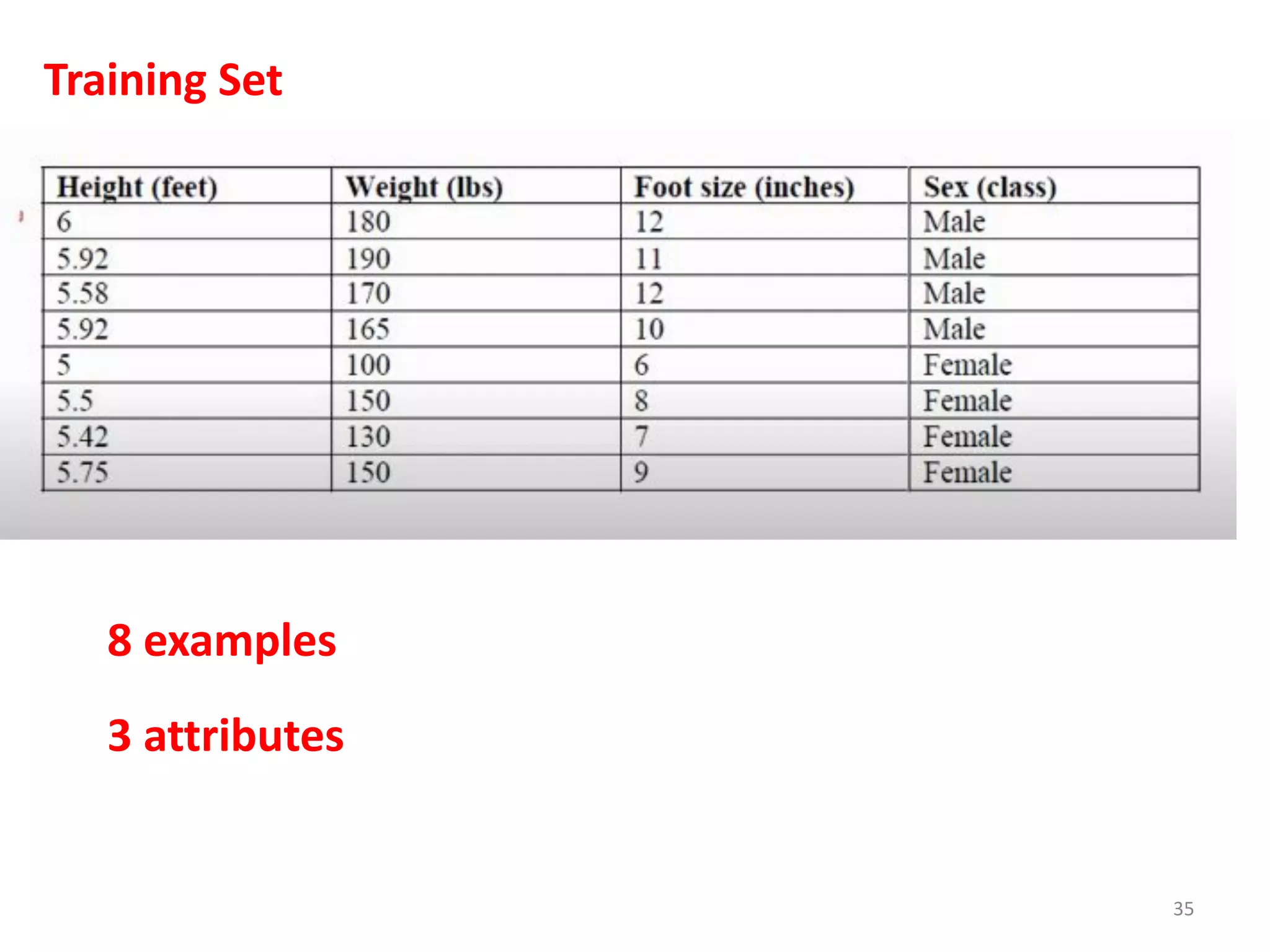
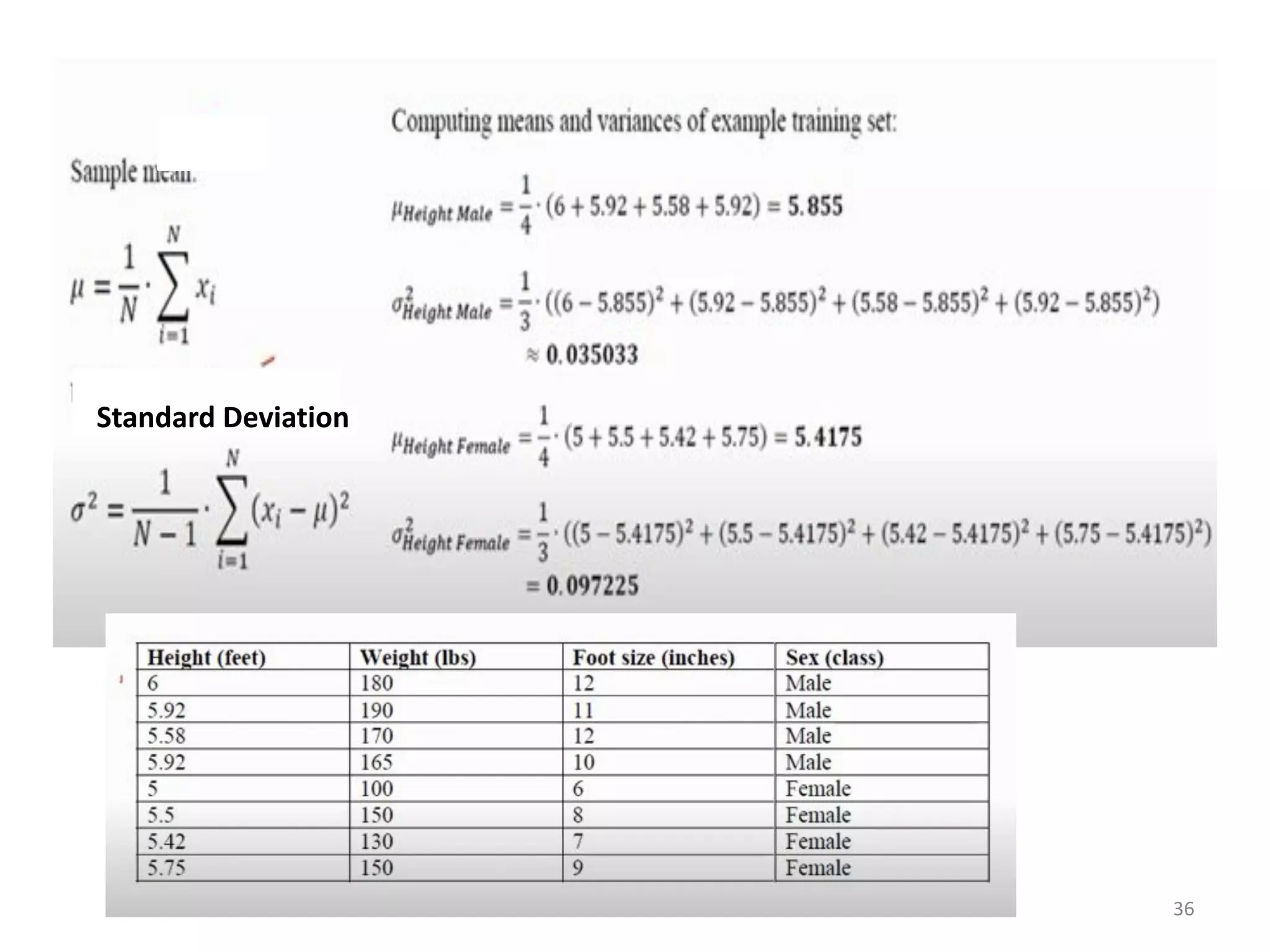
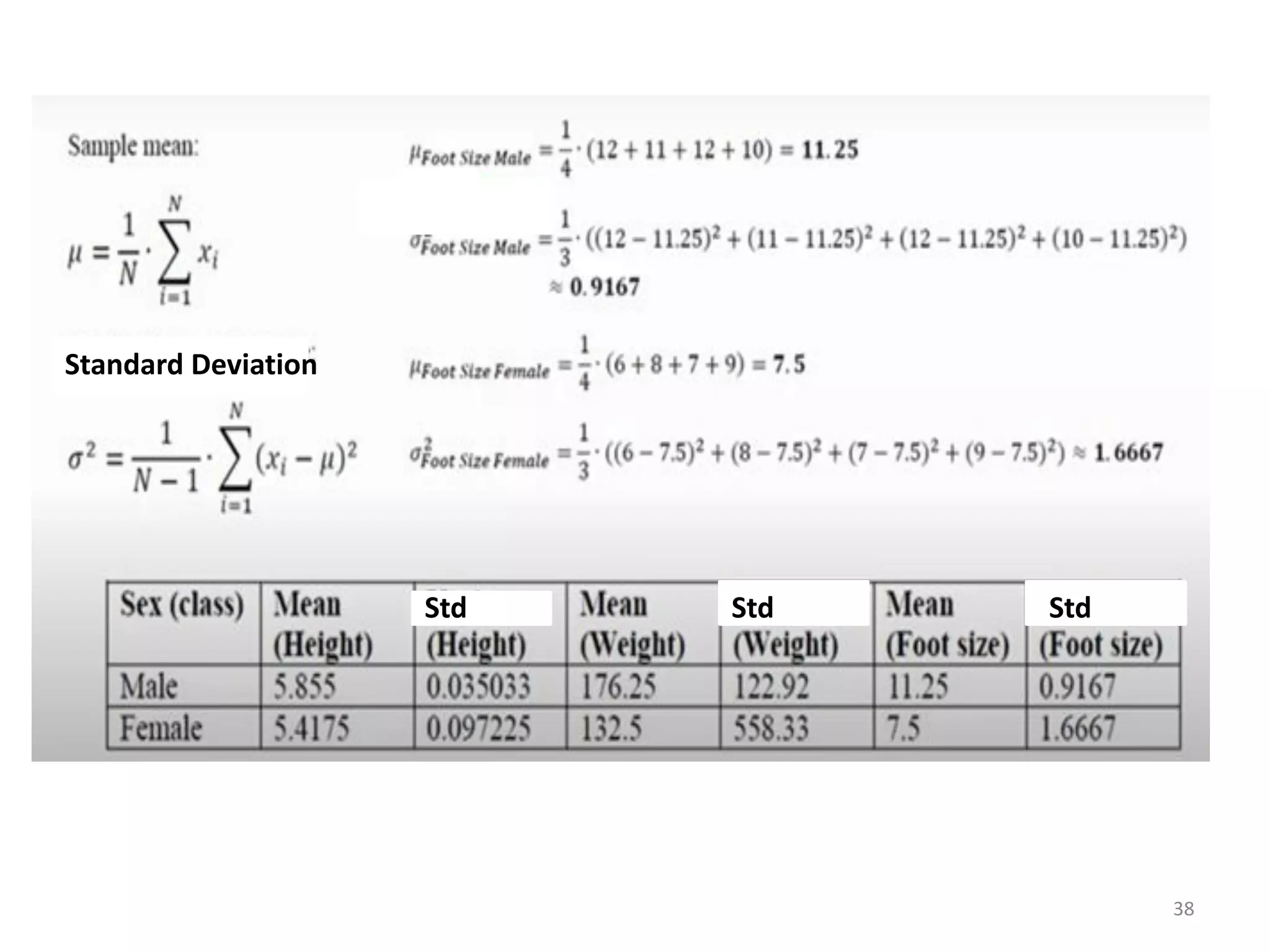
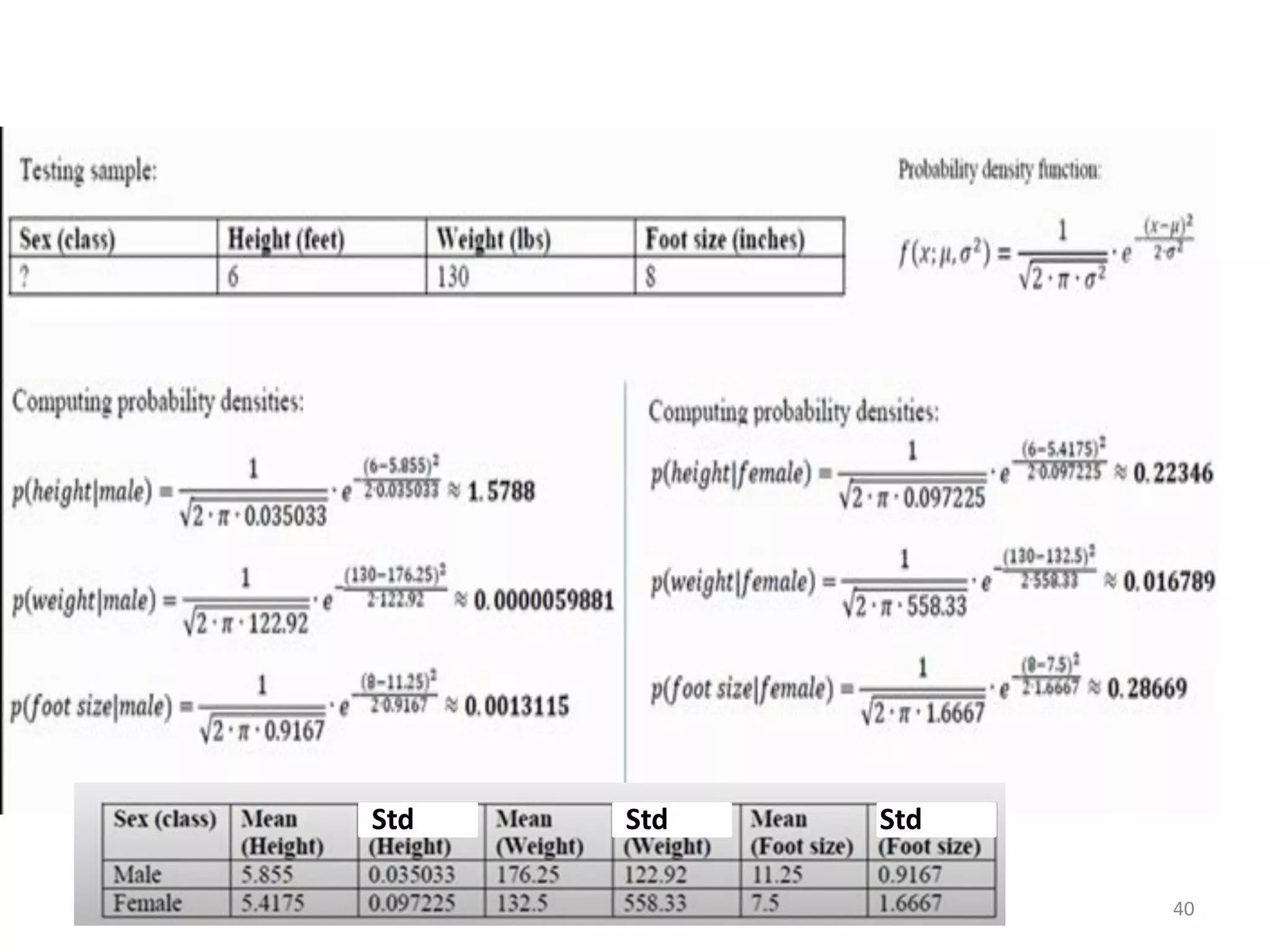
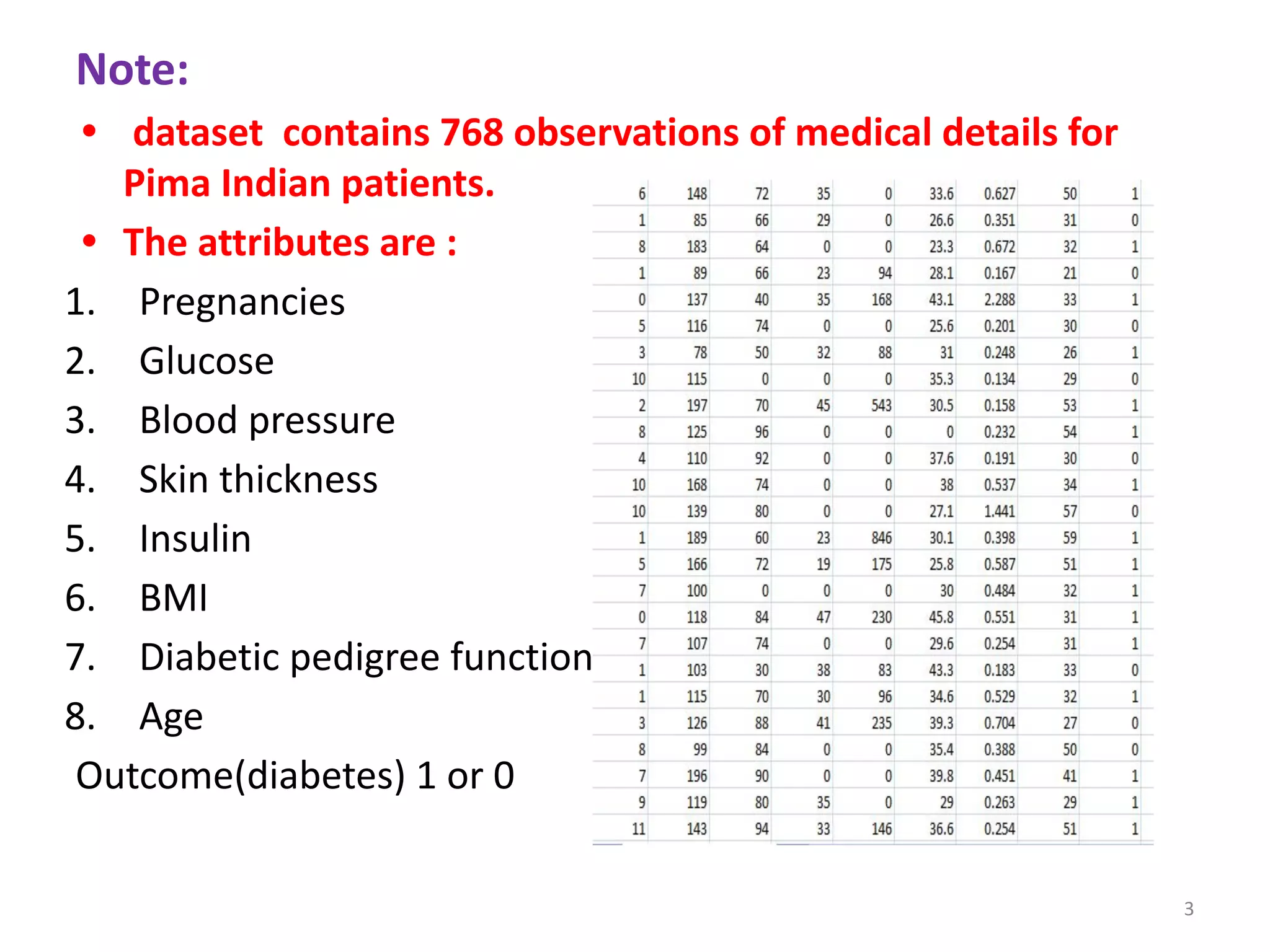
The document discusses a machine learning algorithm to perform classification on a diabetes dataset. It loads and splits the dataset into training and test sets. It then calculates the mean and standard deviation for each attribute within each class in the training set. These statistics are used to predict the class of each test instance and calculate the overall accuracy.

