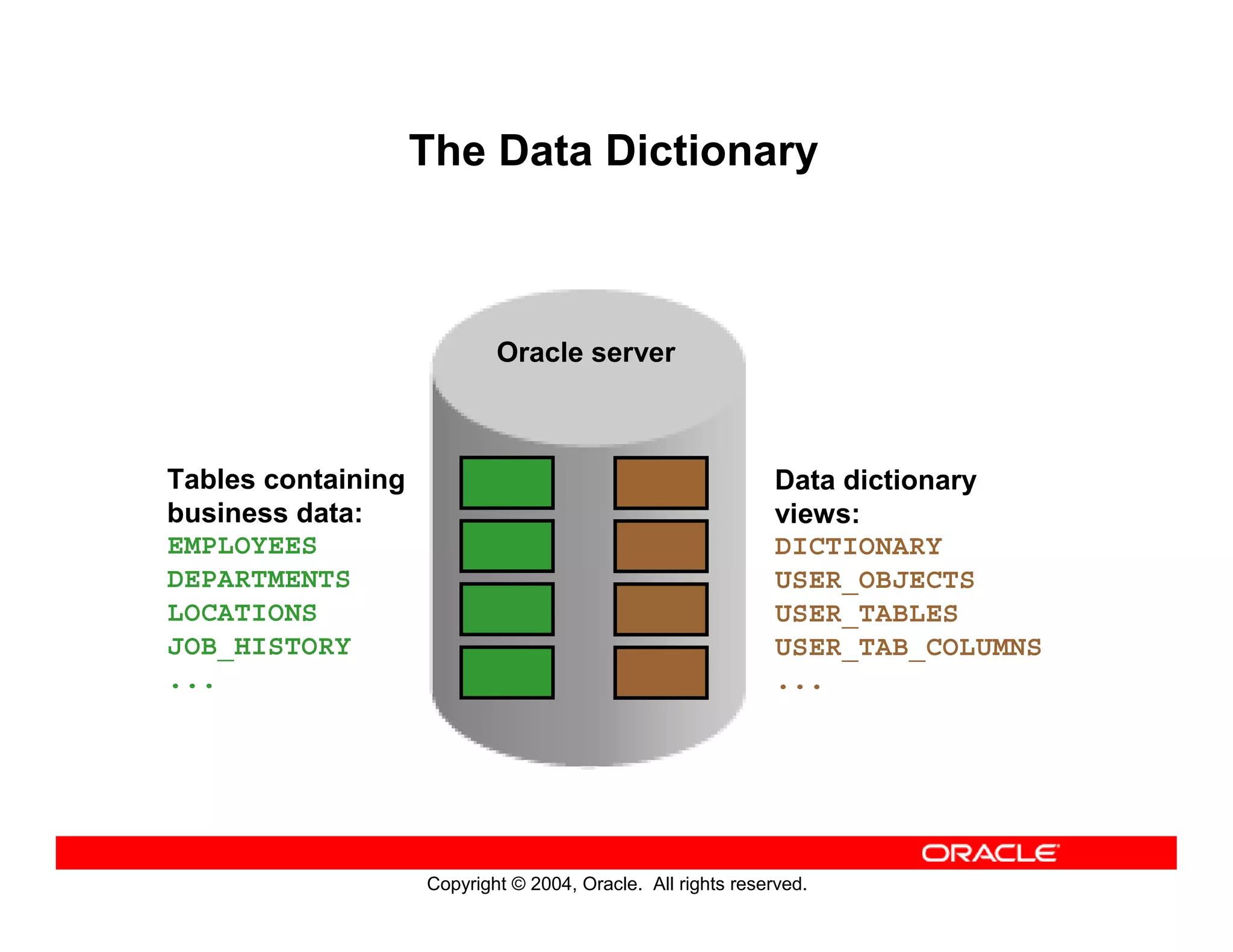
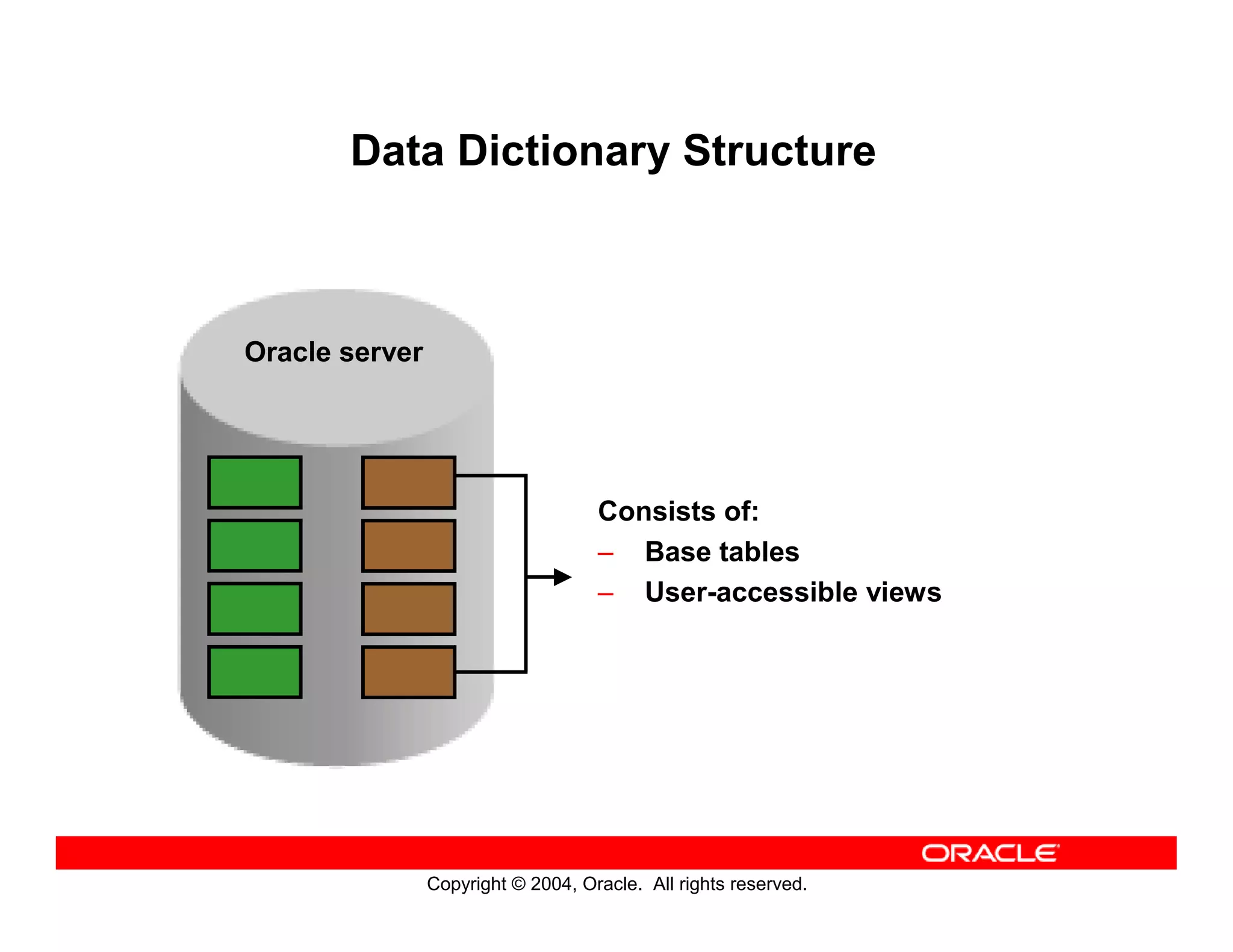
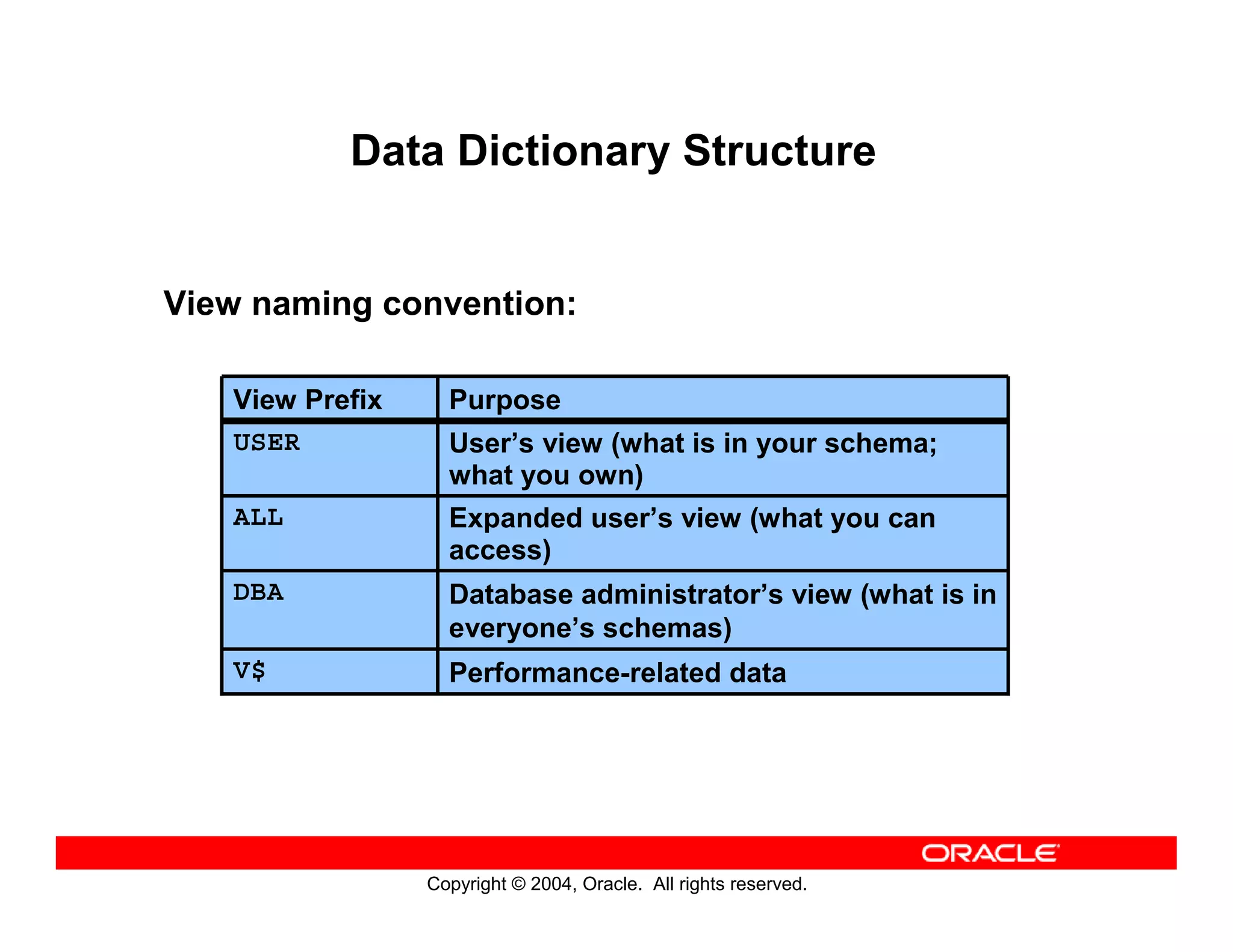
