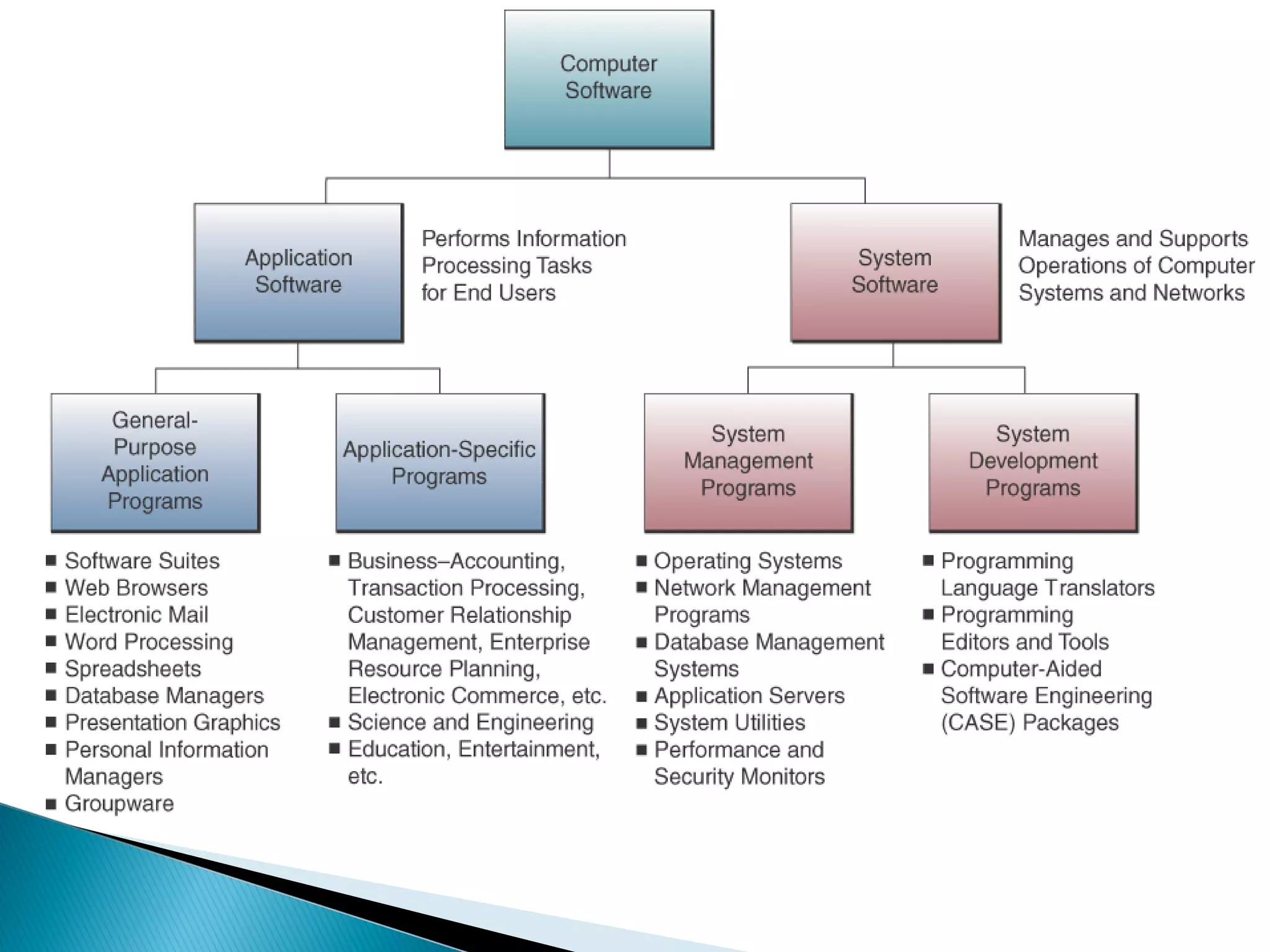
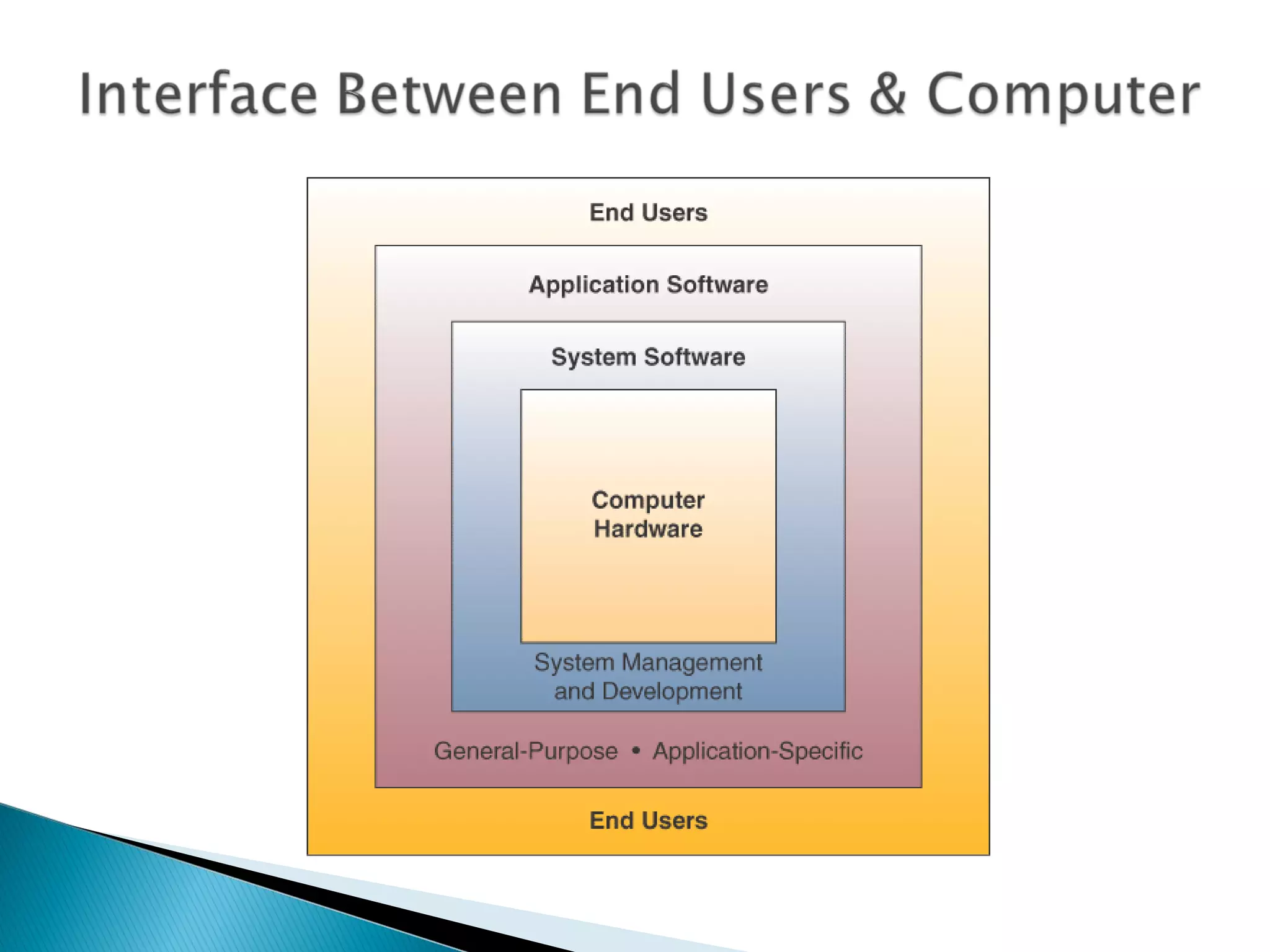
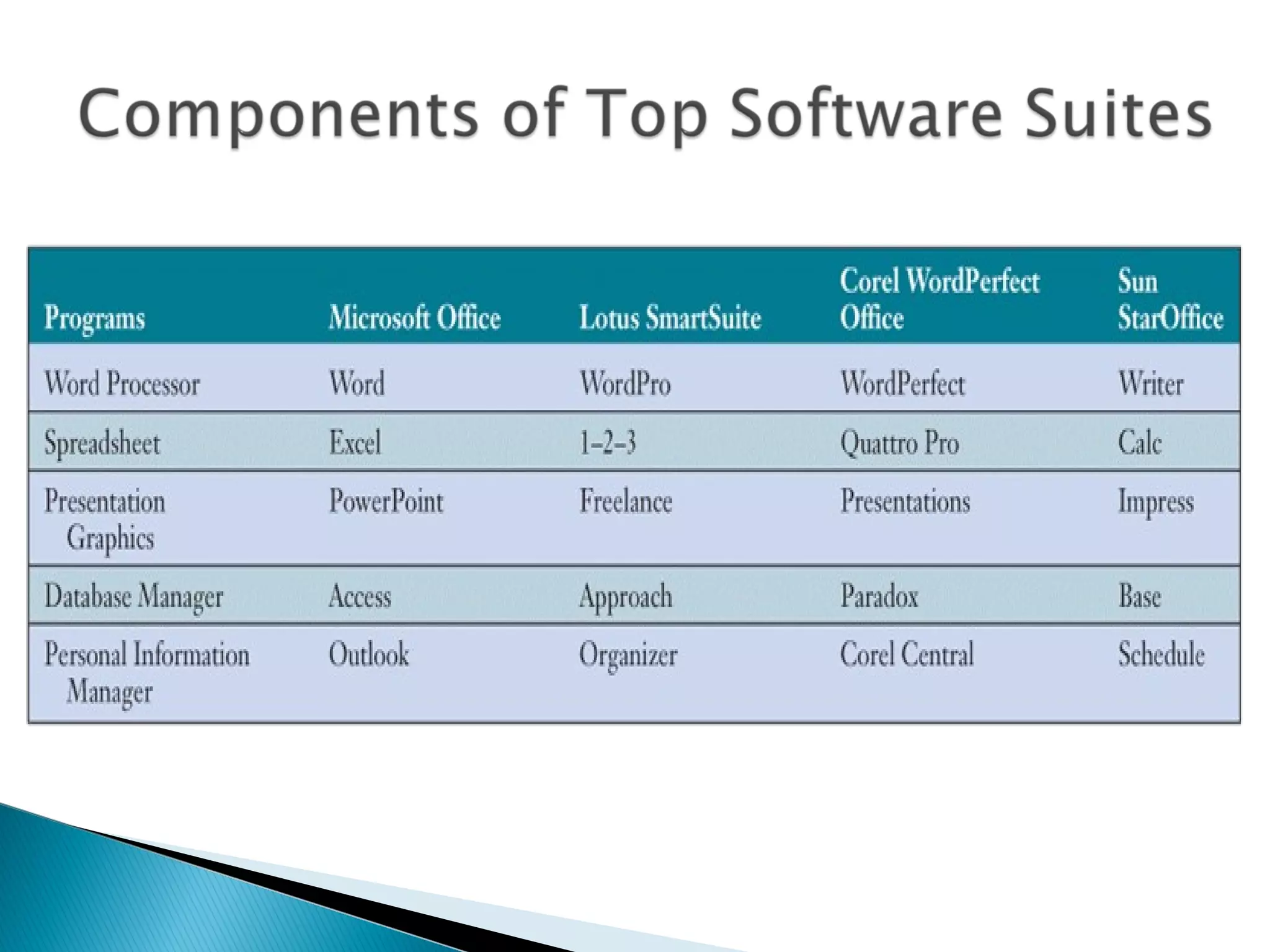
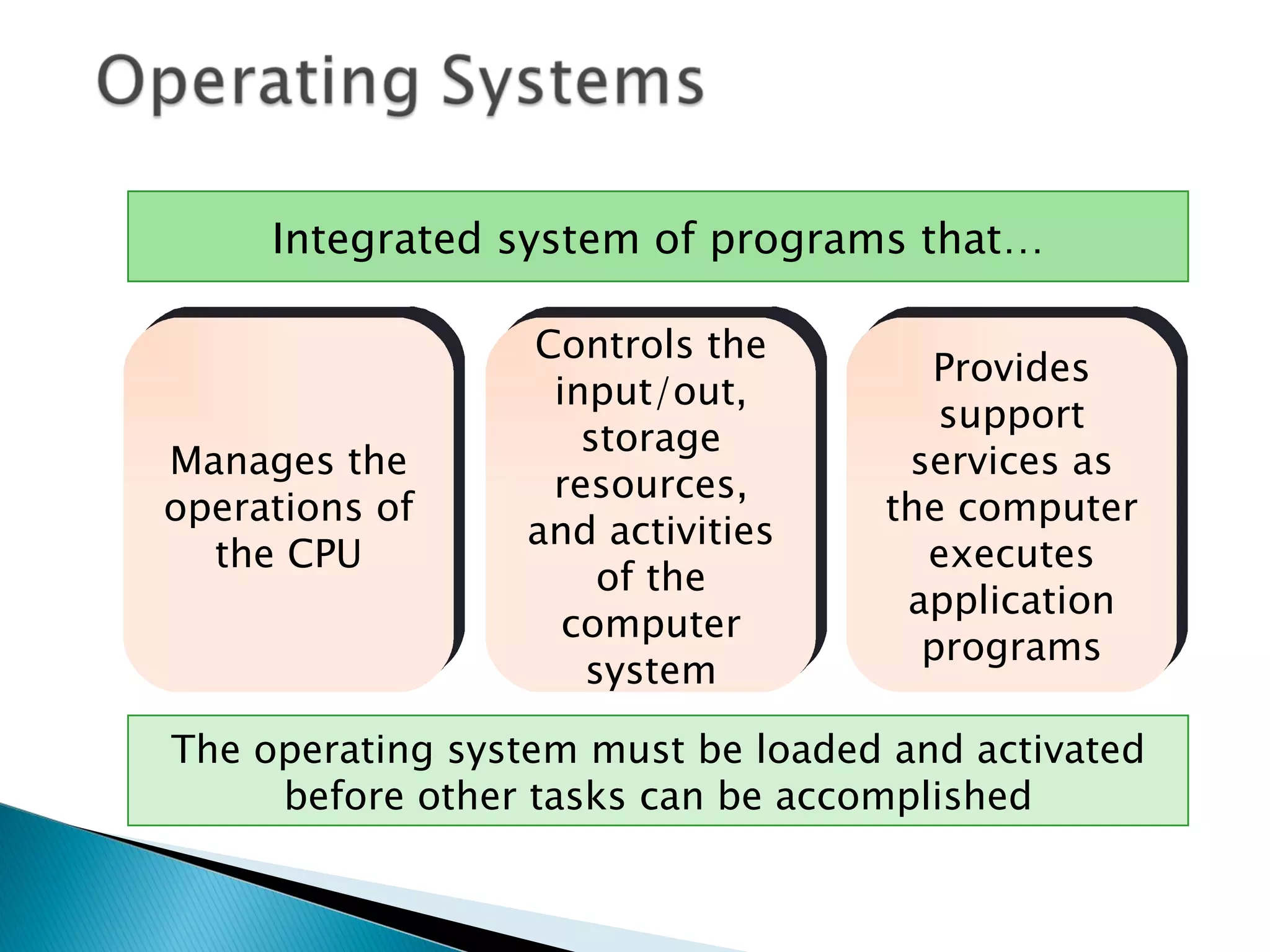
The document defines computer software and describes different types. It outlines the main functions of an operating system and describes trends in programming languages. System software includes operating systems and utilities that enable basic computer functions. Application software performs specific tasks for users like payroll or word processing. Open source software has publicly available code while proprietary software restricts use and modification through legal or technical means.