![# Loading the Data from csv file of
pima-indians-diabetes dataset.
def loadCsv(filename):
lines = csv.reader(open(filename, "r"));
#open csv file in read mode and read file
dataset = list(lines)
for i in range(len(dataset)):
# converting the attributes from string to floating point numbers
dataset[i] = [float(x) for x in dataset[i]]
return dataset
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-2-2048.jpg)
![def splitDataset(dataset, splitRatio):
testSize = int(len(dataset) * splitRatio); (768*0.2)=153
trainSet = list(dataset); // All 768 examples
testSet = [] // testSet is initially empty
while len(testSet) < testSize: #untill len(testSet) becomes 153
#randomly pick an instance from training data
index = random.randrange(len(trainSet));
testSet.append(trainSet.pop(index))
return [trainSet, testSet]
#Function will split dataset into trainingSet and testSet
#trainSet contains initially 768 examples
#randomly pick 153 instances from trainSet, remove it and
place it in testSet
i.e trainSet+testSet=768
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-4-2048.jpg)
![def separateByClass(dataset):
separated = {}
for i in range(len(dataset)):
x = dataset[i] # x contains row of dataset
if (x[-1] not in separated):
separated[x[-1]] = []
separated[x[-1]].append(x)
return separated
#Function separateByClass groups training set into 2 classes.
1 group contains all positive instances.
1 group contains all negative instances.
#separated= dictionary, key 1 value= all positive classification
instances, key=0, value= all negative classification instances
• #Function to categorize the dataset in terms of classes (1 and 0)
• #The function assumes that the last attribute (-1) is the class value.
