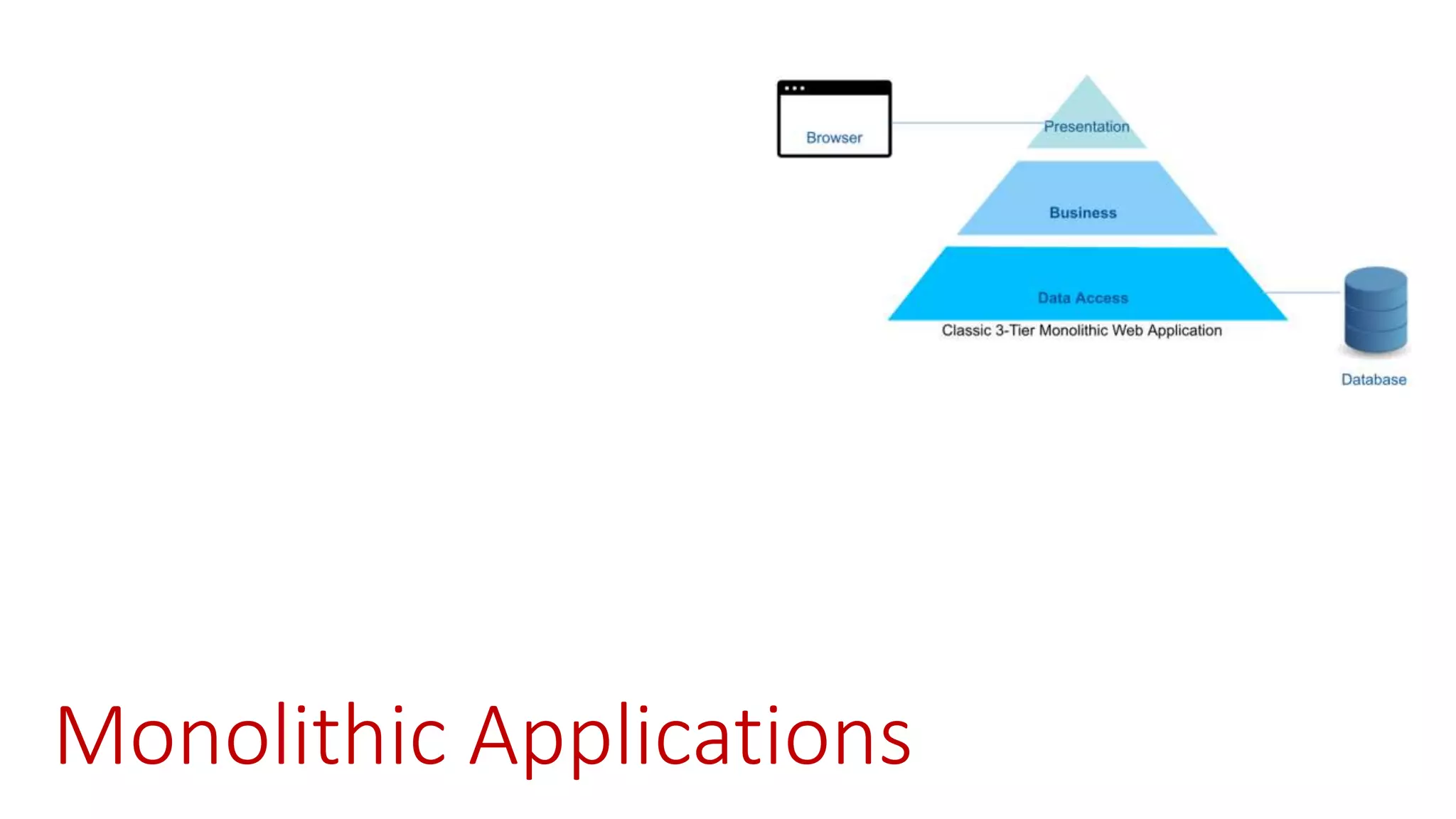
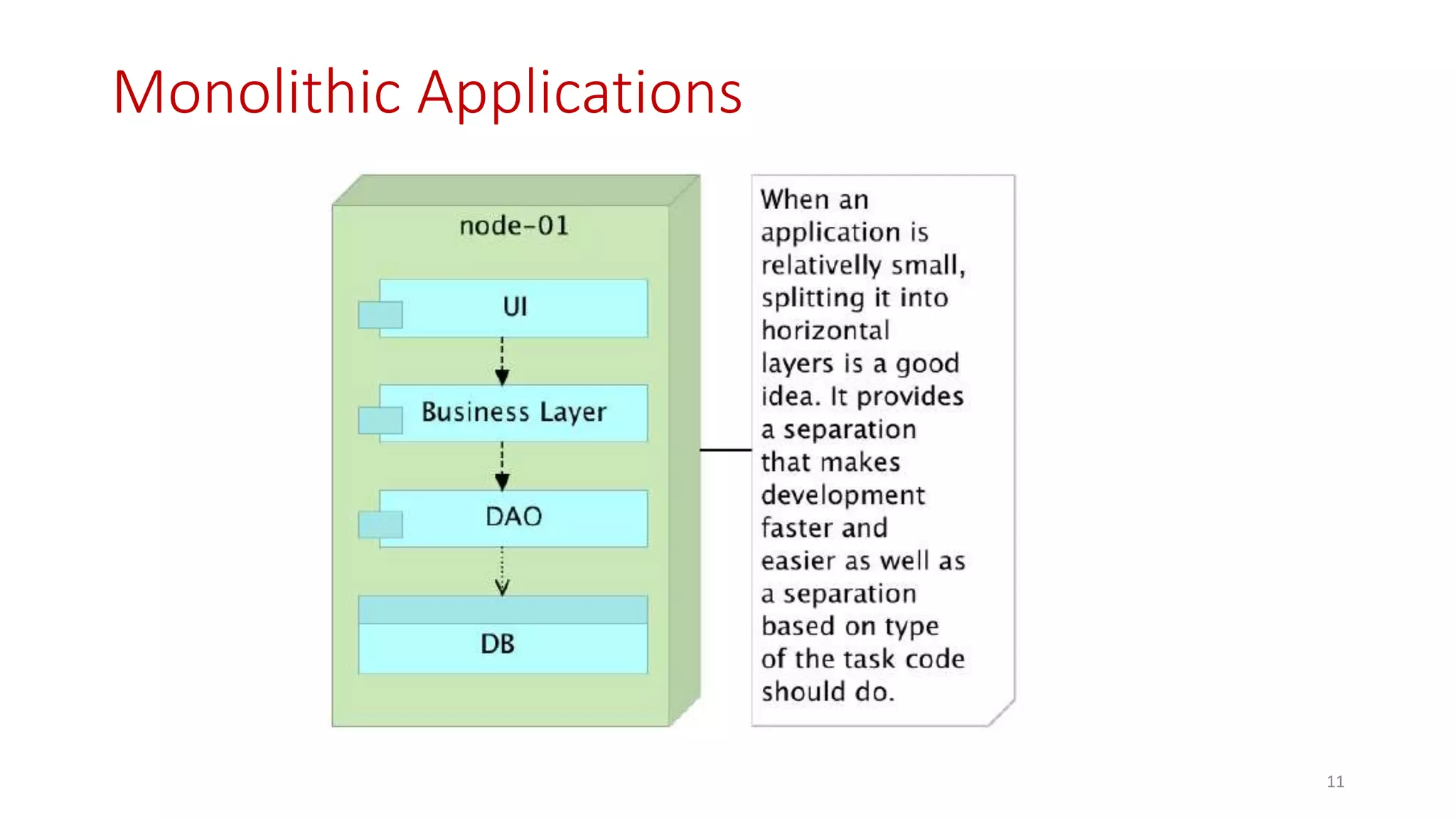
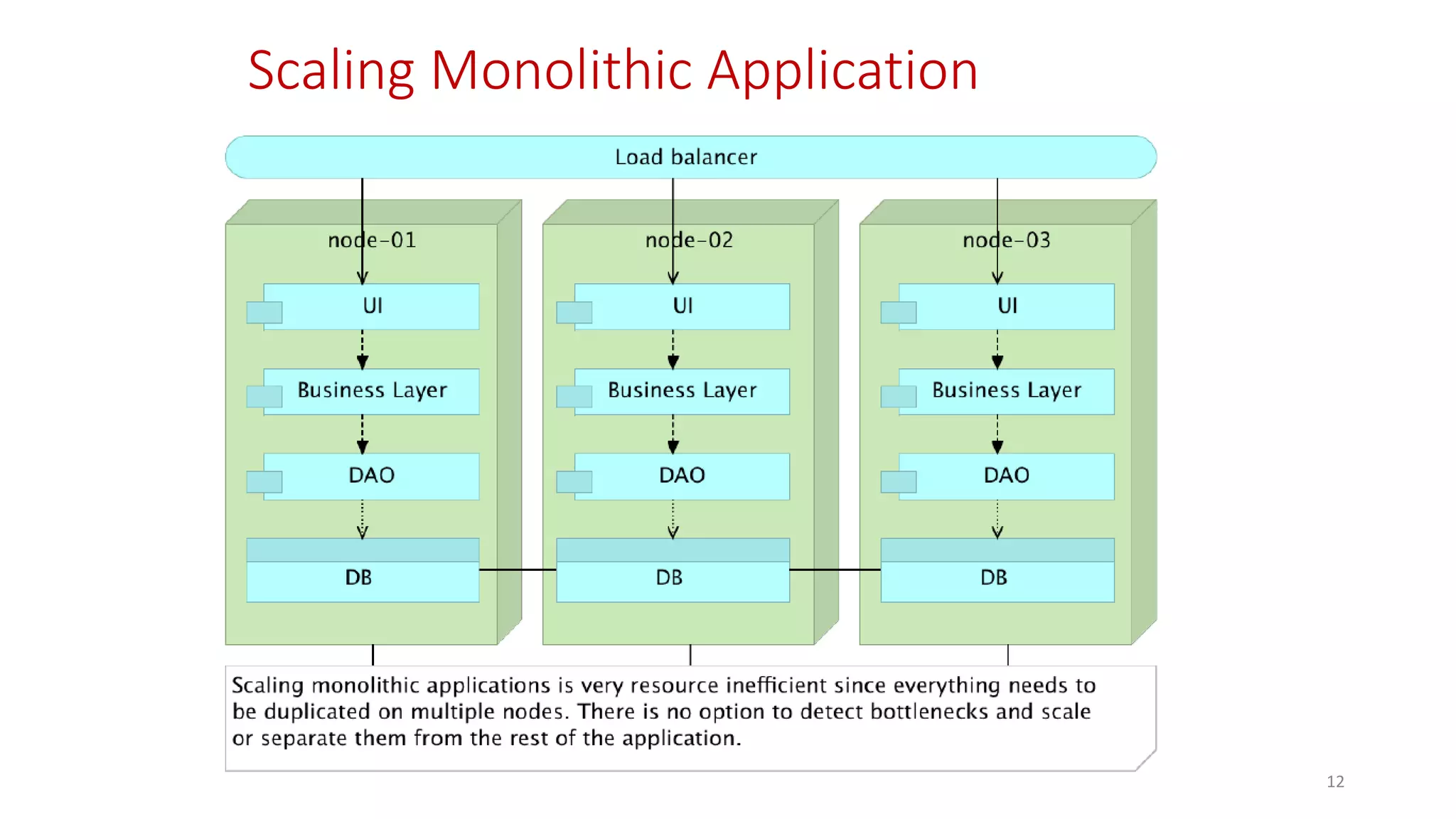
