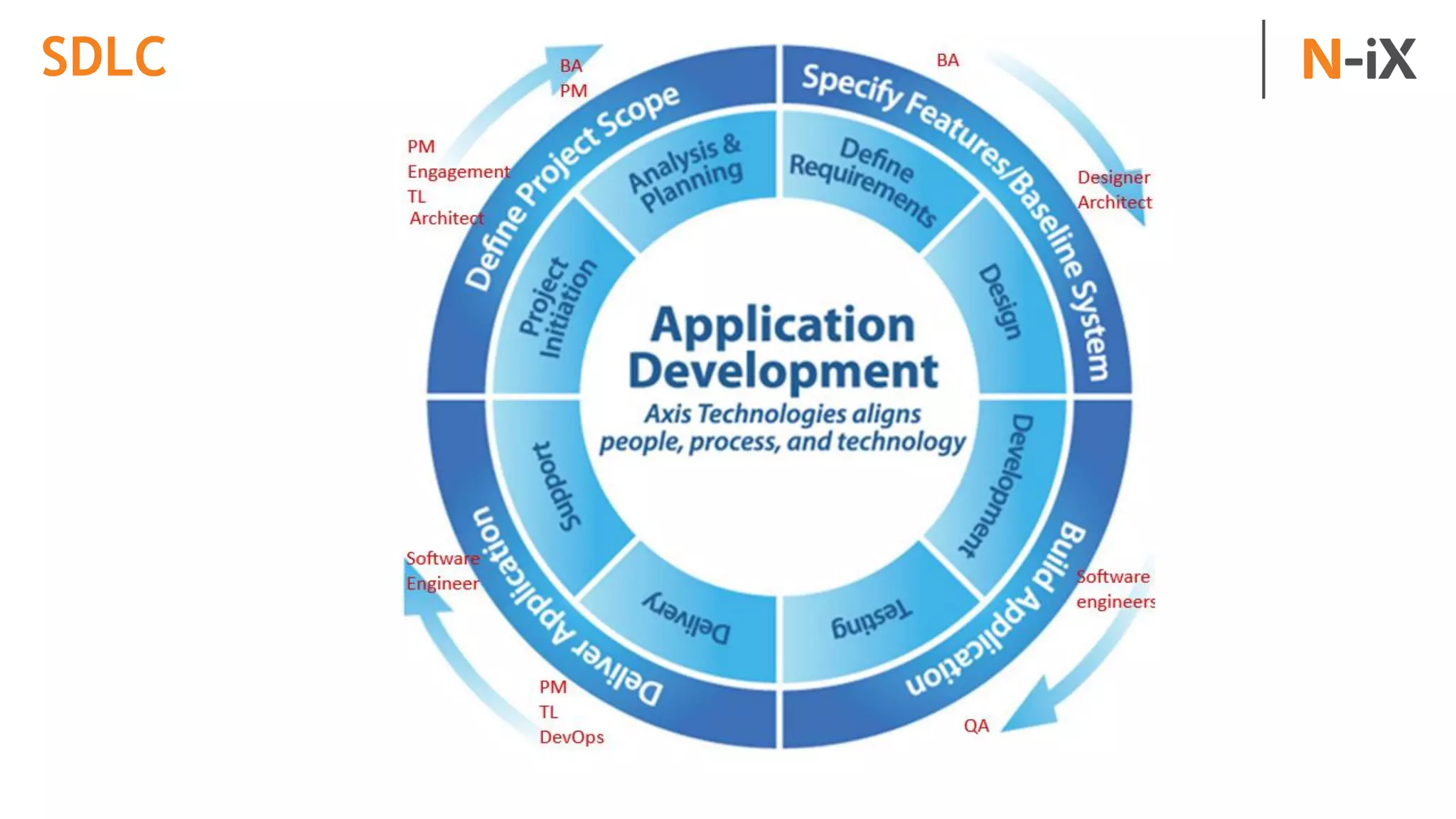
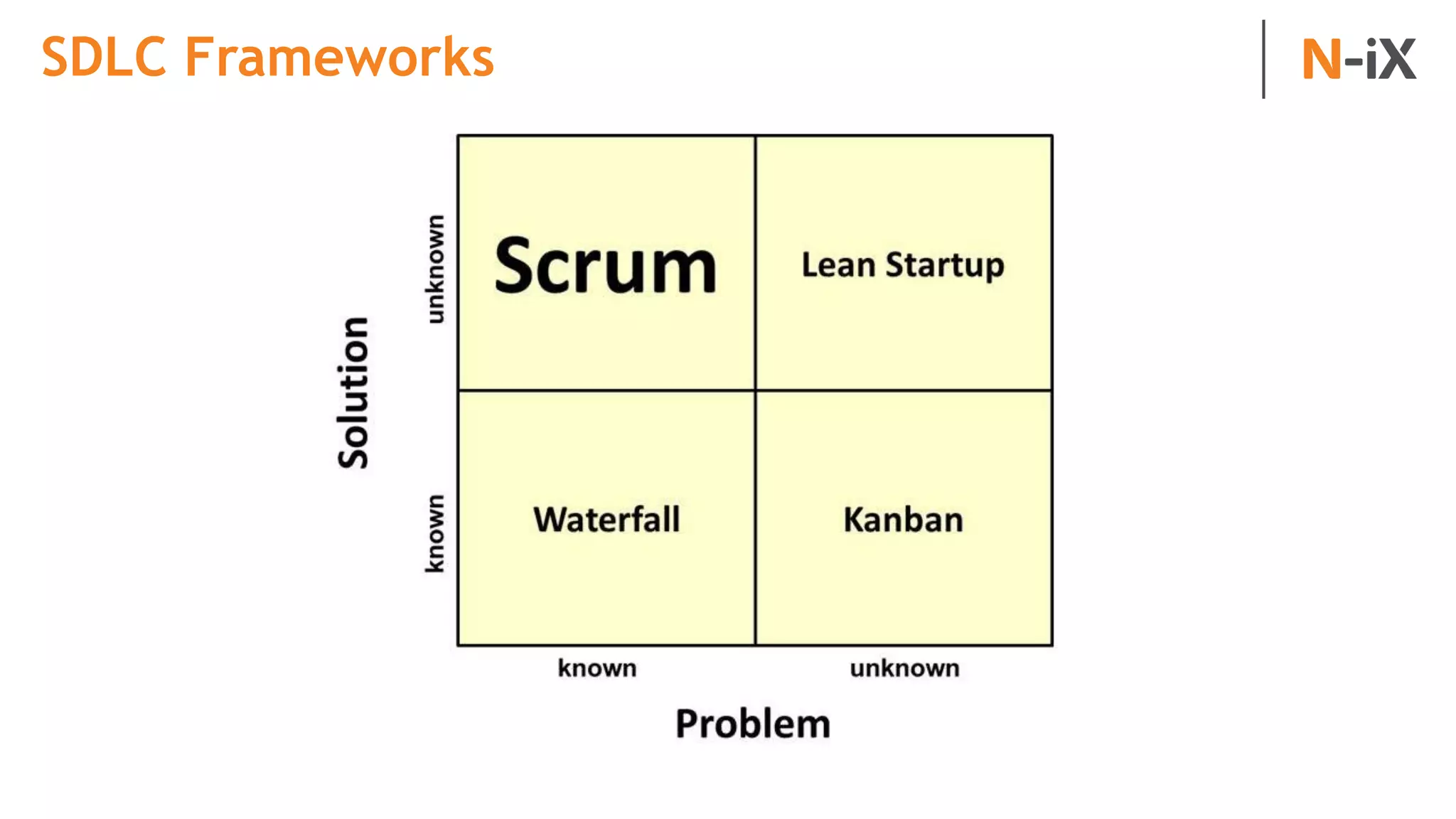
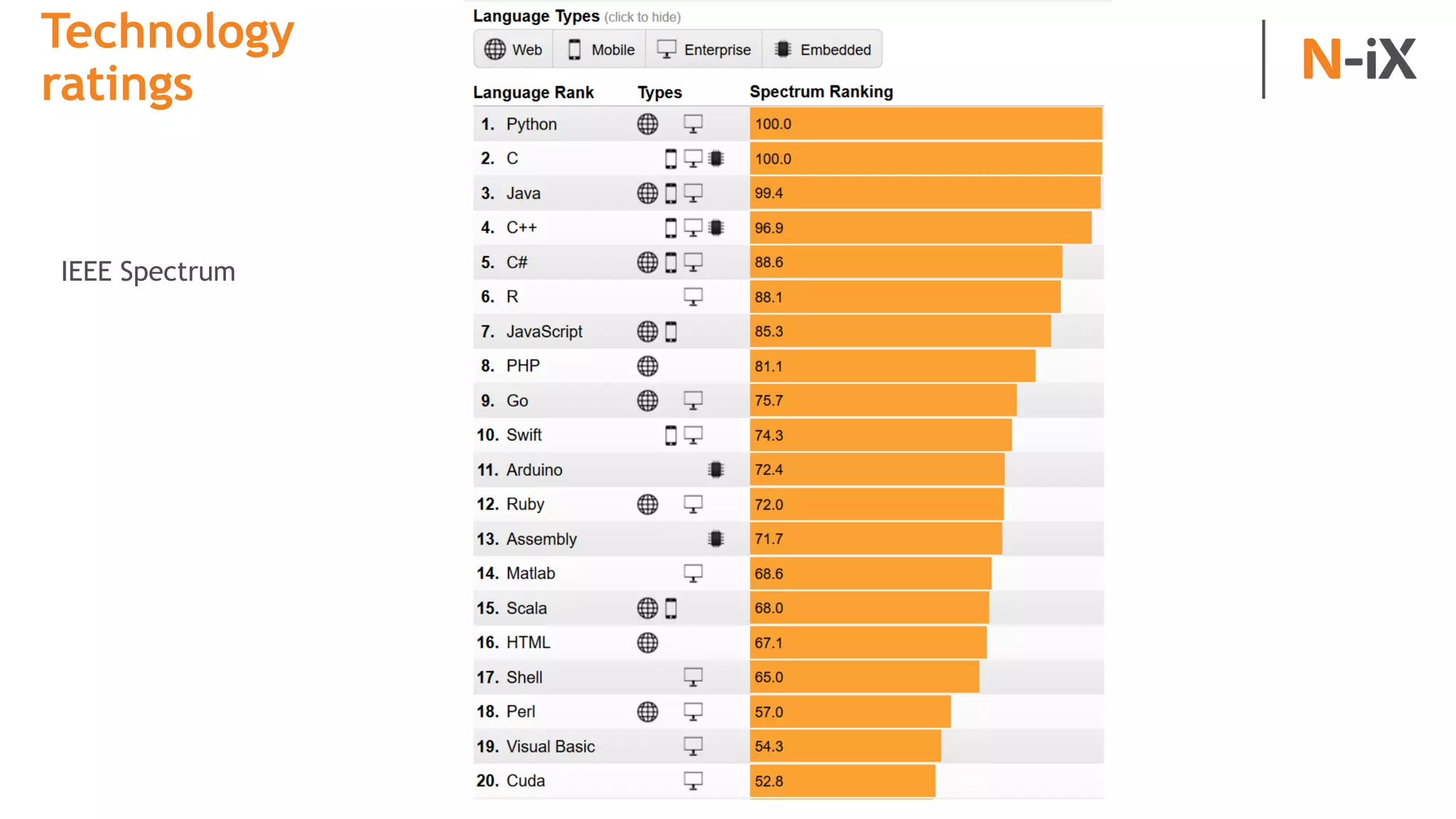
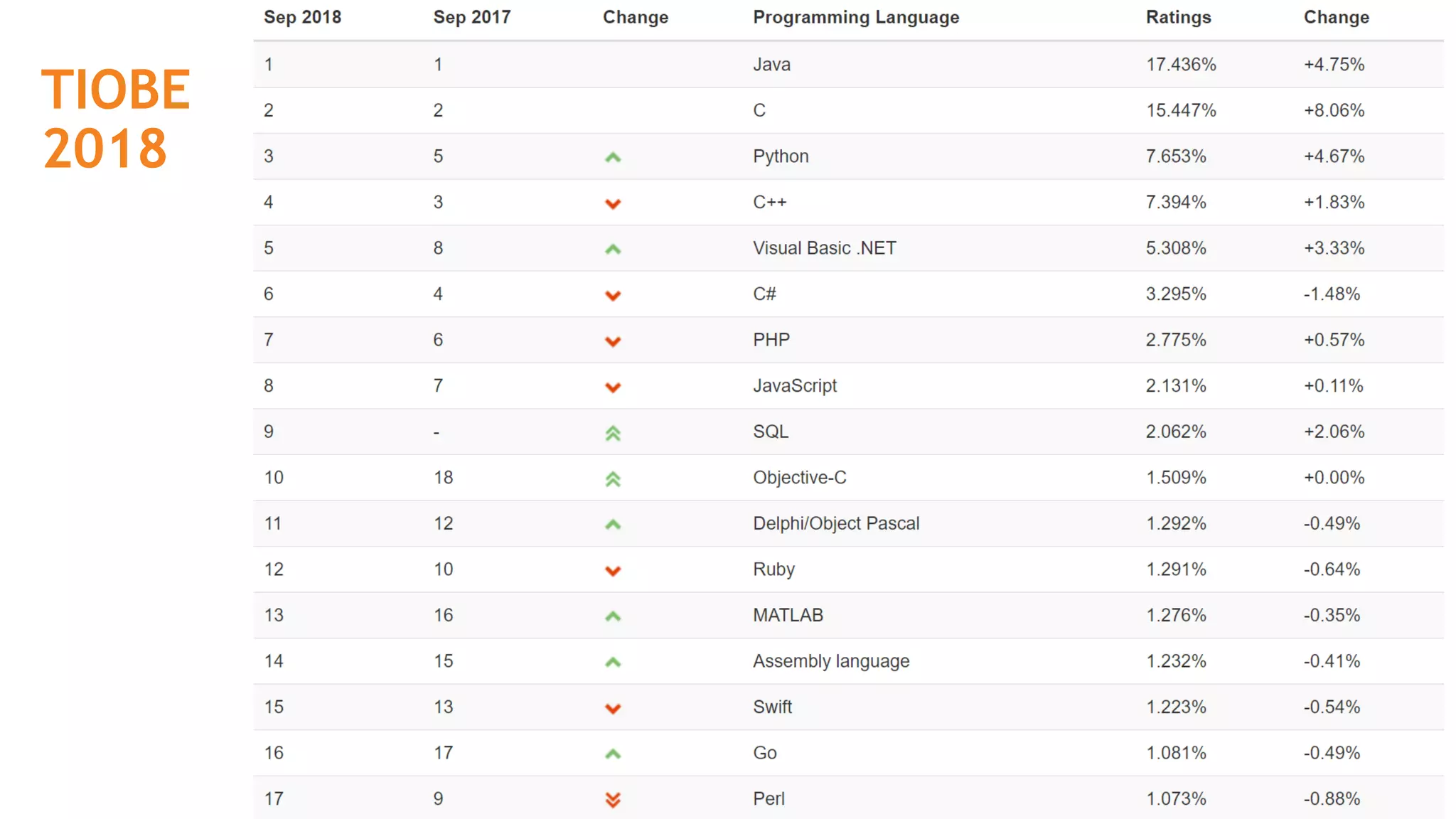