• x[-1]=1 or 0
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-5-2048.jpg)



![def stdev(numbers):
avg=mean(numbers)
variance=sum([pow(x-avg,2) for x in
numbers])/float(len(numbers)-1)
return math.sqrt(variance)
# Function to calculate standard deviation
9
# square root of variance is standard deviation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-9-2048.jpg)
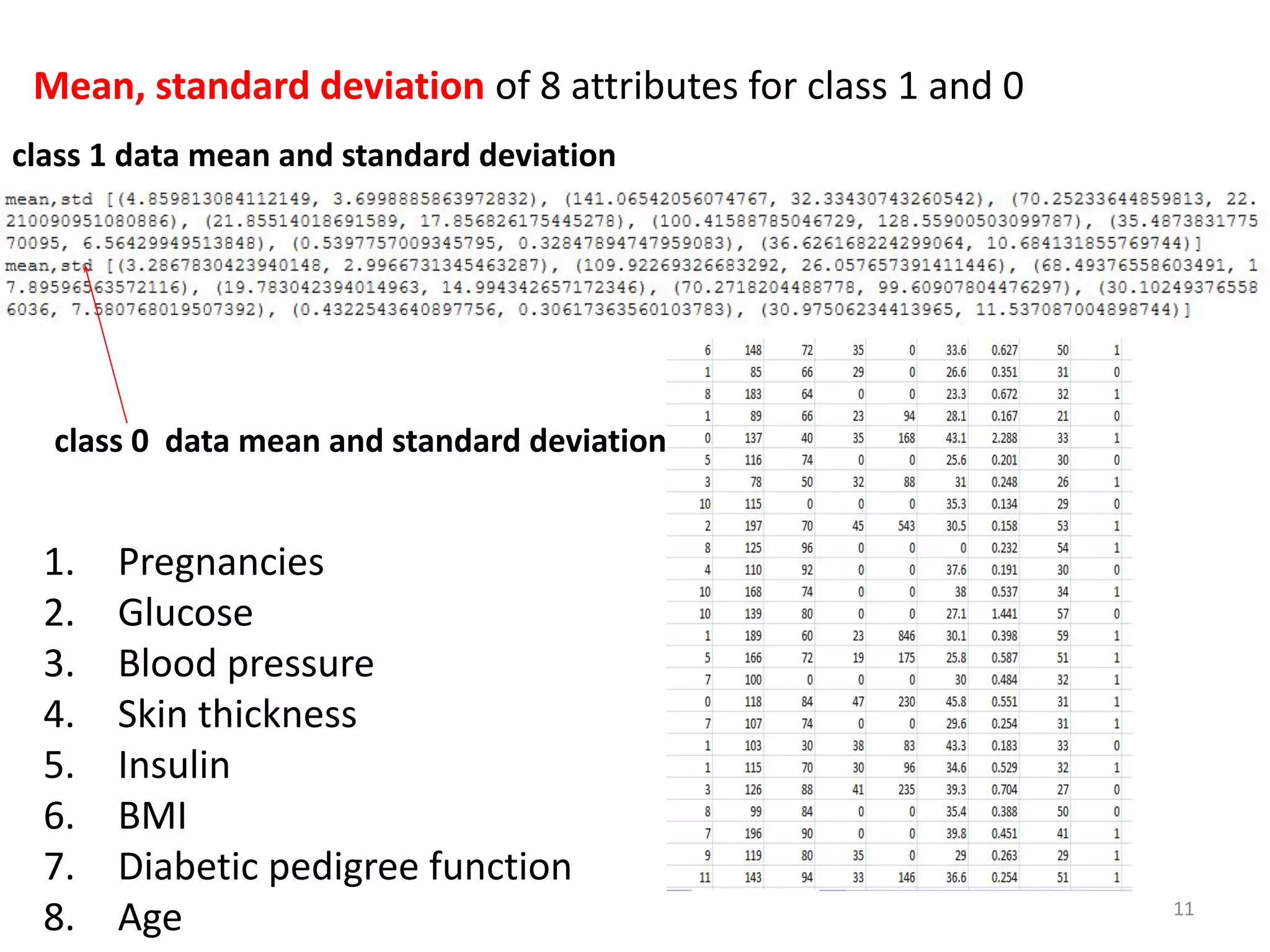
![def compute_mean_std(dataset):
mean_std = [(st.mean(attribute), st.stdev(attribute))for attribute in
zip(*dataset)];
del mean_std[-1] # Exclude mean and standard deviation of last
column of dataset (i.e label 1 and 0)
return mean_std
# All class 1 data are zipped. For all 8 attributes calculate mean and
standard deviation.
# All class 0 data are zipped. For all 8 attributes calculate mean and
standard deviation.
# the function compute_mean computes the mean and standard
deviation of 8 attributes for both positive and negative instances
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-10-2048.jpg)

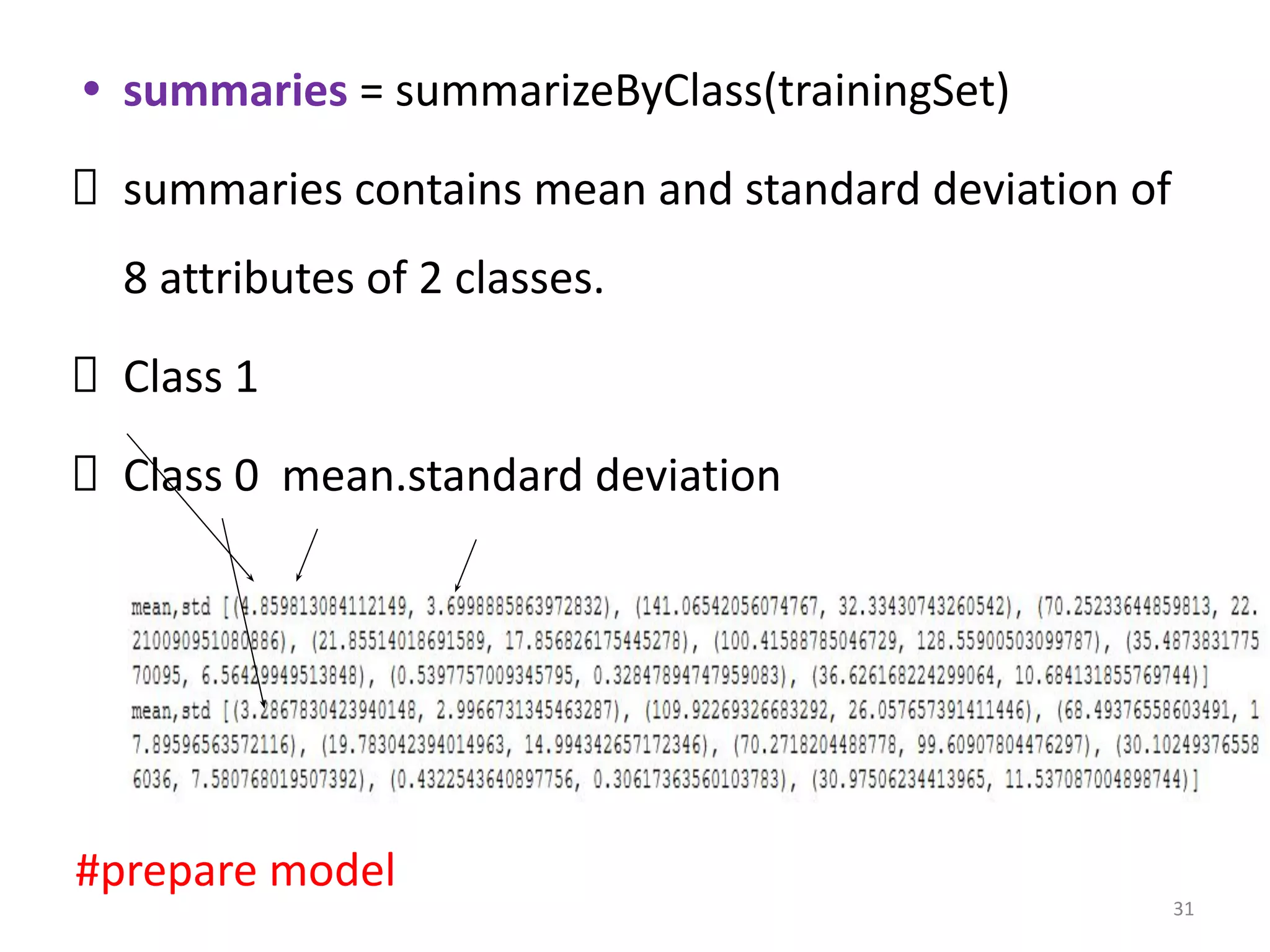
![#separated= dictionary, When key=0 value= all
positive classification instances, When key=1,
value= all negative classification instances
summary = {} # to store mean and standard
deviation of +ve and -ve instances
