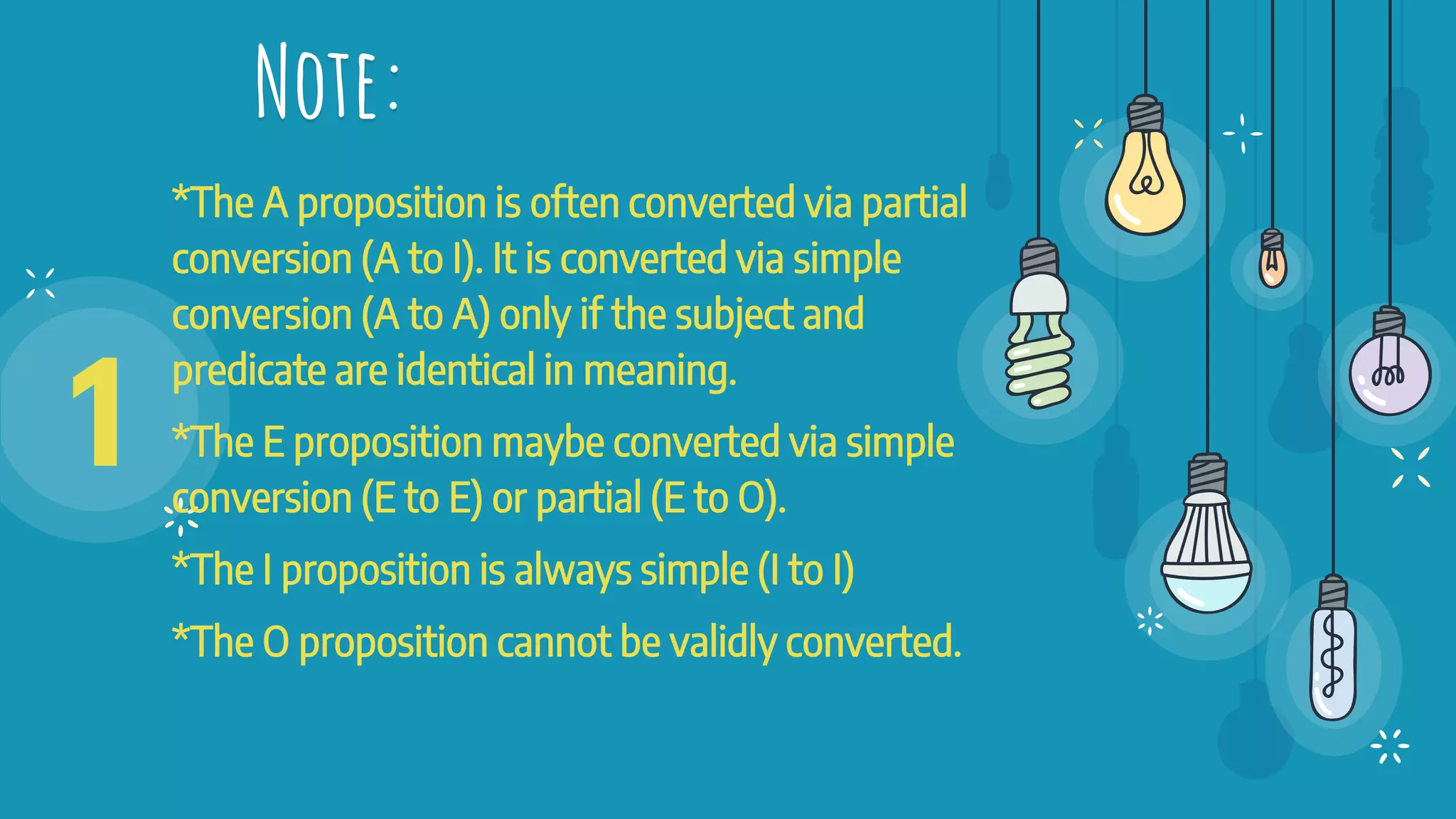
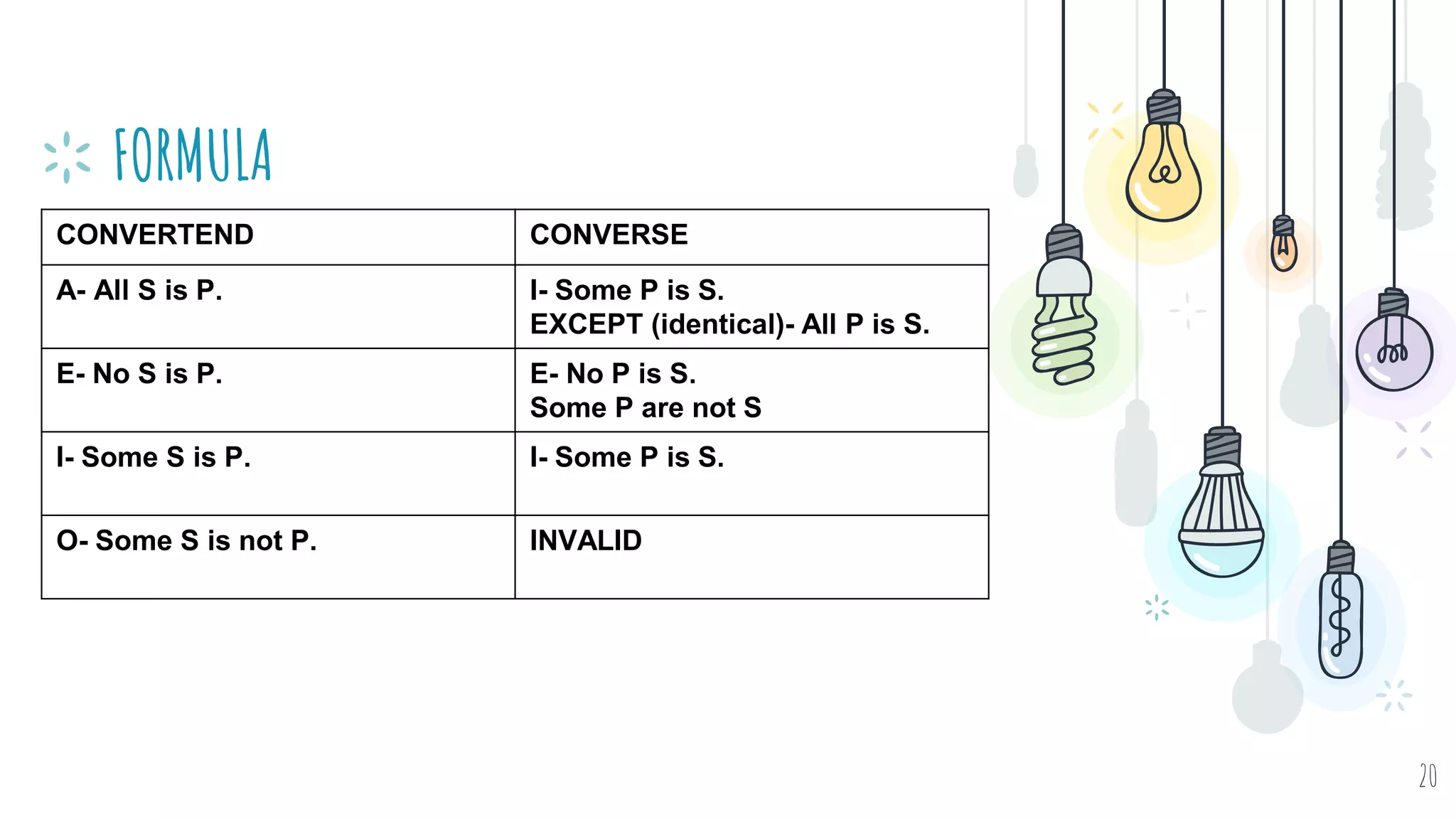
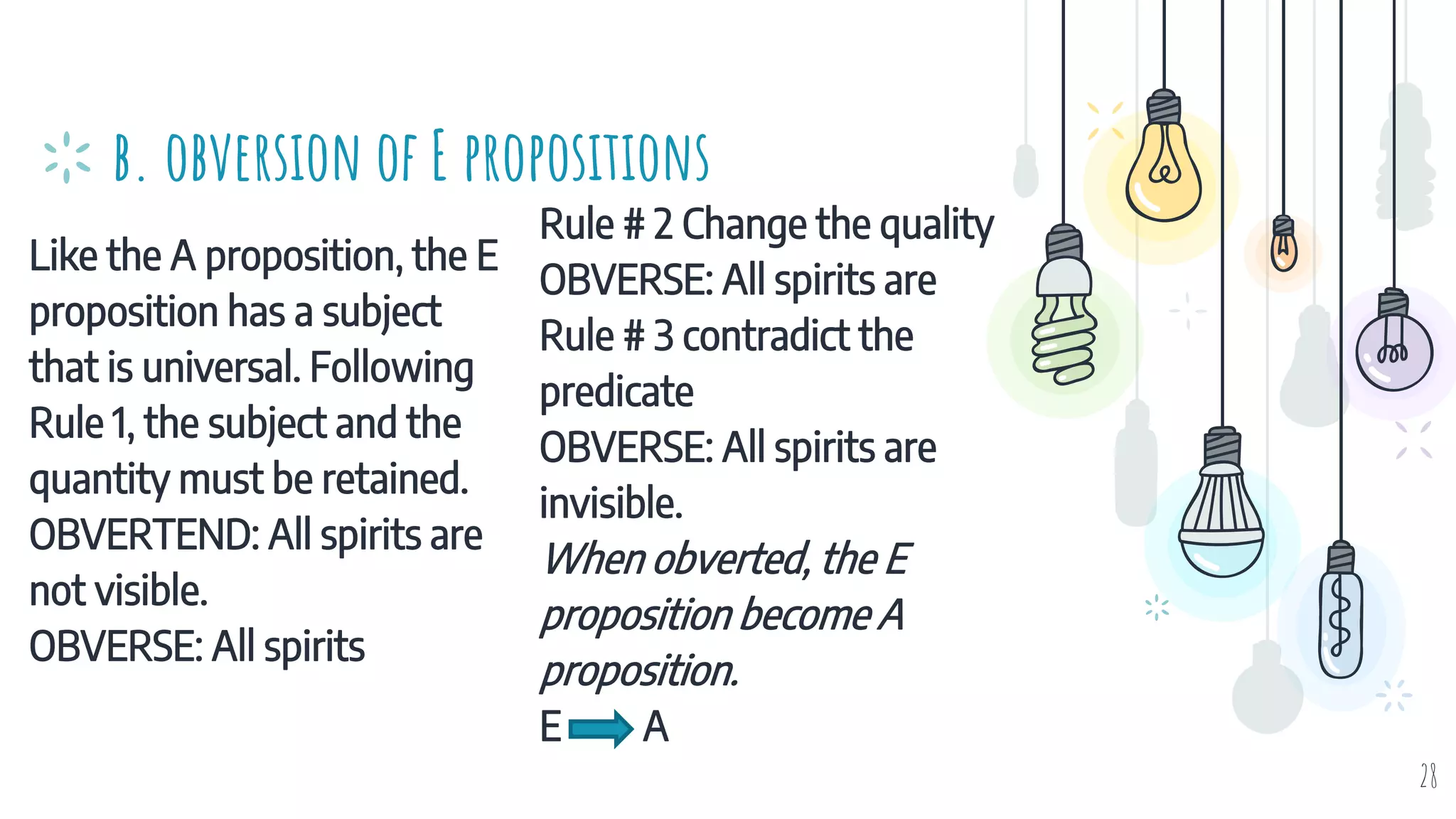
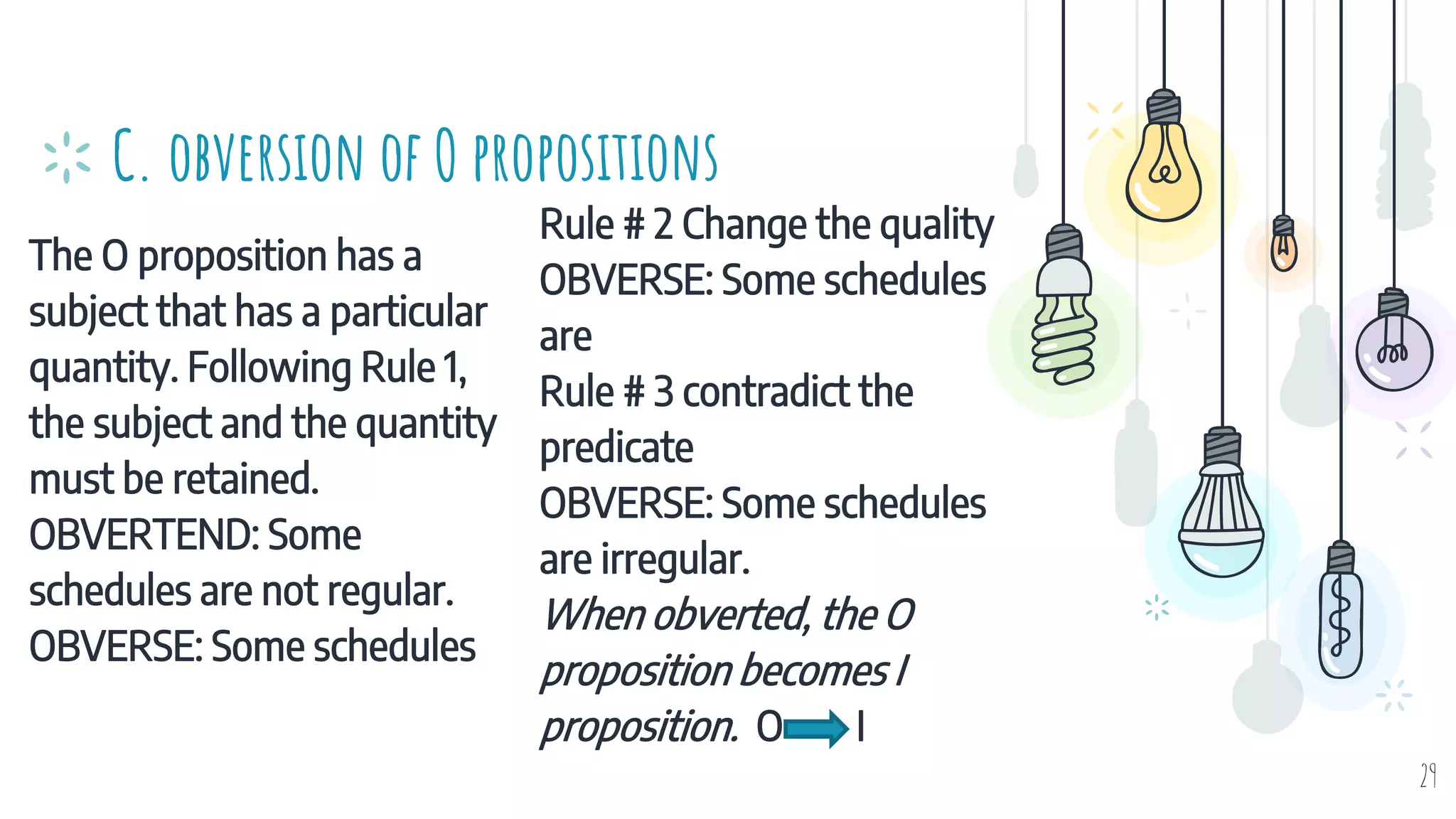
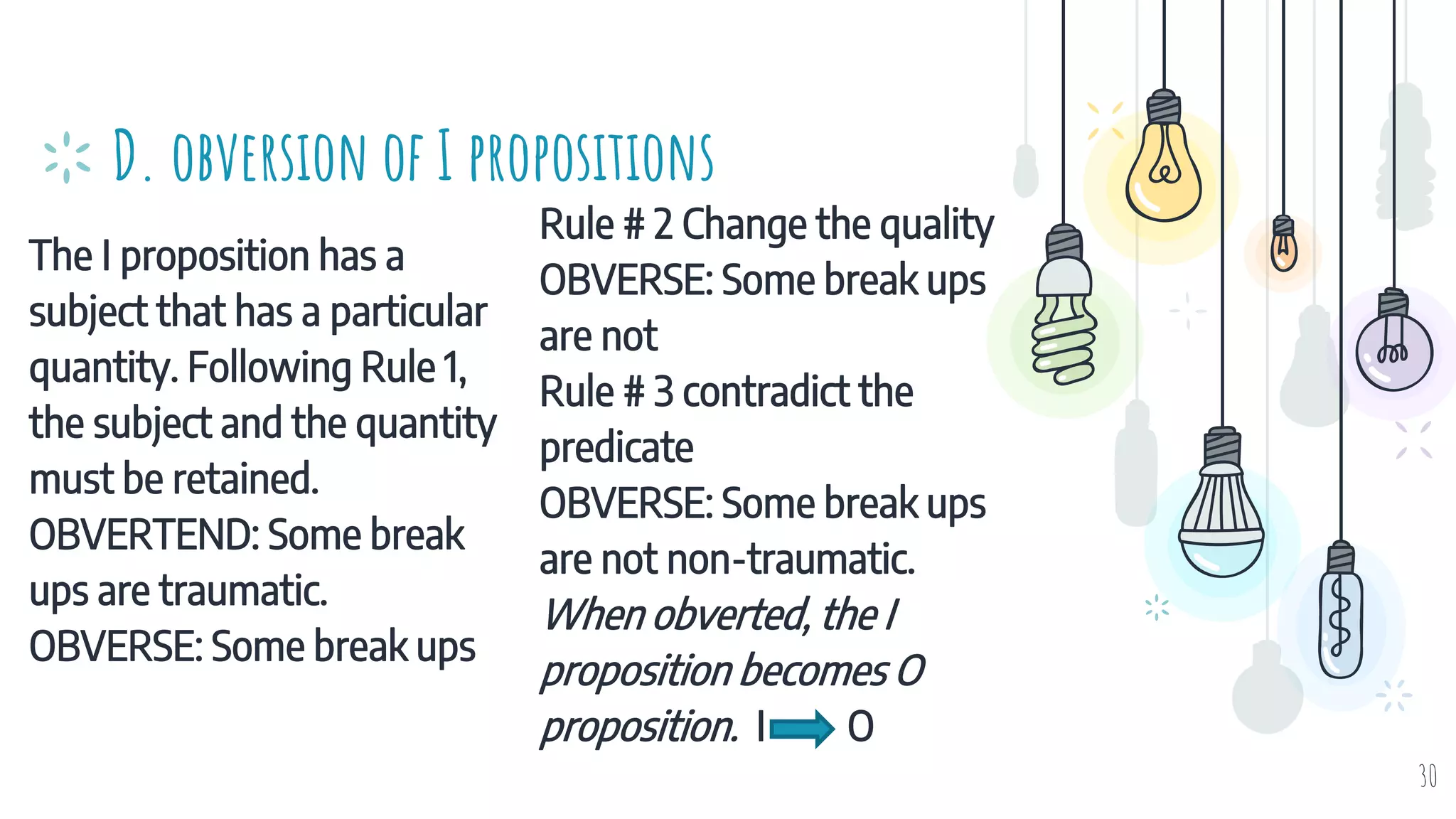
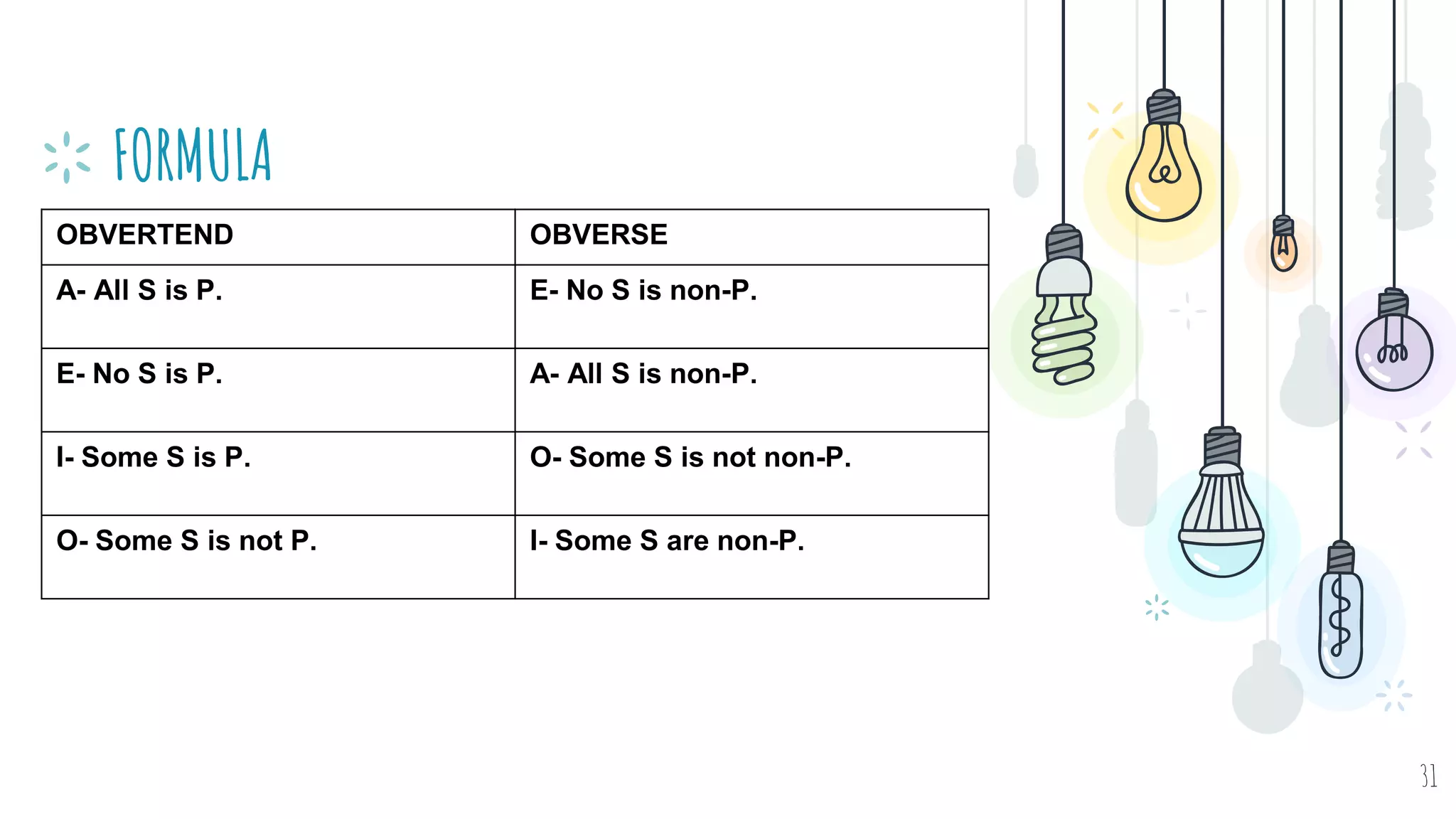
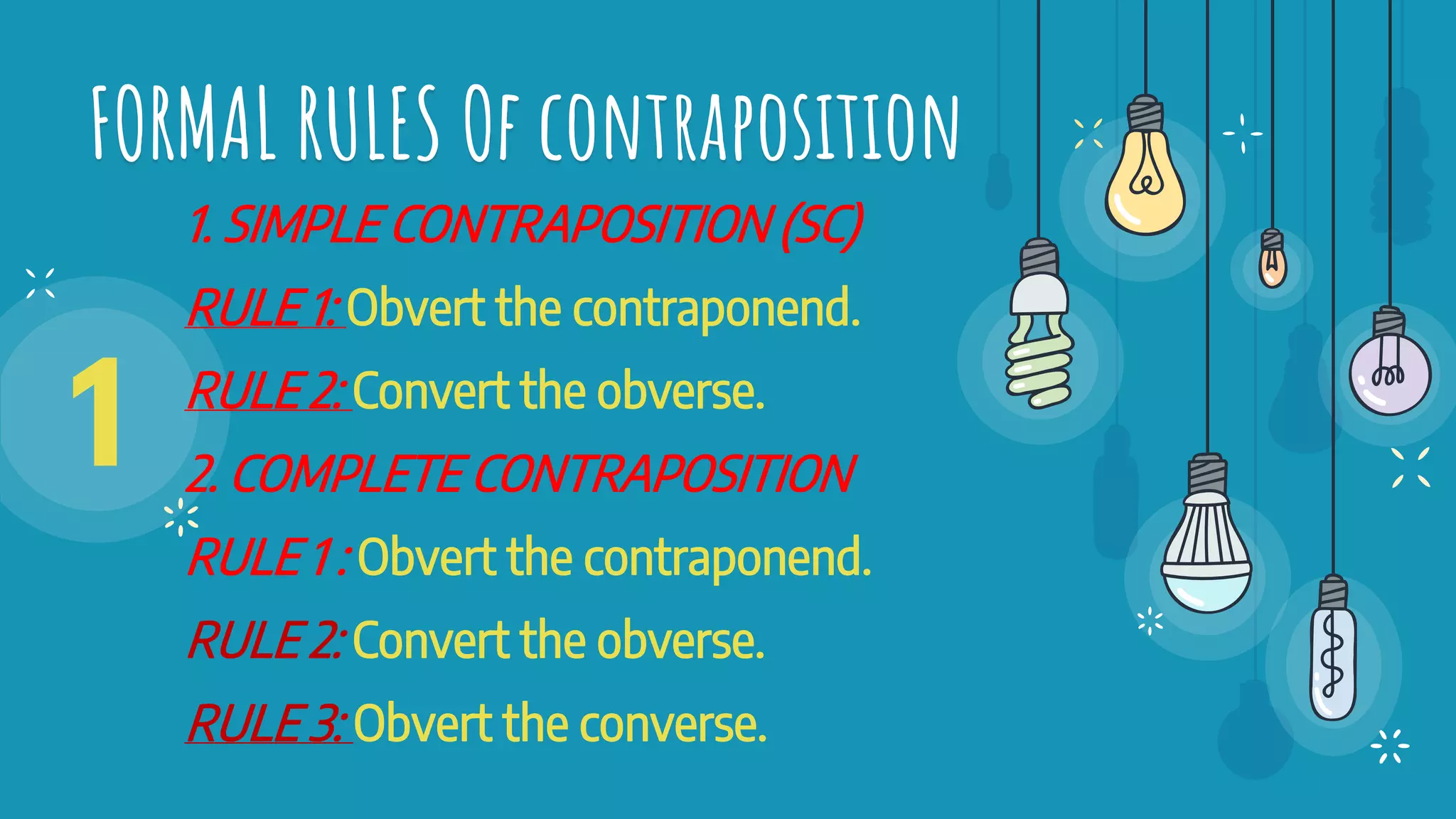