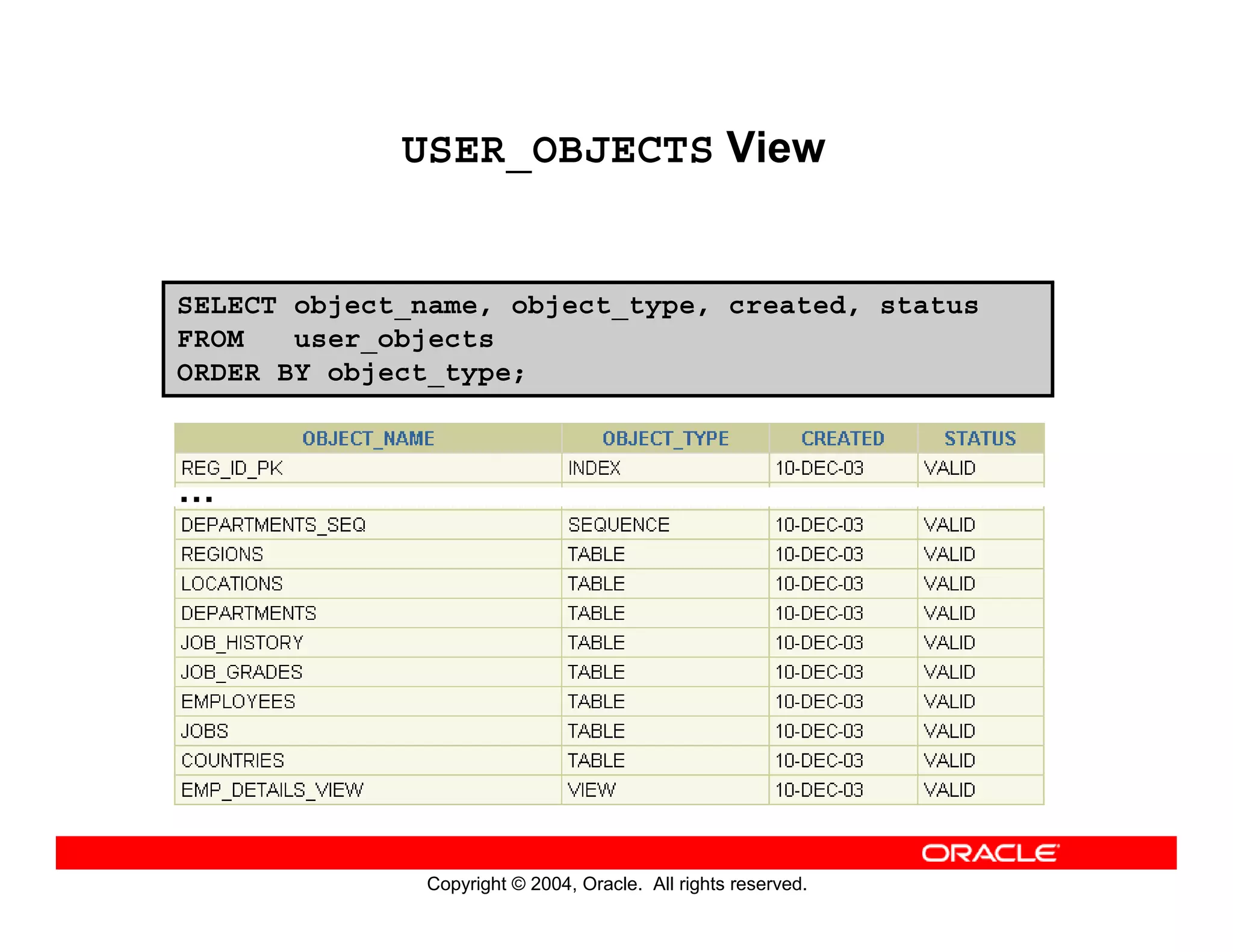
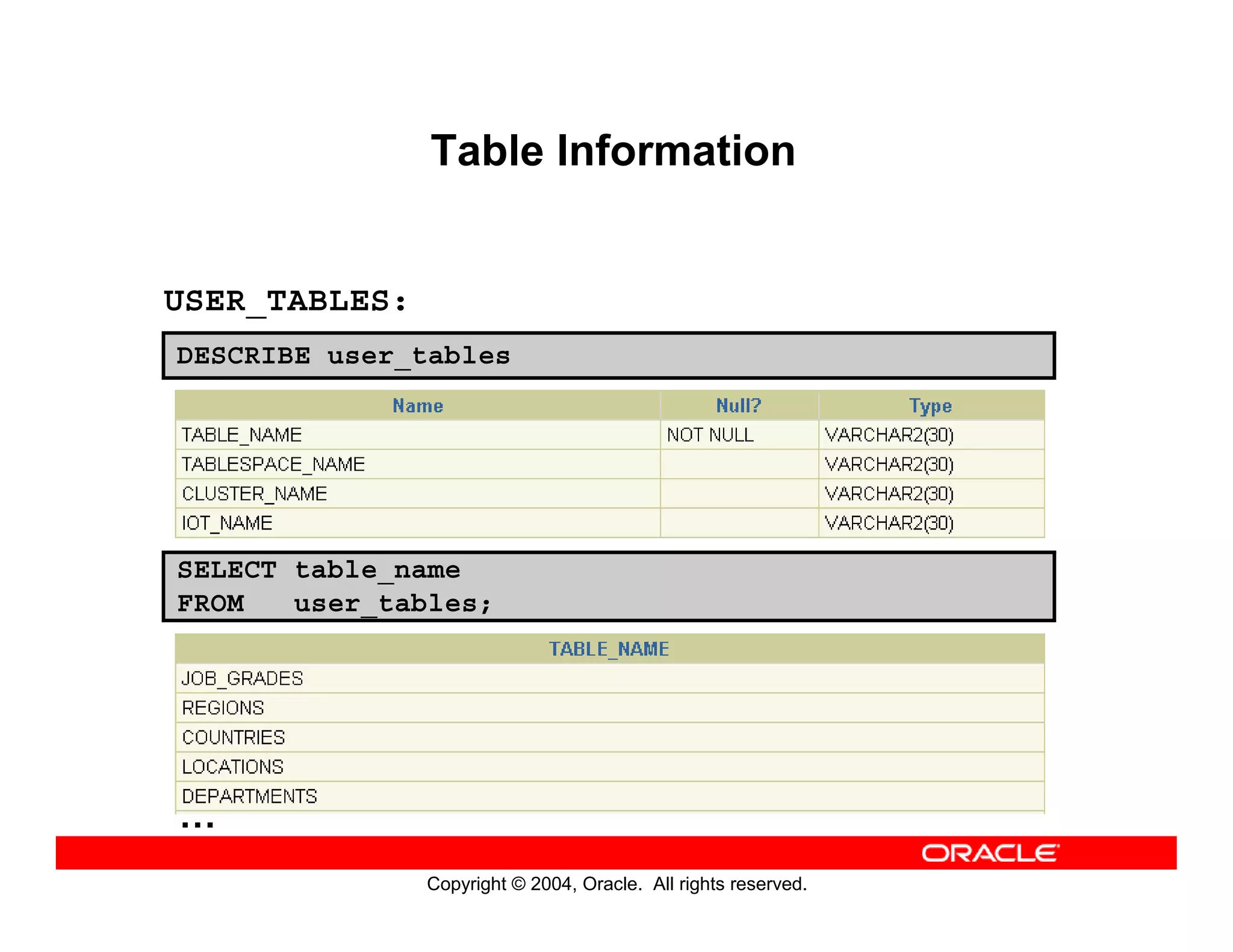
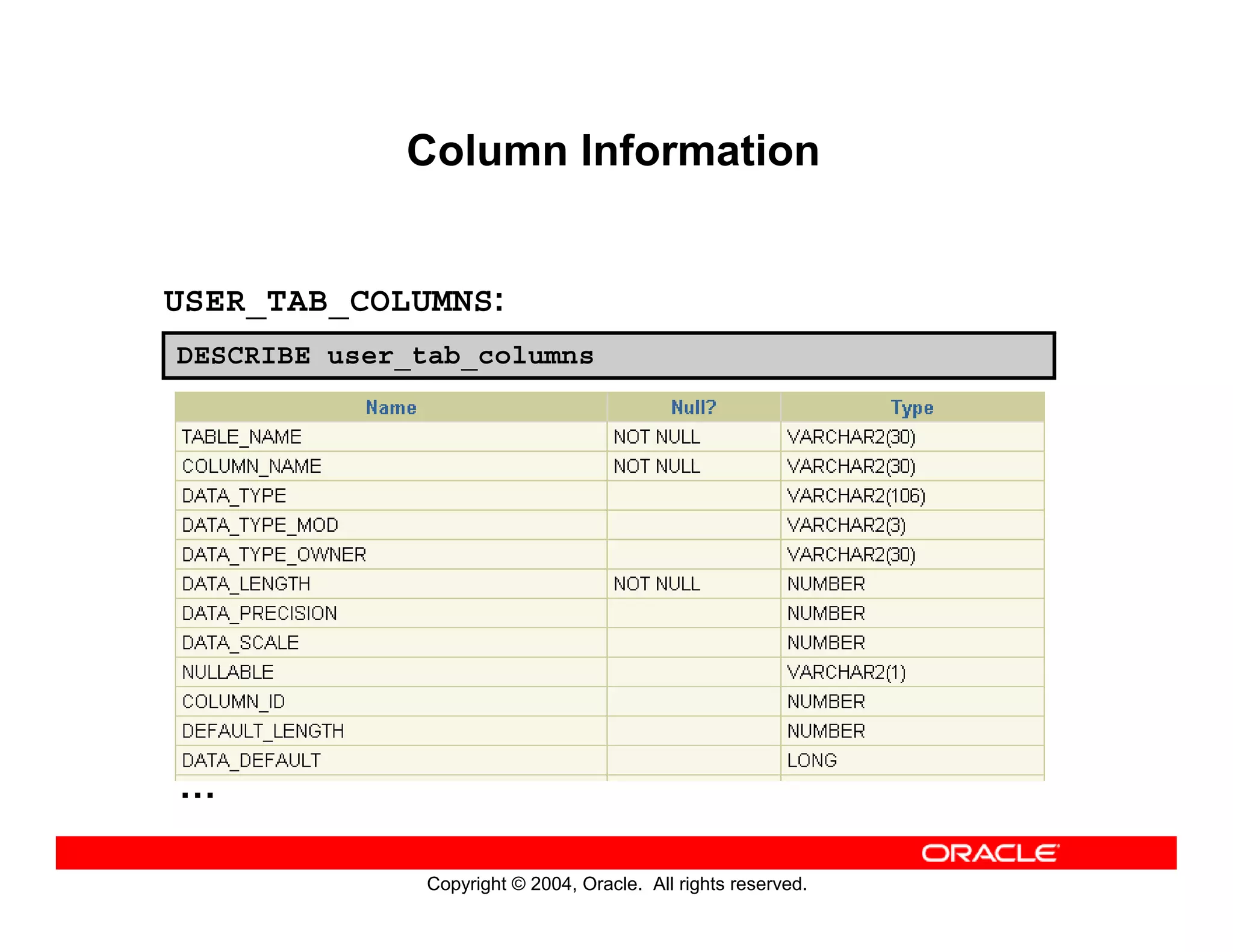
