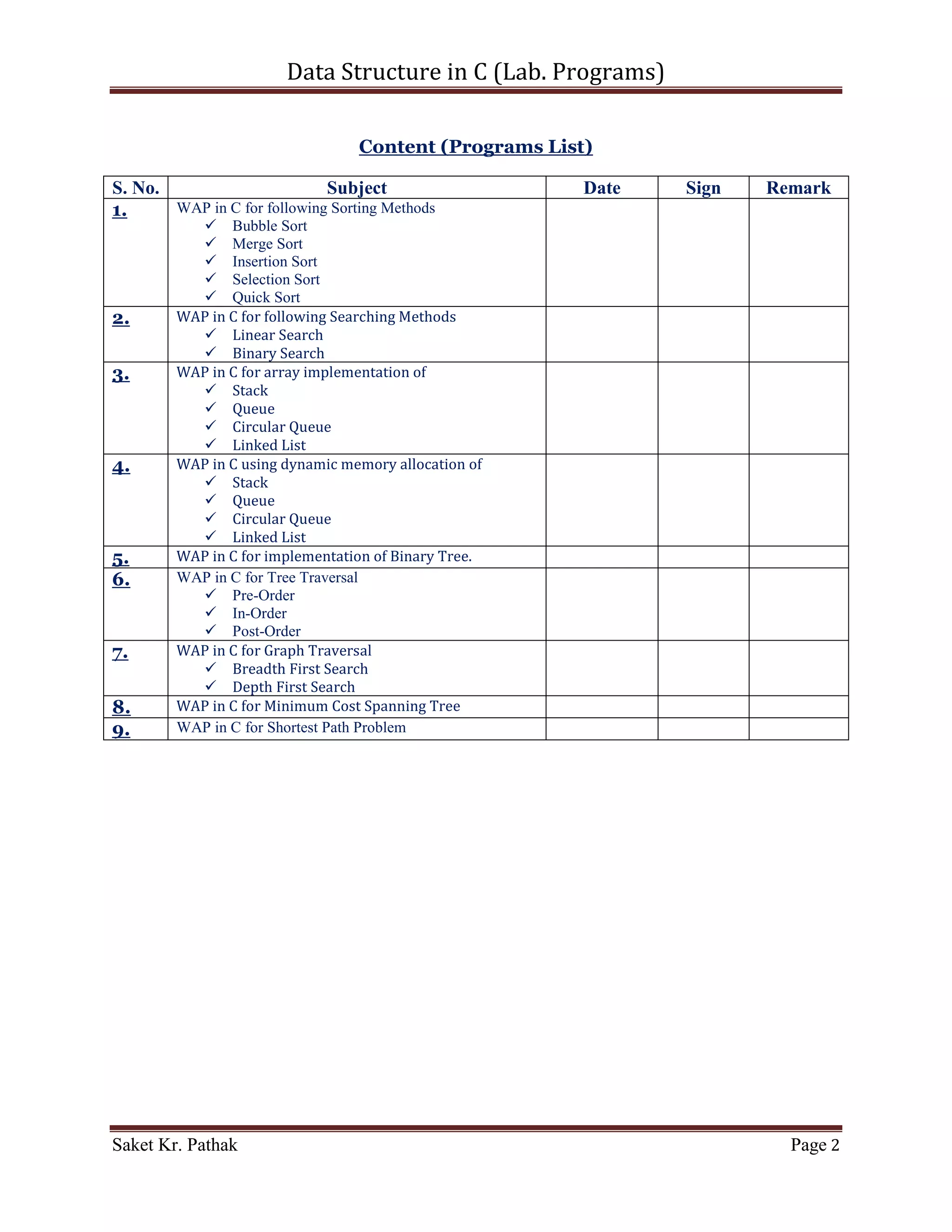
The document details C programming lab exercises focused on data structures and algorithms, including sorting and searching methods like bubble sort, merge sort, insertion sort, selection sort, and quick sort. It provides sample code snippets and algorithm explanations, along with time complexity analysis for each method. The content aims to enhance programming skills and encourage learning through practical implementation.

![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
1. WAP in C for following Sorting Methods
Bubble Sort
Merge Sort
Insertion Sort
Selection Sort
Quick Sort
Program:
Bubble Sort:
Algorithm –
[1] Compare each pair of adjacent elements from the beginning of an array
and, if they are in reversed order, swap them.
[2] If at least one swap has been done, repeat step 1.
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (n) time
Average case: O (n2) time
Worst case: O (n2) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
int* bubble_sort(int i_store[], int i_size);
int* get_elem(int i_size);
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP of Bubble sort.");
printf("nnn");
int i_store_size;
printf("Enter the total number of items to store: ");
scanf("%d", &i_store_size);
int* ip_store = get_elem(i_store_size);
ip_store = bubble_sort(ip_store, i_store_size);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-3-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("nnResult: n");
disp_elem(ip_store, i_store_size);
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int* get_elem(int i_size)
{
int* ip_store = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_size);
int i_count = 0;
int i_temp_size = i_size;
while (i_temp_size)
{
printf("nEnter item for index - %d : ", i_count);
scanf("%d", (ip_store+i_count));
i_count++;
i_temp_size--;
}
disp_elem(ip_store, i_size);
return ip_store;
}
int* bubble_sort(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
int i_temp;
int i_count_0, i_count_1;
printf("nnSwapping Steps: n");
for (i_count_0 = (i_size - 1); i_count_0 > 0; --i_count_0)
{
for (i_count_1 = 1; i_count_1 <= i_count_0;
++i_count_1)
{
if (i_store[i_count_1 - 1] > i_store[i_count_1])
{
i_temp = i_store[i_count_1 - 1];
i_store[i_count_1 - 1] = i_store[i_count_1];
i_store[i_count_1] = i_temp;
disp_elem(i_store, i_size);
}
}
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-4-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
}
return i_store;
}
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
printf("n-------------------------------------------------
------n");
printf("Elements stored in order: ");
int i_ndx = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("| %d |",i_store[i_ndx]);
i_ndx++;
i_size--;
}
printf("n-------------------------------------------------
------");
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Merge Sort:
Algorithm –
[1] If the input sequence has fewer than two elements, return.