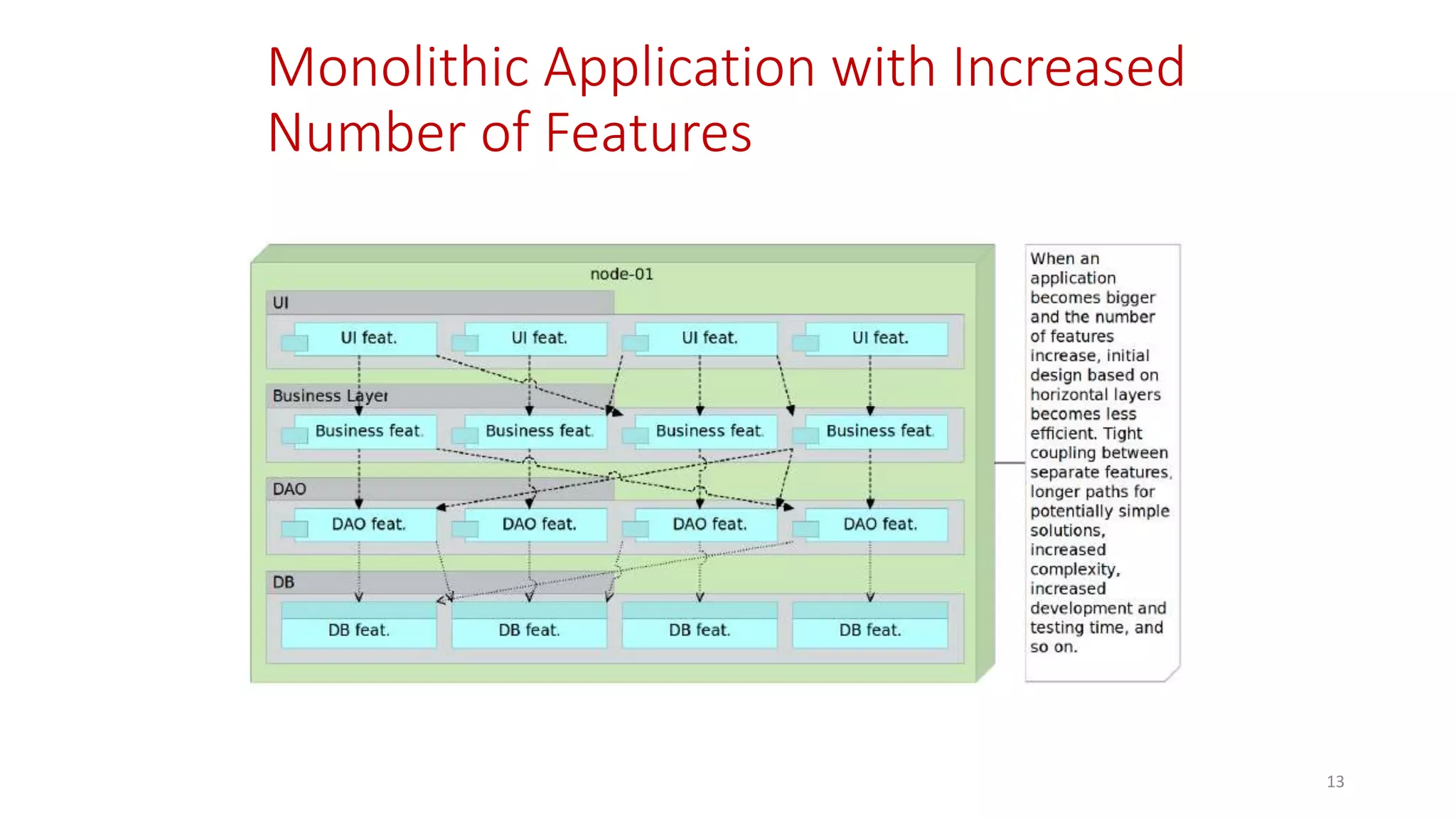
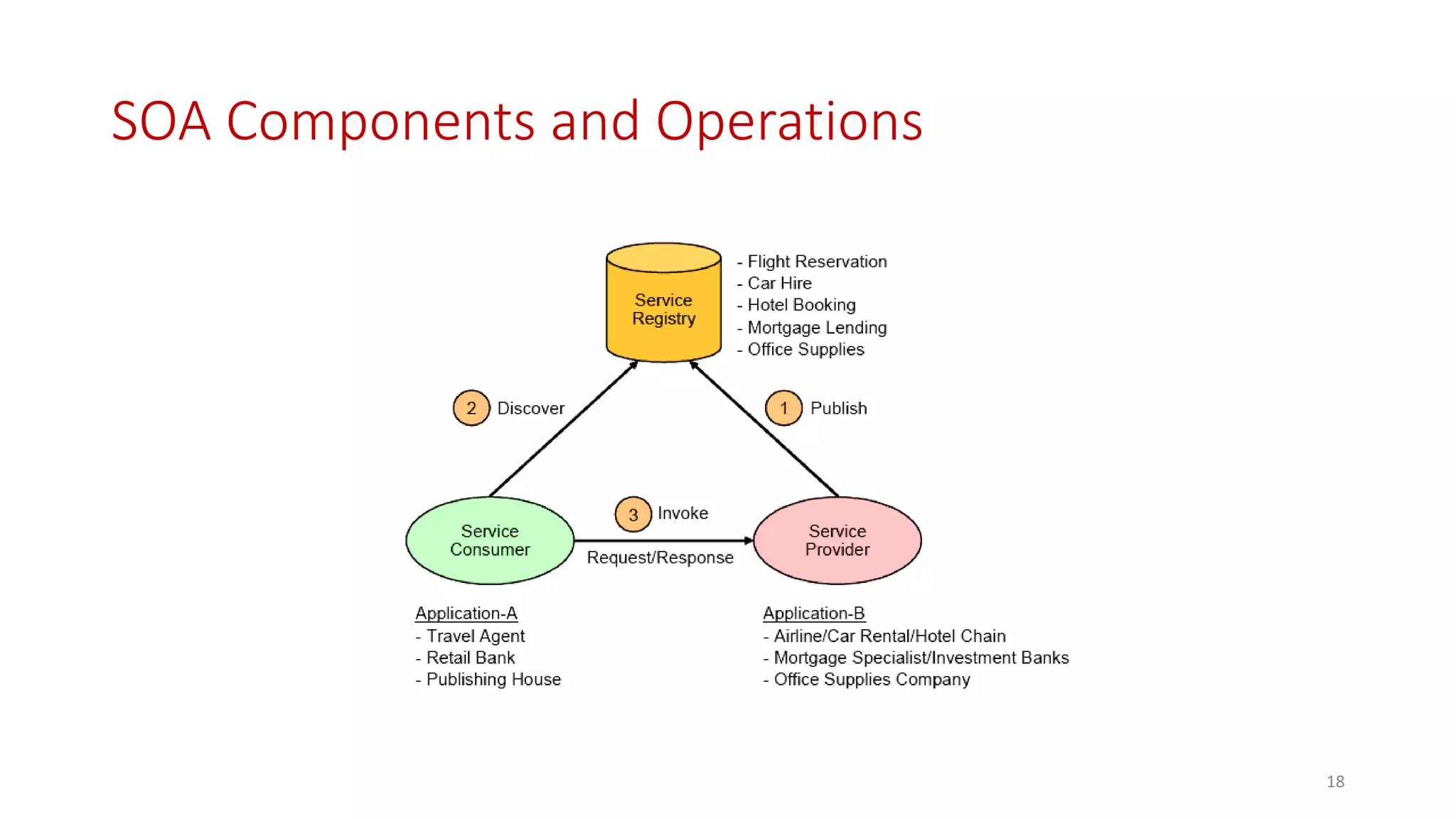
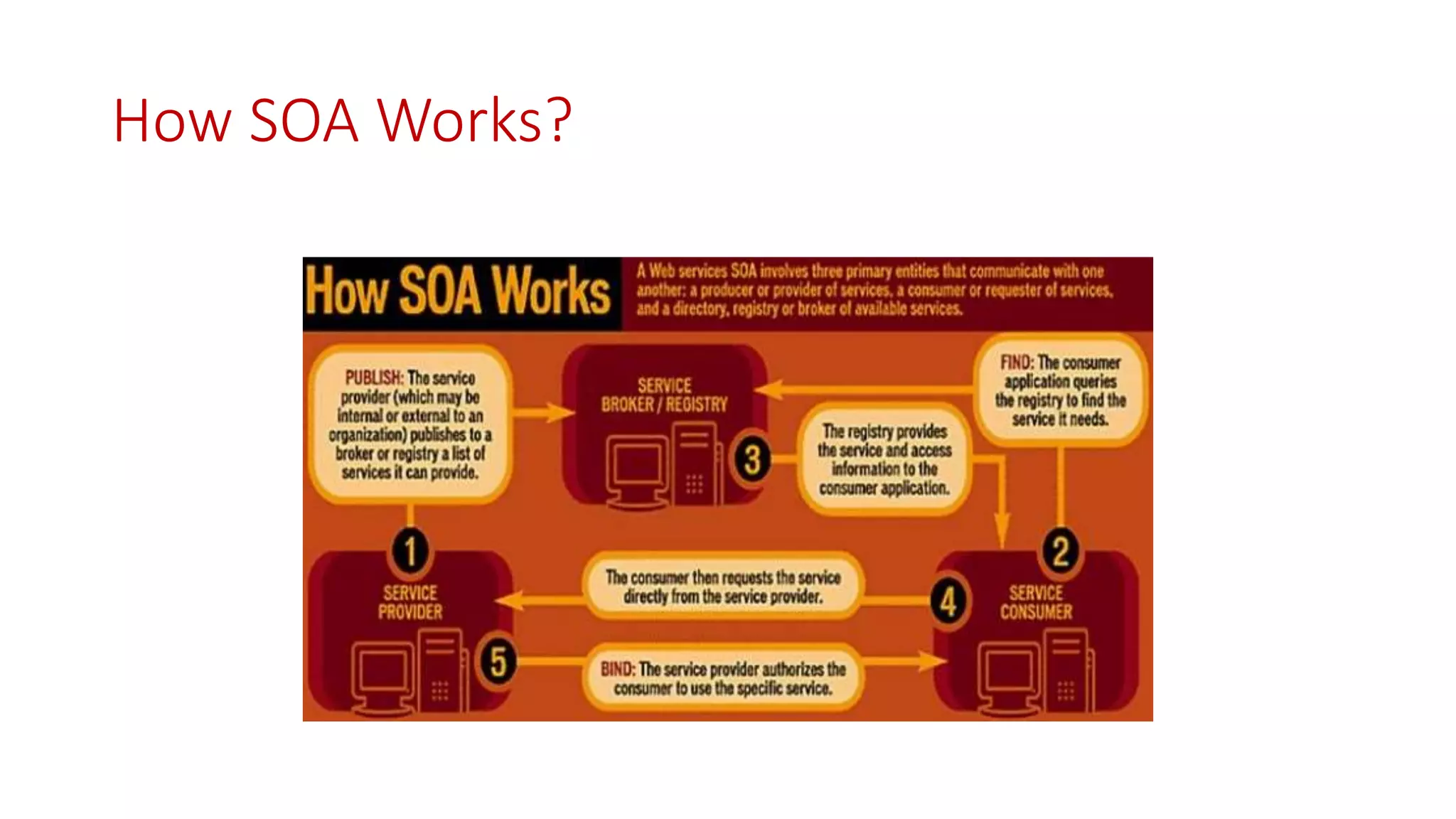