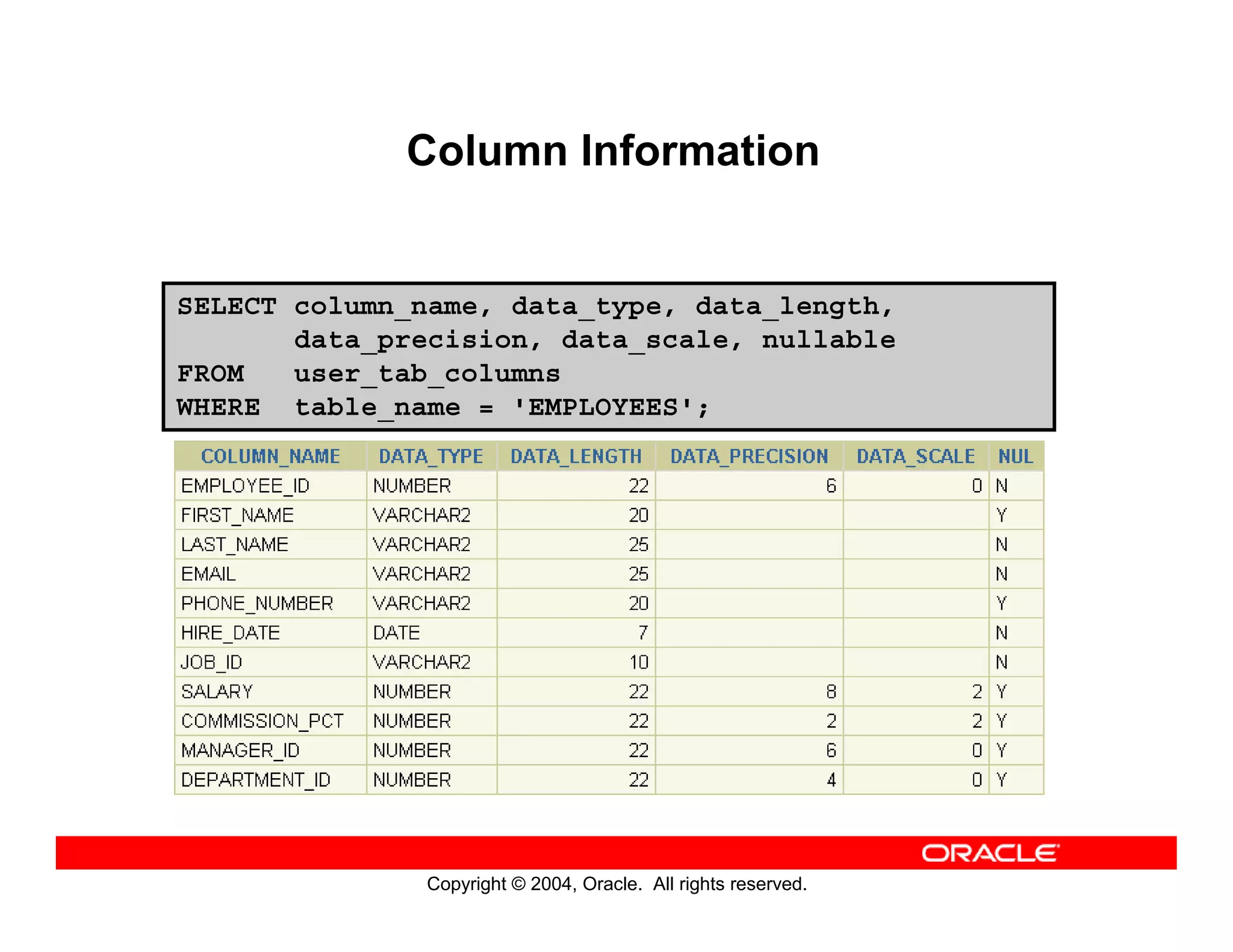
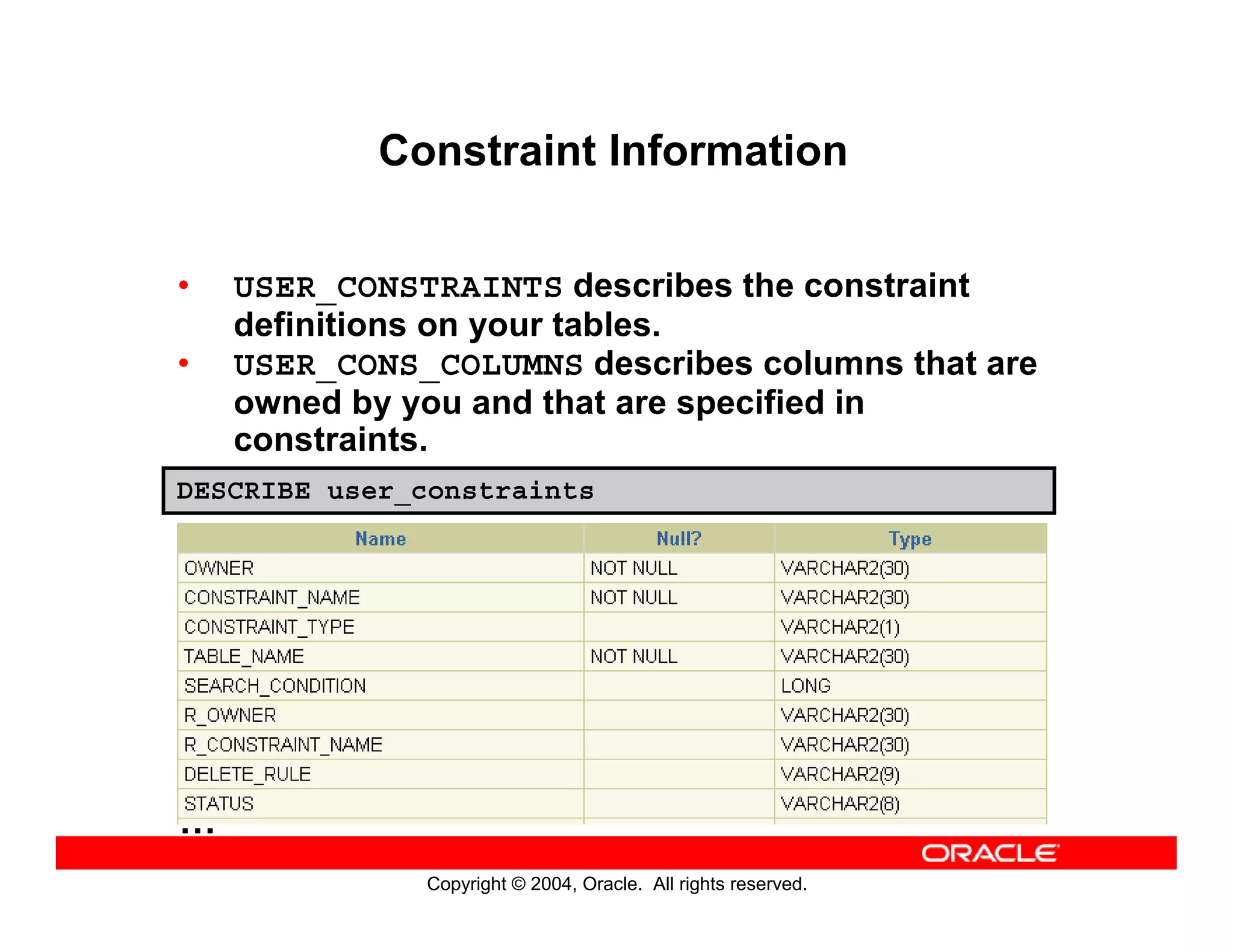
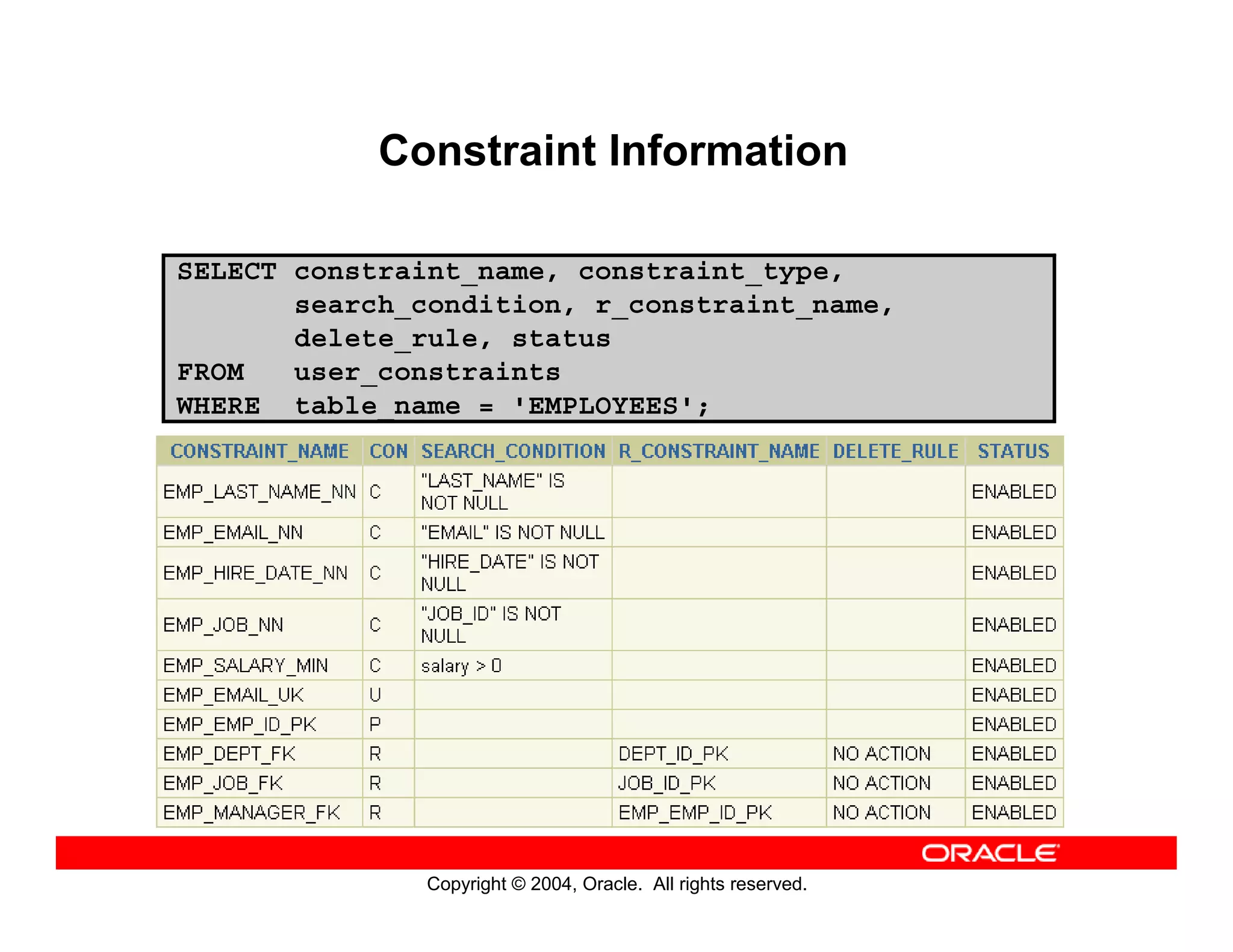
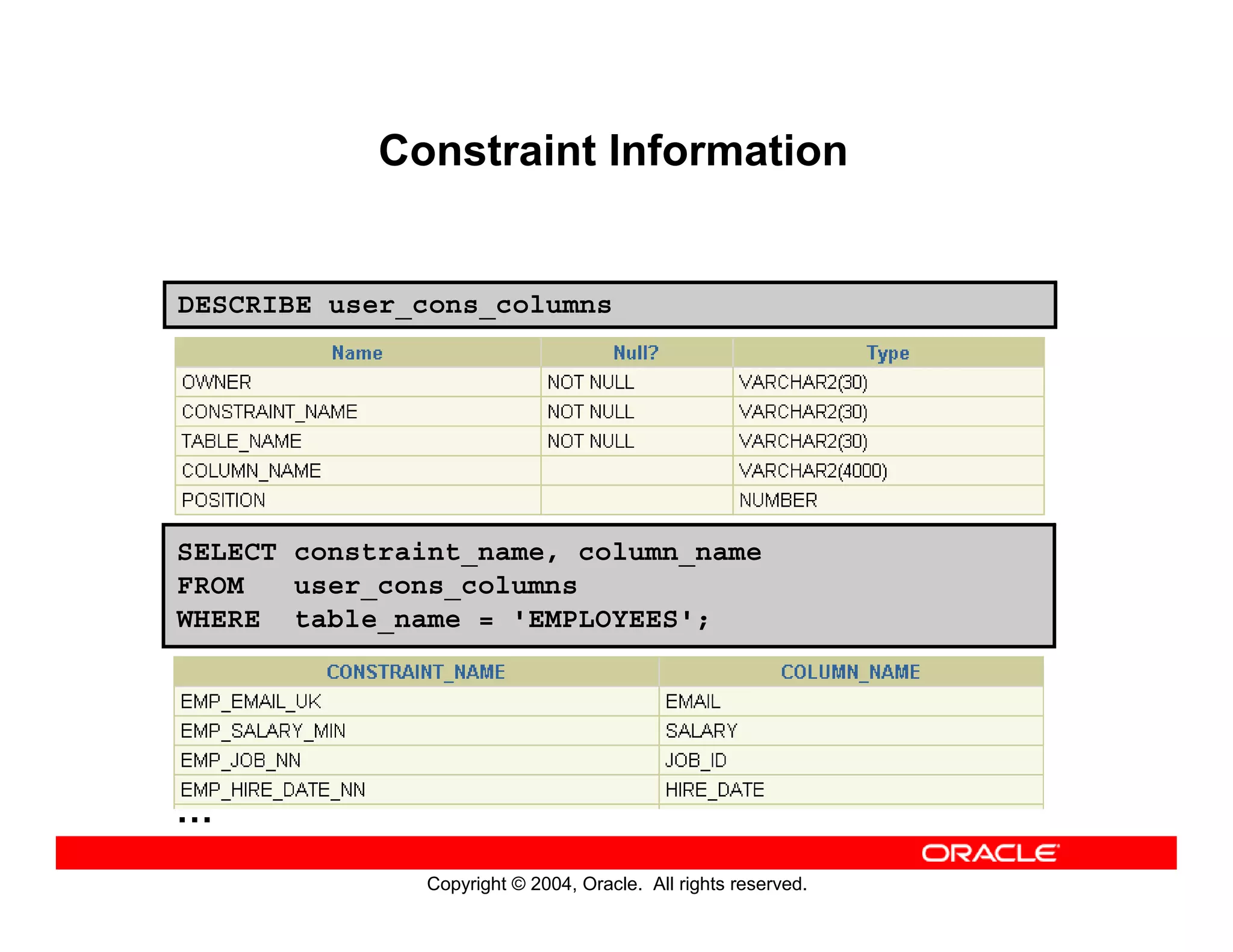
