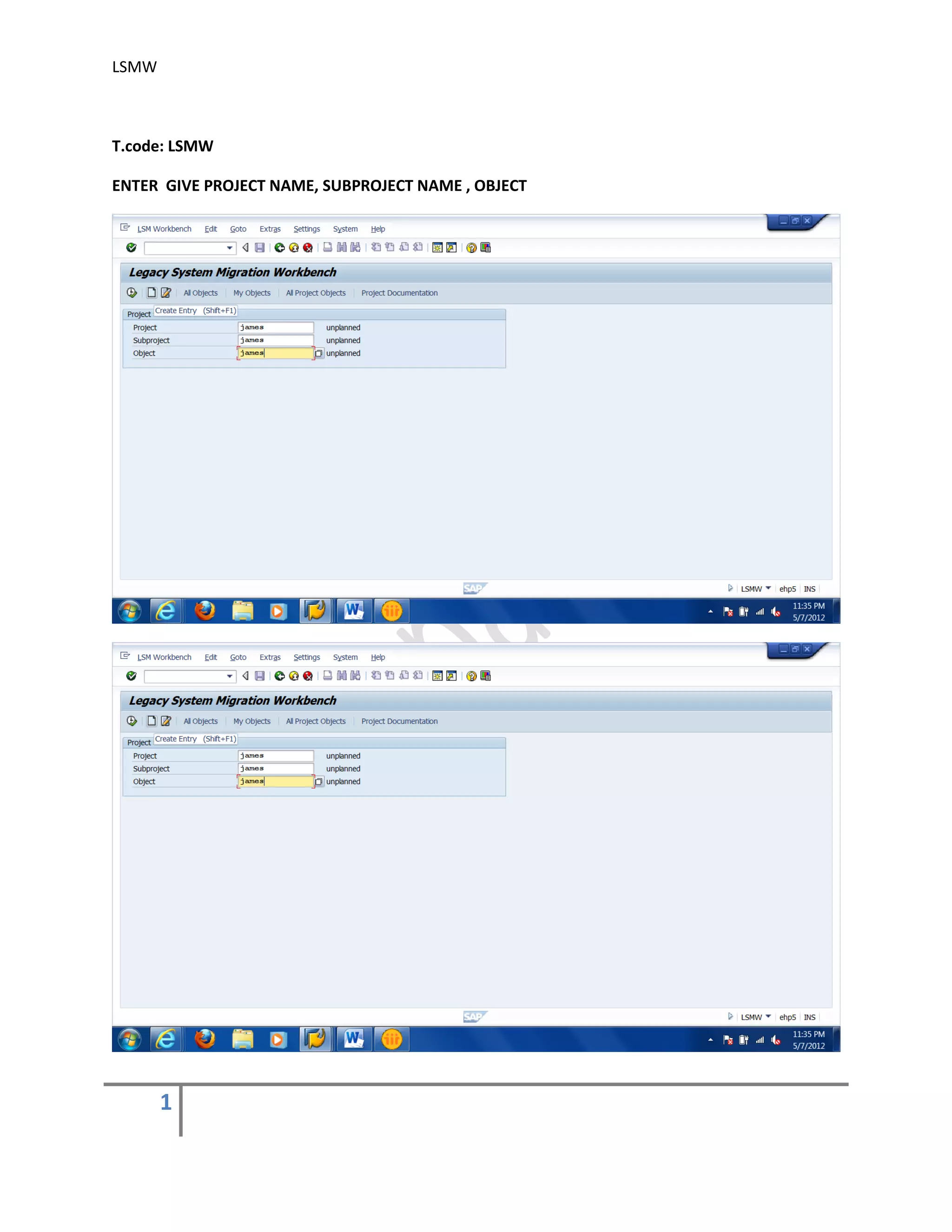
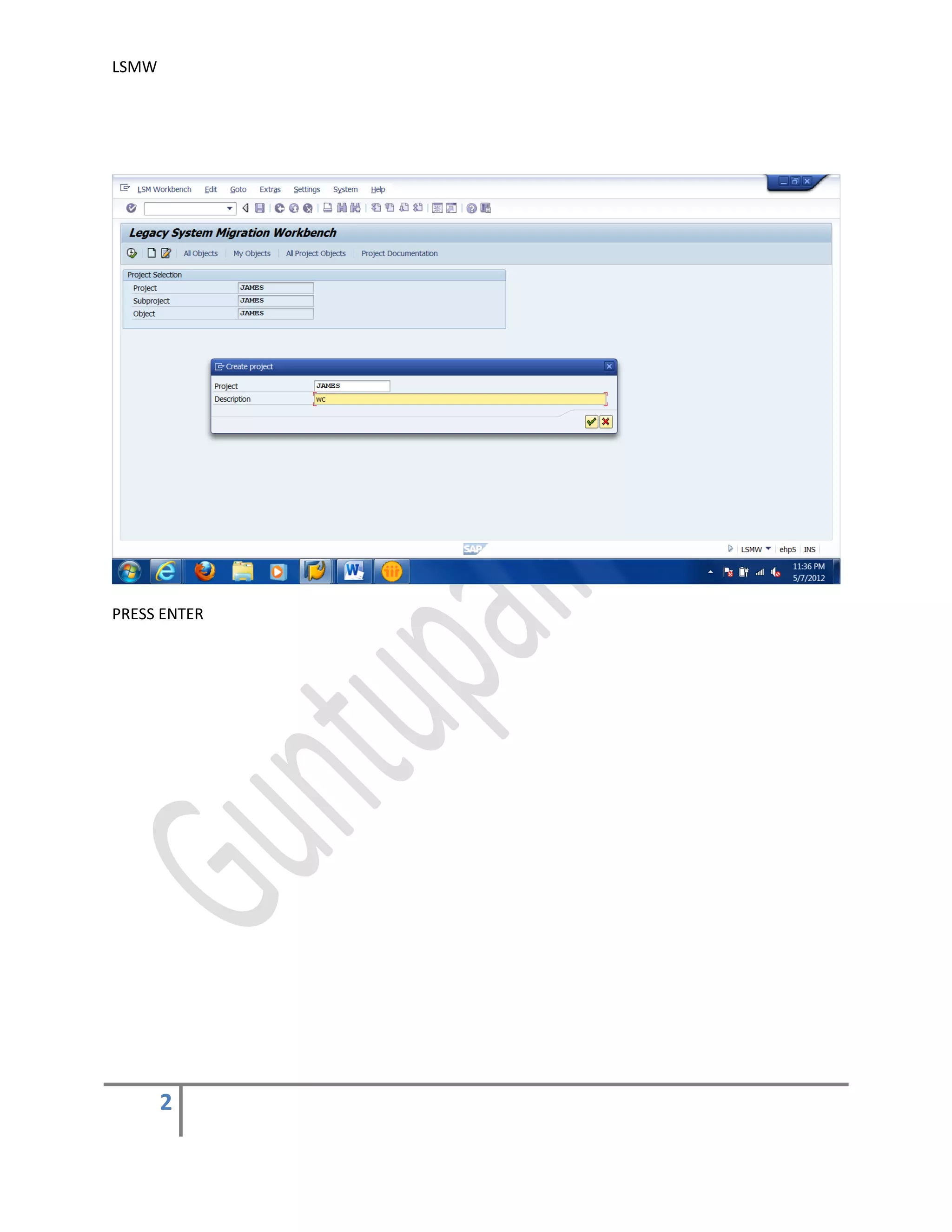
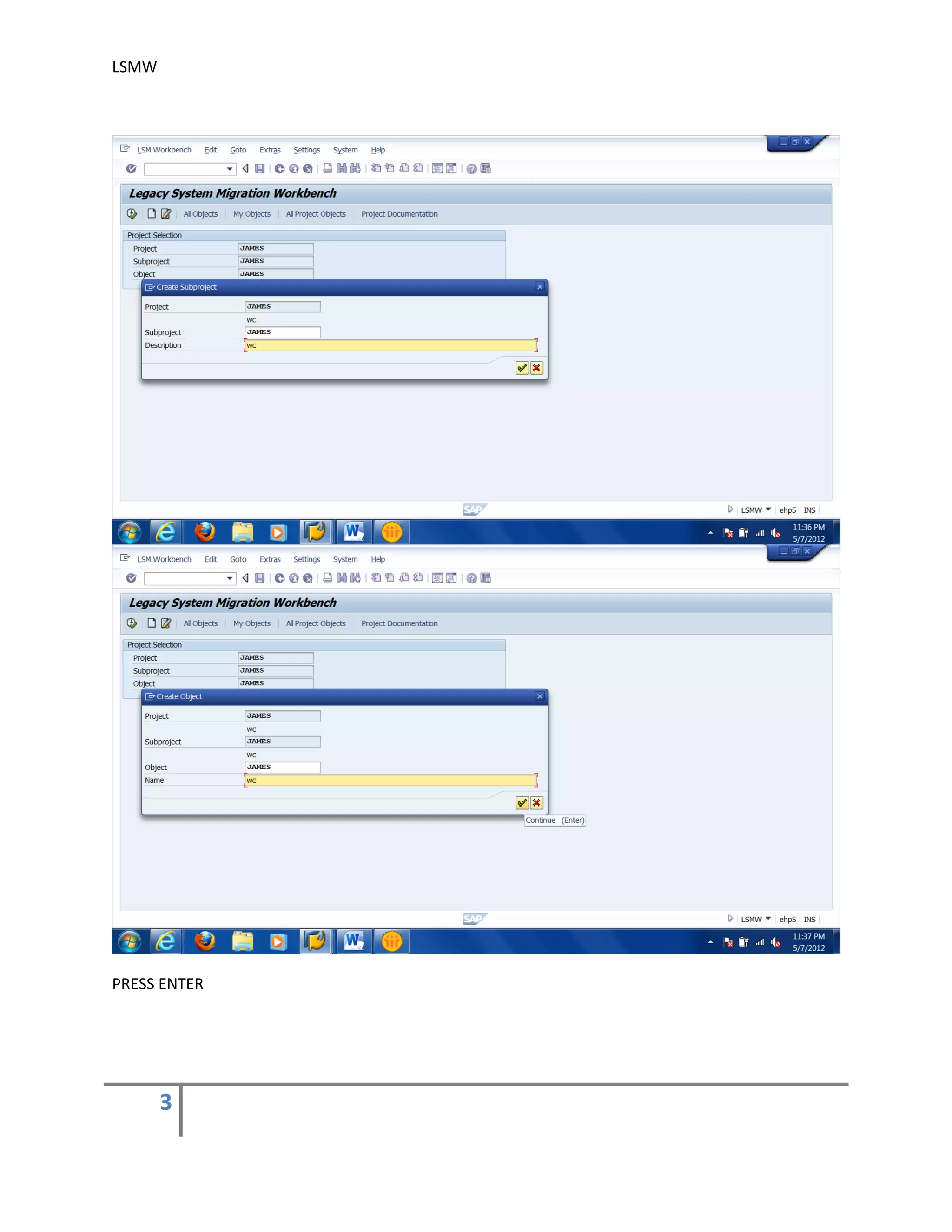
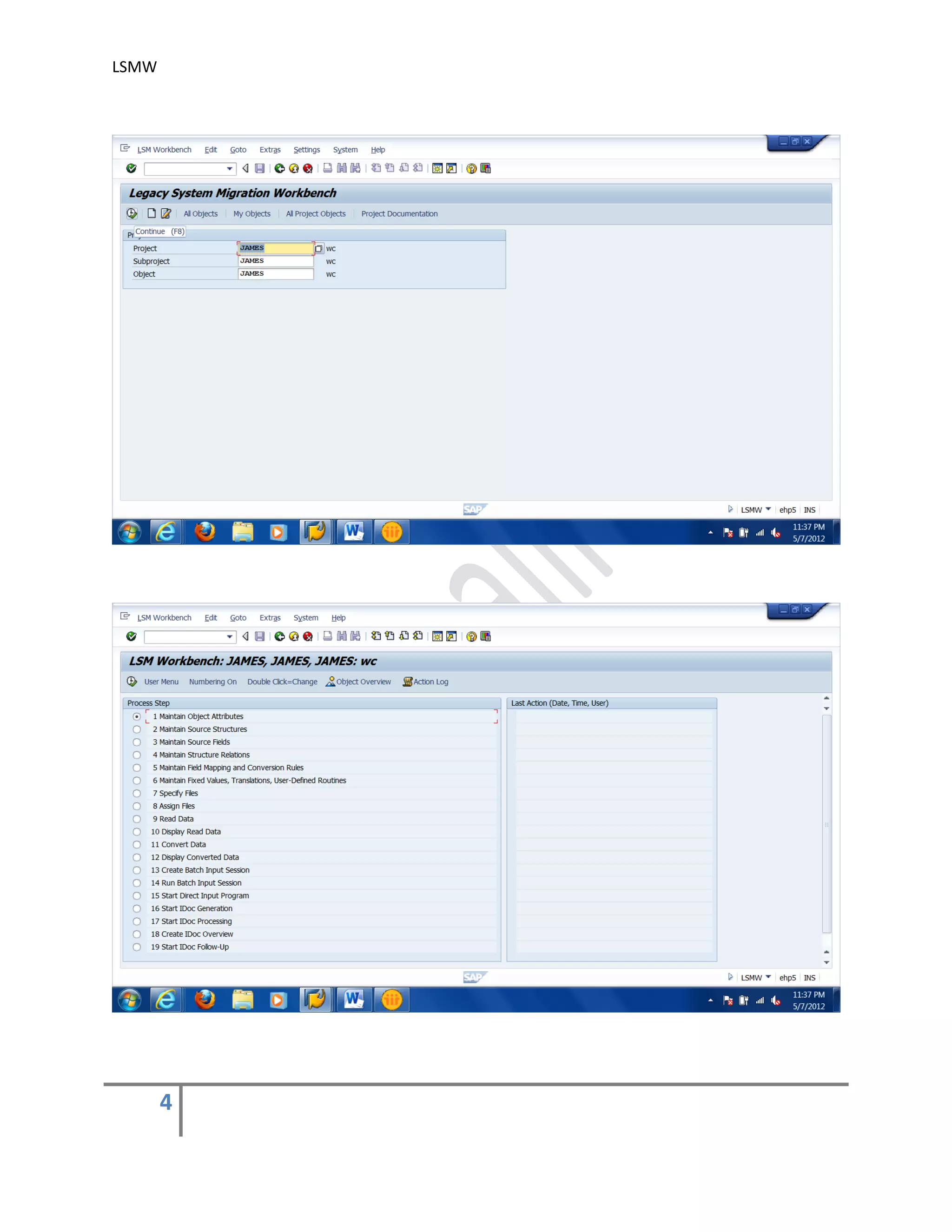
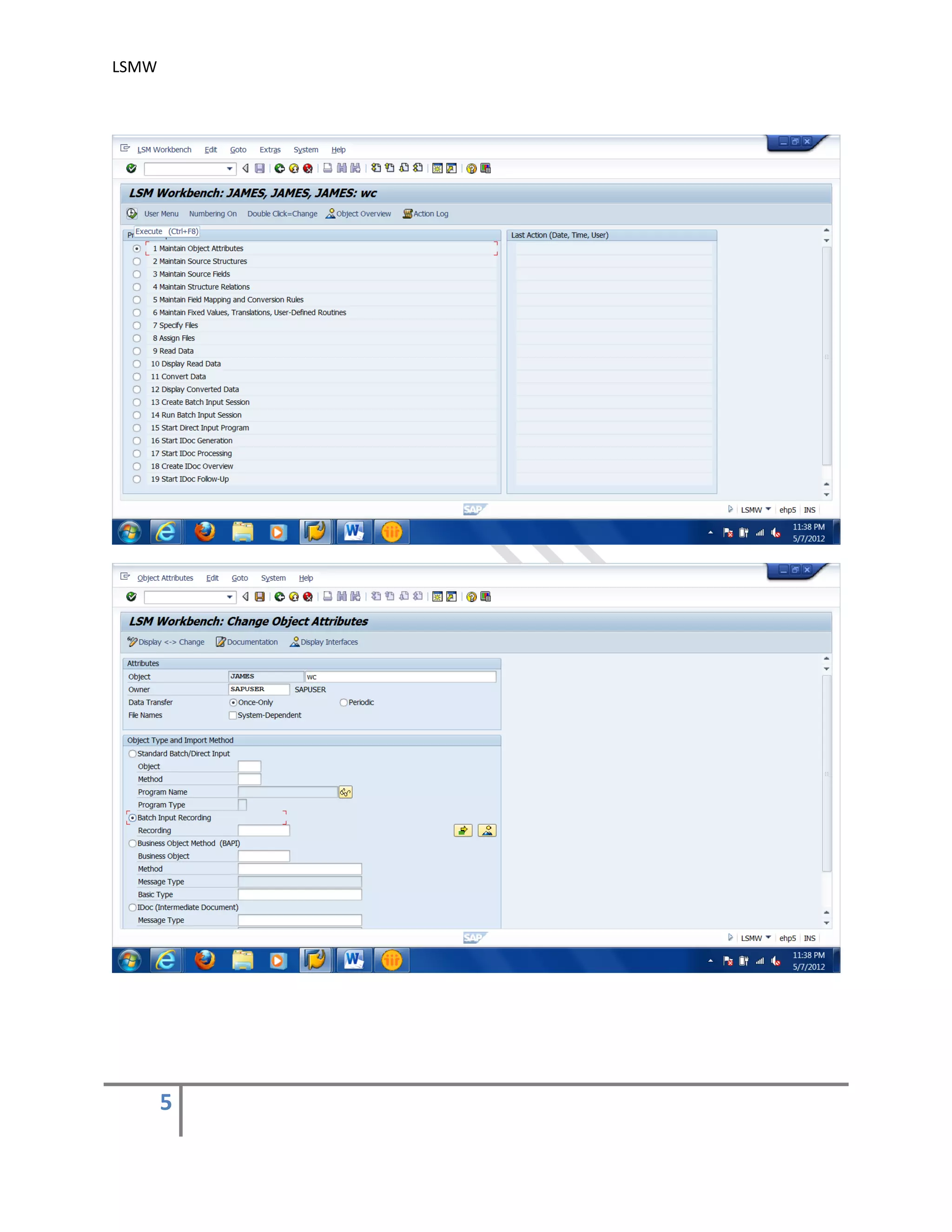
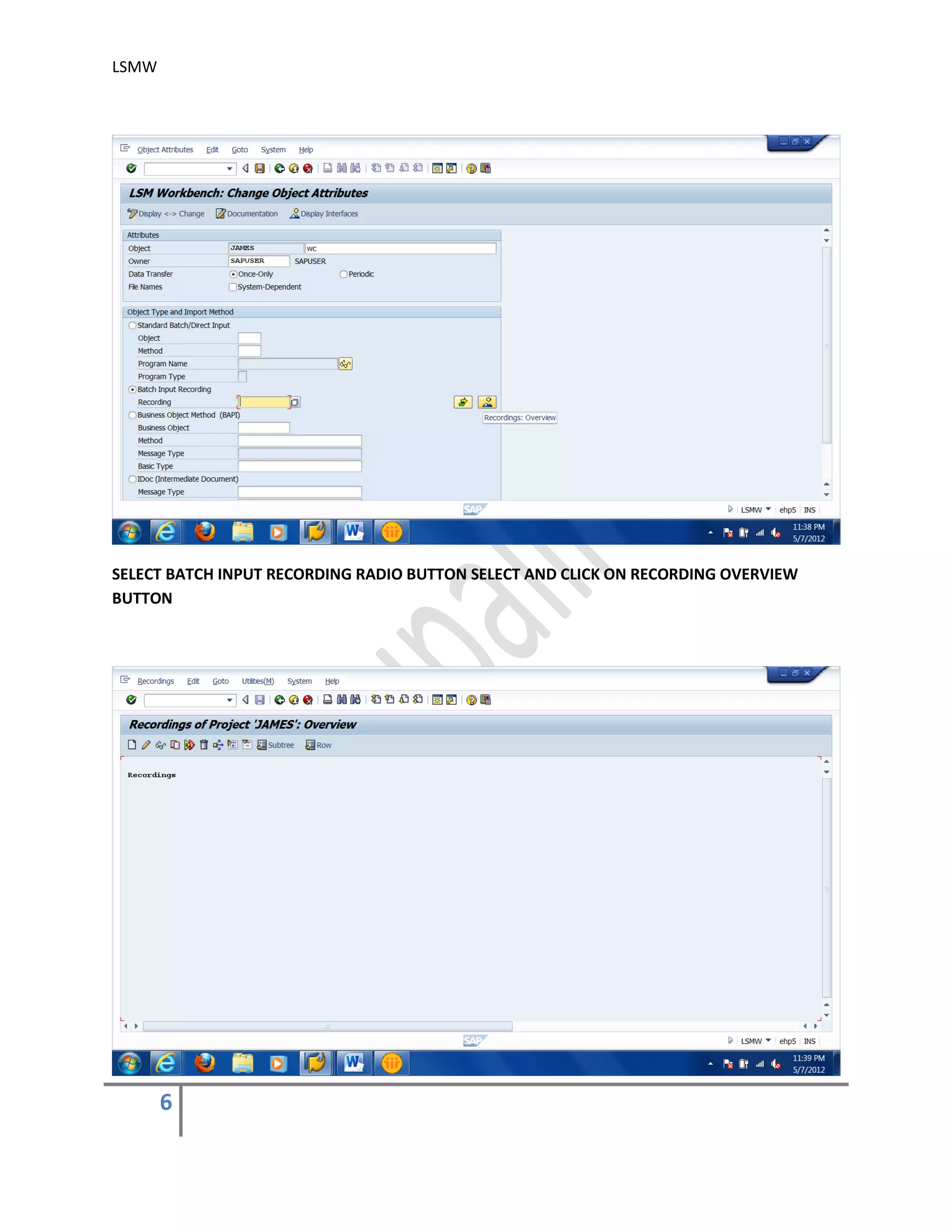
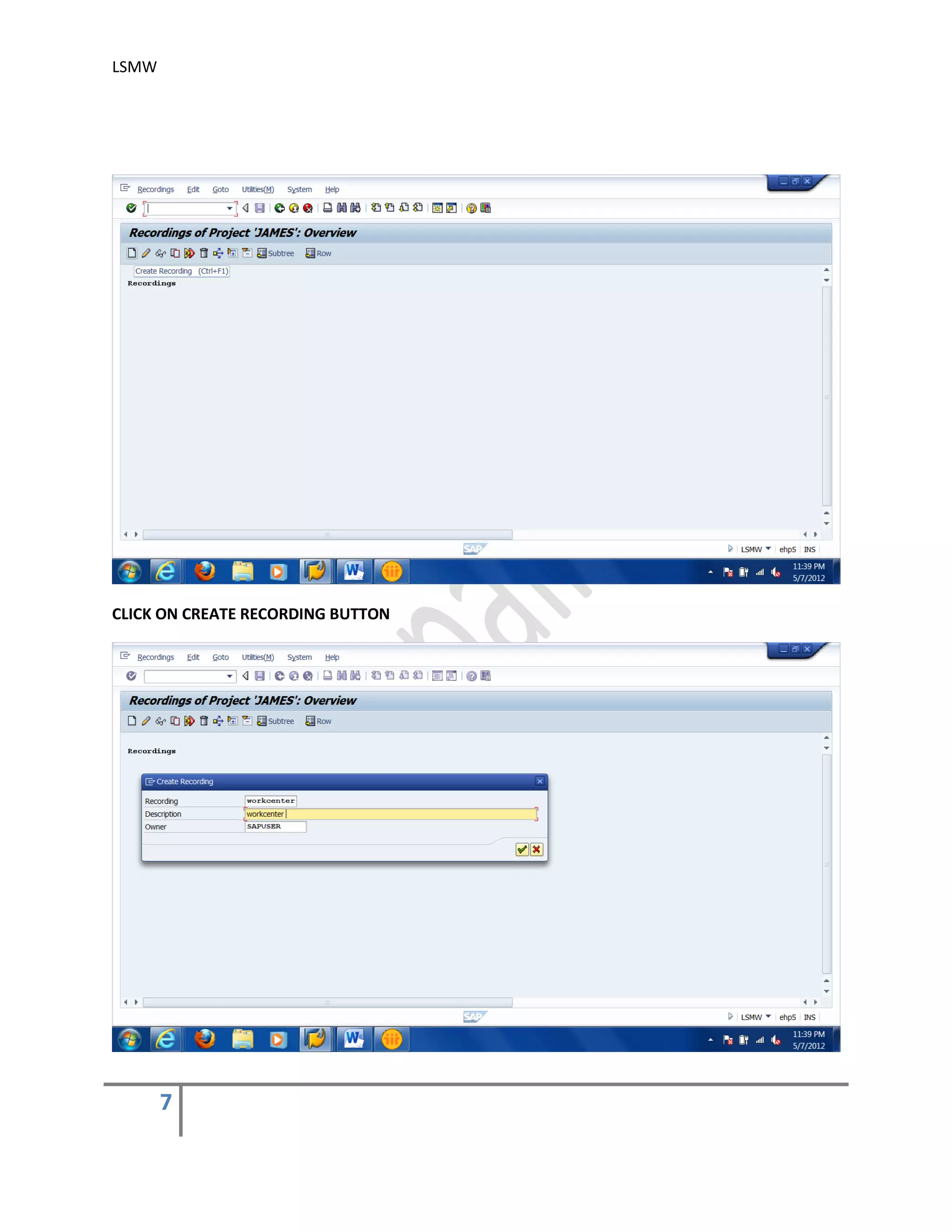
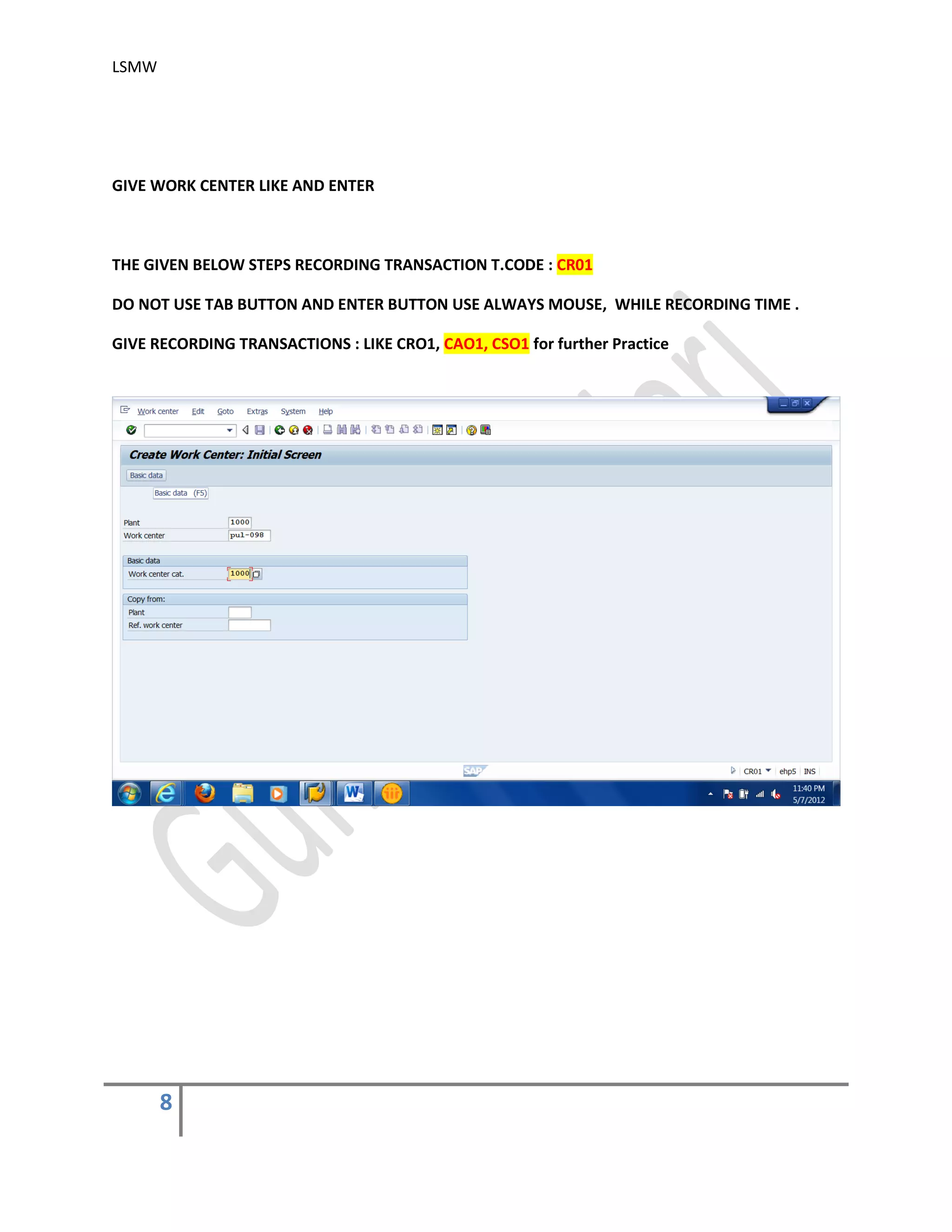
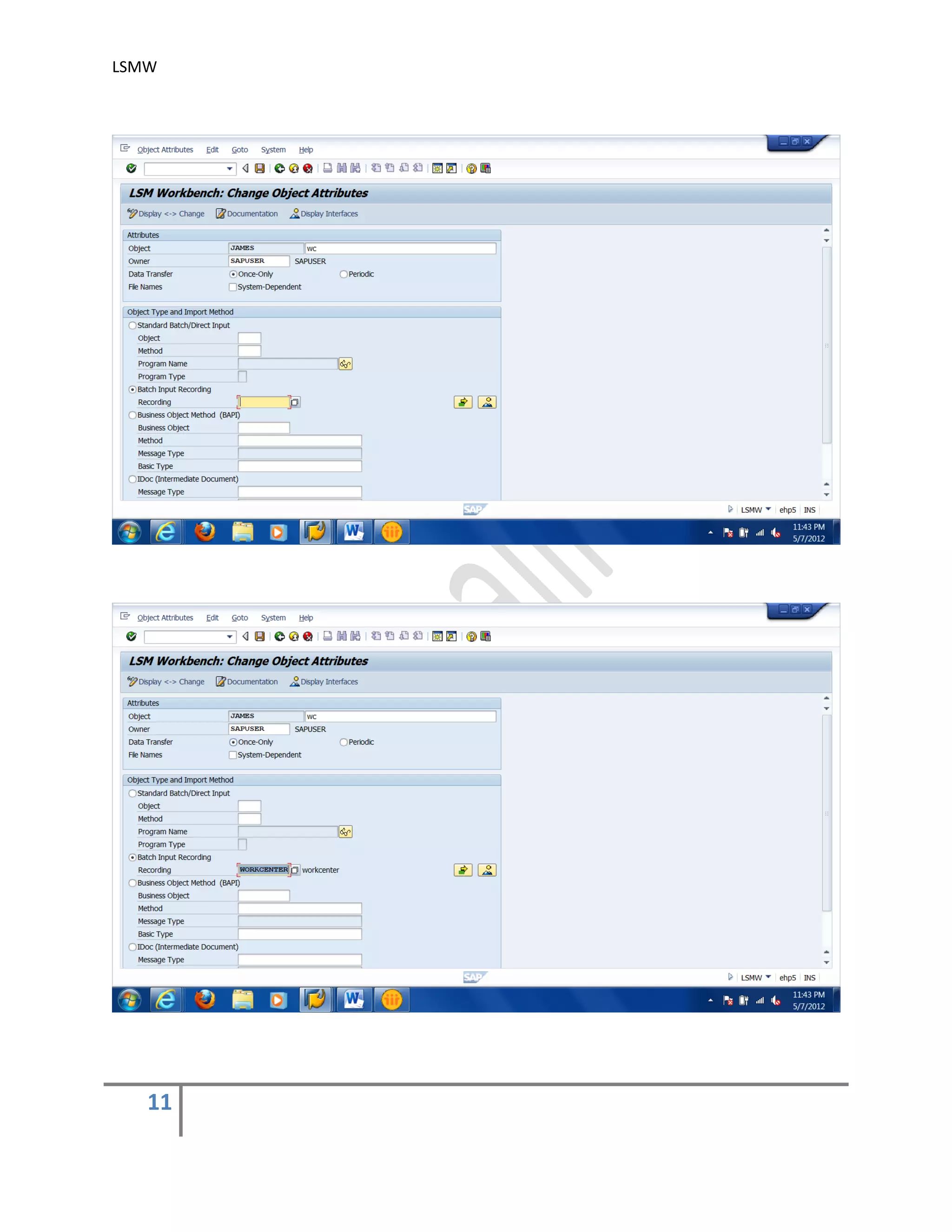
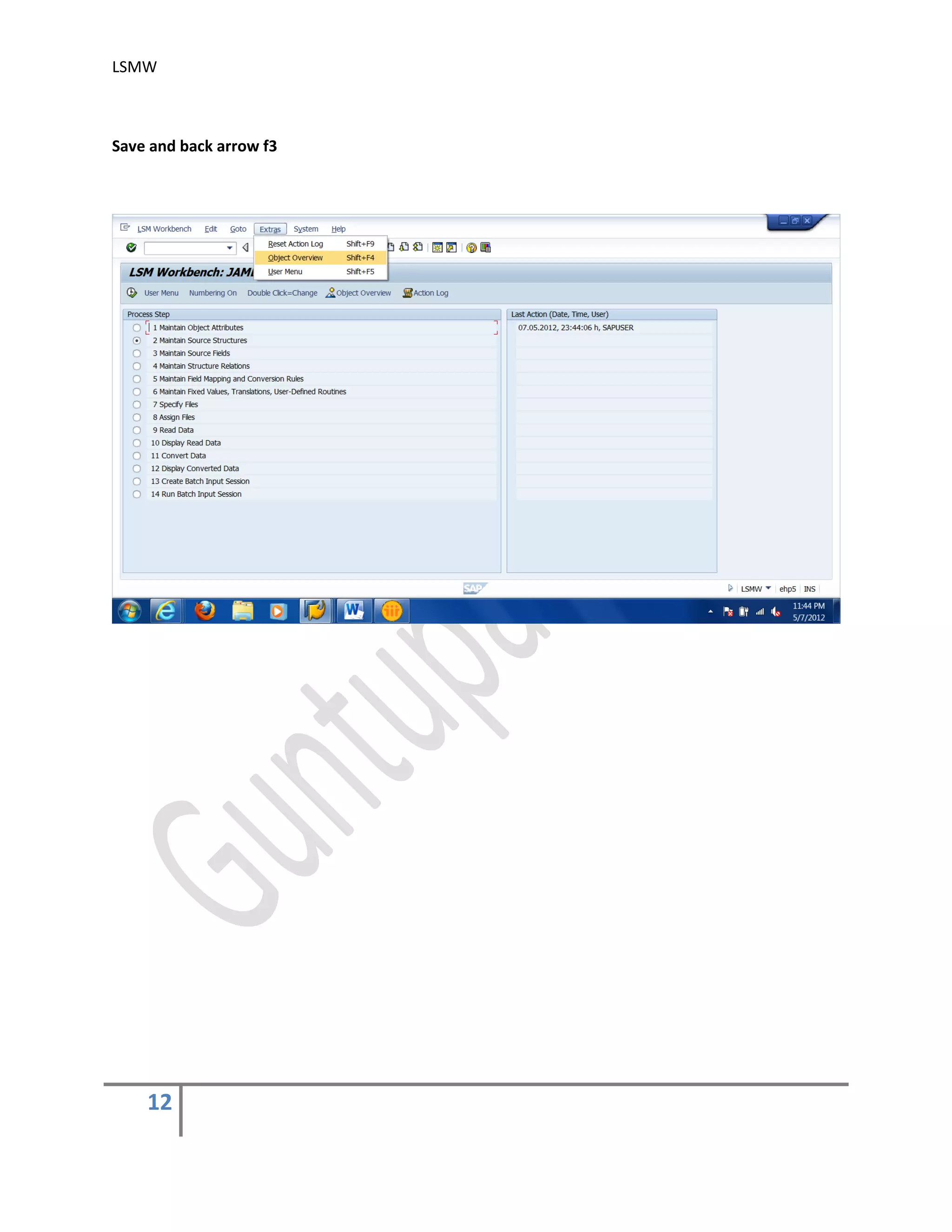