for classValue, instances in separated.items():
summary[classValue] = compute_mean_std(instances)
return summary
#summary is a dictionary of tuples(mean,std) for each
class value 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-13-2048.jpg)
![for classValue, instances in separated.items():
#summary is a dictionary of tuples(mean,std) for each class value
summary[classValue] = compute_mean_std(instances)
return summary
classValue =1, instances= all positive class instances
classValue=0, instances=all negative class instances
14
separated is a dictionary with key values 1 and 0
When key=1, values are all positive instances
When key=0, values are all negative instances](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-14-2048.jpg)
![summary[classValue] = compute_mean_std(instances)
summary[1]=mean and standard deviation of all positive instances
summary[0]=mean and standard deviation of all negative instances
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-15-2048.jpg)
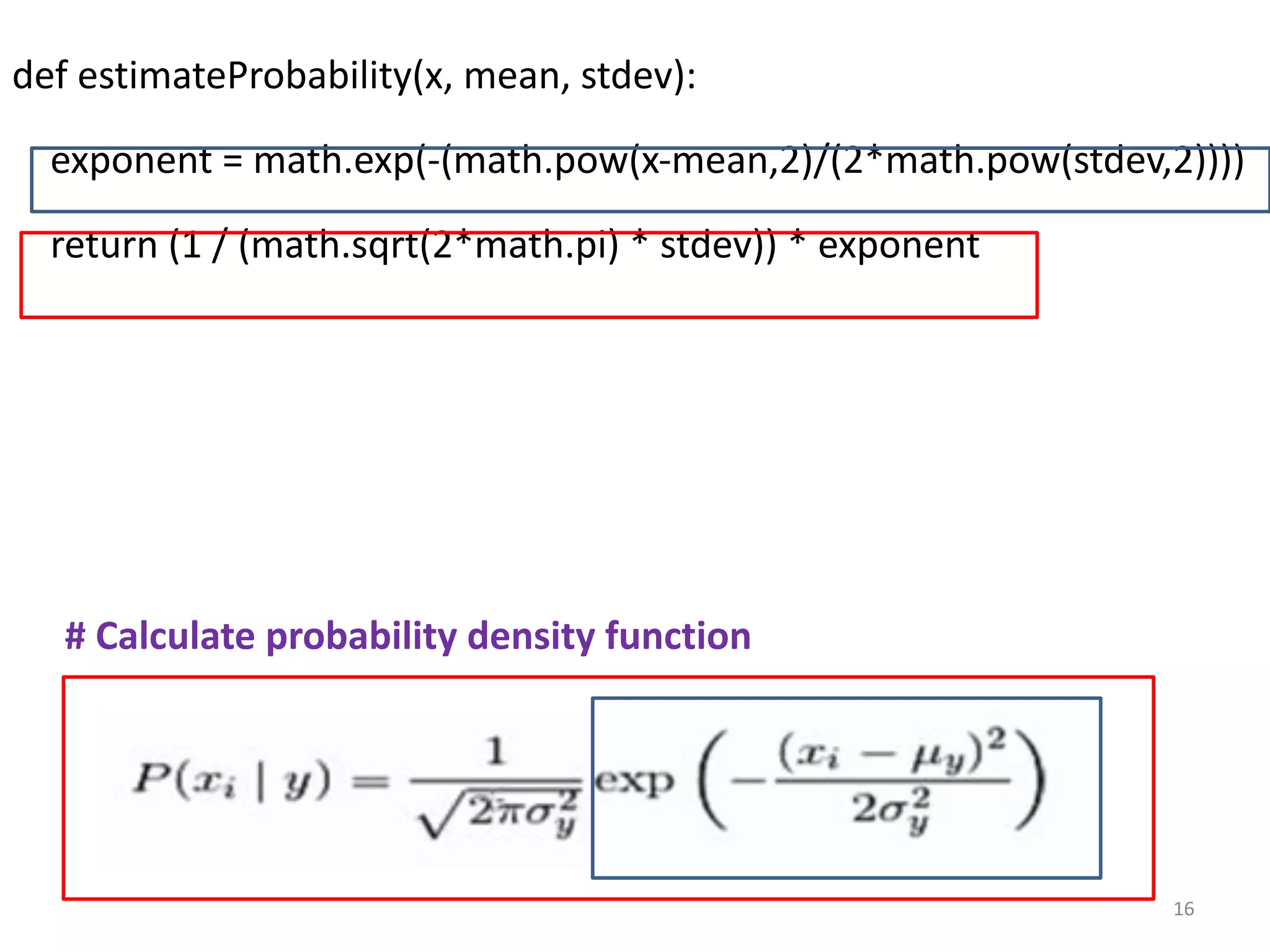
![def calculateClassProbabilities(summaries, testVector):
p = {} testinstance
#class and attribute information as mean and standard deviation
for classValue, classSummaries in summaries.items():
p[classValue] = 1 #Initially p[1]=1 and p[0]=0
for i in range(len(classSummaries)):