[2] Partition the input sequence into two halves.
[3] Sort the two subsequences using the same algorithm.
[4] Merge the two sorted subsequences to form the output sequence.
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (n * log (n)) time
Average case: O (n * log (n)) time
Worst case: O (n * log (n)) time
Code – Snippet:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE 1024
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-5-2048.jpg)

![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
void conquer_(int* ip_storage, int i_low, int i_mid, int i_high)
{
int* ip_temp_store_1 = malloc(sizeof(int) * ARRAY_SIZE);
int* ip_temp_store_2 = malloc(sizeof(int) * ARRAY_SIZE);
int n1,n2,i,j,k;
n1 = i_mid - i_low + 1;
n2 = i_high - i_mid;
printf("ntMerge low(%d) | mid(%d) | high(%d): ", i_low,
i_mid, i_high);
printf("ntip_temp_store_1: ");
for(i=0; i<n1; i++)
{
ip_temp_store_1[i] = ip_storage[i_low+i];
printf("%d", i, ip_temp_store_1[i]);
}
printf("ntip_temp_store_2: ");
for(j=0; j<n2; j++)
{
ip_temp_store_2[j] = ip_storage[i_mid+j+1];
printf("%d", j, ip_temp_store_2[j]);
}
// To mark the end of each temporary array
ip_temp_store_1[i] = 10000000;
ip_temp_store_2[j] = 10000000;
combine_(ip_storage, ip_temp_store_1, ip_temp_store_2,
i_low, i_high);
}
void combine_(int* storage, int* temp_arr_1, int* temp_arr_2,
int i_low, int i_height)
{
int i=0;
int j=0;
int k;
printf("nResult: ");
for (k=i_low; k<=i_height; k++)
{
if (temp_arr_1[i] <= temp_arr_2[j])
storage[k] = temp_arr_1[i++];
else
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-7-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
storage[k]=temp_arr_2[j++];
printf("%d", storage[k]);
}
printf("n");
}
void disp_elements(int* i_storage)
{
printf("nnn");
int i_count;
printf("Elements: ");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_size; ++i_count)
{
printf("%d",*(i_storage + i_count));
}
printf("nnn");
}
int* get_elements(void)
{
int i_count;
printf("Enter the size of array: ");
scanf("%d",&i_size);
int* i_storage = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int) * i_size);
for(i_count = 0; i_count < i_size; i_count++)
{
printf("Enter the element at pos[%d]: ", i_count);
scanf("%d",(i_storage + i_count));
}
return i_storage;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Insertion Sort:
Algorithm –
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-8-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
[1] Start with the result as the first element of the input.
[2] Loop over the input until it is empty, "removing" the first remaining
(leftmost) element.
[3] Compare the removed element against the current result, starting from the
highest (rightmost) element, and working left towards the lowest element.
[4] If the removed input element is lower than the current result element,
copy that value into the following element to make room for the new
element below, and repeat with the next lowest result element.
[5] Otherwise, the new element is in the correct location; save it in the cell left
by copying the last examined result up, and start again from (2) with the
next input element.
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (n) time
Average case: O (n2) time
Worst case: O (n2) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
int* insertion_sort(int i_store[], int i_size);
int* get_elem(int i_size);
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP of Insertion sort.");
printf("nnn");
int i_store_size;
printf("Enter the total number of items to store: ");
scanf("%d", &i_store_size);
int* ip_store = get_elem(i_store_size);
ip_store = insertion_sort(ip_store, i_store_size);
disp_elem(ip_store, i_store_size);
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int* get_elem(int i_size)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-9-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
int* ip_store = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_size);
int i_count = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("nEnter item for index - %d : ", i_count);
scanf("%d", (ip_store+i_count));
i_count++;
i_size--;
}
return ip_store;
}
int* insertion_sort(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
int i_temp;
int i_count_0, i_count_1, i_count_2;
for (i_count_0 = 1; i_count_0 <= (i_size-1); ++i_count_0)
{
for (i_count_1 = 0; i_count_1 < i_count_0; ++i_count_1)
{
if (i_store[i_count_1] > i_store[i_count_0])
{
i_temp = i_store[i_count_1] ;
i_store[i_count_1] = i_store[i_count_0] ;
for (i_count_2 = i_count_0; i_count_2 >
i_count_1; i_count_2--)
i_store[i_count_2] = i_store[i_count_2
- 1] ;
i_store[i_count_2 + 1] = i_temp ;
}
}
}
return i_store;
}
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
printf("nDisplaying Elements of store: ");
int i_ndx = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("%d", i_store[i_ndx]);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-10-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
i_ndx++;
i_size--;
}
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Selection Sort:
Algorithm –
[1] Get a hand of unsorted cards/numbers.
