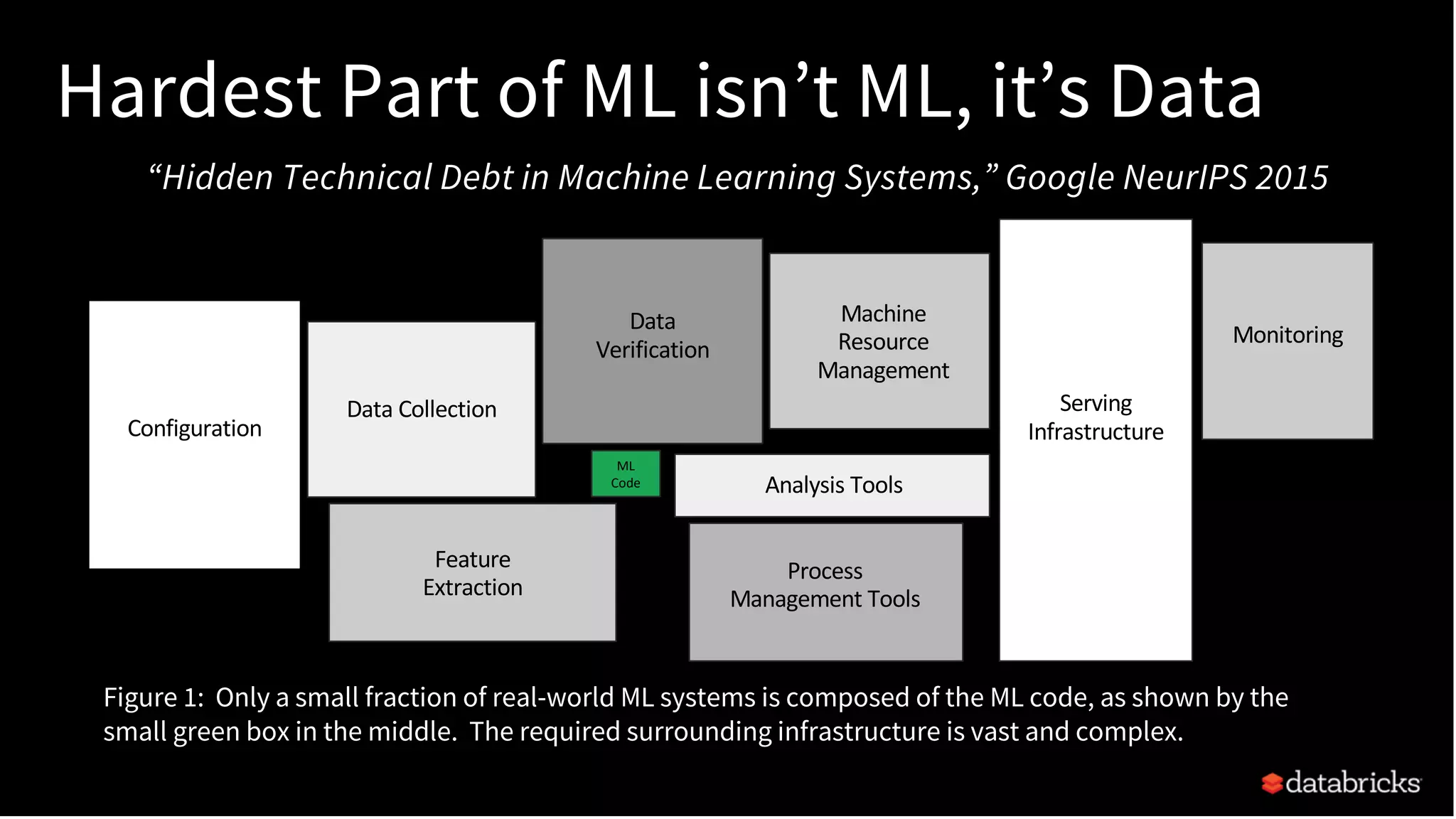
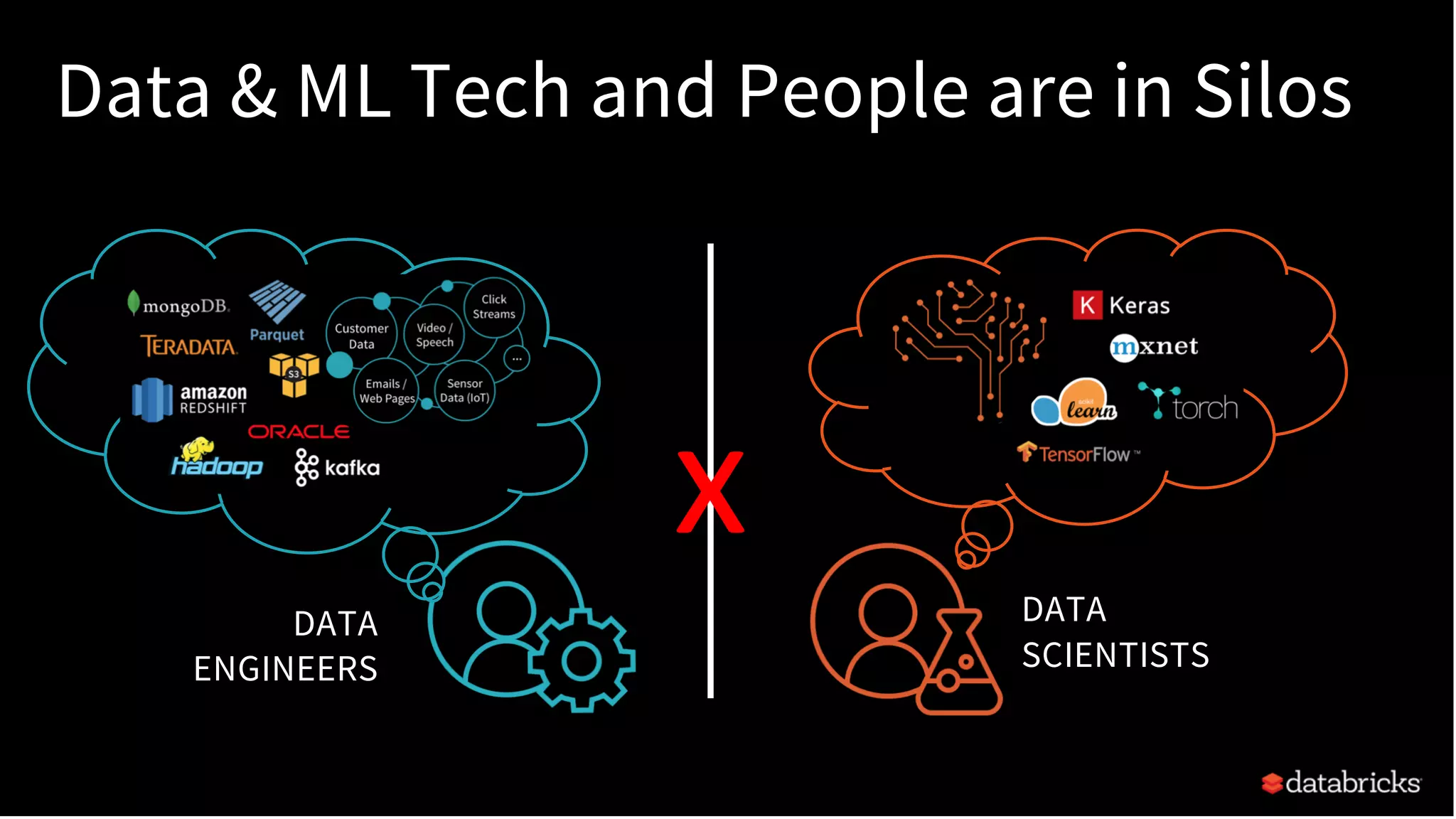
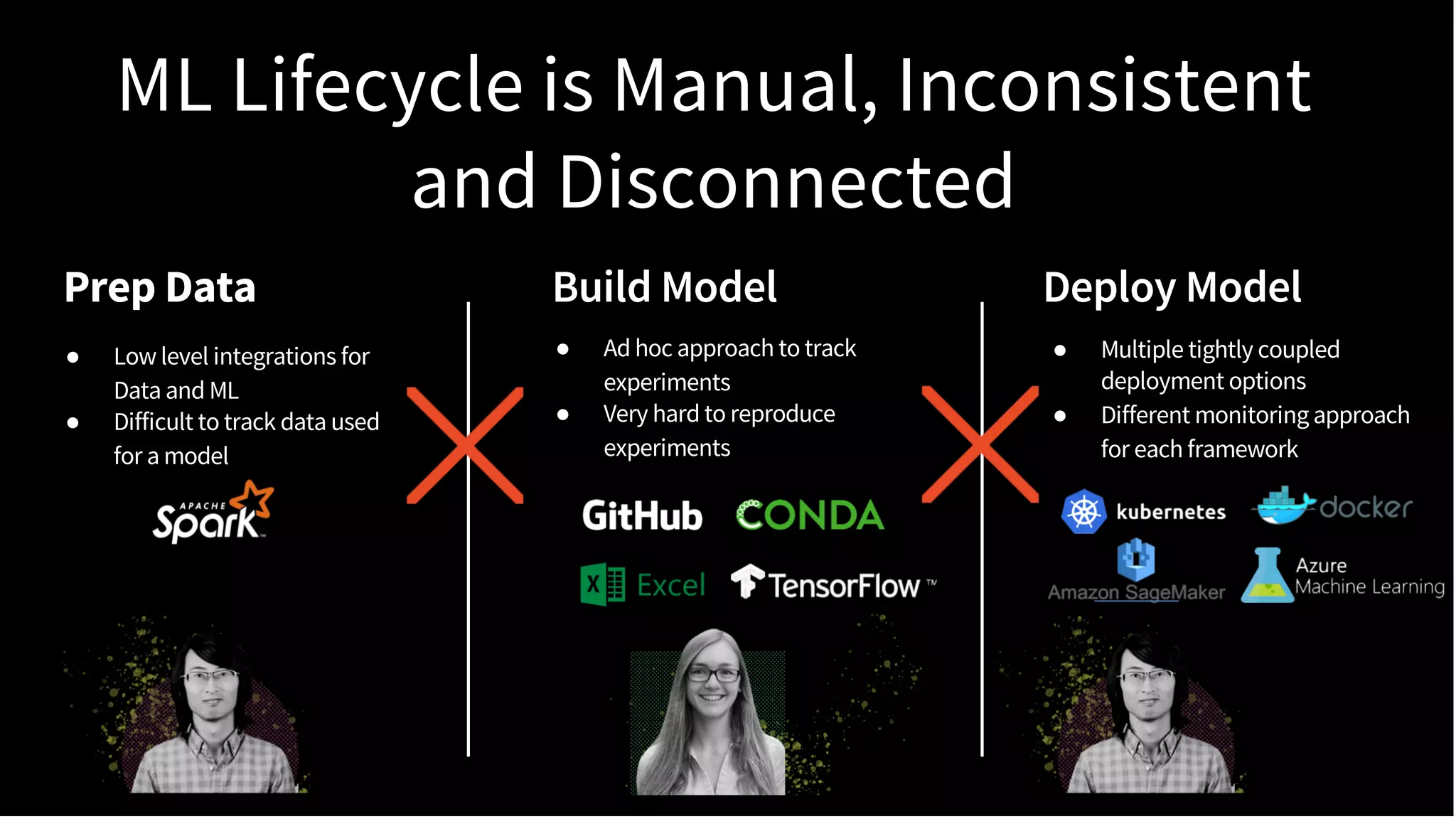