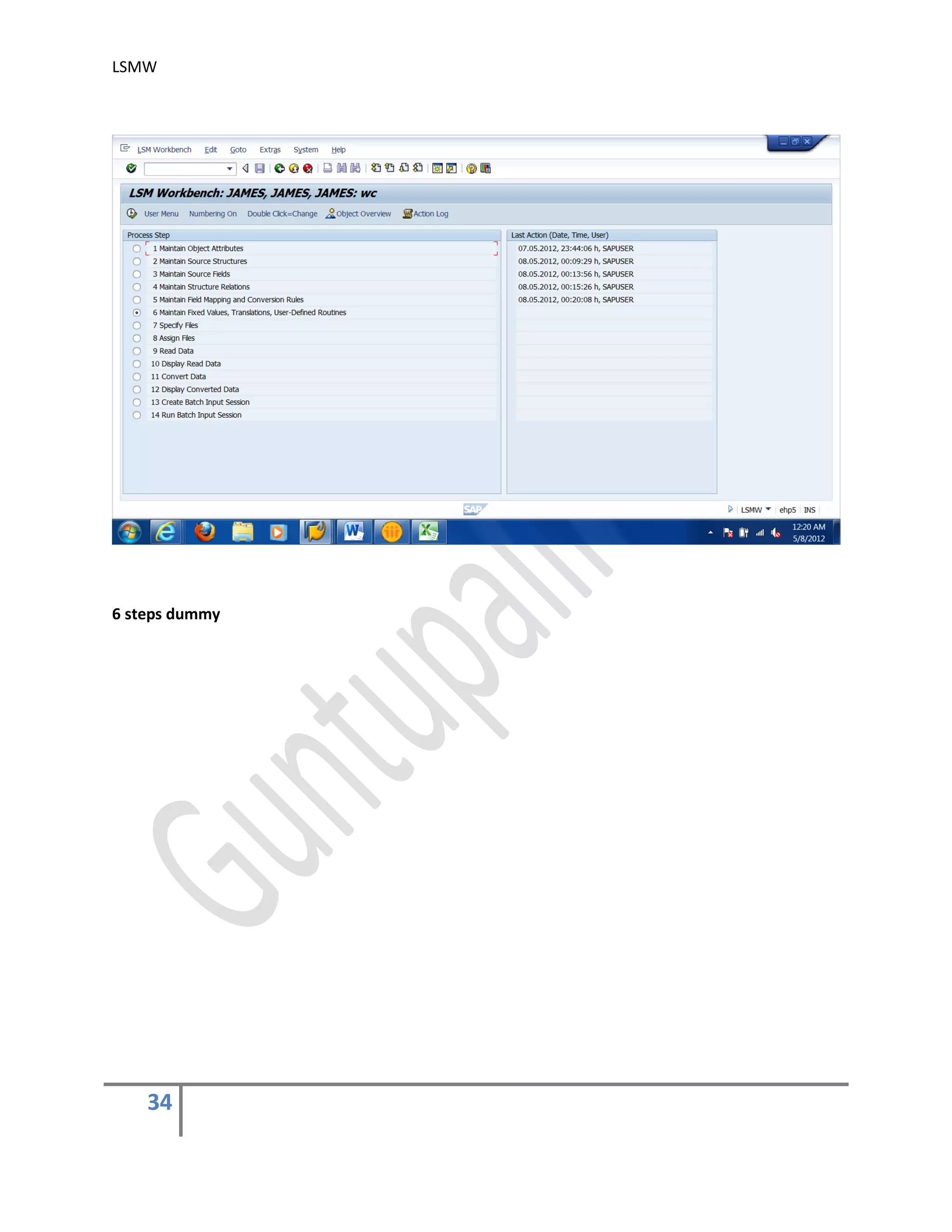
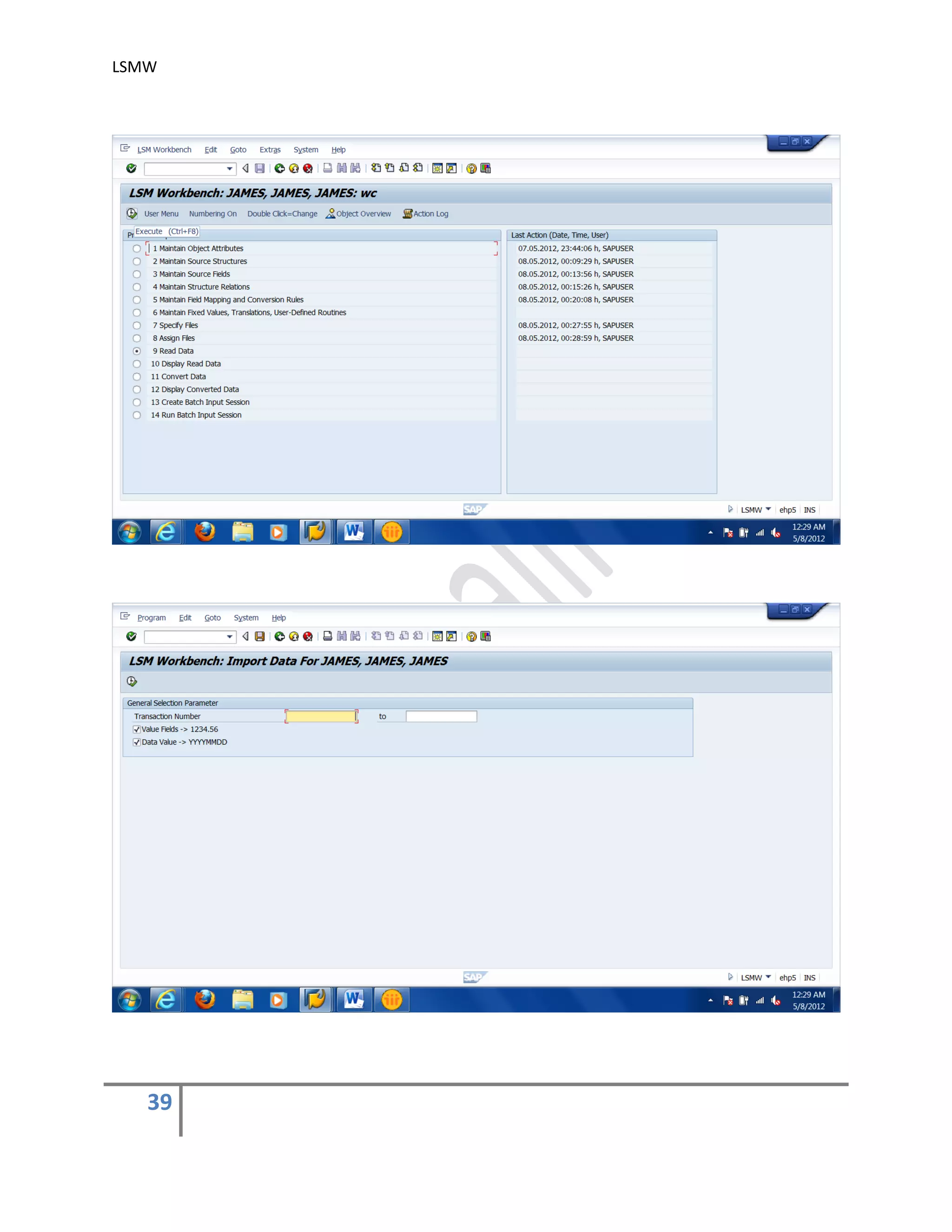
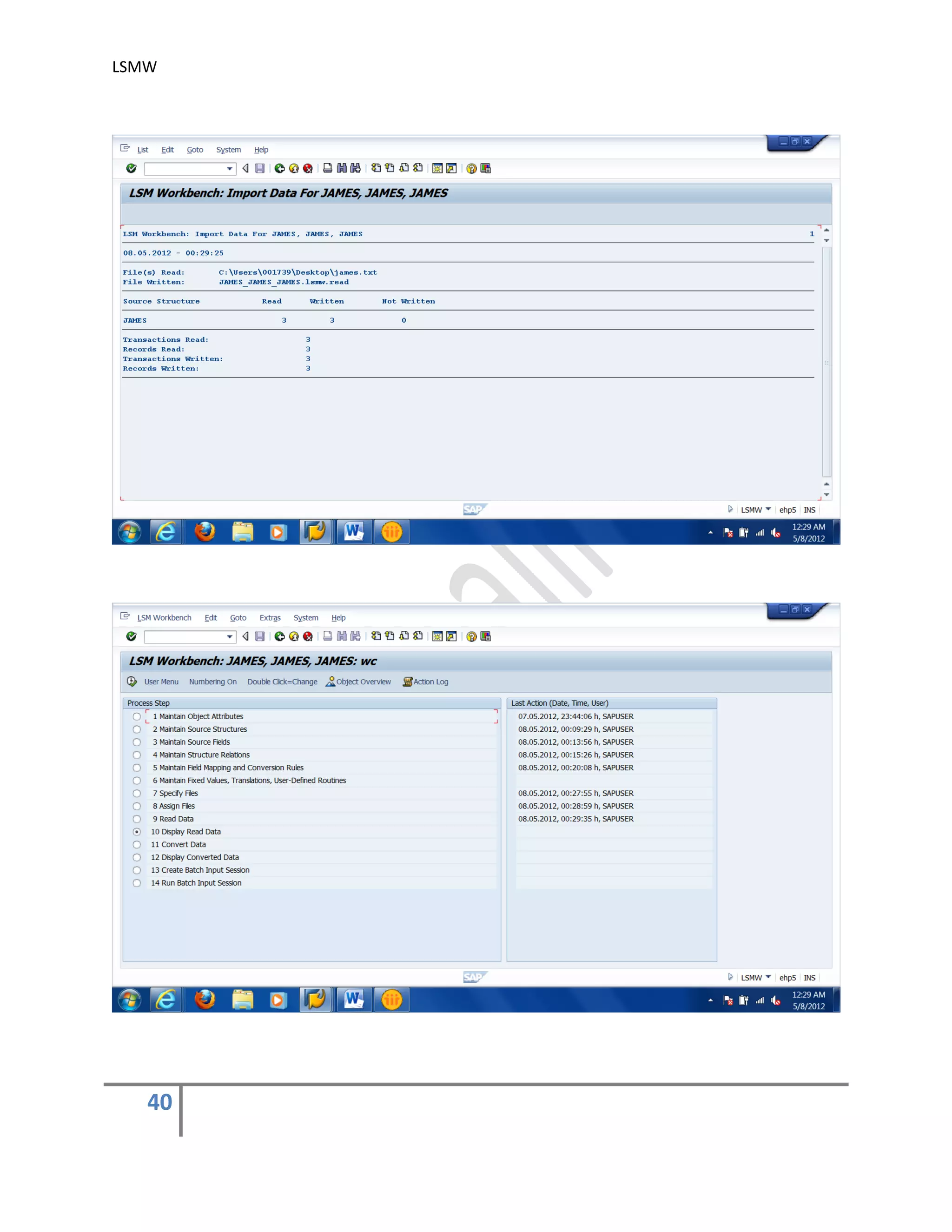
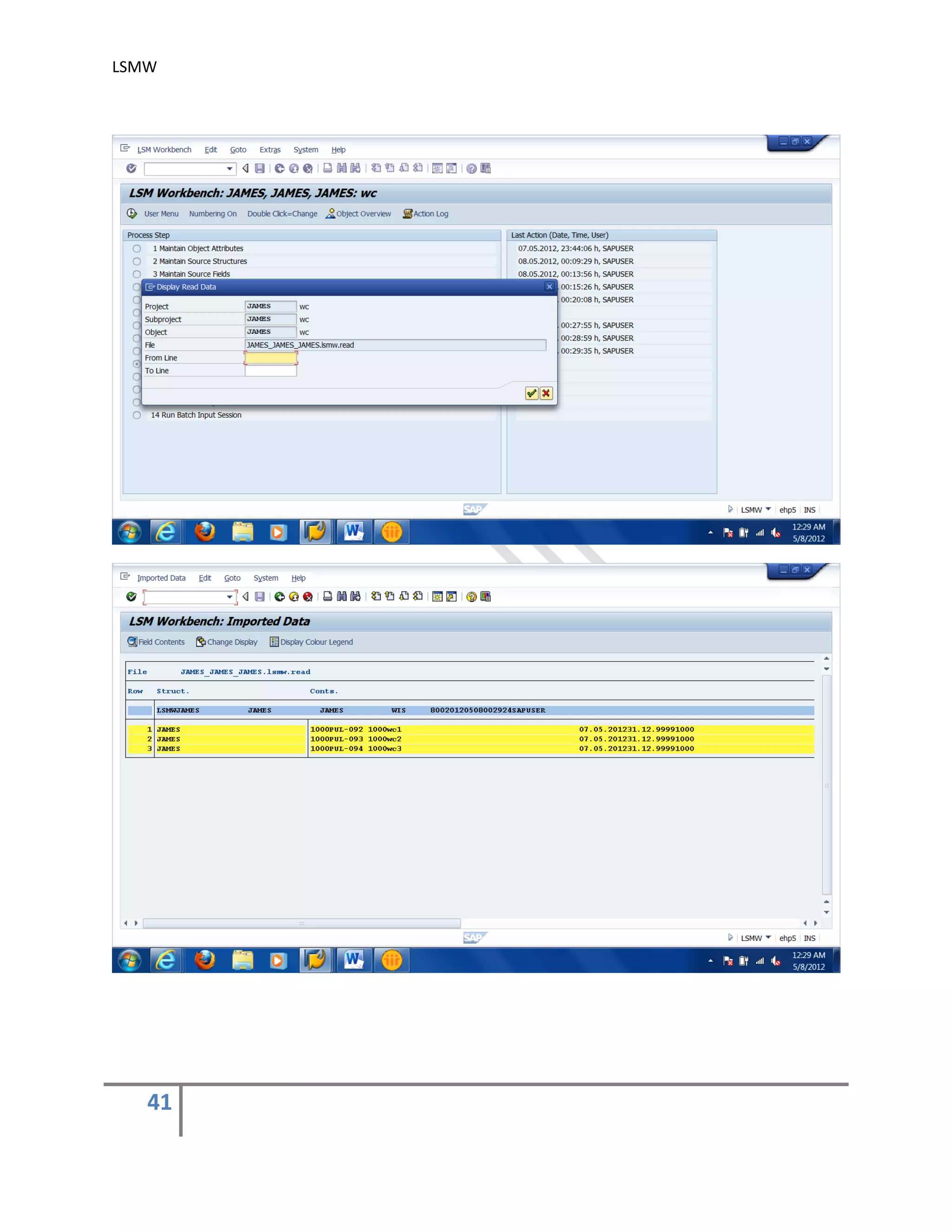
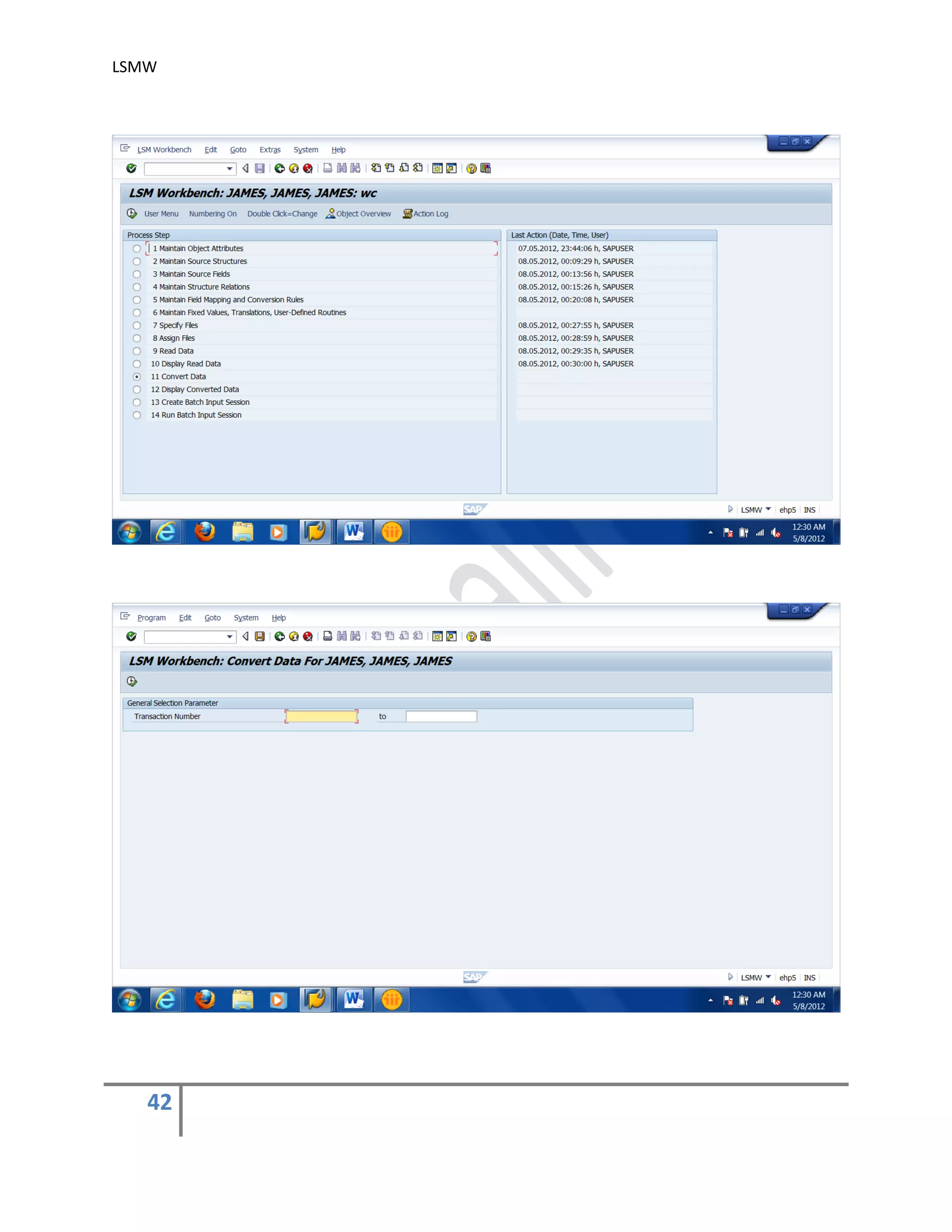
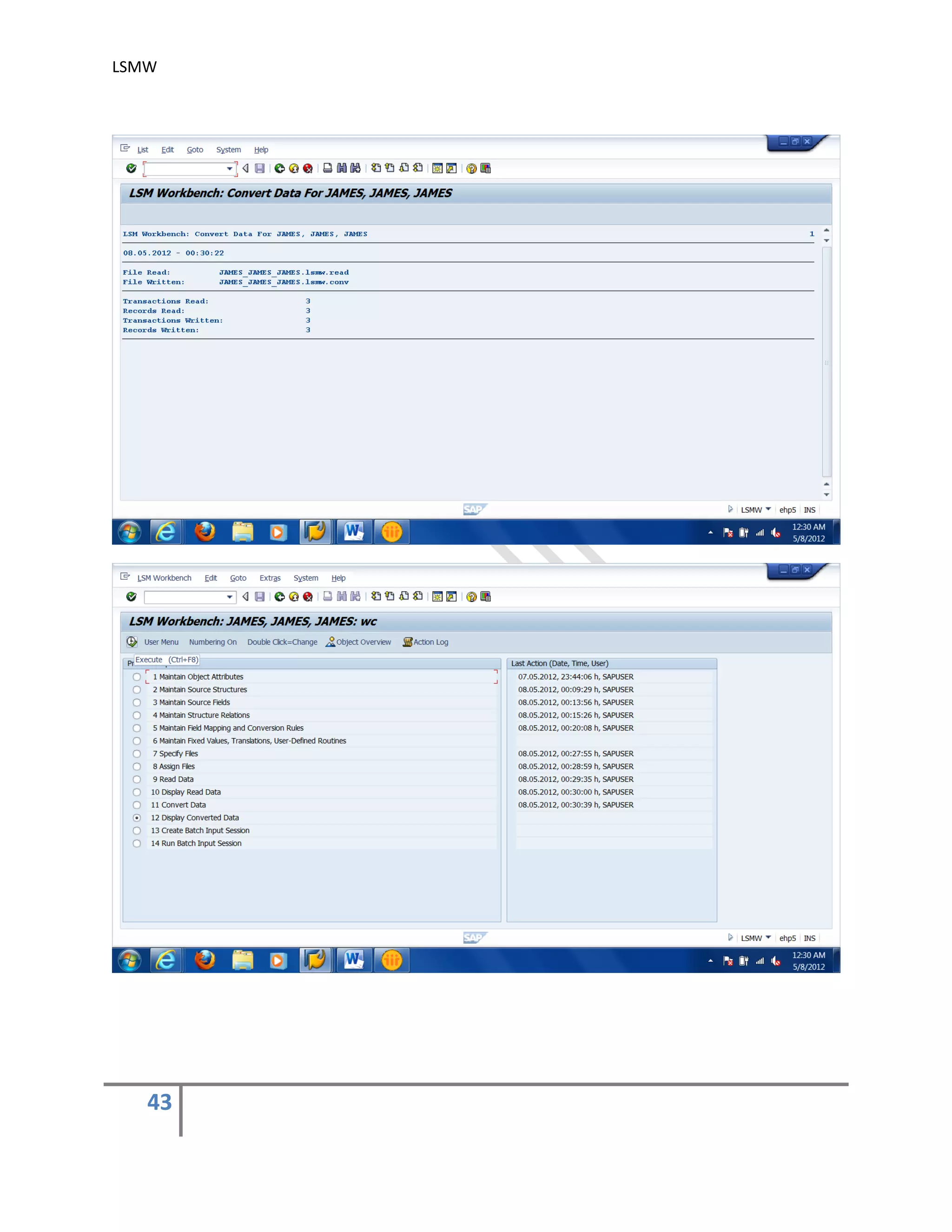
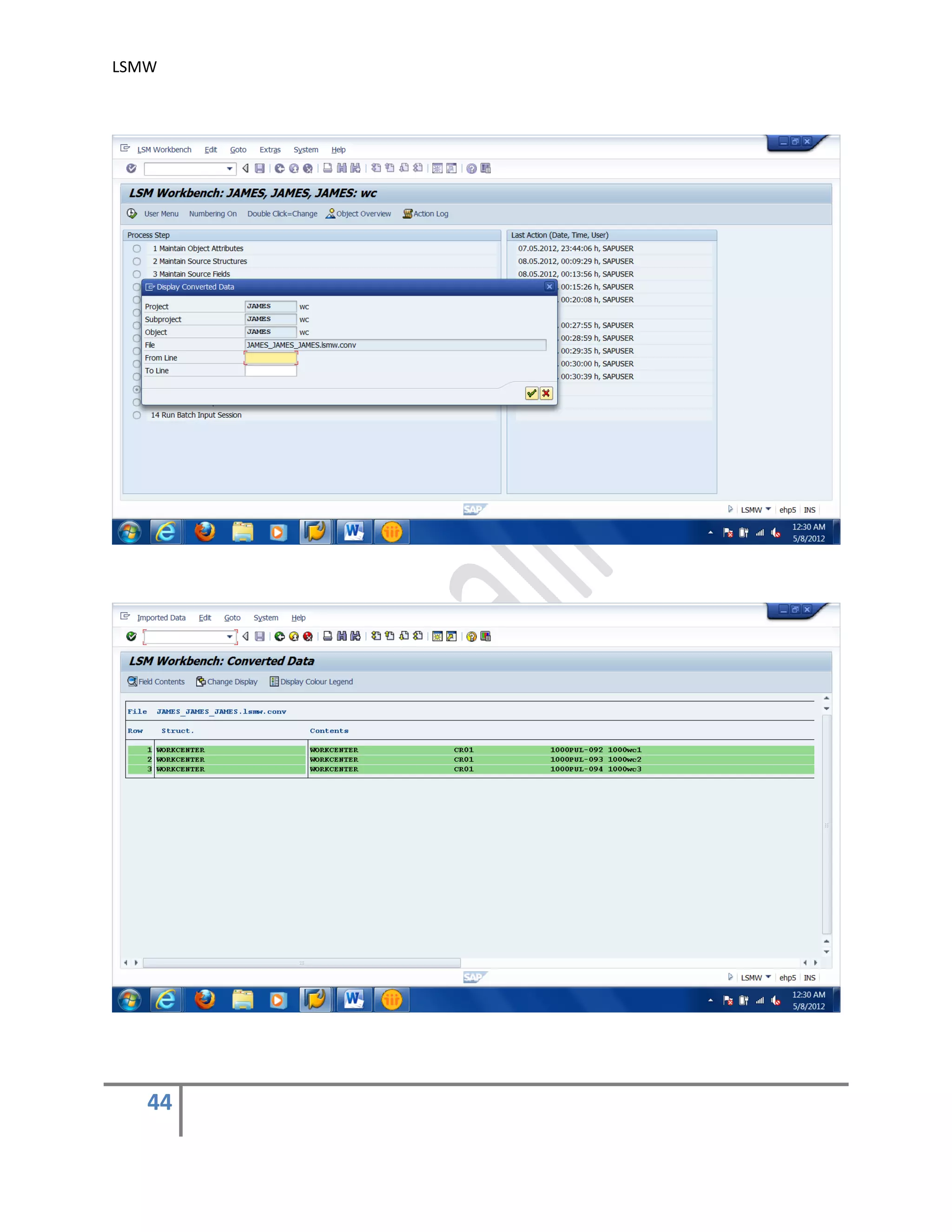
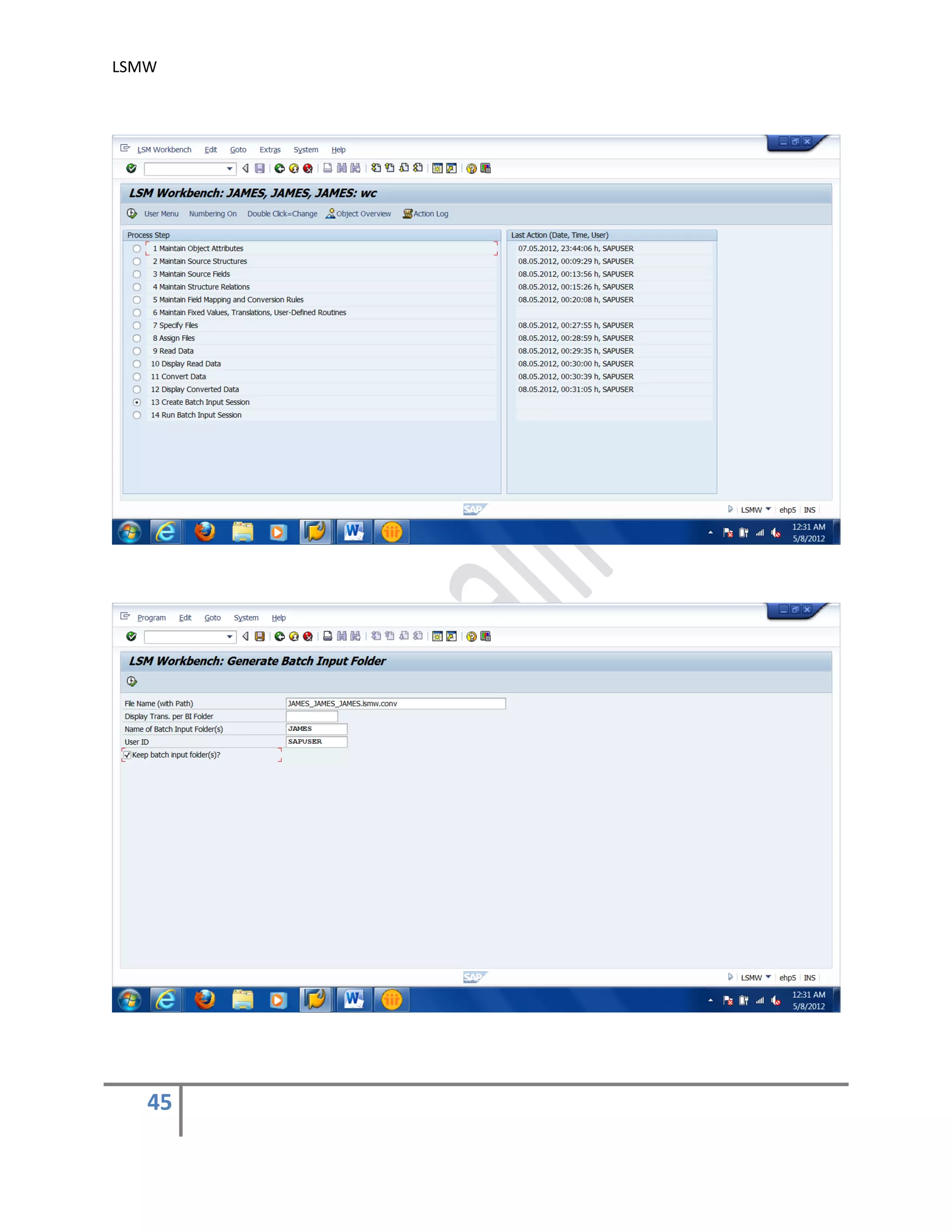
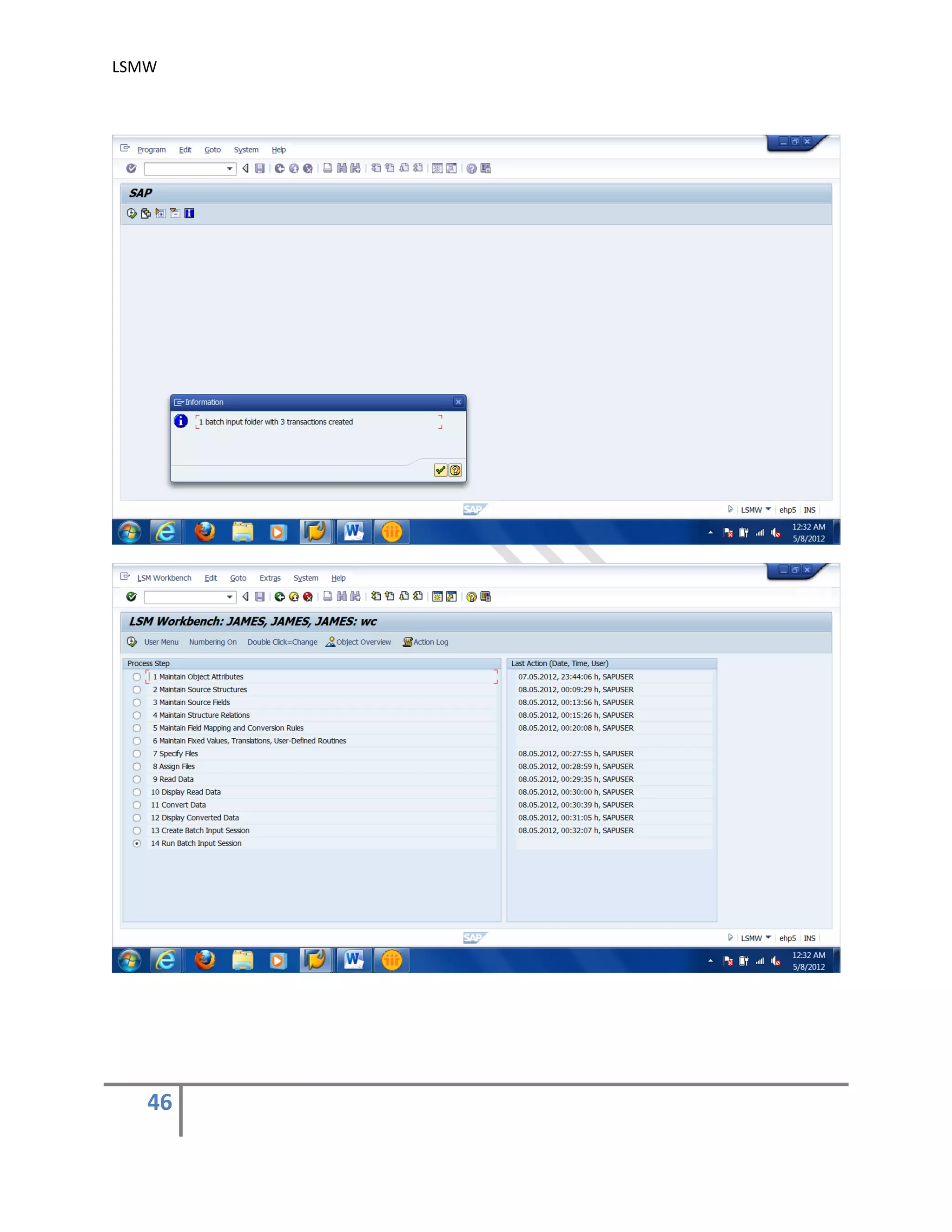