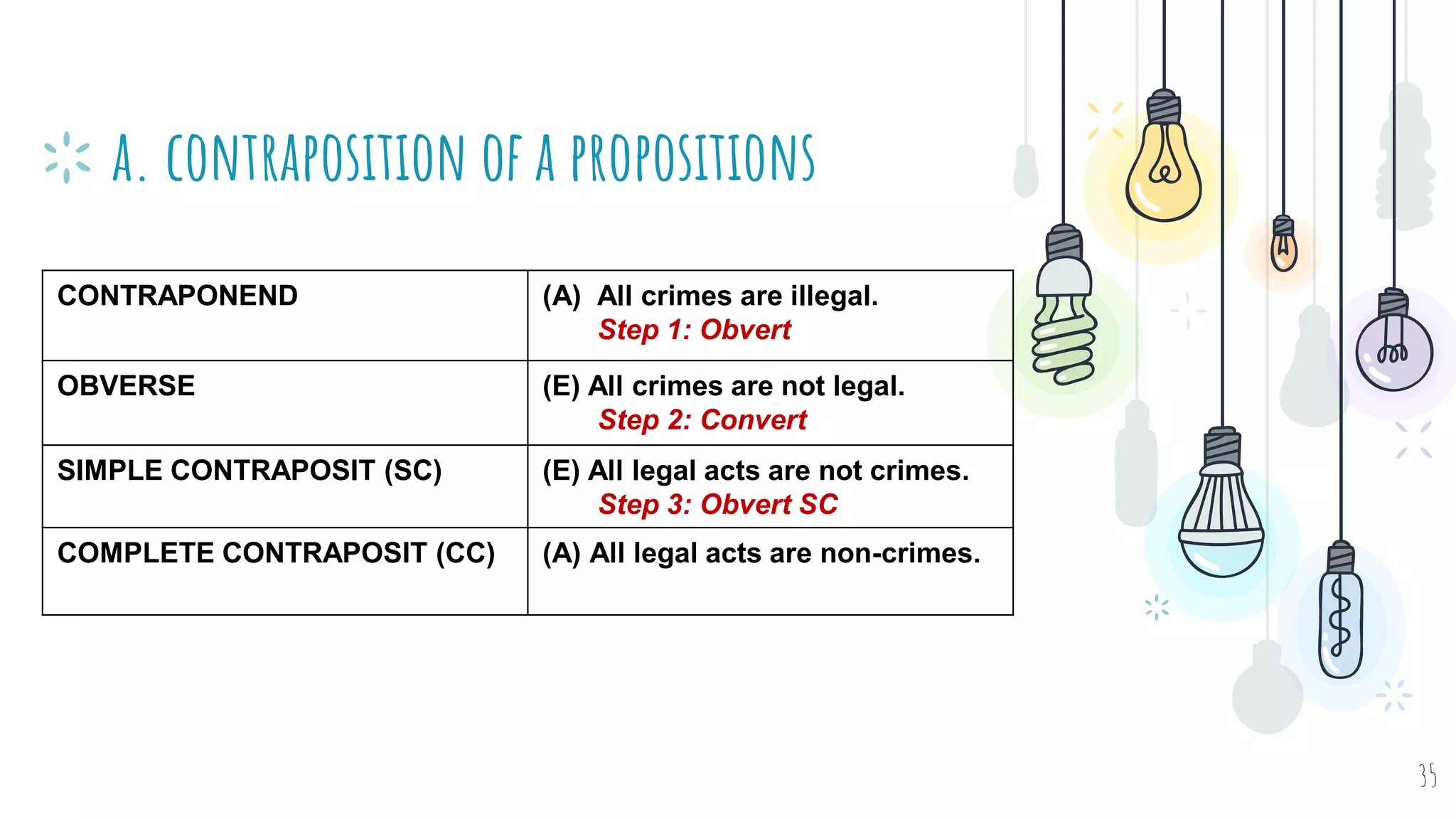
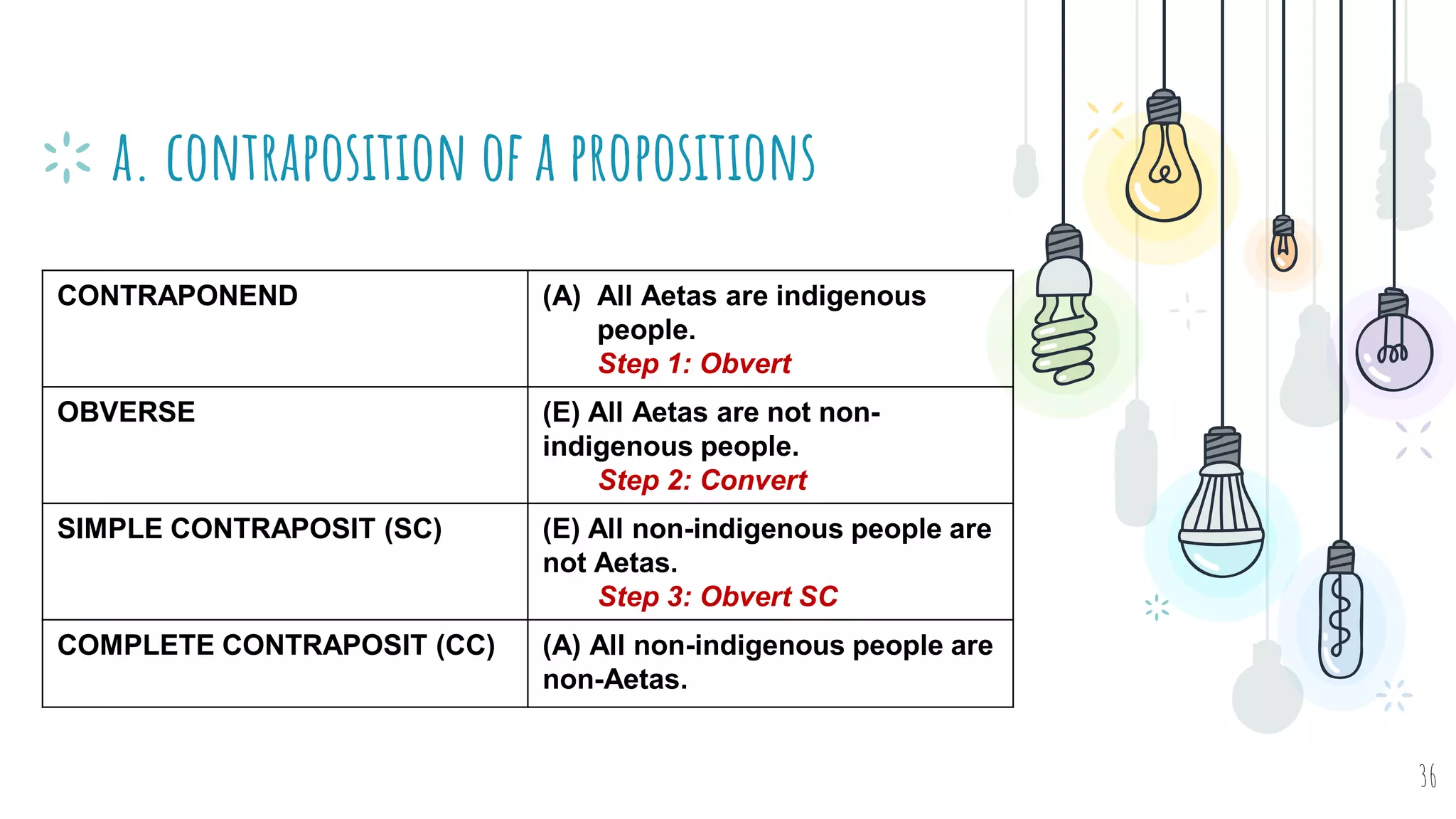
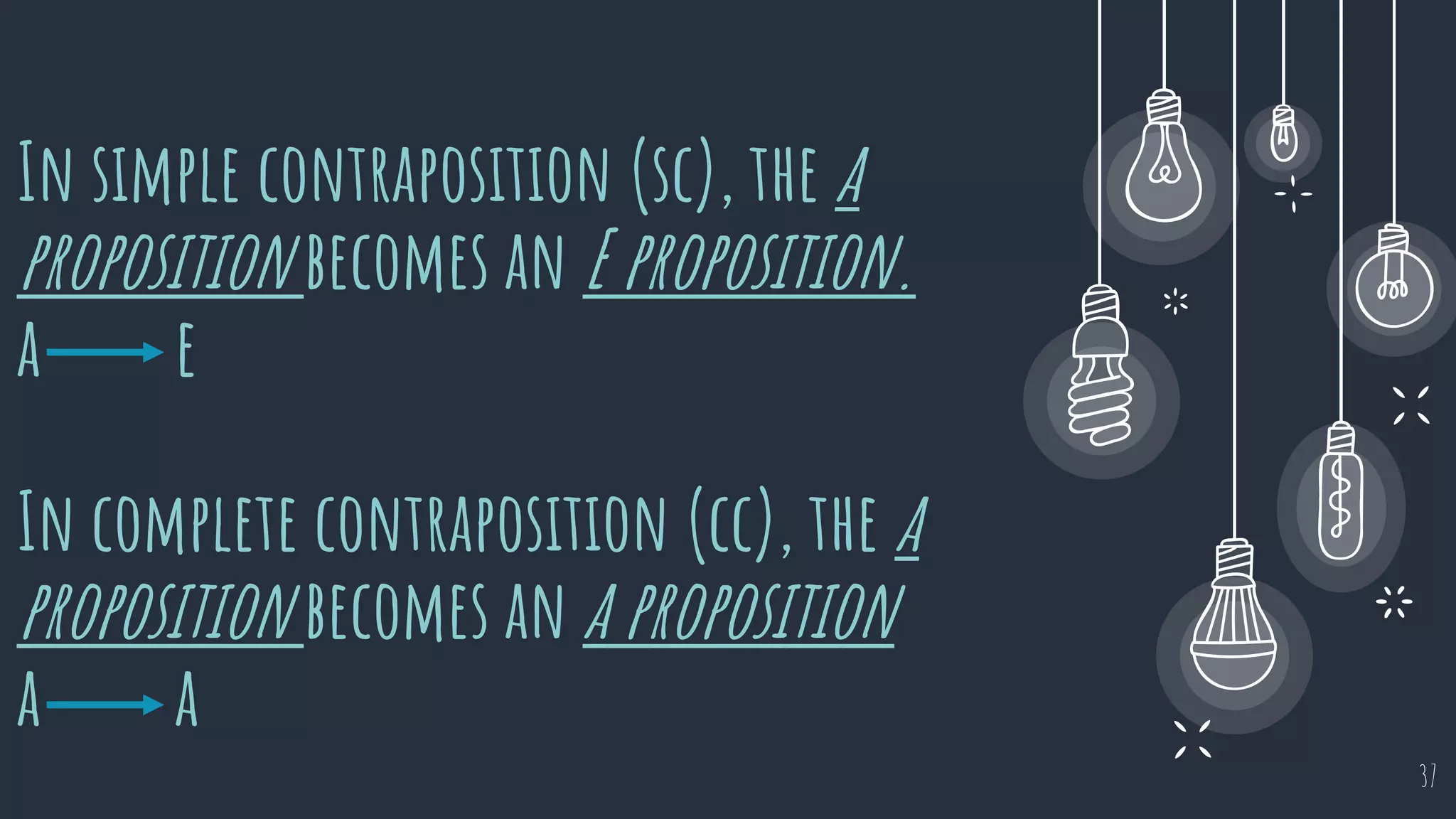
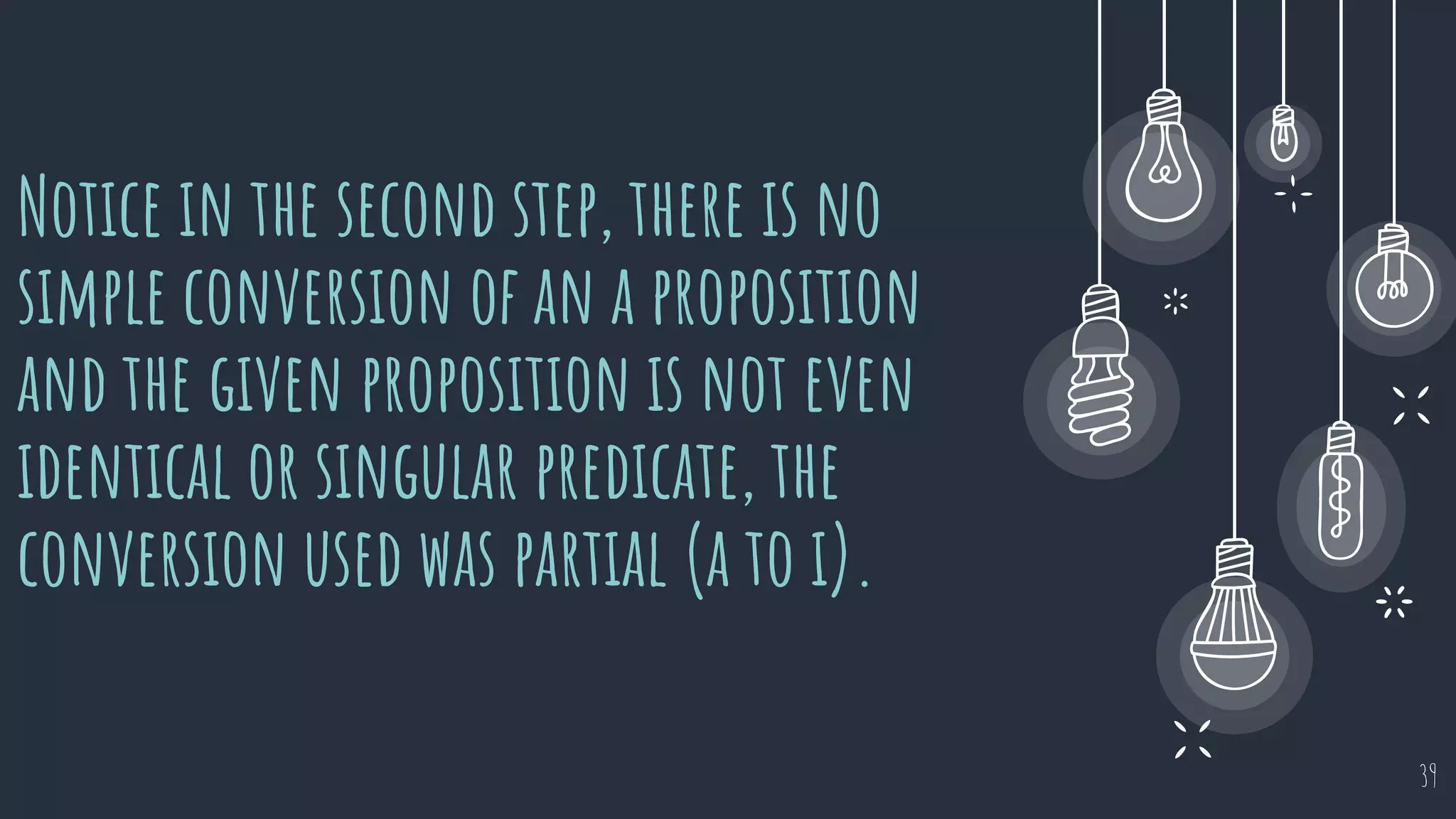
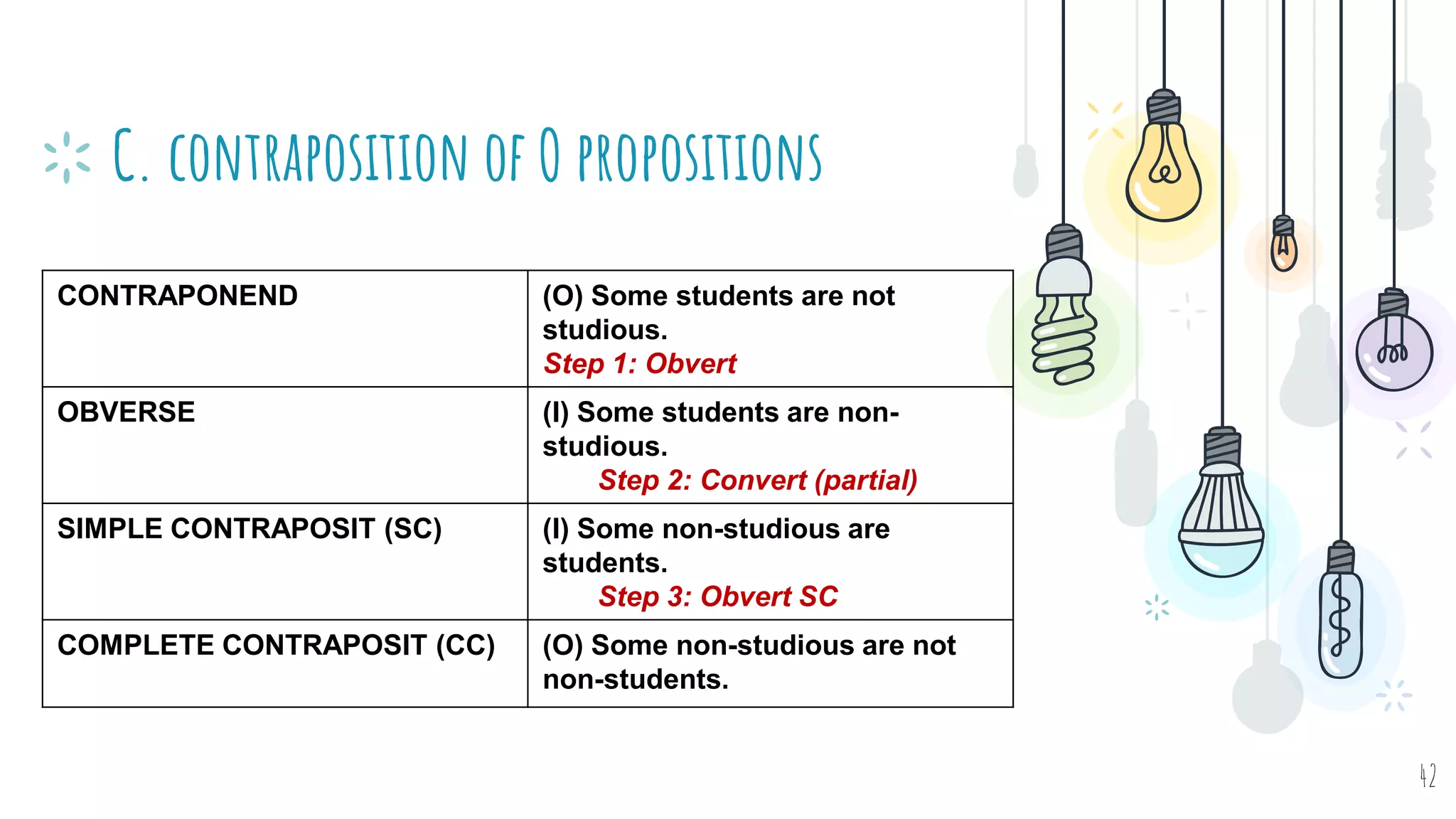
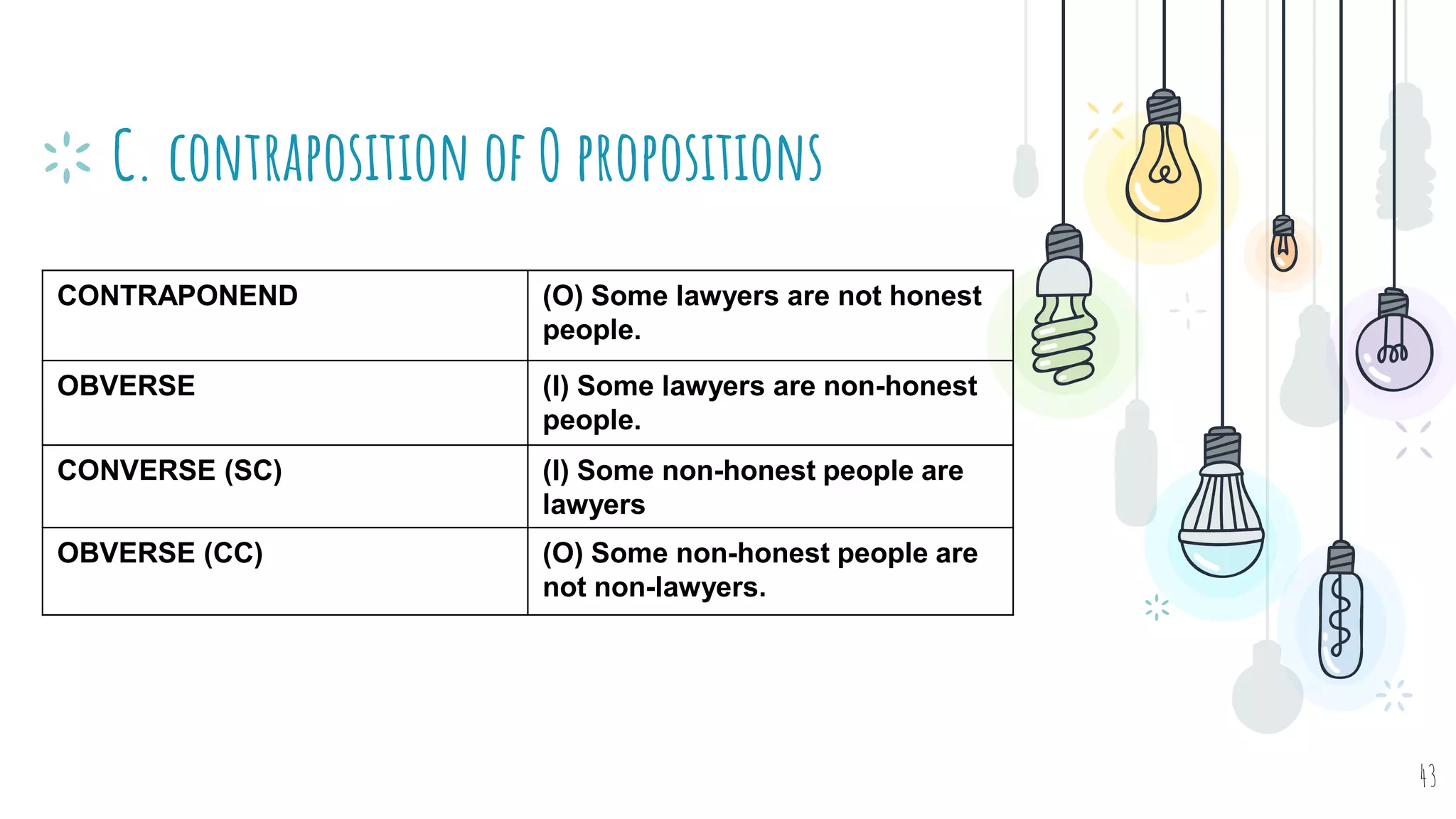