mean, stdev = classSummaries[i]
x = testVector[i] #testvector's first attribute
p[classValue] *= estimateProbability(x, mean, stdev);
return p
#classValue will be 1 and 0
#classSummaries contains mean and standard deviation of each
class
#summaries contains mean and standard deviation of 8 attributes of
2 classes. 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-17-2048.jpg)
![for i in range(len(classSummaries)):
mean, stdev = classSummaries[i]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-18-2048.jpg)
![x = testVector[i] #testSet’s first attribute
p[classValue] *= estimateProbability(x, mean, stdev);
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-19-2048.jpg)



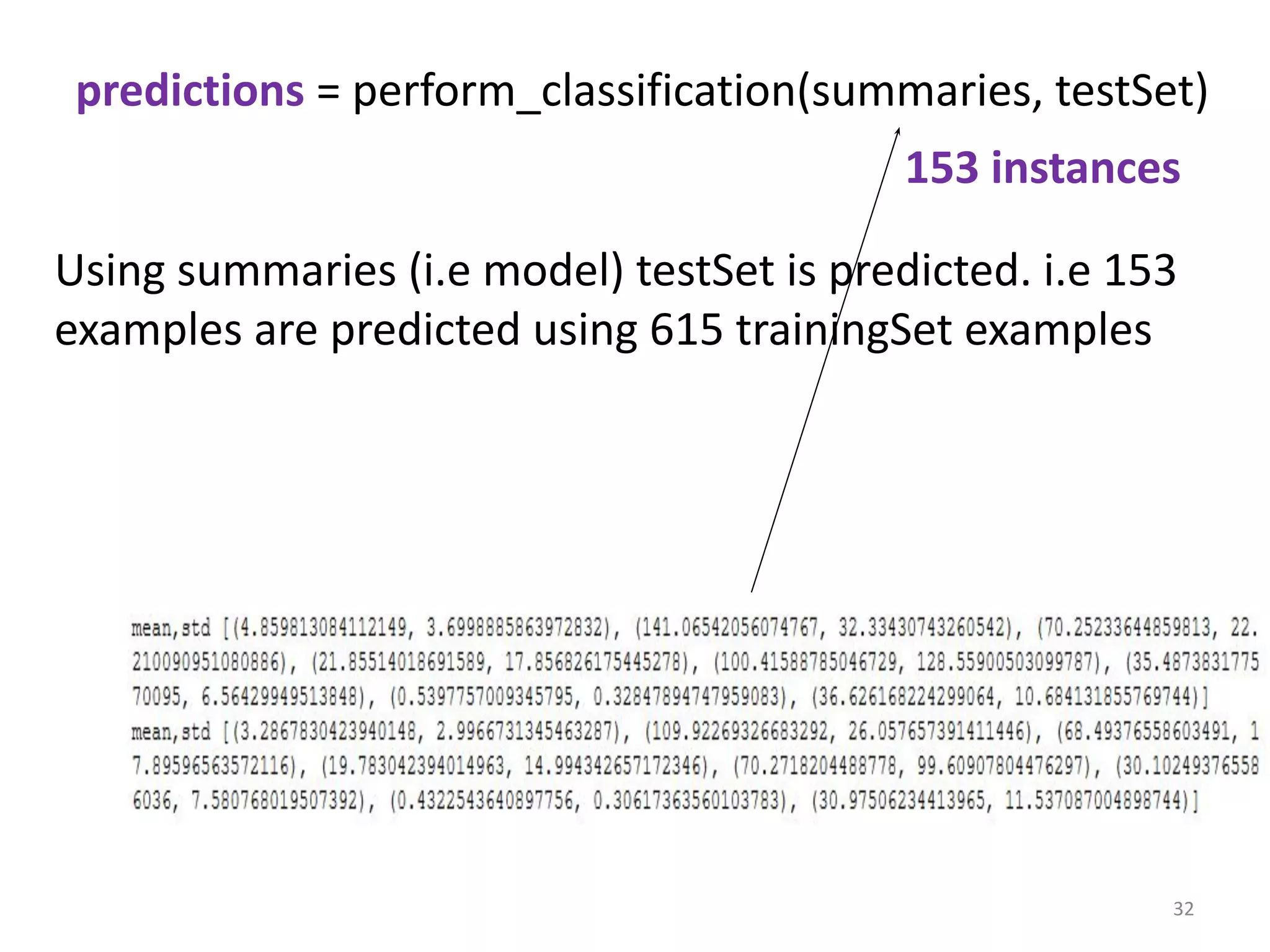
![def perform_classification(summaries, testSet):
predictions = []
for i in range(len(testSet)):
result = predict(summaries, testSet[i])
predictions.append(result)
return predictions
// Function perform_classification return predictions
of all testSets (153)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-23-2048.jpg)
![def perform_classification(summaries, testSet):
predictions = [] # predictions list will store predicted
values of 153 testsets
# initially predictions list is empty
summaries contains mean and standard deviation of
8 attributes of 2 classes.
