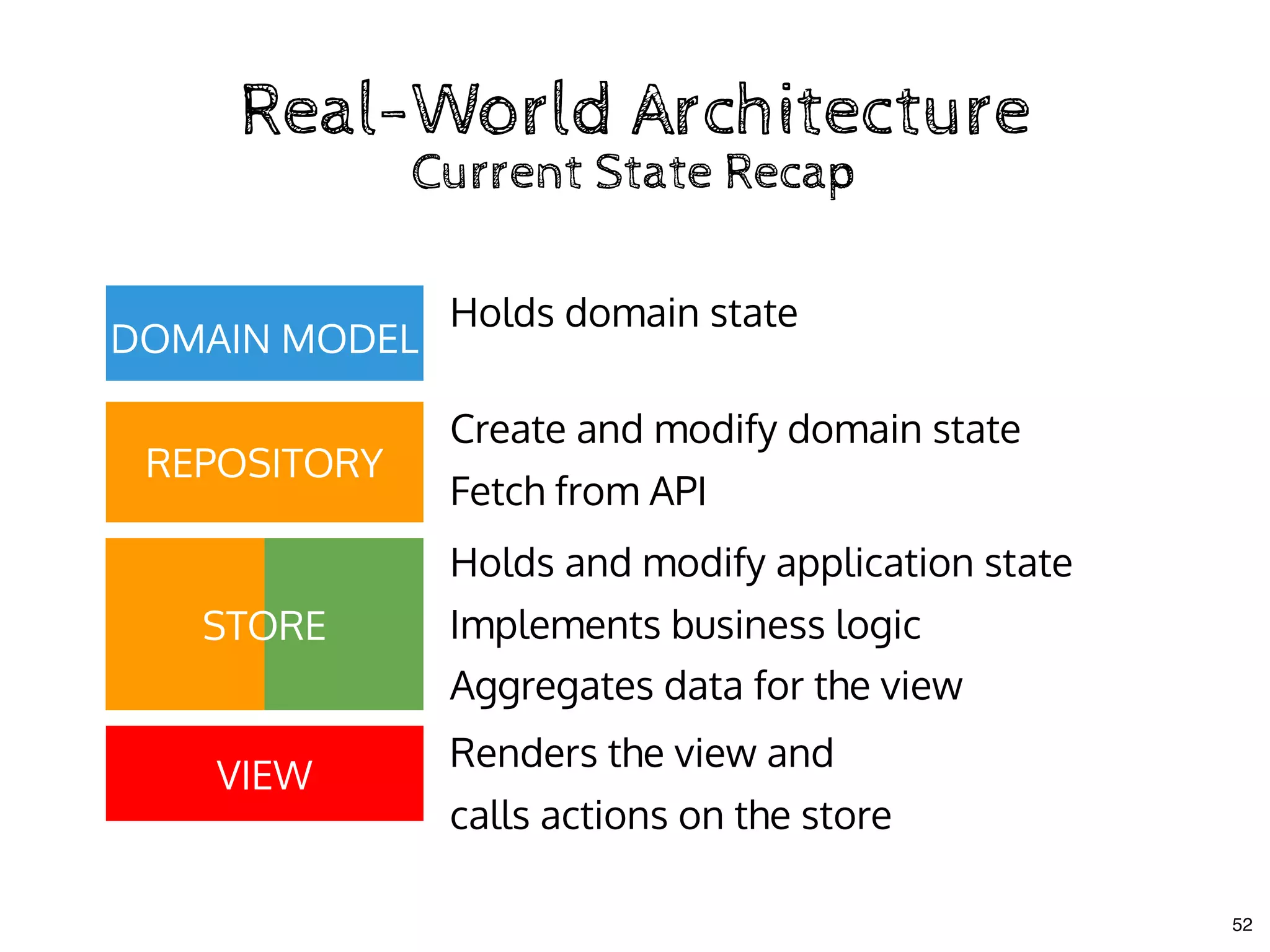
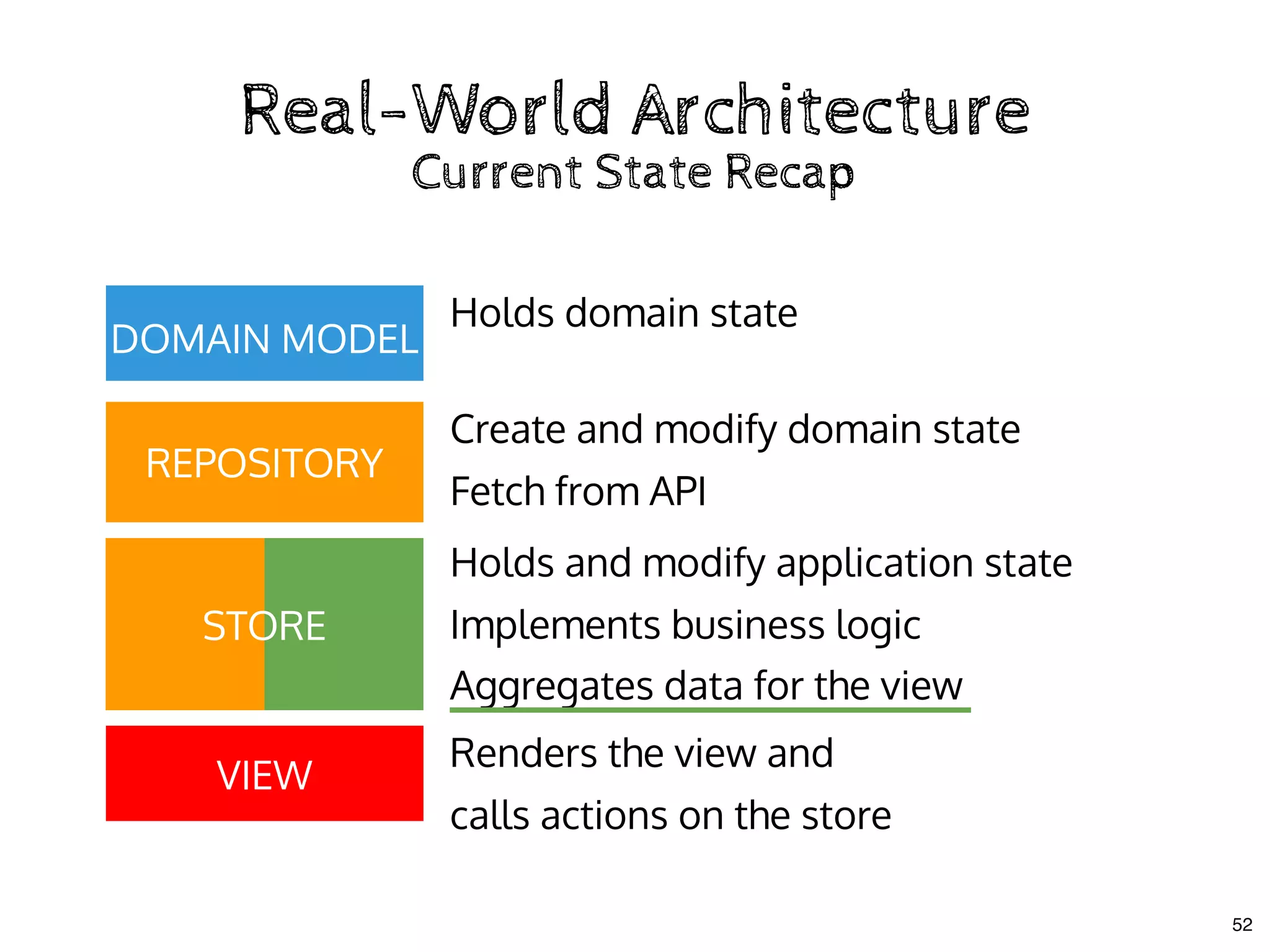
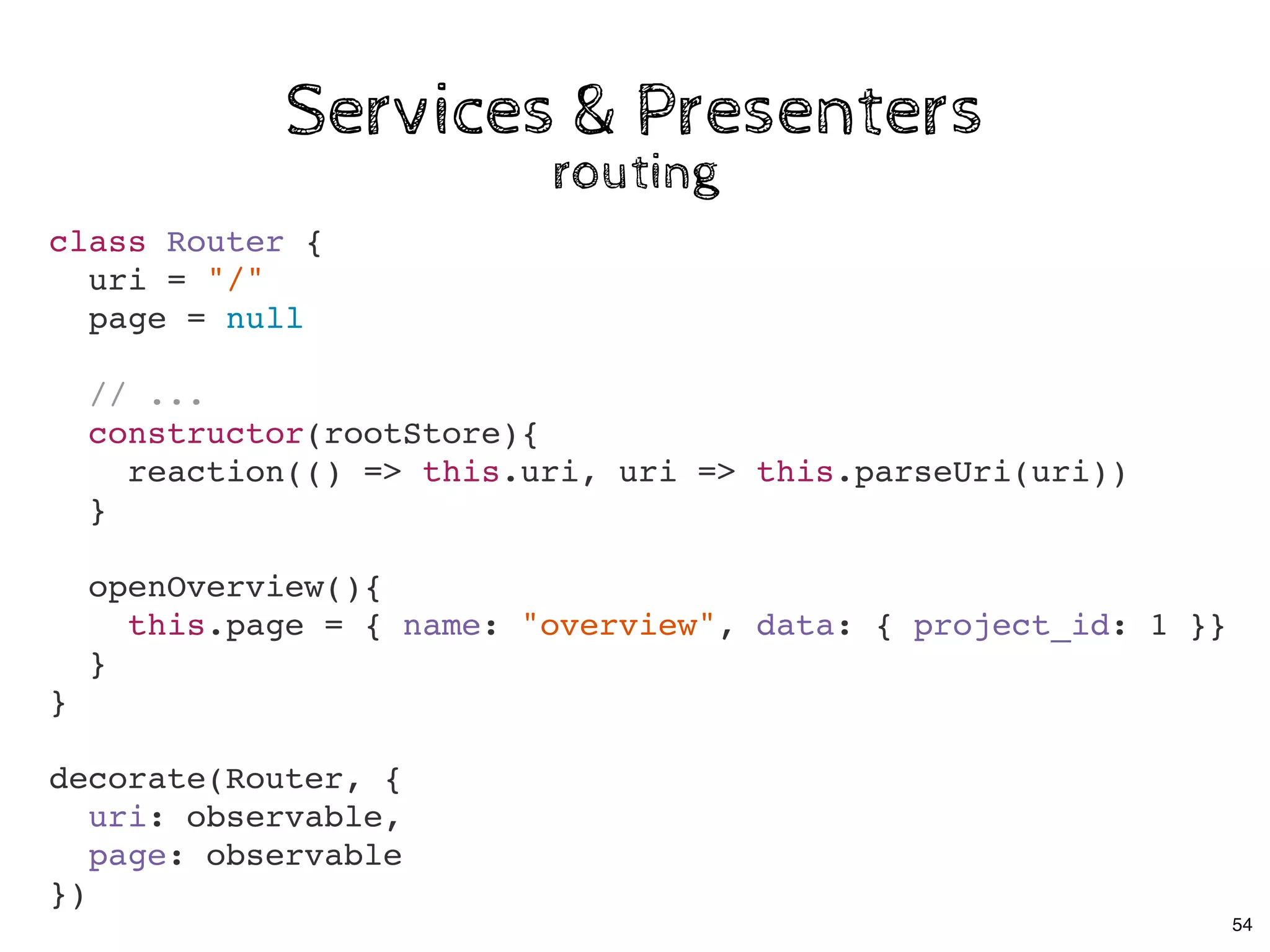
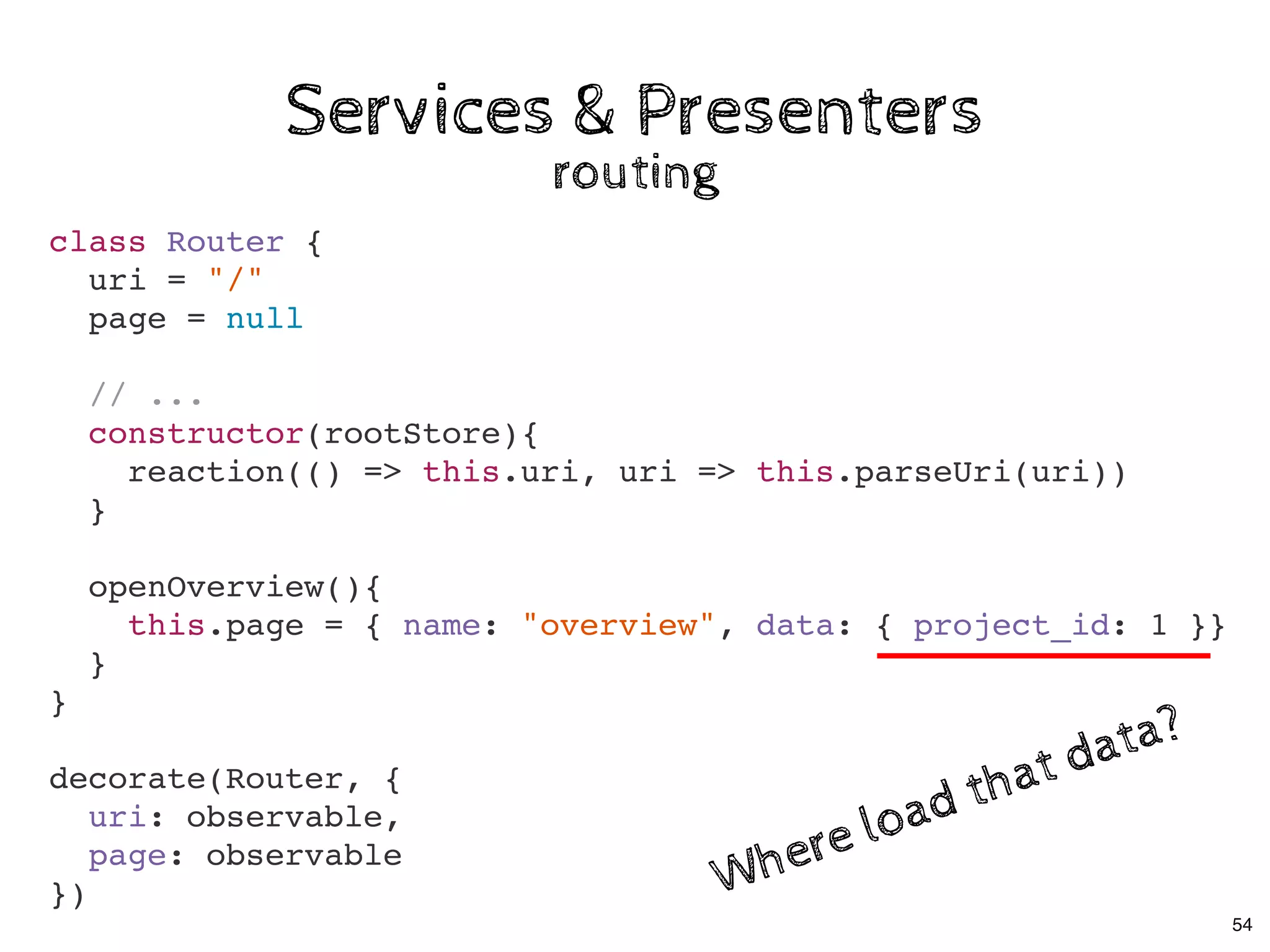
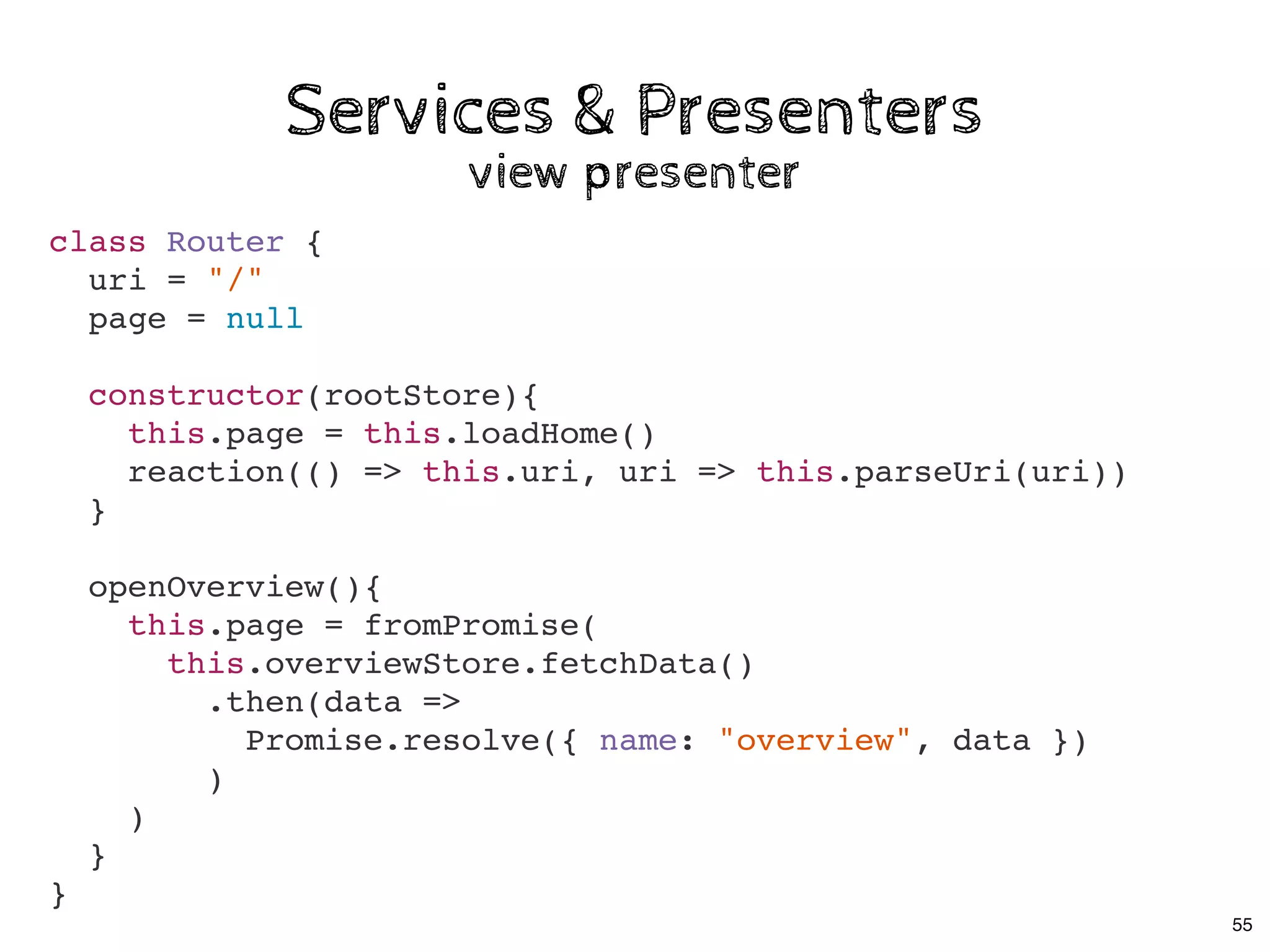
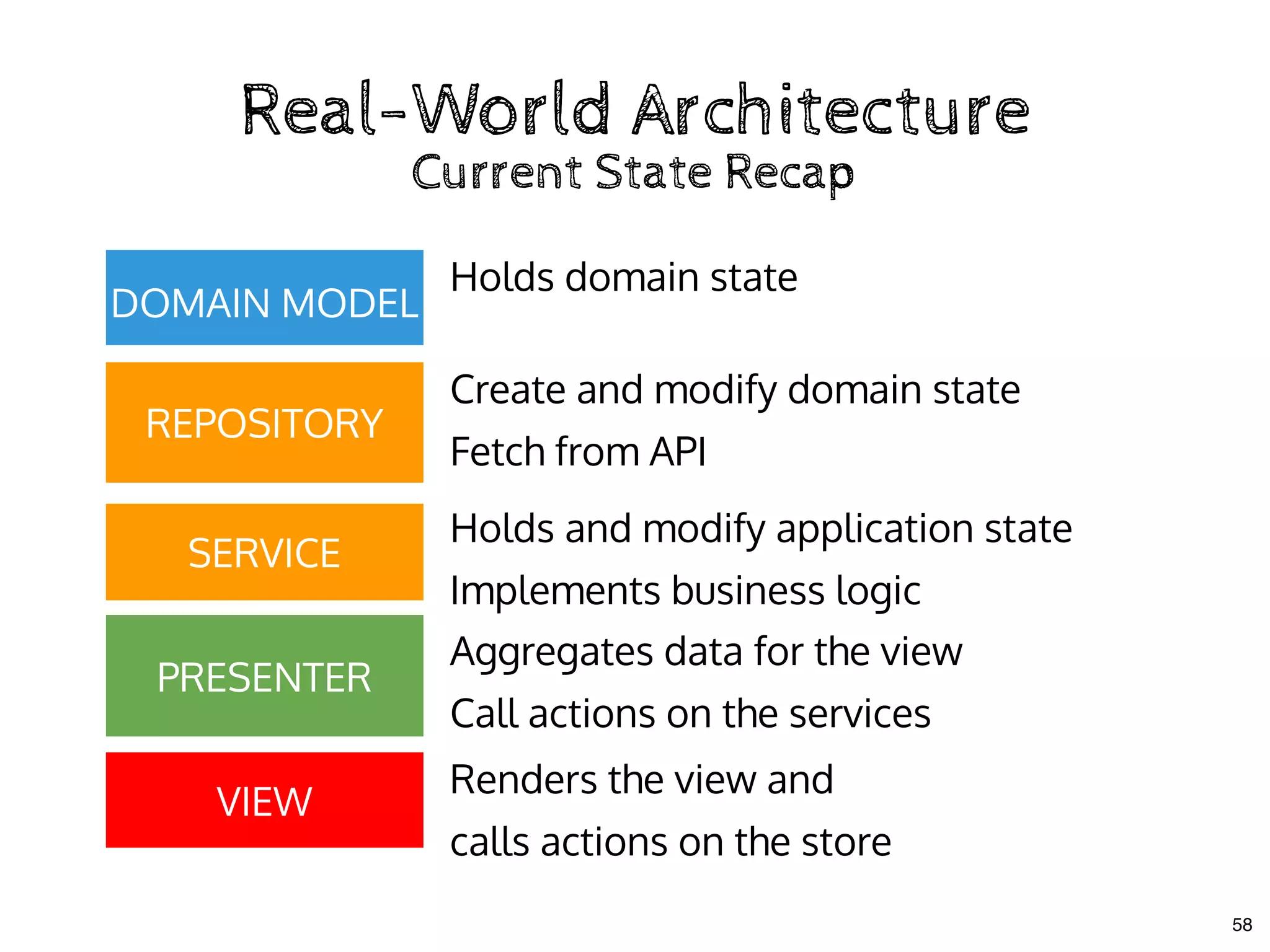
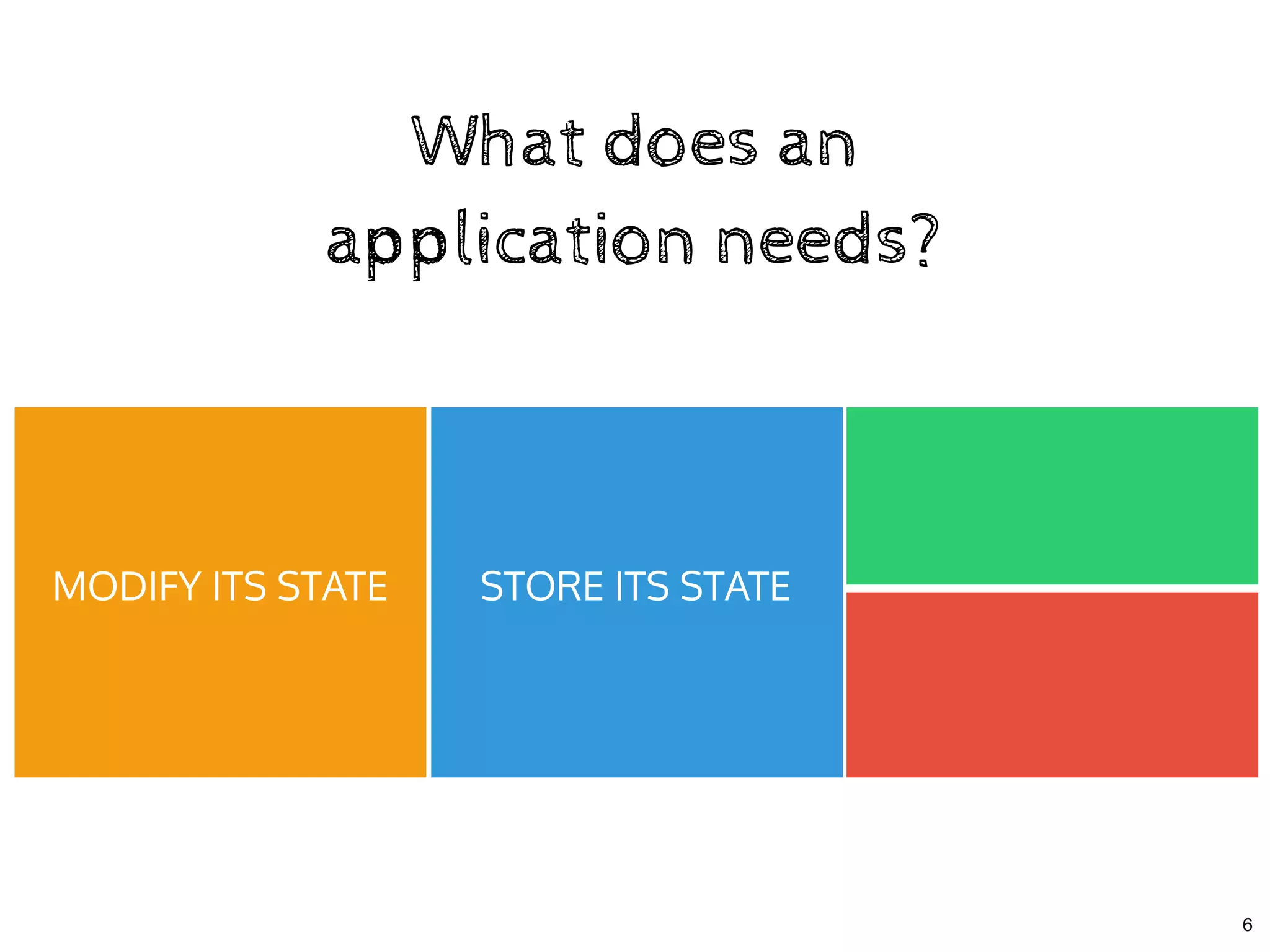
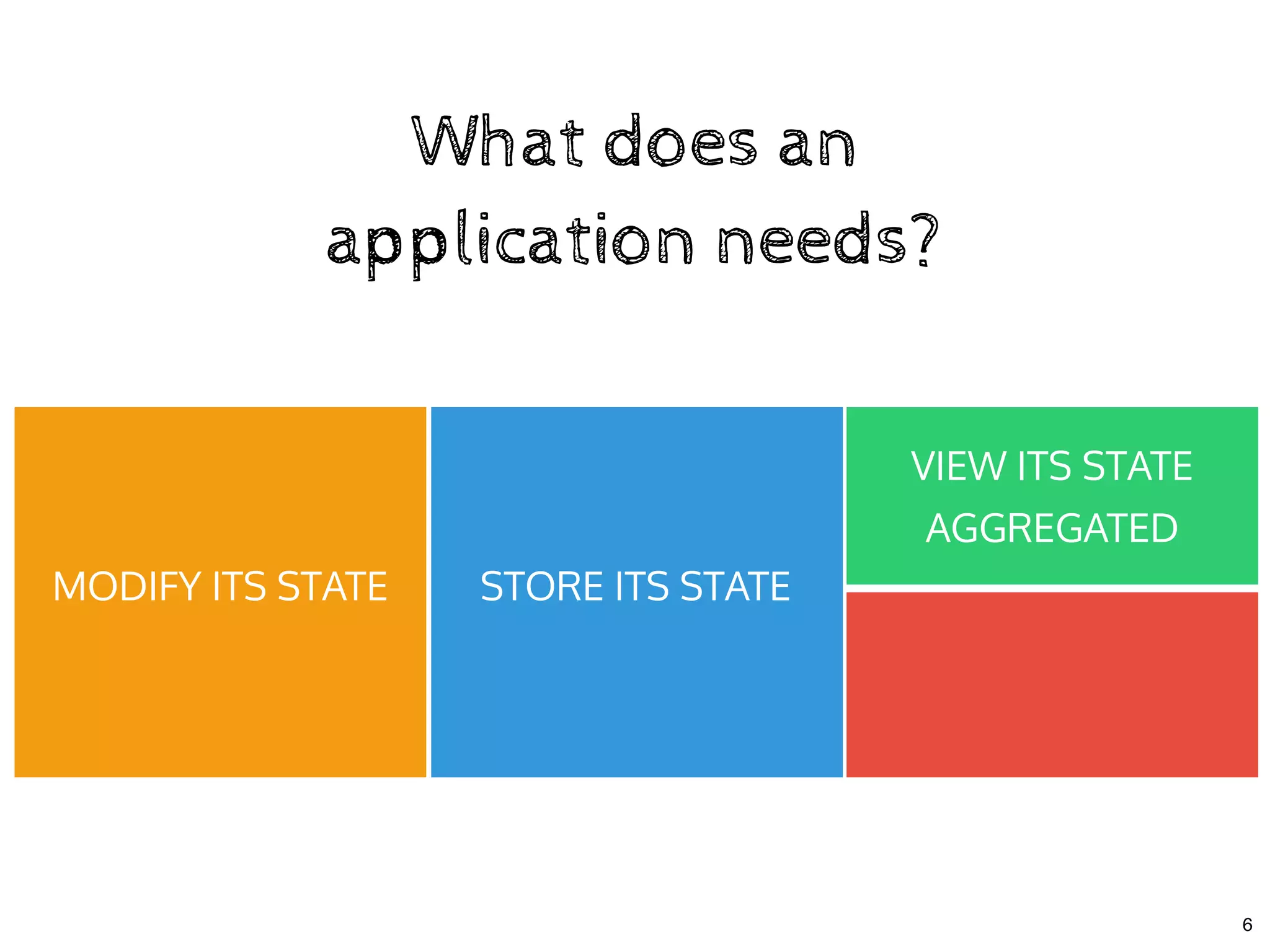