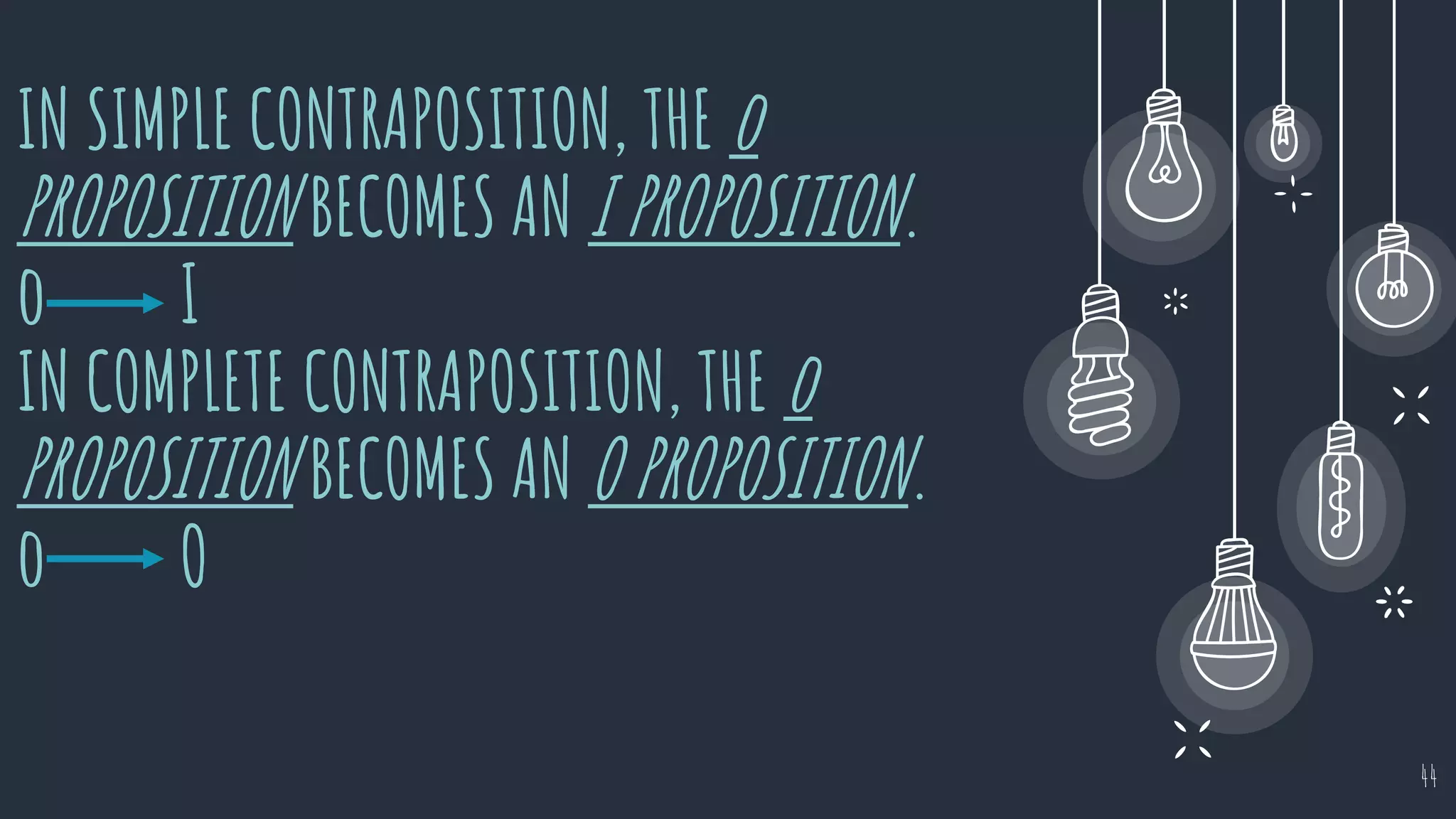
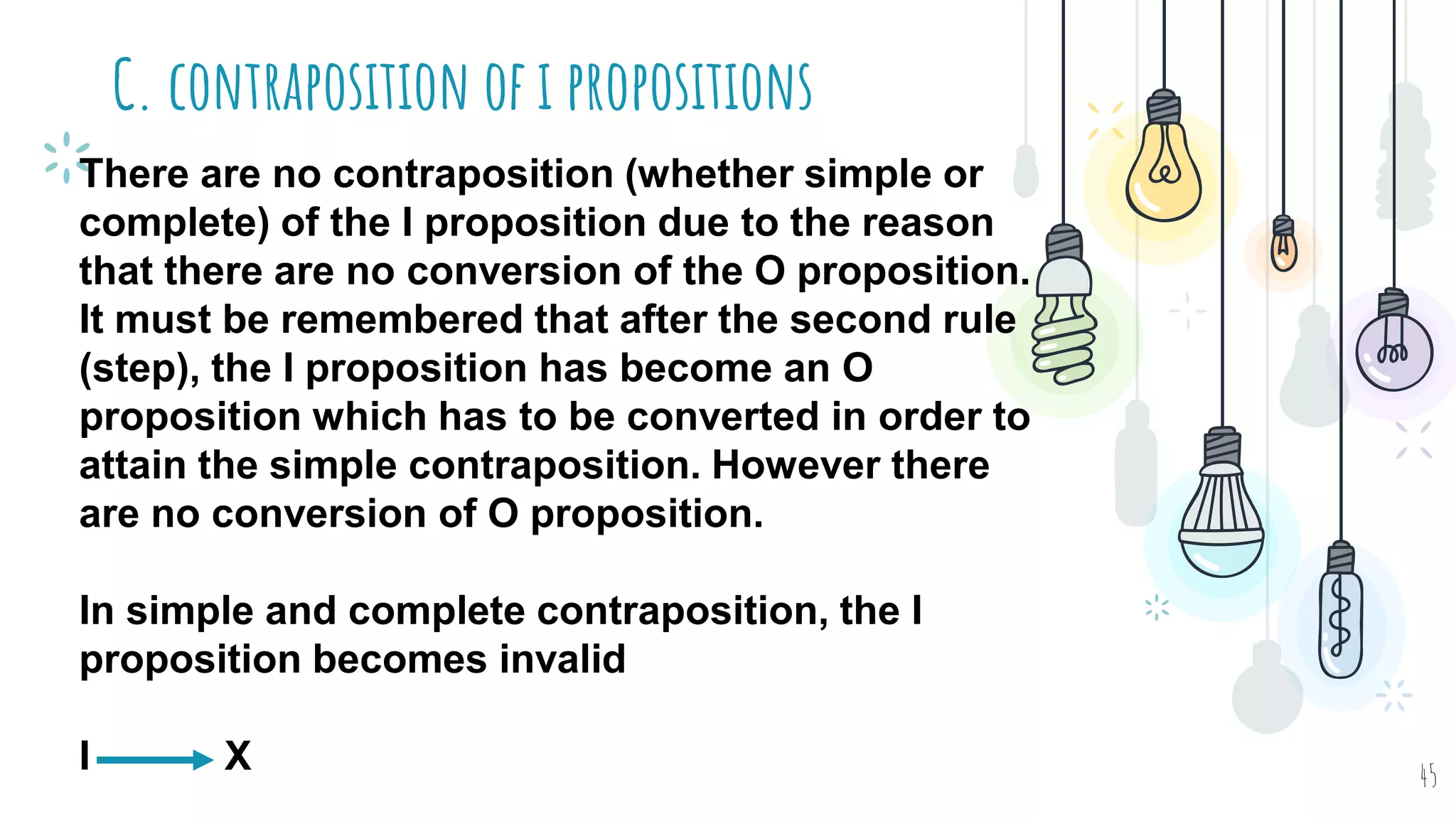
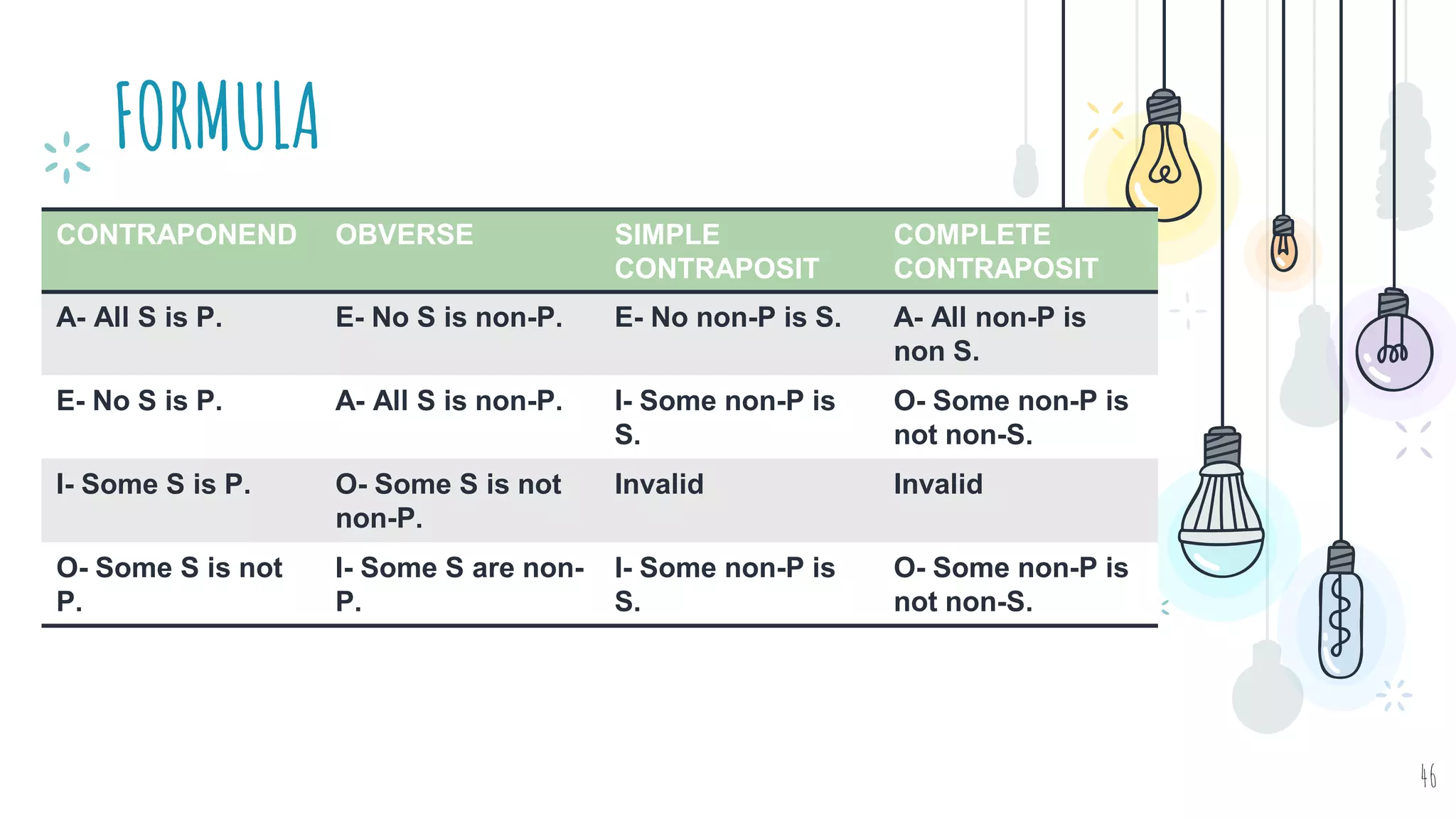
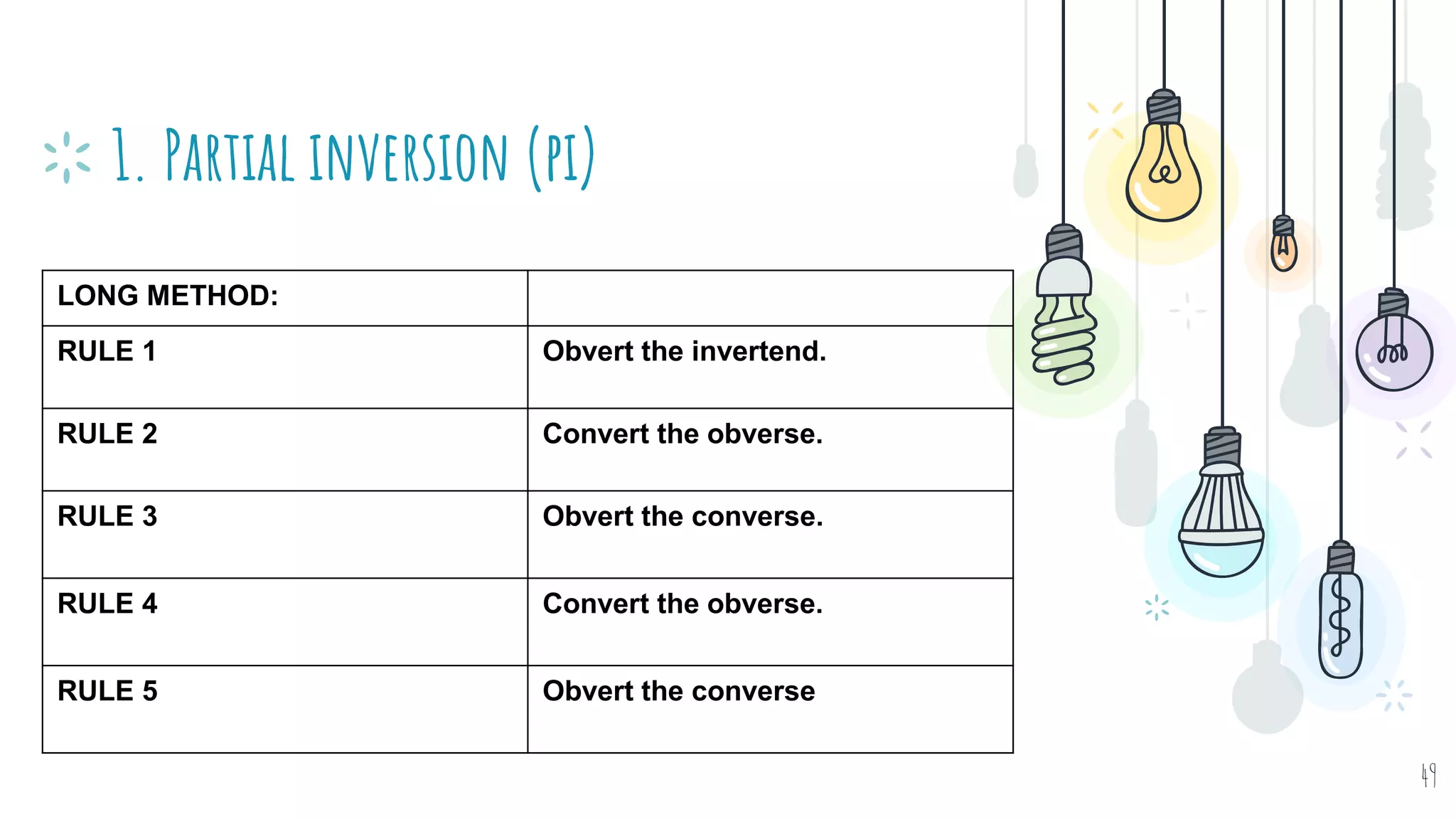
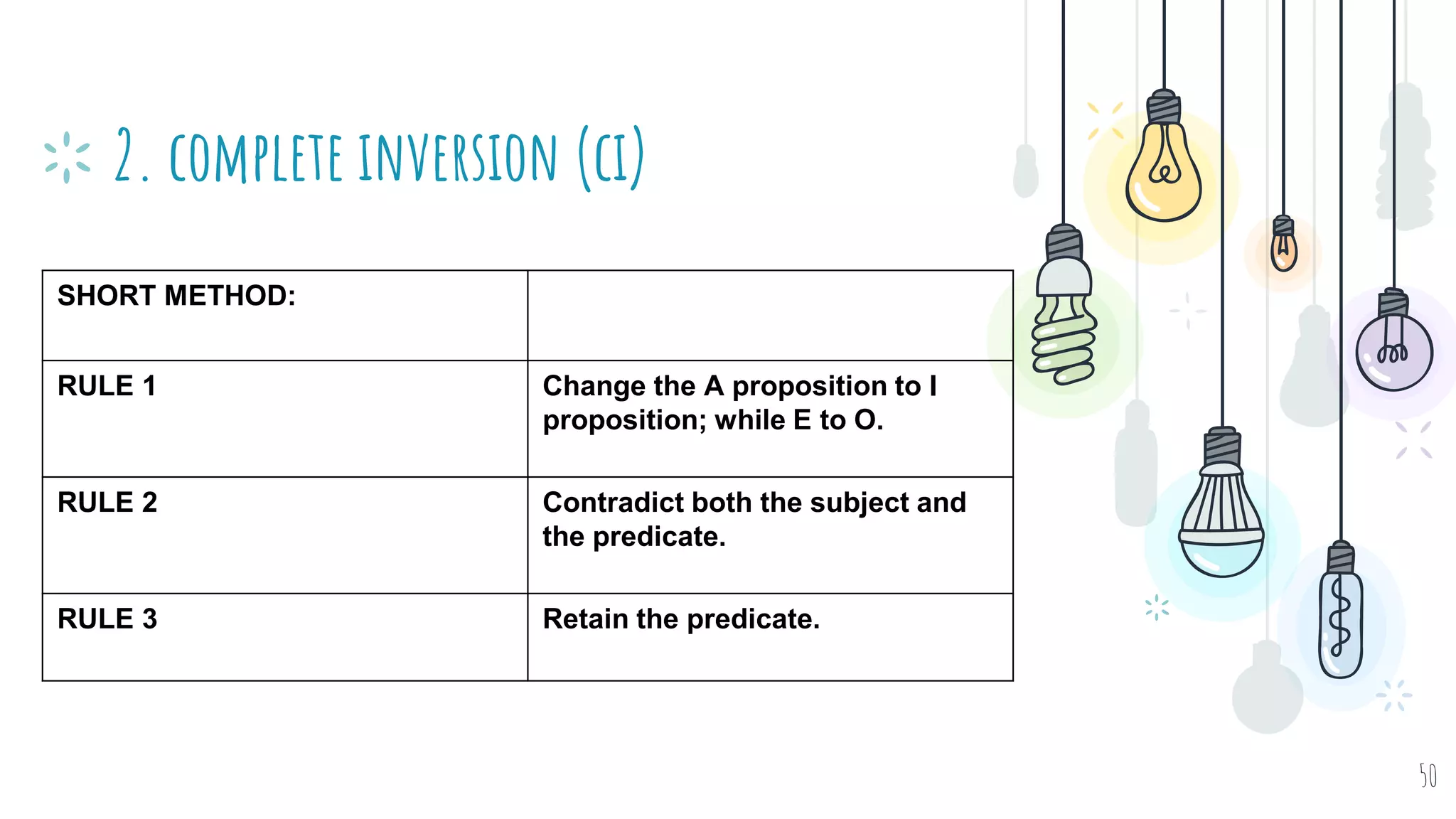
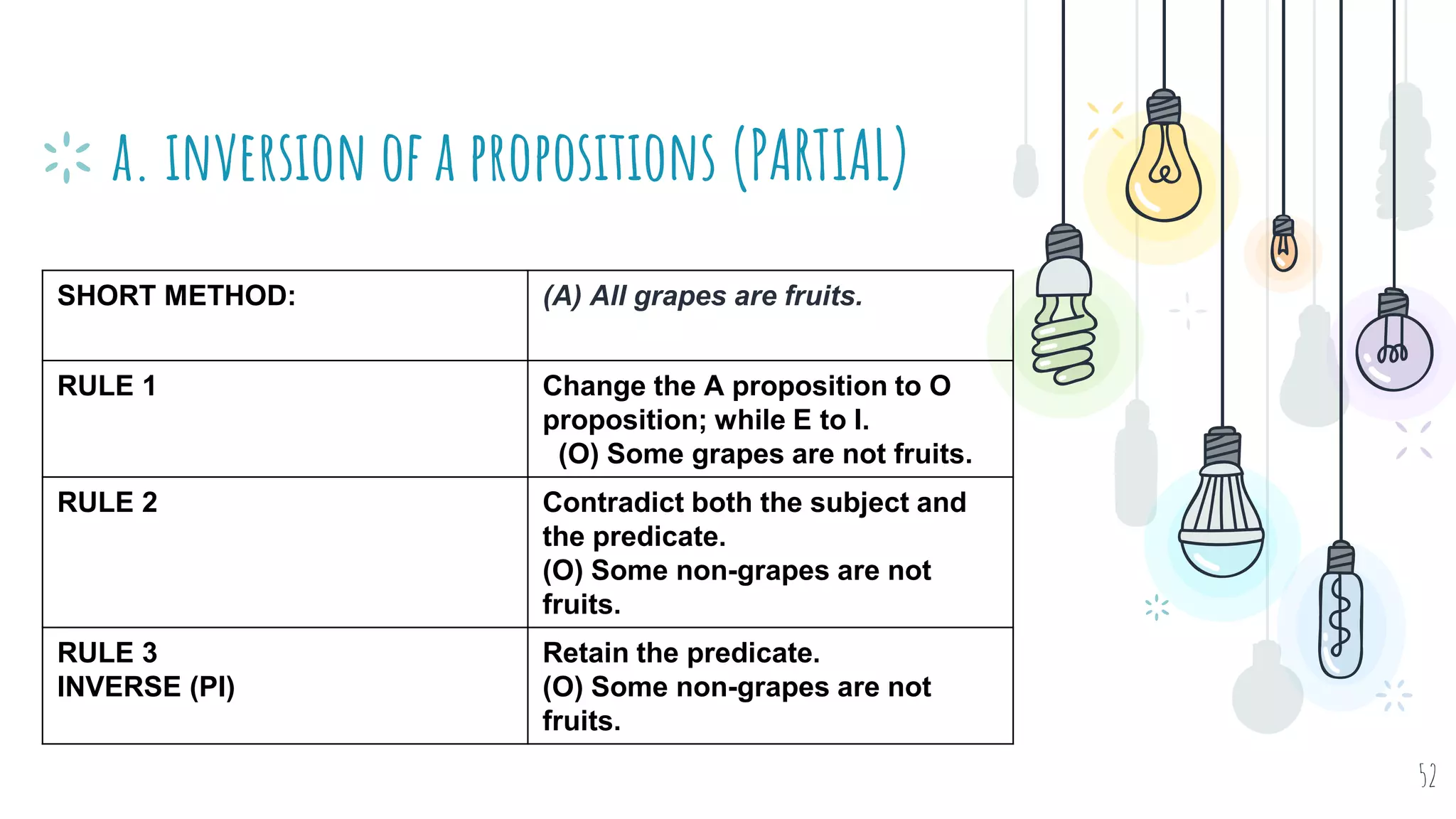
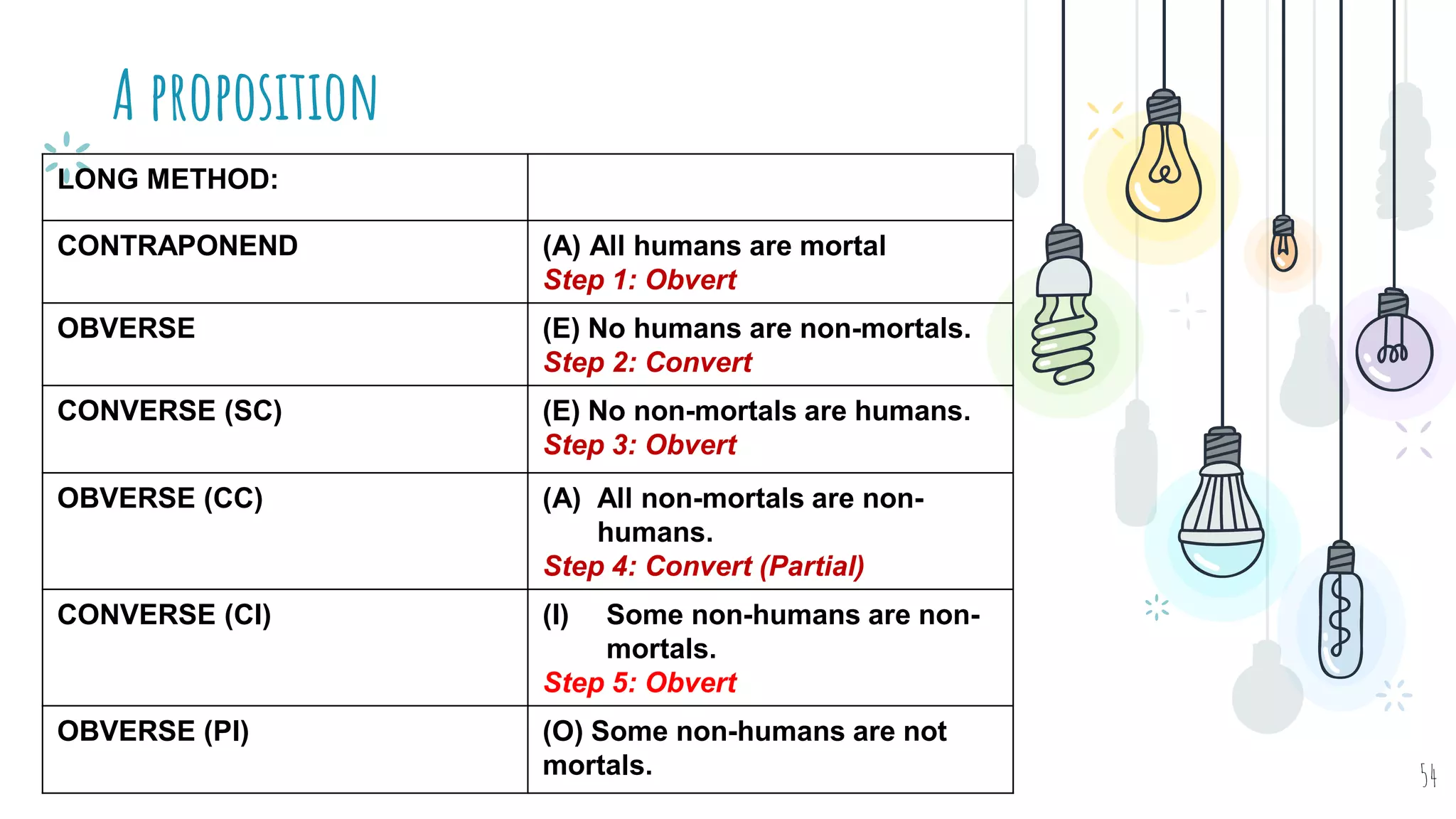