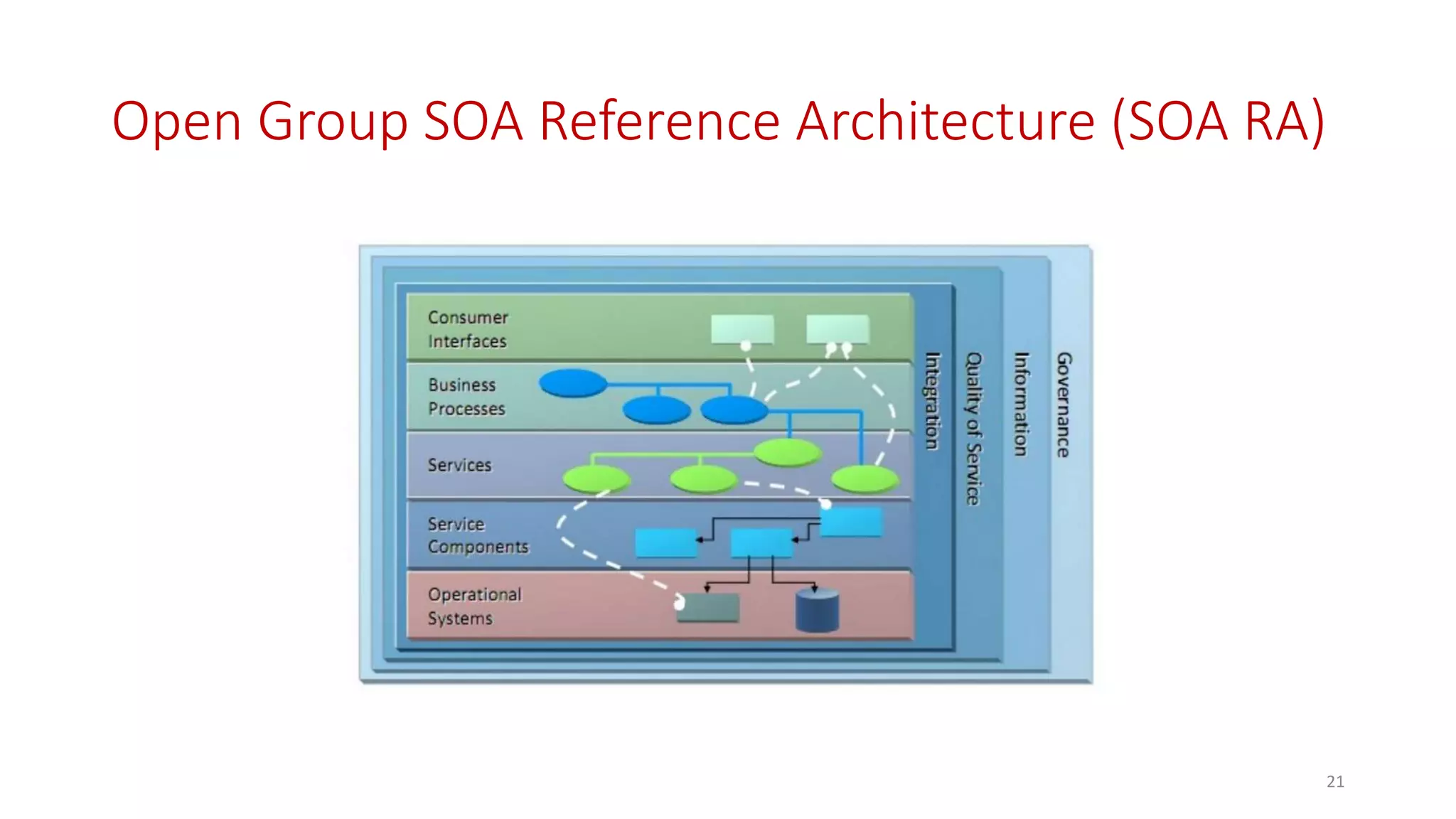
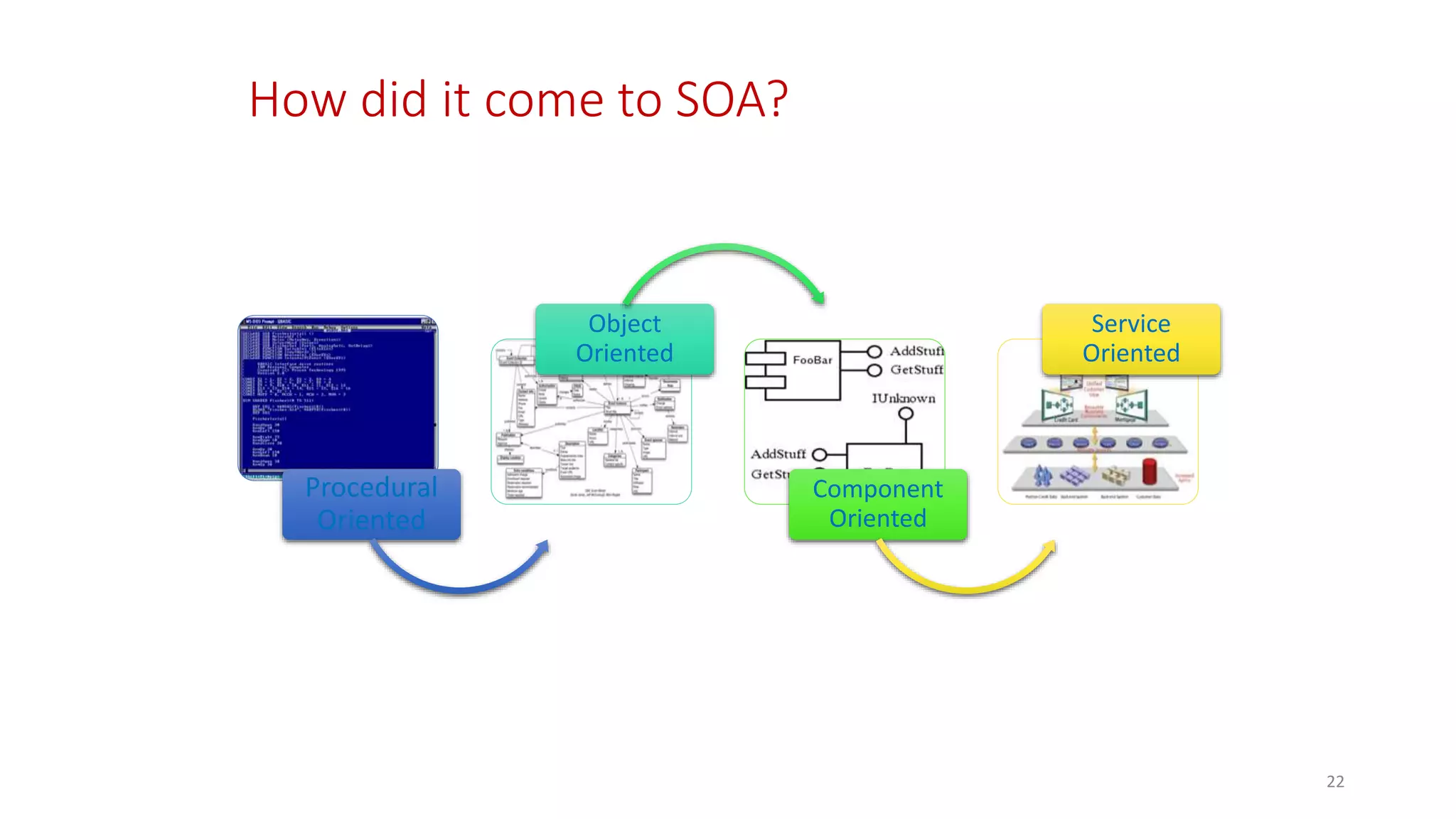
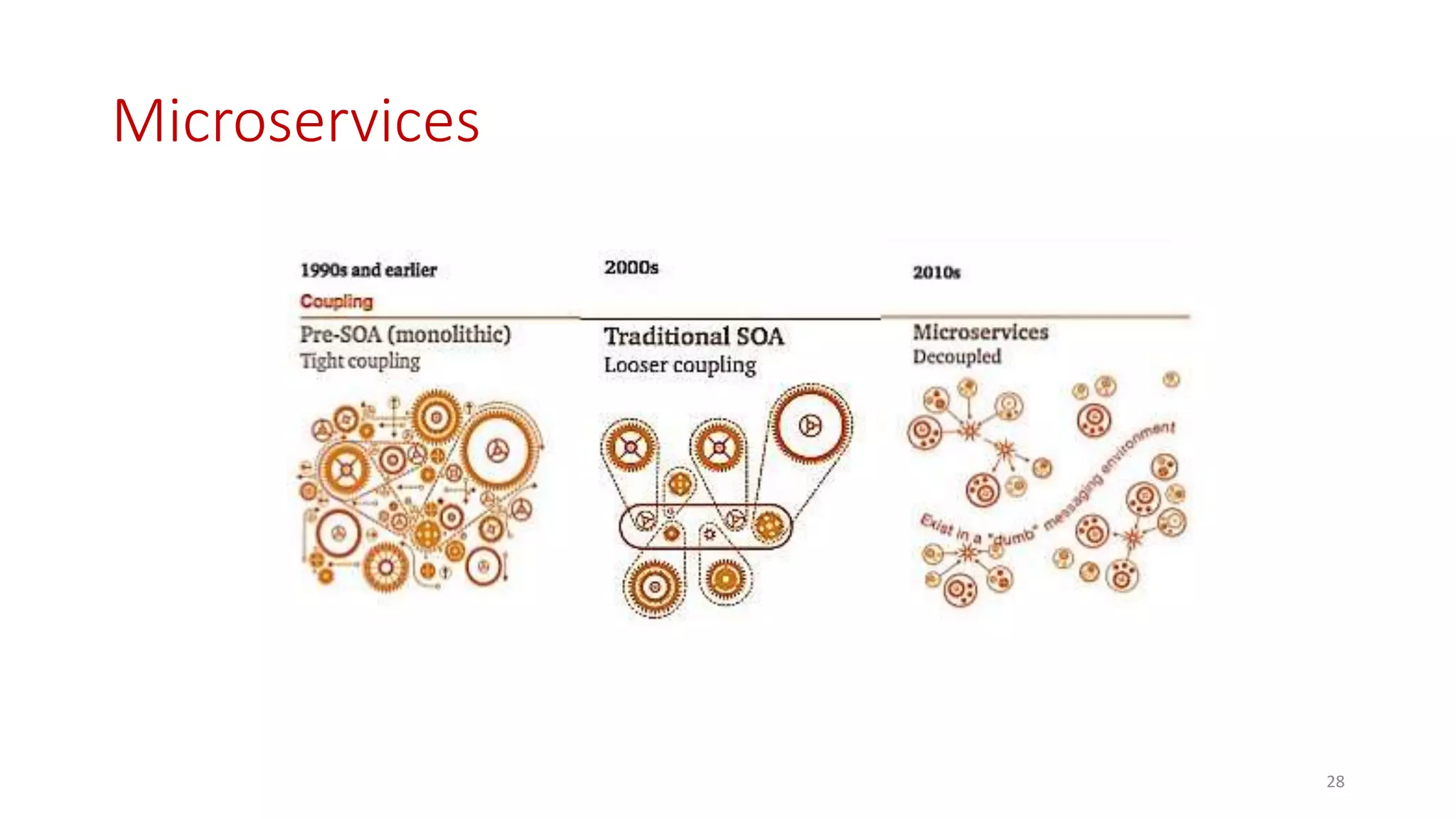