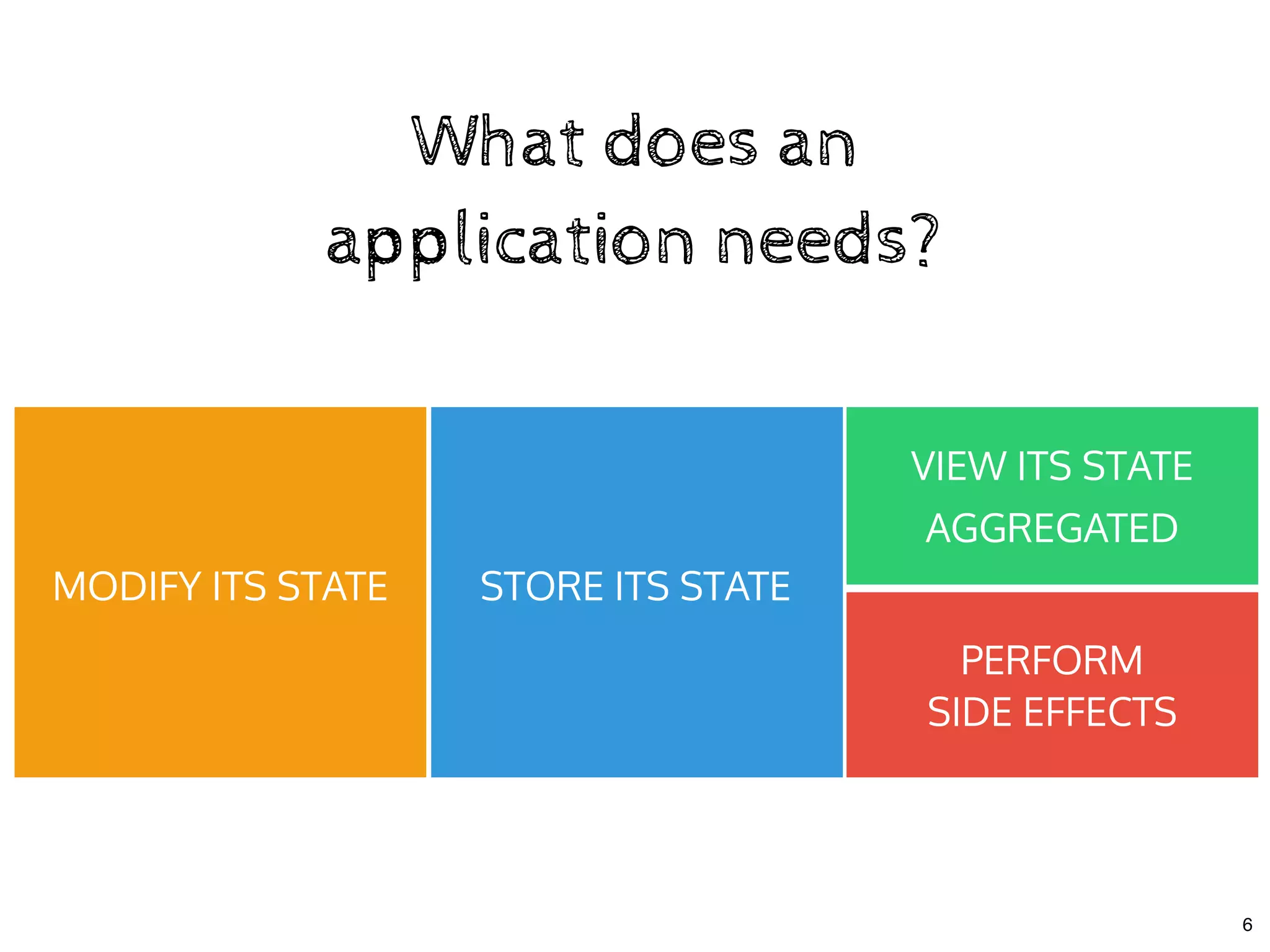
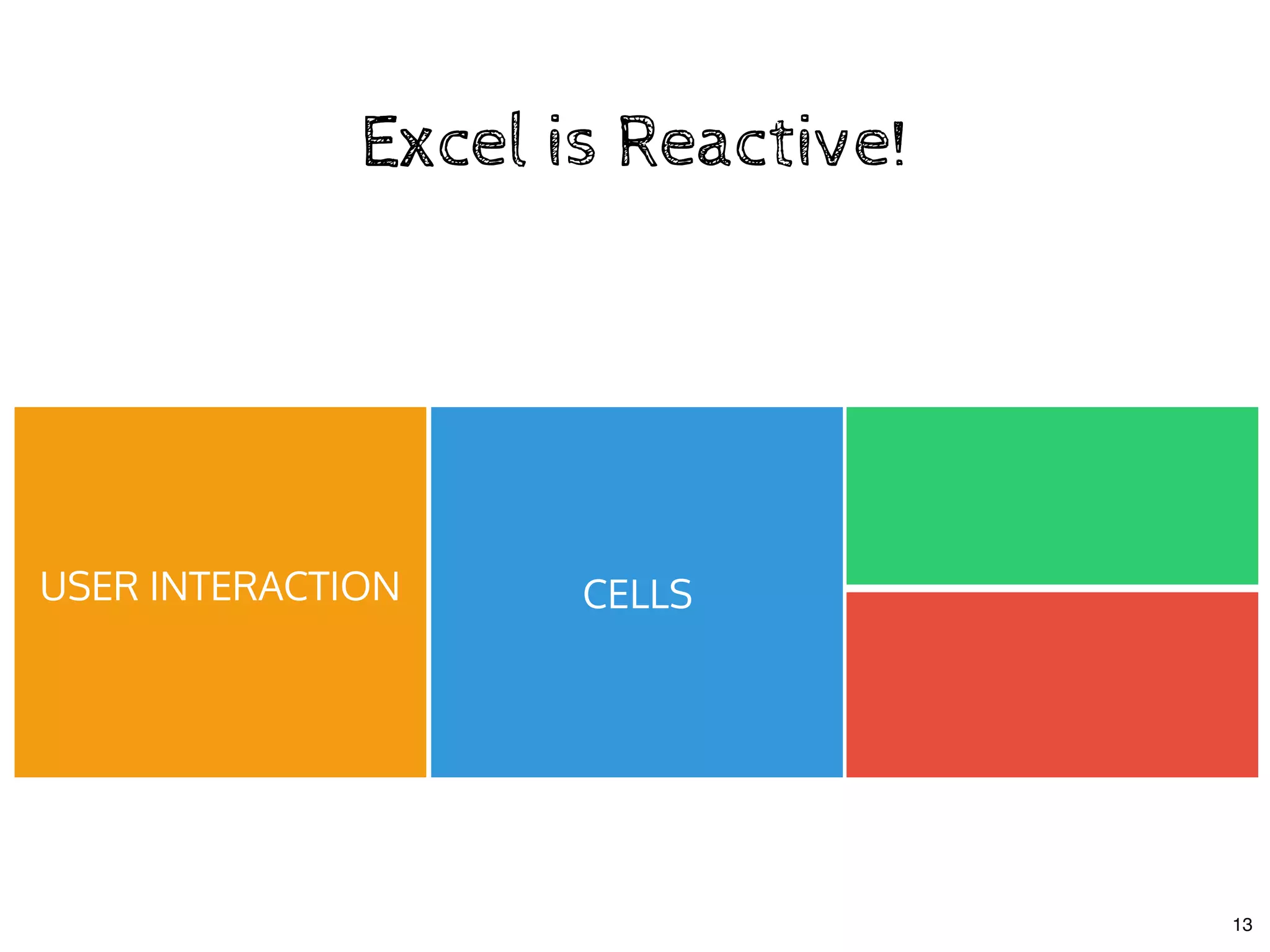
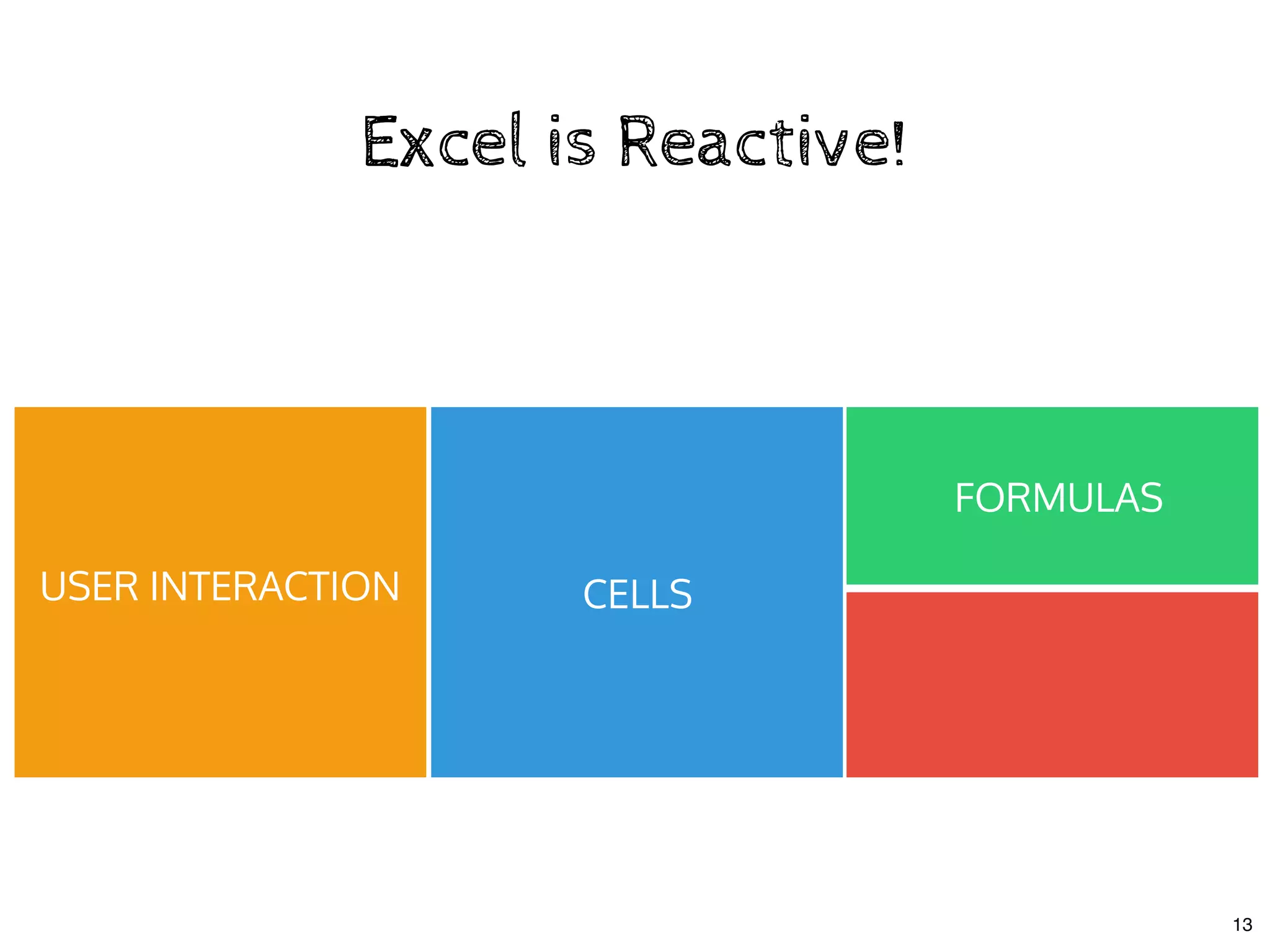
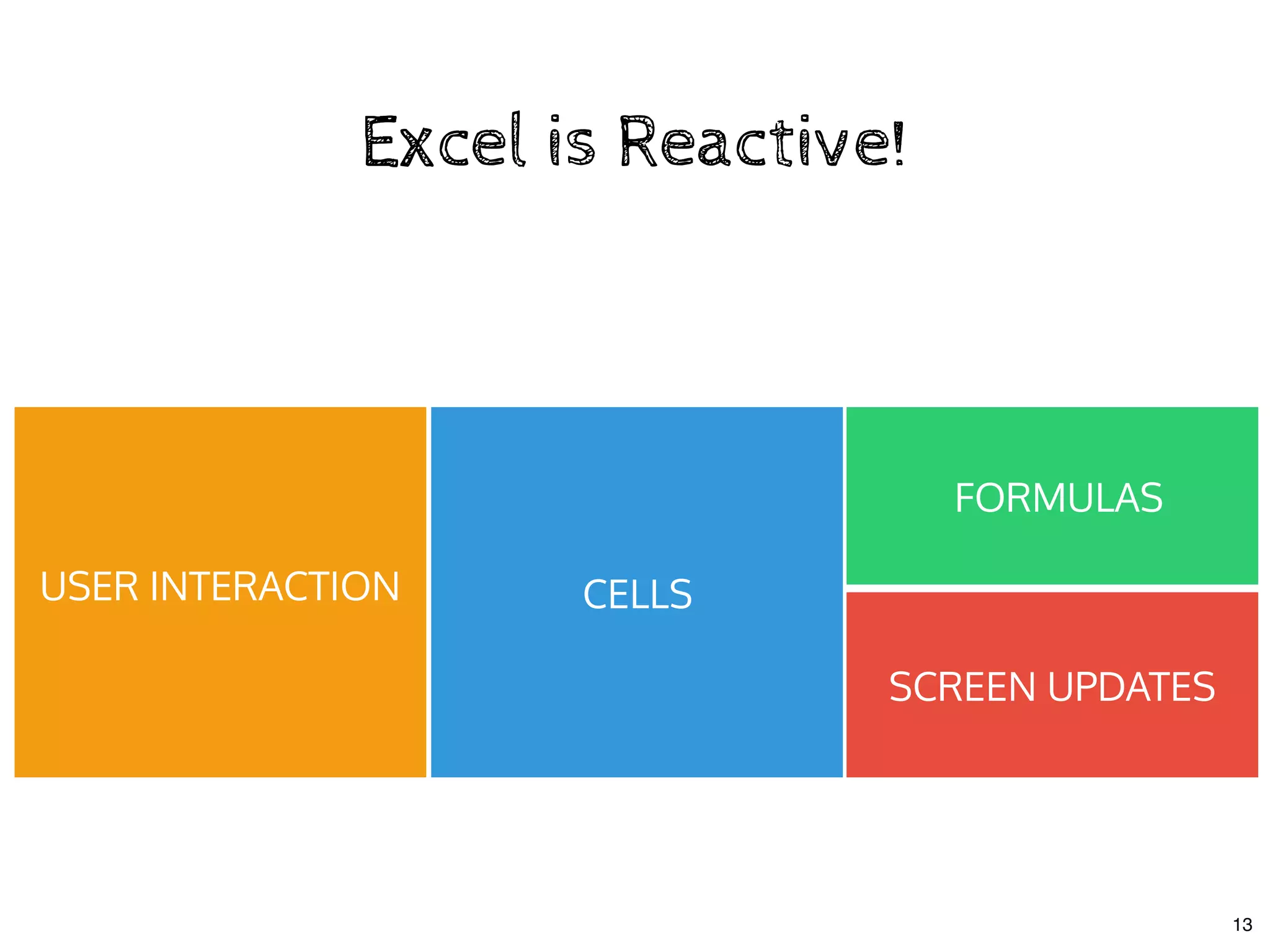
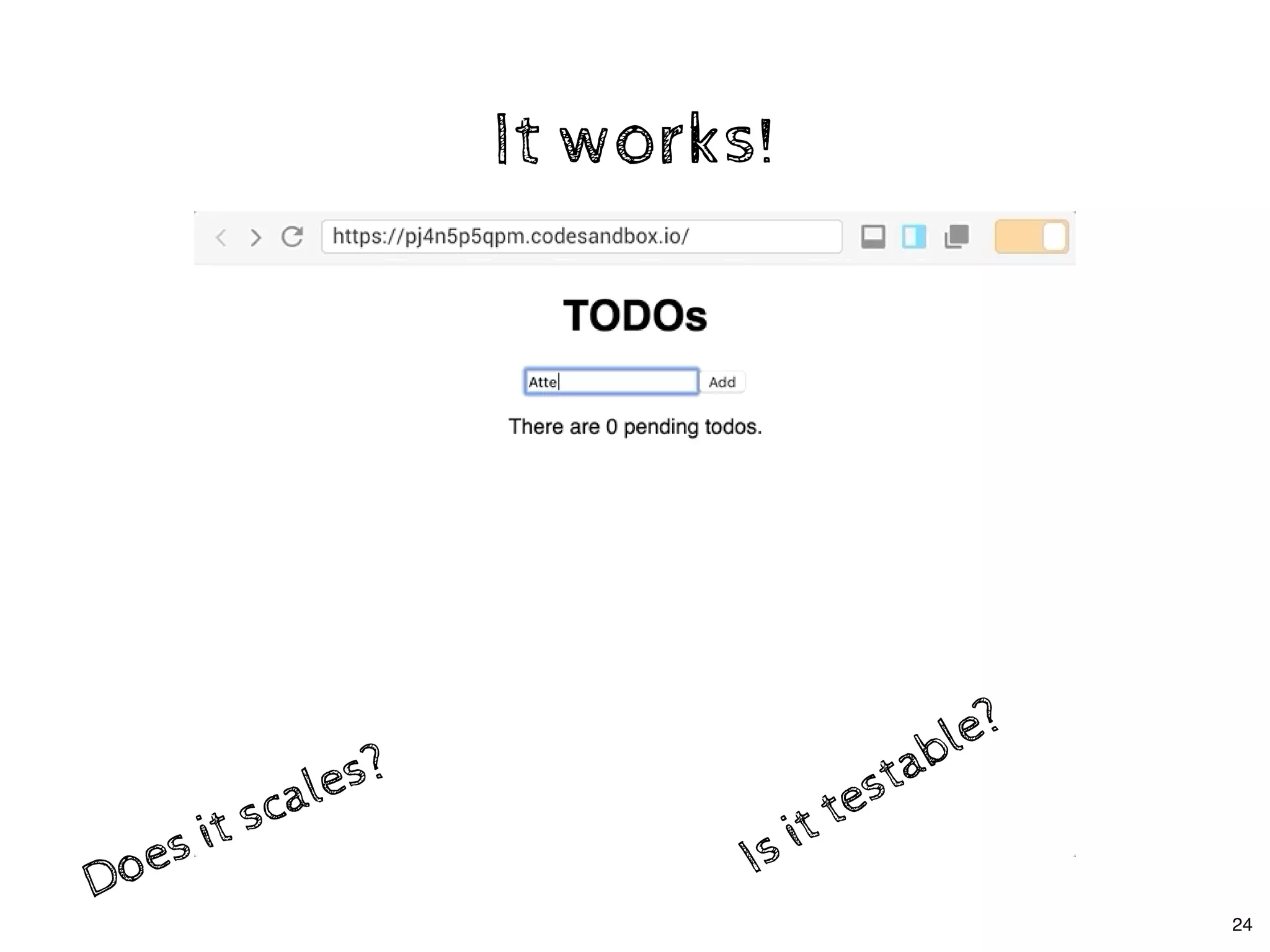
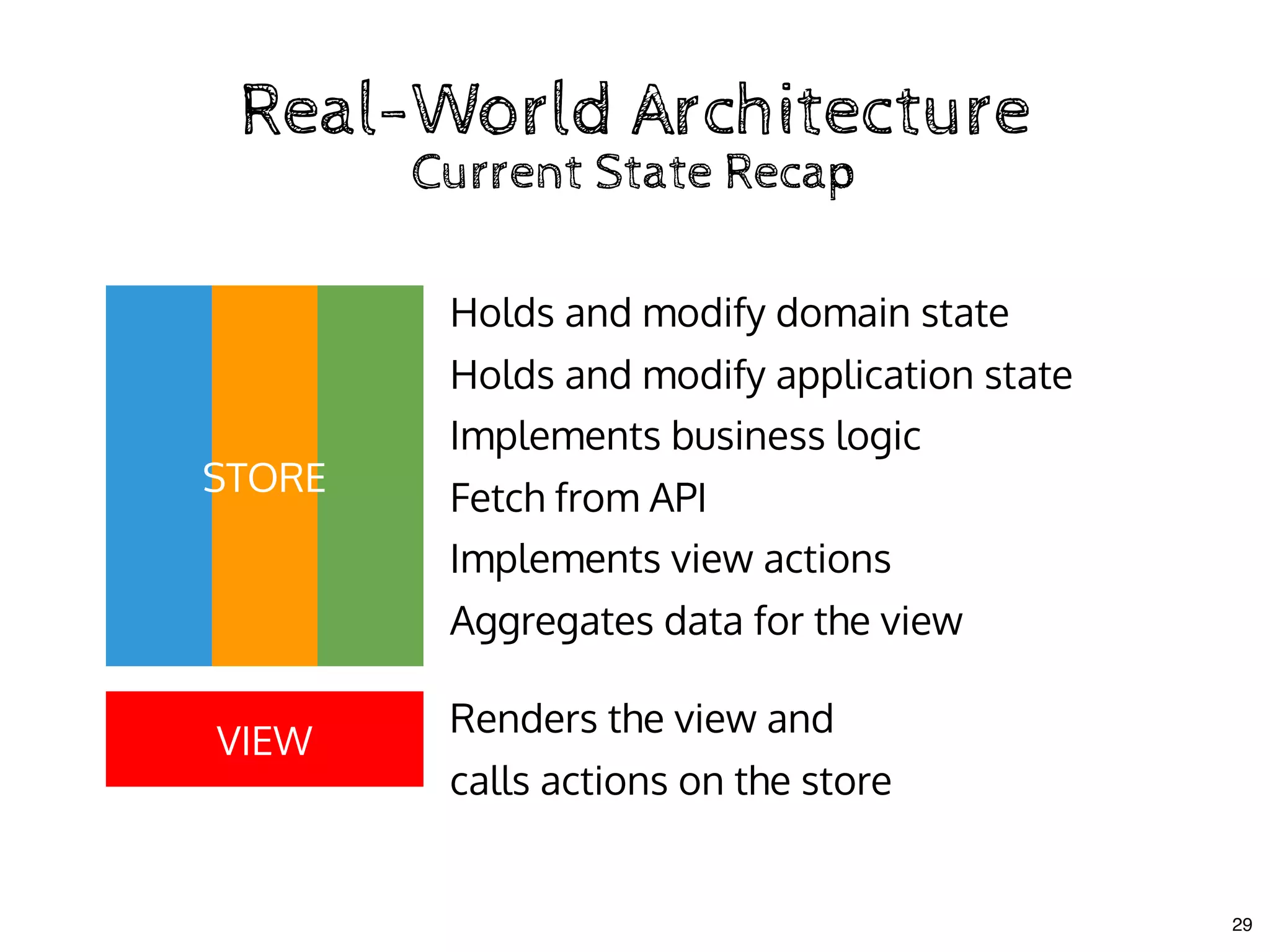
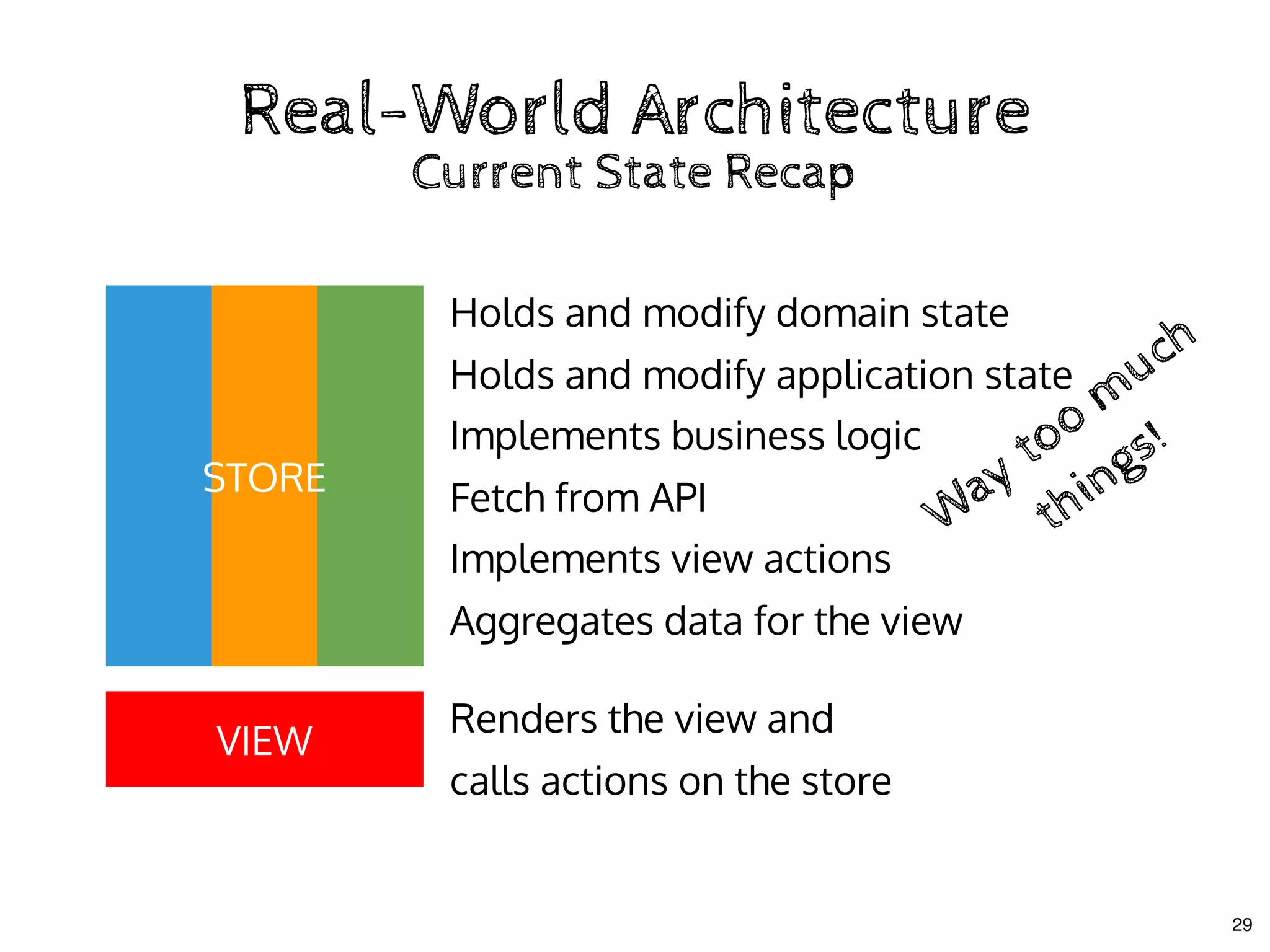
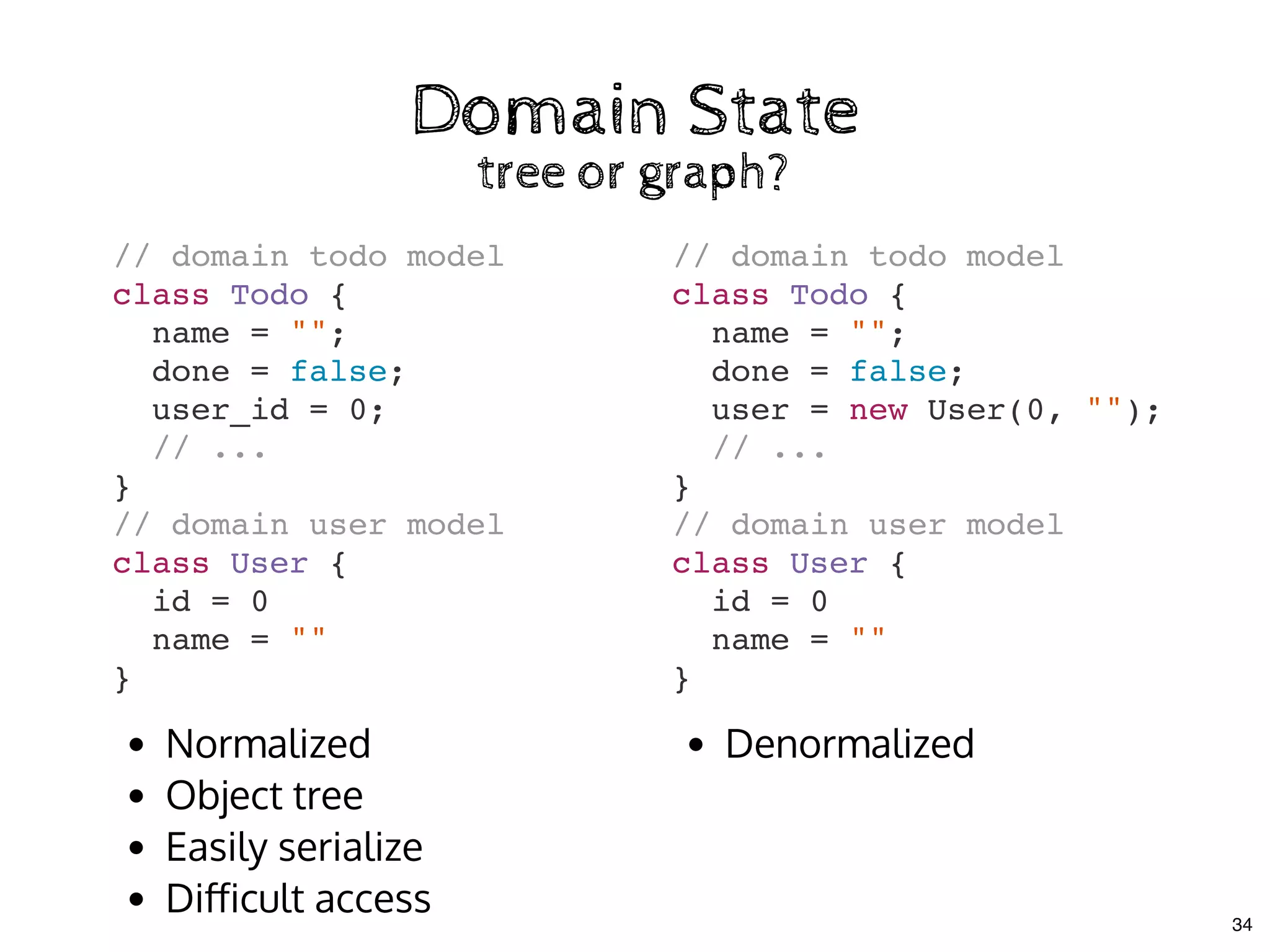