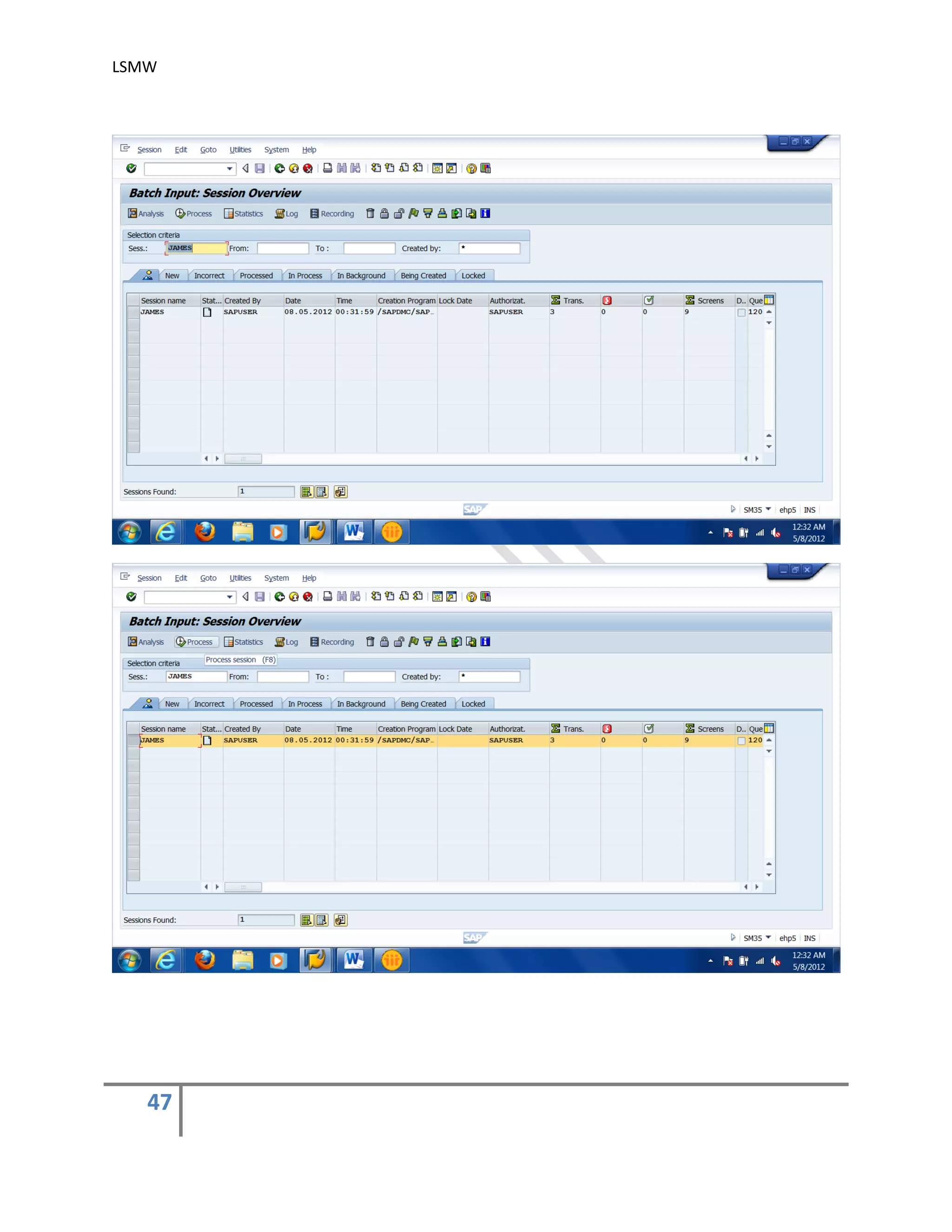
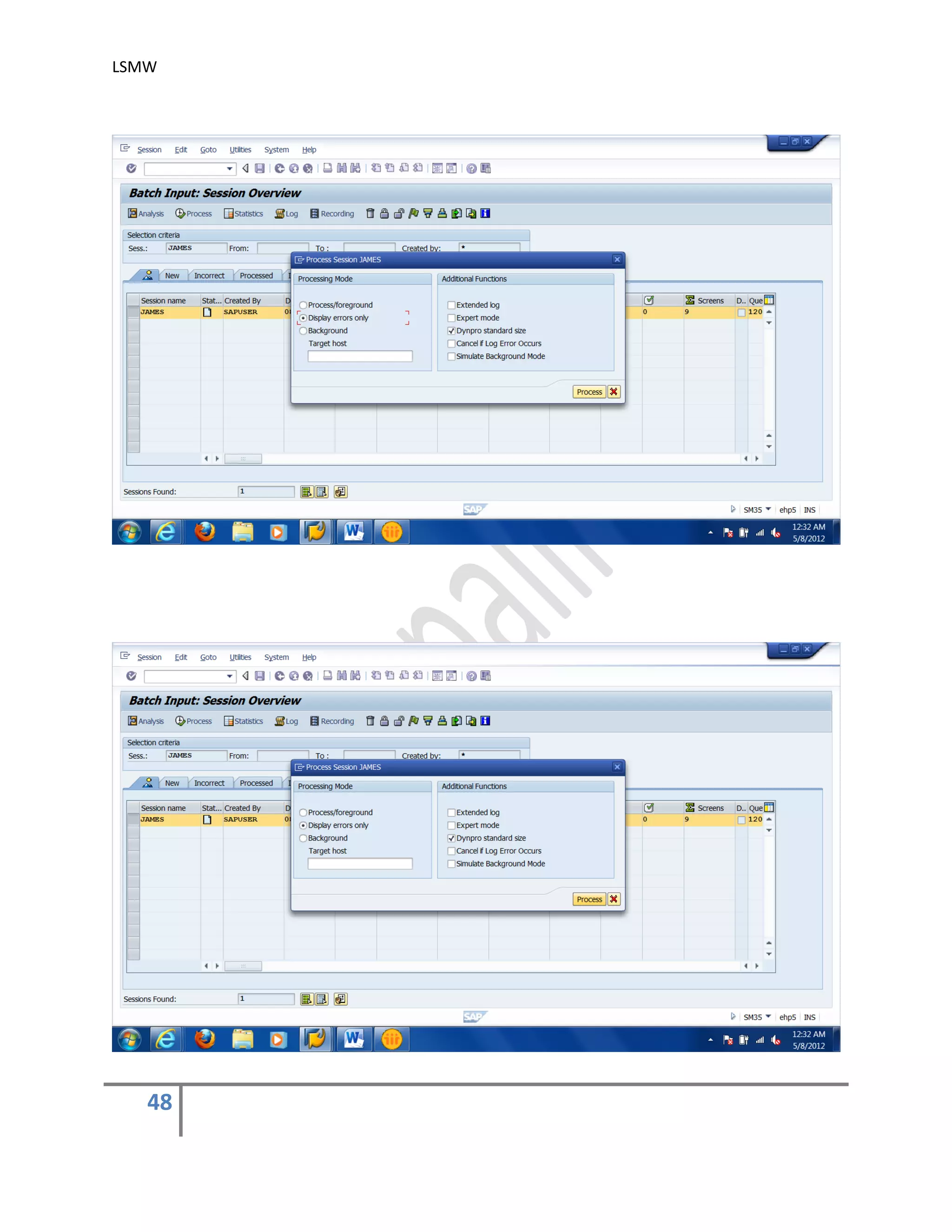
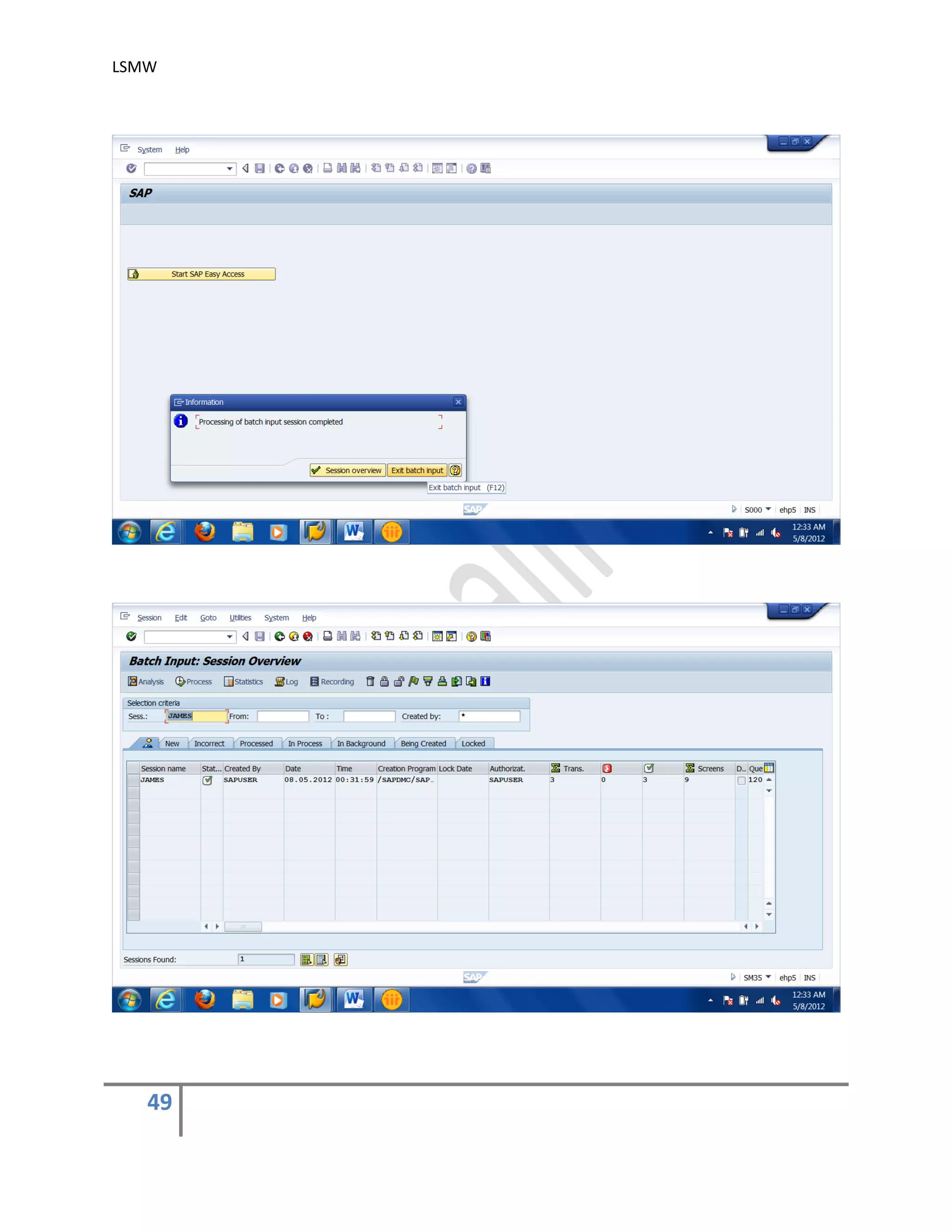
The document provides an overview of the LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench) tool in SAP. LSMW allows periodic or one-time transfer of data from legacy systems to SAP R/3. It supports various methods for data transfer, including batch input, BAPI, IDOC, and direct input. The document outlines the typical 14 processing steps used for batch input data transfer with LSMW, including maintaining object attributes, source structures and fields, field mapping, reading and converting data, and creating and running a batch input session. An example of using LSMW to update customer master records from an external file is also provided.



