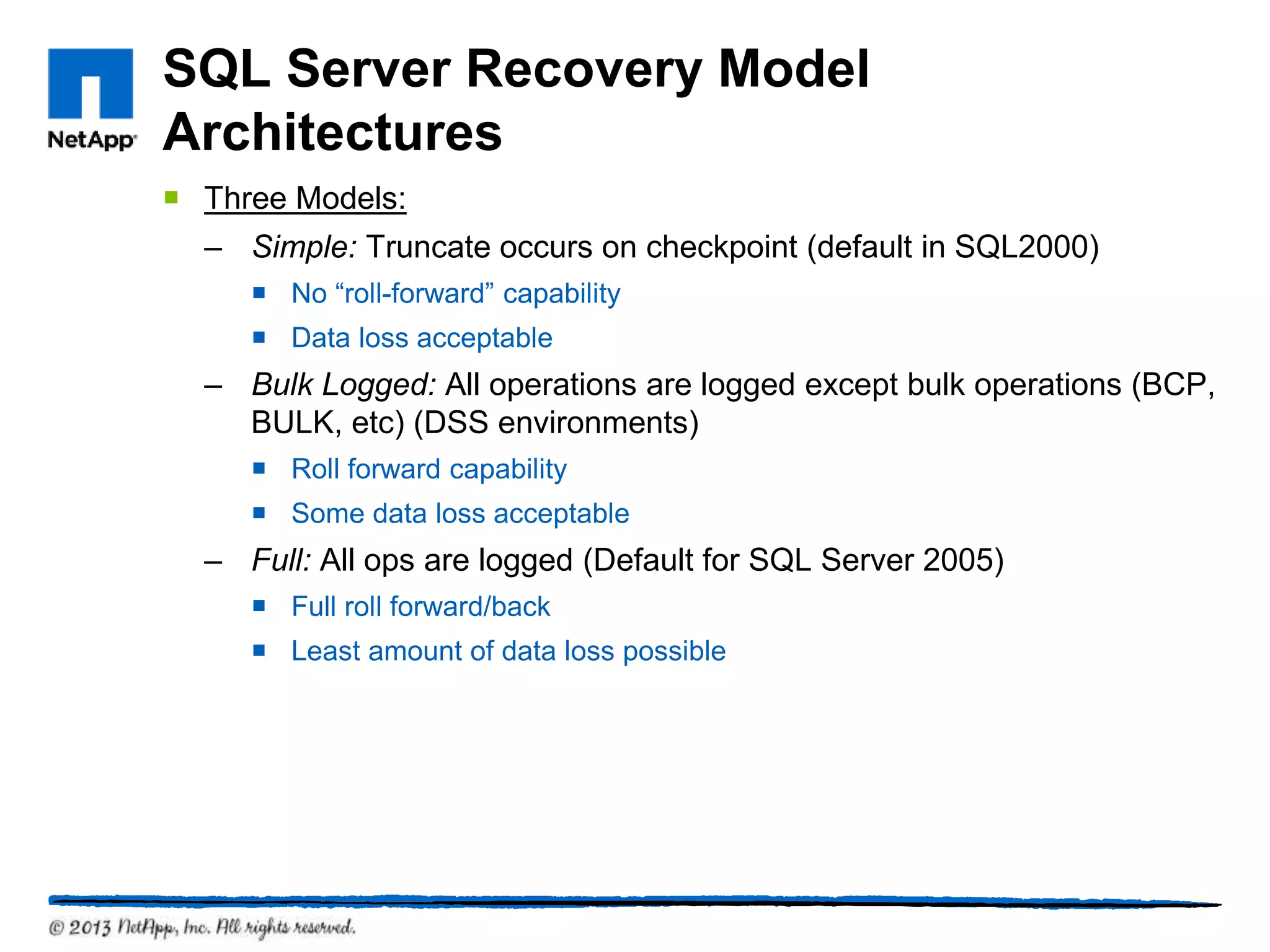
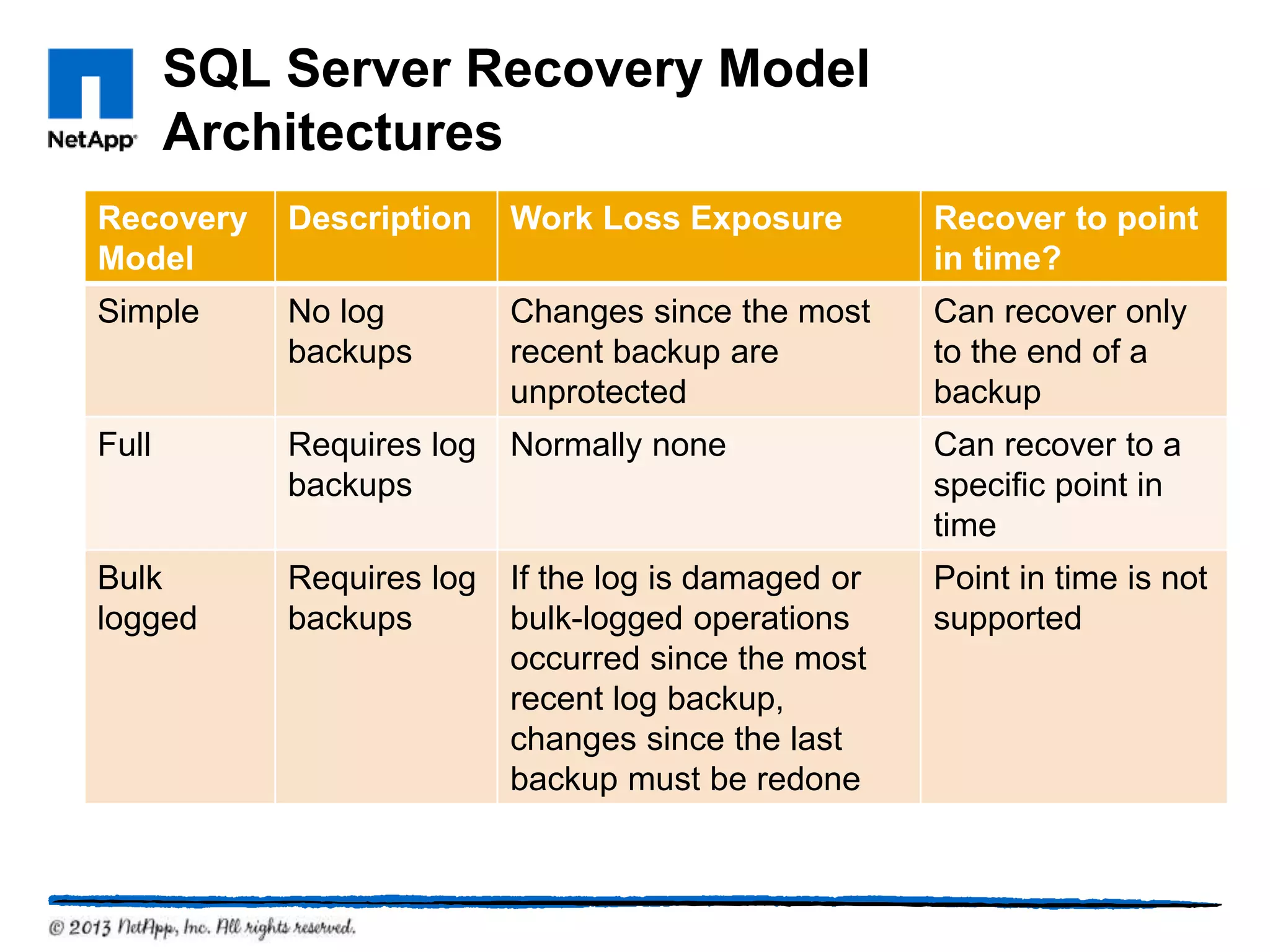
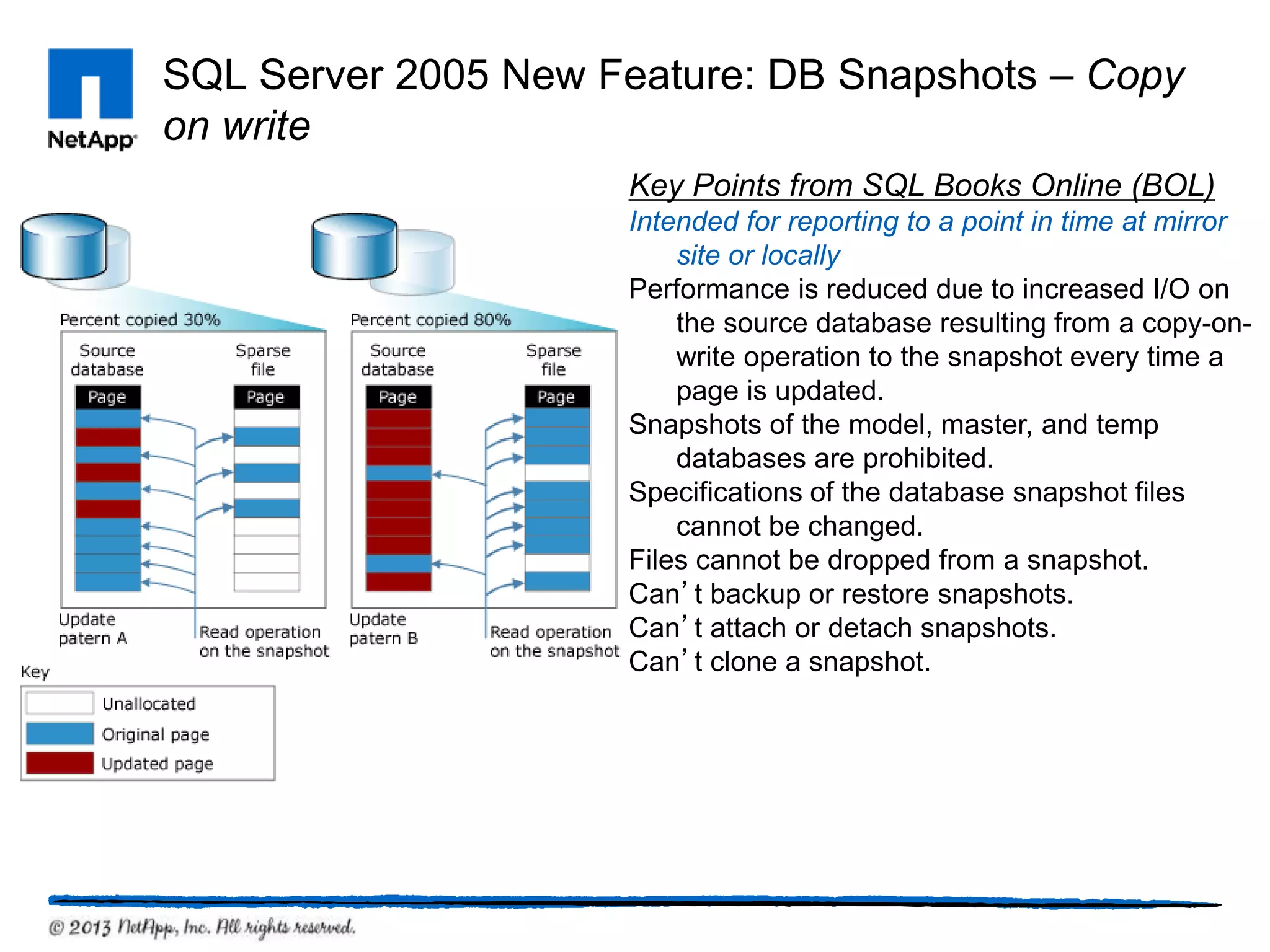
