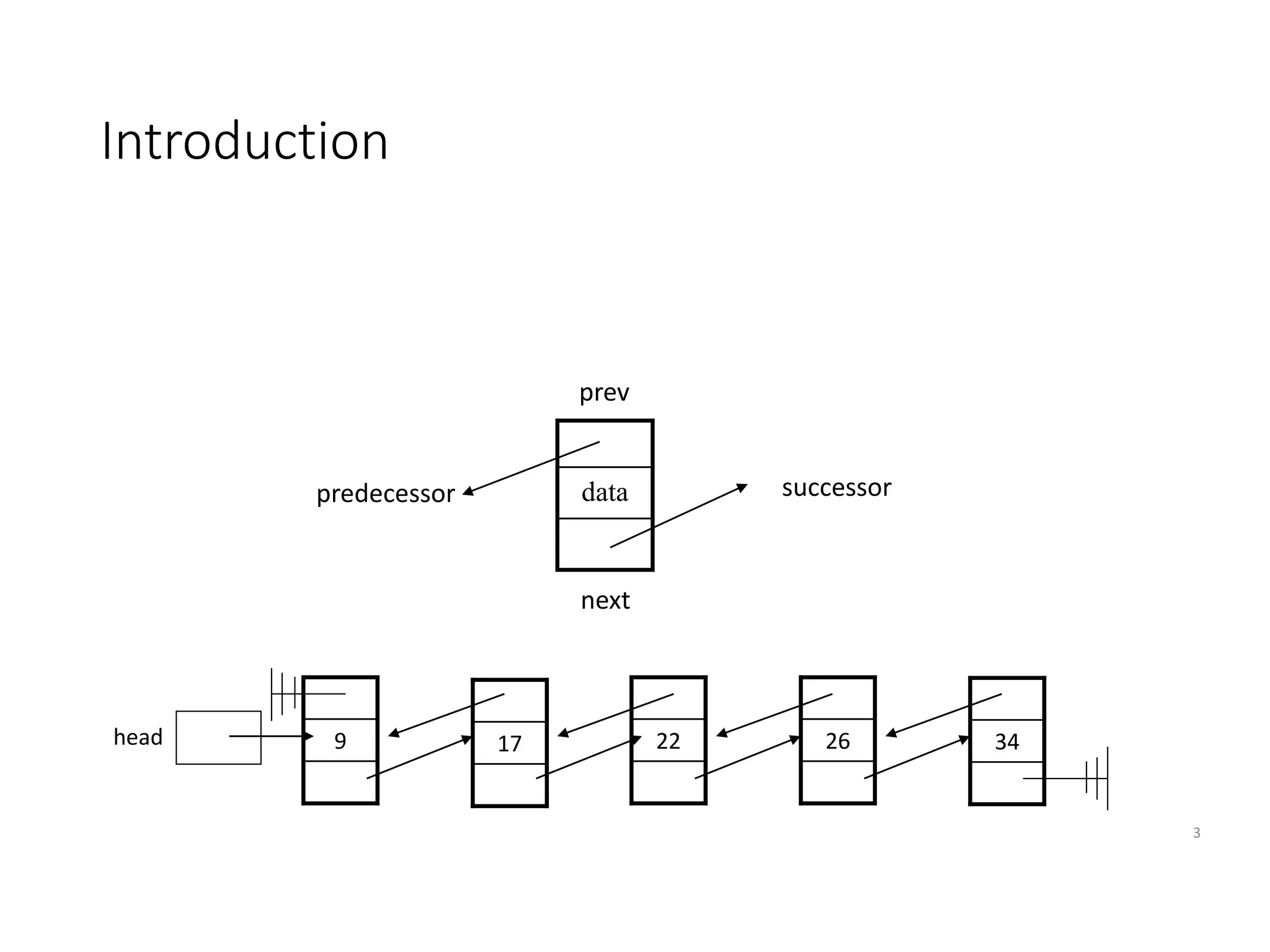
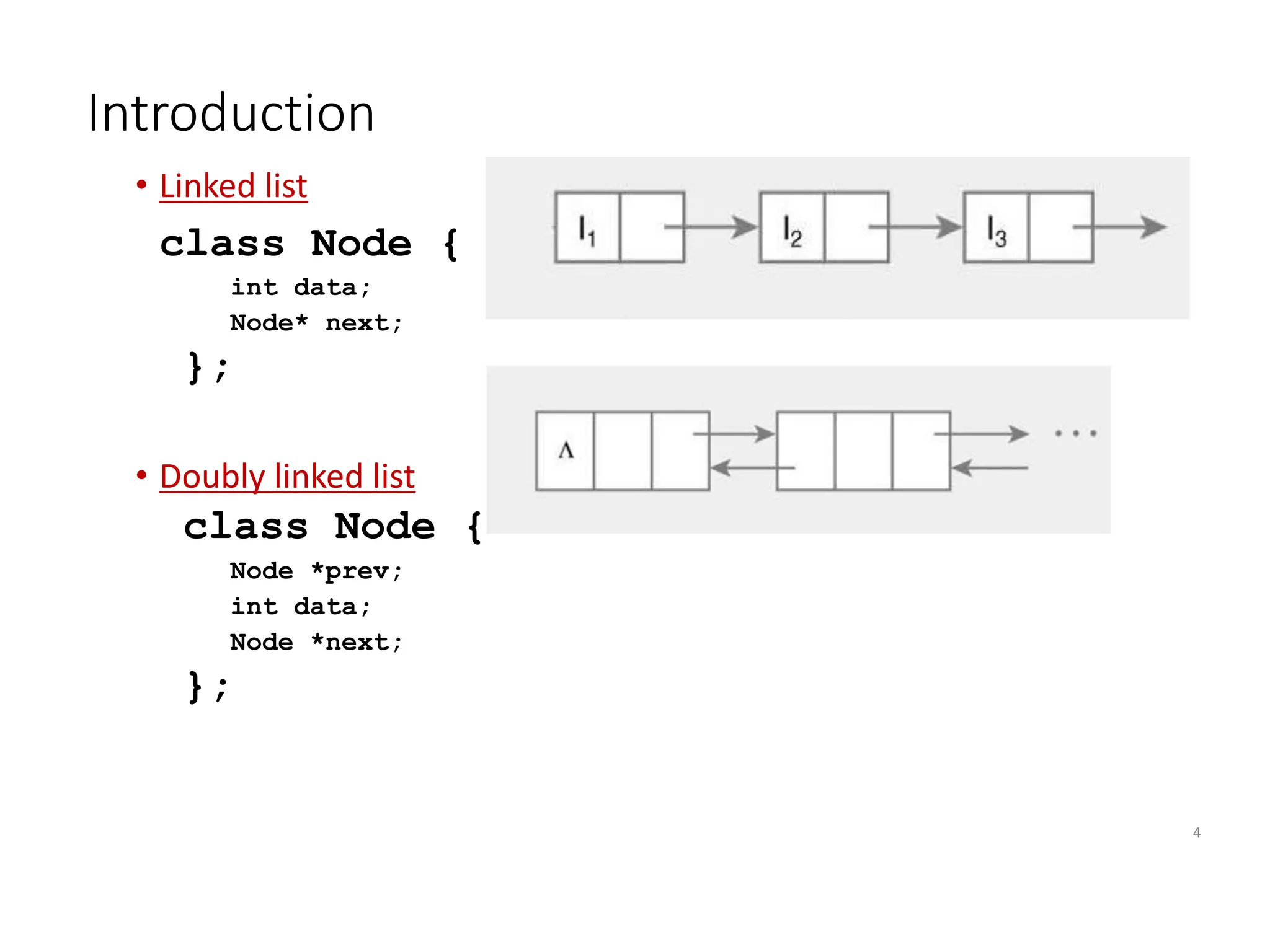
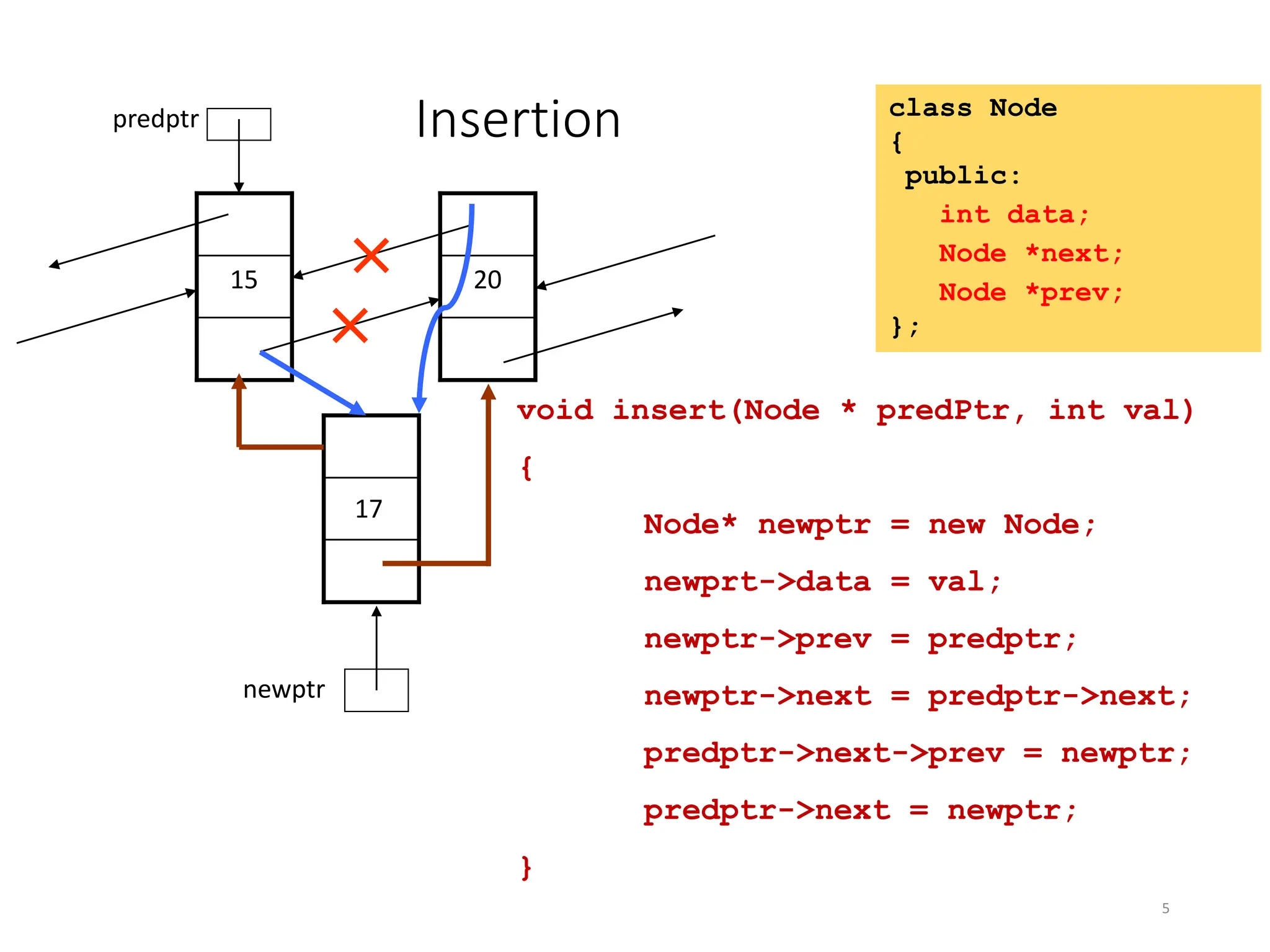
