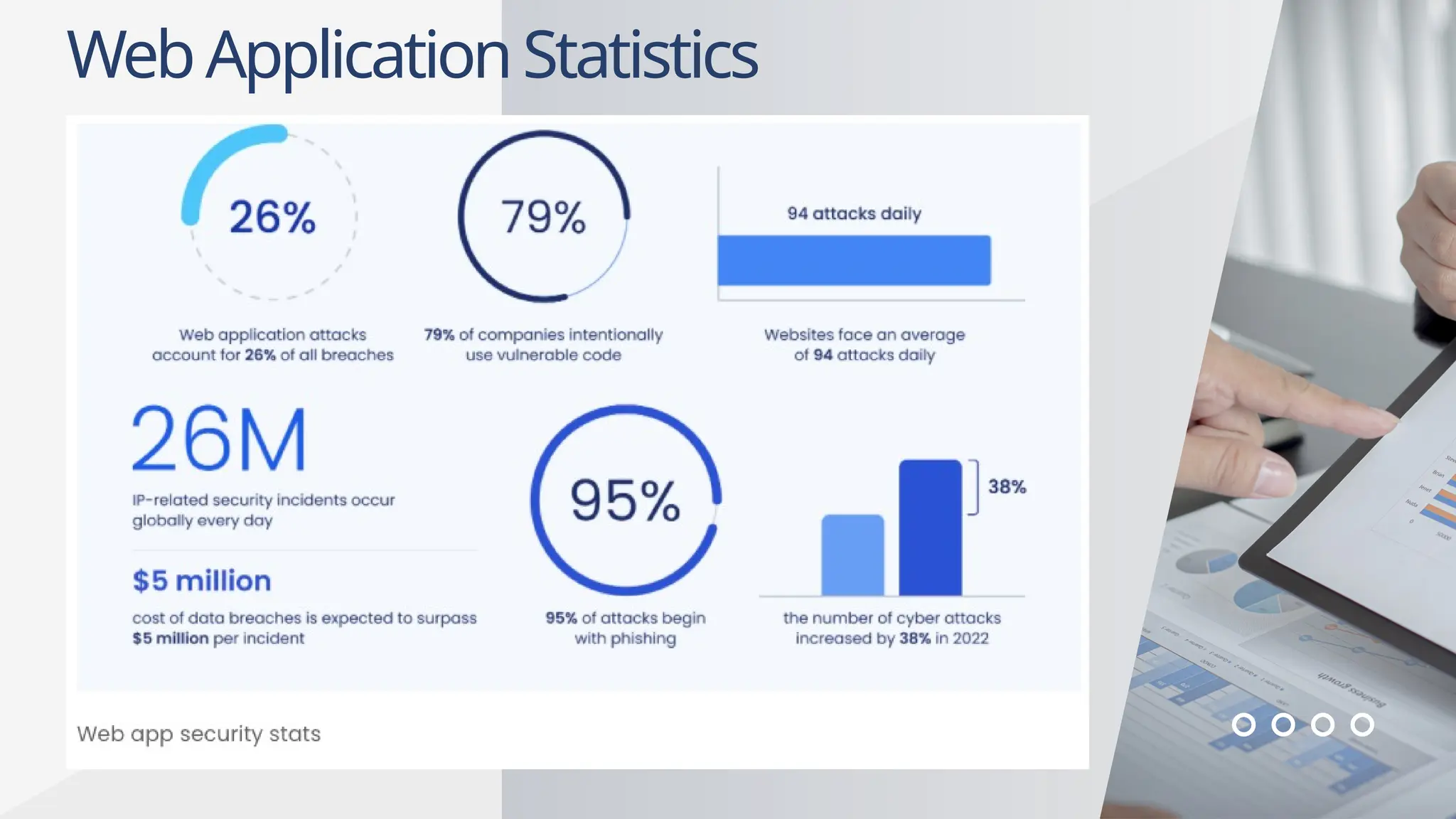
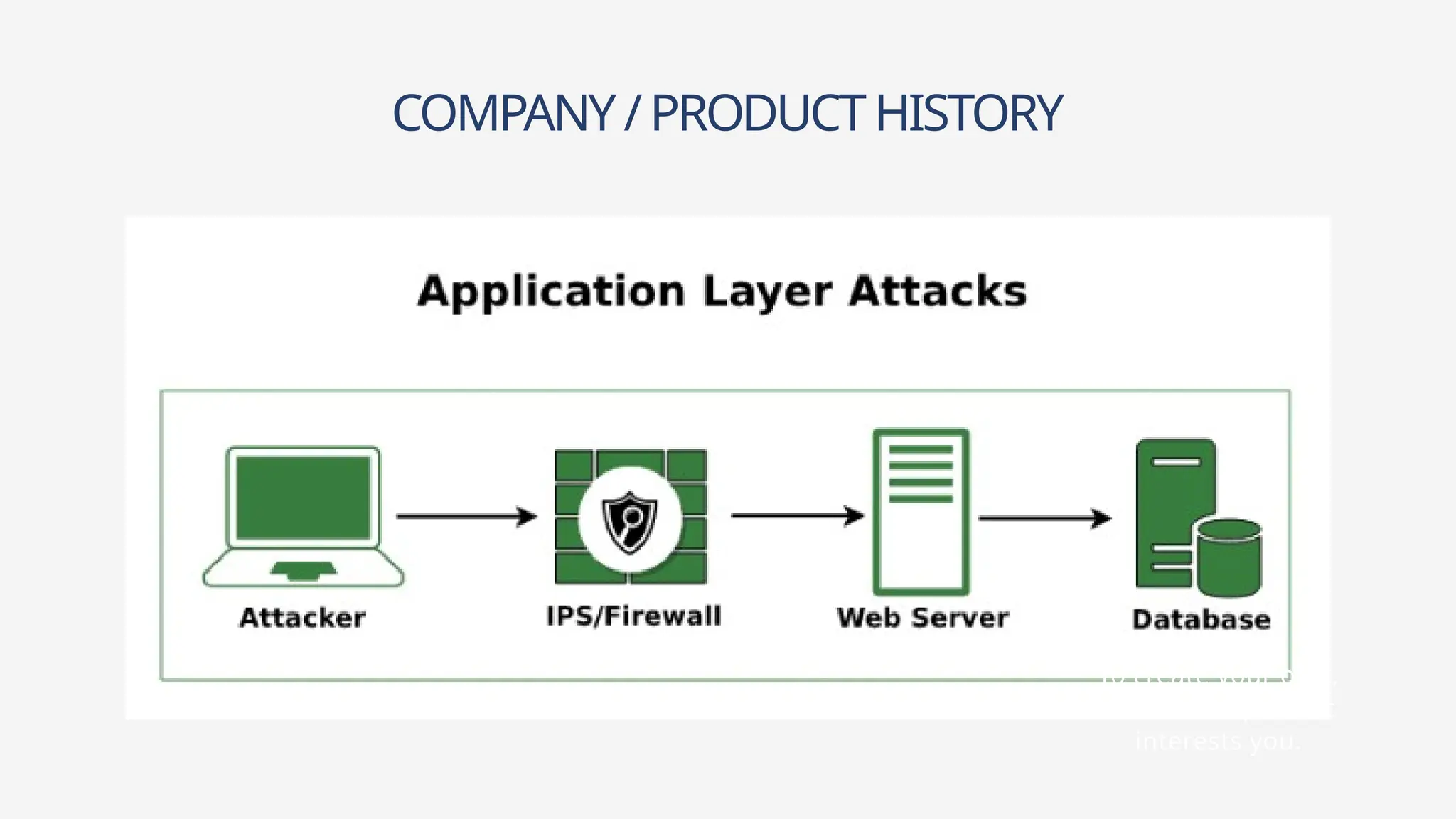