[2] Set a marker for the sorted section after the first card of the hand.
[3] Repeat steps 4 through 6 until the unsorted section is empty.
[4] Select the first unsorted card.
[5] Swap this card to the left until it arrives at the correct sorted position.
[6] Advance the marker to the right one card.
[7] Stop
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (n2) time
Average case: O (n2) time
Worst case: O (n2) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
int* selection_sort(int i_store[], int i_size);
int* get_elem(int i_size);
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP of Selection sort.");
printf("nnn");
int i_store_size;
printf("Enter the total number of items to store: ");
scanf("%d", &i_store_size);
int* ip_store = get_elem(i_store_size);
ip_store = selection_sort(ip_store, i_store_size);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-11-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
disp_elem(ip_store, i_store_size);
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int* get_elem(int i_size)
{
int* ip_store = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_size);
int i_count = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("nEnter item for index - %d : ", i_count);
scanf("%d", (ip_store+i_count));
i_count++;
i_size--;
}
return ip_store;
}
int* selection_sort(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
int i_temp;
int i_count_0, i_count_1;
for (i_count_0 = 0; i_count_0 < (i_size-1); ++i_count_0)
{
for (i_count_1 = (i_count_0+1); i_count_1 < i_size;
++i_count_1)
{
if (i_store[i_count_0] > i_store[i_count_1])
{
i_temp = i_store[i_count_0];
i_store[i_count_0] = i_store[i_count_1];
i_store[i_count_1] = i_temp;
}
}
}
return i_store;
}
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
printf("nDisplaying Elements of store: ");
int i_ndx = 0;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-12-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
while (i_size)
{
printf("%d", i_store[i_ndx]);
i_ndx++;
i_size--;
}
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Quick Sort:
Algorithm –
[1] Choosing the pivot.
[2] Partitioning.
[3] Recursively quick-sort the left and the right parts.
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (n * log (n)) time
Average case: O (n * log (n)) time
Worst case: O (n2) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
int* quick_sort(int i_store[], int i_start, int i_end);
int* get_elem(int i_size);
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP of Quick sort.");
printf("nnn");
int i_store_size;
printf("Enter the total number of items to store: ");
scanf("%d", &i_store_size);
int* ip_store = get_elem(i_store_size);
ip_store = quick_sort(ip_store, 0, i_store_size);
disp_elem(ip_store, i_store_size);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-13-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int* get_elem(int i_size)
{
int* ip_store = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_size);
int i_count = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("nEnter item for index - %d : ", i_count);
scanf("%d", (ip_store+i_count));
i_count++;
i_size--;
}
return ip_store;
}
int* quick_sort(int i_store[], int i_start, int i_end)
{
int i_begin, i_finish, i_pivot, i_temp;
if (i_finish > i_begin)
{
i_begin = i_start;
i_finish = i_end;
i_pivot = i_begin;
while (i_begin < i_finish)
{
while ((i_store[i_begin] <= i_store[i_pivot]) &&
(i_begin < i_end))
{
++i_begin;
}
while (i_store[i_finish] > i_store[i_pivot])
{
--i_finish;
}
if (i_begin < i_finish)
{
i_temp = i_store[i_begin];
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-14-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
i_store[i_begin] = i_store[i_finish];
i_store[i_finish] = i_temp;
}
}
i_temp = i_store[i_pivot];
i_store[i_pivot] = i_store[i_finish];
i_store[i_finish] = i_temp;
quick_sort(i_store, i_start, i_finish - 1);
quick_sort(i_store, i_finish + 1, i_end);
}
return i_store;
}
void disp_elem(int i_store[], int i_size)
{
printf("nDisplaying Elements of store: ");
int i_ndx = 0;
while (i_size)
{
printf("%d", i_store[i_ndx]);
i_ndx++;
i_size--;
}
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-15-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
2. WAP in C for following Searching Methods
Linear Search
Binary Search
Program:
Linear Search:
Algorithm –
[1] Input: Array D of Business objects, phone number key.
[2] Output: first index where key’s phone number matches D, or -1 if not
found
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (1) time
Average case: O (n) time
Worst case: O (n) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
void linear_search(int* i_storage, int i_srch_item, int
i_num_item)
{
int i_count;
bool b_flag = false;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_num_item; ++i_count)
{
if (i_storage[i_count] == i_srch_item)
{
b_flag = true;
printf("Item (%d) is found at position: %d",
i_srch_item, i_count);
break;
}
}
if (!b_flag)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-16-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("Item not found.");
}
void get_input(int* i_storage, int i_num_item)
{
printf("Your Storage Items are: nt");
int i_loop_count;
for(i_loop_count = 0; i_loop_count < i_num_item;
++i_loop_count)
{
printf("%d, ", i_storage[i_loop_count]);
}
printf("nnn");
int i_srch_item;
printf("Please Enter the item (number) to search: ");
scanf("%d", &i_srch_item);
printf("nnn");
linear_search(i_storage, i_srch_item, i_num_item);
}
void set_argument(void)
{
printf("WAP for Linear - Search.");
printf("nLimitation: nt-> Items are restrickted with
integer number.nt-> Starting index of storage is 0.");
printf("nnn");
int i_storage[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
get_input(i_storage, (sizeof(i_storage)/sizeof(int)));
}
int main()
{
set_argument();
printf("nnn");
getch();
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-17-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
Binary Search:
Algorithm –
[1] Get the middle element;
[2] If the middle element equals to the searched value, the algorithm stops;
[3] Otherwise, two cases are possible:
Searched value is less, than the middle element. In this case, go to
the step 1 for the part of the array, before middle element.