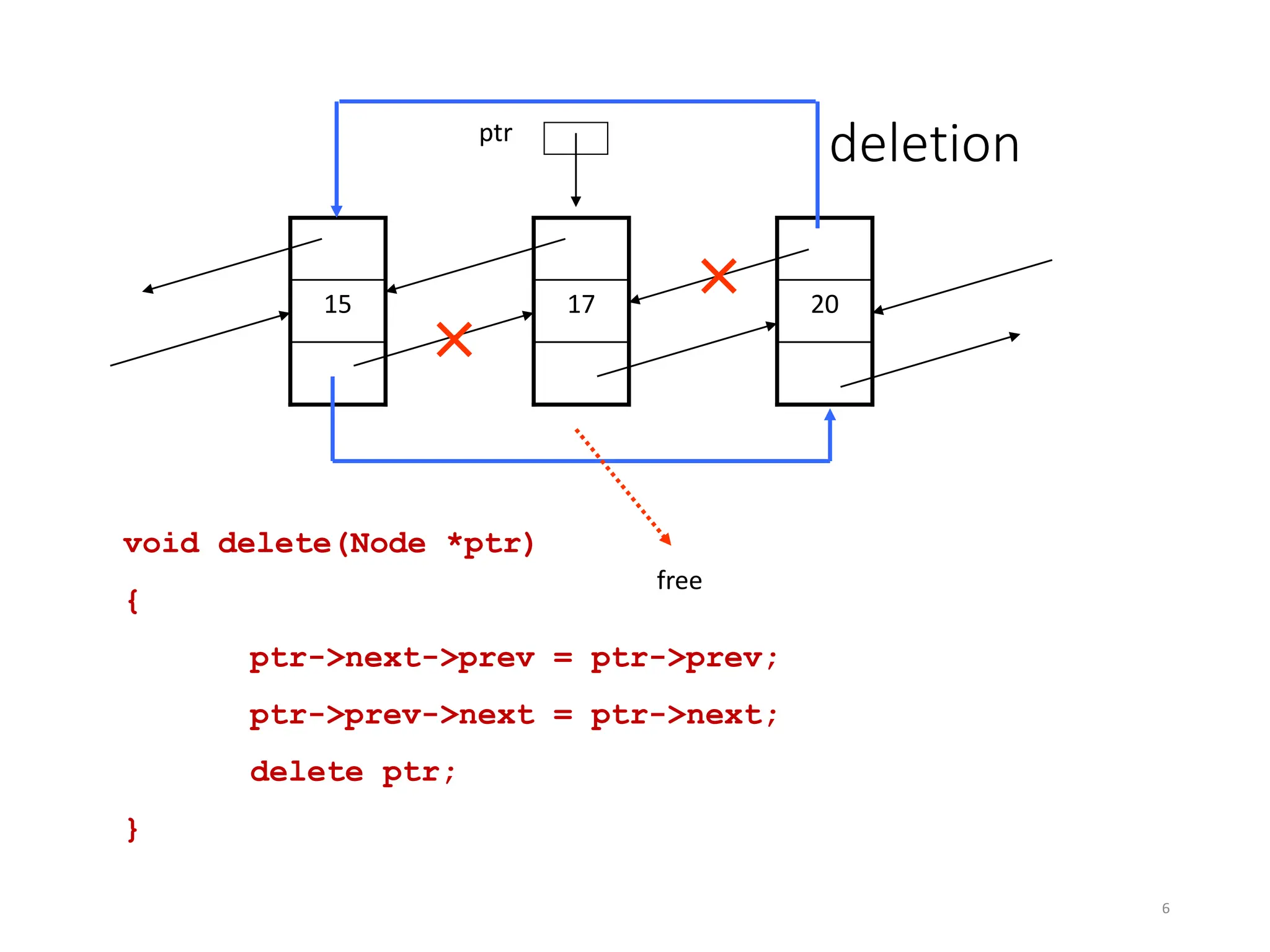
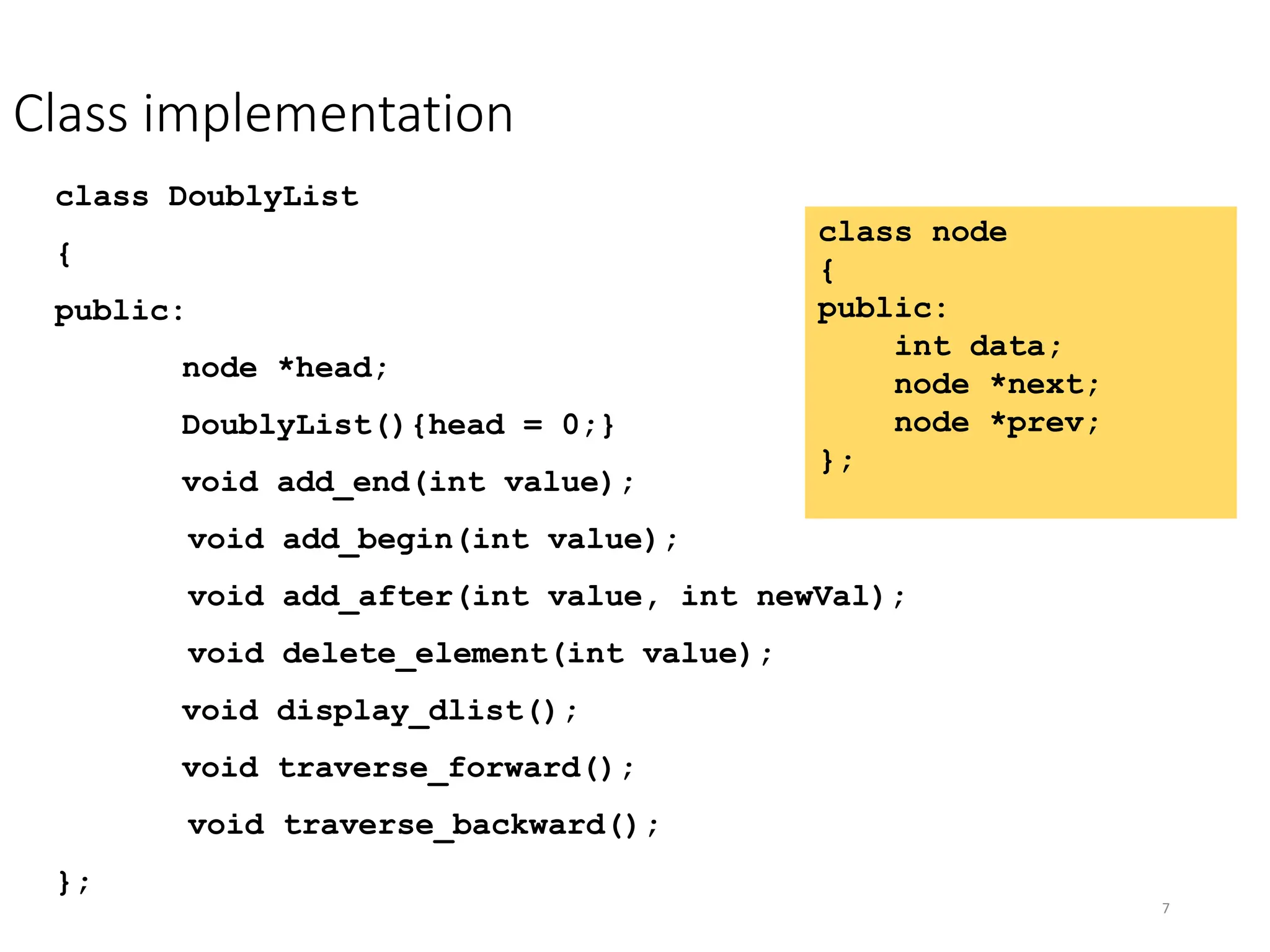
