Linux celebrated its 25th birthday on August 25, 2015. The document discusses the history and basics of Linux, including:
- Linux was created in 1991 by Linus Torvalds as an open-source kernel based on UNIX.
- It discusses Linux security models and permissions. Files have owners, groups, and permissions to control access.
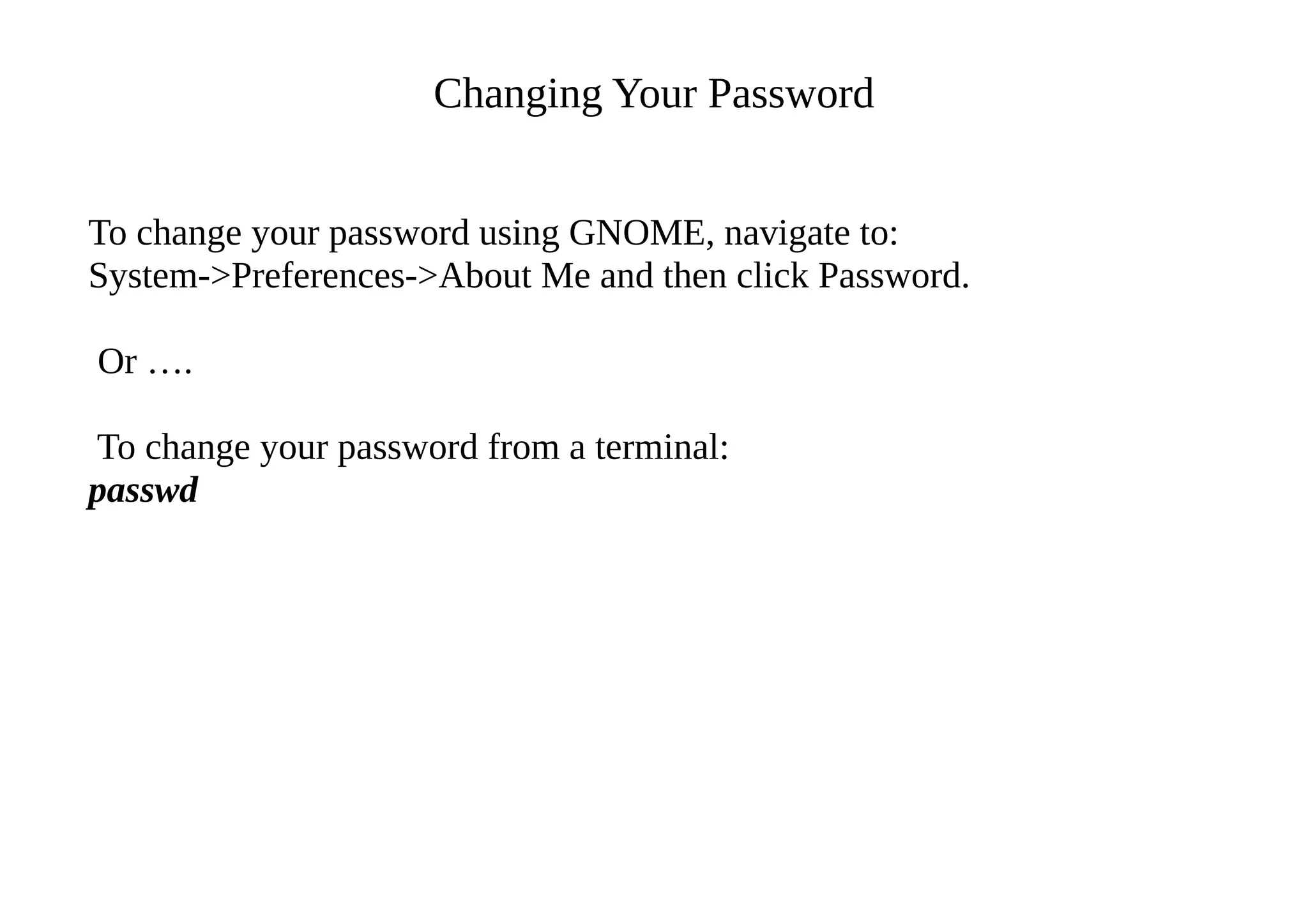
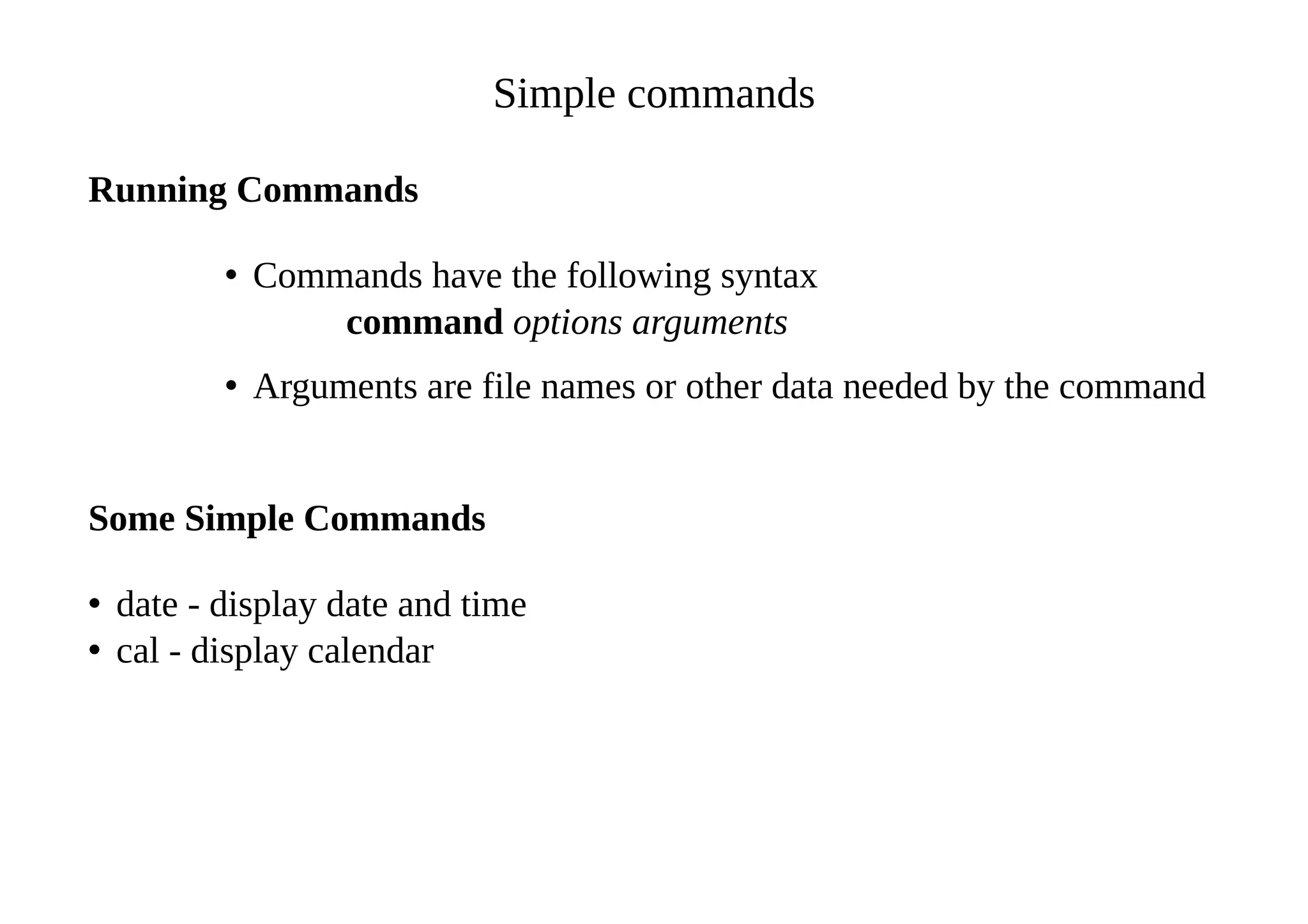
- It provides an overview of basic Linux commands for starting the X server, changing passwords, editing text files, running commands and getting help.


