Searched value is greater, than the middle element. In this case, go
to the step 1 for the part of the array, after middle element.
Time Complexity –
Best case: O (1) time
Average case: O (log (n)) time
Worst case: O (n) time
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
bool check_item_order(int* i_storage)
{
//Function to check the Item - List is in Sorted order.
return true;
}
void recursive_bin_search(int* i_storage, int i_srch_item, int
i_low, int i_mid, int i_hi)
{
if(i_low < i_hi)
{
if(i_storage[i_mid] == i_srch_item)
{
printf("Item (%d) is found at position: %d", i_srch_item,
i_mid);
}
else if(i_storage[i_mid] > i_srch_item)
{
i_hi = i_mid;
i_mid = (i_low + i_hi)/2;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-18-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
recursive_bin_search(i_storage, i_srch_item, i_low, i_mid,
i_hi);
}
else if(i_storage[i_mid] < i_srch_item)
{
i_low = i_mid;
i_mid = (i_low + i_hi)/2;
recursive_bin_search(i_storage, i_srch_item, i_low, i_mid,
i_hi);
}
}
}
void recursive_binary_search(int* i_storage, int i_num_item)
{
bool b_check = check_item_order(i_storage);
printf("Your Storage Items are: nt");
int i_loop_count;
for(i_loop_count = 0; i_loop_count < i_num_item;
++i_loop_count)
{
printf("%d, ", i_storage[i_loop_count]);
}
printf("nnn");
int i_srch_item;
printf("Please Enter the item (number) to search: ");
scanf("%d", &i_srch_item);
printf("nnn");
int i_low = 0;
int i_hi = i_num_item;
int i_mid = (i_low + i_hi)/2;
if(b_check)
recursive_bin_search(i_storage, i_srch_item, i_low,
i_mid, i_hi);
else
printf("nItems are not in Order.n");
}
void binary_search(void)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-19-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
printf("WAP for Binary - Search.");
printf("nLimitation: nt-> Items are restrickted with integer
number.nt-> Starting index of storage is 0.");
printf("nnn");
int i_storage[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
recursive_binary_search(i_storage,
(sizeof(i_storage)/sizeof(int)));
}
int main()
{
binary_search();
printf("nnn");
getch();
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-20-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
3. WAP in C for array implementation of
Stack
Queue
Circular Queue
Linked List
Program:
Stack:
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define STACK_SIZE 1024
int i_top = -1;
int stack[STACK_SIZE];
int select_choice(void)
{
{
printf("ntTo Push Item: tt(Press) 1");
printf("ntTo Pop Item: tt(Press) 2");
printf("ntTo Display Item: t(Press) 3");
printf("ntTo Exit: tt(Press) 4");
}
int i_choice;
printf("nntPlease Enter Your Choice: ");
scanf("%d", &i_choice);
if((i_choice > 0) && (i_choice < 5))
return i_choice;
else
return 0;
}
int push_item(int i_item)
{
if(i_top == (STACK_SIZE - 1))
{
printf("ntStack Overflow.");
return 0;
}
else
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-21-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
stack[++i_top] = i_item;
printf("ntItem - %d, has successfully pushed into
Stack.", i_item);
return 1;
}
}
int pop_item(int i_item)
{
if(i_top == -1)
{
printf("ntStack is Underflow.");
return 0;
}
else
{
bool b_flag = false;
int i_count;
for(i_count = 0; i_count <= i_top; ++i_count)
{
if((stack[i_count] == i_item)&&(!b_flag))
{
stack[i_count] = stack[i_count+1];
b_flag = true;
}
else if(b_flag)
{
stack[i_count] = stack[i_count+1];
}
}
i_top = (i_count - 2);
//Substracting: 2 = (additional loop increment + 1 deleted
item)
return 1;
}
}
int disp_item(void)
{
if(i_top == -1)
{
printf("ntStack is Empty.");
return 0;
}
else
{
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-22-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
int i_count;
printf("ntElements of Stack are:");
for(i_count = 0; i_count <= i_top; ++i_count)
{
printf("ntIndex: %d | Item: %d", i_count,
stack[i_count]);
}
return 1;
}
}
int process_stack(int i_choice)
{
switch(i_choice)
{
case 1:
{
printf("ntTo Push Item into Stack.");
int i_item = 0;
printf("ntPlease Enter the item: ");
scanf("%d", &i_item);
int i_check = push_item(i_item);
if(i_check == 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
case 2:
{
printf("ntTo Pop Item from Stack.");
int i_item = 0;
printf("ntPlease Enter the item: ");
scanf("%d", &i_item);
int i_check = pop_item(i_item);
if(i_check == 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
case 3:
{
printf("ntTo Display Item of Stack.");
int i_check = disp_item();
if(i_check == 1)
return 1;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-23-2048.jpg)

![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
i_state = 0;
}
while(i_state == 1);
}
printf("nnn");
getch();
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Queue:
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define QUEUE_SIZE 1024
int i_front = -1;
int i_rear = -1;
int queue[QUEUE_SIZE];
int main()
{
int i_check = set_Argument();
if(i_check == 0)
printf("nnntInvalid input.");
else
{
int i_state;
do
{
i_state = process_stack(i_check);
i_check = set_Argument();
if(i_check == 4) //Check
for Exit.