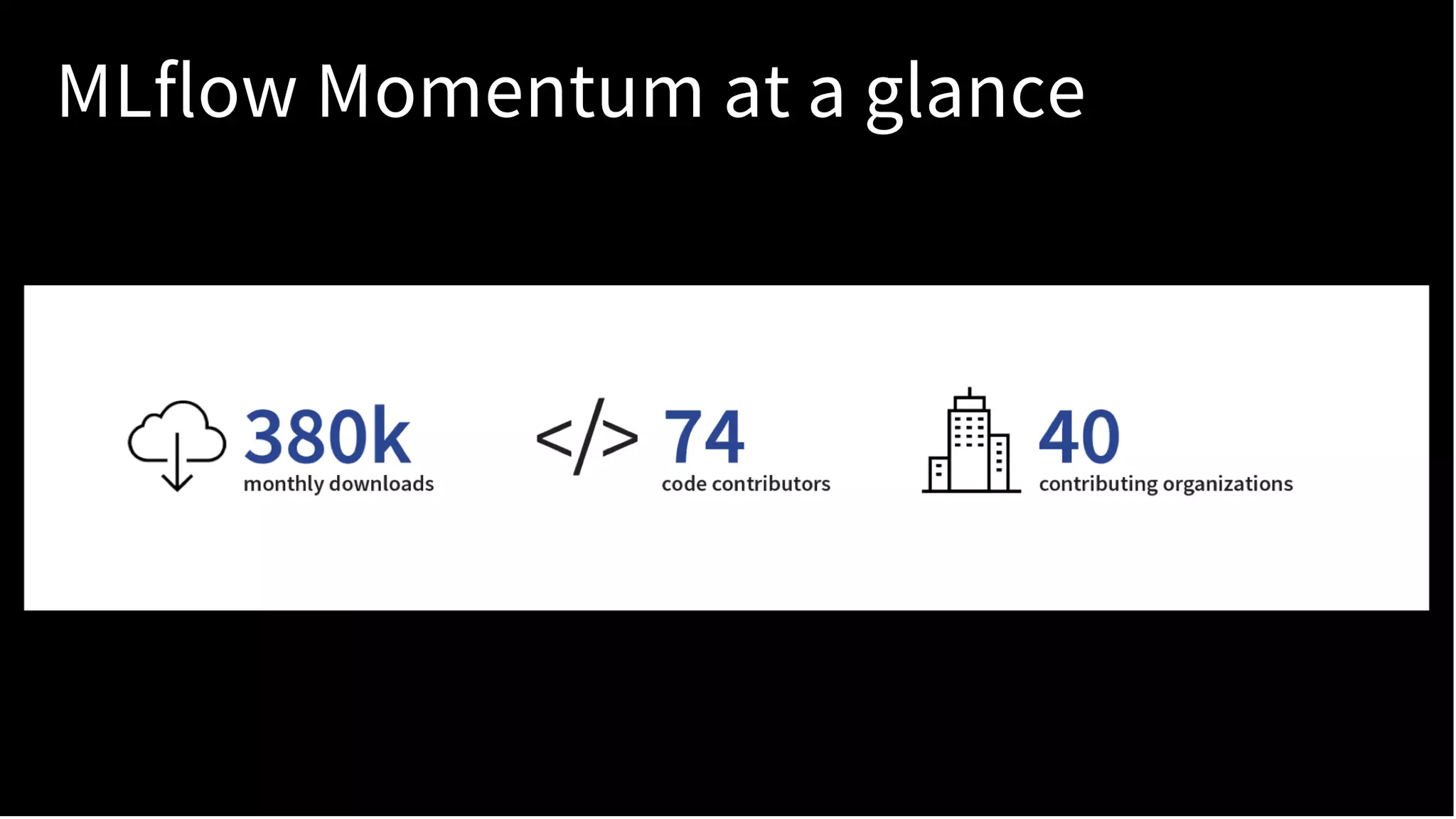
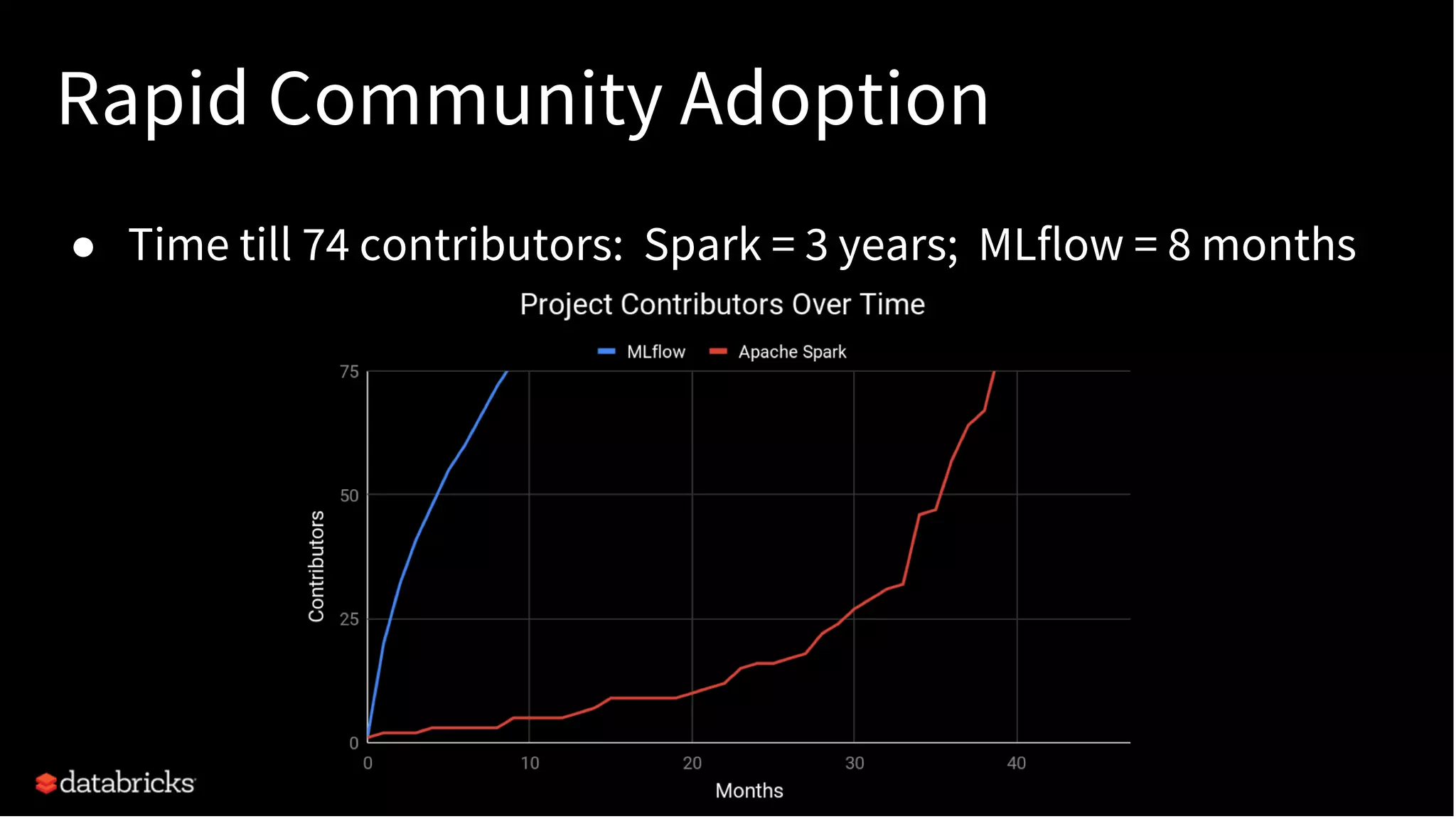
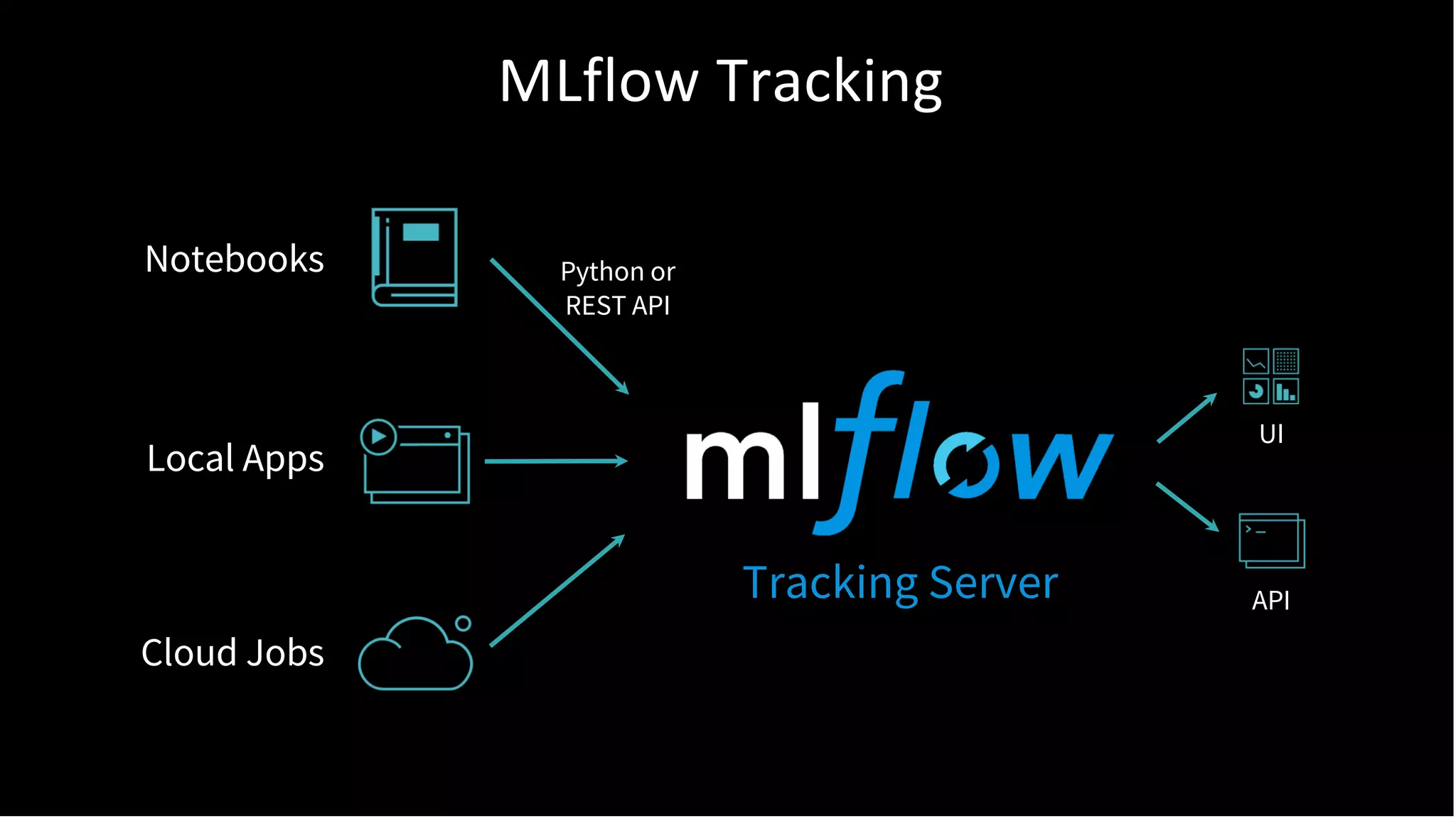