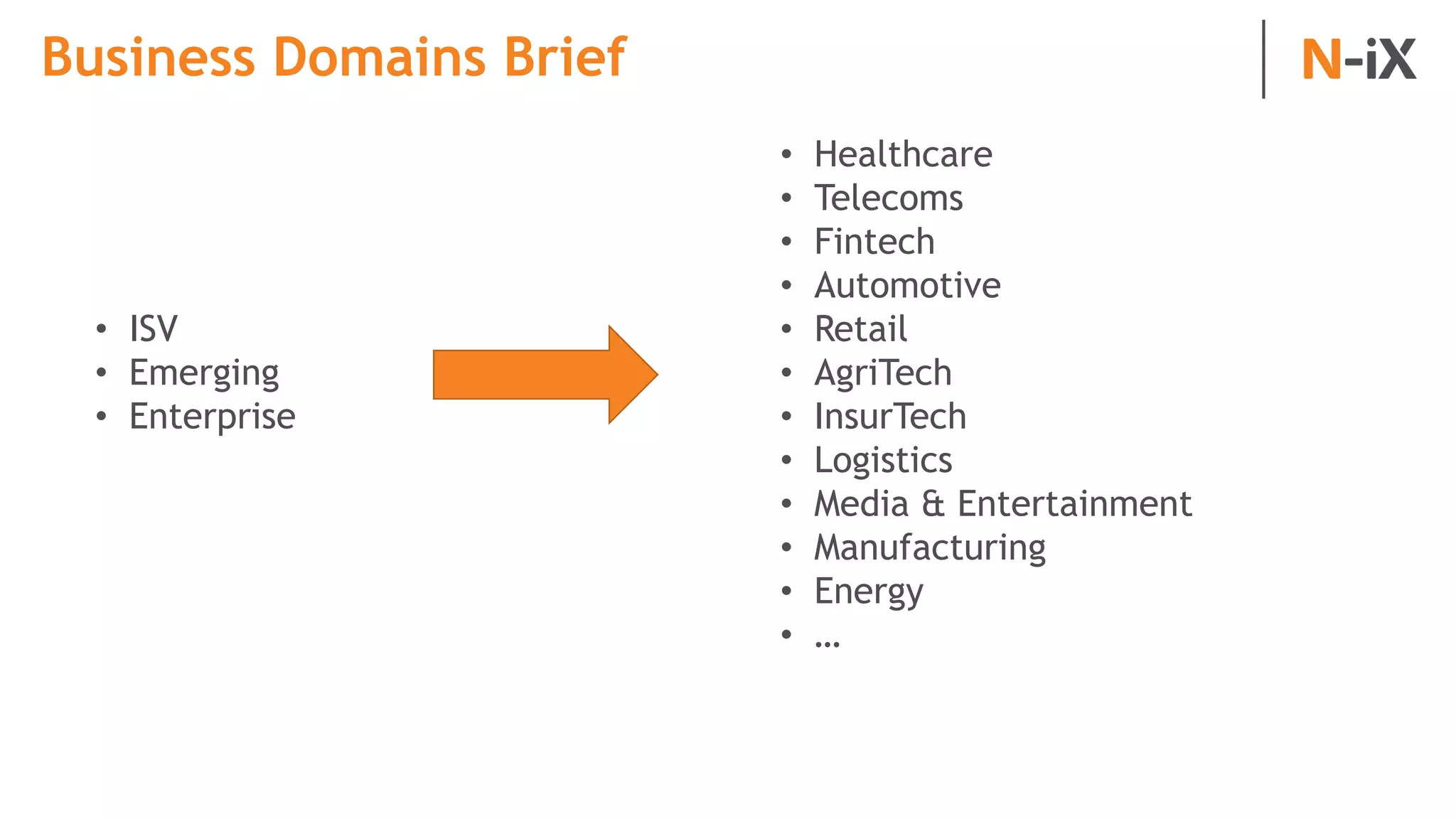
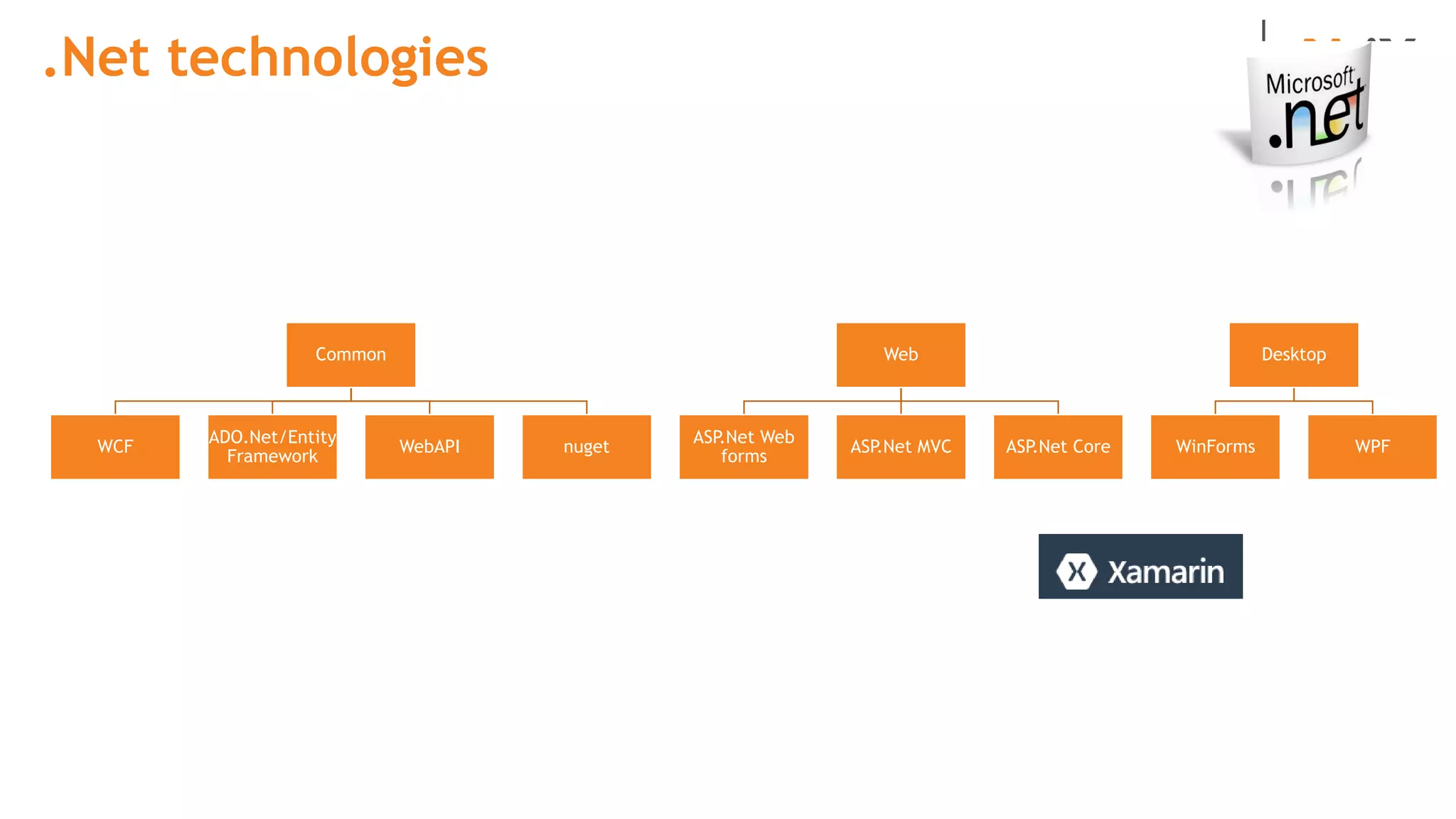
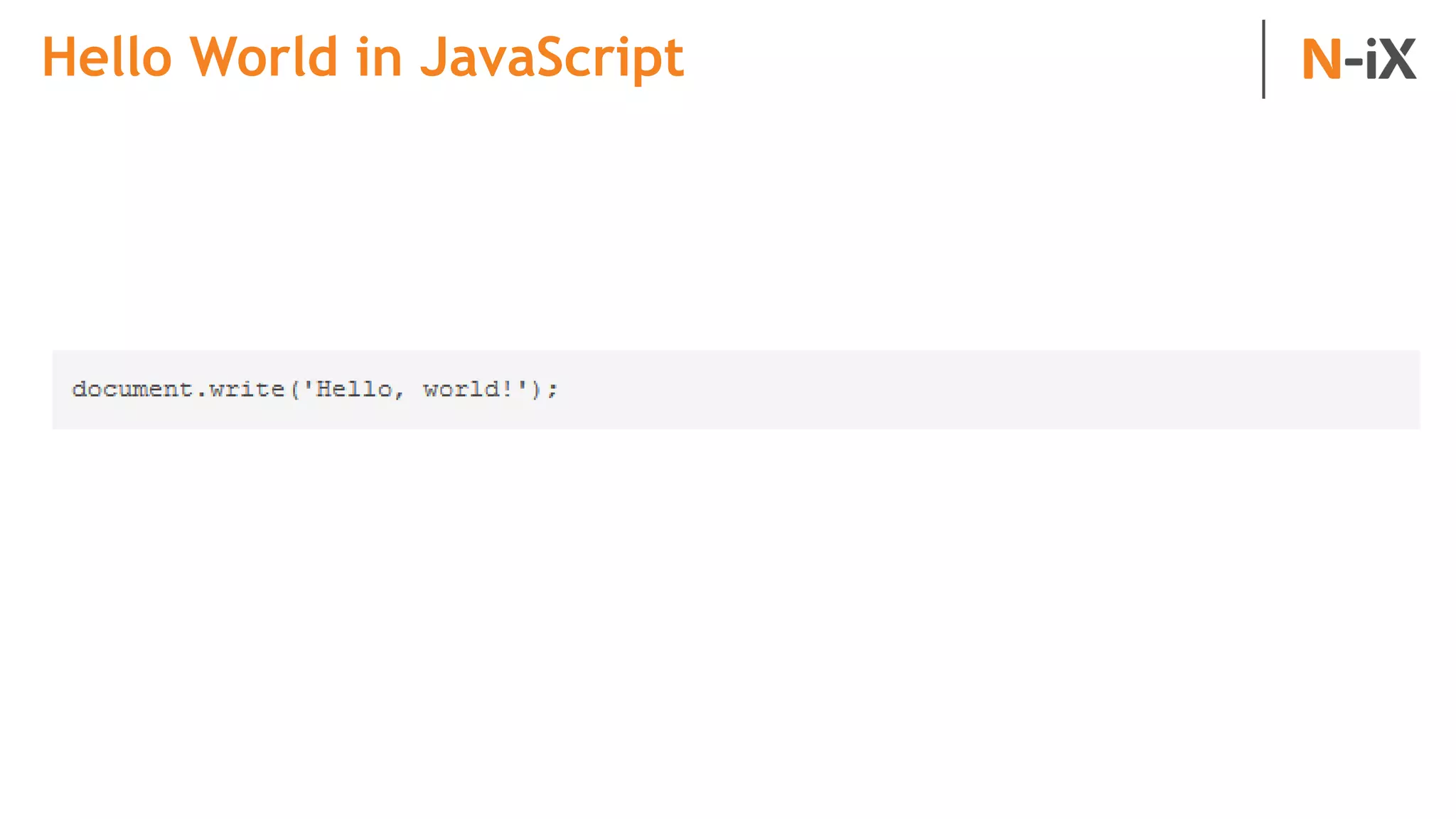