i_state = 0;
}
while(i_state == 1);
}
printf("nnn");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-25-2048.jpg)

![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
i_front = 0;
queue[++i_rear] = i_item;
printf("ntItem - %d, has successfully pushed into
Stack.", i_item);
return 1;
}
}
int pop_item(int i_item)
{
if((i_front == -1)||(i_front > i_rear))
{
printf("ntQueue is Underflow.");
return 0;
}
else
{
bool b_flag = false;
int i_count;
for(i_count = i_front; i_count <= i_rear; ++i_count)
{
if((queue[i_count] == i_item)&&(!b_flag))
{
queue[i_count] = queue[i_count+1];
b_flag = true;
}
else if(b_flag)
{
queue[i_count] = queue[i_count+1];
}
}
i_rear = (i_count - 2);
//Substracting: 2 = (additional loop increment + 1 deleted
item)
return 1;
}
}
int disp_item(void)
{
if(i_front == -1)
{
printf("ntQueue is Empty.");
return 0;
}
else
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-27-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
printf("ntElements of Queue are:");
int i_count;
for(i_count = i_front; i_count <= i_rear; ++i_count)
{
printf("ntIndex: %d | Item: %d", i_count,
queue[i_count]);
}
return 1;
}
}
int process_stack(int i_choice)
{
switch(i_choice)
{
case 1:
{
printf("ntTo Push Item into Queue.");
int i_item = 0;
printf("ntPlease Enter the item: ");
scanf("%d", &i_item);
int i_check = push_item(i_item);
if(i_check == 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
case 2:
{
printf("ntTo Pop Item from Queue.");
int i_item = 0;
printf("ntPlease Enter the item: ");
scanf("%d", &i_item);
int i_check = pop_item(i_item);
if(i_check == 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
case 3:
{
printf("ntTo Display Item of Queue.");
int i_check = disp_item();
if(i_check == 1)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-28-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
return 1;
else
return 0;
break;
}
case 4:
{
printf("ntTo Exit.");
return 0;
break;
}
default:
{
return 0;
break;
}
}
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Circular Queue:
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define QUEUE_SIZE 1024
int i_front = -1;
int i_rear = -1;
int circular_queue[QUEUE_SIZE];
int select_choice(void)
{
{
printf("ntTo Push Item: tt(Press) 1");
printf("ntTo Pop Item: tt(Press) 2");
printf("ntTo Display Item: t(Press) 3");
printf("ntTo Exit: tt(Press) 4");
}
int i_choice;
printf("nntPlease Enter Your Choice: ");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-29-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
scanf("%d", &i_choice);
if((i_choice > 0) && (i_choice < 5))
return i_choice;
else
return 0;
}
int push_item(int i_item)
{
if(((i_front == 0) && (i_rear == (QUEUE_SIZE - 1))) ||
(i_front == i_rear + 1))
{
printf("ntQueue Overflow.");
return 0;
}
else
{
if(i_rear == -1)
{
i_rear = 0;
i_front = 0;
}
else if(i_rear == QUEUE_SIZE-1)
i_rear = 0;
else
i_rear++;
circular_queue[i_rear] = i_item;
printf("ntItem - %d, has successfully pushed into
Stack.", i_item);
return 1;
}
}
int pop_item(int i_item)
{
if(i_front == -1)
{
printf("ntQueue is Underflow.");
return 0;
}
else
{
bool b_flag = false;
int i_count;
for(i_count = i_front; i_count <= i_rear; ++i_count)
{
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-30-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
if((circular_queue[i_count] ==
i_item)&&(!b_flag))
{
circular_queue[i_count] =
circular_queue[i_count+1];
b_flag = true;
}
else if(b_flag)
{
circular_queue[i_count] =
circular_queue[i_count+1];
}
}
i_rear = (i_count - 2);
//Substracting: 2 = (additional loop increment + 1 deleted
item)
return 1;
}
}
int disp_item(void)
{
if((i_front == -1) || (i_front == i_rear + 1))
{
printf("ntQueue is Empty.");
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("ntElements of Queue are:");
int i_count;
for(i_count = i_front; i_count <= i_rear; ++i_count)
{
printf("ntIndex: %d | Item: %d", i_count,
circular_queue[i_count]);
}
return 1;
}
}
int process_stack(int i_choice)
{
switch(i_choice)
{
case 1:
{
printf("ntTo Push Item into Queue.");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-31-2048.jpg)


![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define LINKED_LIST_SIZE 1024
int set_argument(void);
int select_choice(void);
int process_stack(int i_choice);
int push_node(int i_item, int i_indx);
int disp_node(void);
int pop_node(int i_option);
struct node
{
int i_val;
int i_next_idx;
}ll_node[LINKED_LIST_SIZE];
int i_ll_size = 0;
int main()
{
int i_check = set_argument();
if(i_check == 0)
printf("nnntInvalid input.");
else
{
int i_state;
do
{
i_state = process_stack(i_check);
i_check = set_argument();
if(i_check == 4) //Check for Exit.