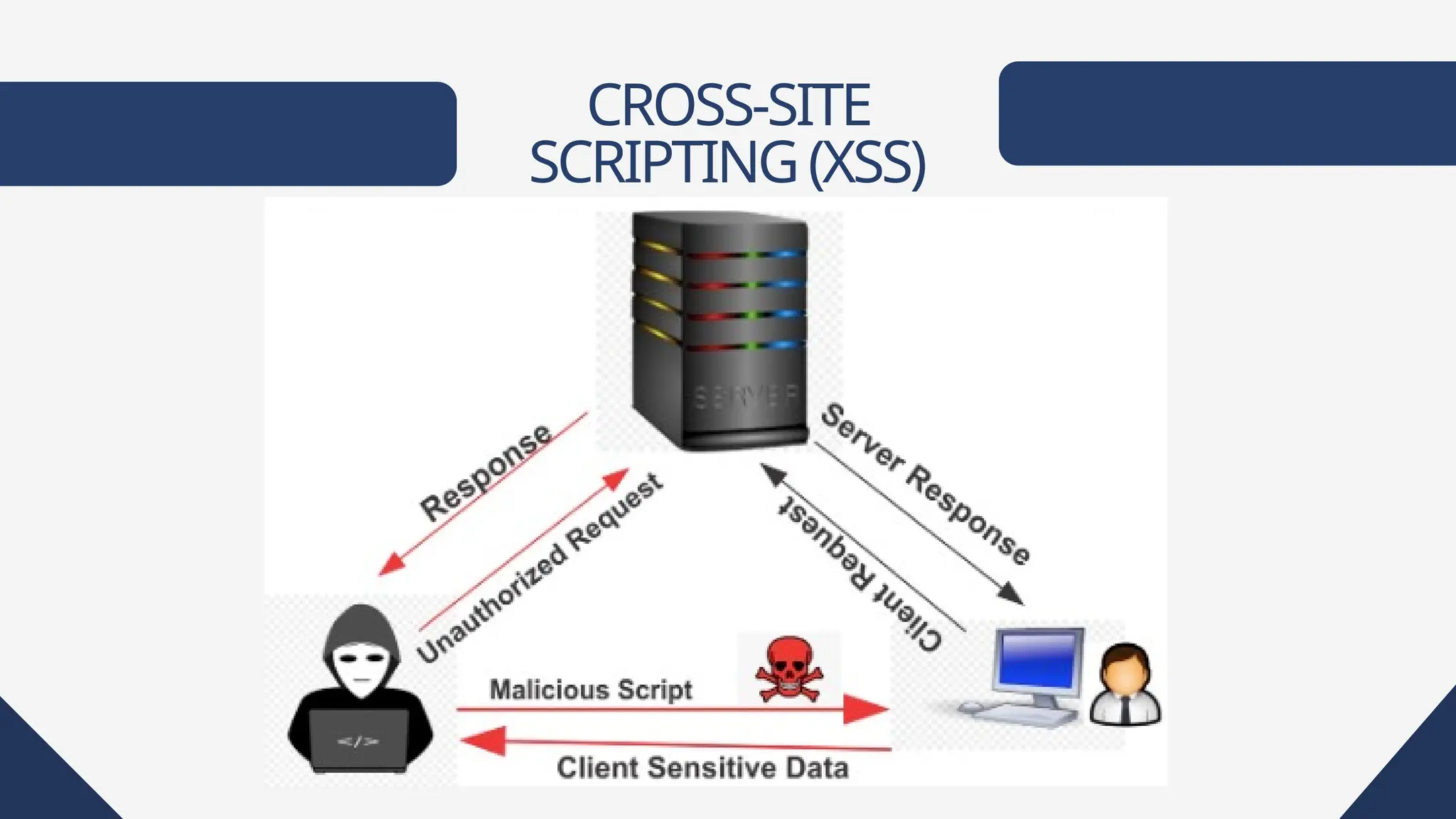
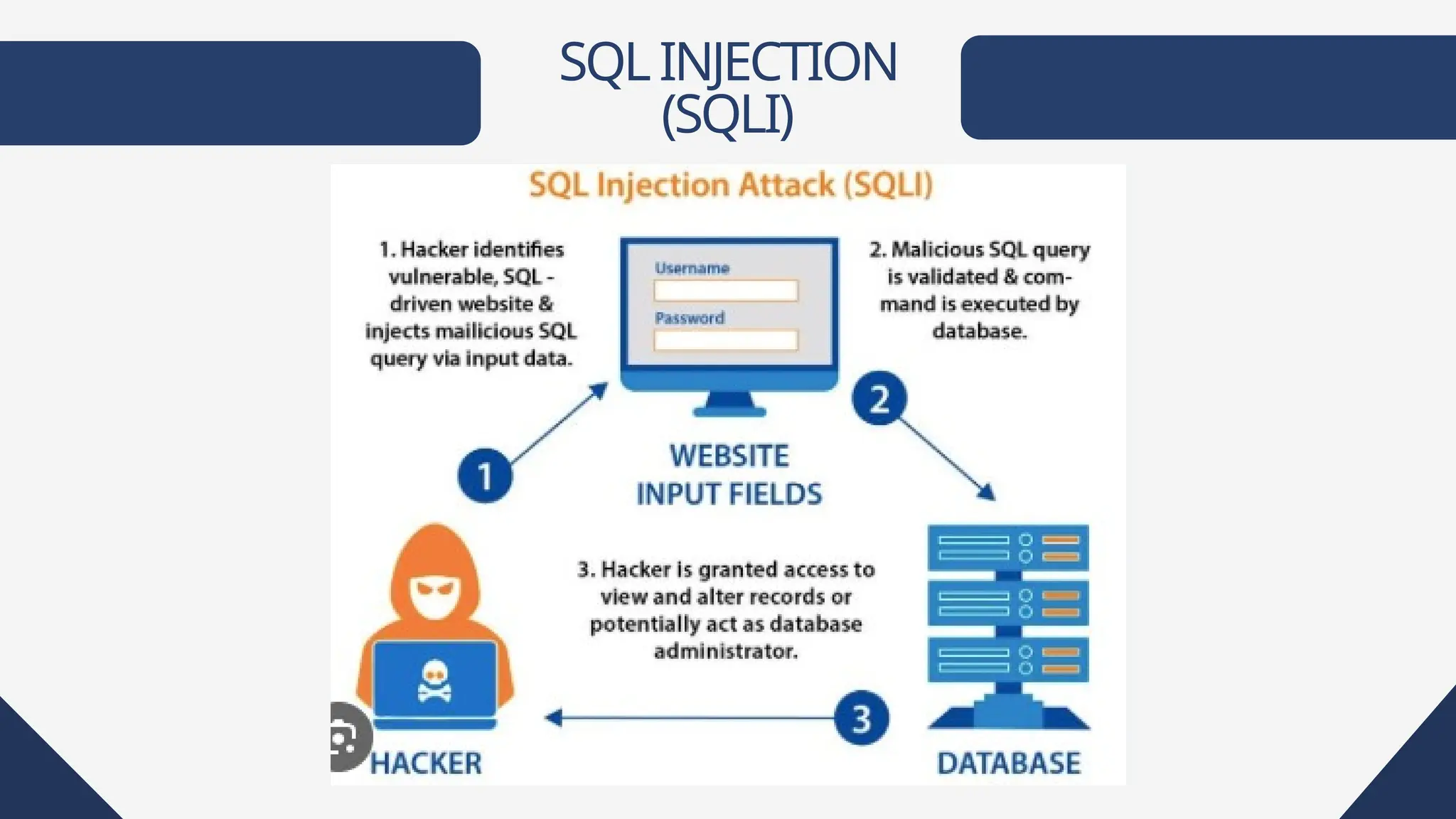
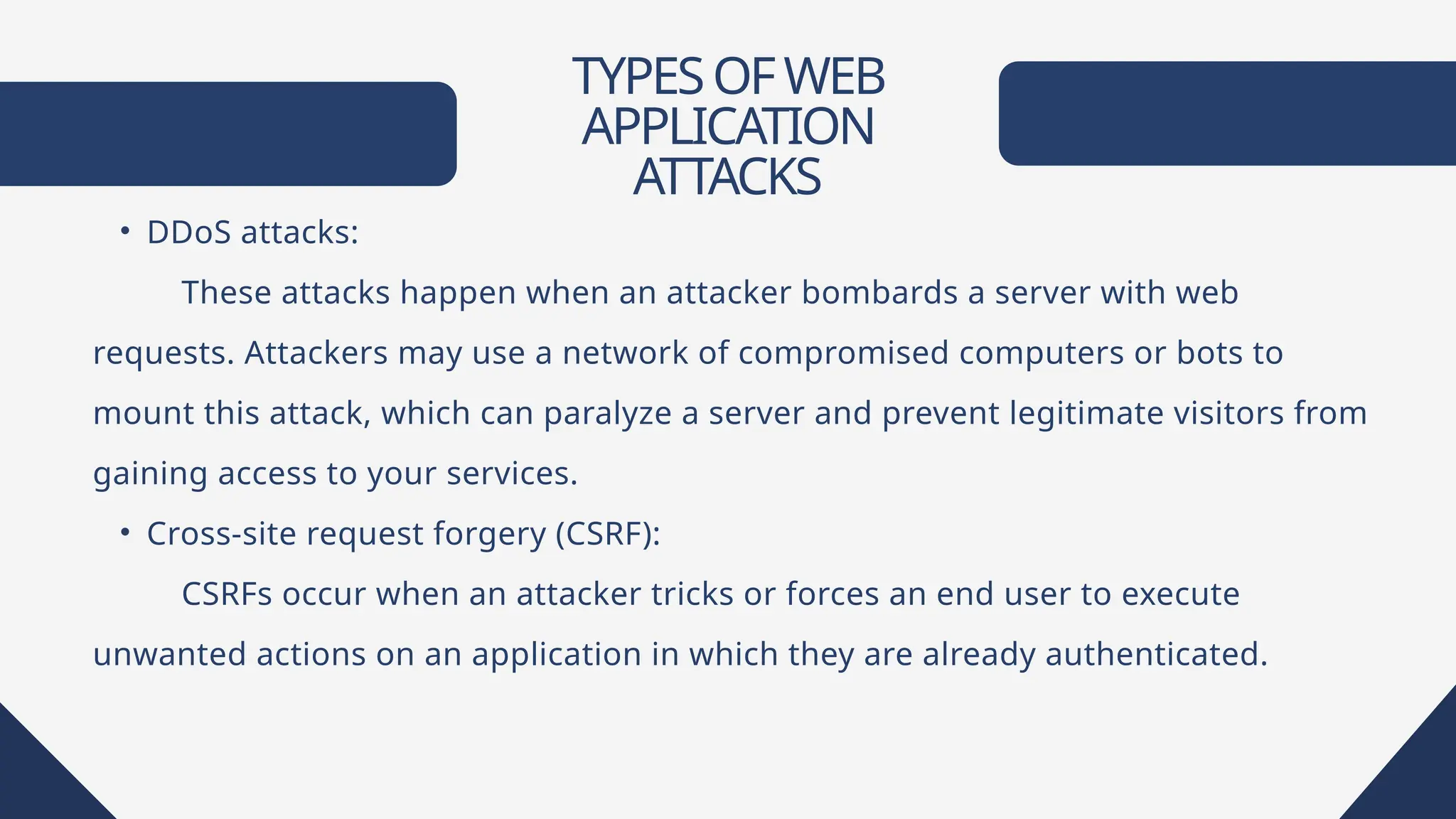