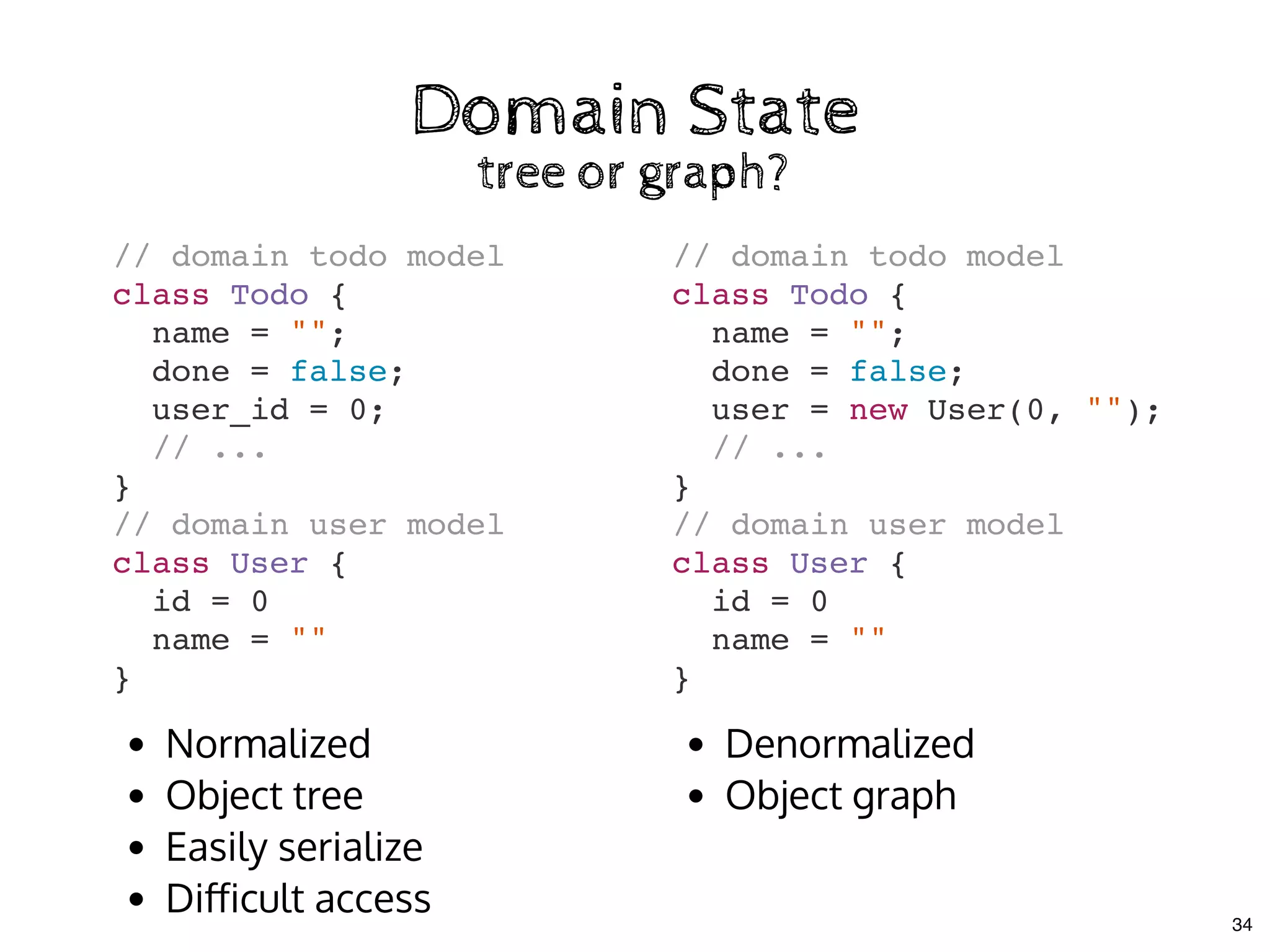
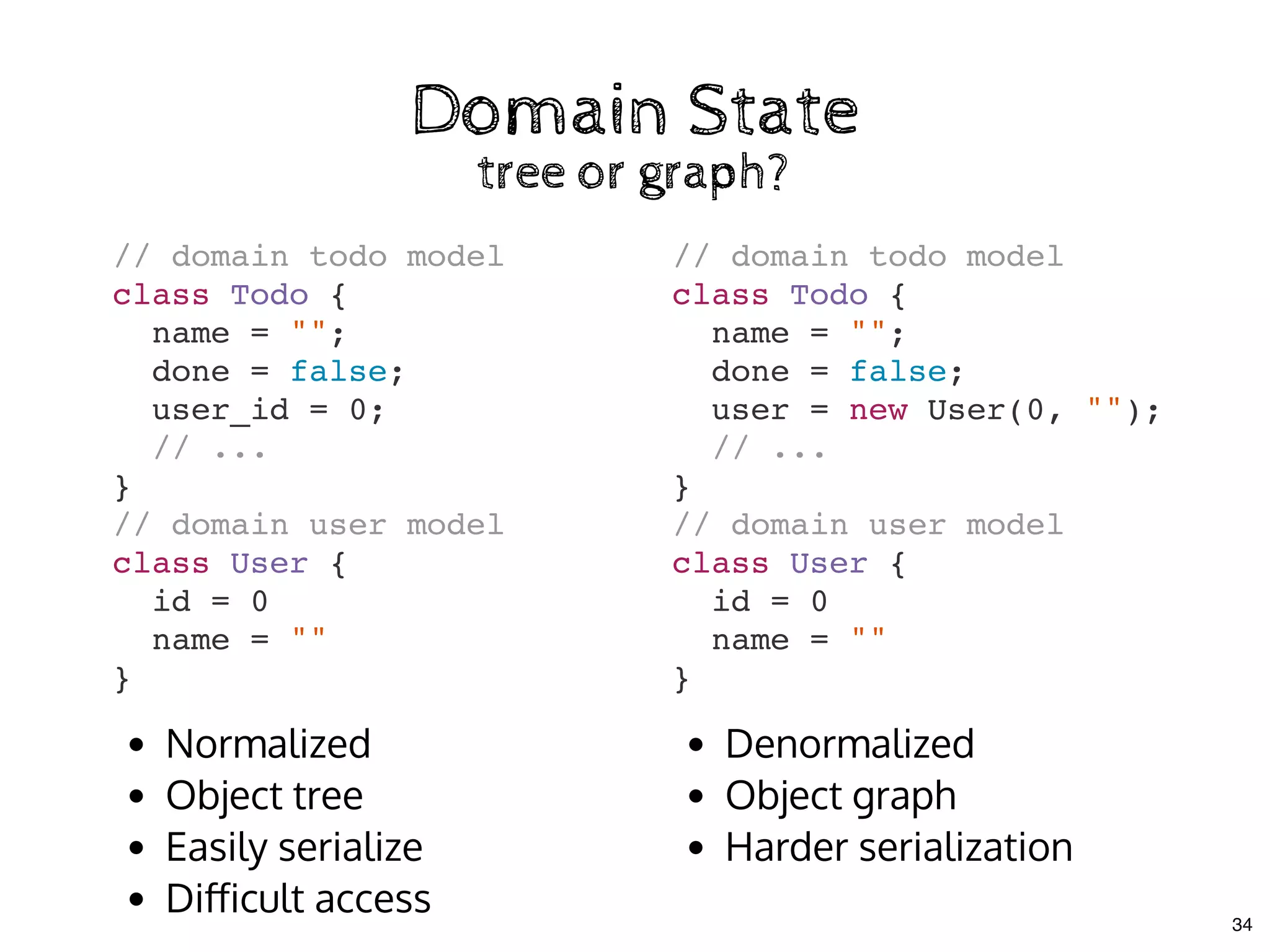
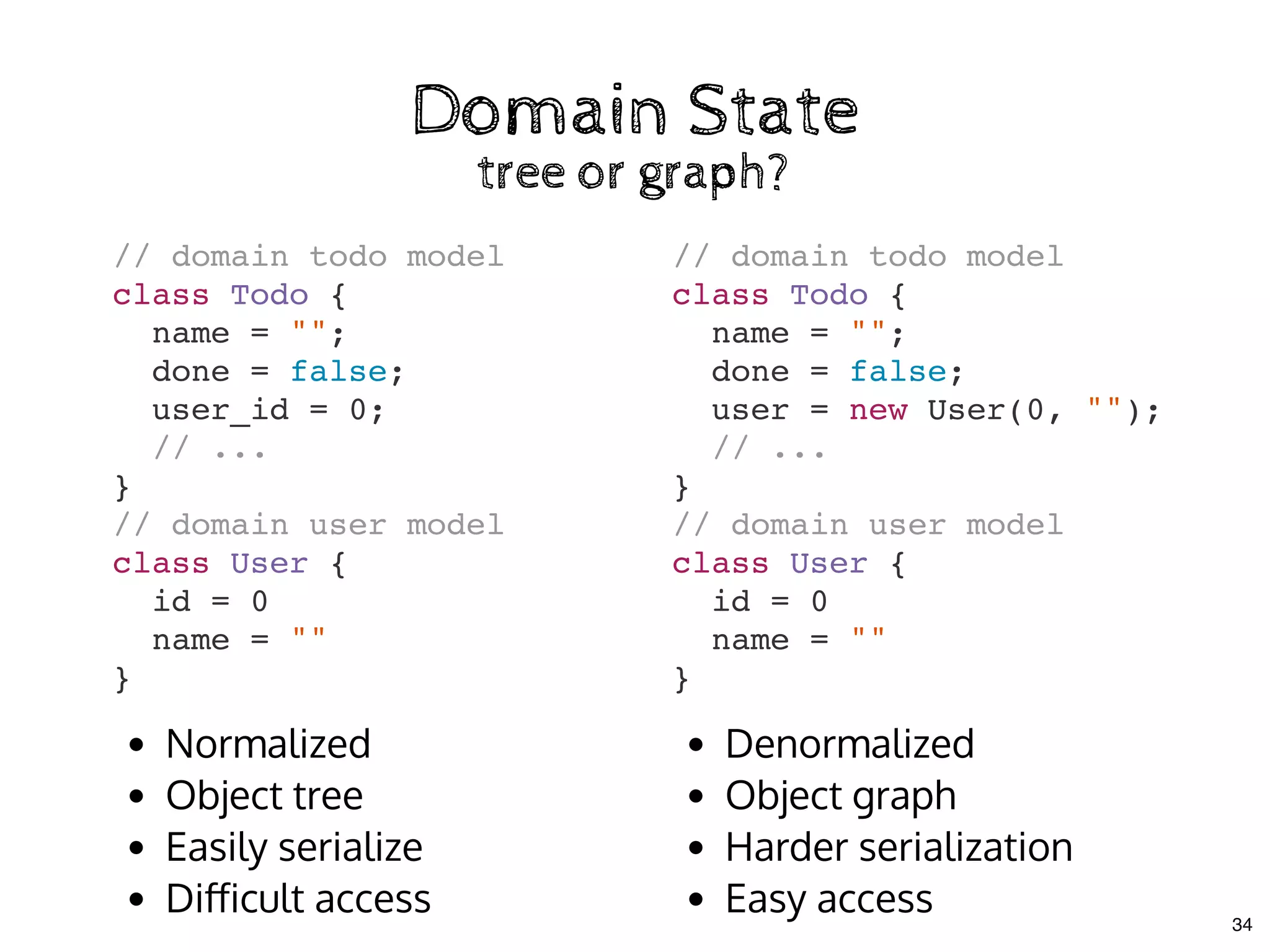
The document discusses the use of MobX, a reactive state management library for JavaScript applications, focusing on managing application state through observables and actions. It also highlights best practices in structuring applications, advocating for a separation of business logic from UI components and the use of provider/inject patterns for store access. Additionally, real-world examples, particularly a todo list application, demonstrate how to effectively implement these concepts in React.