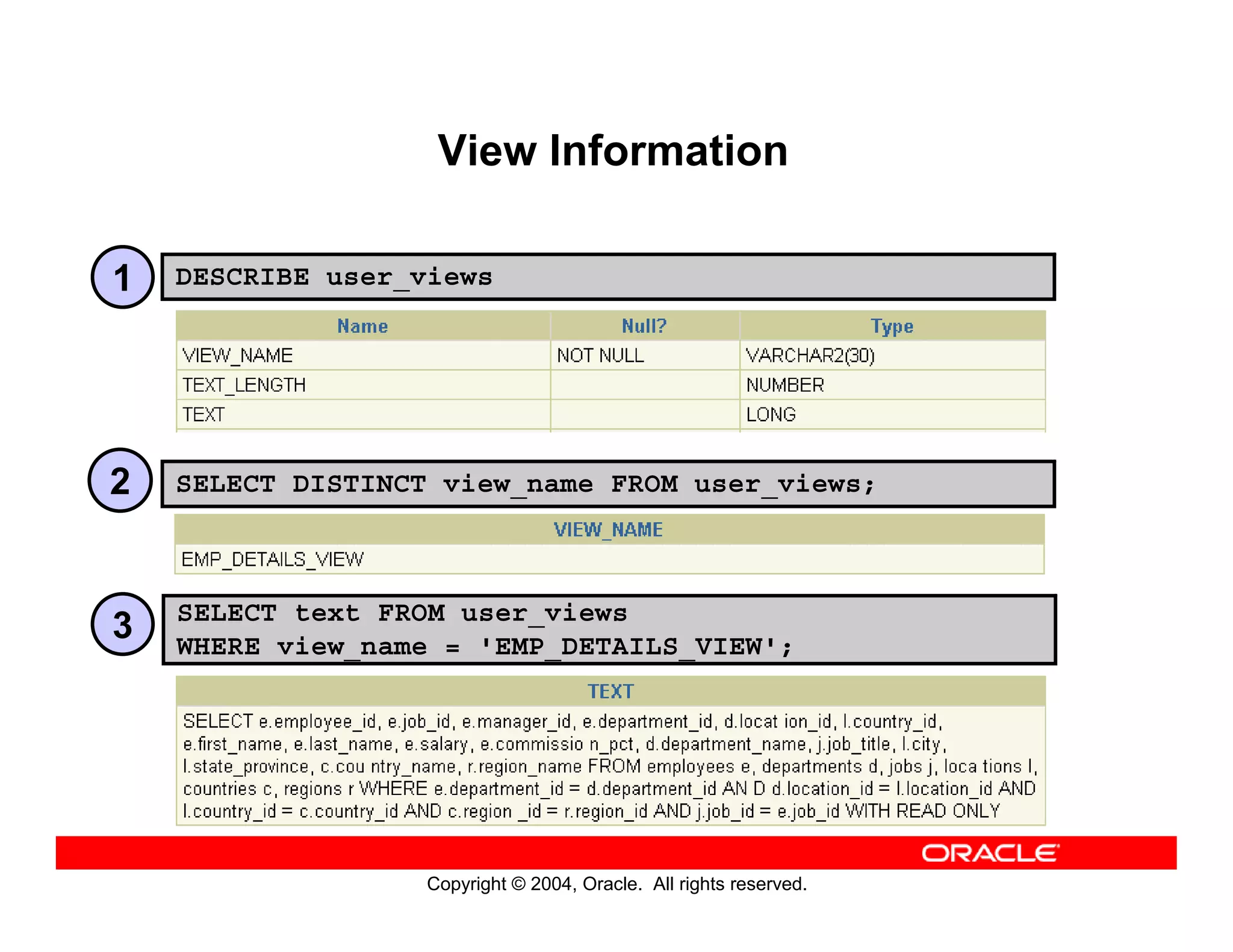
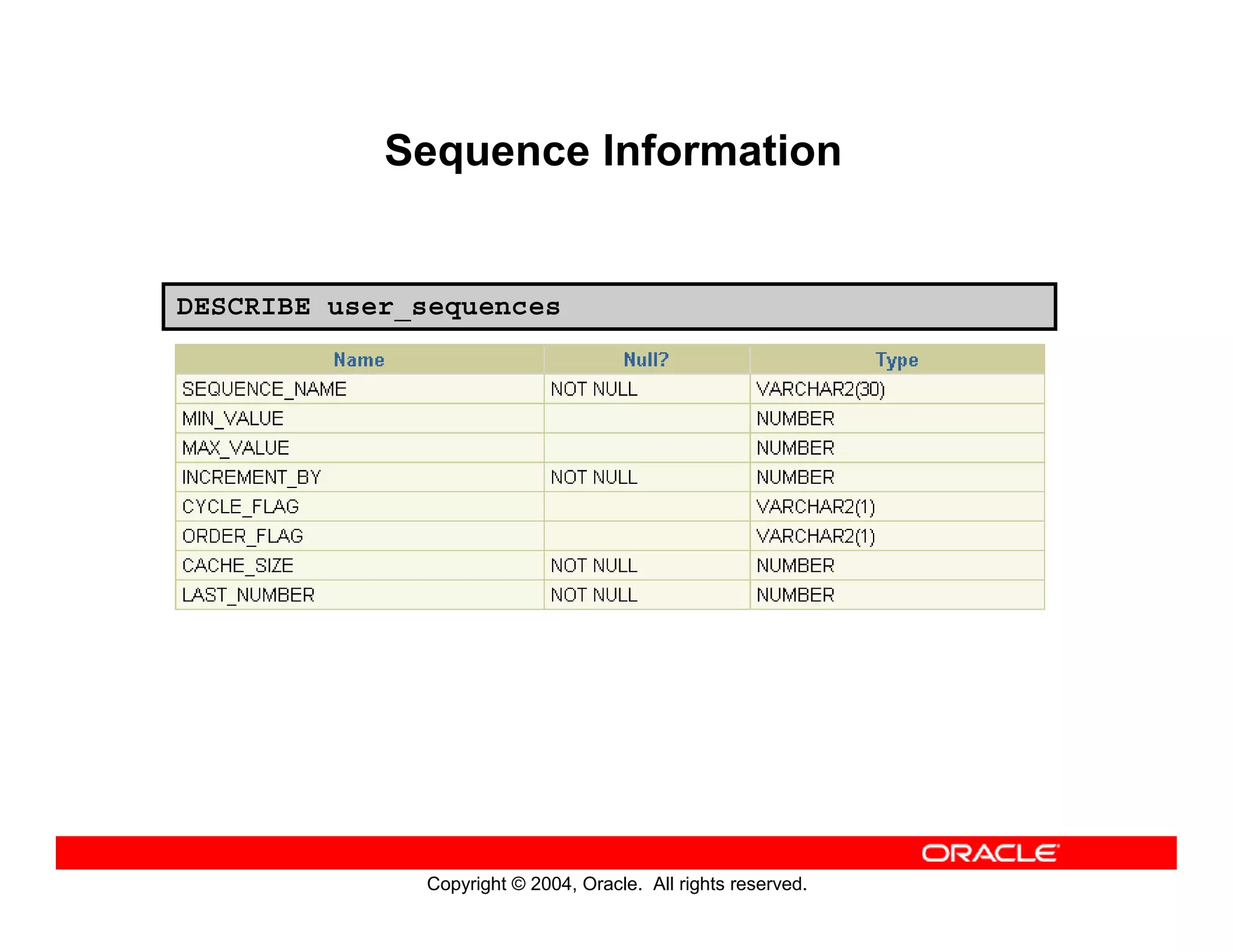
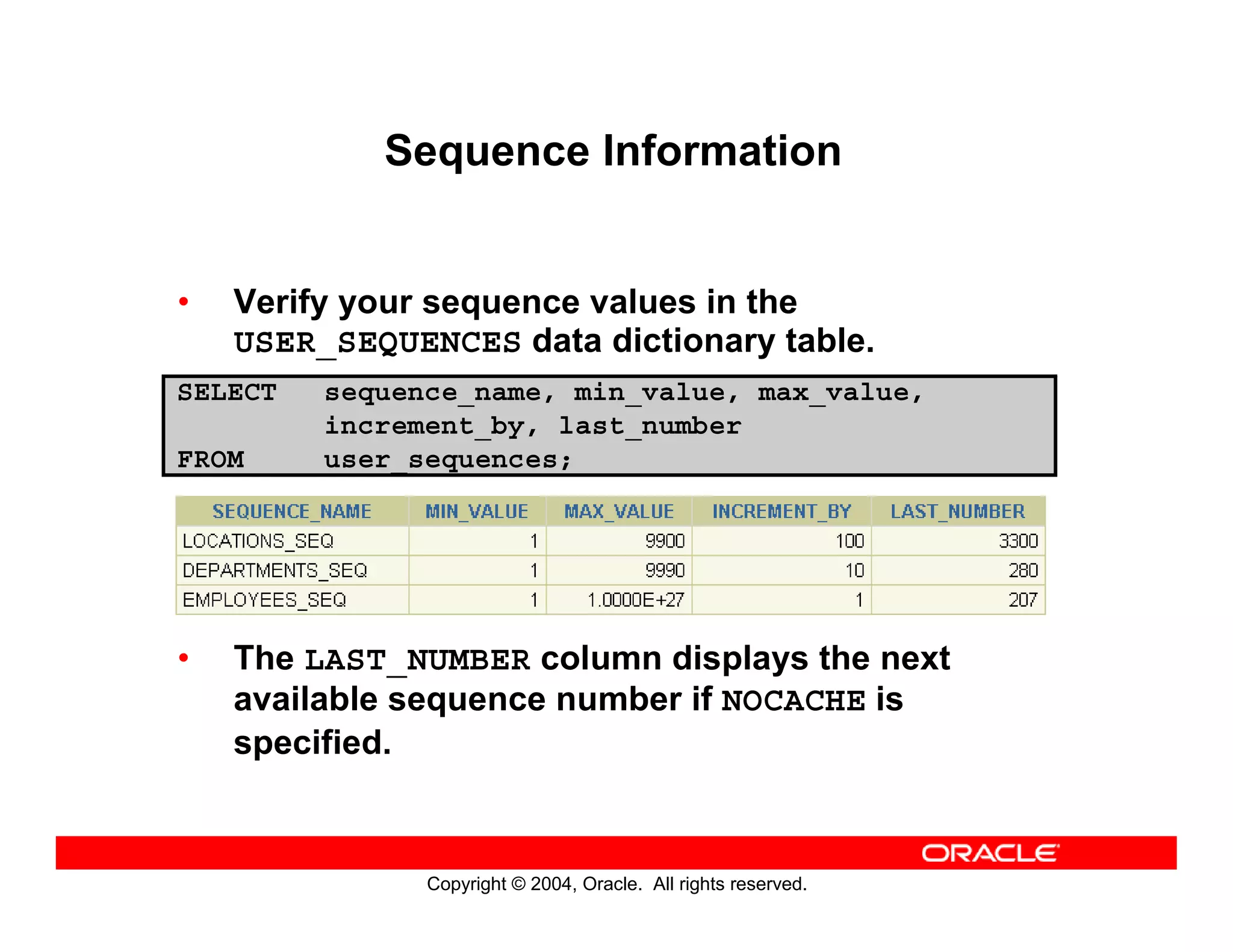