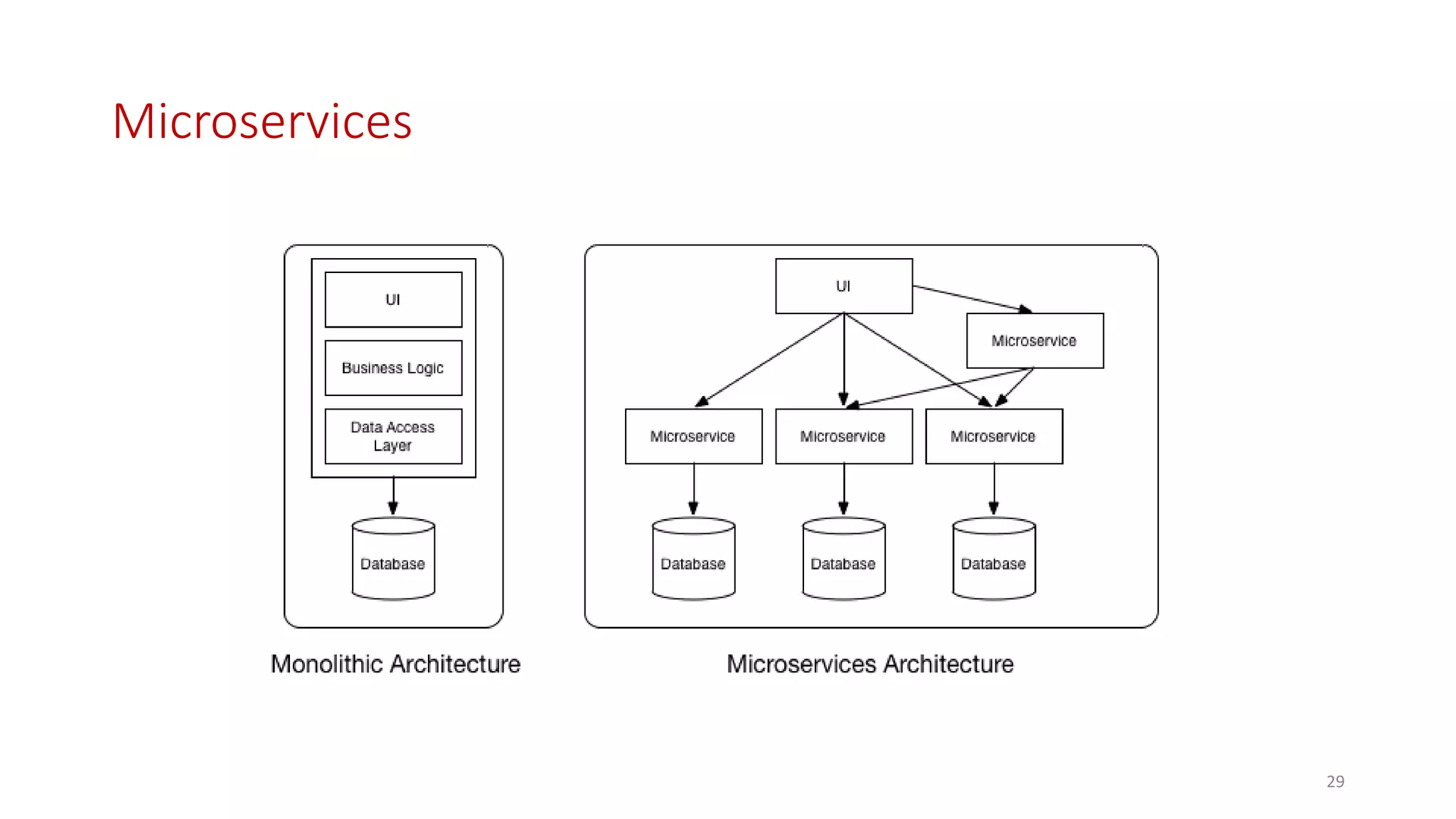
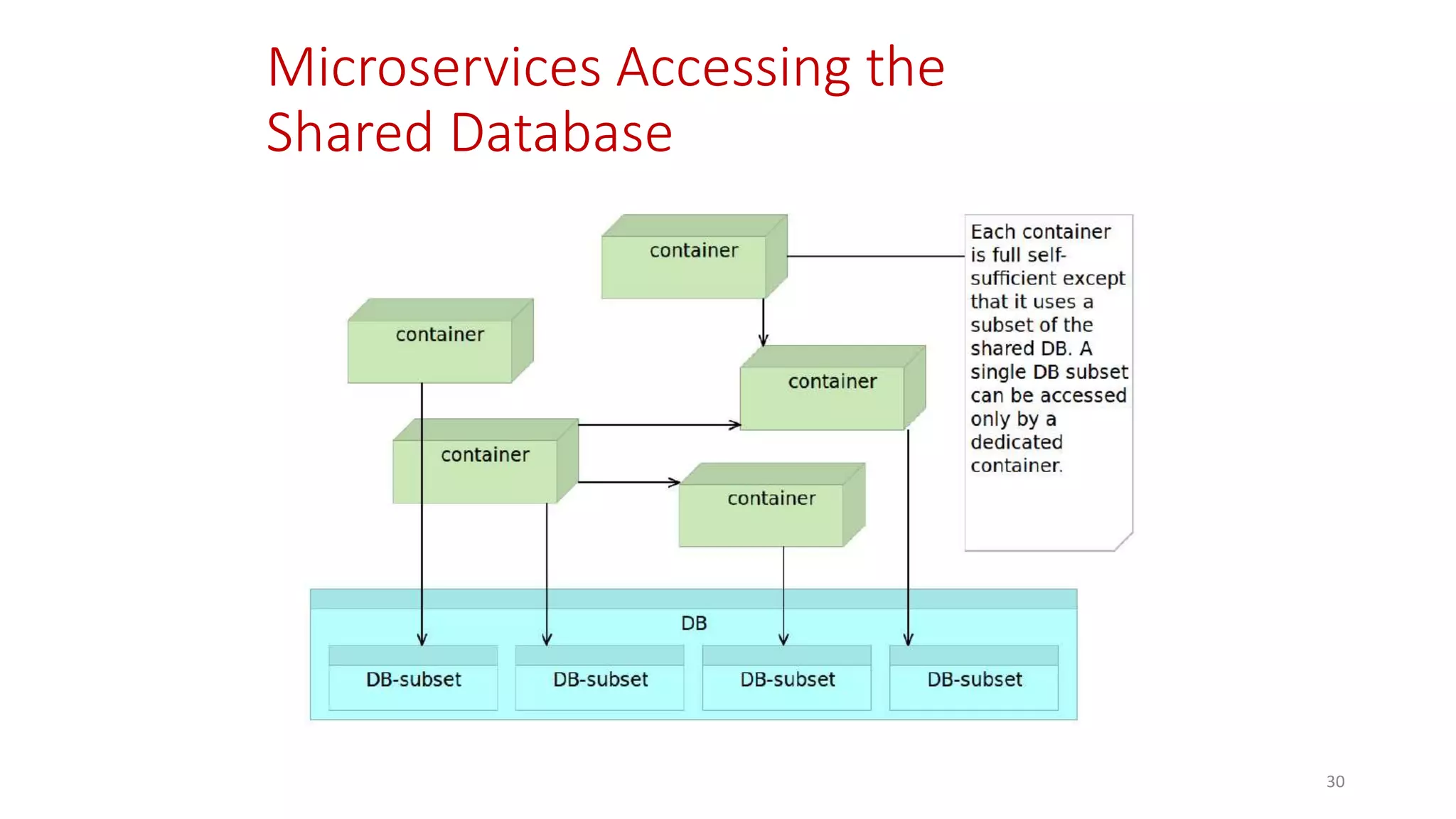
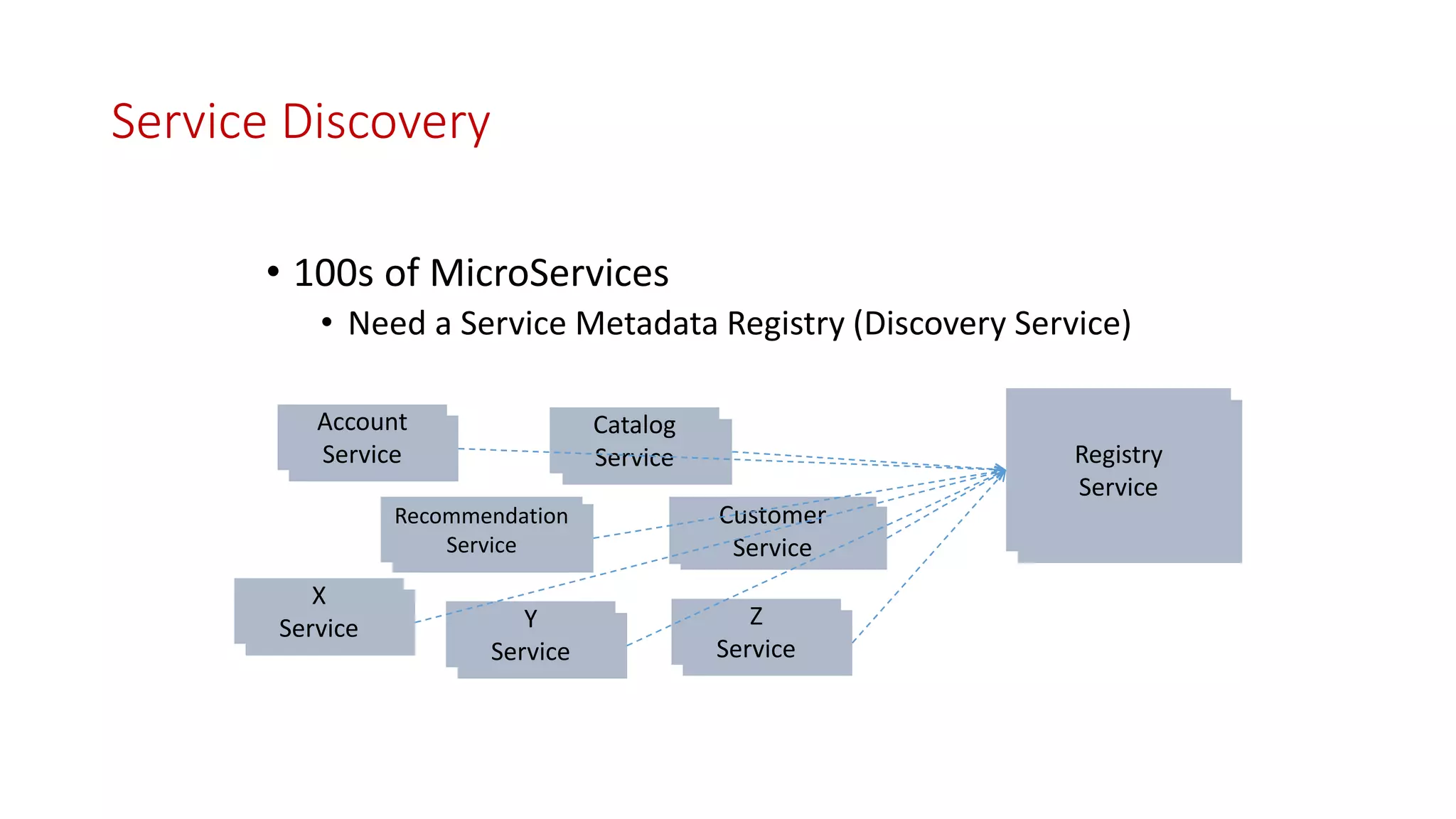