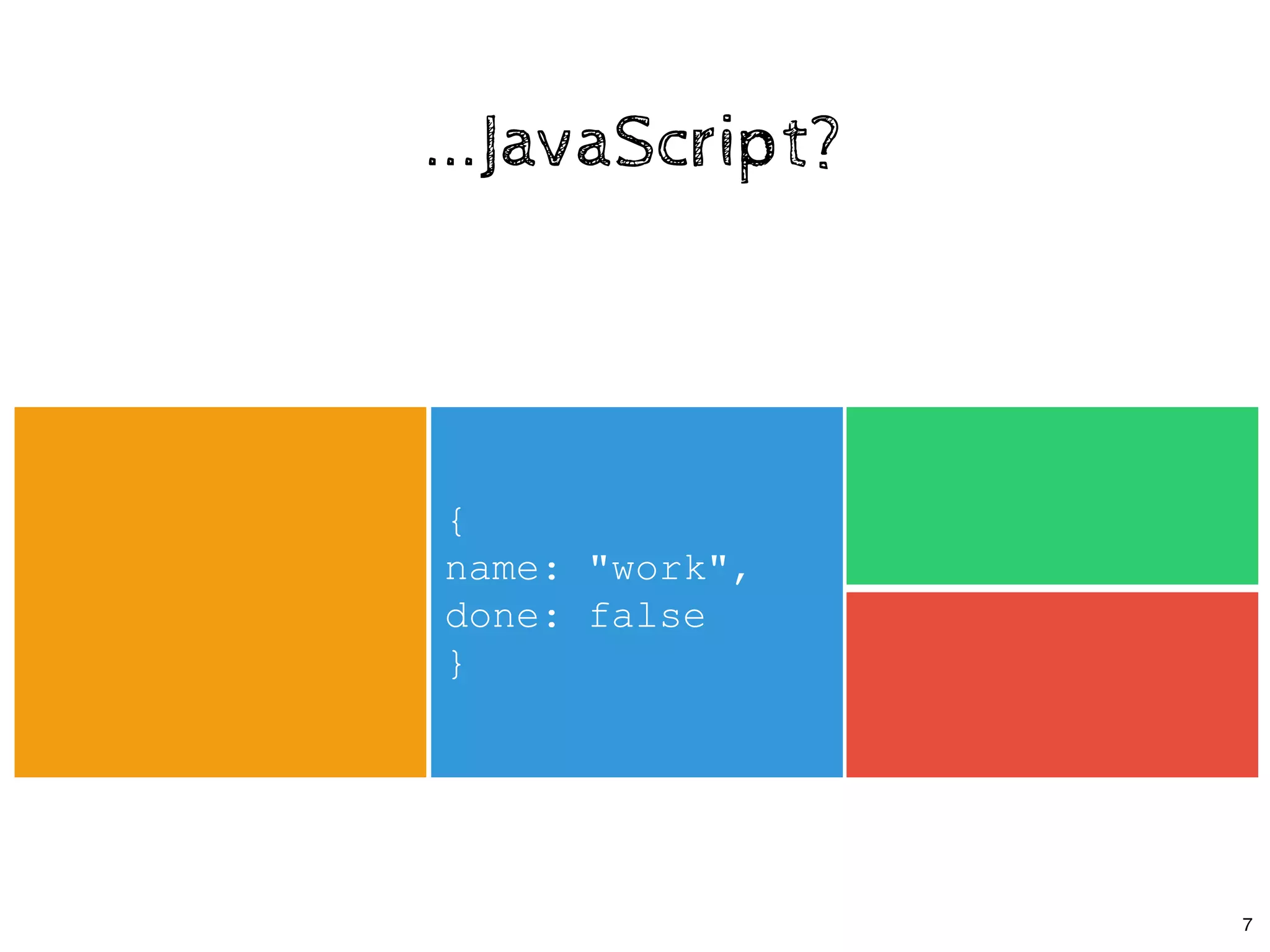

















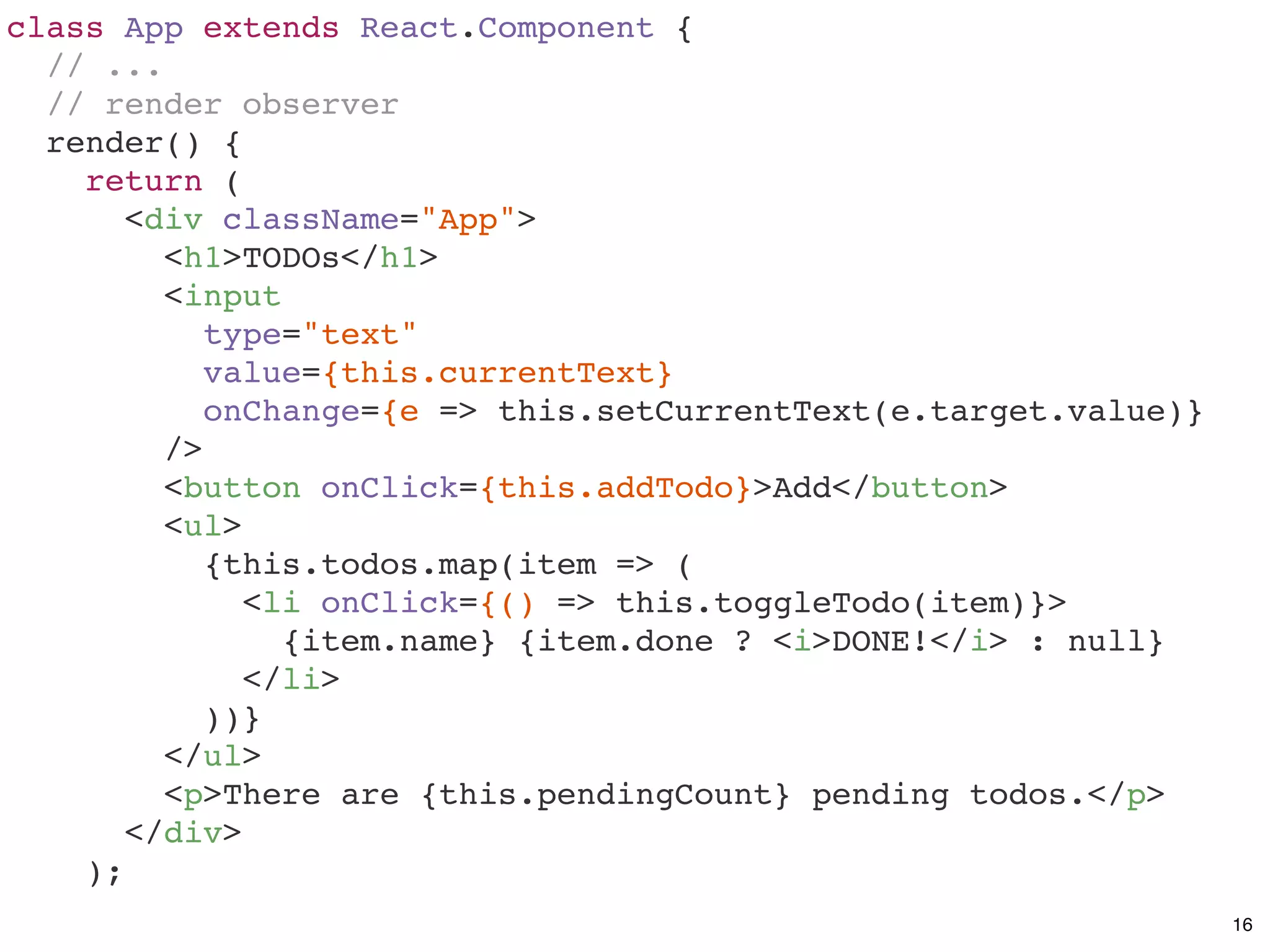
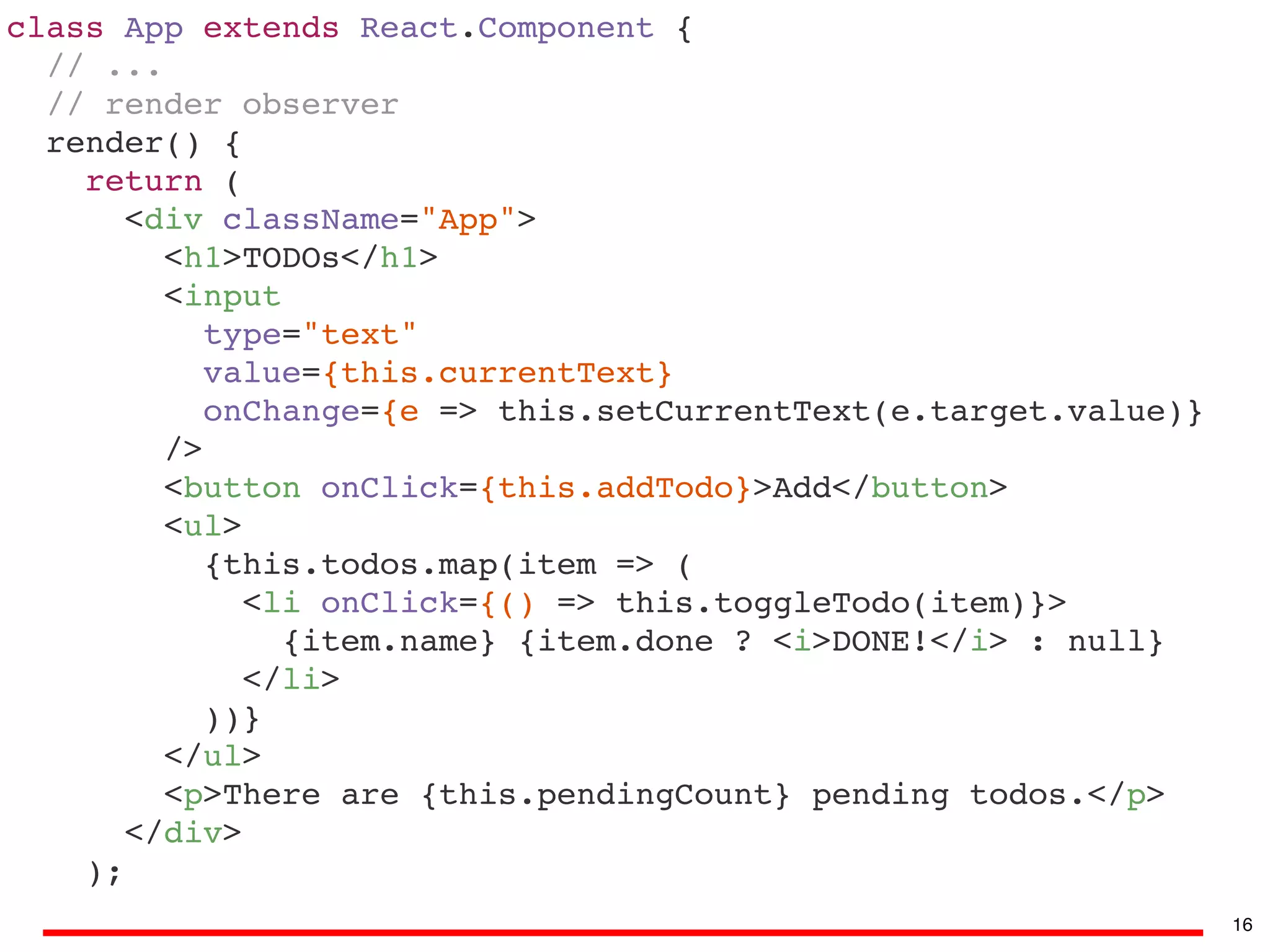
![class App extends React.Component {
// observable values
currentText = "";
todos = [];
// actions
addTodo = () => {
this.todos.push({ name: this.currentText, done: false });
this.currentText = "";
};
toggleTodo = todo => {
todo.done = !todo.done;
};
setCurrentText = text => {
this.currentText = text;
};
// computed
get pendingCount() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.done).length;
}
// ...
} 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-40-2048.jpg)
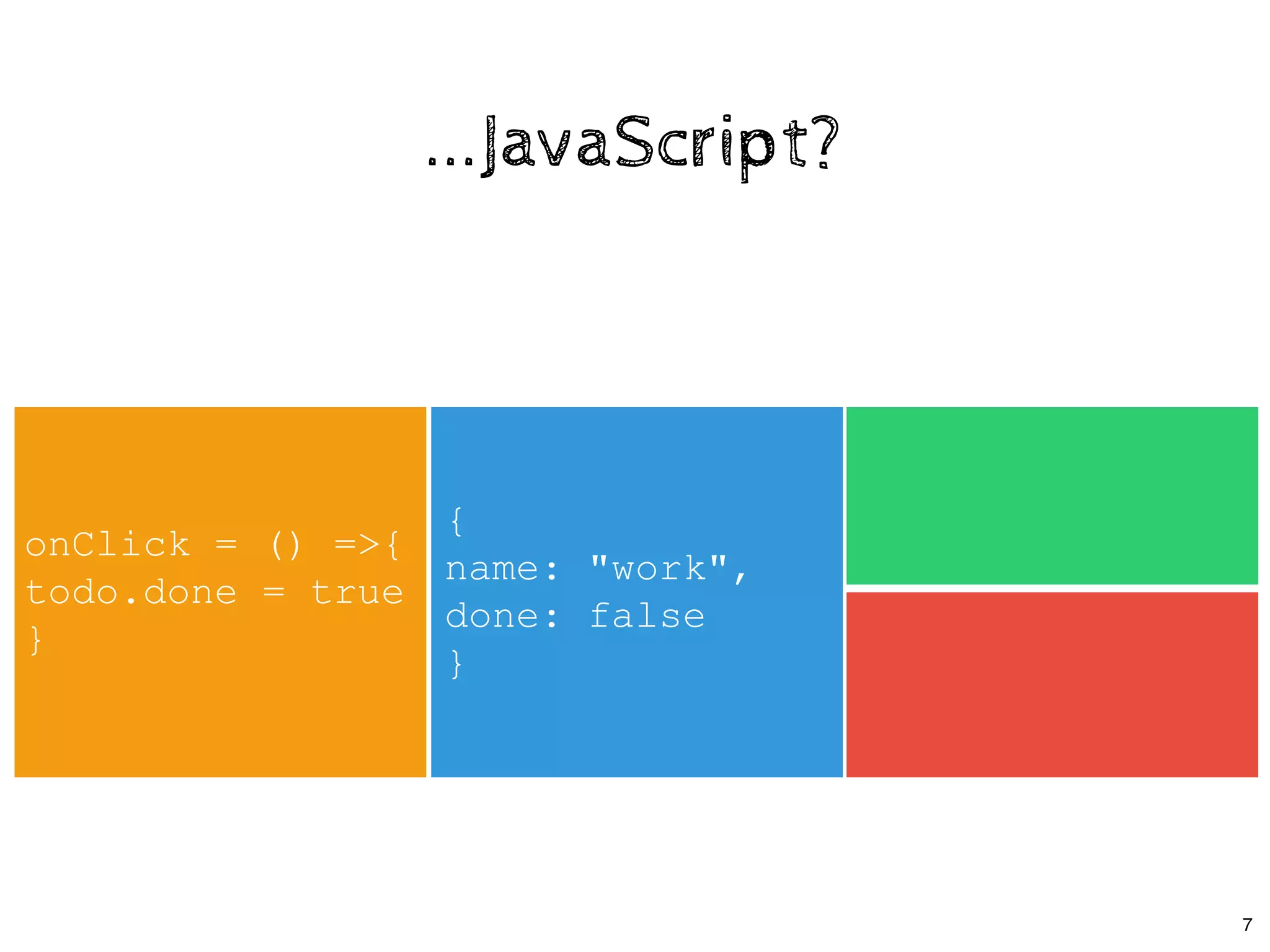
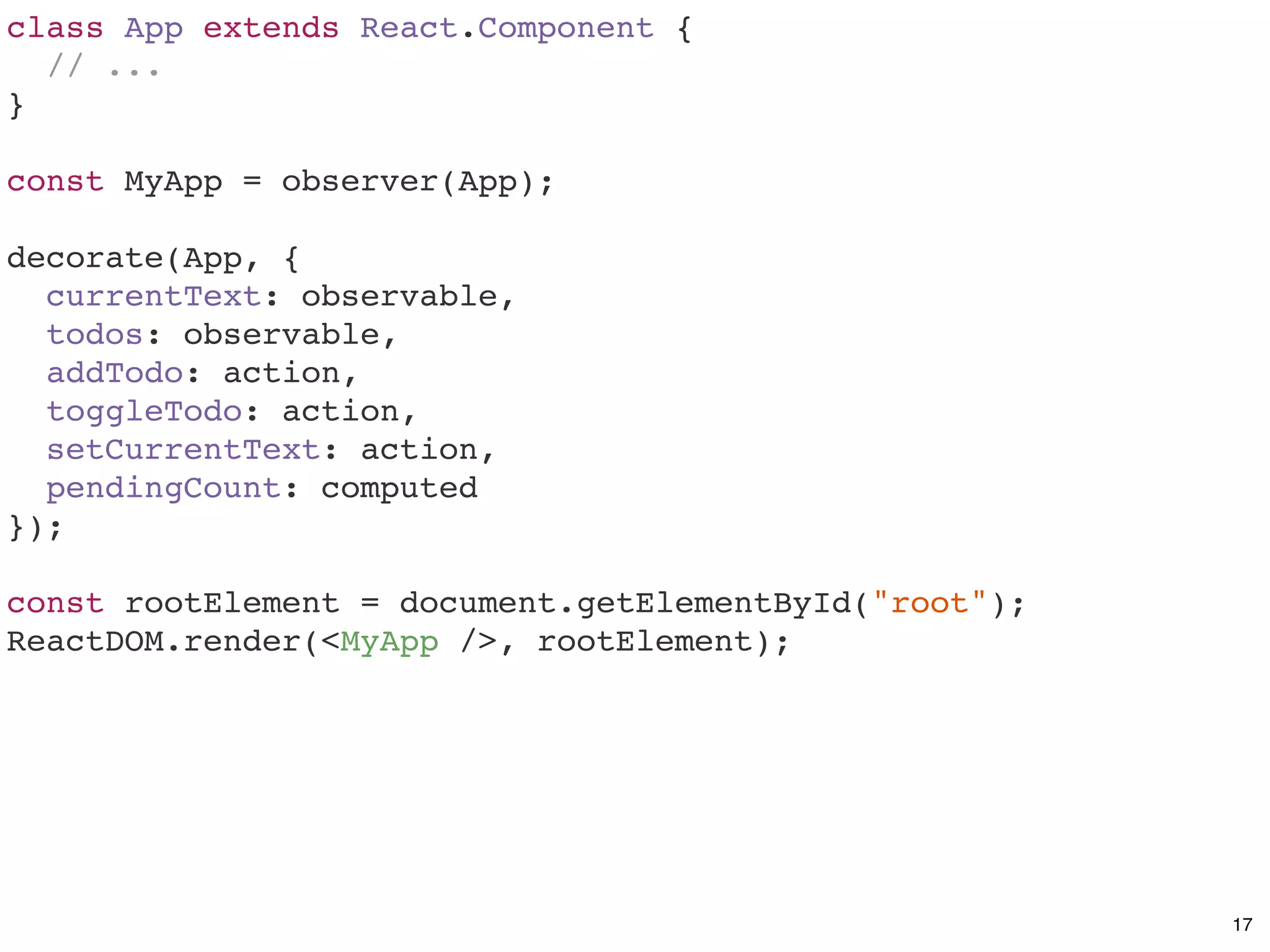
![class App extends React.Component {
// observable values
currentText = "";
todos = [];
// actions
addTodo = () => {
this.todos.push({ name: this.currentText, done: false });
this.currentText = "";
};
toggleTodo = todo => {
todo.done = !todo.done;
};
setCurrentText = text => {
this.currentText = text;
};
// computed
get pendingCount() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.done).length;
}
// ...
} 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-41-2048.jpg)
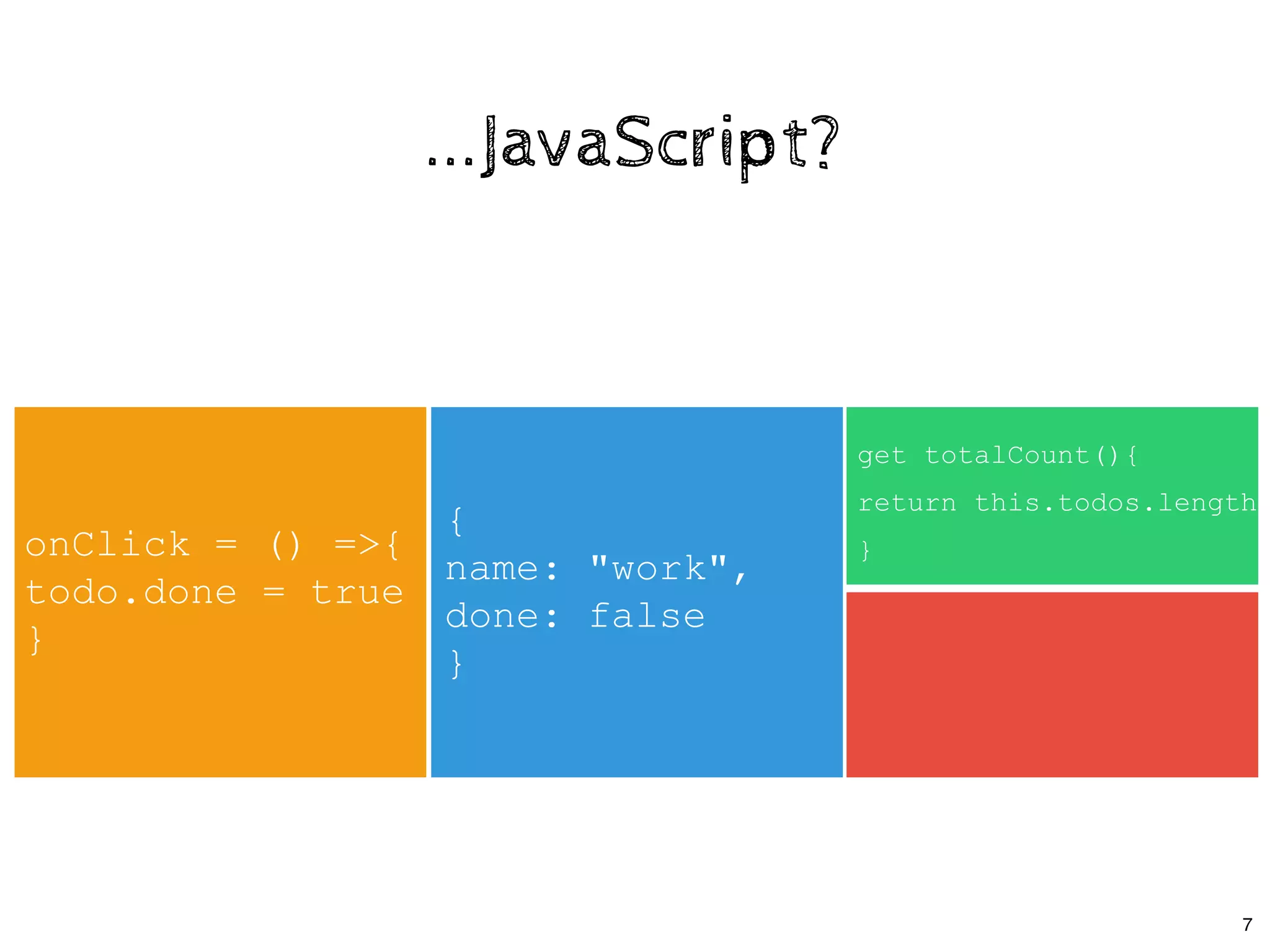
![class App extends React.Component {
// observable values
currentText = "";
todos = [];
// actions
addTodo = () => {
this.todos.push({ name: this.currentText, done: false });
this.currentText = "";
};
toggleTodo = todo => {
todo.done = !todo.done;
};
setCurrentText = text => {
this.currentText = text;
};
// computed
get pendingCount() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.done).length;
}
// ...