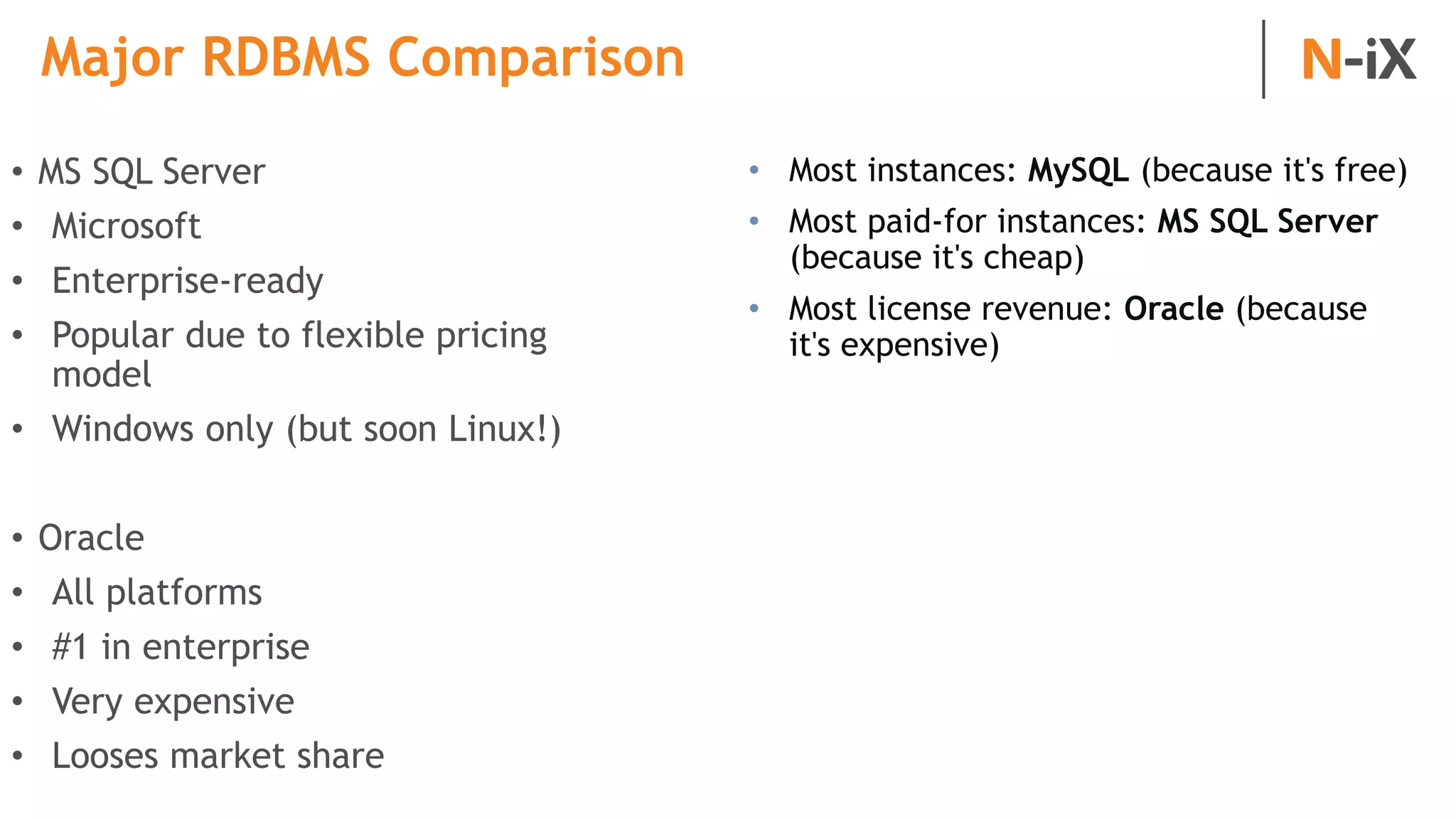
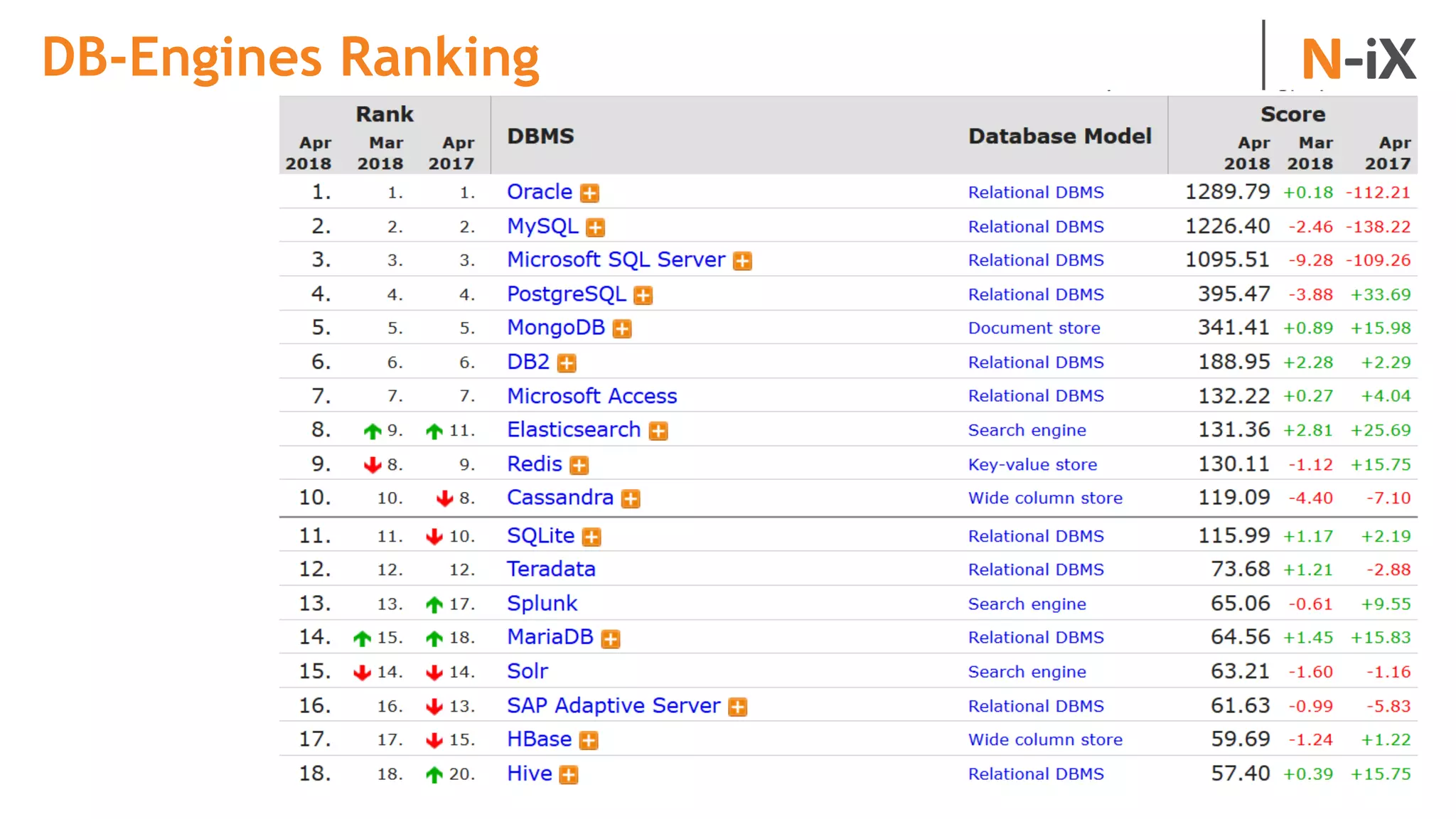
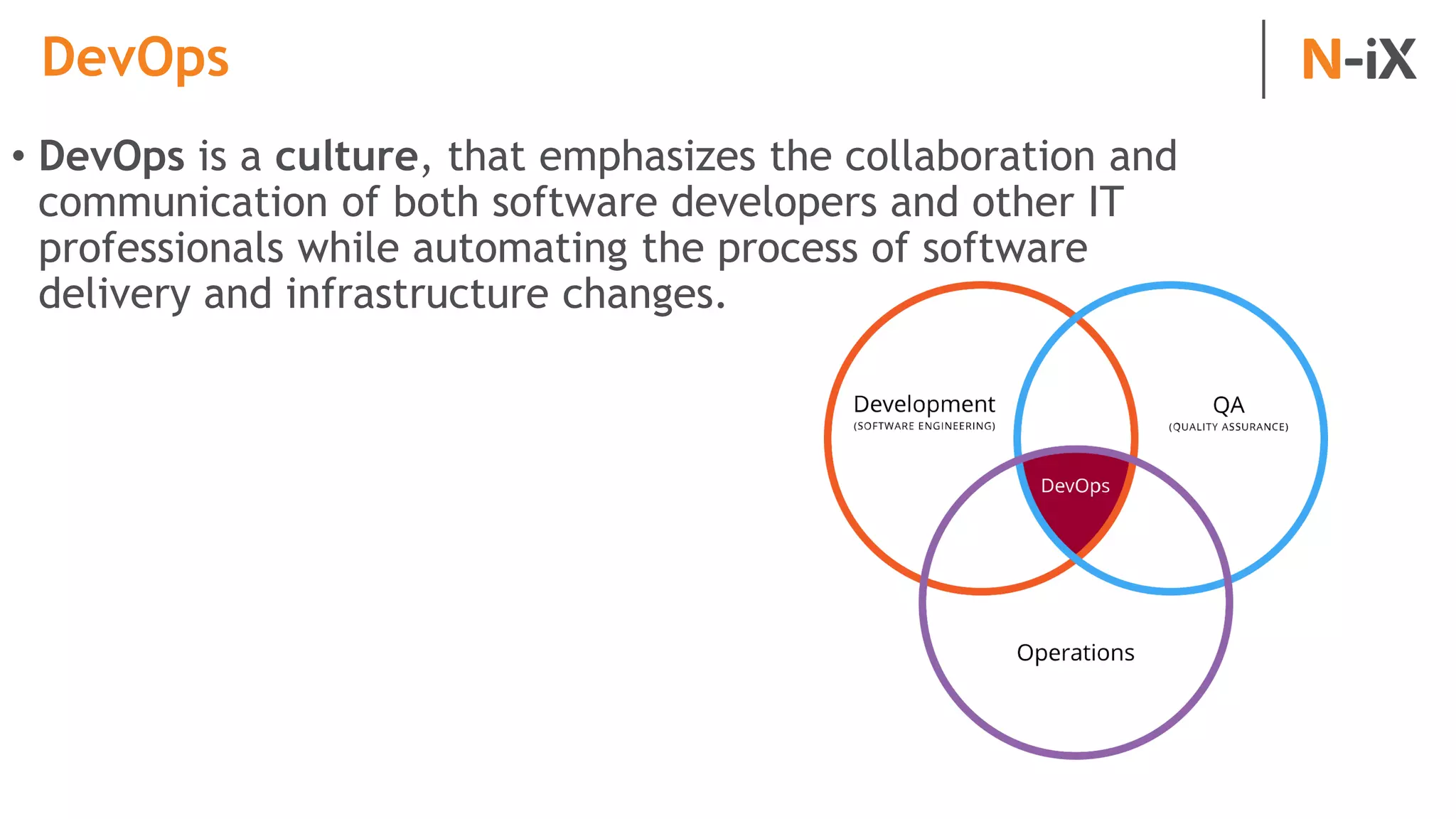
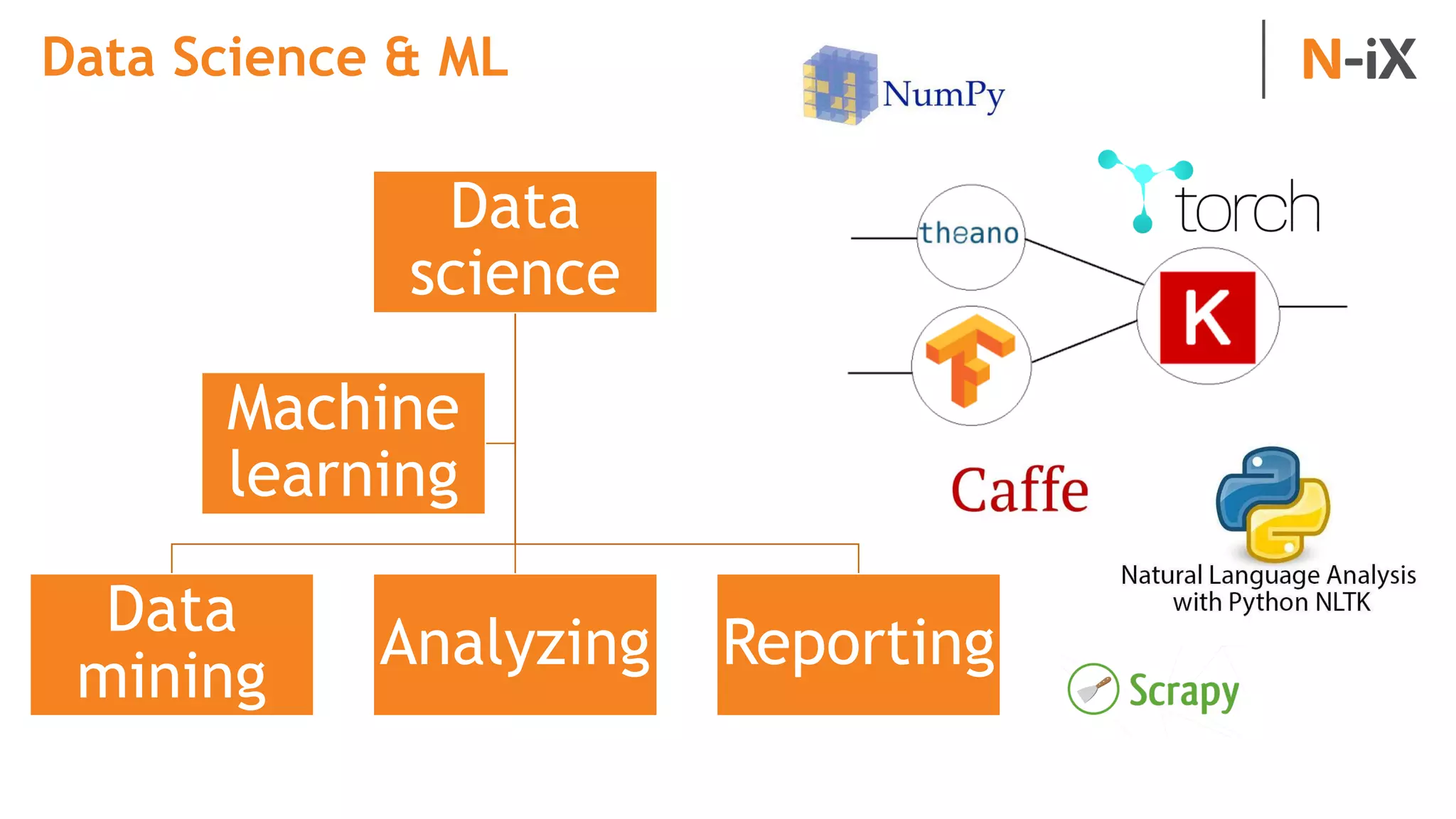