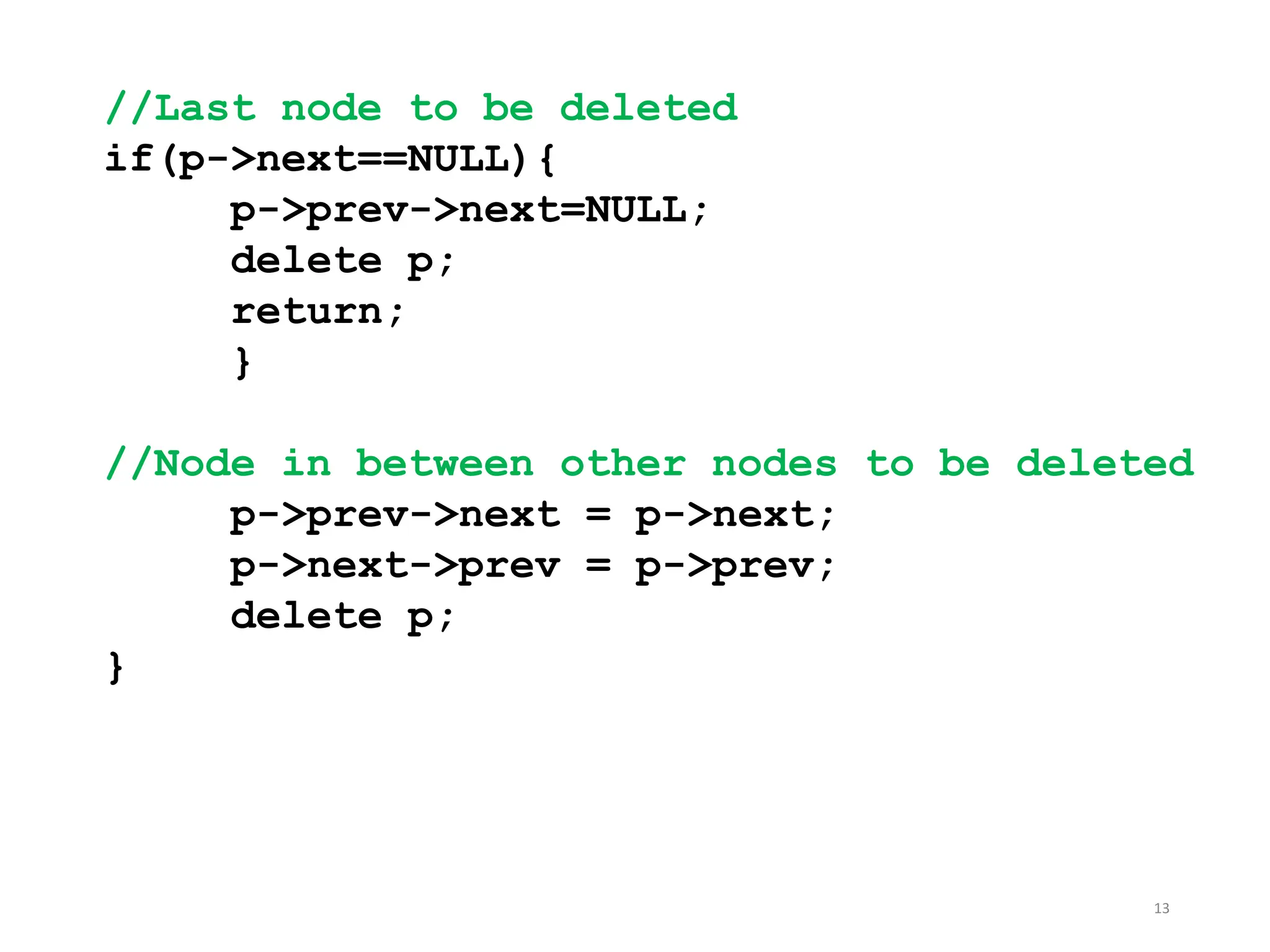
The document provides an introduction to doubly linked lists, highlighting their structure where each node contains two pointers: one for the next node and one for the previous node. It presents classes and methods for inserting, deleting, and displaying elements in a doubly linked list. Additionally, the document includes code snippets demonstrating various operations and implementations related to doubly linked lists.