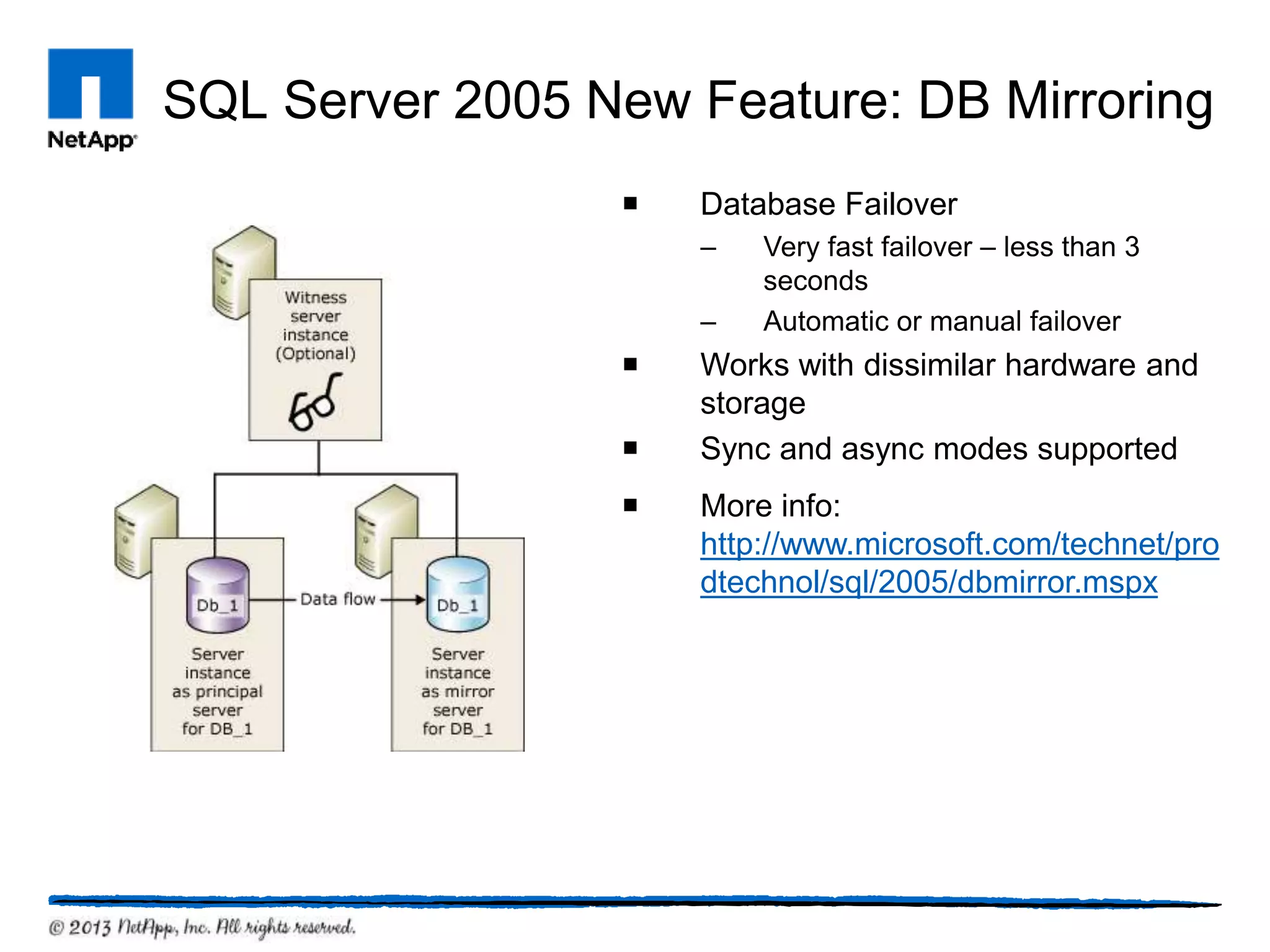
This document provides an overview of SQL Server architecture and components. It discusses common SQL Server versions, the different components that make up SQL Server like databases, files, transaction logs, and recovery models. It also covers new features introduced in SQL Server 2005 and 2012 like data partitioning using file groups, database snapshots, database mirroring, and availability groups.