} 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-42-2048.jpg)
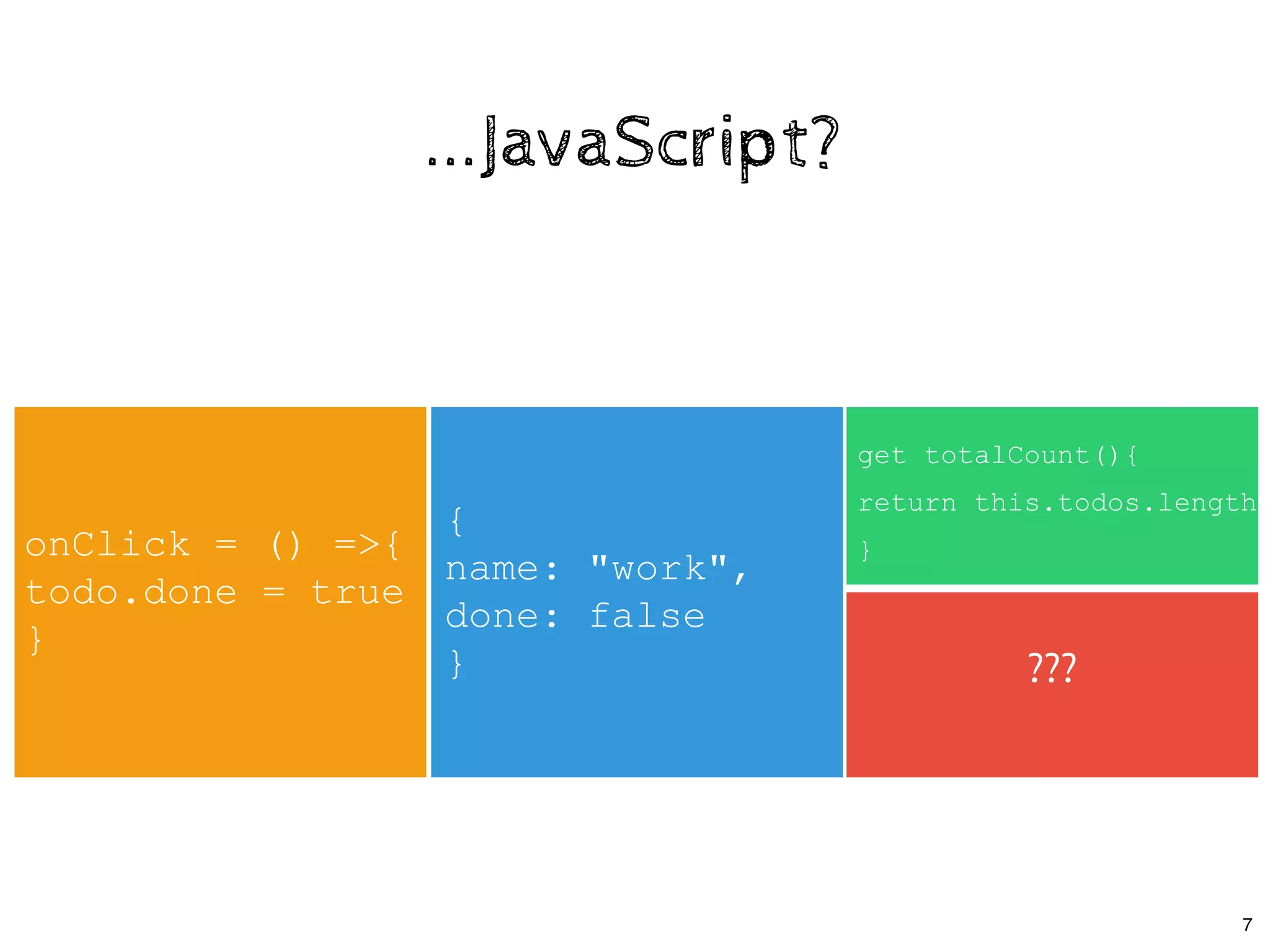
![class App extends React.Component {
// observable values
currentText = "";
todos = [];
// actions
addTodo = () => {
this.todos.push({ name: this.currentText, done: false });
this.currentText = "";
};
toggleTodo = todo => {
todo.done = !todo.done;
};
setCurrentText = text => {
this.currentText = text;
};
// computed
get pendingCount() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.done).length;
}
// ...
} 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-43-2048.jpg)
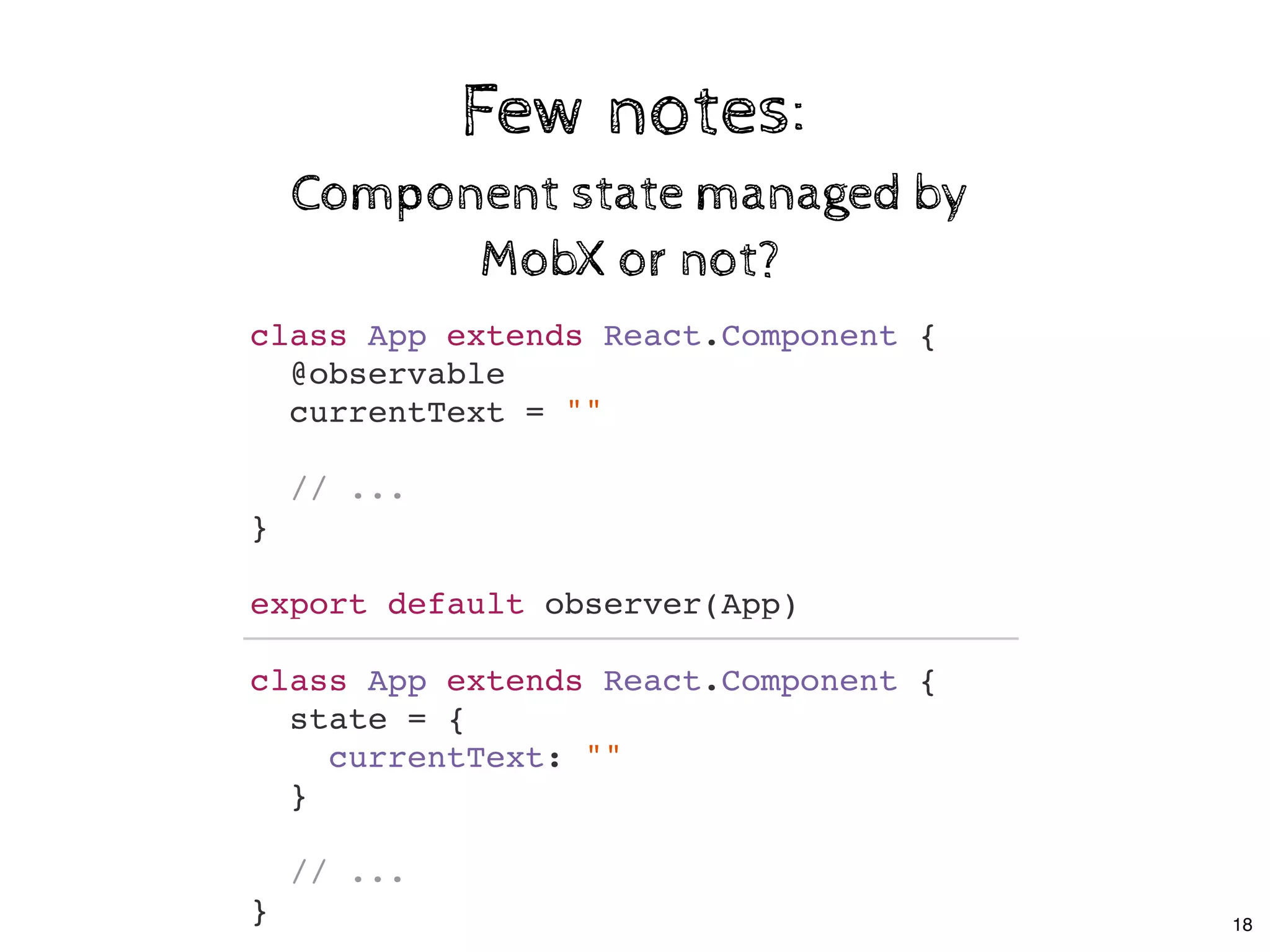
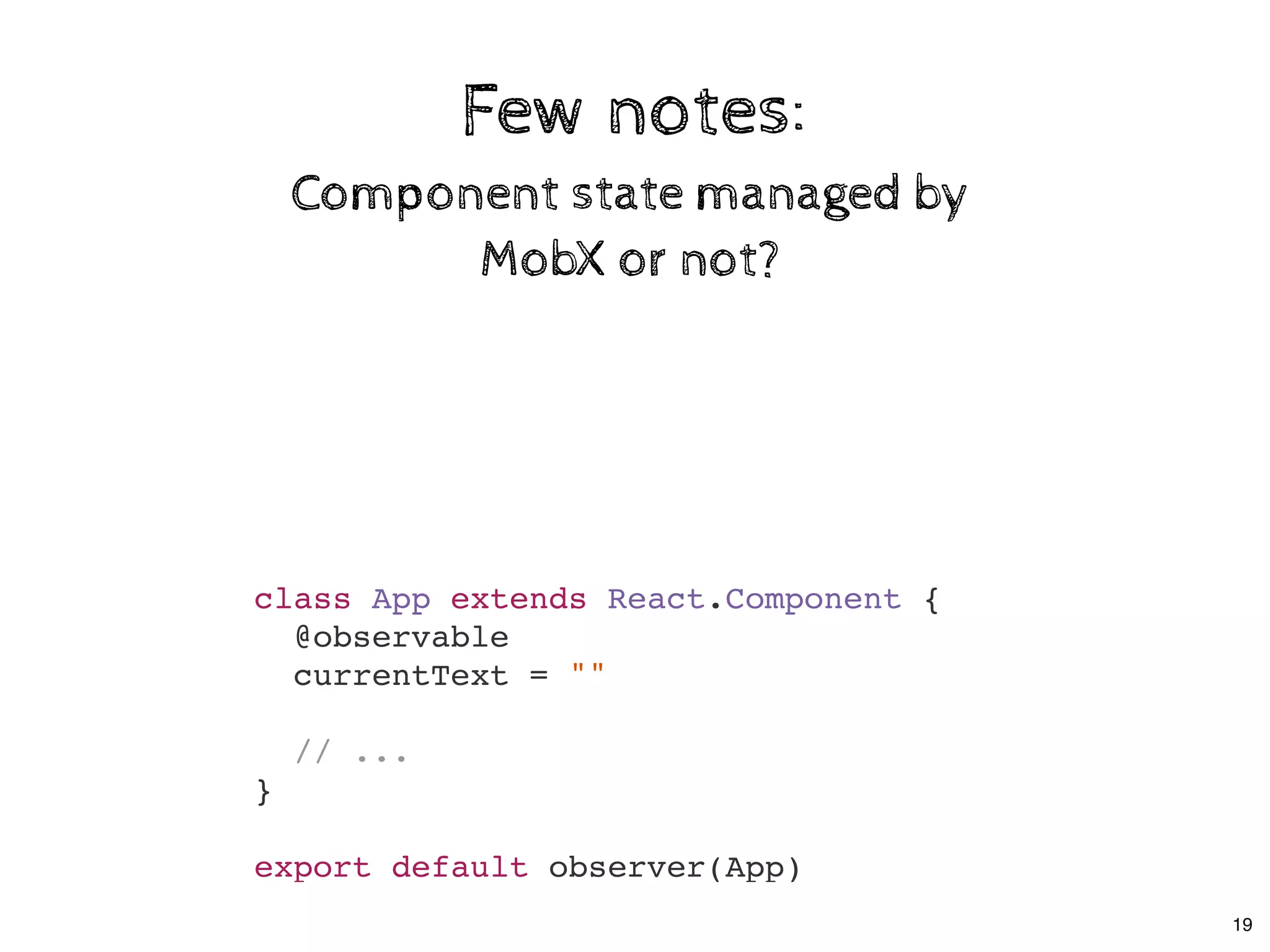

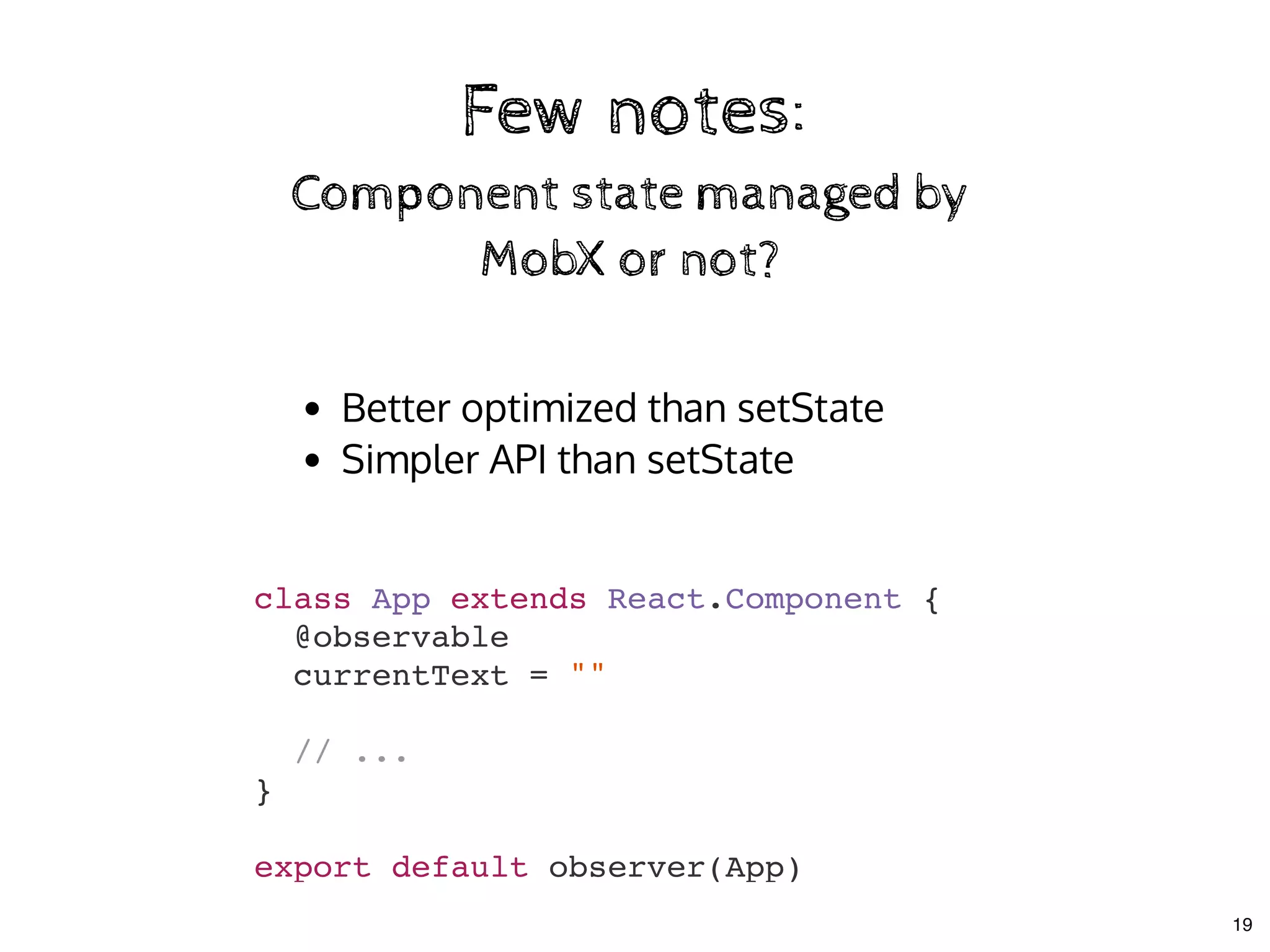

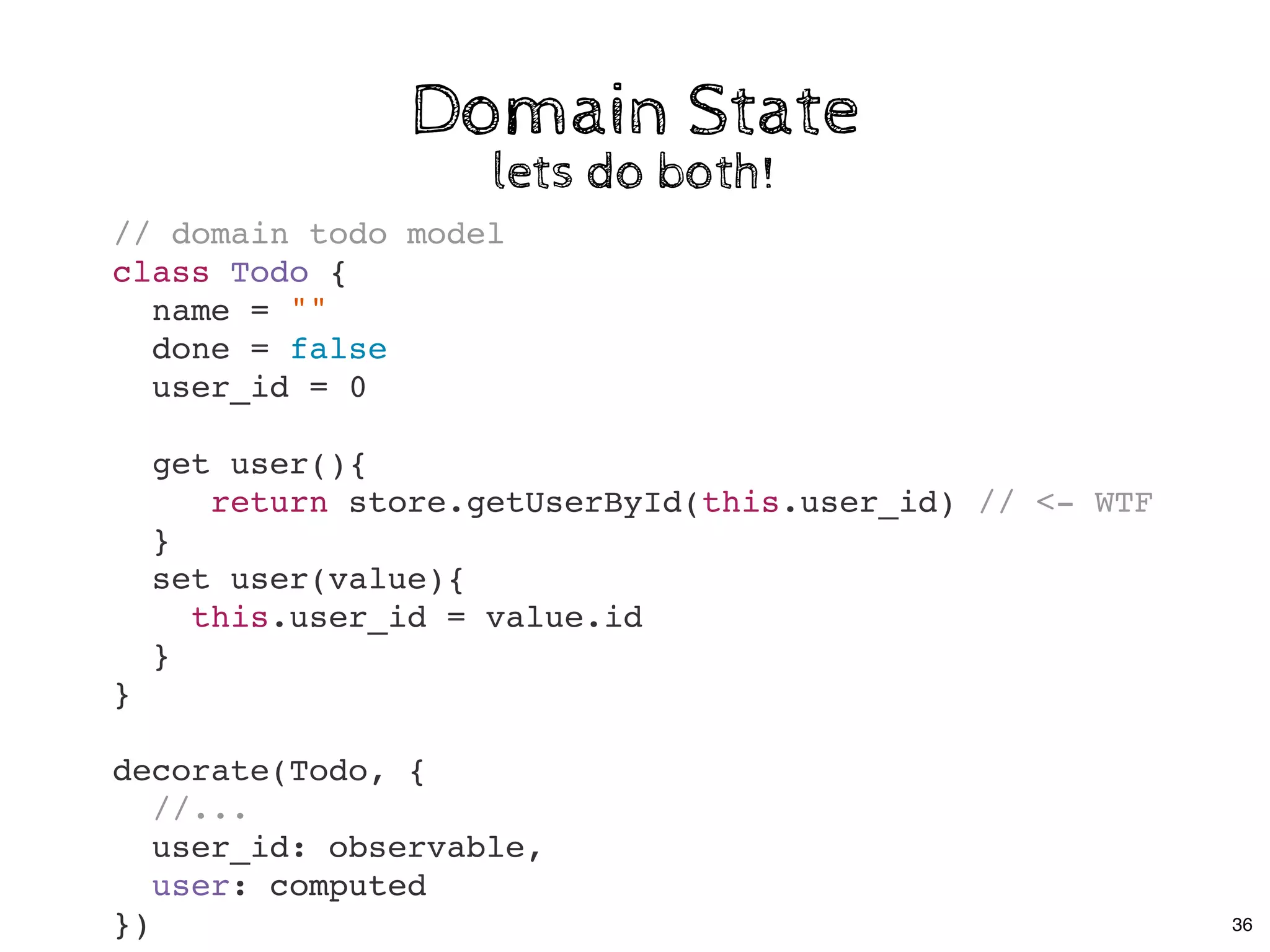
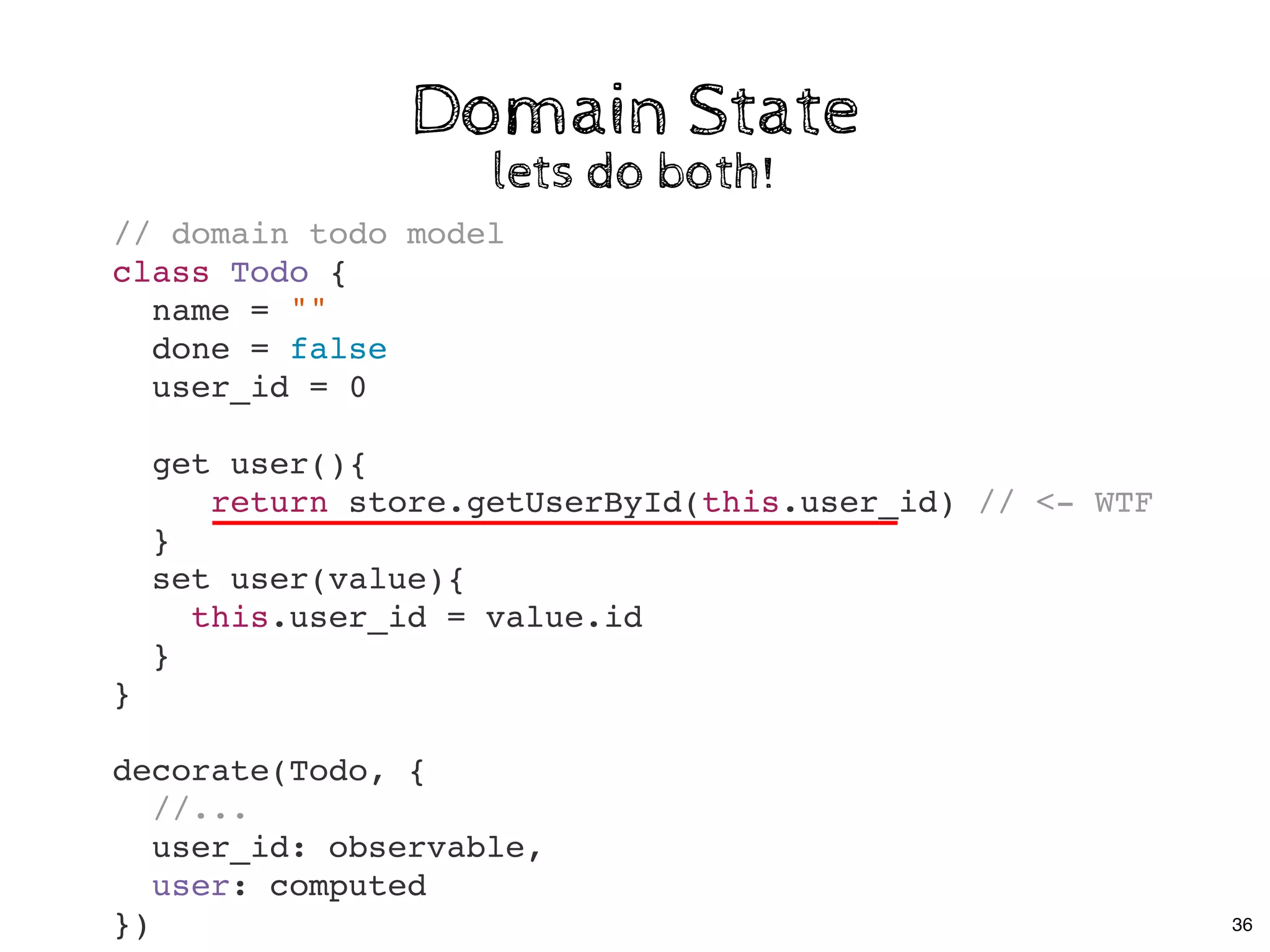
![Few notes:Few notes:
Decorators are optionalDecorators are optional
class Store {
@observable
todos = []
}
class Store {
todos = []
}
decorate(Store, {
todos: observable
});
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-53-2048.jpg)
![Few notes:Few notes:
Classes are optionalClasses are optional
class Store {
@observable
todos = []
}
const store = new Store()
const store = observable({
todos: []
})