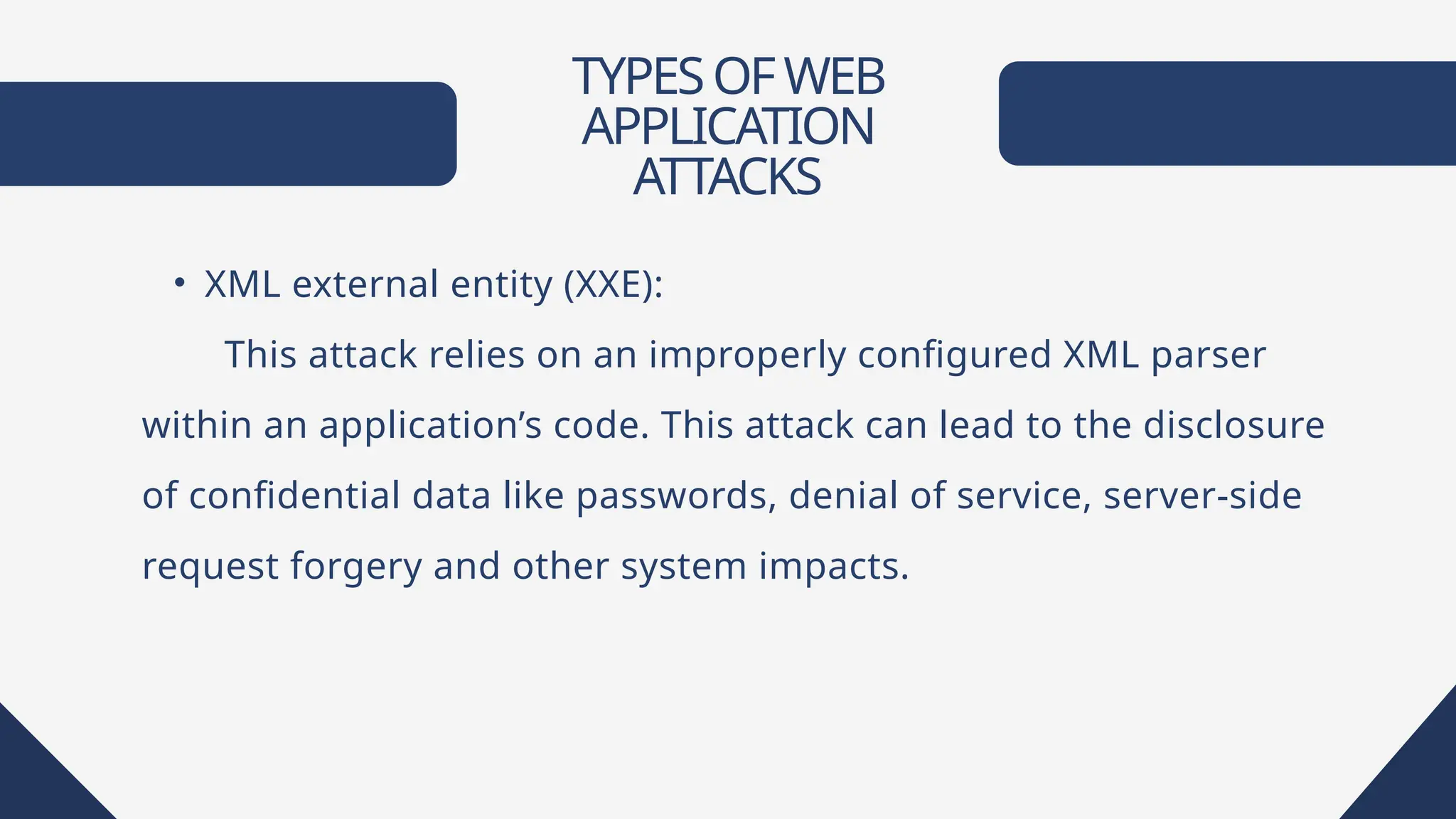
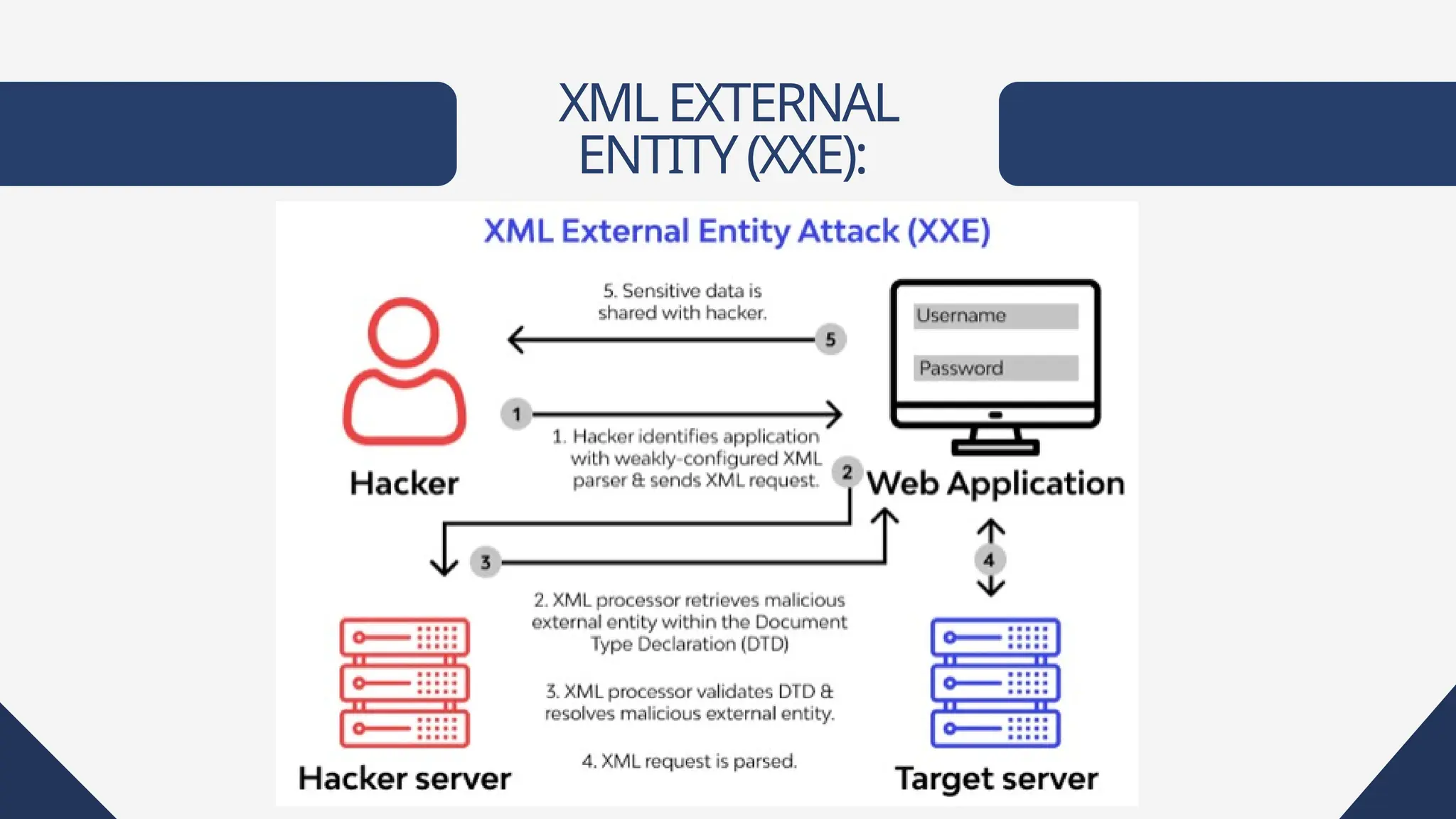
Web applications are software accessible via web browsers, distinct from local apps. Various web application attacks, including cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection (SQLi), and DDoS attacks, exploit vulnerabilities leading to unauthorized access and data theft. Protection measures include automated vulnerability scanning, web application firewalls, and secure development practices.