![LSMW
51
Recording, and
the transaction code as XD02(FS00 in case of gl accounts)
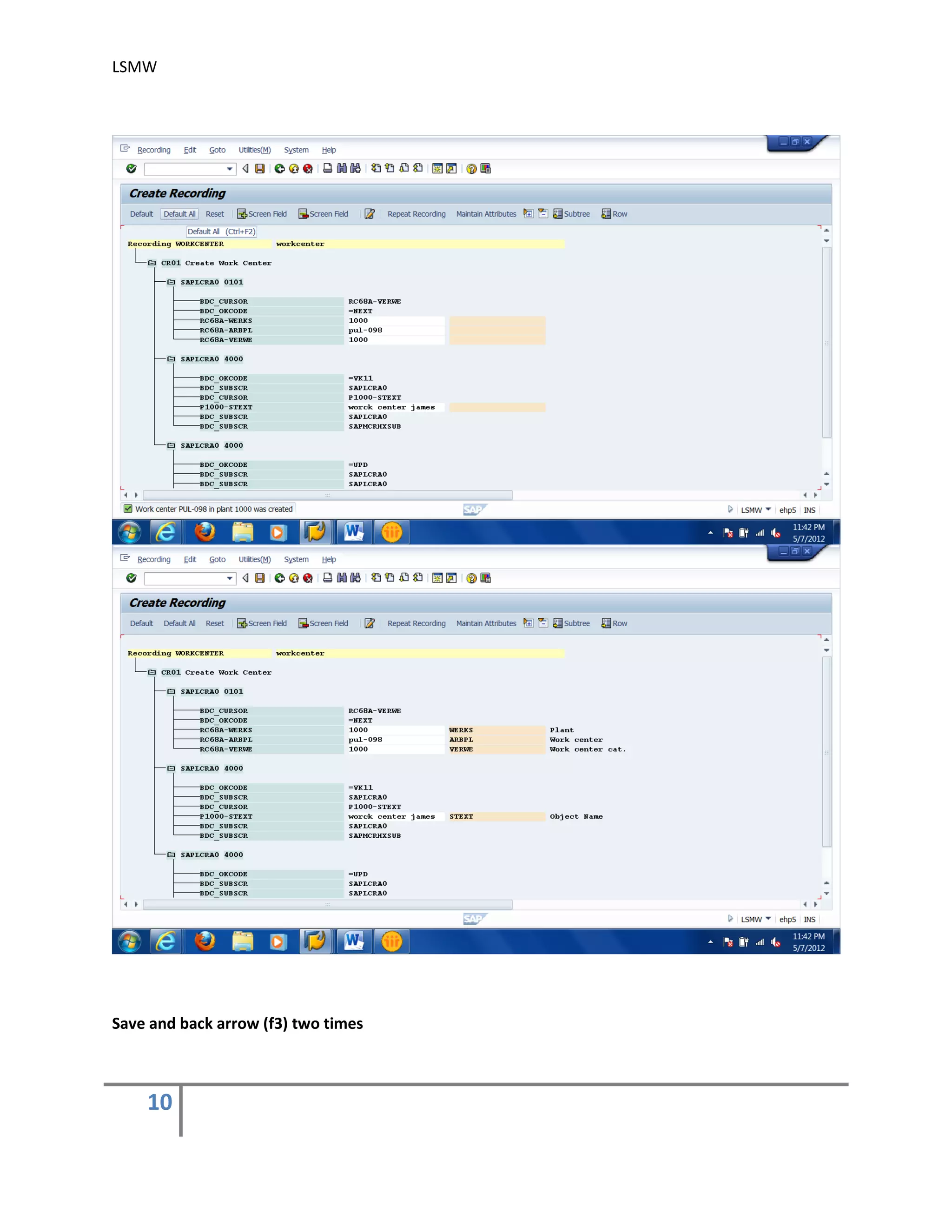
Once the transaction is completed, R/3 records the flow of screens and fields and saves the
information,
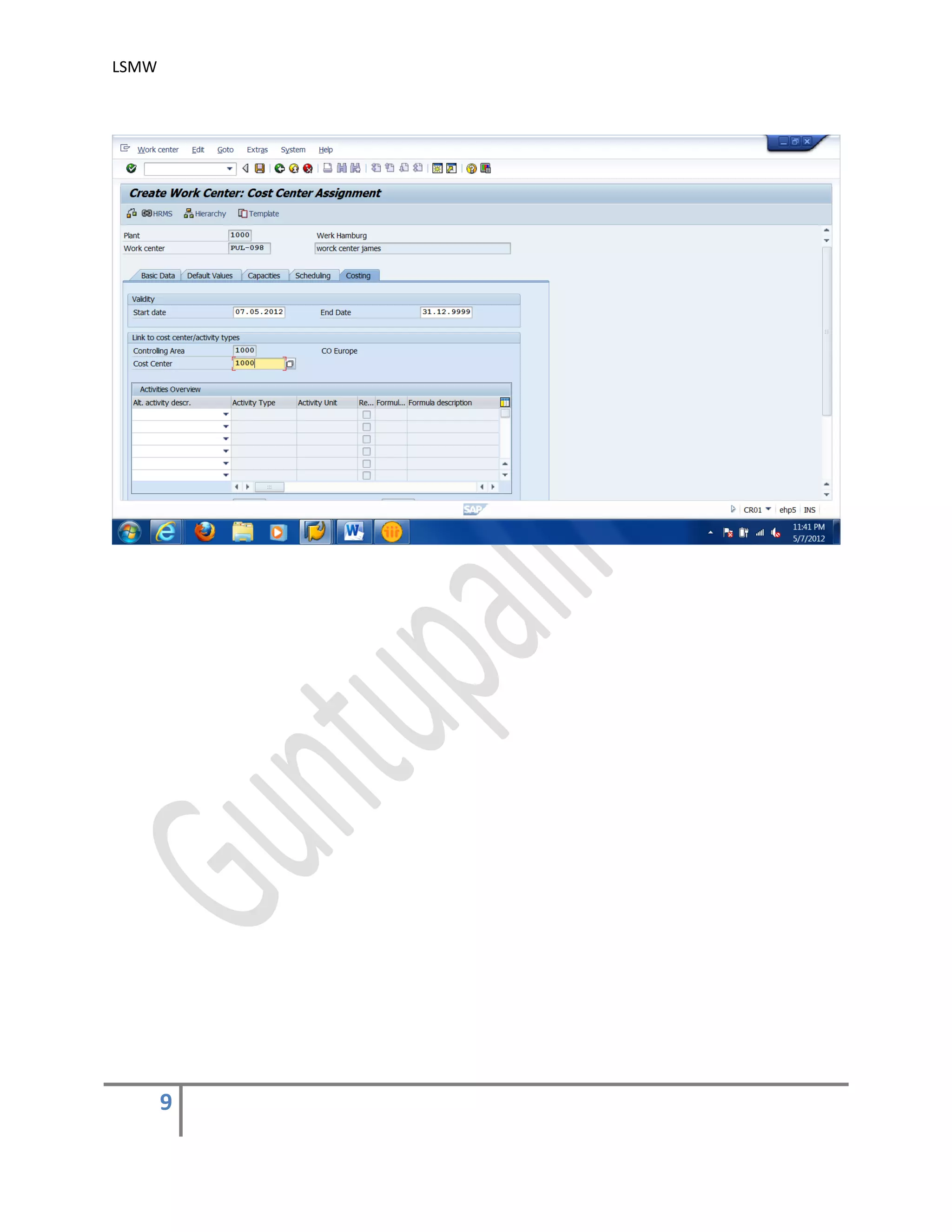
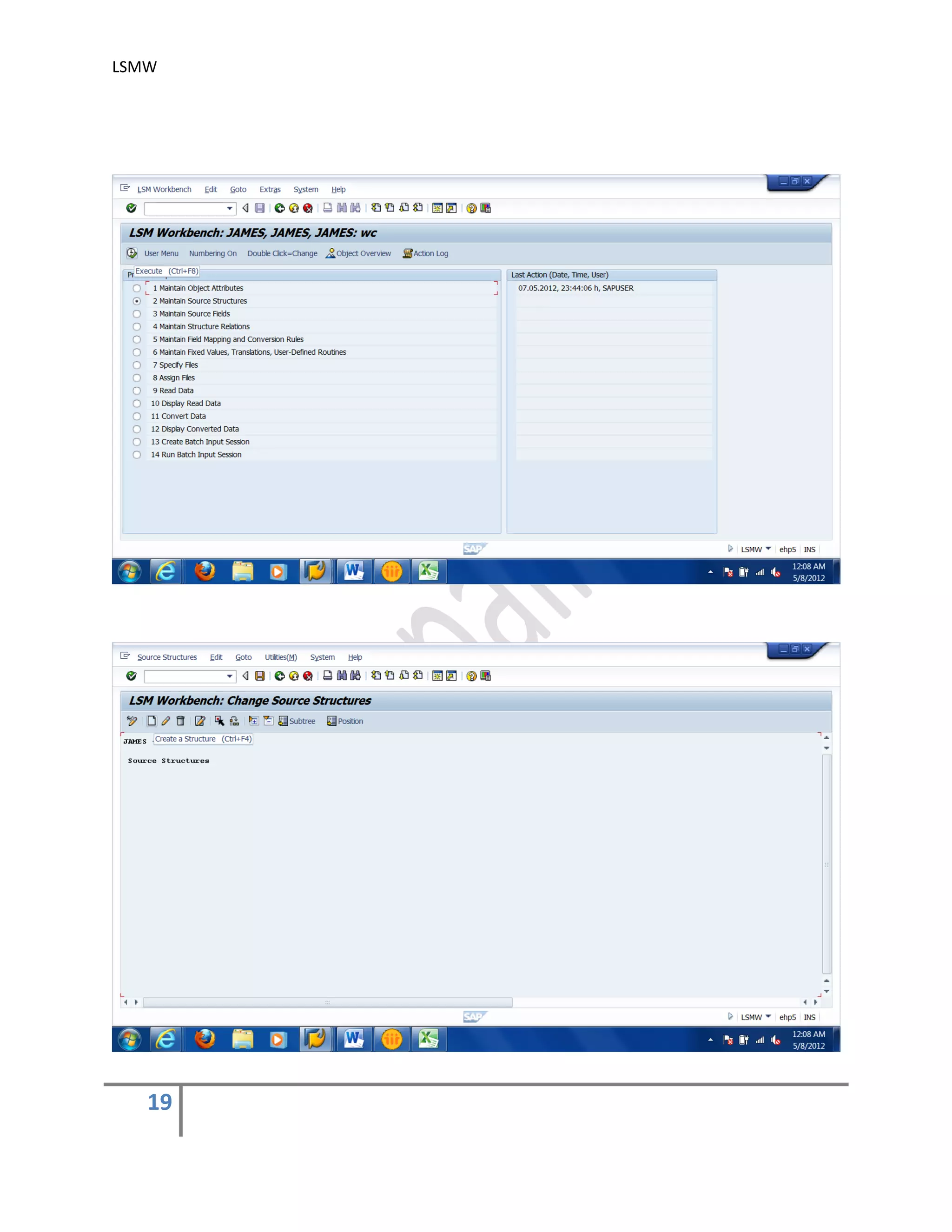
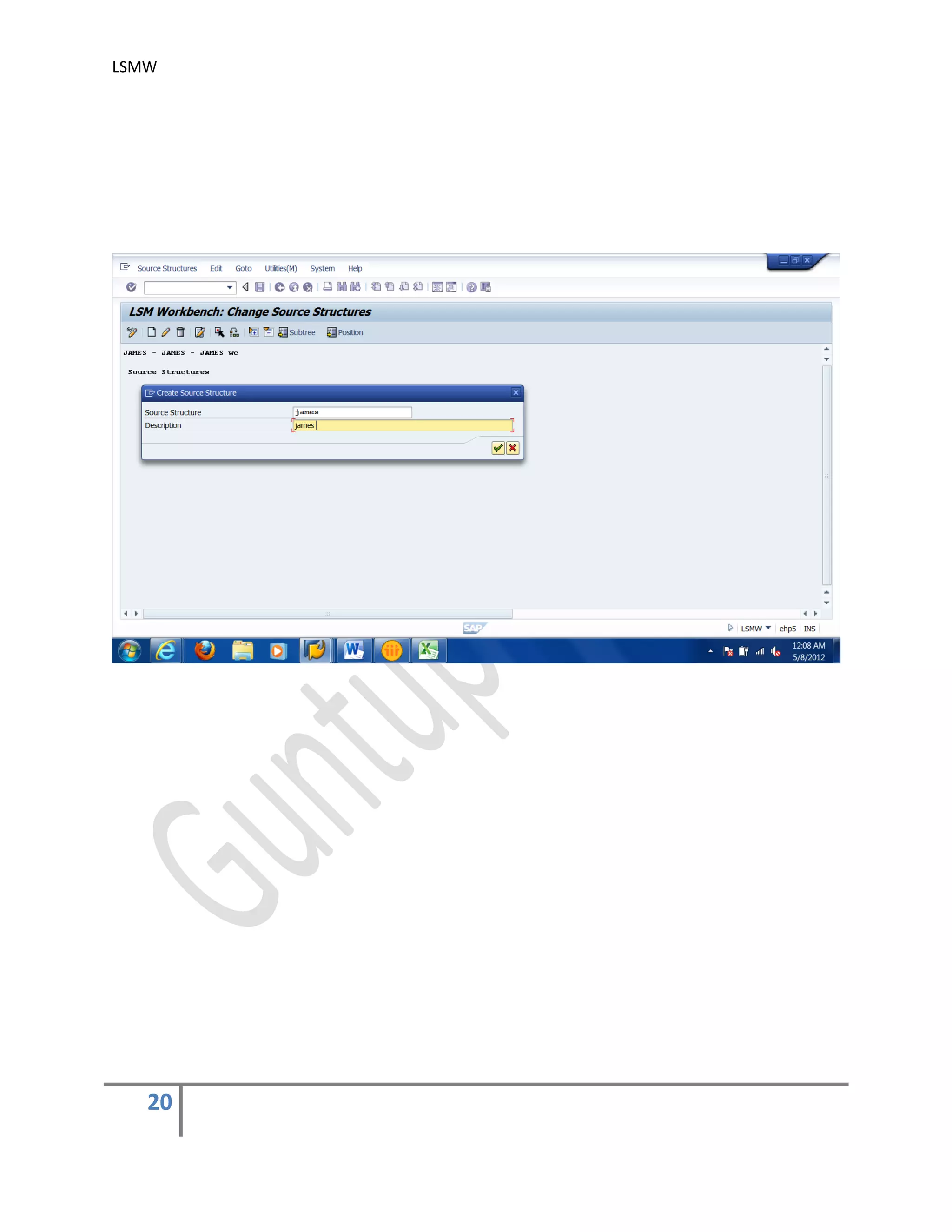
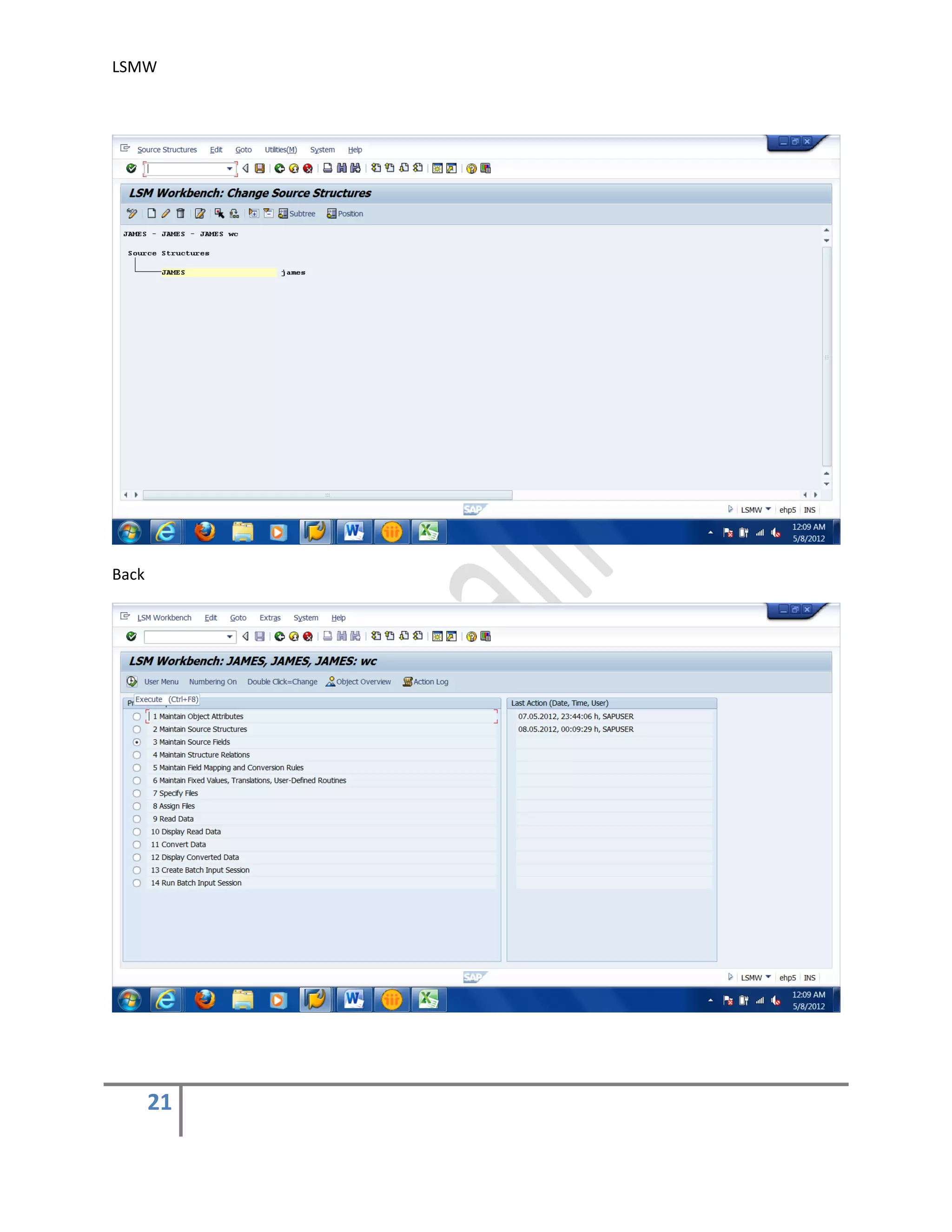
2) Maintain Source Structures.
Give a name and a description to the source structure
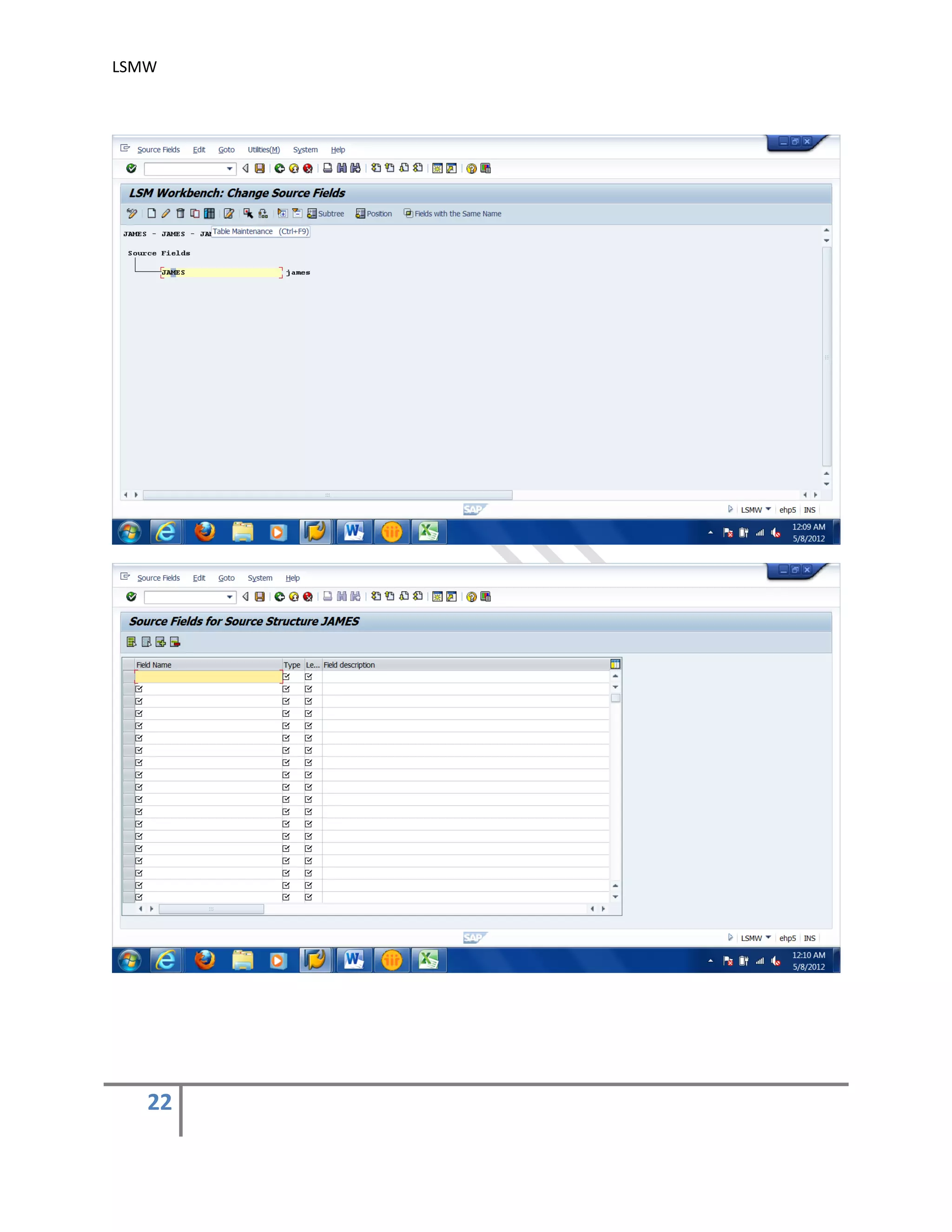
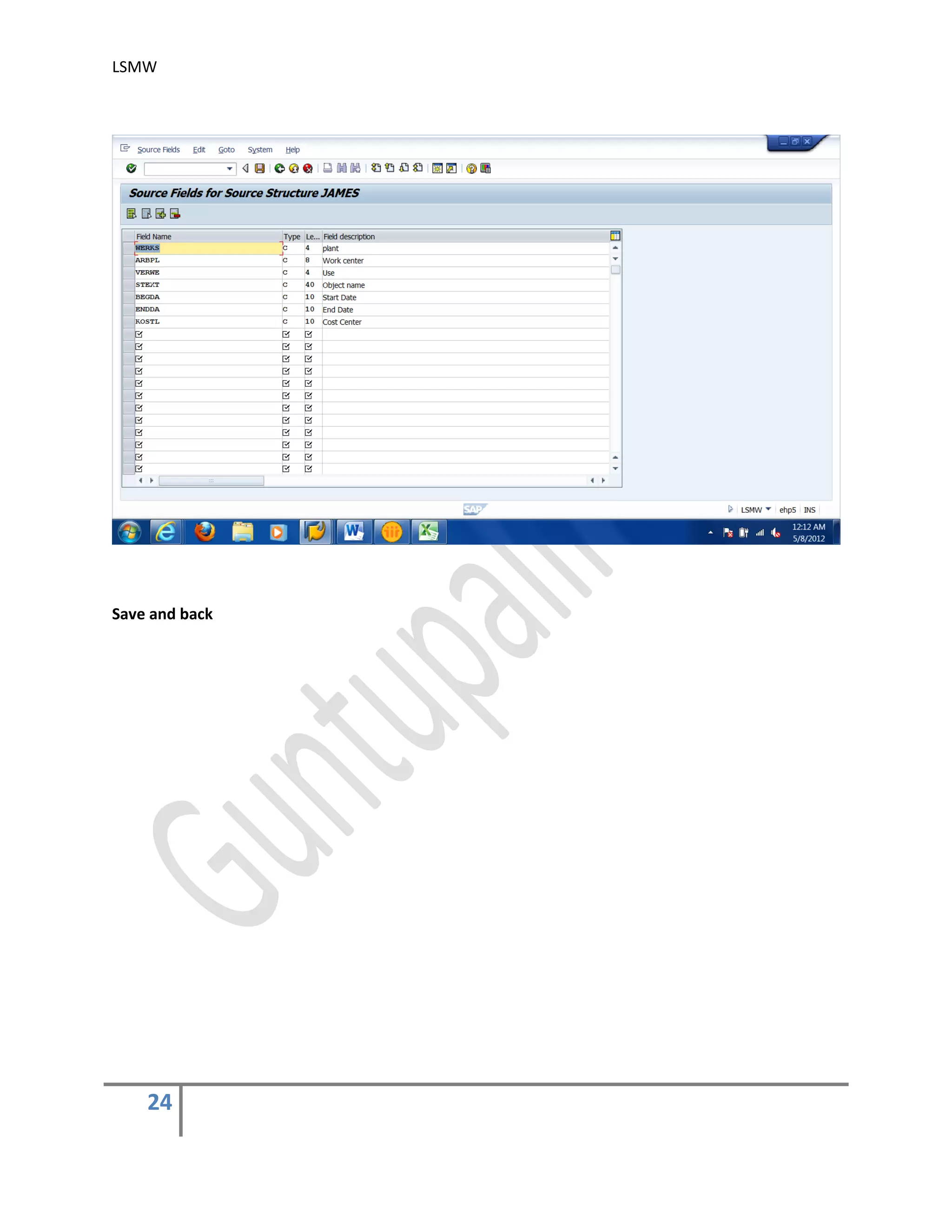
3) Maintain Source Fields.