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-54-2048.jpg)













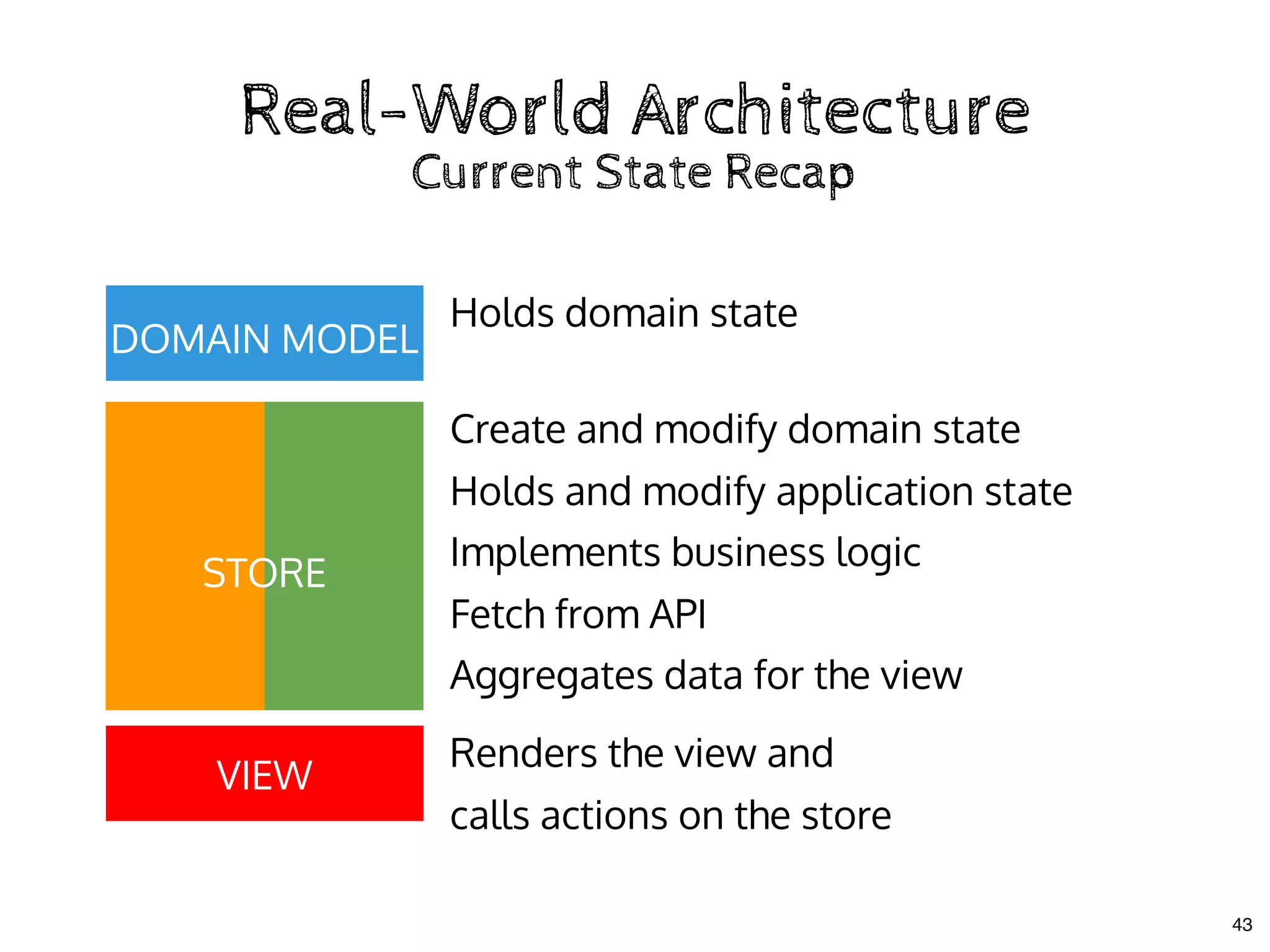
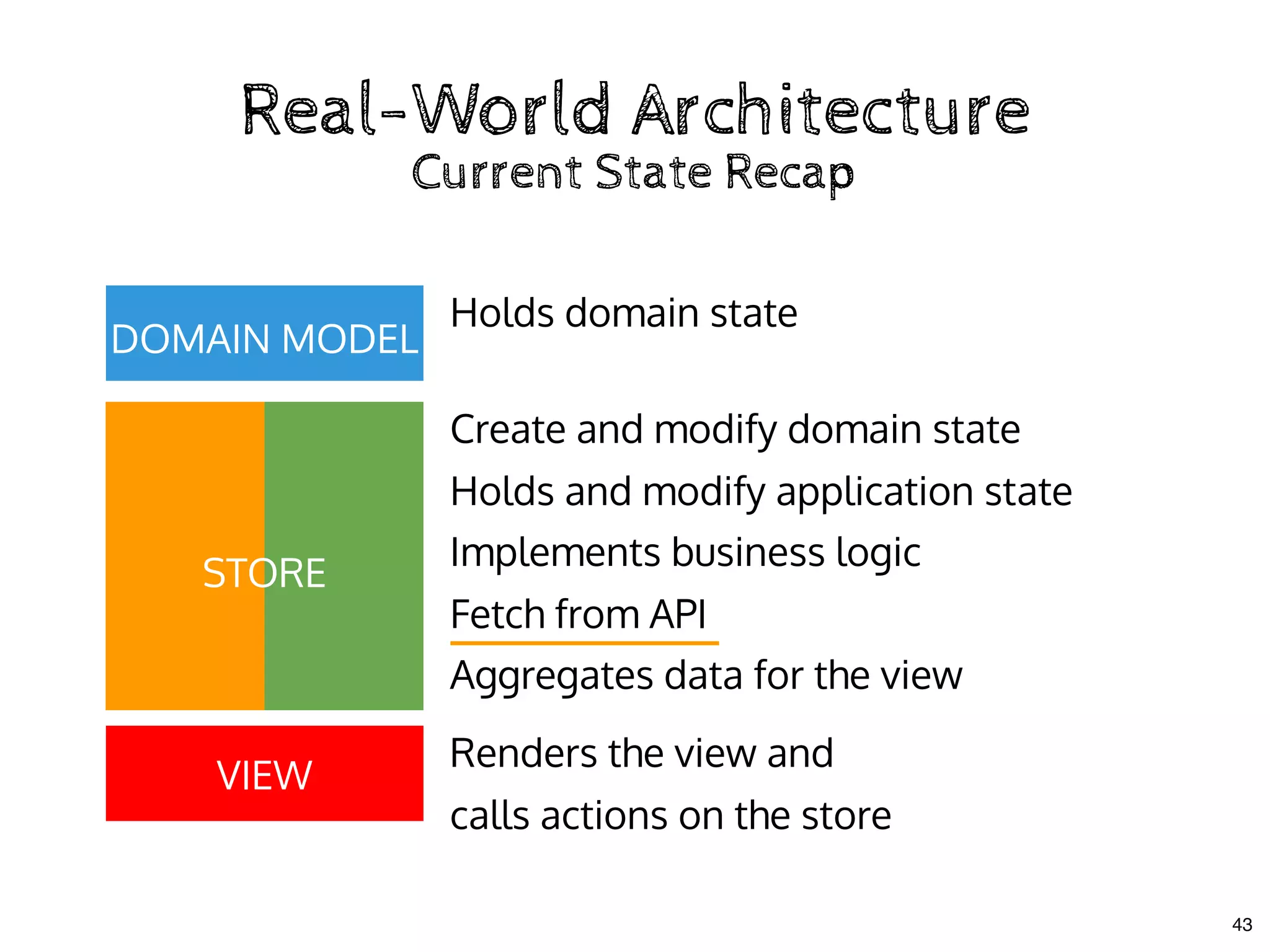
![Don't mix Business Logic & UIDon't mix Business Logic & UI
class Store {
// observable values
currentText = "";
todos = [];
// actions
addTodo = () => {
this.todos.push({ name: this.currentText, done: false });
this.currentText = "";
};
toggleTodo = todo => { todo.done = !todo.done; };
setCurrentText = text => { this.currentText = text; };
// computed
get pendingCount() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.done).length;
}
}
Extracting the StoreExtracting the Store
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-71-2048.jpg)










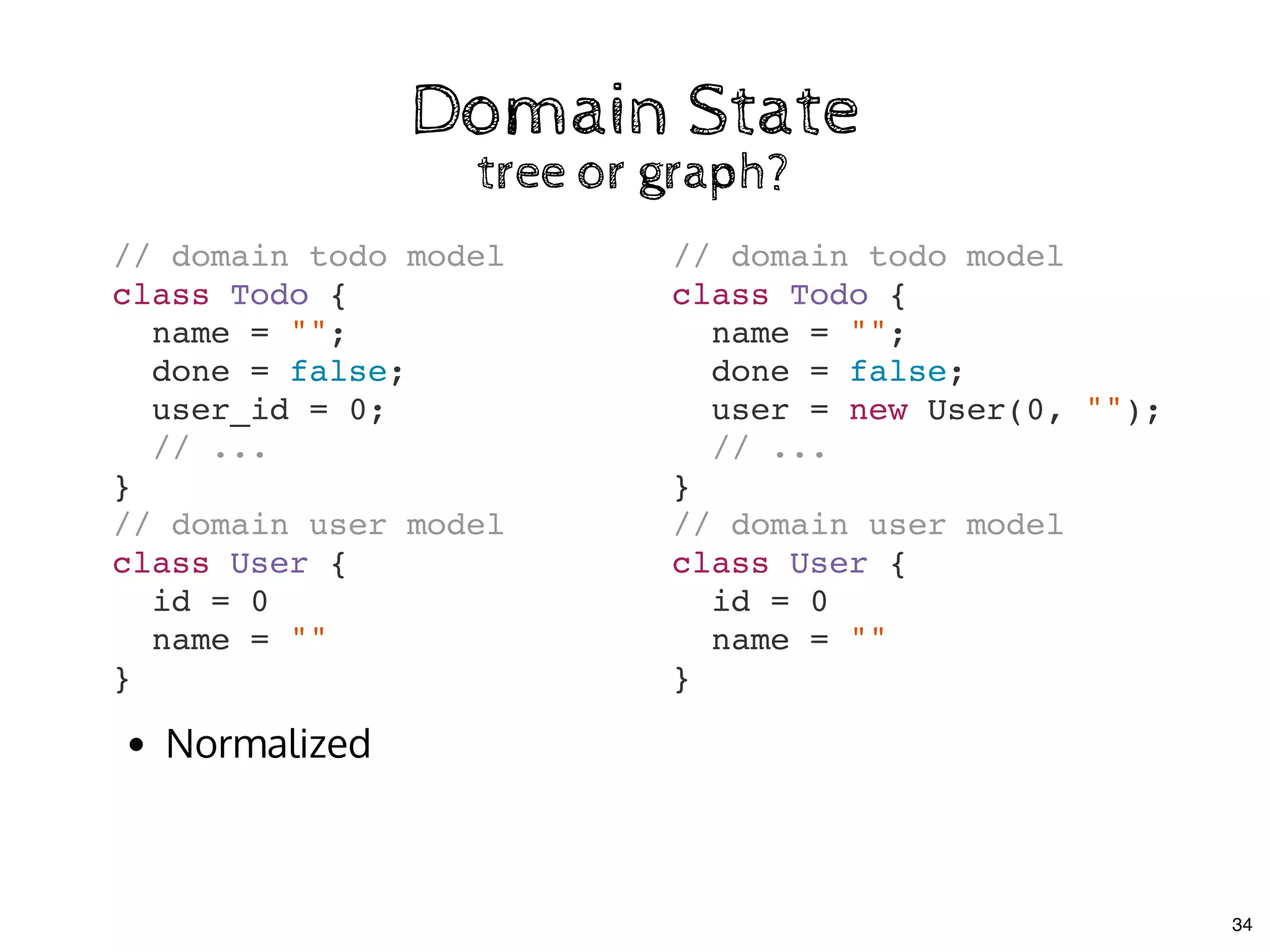
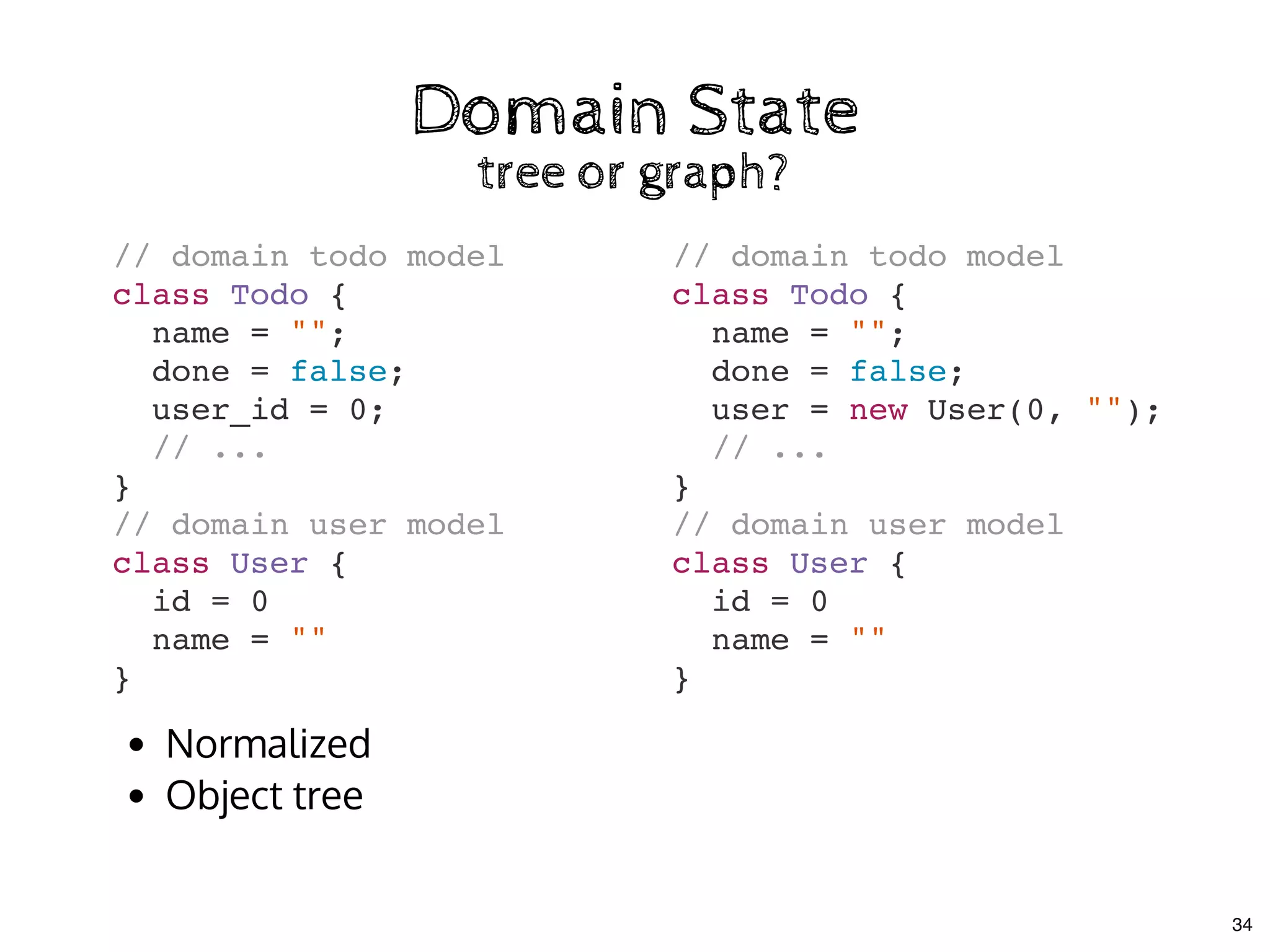
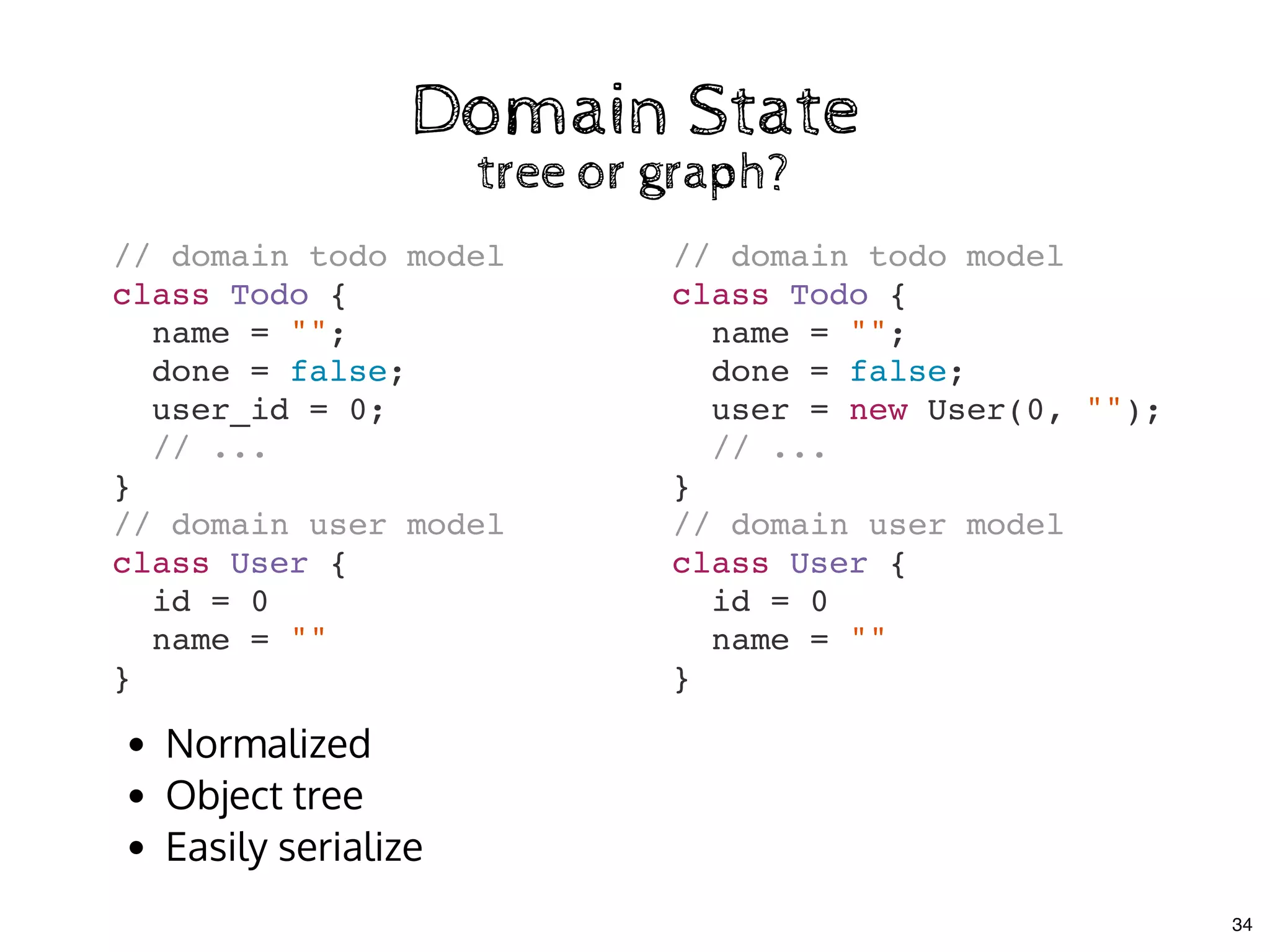
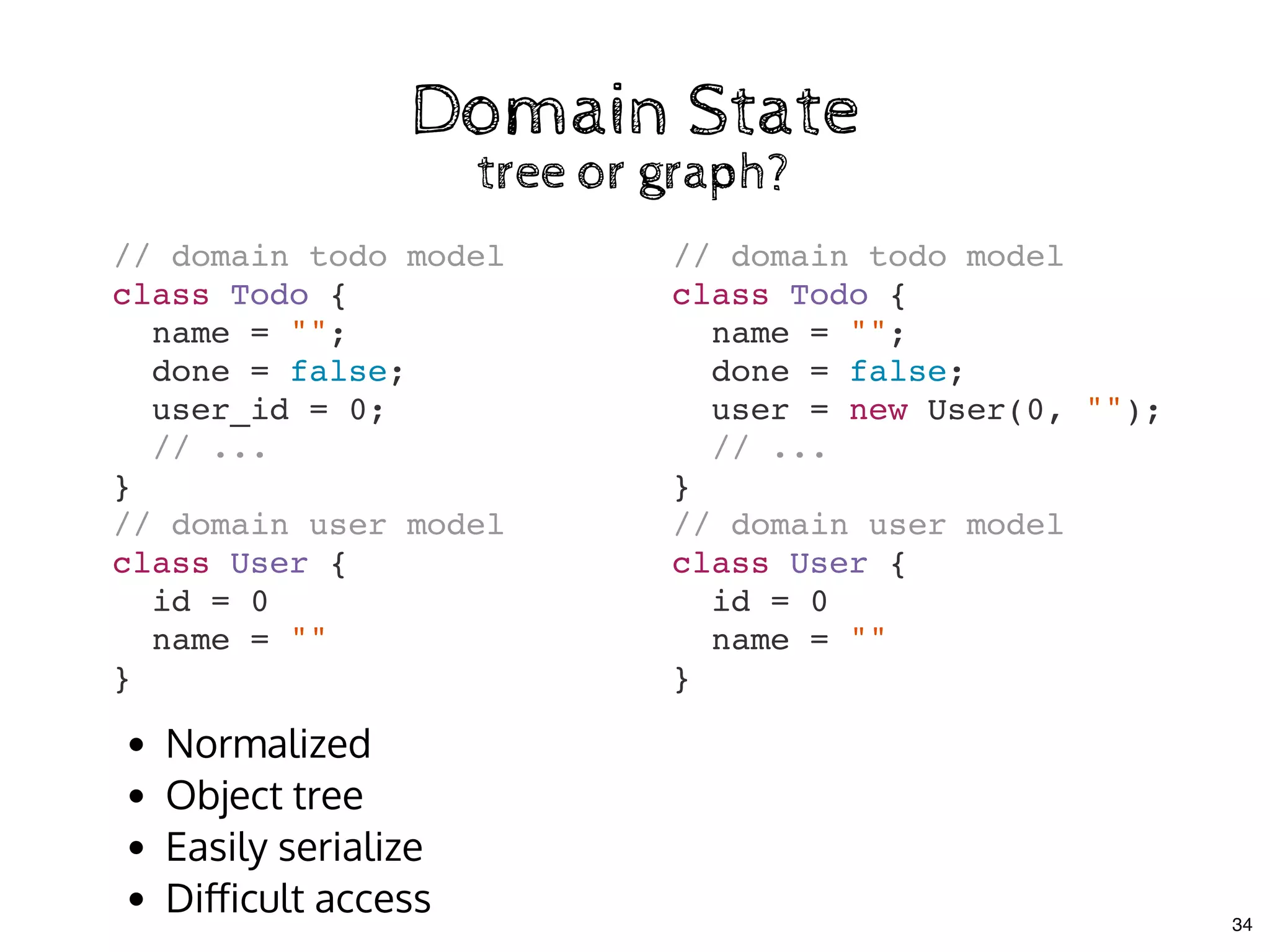













![Multiple Store CommunicationMultiple Store Communication
back to our problemback to our problem
test("it should restore data from API", async t => {
const fakeFetch = () => Promise.resolve({
data: [{id: 1, name: "Mattia"}]
})
const store = new RootStore(fakeFetch)
await store.userStore.fetchAll()
t.equal(store.userStore.users[0].name, "Mattia")
})
