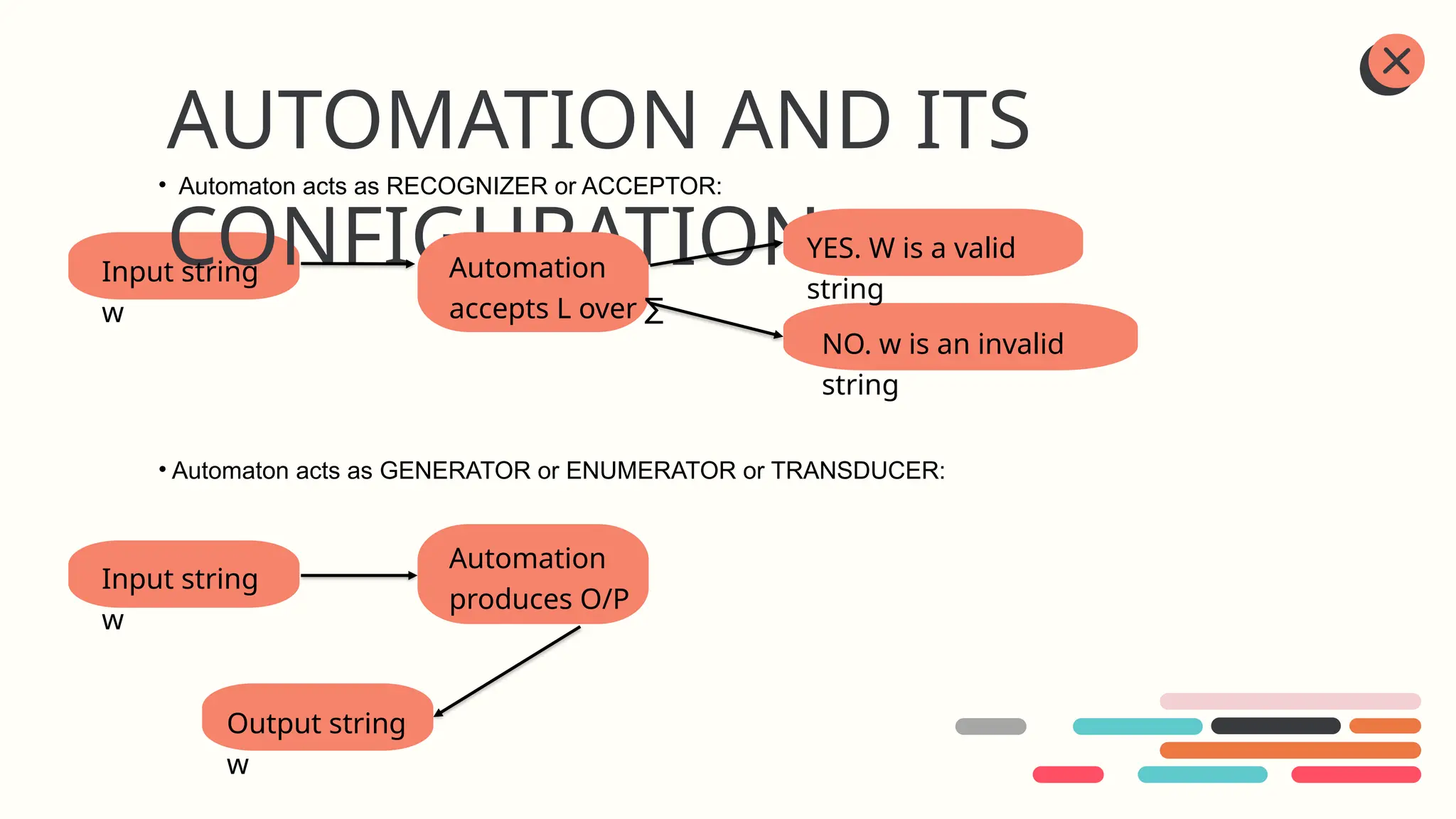
Automata theory is a branch of computer science focused on abstract computing devices called automata, which compute functions and solve problems through a series of states. The Turing machine is the most powerful type of automaton, serving as a model for modern computation. Key concepts include alphabets, strings, concatenation, and finite automata, which can be categorized as acceptors or transducers.