In this step, you need to list what fields are present in the source structure. The easiest
way is to click on ‘Table Maintenance’ icon to enter Fieldname, Type and Length for
each field
Note that your input file will have four fields as key fields and you need to update three
fields in the system
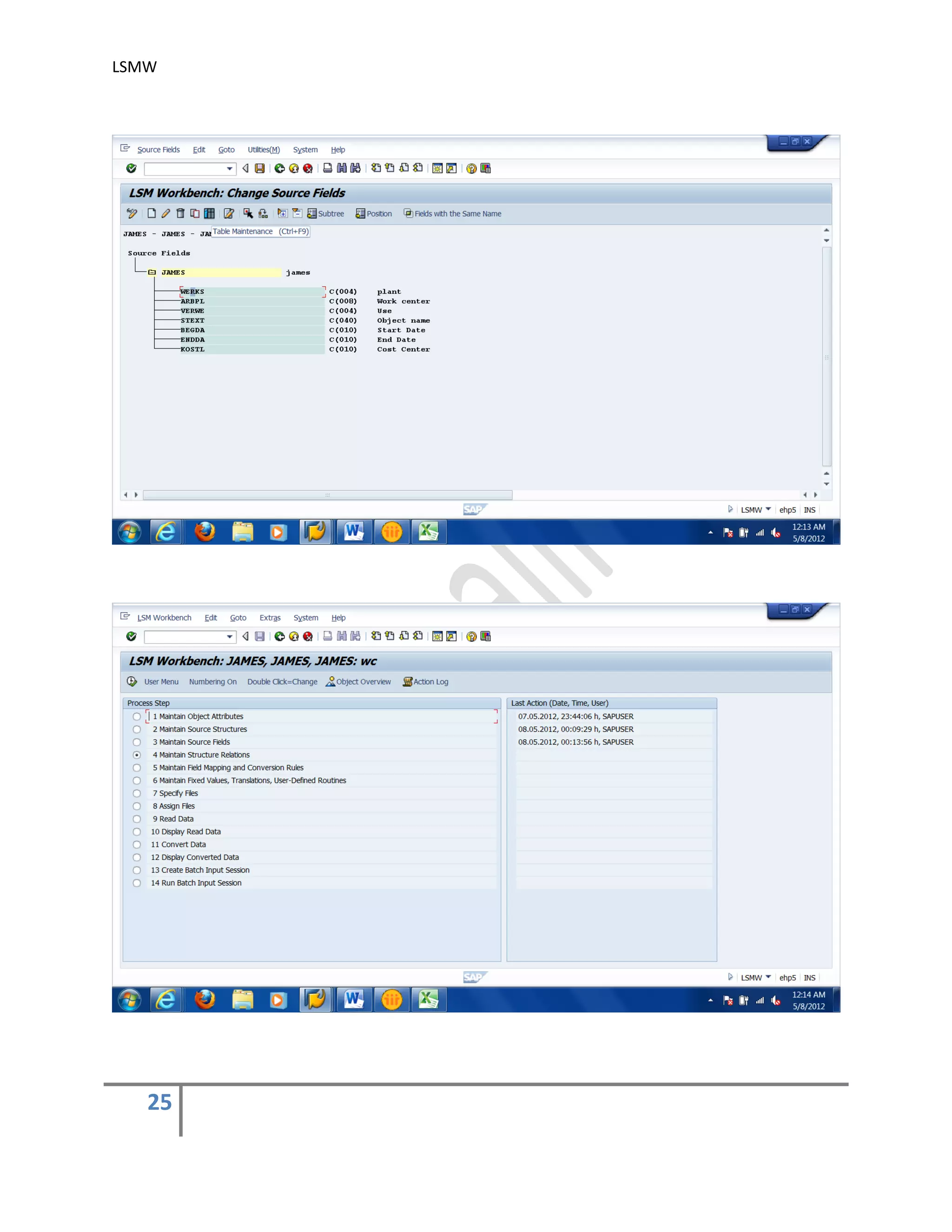
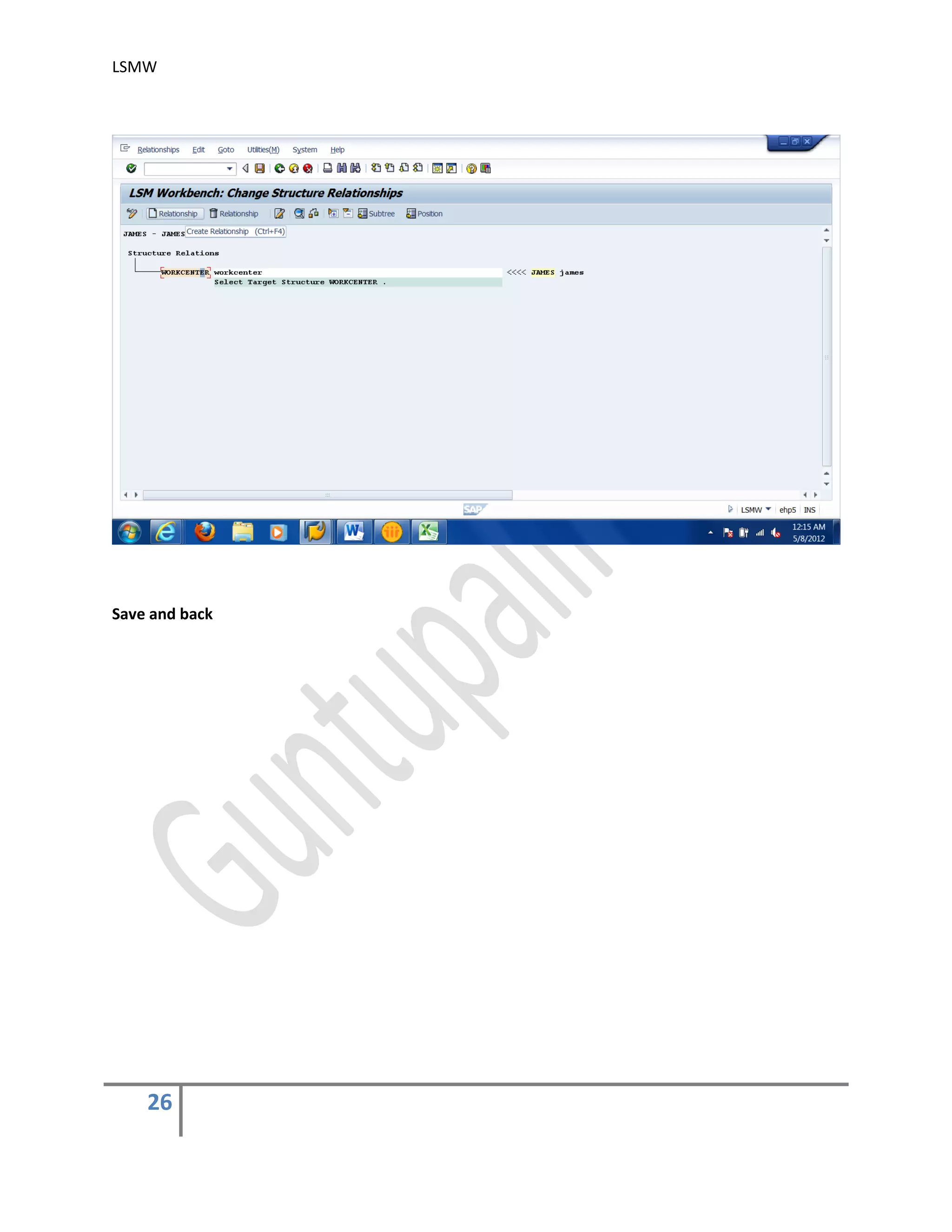
4) Maintain Structure Relations
Execute a step to ‘Maintain Structure Relations’. Since, there is only one Source and
Target Structure, the relationship is defaulted automatically
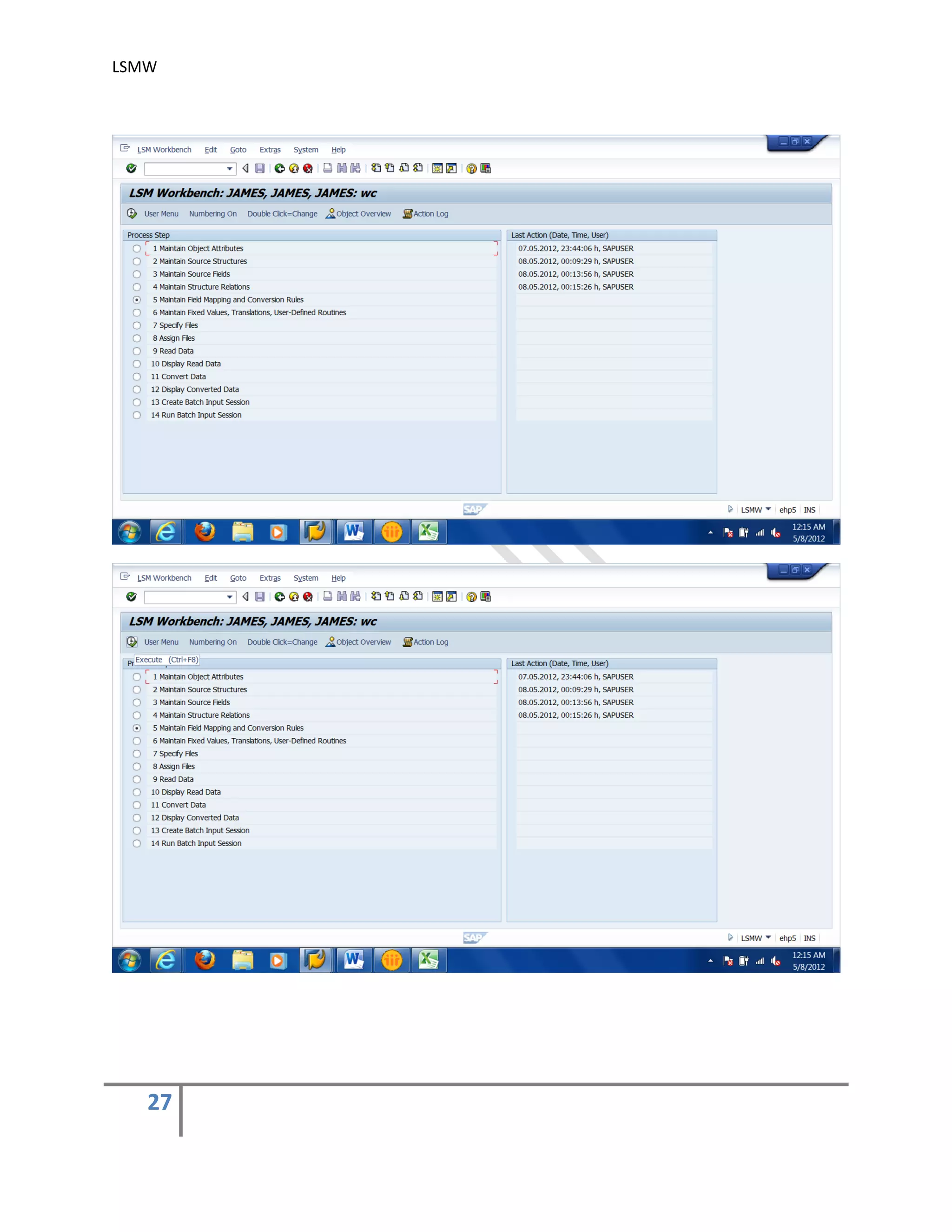
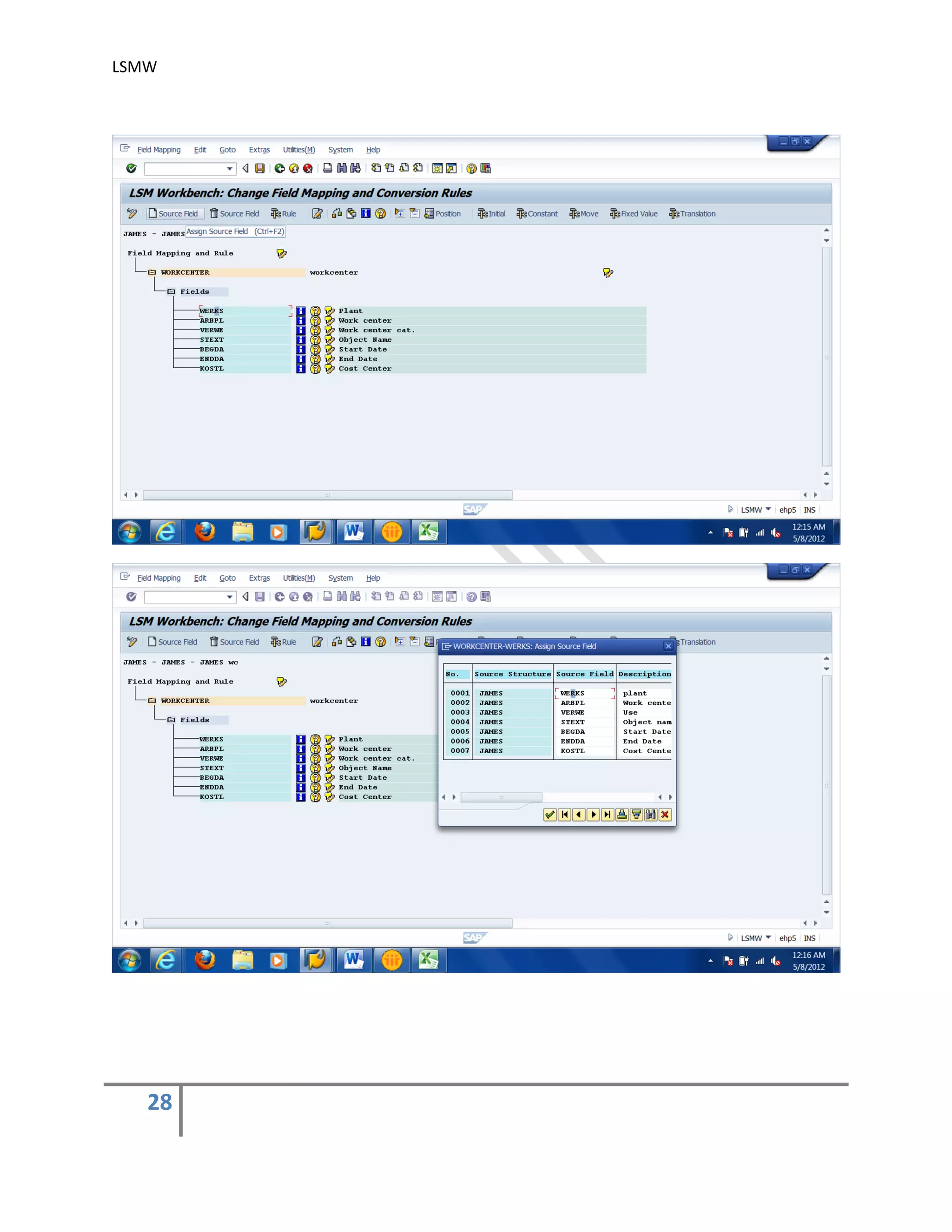
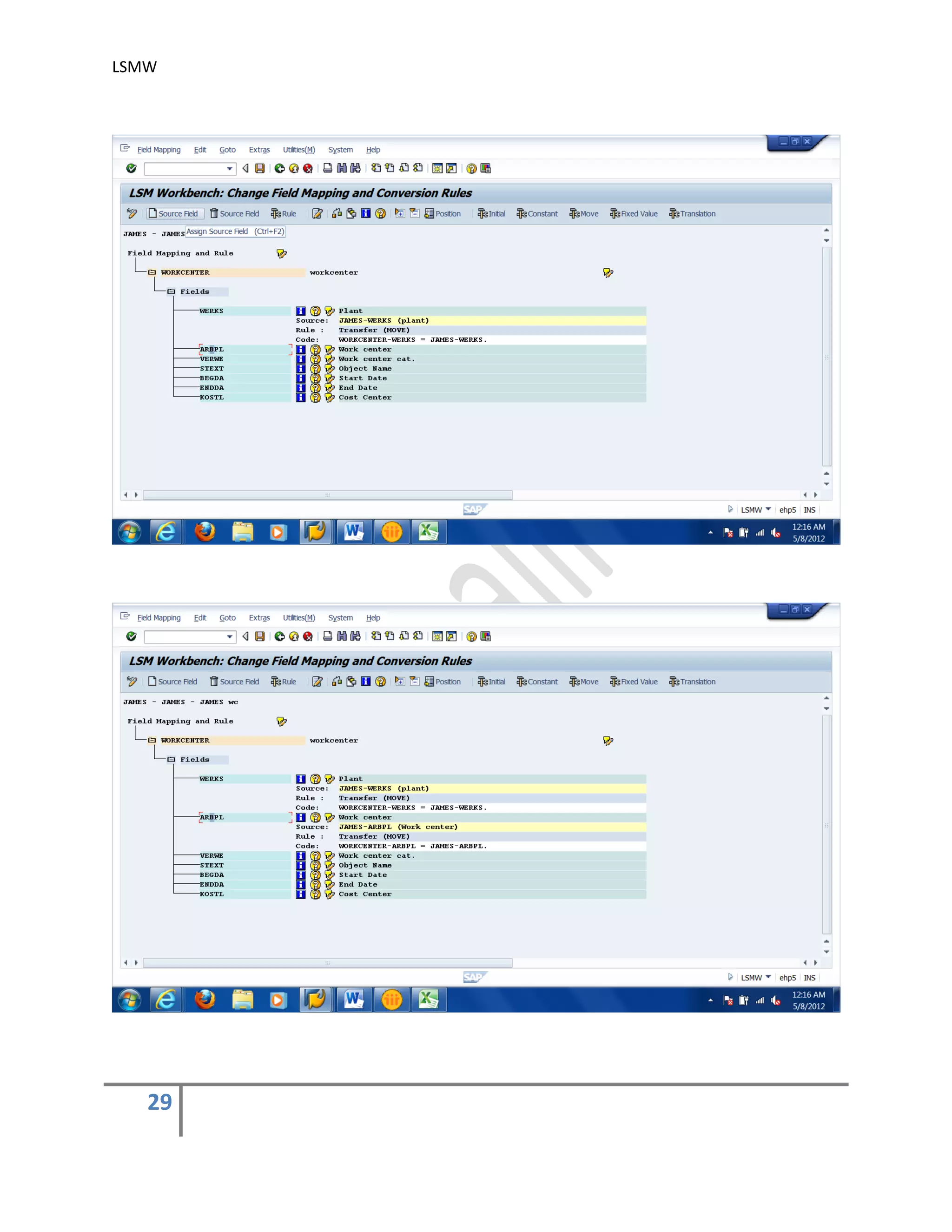
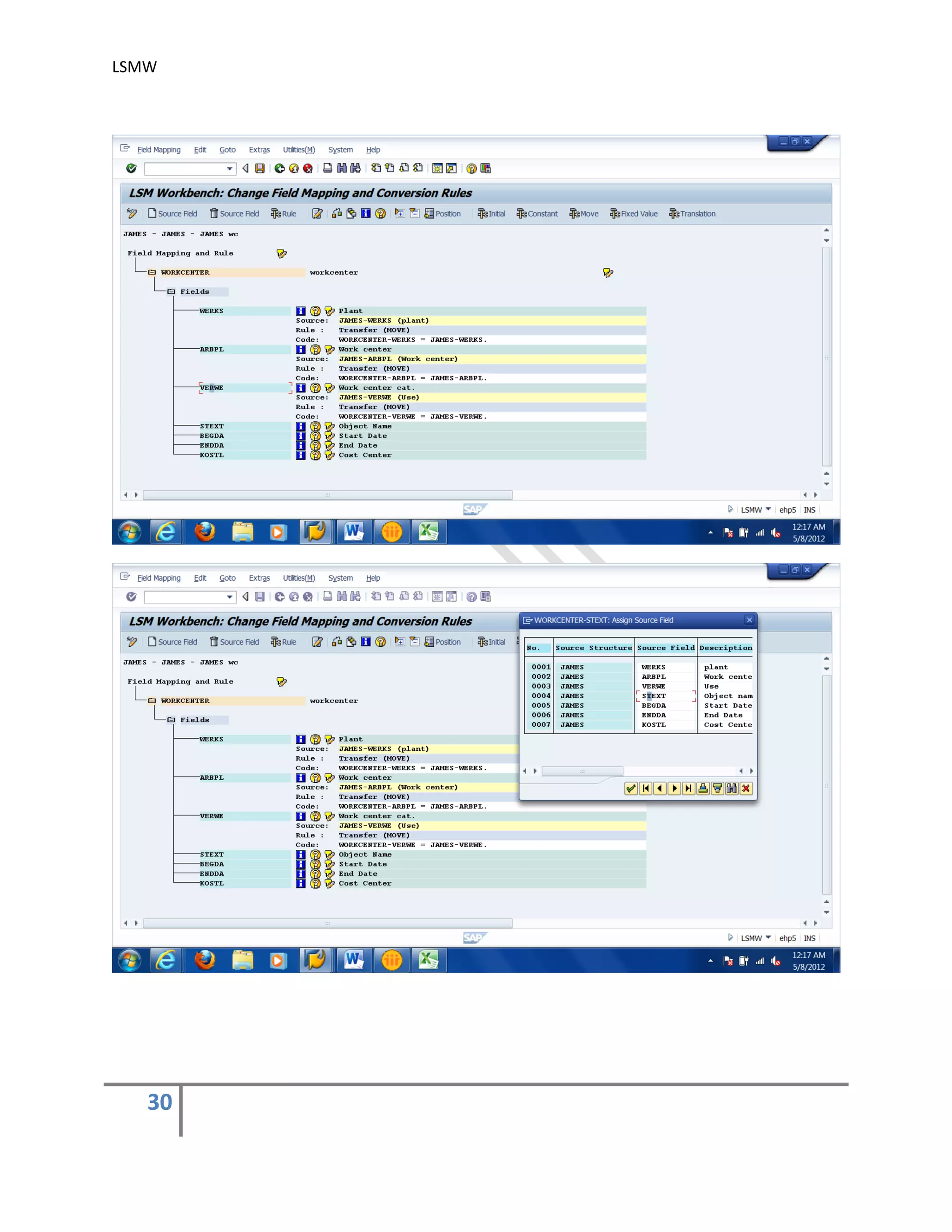
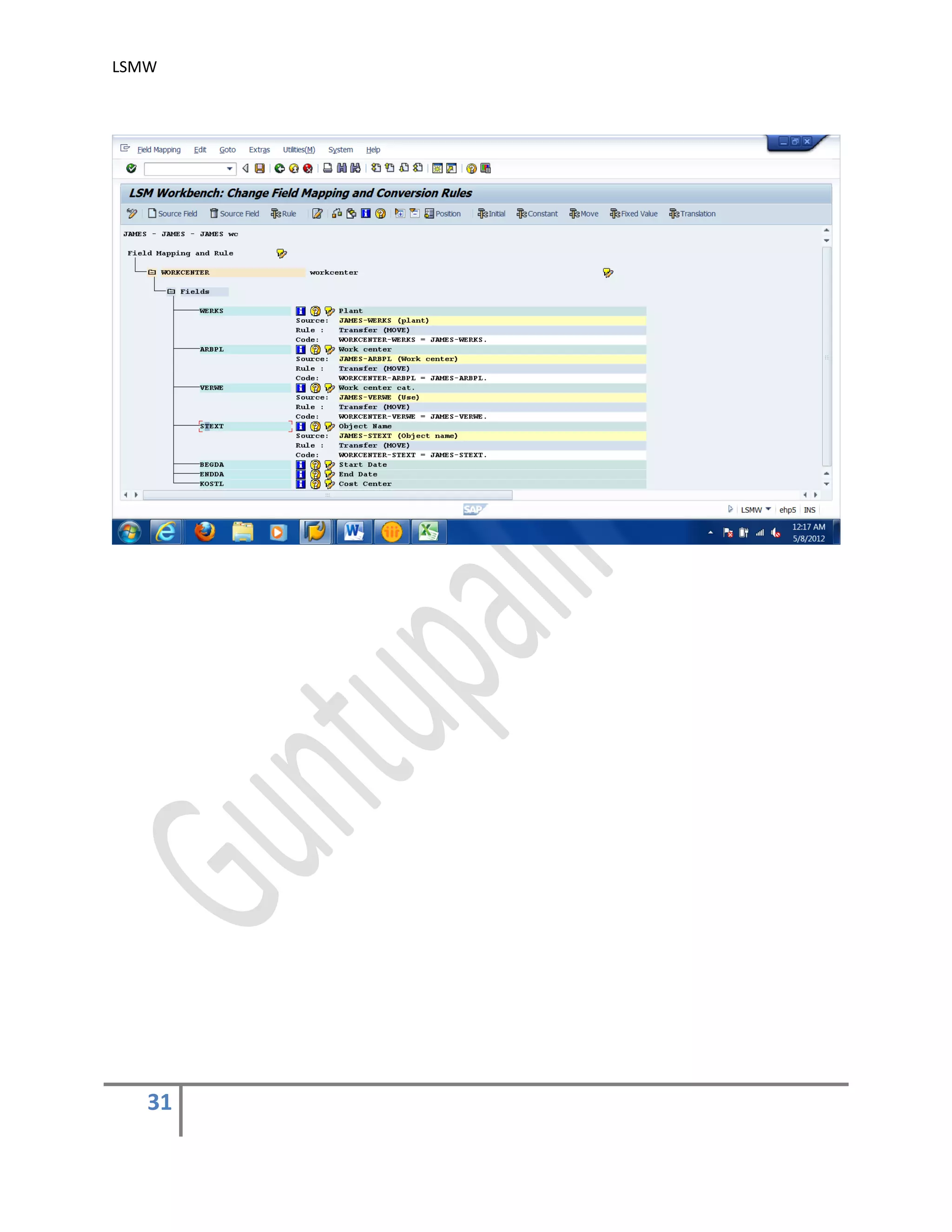
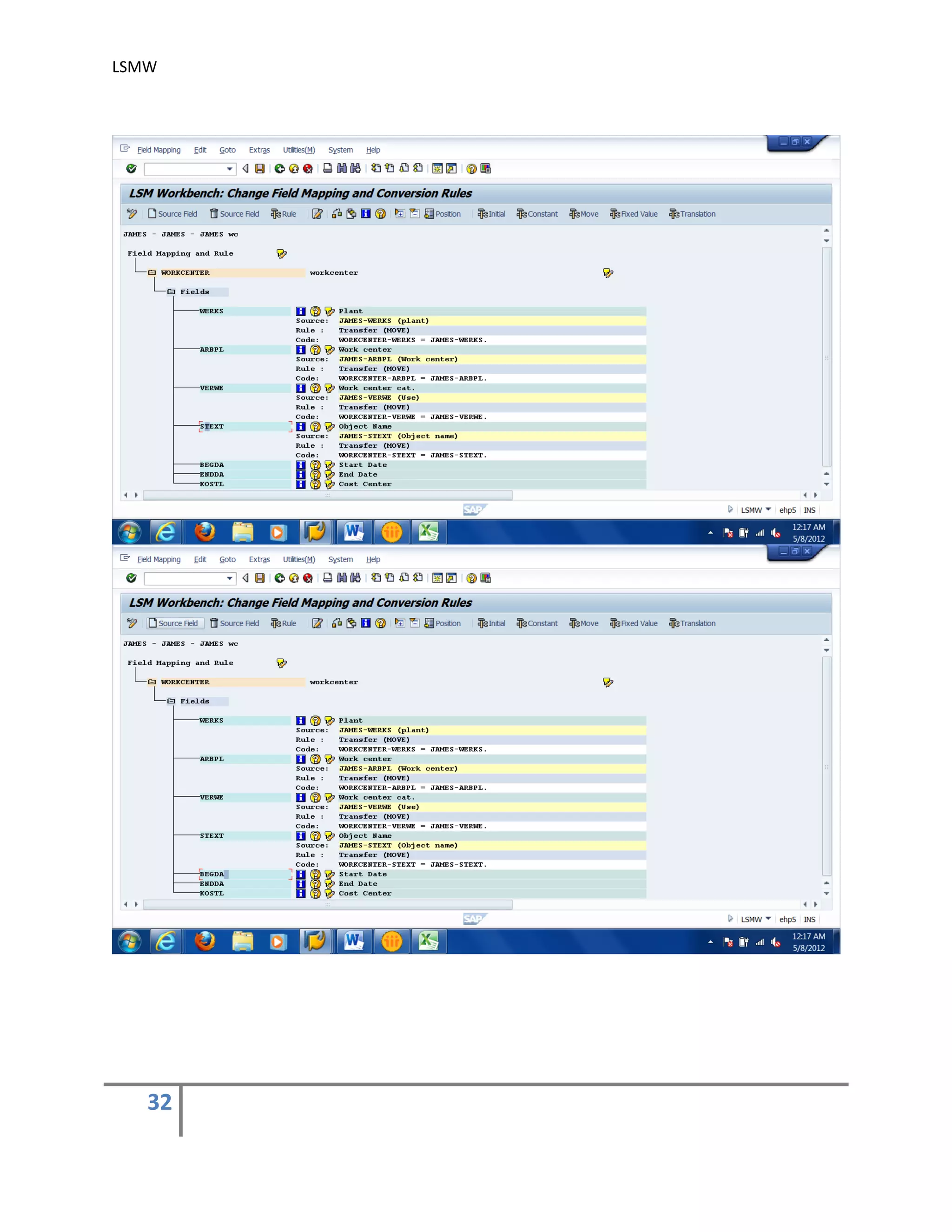
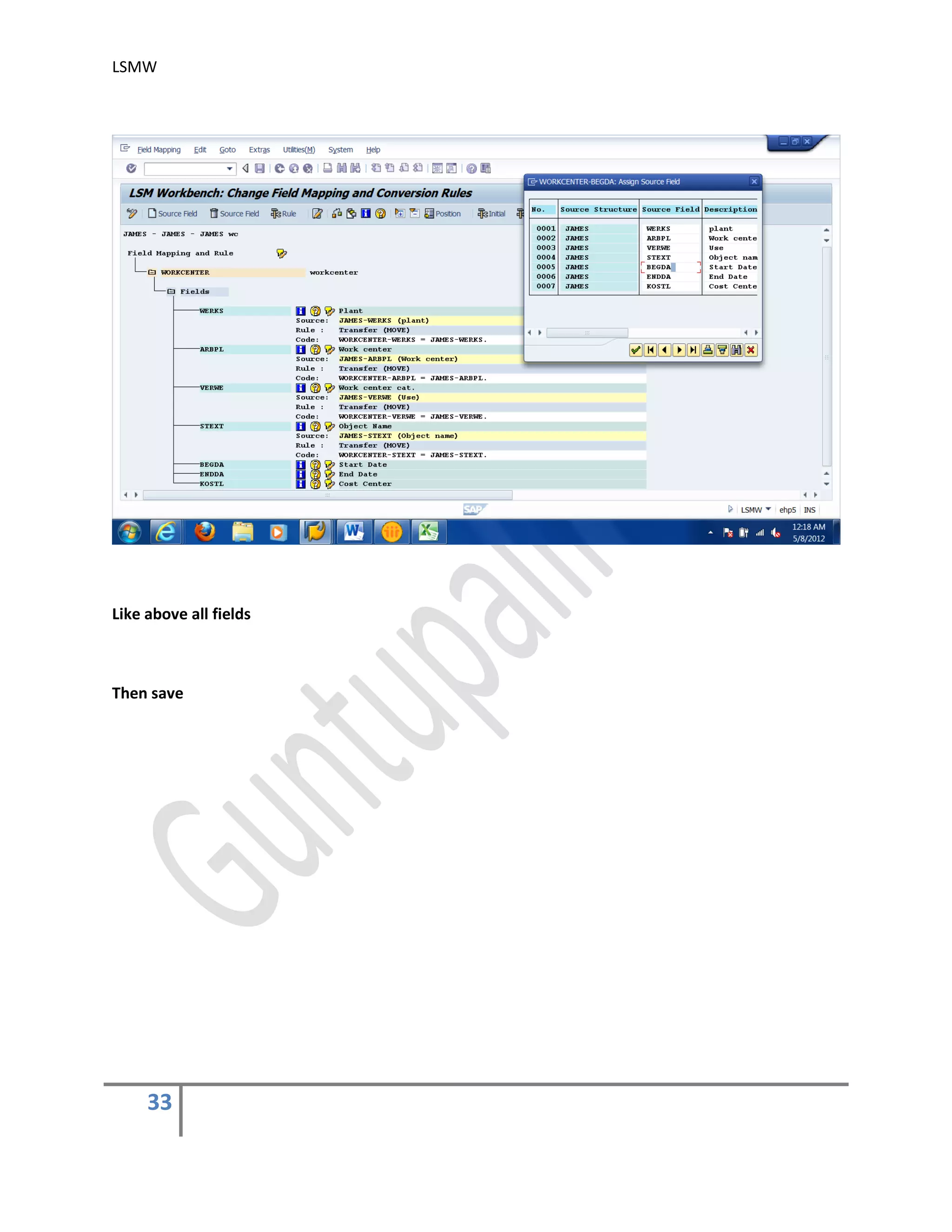