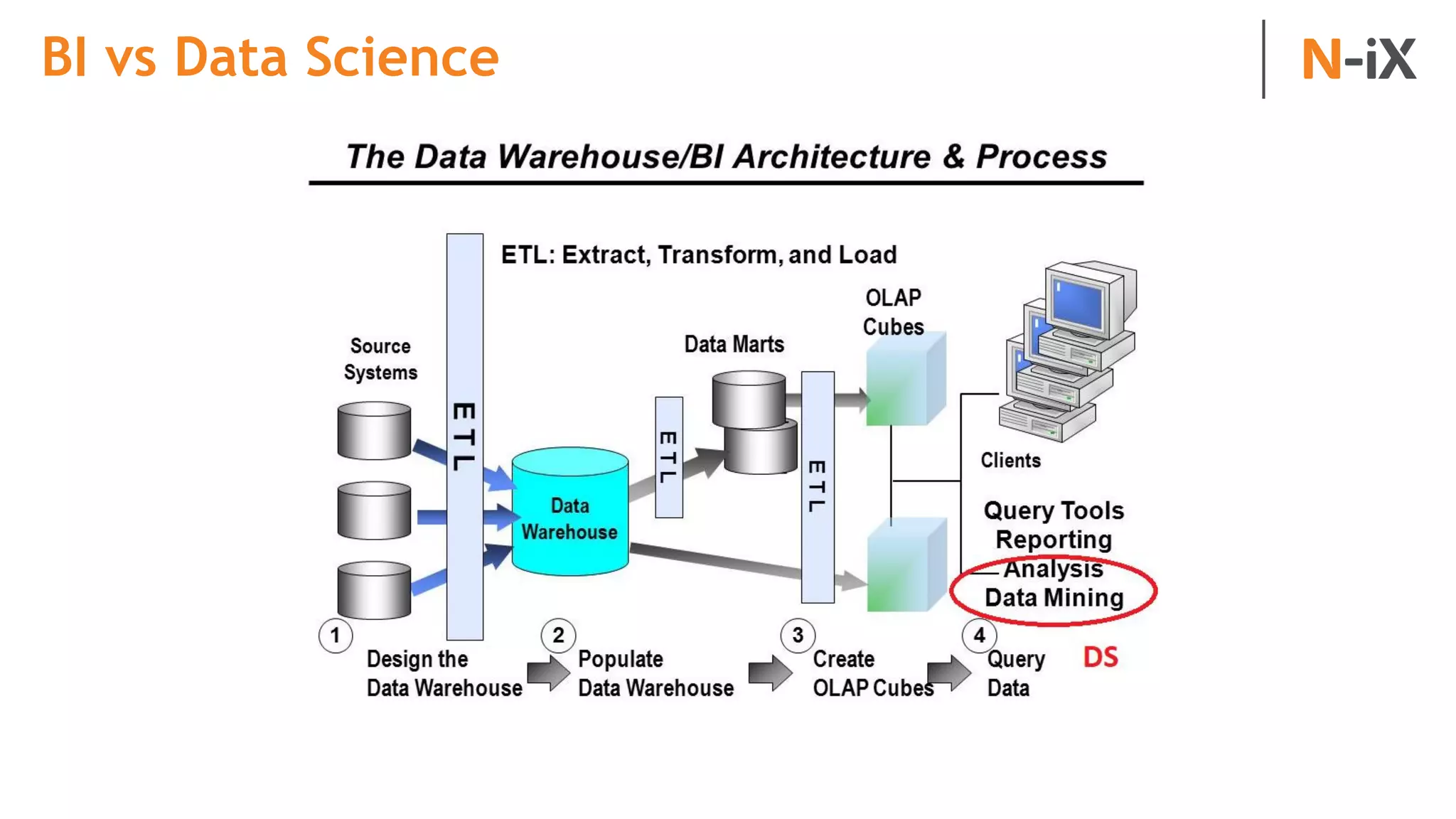
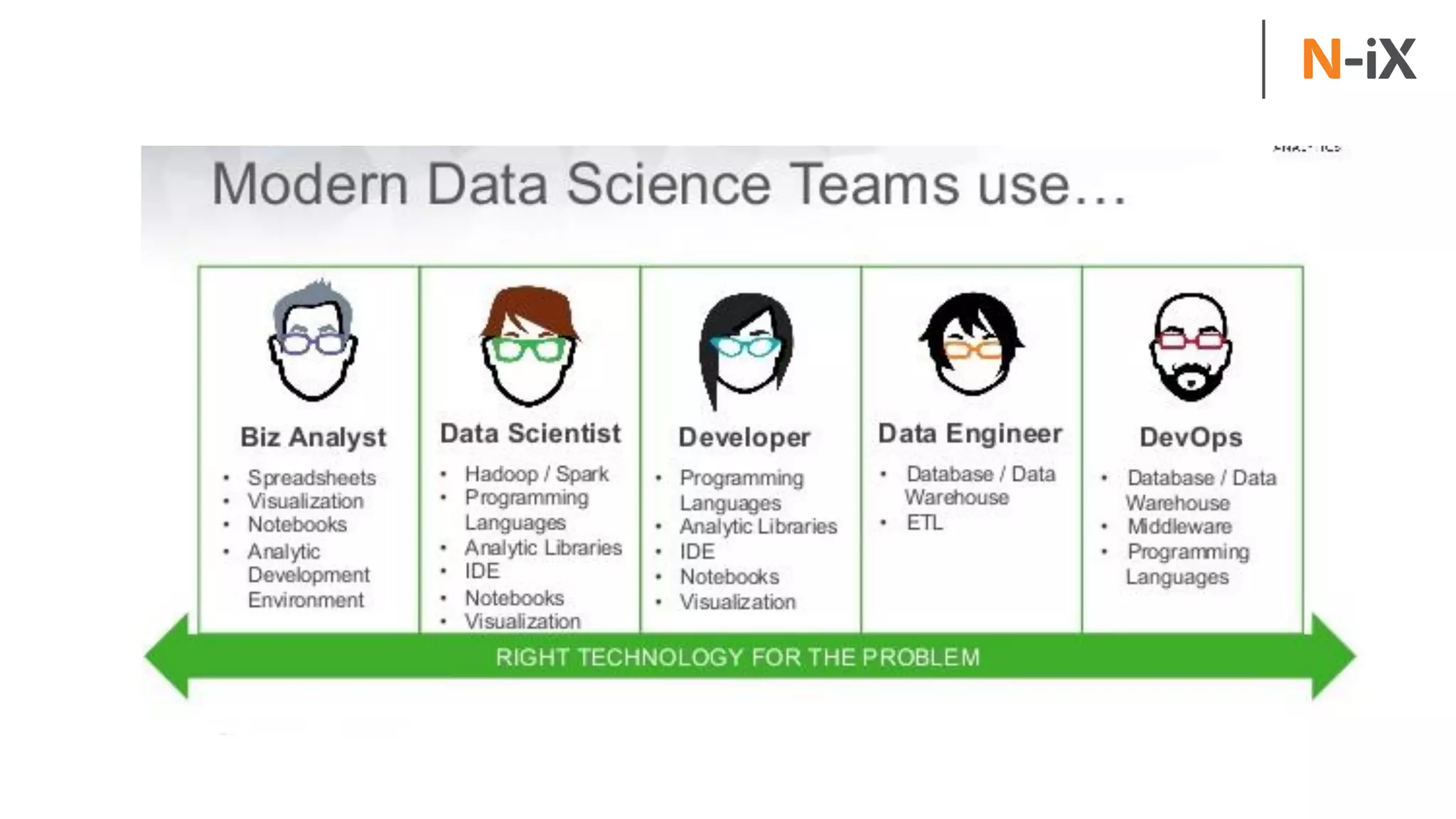
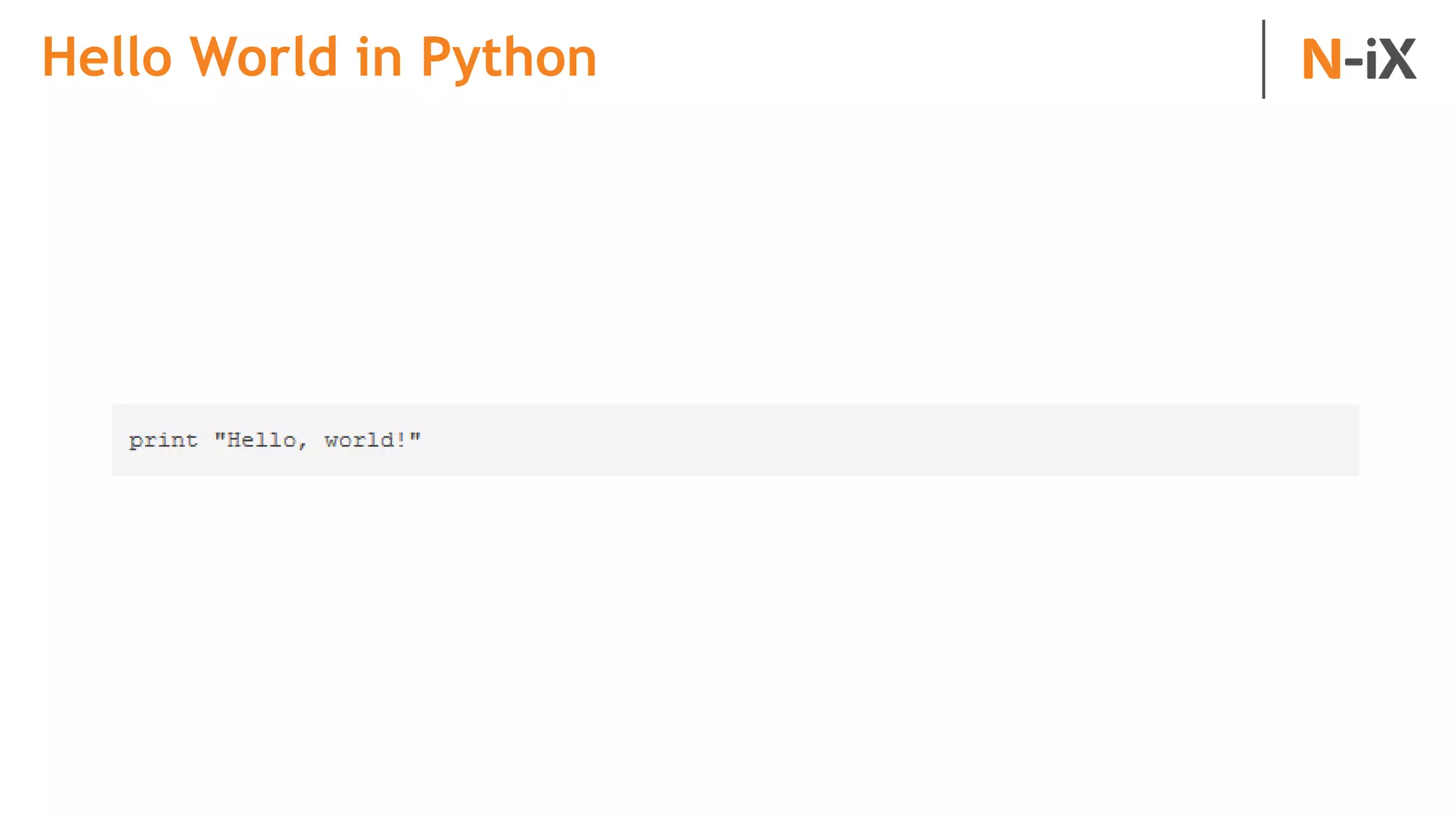
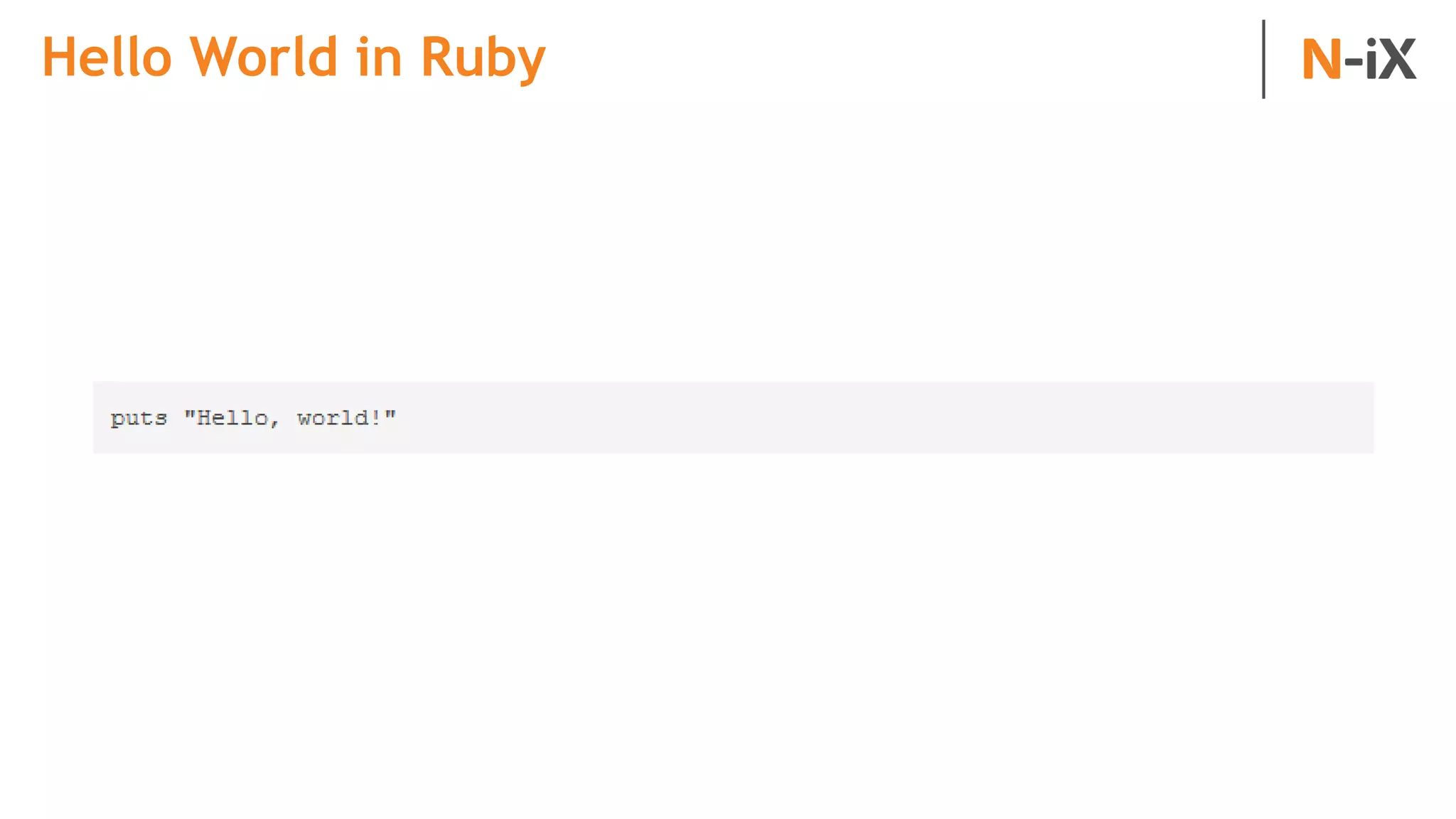