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-112-2048.jpg)



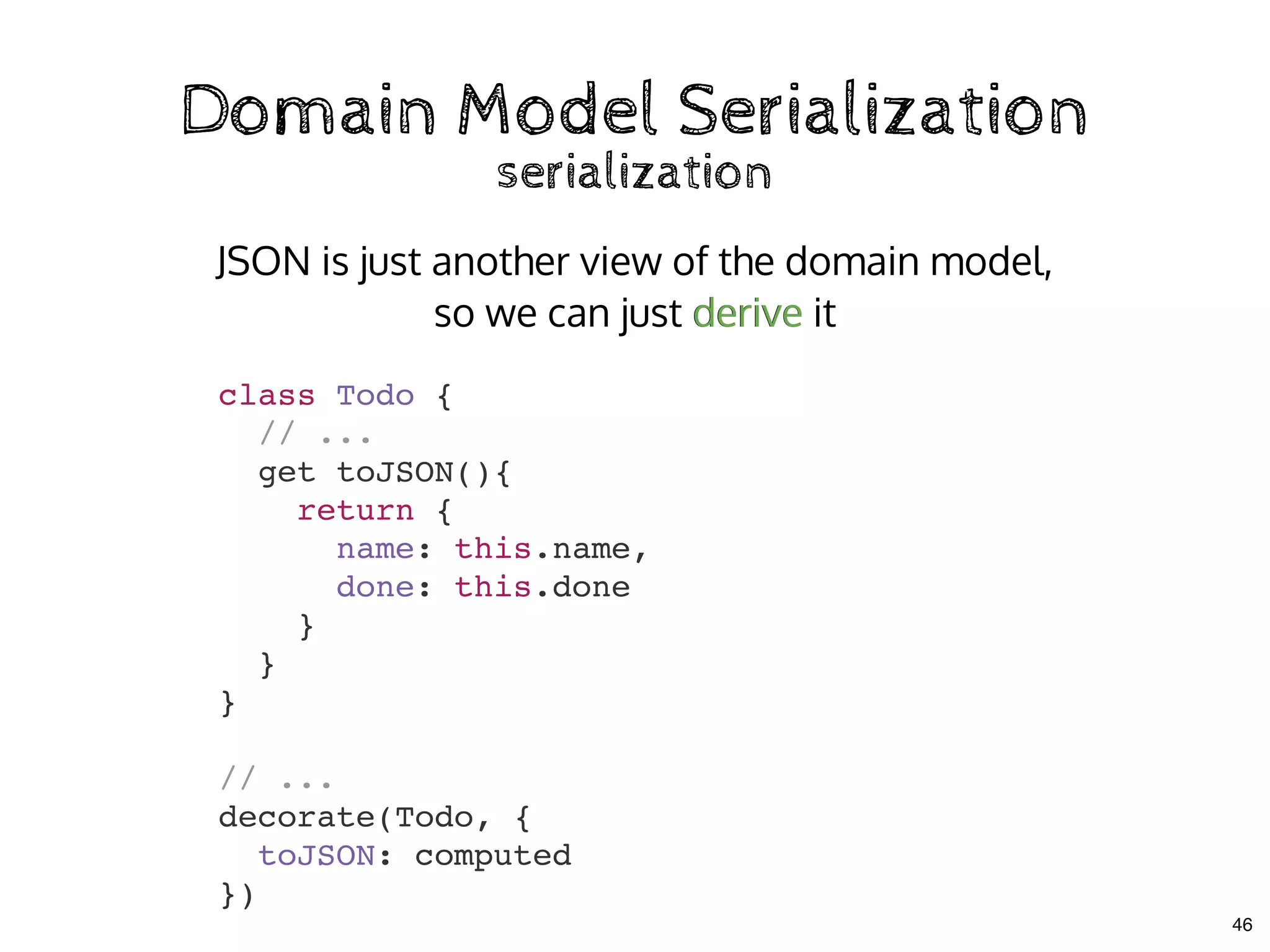
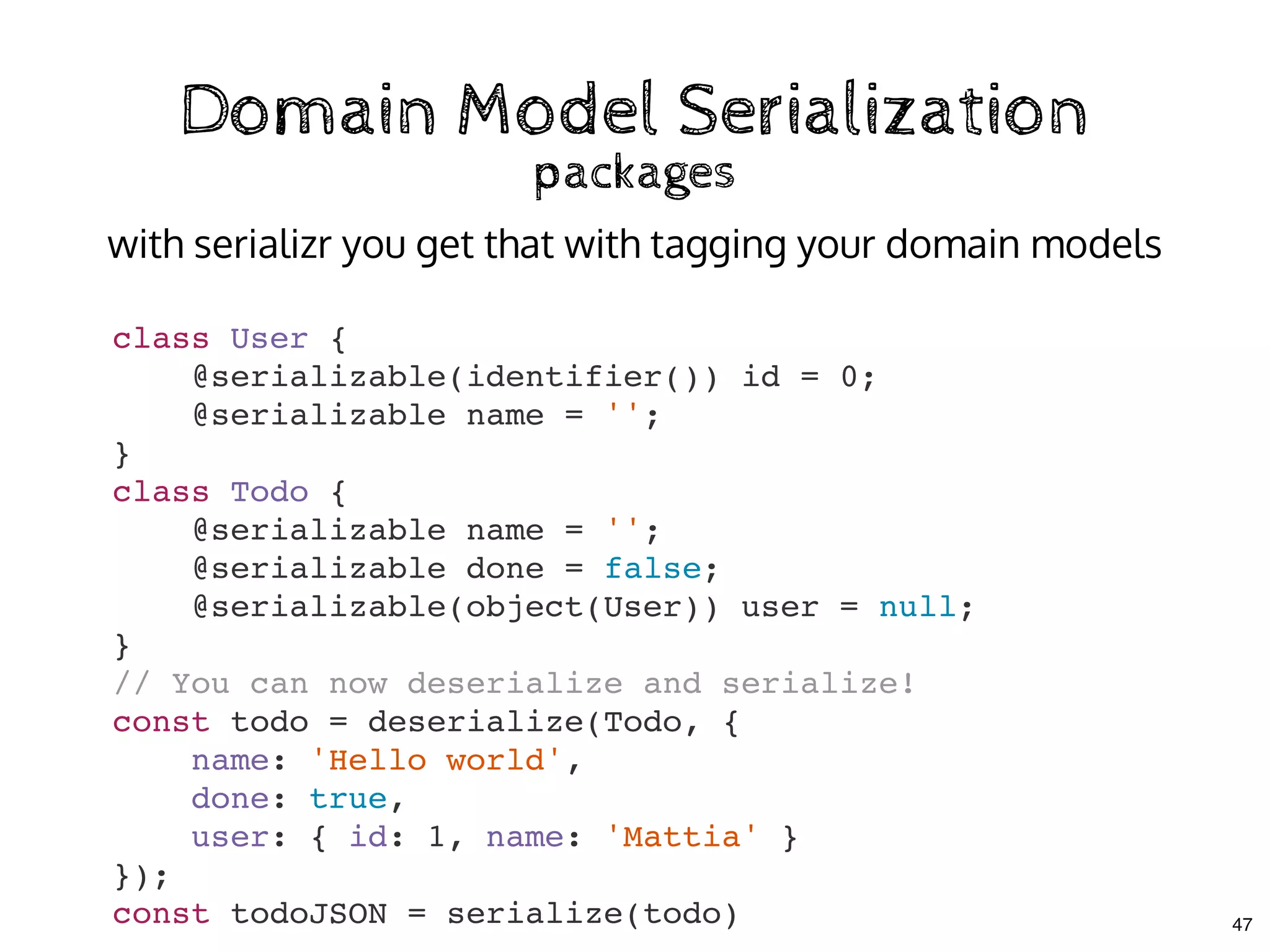
![Domain Model SerializationDomain Model Serialization
the deserialization problemthe deserialization problem
class TodoStore {
todos = []
fromCache(){
const cachedData = localStorage.getItem("todos")
|| "[]"
this.todos = JSON.parse(cachedData)
.map(data => new Todo(this, data)
}
getById = id => this.todos
.find(item => item.id === id)
}
decorate(TodoStore, {
fromCache: action
})
deserializing is memory intensive!
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-123-2048.jpg)
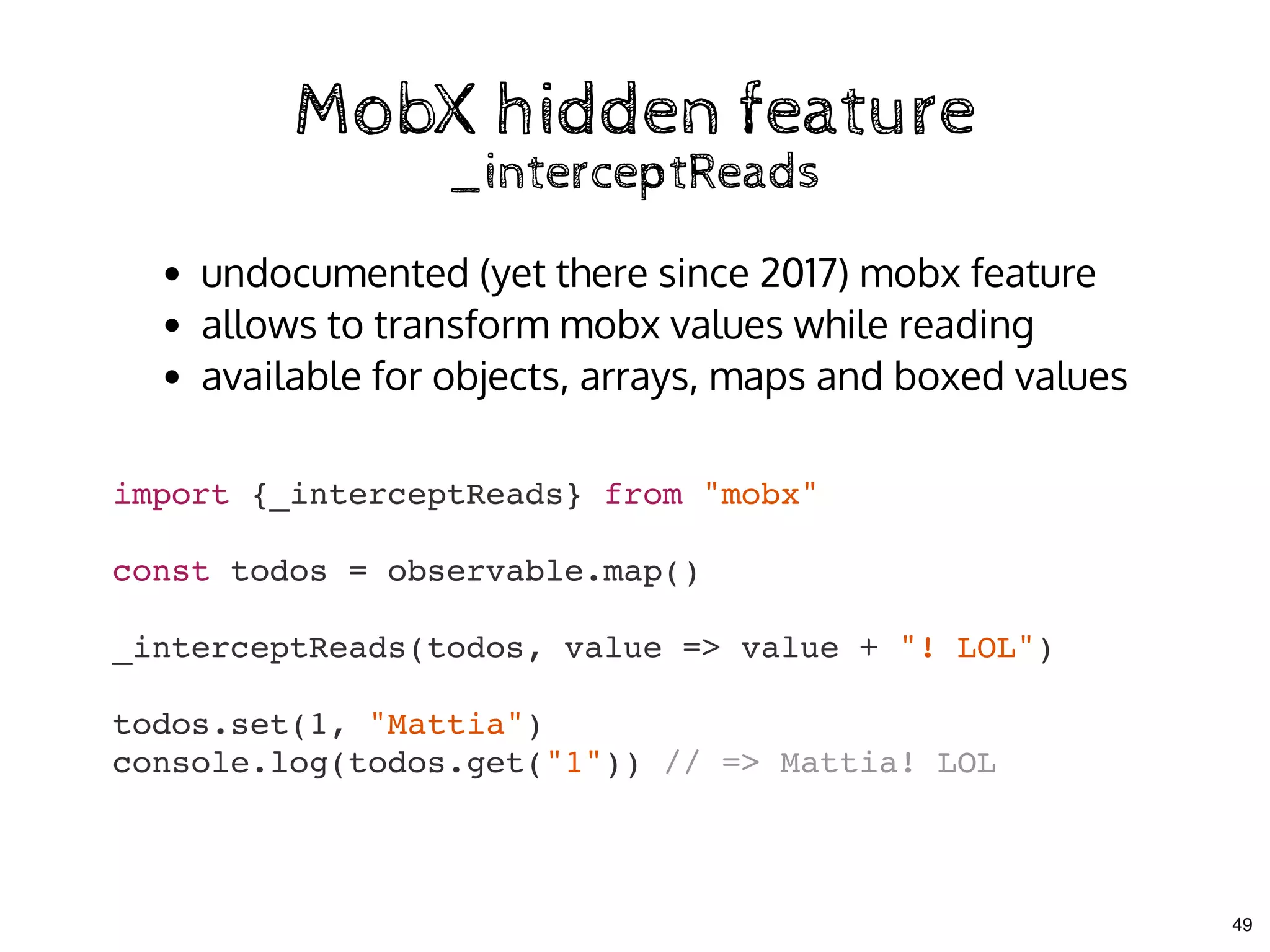
![MobX hidden featureMobX hidden feature
_interceptReads to the rescue!_interceptReads to the rescue!
class TodoStore {
todos = []
_cache = {}
constructor(rootStore){
this.rootStore = rootStore
// ...
_interceptReads(this.todos, this.unboxTodo)
}
unboxTodo = data => {
if(this._cache[data.id]){
return this._cache[data.id]
}
this._cache[data.id] = new Todo(this, data)
return this._cache[data.id]
}
}
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/real-world-mobx-190517115323/75/Mattia-Manzati-Real-World-MobX-Project-Architecture-Codemotion-Rome-2019-125-2048.jpg)