5) Maintain Field Mapping and conversion rules .
In this step, source/legacy fields in each structure are assigned to R/3 fields. It may be
done individually for each R/3 field, which being time-consuming for complex structures or
we can use automatic mapping utility (Extras > Auto-Field mapping).
We can specify the conversion rule to be used to convert an LS field into the corresponding
R/3 field. For this, use predefined conversion rules or create your own conversion rules in
the editor.
You may use the buttons ‘Initial’, ‘Constant’, ‘Move’ & ‘Fixed Value’ to assign different
values. You may also assign different rules by using the button ‘Rule’. automatic mapping
utility (Extras > Auto-Field mapping).
6) Maintain Fixed Values, translations ,user defined routines.
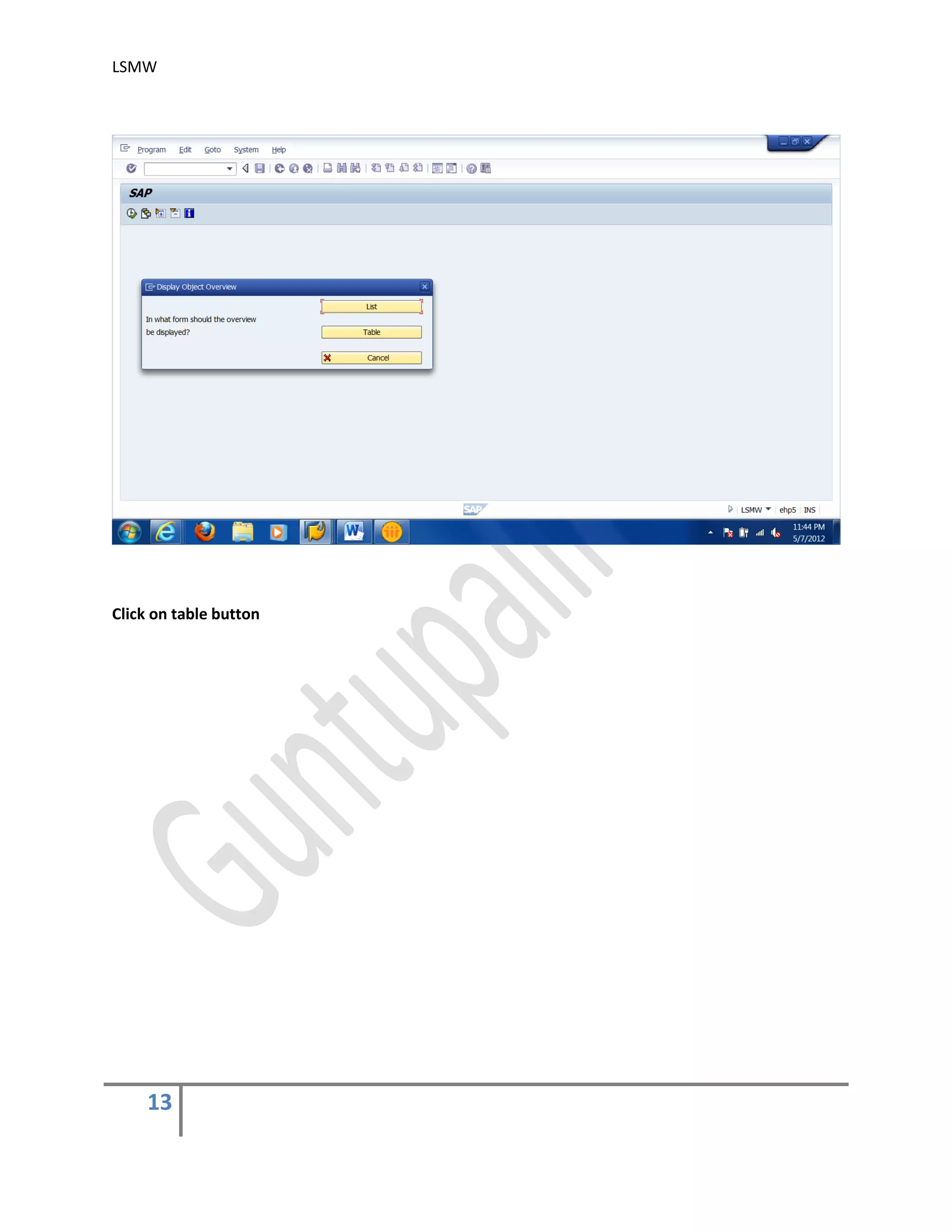
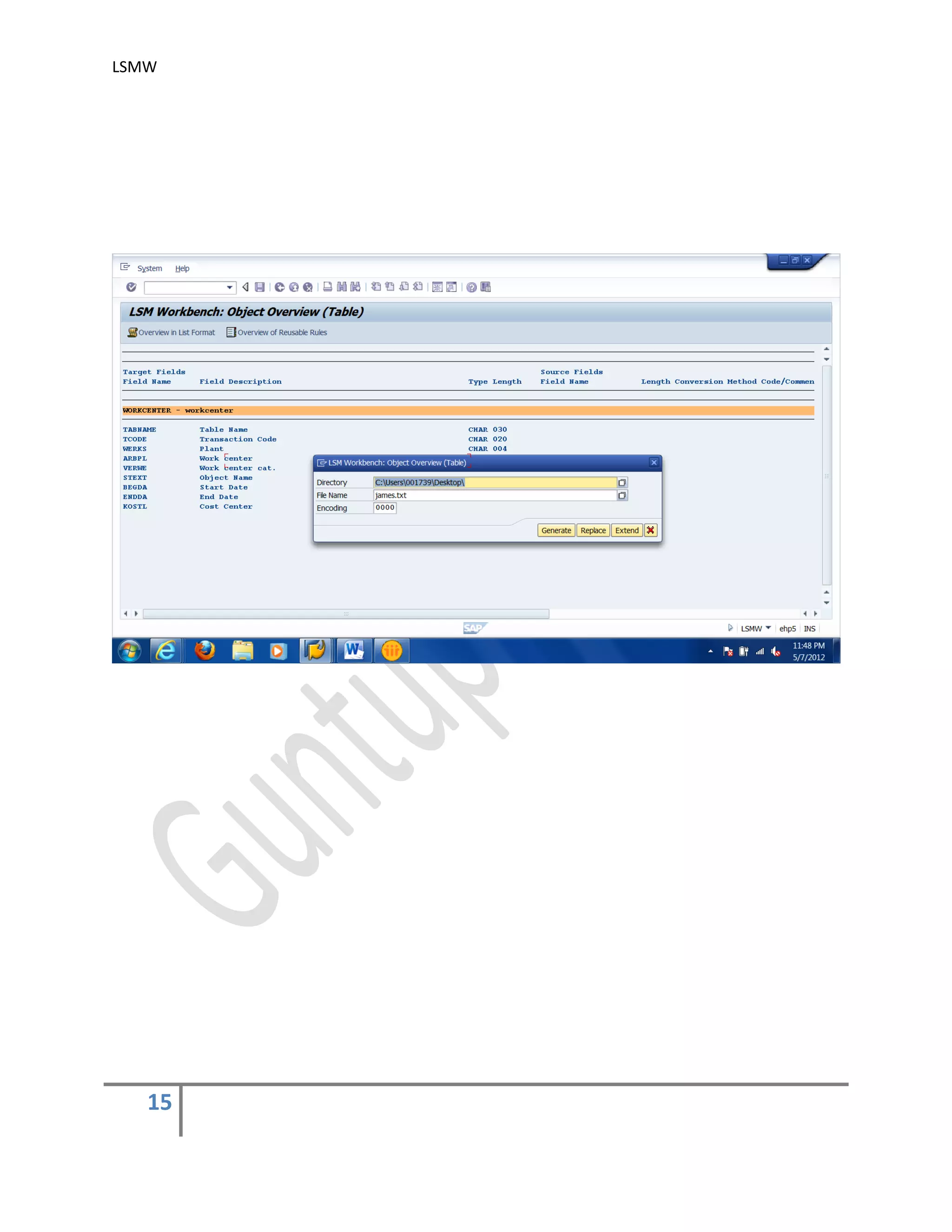