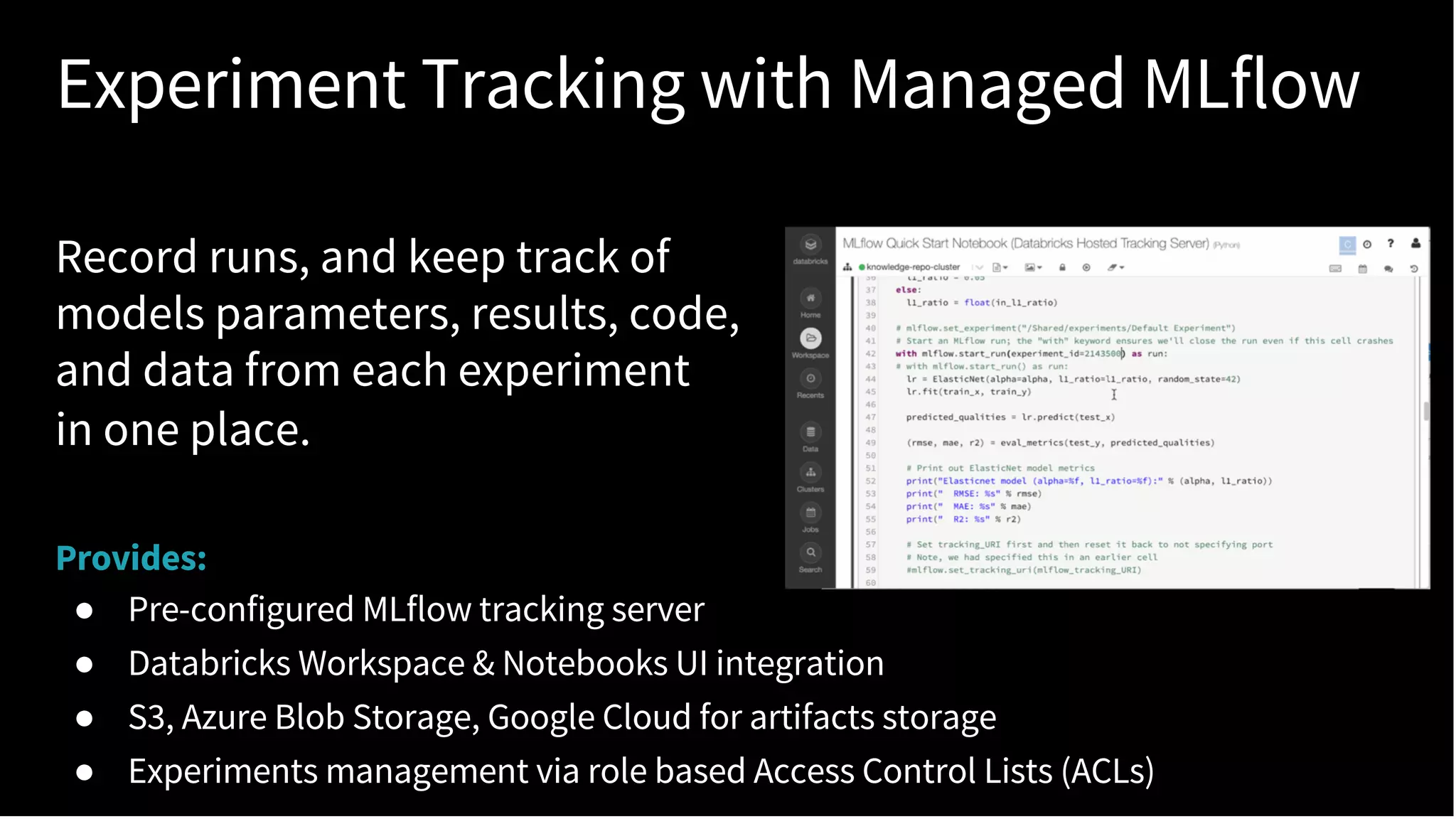
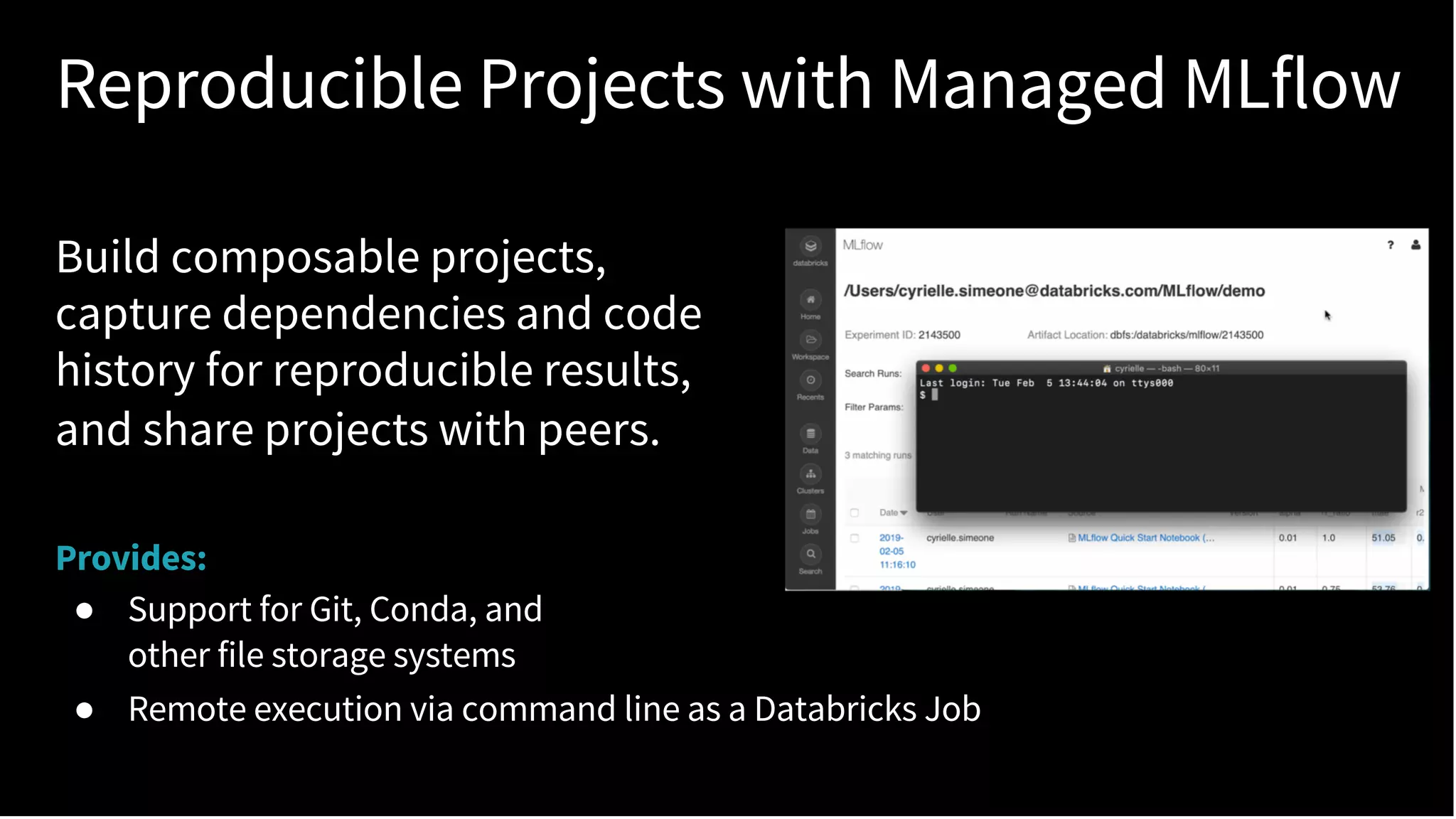