i_state = 0;
}
while(i_state == 1);
}
printf("nnn");
getch();
return 0;
}
int set_argument(void)
{
printf("nt-----------------------------------------------
---n");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-34-2048.jpg)


![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("ntt---------------------------");
{
printf("nttBy Item: tt(Press) 1");
printf("nttBy Reference: tt(Press) 2");
}
int i_choice;
printf("nnttPlease Enter Your Choice: ");
scanf("%d", &i_choice);
printf("ntt---------------------------");
if((i_choice > 0) && (i_choice < 5))
return i_choice;
else
return 0;
}
int pop_node(int i_option)
{
if (i_option == 1)
{
int i_del_item;
printf("ntItem to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &i_del_item);
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
bool b_flag = false;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1), i_size
< i_ll_size; )
{
if ((ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)&&(!b_flag))
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_val == i_del_item)
{
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
b_flag = true;
}
else if (b_flag)
{
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-37-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
}
else
{
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
}
}
else
break;
}
}
else if (i_option == 2)
{
int i_del_idx;
printf("ntIndex to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &i_del_idx);
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
bool b_flag = false;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1),
i_size < i_ll_size; )
{
if ((ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)&&(!b_flag))
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx == i_del_idx)
{
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
b_flag = true;
}
else if (b_flag)
{
int i_nxt_idx =
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-38-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
}
else
{
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
}
}
else
break;
}
}
return 1;
}
int push_node(int i_item, int i_indx)
{
if (i_indx < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1))
{
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_val = i_item;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_next_idx = i_indx;
i_ll_size = i_indx;
//For Last Node
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_val = 100001;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_next_idx = 0;
//-------------
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int disp_node(void)
{
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1), i_size <
i_ll_size; )
{
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-39-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
if (ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)
{
printf("ntItem: %d", ll_node[i_count].i_val);
printf("ntNext Index: %d",
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx);
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
printf("nt************************n");
}
else
break;
}
return 1;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Code – Snippet: (Doubly Linked List)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define LINKED_LIST_SIZE 1024
int set_argument(void);
int select_choice(void);
int process_stack(int i_choice);
int push_node(int i_item, int i_indx);
int disp_node(void);
int pop_node(int i_option);
struct node
{
int i_prev_idx;
int i_val;
int i_next_idx;
}ll_node[LINKED_LIST_SIZE];
int i_ll_size = 0;
int main()
{
int i_check = set_argument();
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-40-2048.jpg)



![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("ntItem to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &i_del_item);
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
bool b_flag = false;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1), i_size
< i_ll_size; )
{
if ((ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)&&(!b_flag))
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_val == i_del_item)
{
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_prev_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_prev_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
b_flag = true;
}
else if (b_flag)
{
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_prev_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_prev_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
}
else
{
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
}
}
else
break;
}
}
else if (i_option == 2)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-44-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
{
int i_del_idx;
printf("ntIndex to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &i_del_idx);
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
bool b_flag = false;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1),
i_size < i_ll_size; )
{
if ((ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)&&(!b_flag))
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx == i_del_idx)
{
int i_nxt_idx = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
b_flag = true;
}
else if (b_flag)
{
int i_nxt_idx =
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
ll_node[i_count].i_val =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_val;
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx =
ll_node[i_nxt_idx].i_next_idx;
i_count = i_nxt_idx;
i_size++;
}
else
{
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
}
}
else
break;
}
}
return 1;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-45-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
}
int push_node(int i_item, int i_indx)
{
if (i_indx < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1))
{
if (i_ll_size == 0)
{
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_prev_idx = 0;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_val = i_item;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_next_idx = i_indx;
i_ll_size = i_indx;
}
else
{
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_prev_idx =
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_prev_idx;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_val = i_item;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_next_idx = i_indx;
i_ll_size = i_indx;
//For Last Node
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_prev_idx = i_indx;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_val = 100001;
ll_node[i_ll_size].i_next_idx = 0;
//-------------
}
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int disp_node(void)
{
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1), i_size <
i_ll_size; )
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)
{
printf("ntPrev Index: %d",
ll_node[i_count].i_prev_idx);
printf("ntItem: %d", ll_node[i_count].i_val);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-46-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("ntNext Index: %d",
ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx);
i_count = ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx;
i_size++;
printf("nt************************n");
}
else
break;
}
return 1;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-47-2048.jpg)


























![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
}
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int disp_node(void)
{
int i_count = 0;
int i_size = 0;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < (LINKED_LIST_SIZE-1), i_size <
i_ll_size; )
{
if (ll_node[i_count].i_next_idx != 0)
{
printf("ntPrev Index: %d", (*(ll_node +
i_count)).i_prev_idx);
printf("ntItem: %d", (*(ll_node +
i_count)).i_val);
printf("ntNext Index: %d", (*(ll_node +
i_count)).i_next_idx);
i_count = (*(ll_node + i_count)).i_next_idx;
i_size++;
printf("nt************************n");
}
else
break;
}
return 1;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-74-2048.jpg)












![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
7. WAP in C for Graph Traversal
Breadth First Search
Depth First Search
Program:
Breadth First Search:
Algorithm –
[1] Enqueue the root node.
[2] Dequeue a node and examine it
a. If the element sought is found in this node, quit the search and return a
result.
b. Otherwise enqueue any successors (the direct child nodes) that have not
yet been discovered.
[3] If the queue is empty, every node on the graph has been examined – quit the
search and return "not found".
[4] If the queue is not empty, repeat from Step 2
Time Complexity –
The total time for initializing is O (n) and the total time for the queuing
operations is O (n) because each node is put on the queue exactly once. The total time in
the main loop is O (e) because we look at each edge at most twice, once from each
direction. This gives a time complexity of O (n + e).