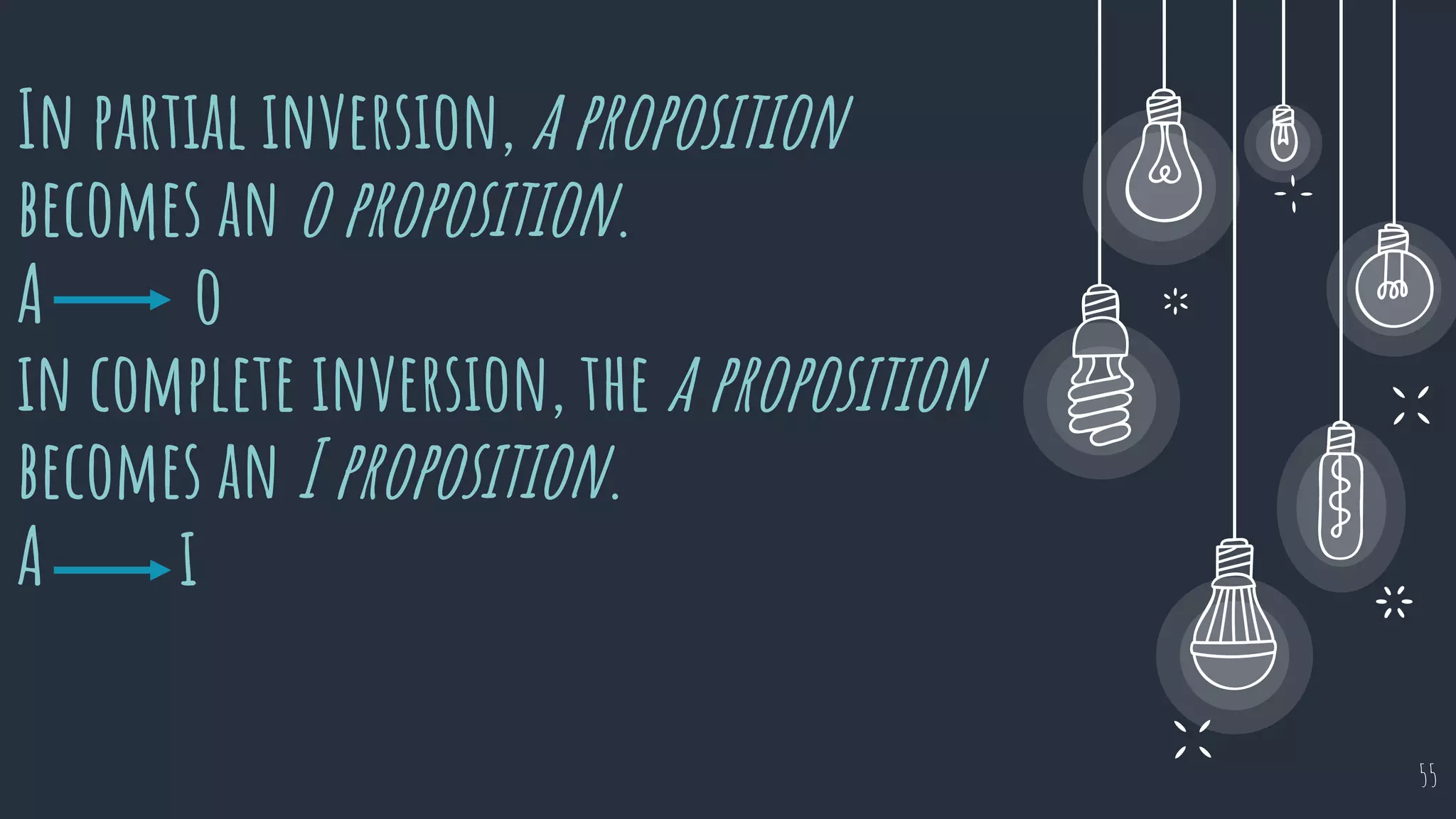
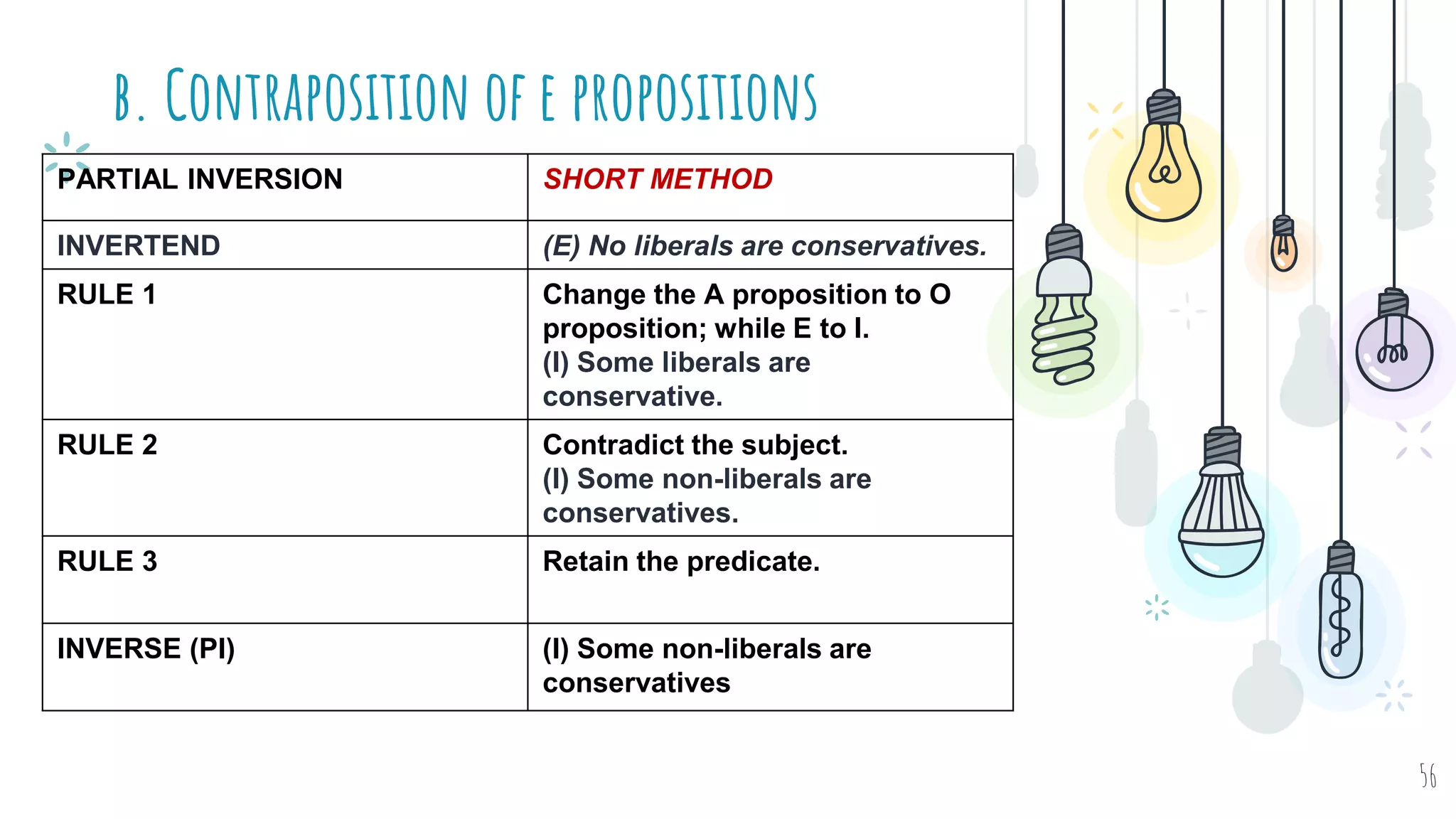
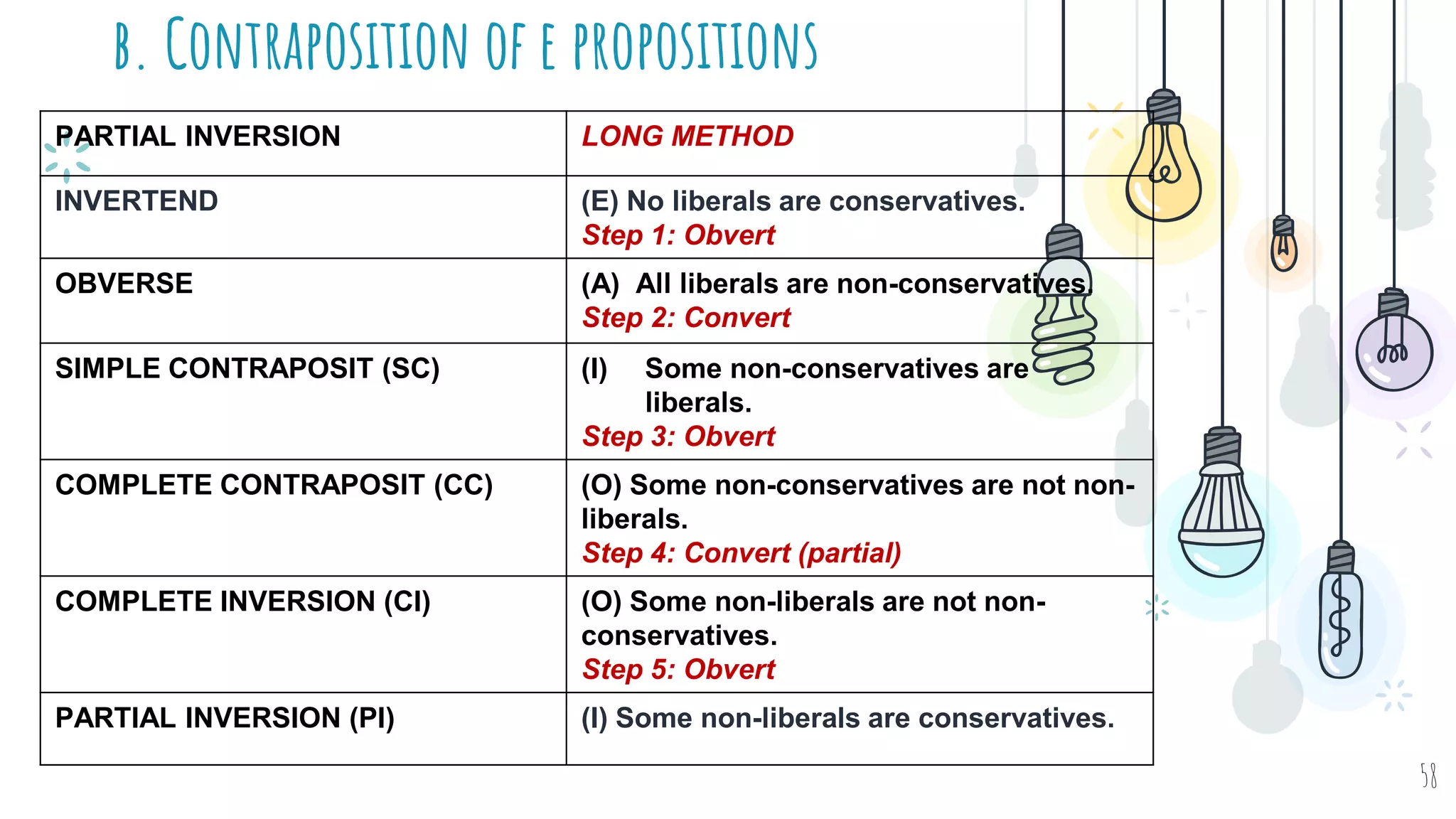
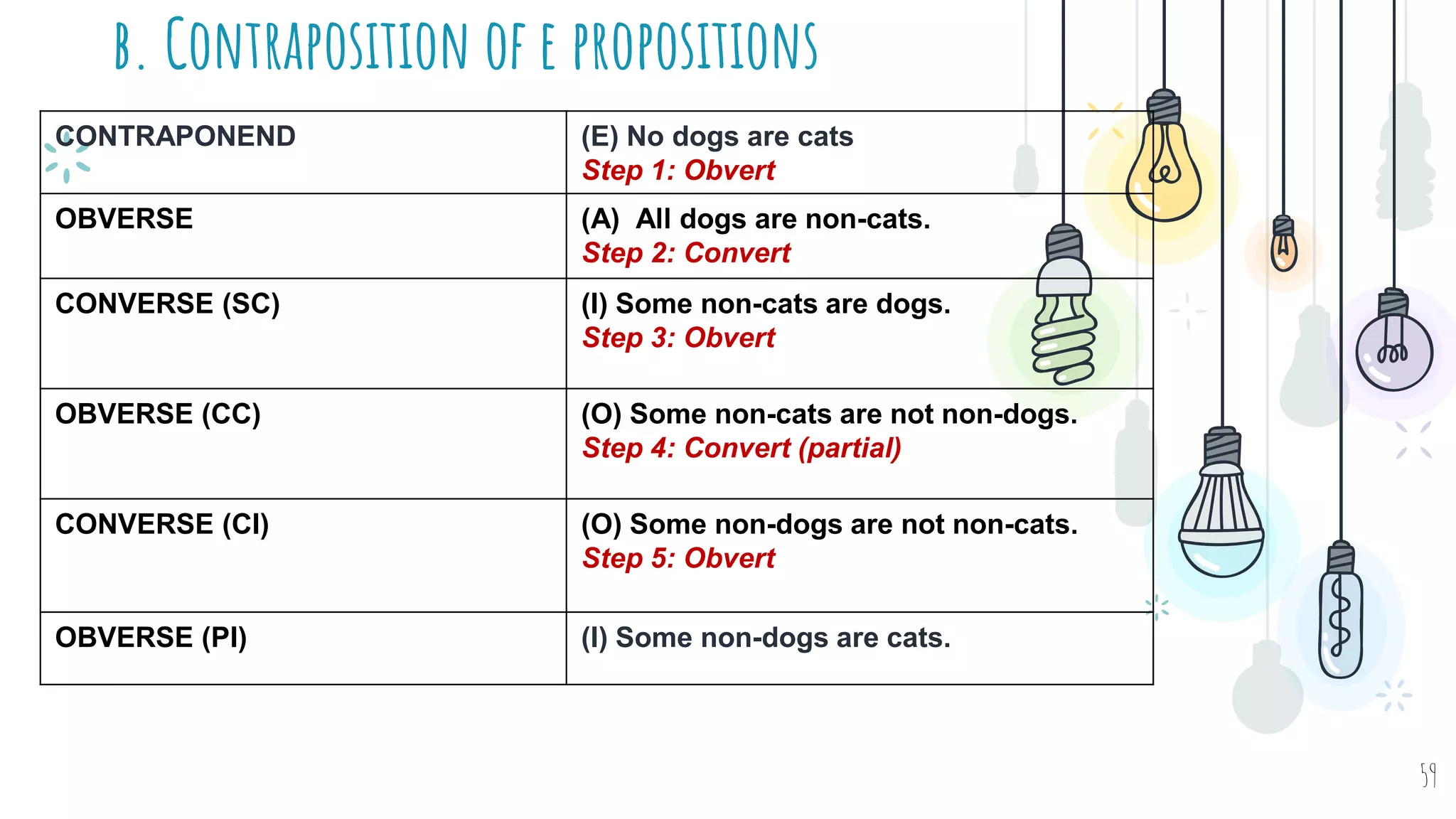
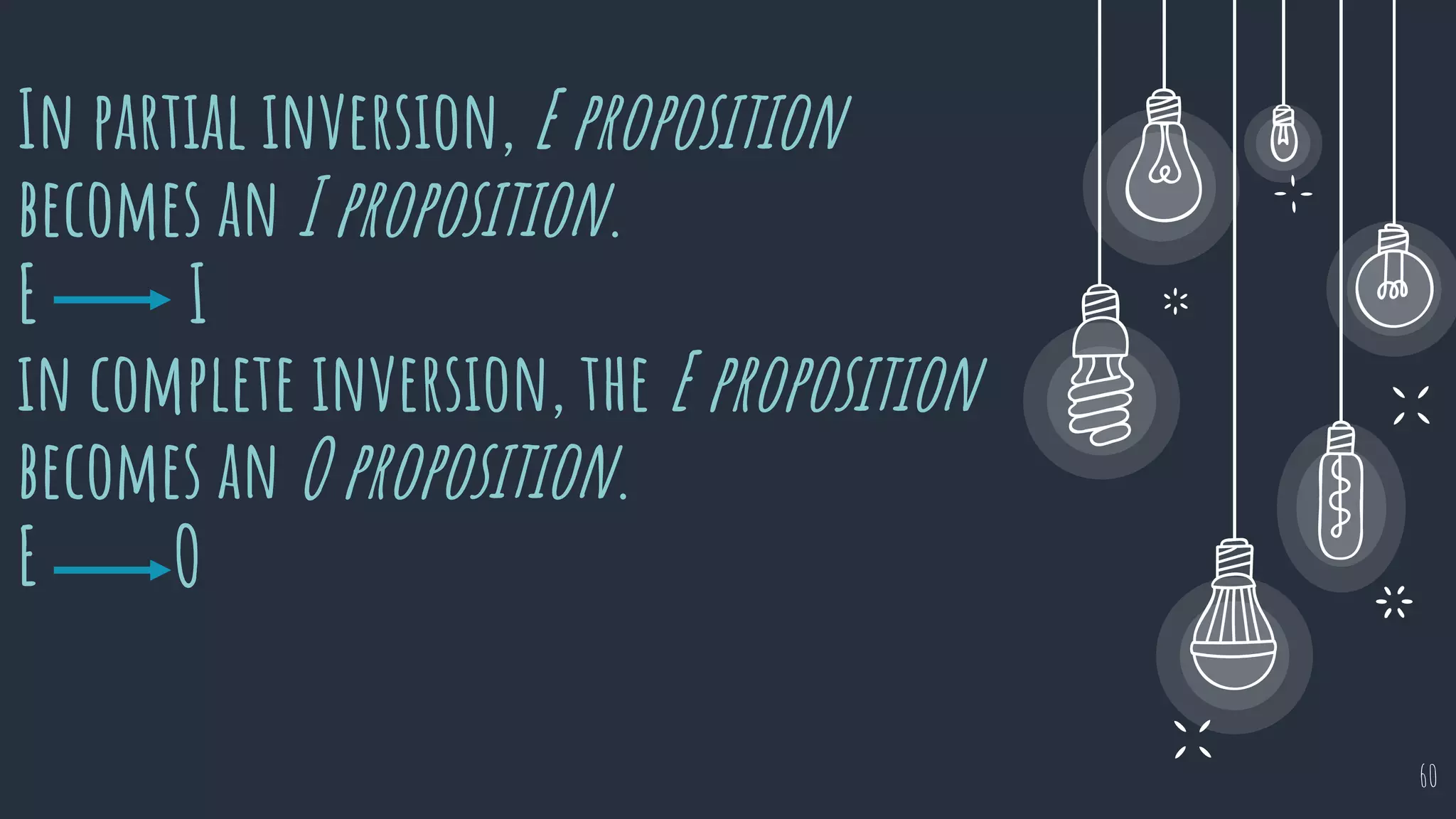
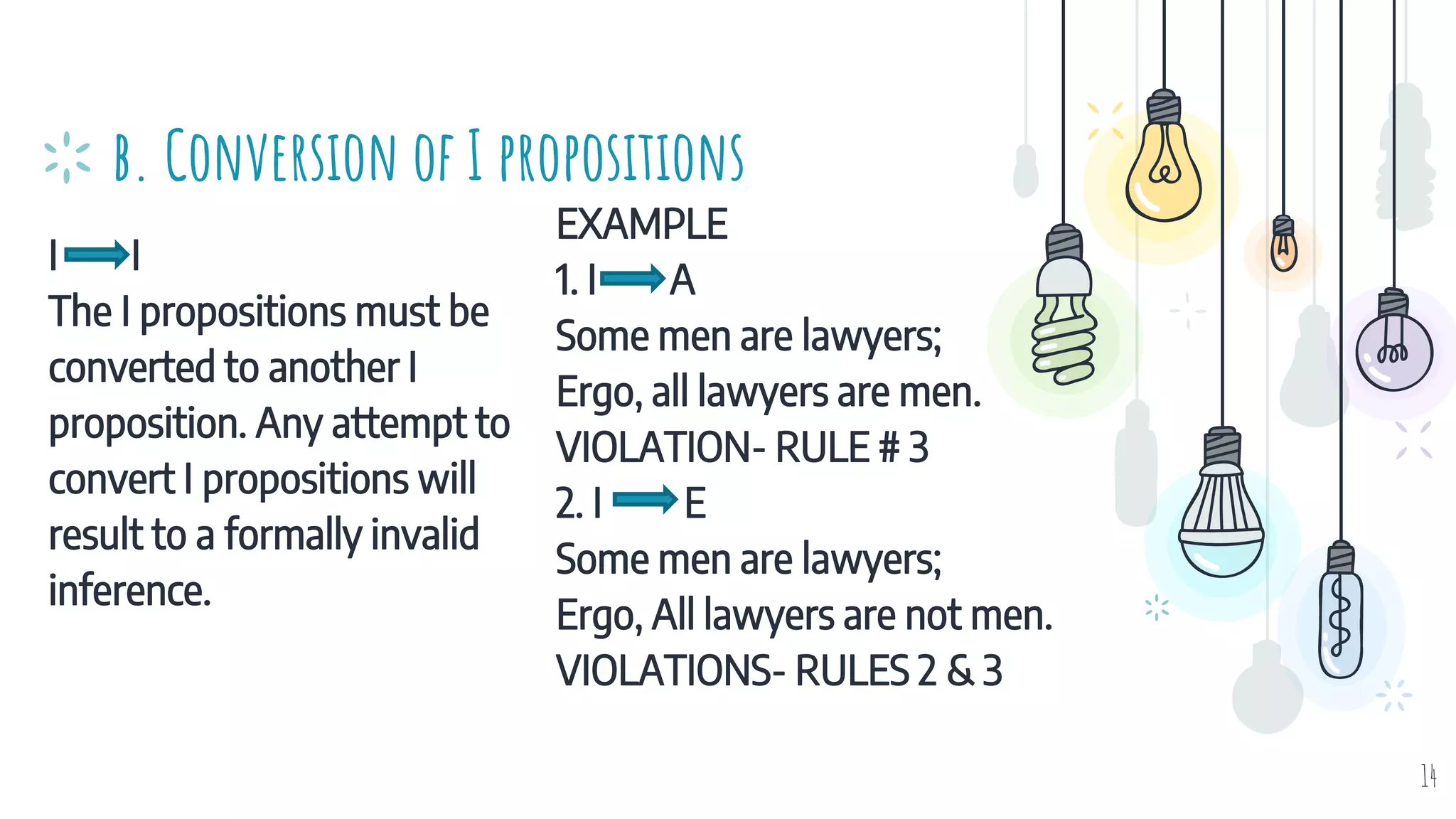
The document discusses different types of logical equivalence and eduction. It defines formal eduction as emphasizing validity based on formal rules of inference structure, while material eduction emphasizes validity based on meaning or thought content. The document then explains various types of logical equivalence/eduction including conversion, obversion, and contraposition. It provides examples and formulas for how each type of proposition (A, E, I, O) can be converted, obverted, or undergo contraposition through a series of logical steps while following formal rules.











![E E or E O
The E propositions may be
converted to another E
proposition or to an O
proposition. Propositions A
and I can not be the
converse since it will
violate RULE # 2.
. Conversion of e propositions
VALID EXAMPLES
1.) (convertend) All doors are
not windows; [E]
(converse) Ergo, All
windows are not doors. [E]
2. ; [E] All pillow case is not
heavy thing.
Ergo, Some heavy things are
not pillow case.[O]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logicalequivalenceformal-230414040713-dfe819f2/75/LOGICAL-EQUIVALENCE-FORMAL-pptx-16-2048.jpg)