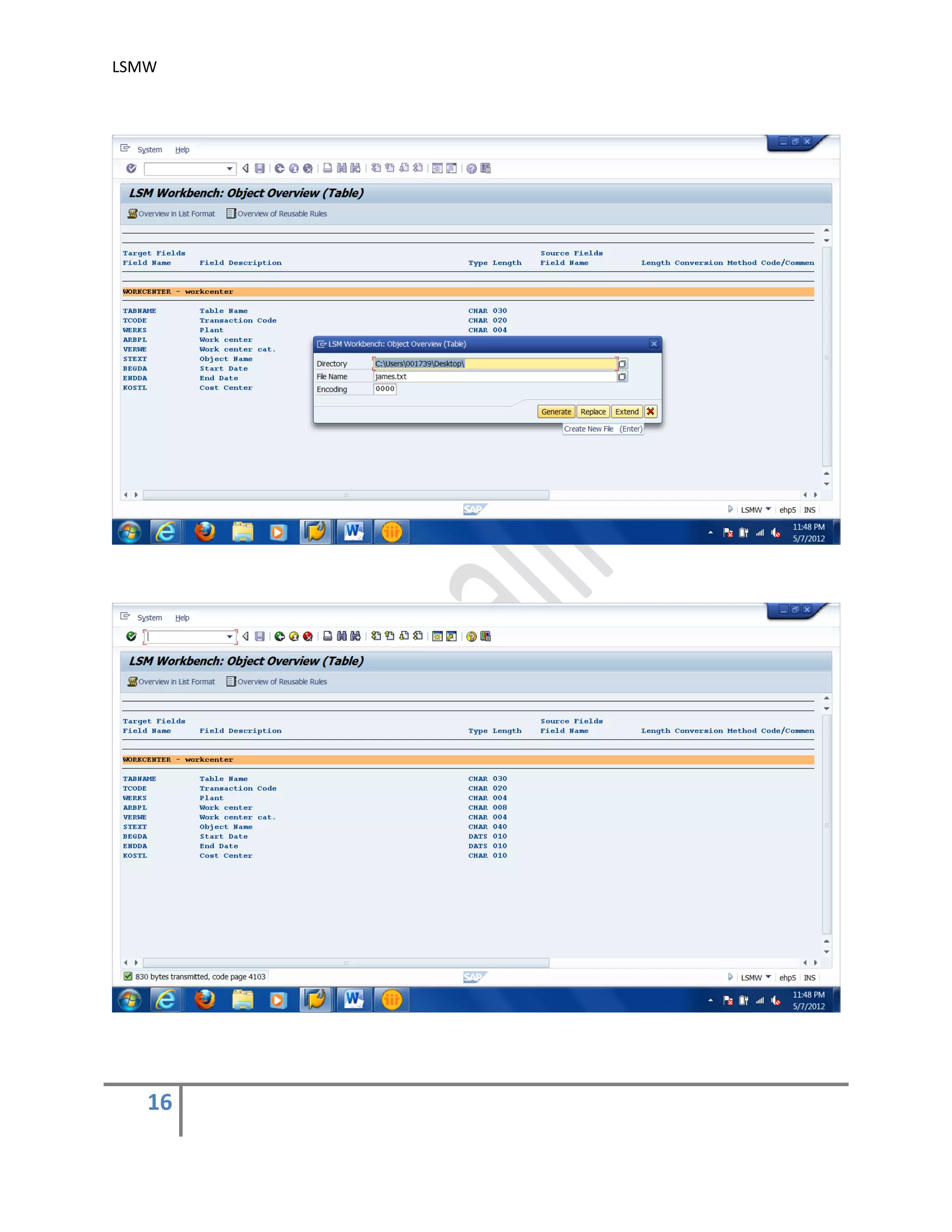
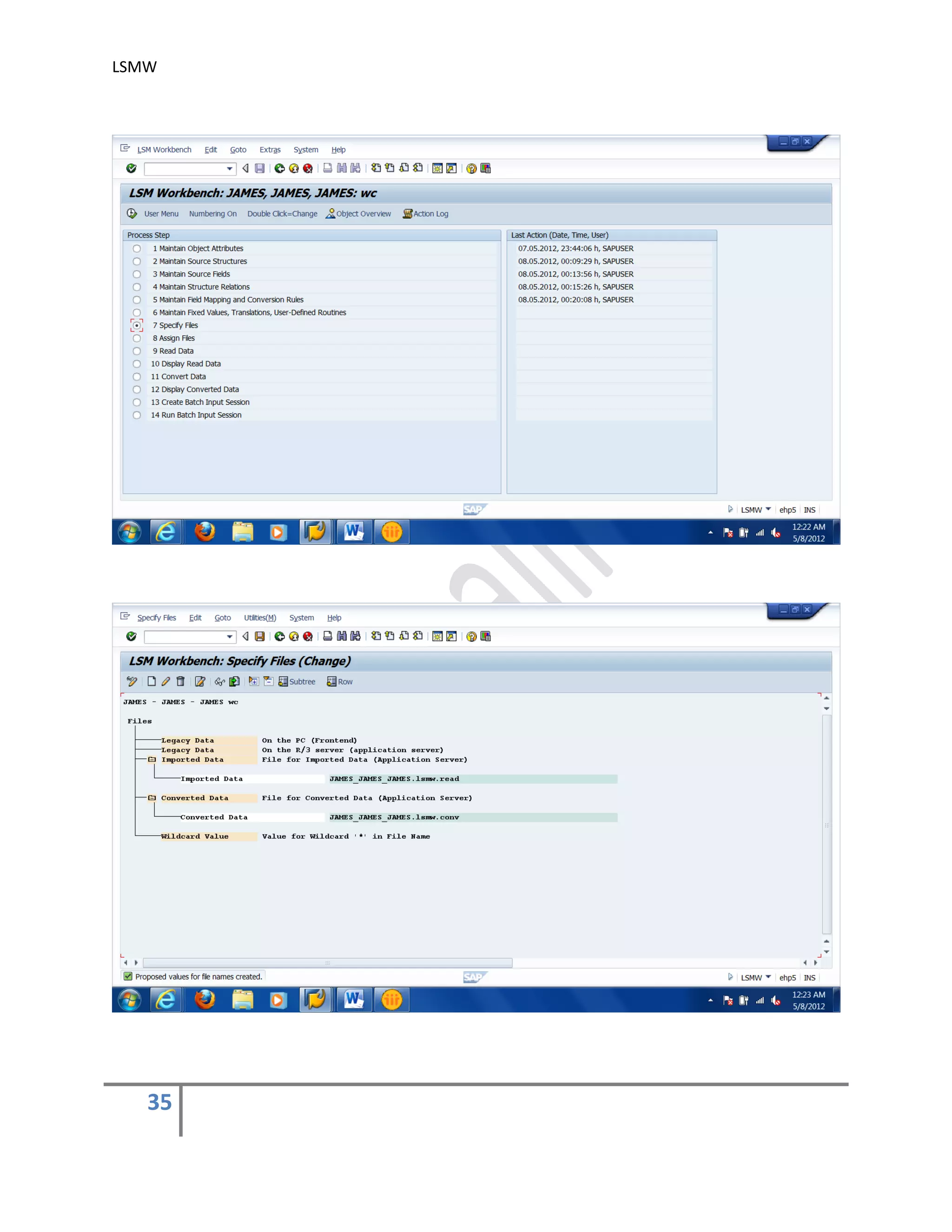
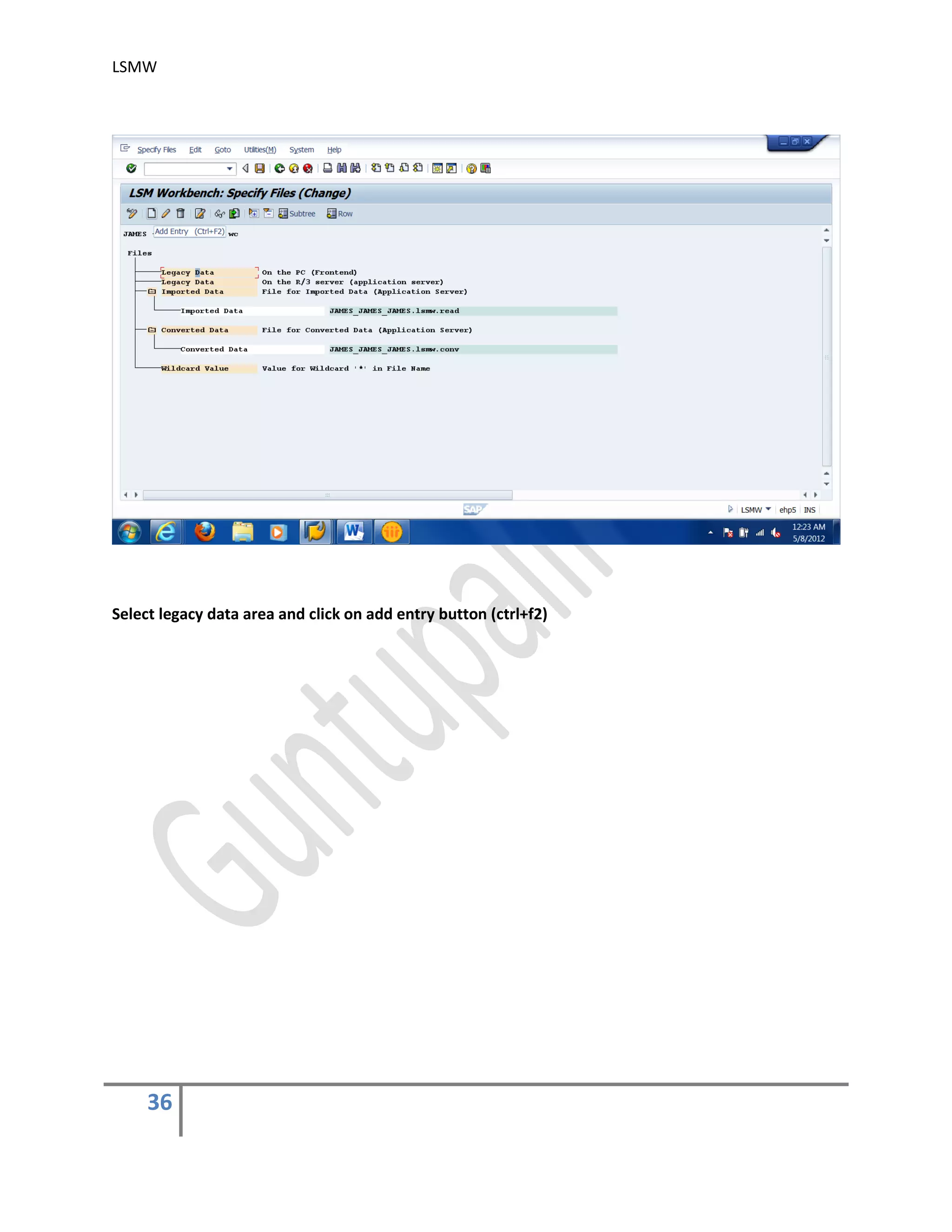
7) Specify Files .
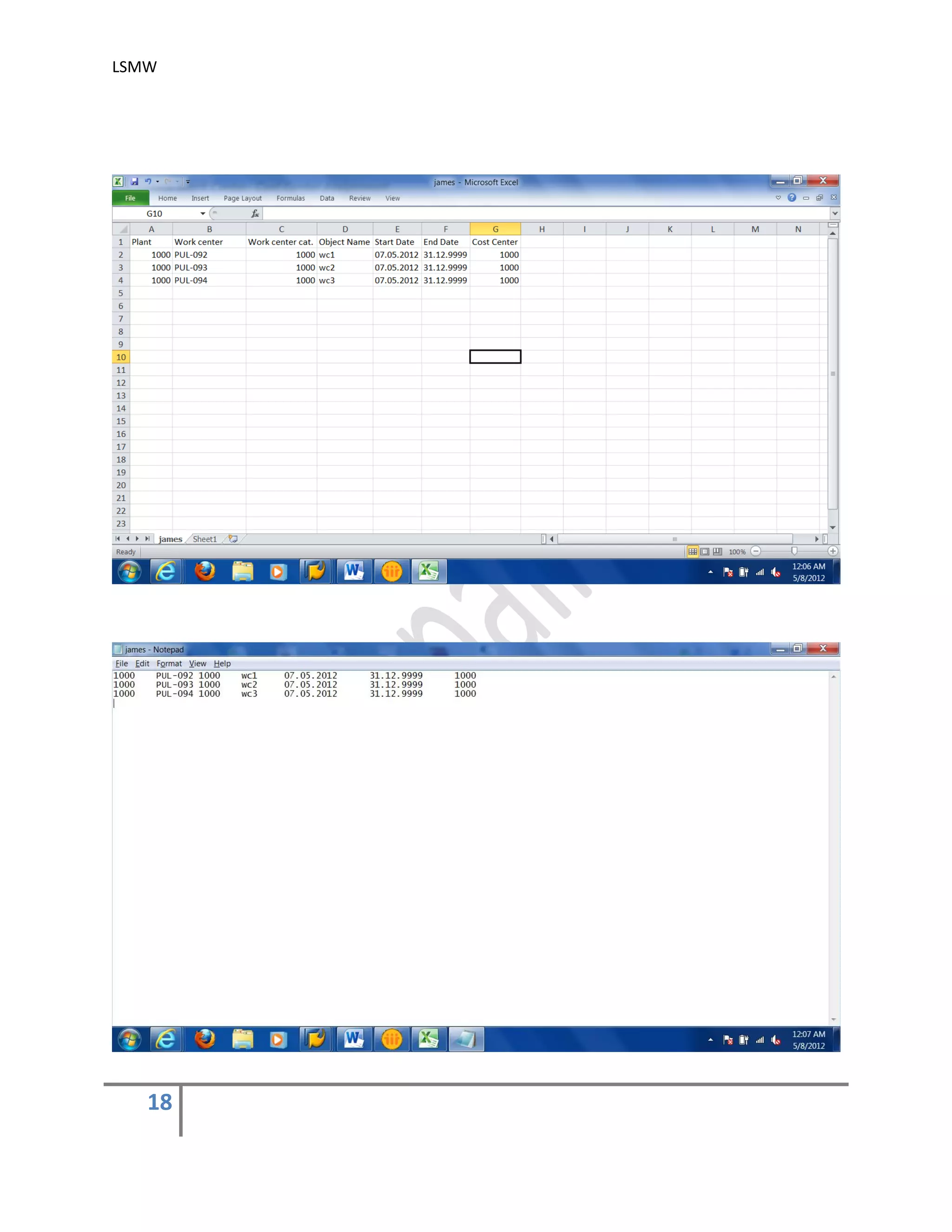
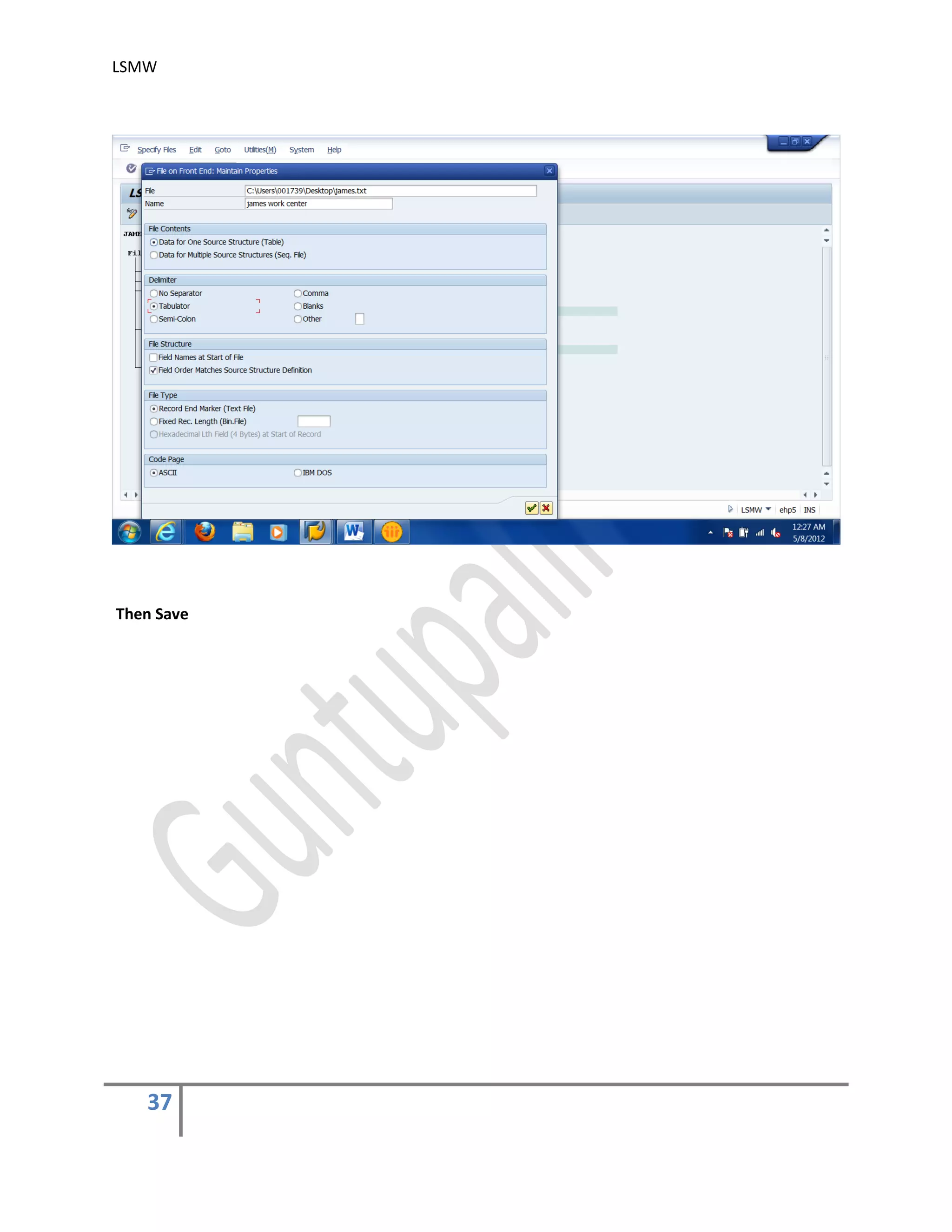
In this step, we define how the layout of the input file is. The input file is a [Tab] delimited
with the first row as field names. It is present on my PC (local drive)
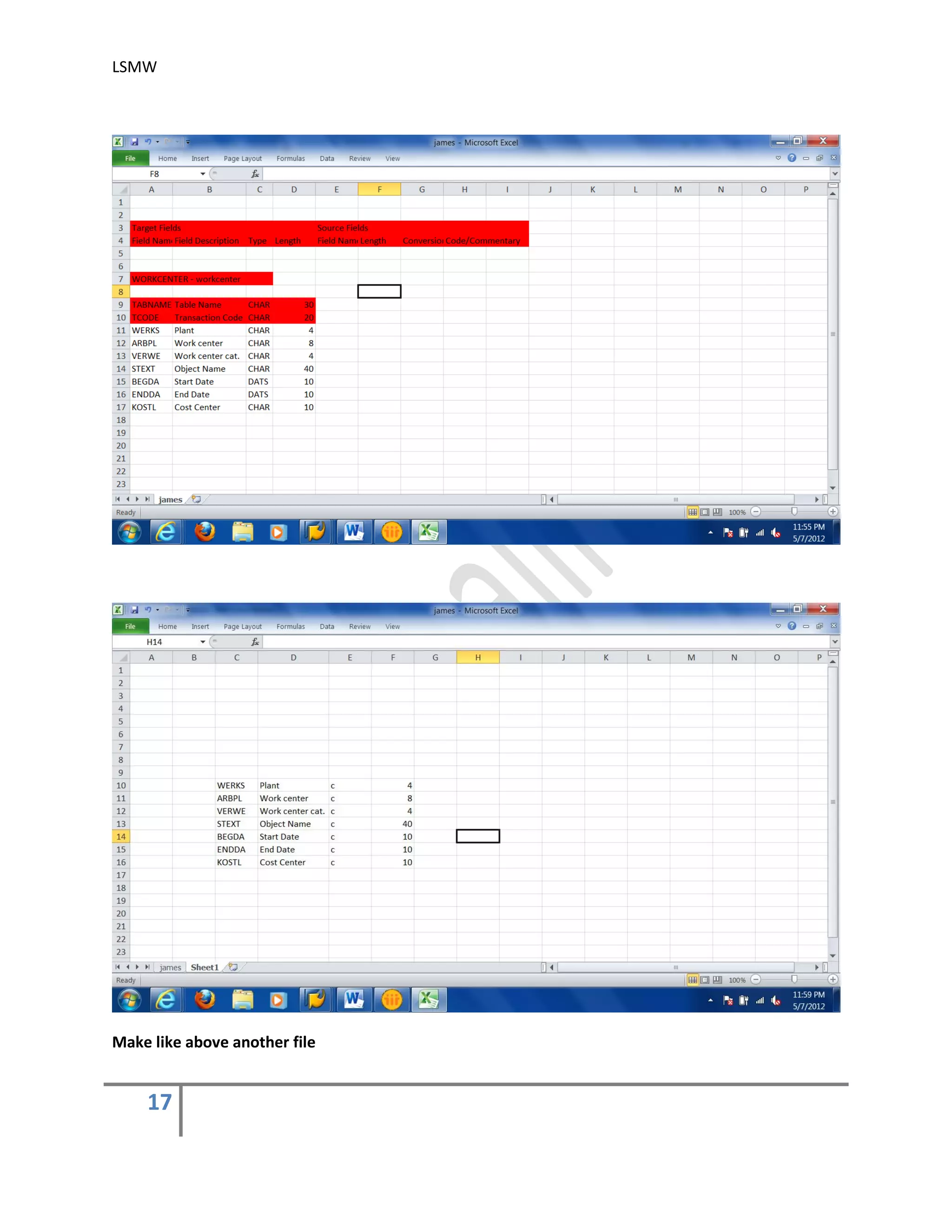
Create an Excel file with your data and save it as a Tab-delimited text file on your local
drive.
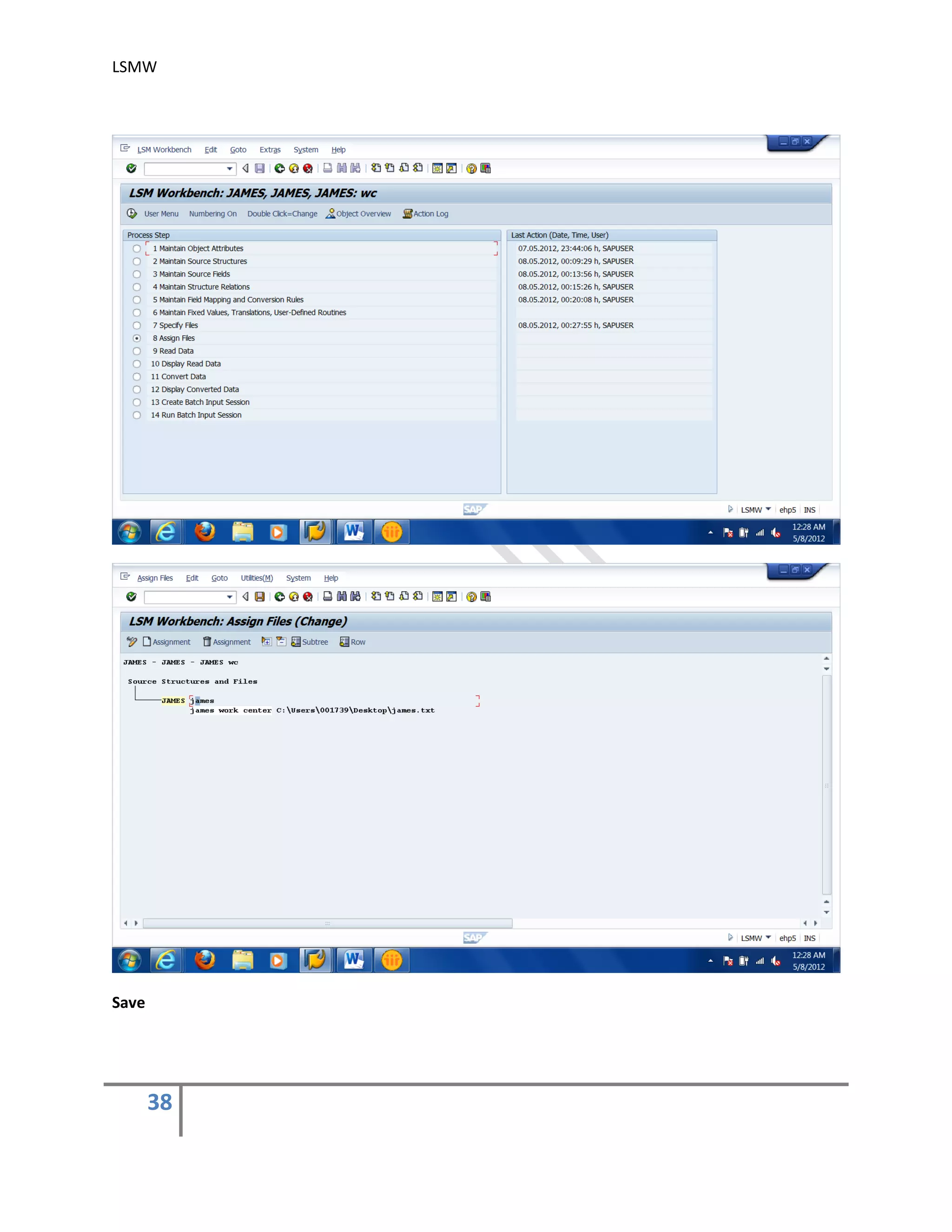
8) Assign Files .
Execute step ‘Assign Files’ and the system automatically defaults the filename to the
source structure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lsmwbyguntupalliharikrishna-151006162725-lva1-app6892/75/Lsmw-by-guntupalliharikrishna-51-2048.jpg)