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int **i_adjacency_matrix;
int *i_nodes_visit;
int *i_bfs_path;
int i_no_nodes;
int flag, n_flag = -1;
bool get_graph_input(void);
bool initialize_nodes(void);
void breadth_first_search(void);
void check_node(int);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-87-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP for Graph Traversal (Depth First
Search).");
printf("nnn");
bool b_check;
b_check = get_graph_input();
if (b_check)
b_check = initialize_nodes();
printf("nnn");
printf("Depth First Path within the given graph:n");
breadth_first_search();
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool get_graph_input(void)
{
printf("Enter Number of Nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &i_no_nodes);
i_adjacency_matrix = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
i_nodes_visit = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
i_bfs_path = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
int i_temp = 0;
int i_count, j_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
*(i_adjacency_matrix + i_count) =
(int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
{
printf("nConection of node %d to node %d is: ",
i_count, j_count);
scanf("%d", &i_temp);
if ((i_temp == 1)||(i_temp == 0))
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] = i_temp;
else
{
printf("Input is invalid.");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 88](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-88-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
return false;
}
}
}
printf("nnnAdjacency Matrix, so formed:");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
printf("n");
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
printf("t%d",
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count]);
}
return true;
}
bool initialize_nodes(void)
{
int i_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
i_nodes_visit[i_count] = 0;
return true;
}
void breadth_first_search(void)
{
int i_count;
int i_start_node;
printf("ntPlease Enter Starting Node: ");
scanf("%d", &i_start_node);
check_node(i_start_node);
for (i_count = 1; i_count <= i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
if (i_nodes_visit[i_count])
printf("%dt",i_count);
else
printf("n Bfs is not possible");
}
void check_node(int i_start_node)
{
int i_count;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 89](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-89-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
for (i_count = 0; i_count <= i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
if ((i_adjacency_matrix[i_start_node][i_count]) &&
(!i_nodes_visit[i_count]))
i_bfs_path[++n_flag] = i_count;
if (flag <= n_flag)
{
i_nodes_visit[i_bfs_path[flag]] = 1;
check_node(i_bfs_path[flag++]);
}
return;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Depth First Search:
Algorithm –
[1] If the initial state is a goal state, quit and return success.
[2] Otherwise, loop until success or failure is signaled.
Generate a state, say E, and let it be the successor of the initial state.
If there is no successor, signal failure.
Call Depth-First Search with E as the initial state.
If success is returned, signal success. Otherwise continue in this
loop.
Time Complexity –
The time complexity is O (E + V).
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_NUM_NODES 1024
int **i_adjacency_matrix;
int *i_nodes_visit;
int i_no_nodes;
bool get_graph_input(void);
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-90-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
bool initialize_nodes(void);
void depth_first_search(void);
void check_node(int);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP for Graph Traversal (Depth First
Search).");
printf("nnn");
bool b_check;
b_check = get_graph_input();
if (b_check)
b_check = initialize_nodes();
printf("nnn");
printf("Depth First Path within the given graph:n");
depth_first_search();
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool get_graph_input(void)
{
printf("Enter Number of Nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &i_no_nodes);
i_adjacency_matrix = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
i_nodes_visit = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
int i_temp = 0;
int i_count, j_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
*(i_adjacency_matrix + i_count) =
(int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
{
printf("nConection of node %d to node %d is: ",
i_count, j_count);
scanf("%d", &i_temp);
if ((i_temp == 1)||(i_temp == 0))
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] = i_temp;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 91](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-91-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
else
{
printf("Input is invalid.");
return false;
}
}
}
printf("nnnAdjacency Matrix, so formed:");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
printf("n");
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
printf("t%d",
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count]);
}
return true;
}
bool initialize_nodes(void)
{
int i_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
i_nodes_visit[i_count] = 0;
return true;
}
void depth_first_search(void)
{
int i_count;
printf("nt");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
if(i_nodes_visit[i_count] == 0)
check_node(i_count);
}
void check_node(int i_node)
{
int i_count;
printf("Node(%d)t", i_node);
i_nodes_visit[i_node] = 1;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 92](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-92-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
if (i_nodes_visit[i_count] == 0)
check_node(i_count);
return;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 93](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-93-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
8. WAP in C for Minimum Cost Spanning Tree
Program:
Algorithm (Prim’s) –
[1] create a tree containing a single vertex, chosen arbitrarily from the graph
[2] create a set containing all the edges in the graph
[3] loop until every edge in the set connects two vertices in the tree
remove from the set an edge with minimum weight that connects a
vertex in the tree with a vertex not in the tree
add that edge to the tree
Time Complexity –
O (E * log (V)) where E is the number of edges and V is the number of
vertices.