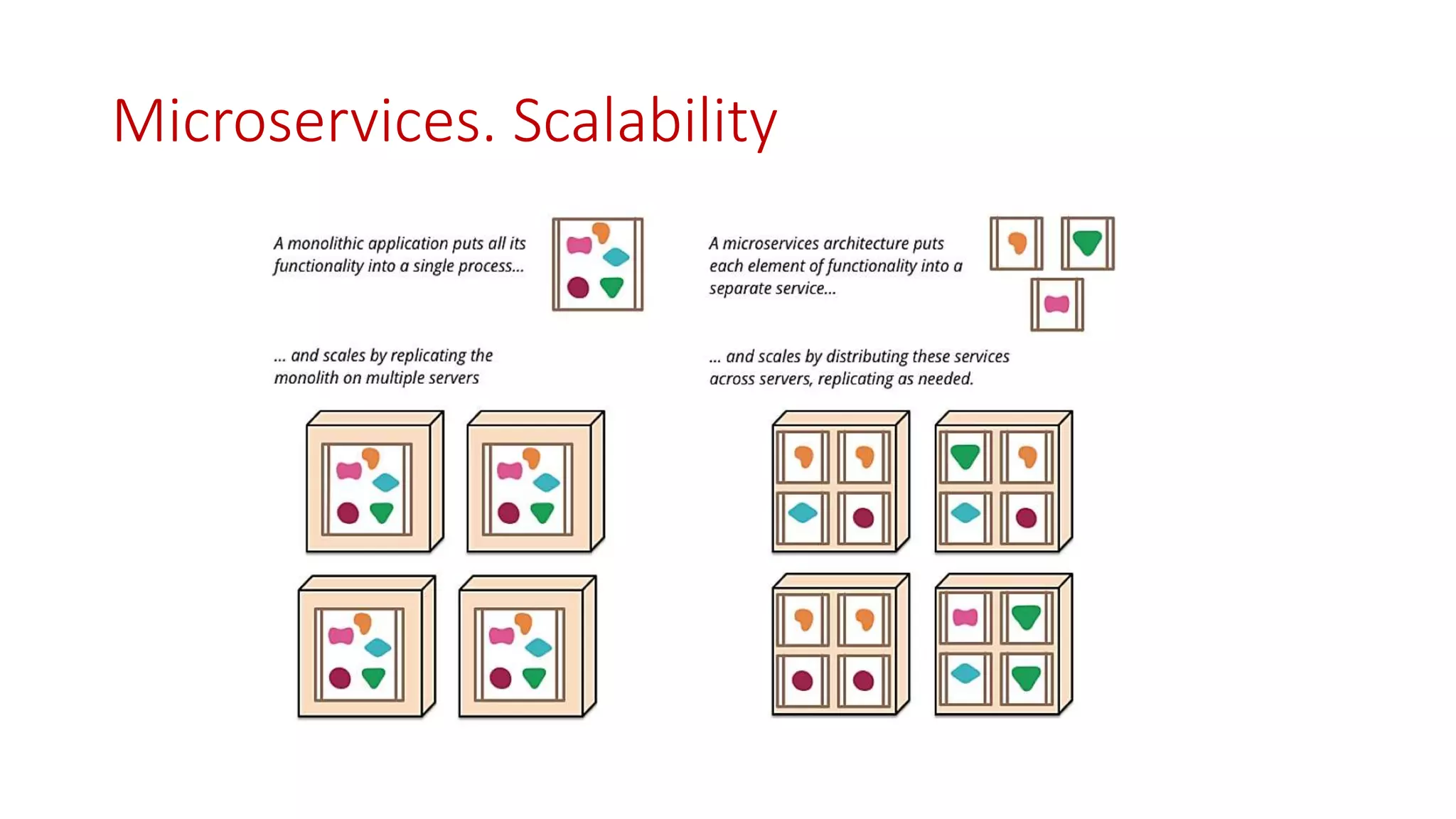
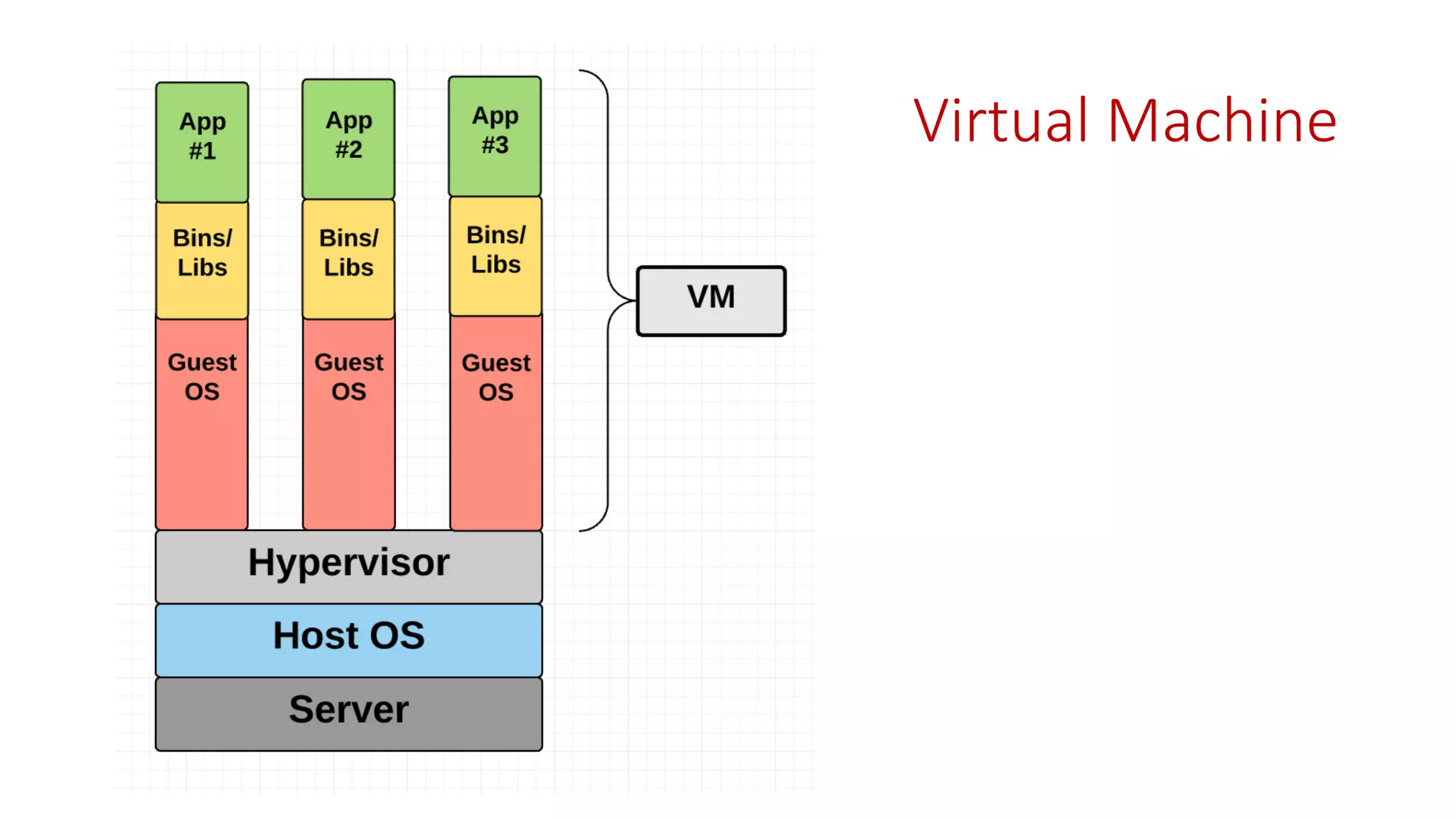
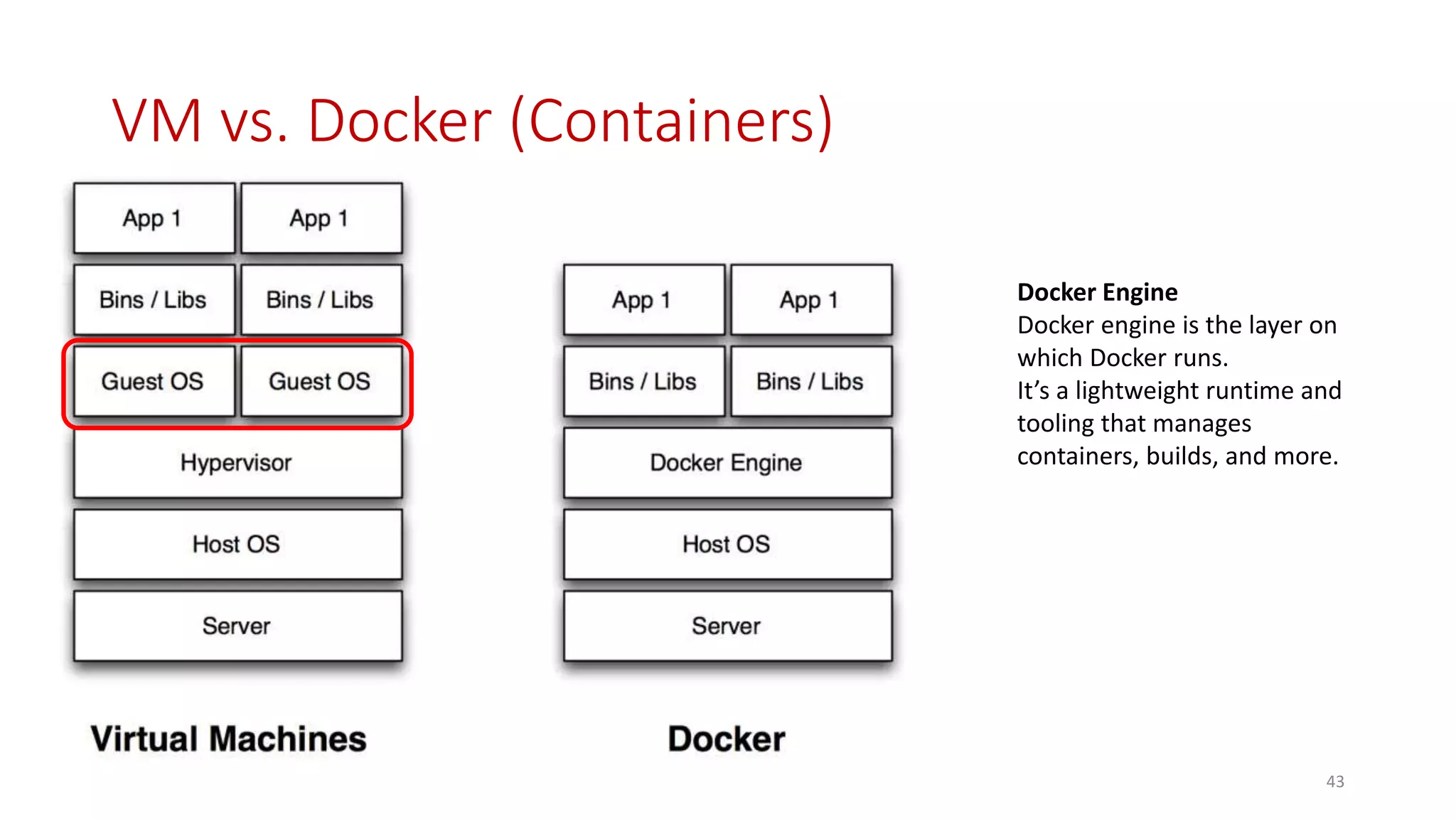
Microservices architecture breaks down monolithic applications into many smaller, independent services. Docker provides a standard way to package applications into containers that are portable and can run anywhere. According to Gartner's Hype Cycle, Docker and microservices are still in the "Peak of Inflated Expectations" phase but moving towards the "Plateau of Productivity."