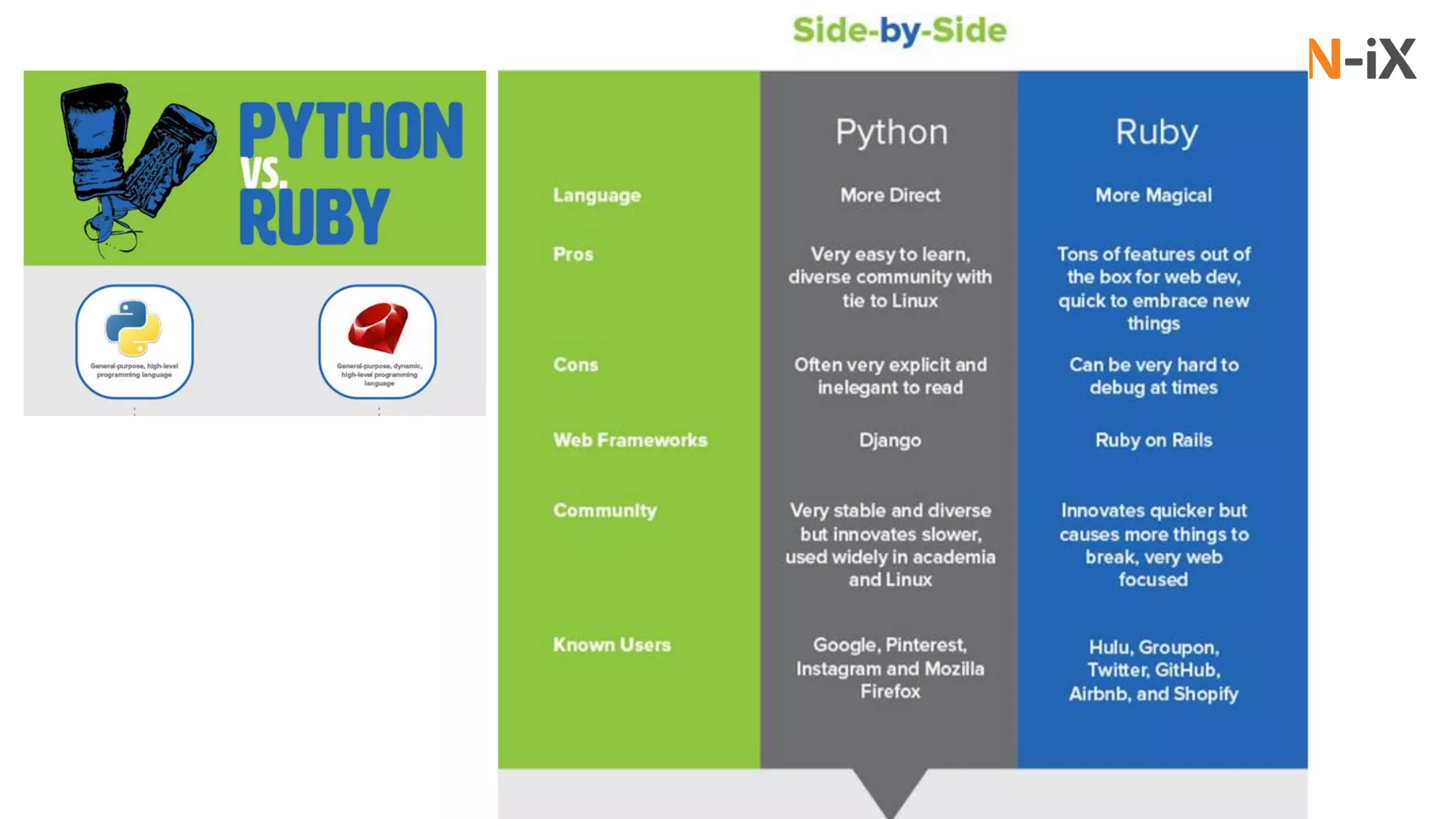
This document provides an introduction to programming terminology, concepts, and technologies for non-technical people. It outlines a training on software development lifecycles, engagement models, business domains, major programming languages, frameworks, and technologies. Key terms from front-end and back-end development, databases, DevOps, data science, and mobile apps are defined. Popular languages, frameworks, and platforms are compared, along with ratings of language popularity. Quality control techniques are briefly introduced.