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MIN_COST 3000
int **i_adjacency_matrix;
int *i_nodes_visit;
int i_no_nodes;
bool get_tree_input(void);
int calc_cost_prims_algo(void);
int main()
{
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP for Minimum Cost Spanning Tree (Prim's
algorithm).");
printf("nnn");
bool b_check;
b_check = get_tree_input();
int i_min_cost_spanning_tree = calc_cost_prims_algo();
printf("n Minimun cost = %d", i_min_cost_spanning_tree);
printf("nnn");
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-94-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool get_tree_input(void)
{
printf("Enter Number of Nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &i_no_nodes);
i_adjacency_matrix = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
i_nodes_visit = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
int i_temp = 0;
int i_count, j_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
*(i_adjacency_matrix + i_count) =
(int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
{
printf("nCost of node %d to node %d is: ",
i_count, j_count);
scanf("%d", &i_temp);
if ((i_temp != 0))
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] = i_temp;
else
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] =
MIN_COST;
}
}
printf("nnnAdjacency Matrix, so formed:");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
printf("n");
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
printf("t%d",
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count]);
}
return true;
}
int calc_cost_prims_algo(void)
{
int i_min_cost, i_total_cost;
int i_count, j_count;
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 95](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-95-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
int i_node_1, i_node_2;
i_nodes_visit[0] = 1;
int i_new_node = 0;
while (i_new_node < i_no_nodes)
{
for (i_count = 0, i_min_cost = MIN_COST; i_count <=
i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
for (j_count = 0; j_count <= i_no_nodes;
++j_count)
if ((i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] <
i_min_cost) && (i_nodes_visit[i_count] != 0))
{
i_min_cost =
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count];
i_node_1 = i_count;
i_node_2 = j_count;
}
if ((i_nodes_visit[i_node_1] == 0) ||
(i_nodes_visit[i_node_2] == 0))
{
printf("n Edge %d:(%d %d) cost:%d",i_new_node++,
i_node_1, i_node_2, i_min_cost);
i_total_cost += i_min_cost;
i_nodes_visit[i_node_2] = 1;
}
i_adjacency_matrix[i_node_1][i_node_2] =
i_adjacency_matrix[i_node_2][i_node_1] = MIN_COST;
}
return i_total_cost;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 96](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-96-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
9. WAP in C for Shortest Path Problem
Program:
Algorithm (Dijkstra’s) –
[1] Assign to every node a tentative distance value: set it to zero for our initial
node and to infinity for all other nodes.
[2] Mark all nodes unvisited. Set the initial node as current. Create a set of the
unvisited nodes called the unvisited set consisting of all the nodes except
the initial node.
[3] For the current node, consider all of its unvisited neighbors and calculate
their tentative distances.
[4] When we are done considering all of the neighbors of the current node,
mark the current node as visited and remove it from the unvisited set. A
visited node will never be checked again.
[5] If the destination node has been marked visited (when planning a route
between two specific nodes) or if the smallest tentative distance among the
nodes in the unvisited set is infinity (when planning a complete traversal),
then stop. The algorithm has finished.
[6] Select the unvisited node that is marked with the smallest tentative
distance, and set it as the new "current node" then go back to step 3.
Time Complexity –
Time complexity of the following algorithm is O (M * log (N)), where M is
number of edges and N is number of vertices.
Code – Snippet:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define UNDEFINED_COST 3000
int **i_adjacency_matrix;
int *i_nodes_visit;
int i_no_nodes;
int get_tree_input(void);
void calc_cost_Dijkstra_algo(int);
int main()
{
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 97](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-97-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("nnn");
printf("tttWAP for Shortest Path Problem (Dijkstra's
algorithm).");
printf("nnn");
int i_source;
i_source = get_tree_input();
calc_cost_Dijkstra_algo(i_source);
printf("nnn");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int get_tree_input(void)
{
printf("Enter Number of Nodes: ");
scanf("%d", &i_no_nodes);
i_adjacency_matrix = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
i_nodes_visit = malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
int i_temp = 0;
int i_count, j_count;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
*(i_adjacency_matrix + i_count) =
(int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * i_no_nodes);
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
{
printf("nCost of node %d to node %d is: ",
i_count, j_count);
scanf("%d", &i_temp);
if ((i_temp != 0))
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] = i_temp;
else
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count] =
UNDEFINED_COST;
}
}
printf("nnnAdjacency Matrix, so formed:");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
printf("n");
for (j_count = 0; j_count < i_no_nodes; ++j_count)
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 98](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-98-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
printf("t%d",
i_adjacency_matrix[i_count][j_count]);
}
int i_source_node;
printf("nEnter the source node: ");
scanf("%d", &i_source_node);
return i_source_node;
}
void calc_cost_Dijkstra_algo(int i_source_node)
{
int i_count, j_count;
int i_counter, i_flag;
int i_init = 1;
int flag[i_no_nodes];
i_nodes_visit[0] = 1;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
flag[i_count] = 0;
i_nodes_visit[i_count] =
i_adjacency_matrix[i_source_node][j_count];
}
i_flag = 1;
while (i_init < i_no_nodes)
{
int i_undef_cost = UNDEFINED_COST;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
{
if ((i_nodes_visit[i_count] < i_undef_cost) &&
(!flag[i_count]))
{
i_undef_cost = i_nodes_visit[i_count];
i_counter = i_count;
}
flag[i_counter] = 1;
i_flag++;
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
if ((i_nodes_visit[i_counter] +
i_adjacency_matrix[i_counter][i_count] < i_nodes_visit[i_count])
&& (!flag[i_count]))
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-99-2048.jpg)
![Data Structure in C (Lab. Programs)
i_nodes_visit[i_count] =
i_nodes_visit[i_counter] +
i_adjacency_matrix[i_counter][i_count];
}
}
printf("n Shortest path so obtained :n");
for (i_count = 0; i_count < i_no_nodes; ++i_count)
if (i_count != i_source_node)
printf("Source: %d to %d,cost=%dn",i_source_node,
i_count, i_nodes_visit[i_count]);
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~************~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Saket Kr. Pathak Page 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab-programming-in-datastructure2-130401164517-phpapp02/75/Data-Structure-in-C-Lab-Programs-100-2048.jpg)