![The man Command
• Provides documentation for commands
• man [<chapter>] <command>
• Pages are grouped into "chapters"
• While viewing a man page
• Navigate with arrows, PgUp, PgDn
• /text searches for text
• n/N goes to next/previous match
• q quits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-33-2048.jpg)



![Listing Directory Contents
• Lists the contents of the current directory or a specified directory
• Usage:
ls [options] [files_or_dirs]
Example:
• ls -a (include hidden files)
• ls -l (display extra information)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-37-2048.jpg)
![Copying Files and Directories
• cp - copy files and directories
• Usage:
cp [options] file destination
or …
cp [options] file1 file2 dest.
Moving and Renaming Files and Directories
• mv - move and/or rename files and directories
• Usage:
mv [options] file destination
or …
mv [options] file1 file2 destination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-38-2048.jpg)
![Creating and Removing Files
• touch - create empty files or update file timestamps
• rm - remove files
• Usage:
rm [options] <file>...
• mkdir creates directories
• rmdir removes empty directories
• rm -rf remove directory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-39-2048.jpg)

![Viewing File Contents “less and cat”
General Syntax
cat [OPTION] [FILE]...
1. Display Contents of File
# cat /etc/passwd
2. View Contents of Multiple Files in terminal
# cat test test1
Hello everybody
Hi world,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-41-2048.jpg)

![Viewing File Contents “head and tail”
• tail command syntax
tail [OPTION]... [FILE]... (tail /path/to/file)
Use -n to change number of lines displayed
when you want to view a certain part at the beginning or at the end of a file,
which prints the last few number of lines (10 lines by default) of a certain
file.
Head command
Head command will obviously on the contrary to tail, it will print the first
10 lines of the file.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-43-2048.jpg)
![head command syntax
head [OPTION]... [FILE]...
As mention earlier print first 10 lines.
# head /etc/passwd
What next ?
Use -n to change number of lines displayed
# head -n <number of lines preceeded with "-"> /path/to/file
# head -n 2 /etc/passwd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-44-2048.jpg)
![Extracting Text by Keyword grep
Prints lines of files or STDIN where a pattern is matched
$ grep 'john' /etc/passwd
$ date --help | grep year
Use -i to search case-insensitively
Use -n to print line numbers of matches
grep syntax
grep [OPTIONS] PATTERN [FILE...]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ff-190922164110/75/Linux-Everyting-as-a-service-45-2048.jpg)
