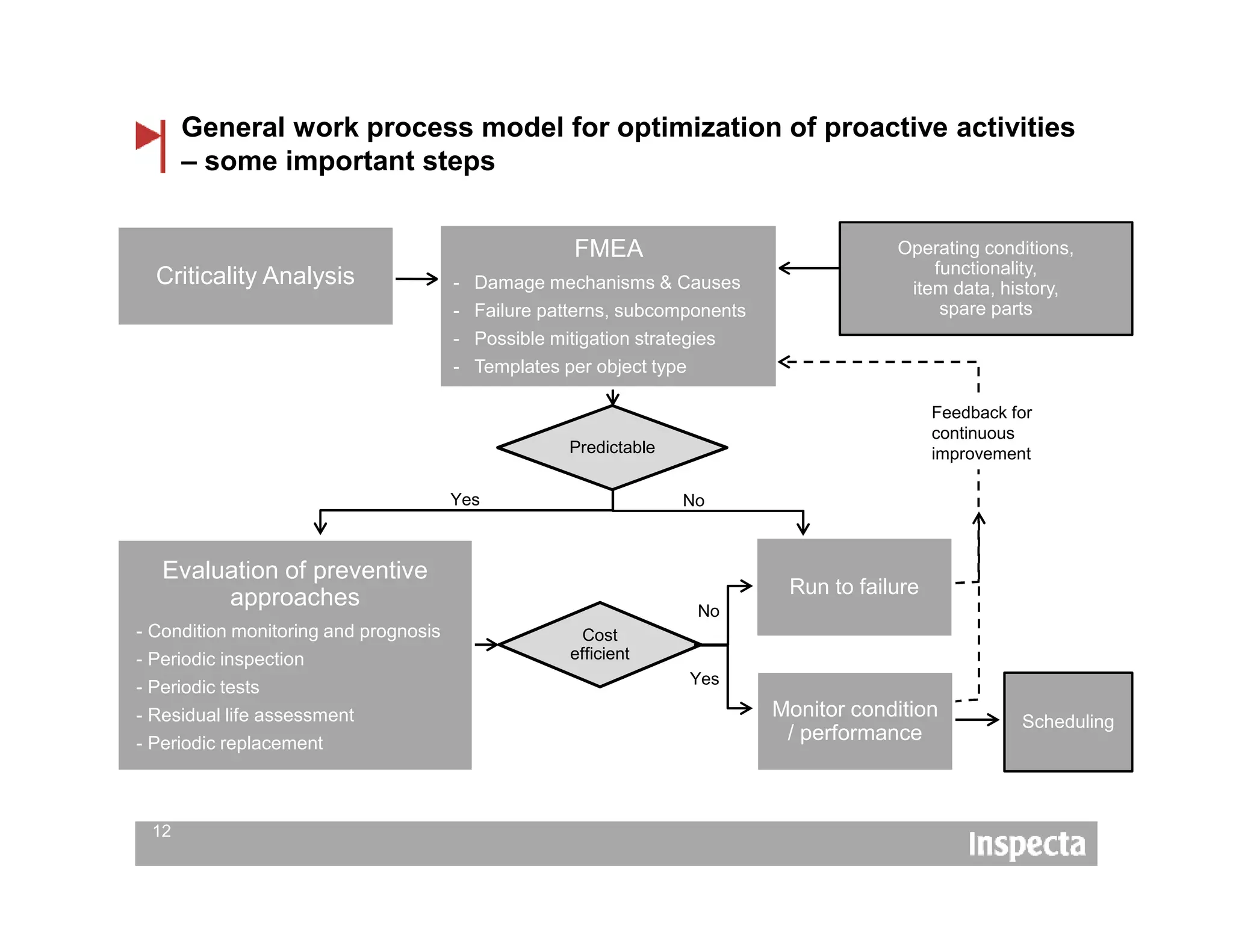
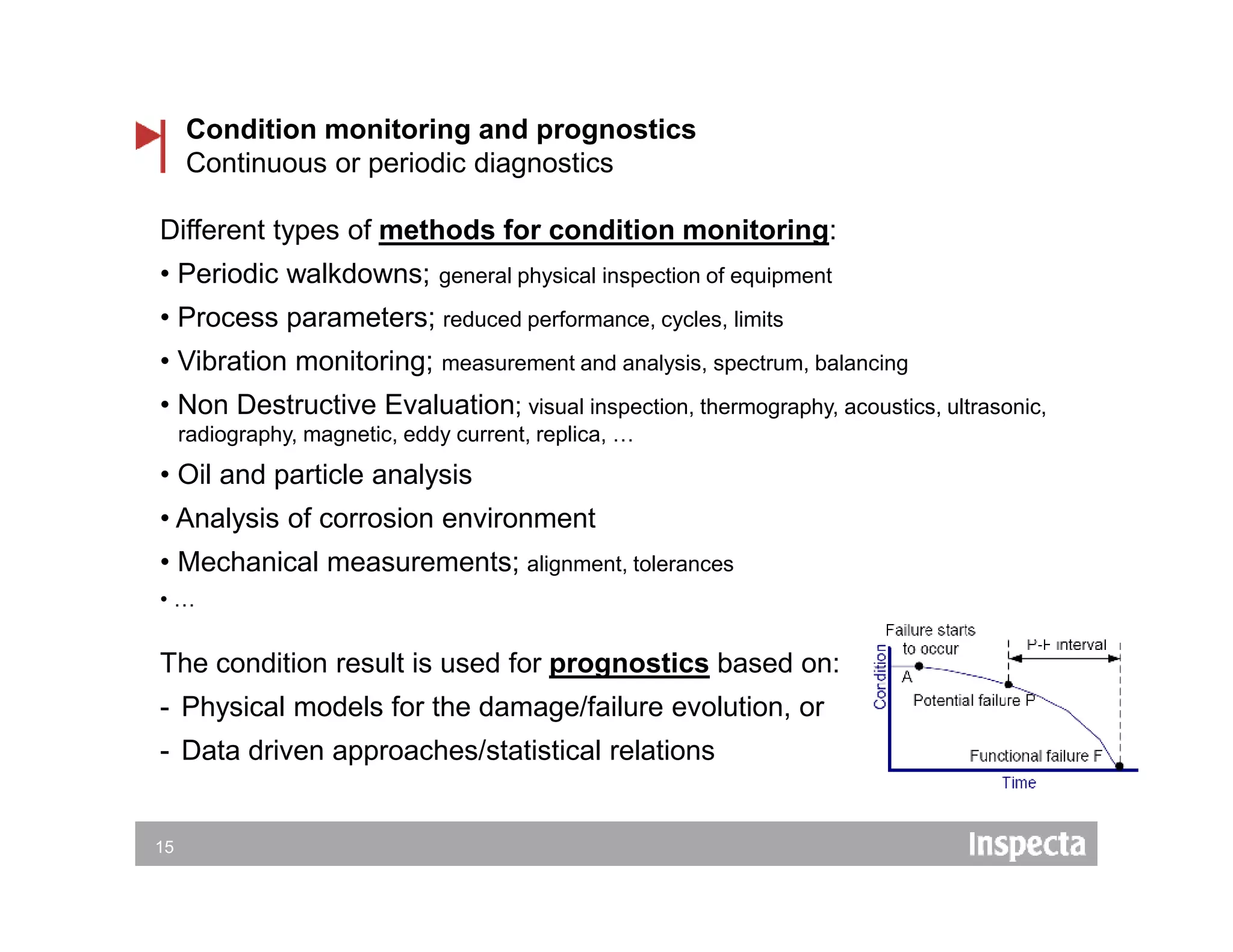
The document discusses the importance of adapting maintenance and inspection strategies to the criticality of equipment to enhance competitiveness and reduce unplanned stops. It outlines common challenges in maintenance practices, opportunities for proactive activities, and a work process model for optimizing these efforts. Conclusions emphasize the necessity of organizational support, training for personnel, and a structured approach to implementing such systems over a typical 2-3 year period.