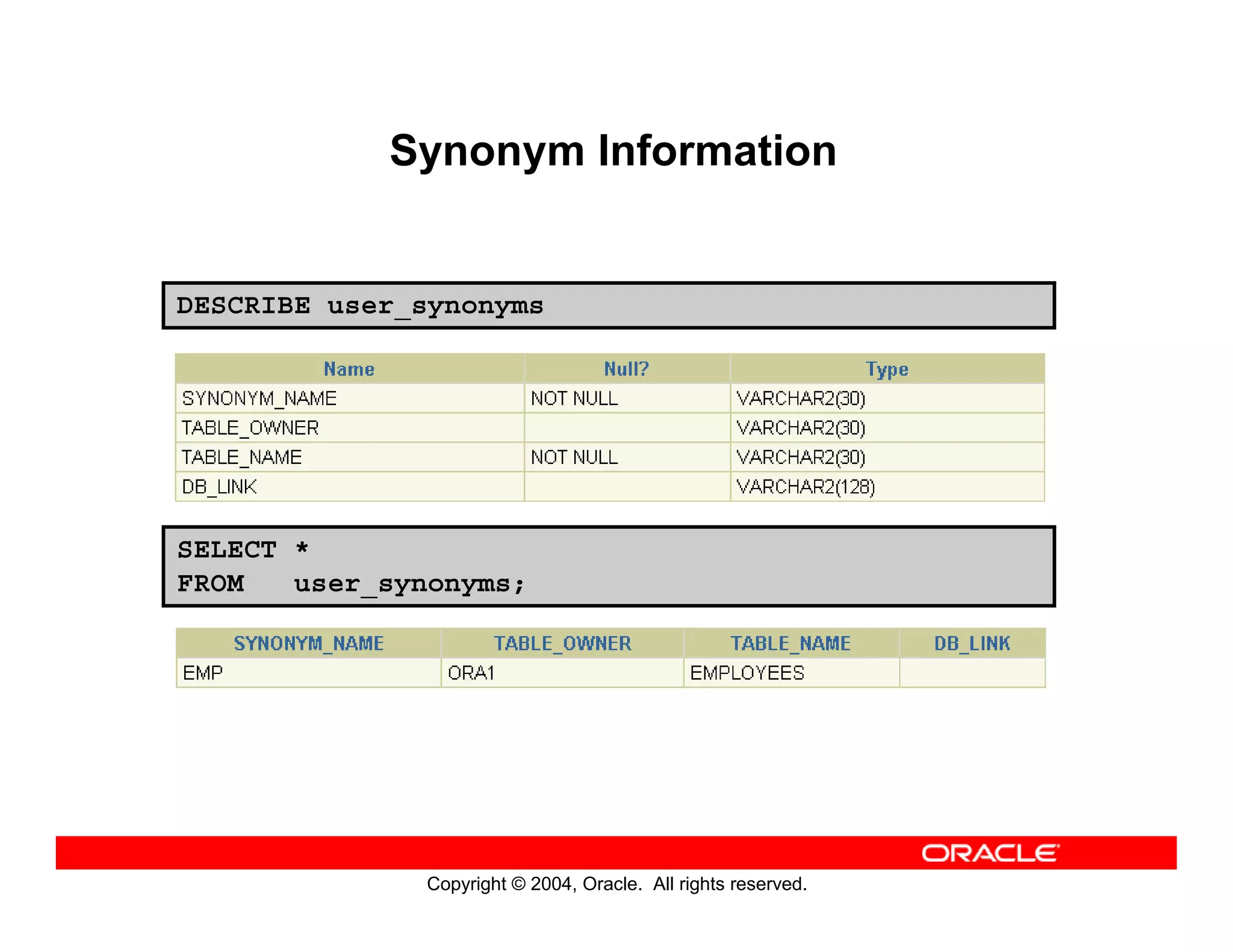
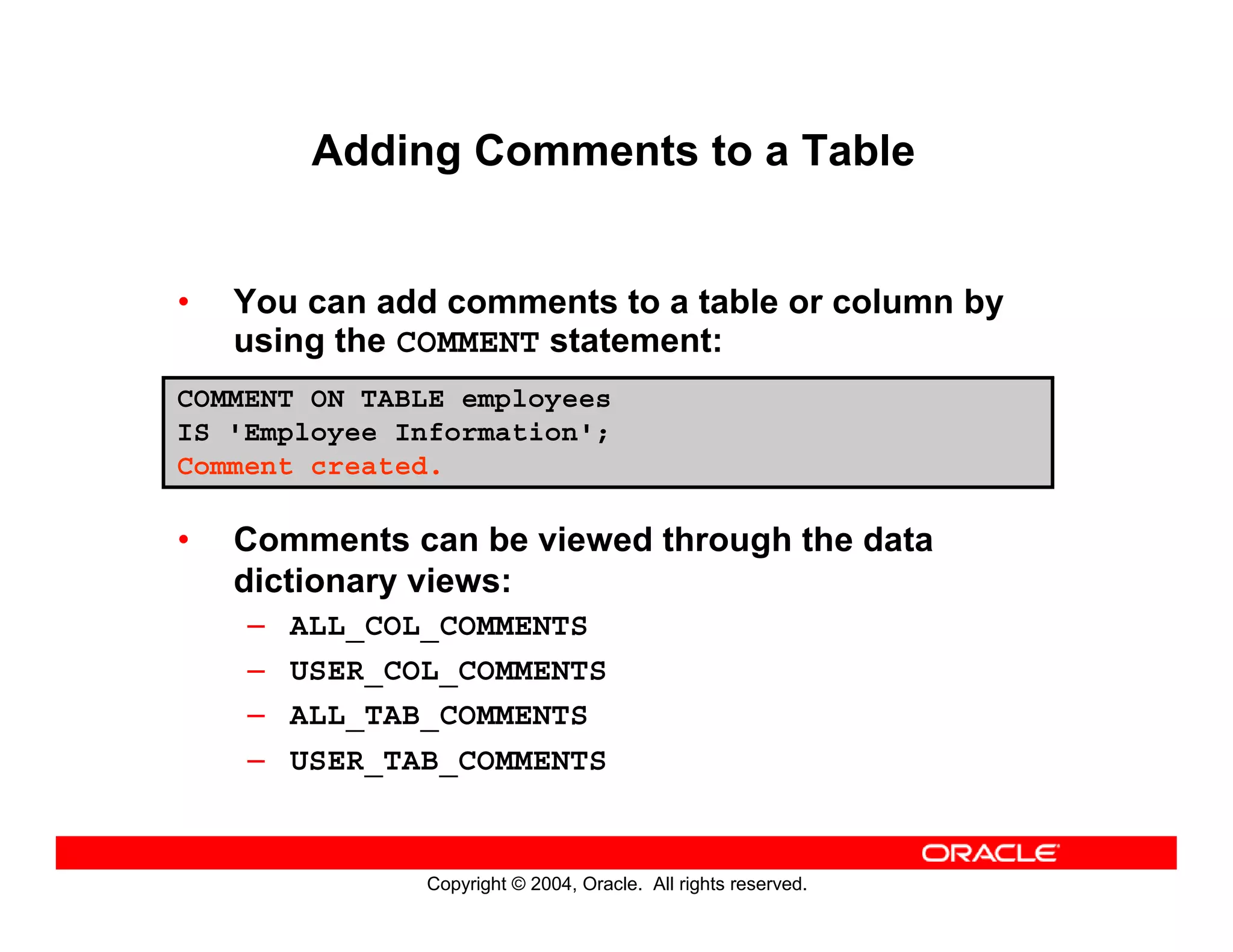
This document discusses how to use data dictionary views in Oracle to manage and obtain information about database objects. It describes the various data dictionary views such as USER_OBJECTS, USER_TABLES, USER_TAB_COLUMNS, USER_CONSTRAINTS, and others that provide metadata about tables, columns, constraints, views, sequences, and synonyms. It also covers adding comments to tables and querying comment information from data dictionary views.