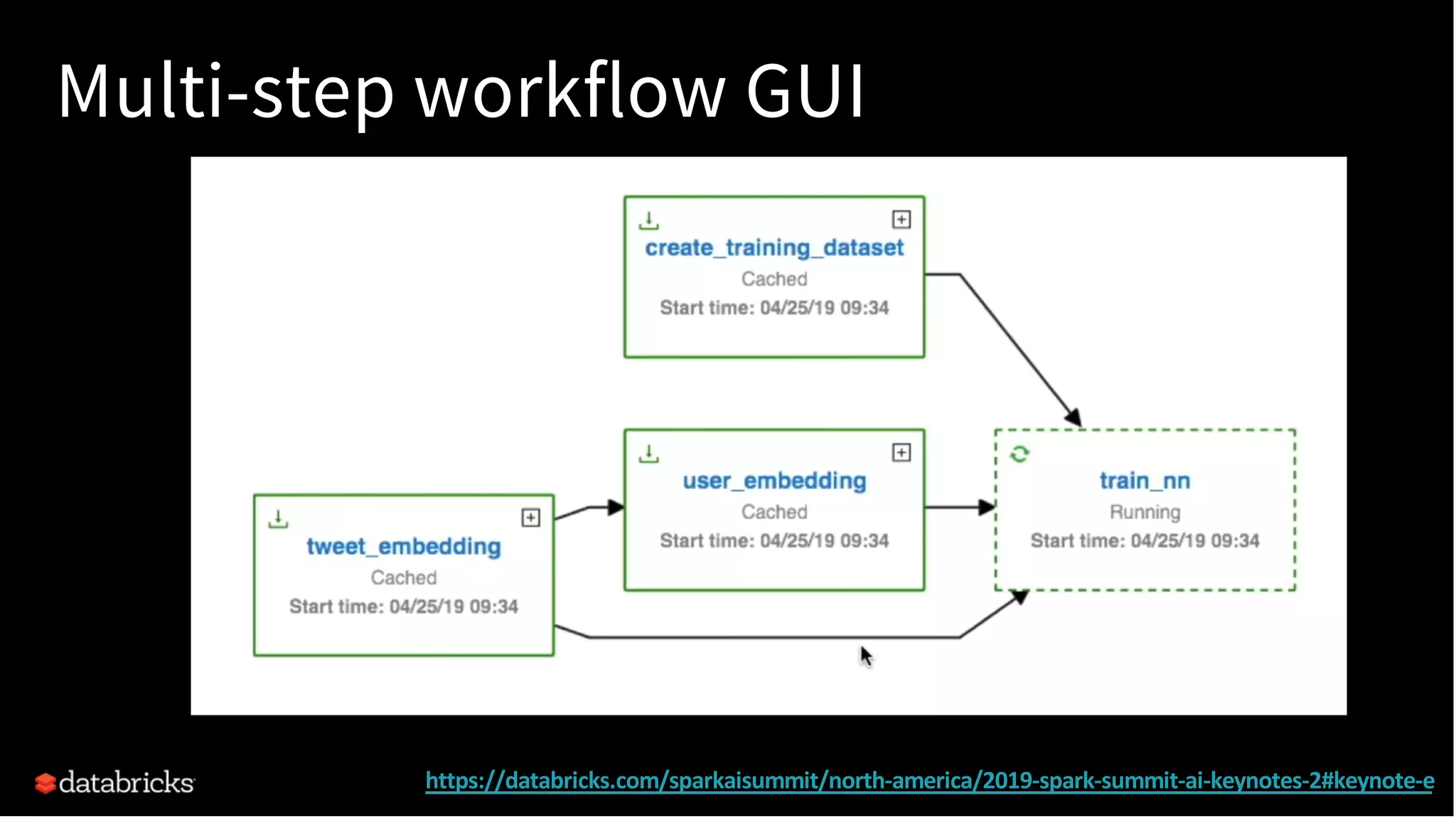
The document discusses standardizing the machine learning lifecycle using MLflow, an open-source framework introduced in June 2018 for managing experiments, projects, and model deployment. MLflow aims to address the complexities and silos in machine learning by providing solutions for tracking experiments, reproducible projects, and model deployment across various platforms. The framework has gained rapid community adoption and offers features like managed tracking servers, integration with cloud storage, and support for diverse deployment tools.