Class 1
Class 0
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-24-2048.jpg)
![for i in range(len(testSet)): # for each testSet instance
result = predict(summaries, testSet[i])
#calculate prediction (1 or 0) and store in result
predictions.append(result)
#append each prediction result to list predictions
return predictions
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-25-2048.jpg)
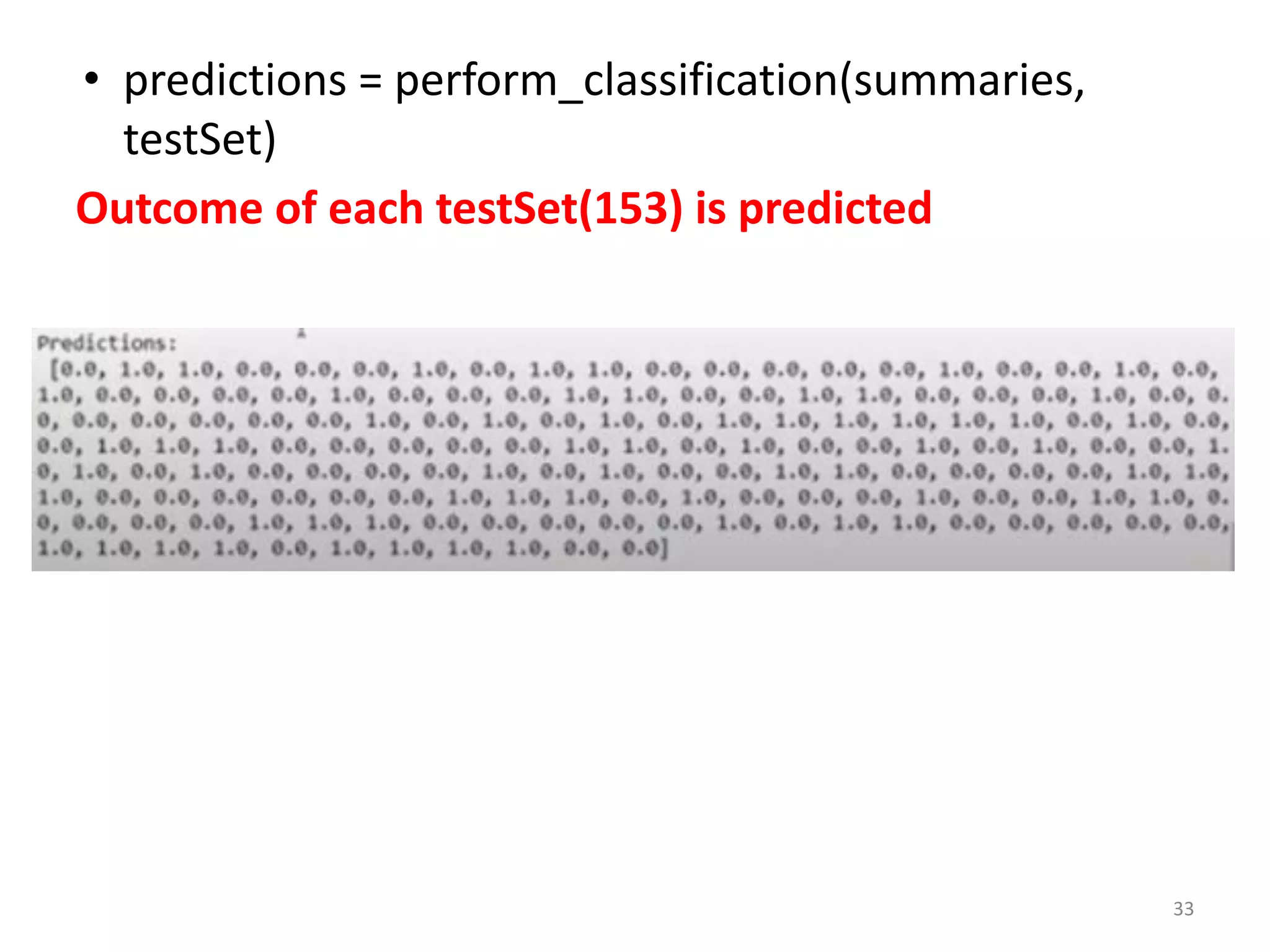
![# Function which return predictions for list of predictions #
For each instance
def getAccuracy(testSet, predictions):
correct = 0
for i in range(len(testSet)):
if testSet[i][-1] == predictions[i]:
correct += 1
return(correct/float(len(testSet))) * 100.0
Function takes 2 arguments testSet and predictions
• If testSet classification value matches with predictions
value of that testSet, then prediction is correct. Then
increment correct by 1.
• Accuracy=how many testSets are correctly predicted by
model.
• Accuracy=(no of correct predictions/153)*100 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-26-2048.jpg)
![dataset = loadCsv('pima-indians-diabetes.csv');
#loadCsv function is called and entire dataset is stored in
dataset
print('Pima Indian Diabetes Dataset loaded...')
print('Total instances available :',len(dataset))
#length of dataset is 768 (number of rows)
print('Total attributes present :',len(dataset[0])-1)
#Attributes of dataset is 8 .
#Last column contains target value (diabetes-Yes/No)
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-27-2048.jpg)
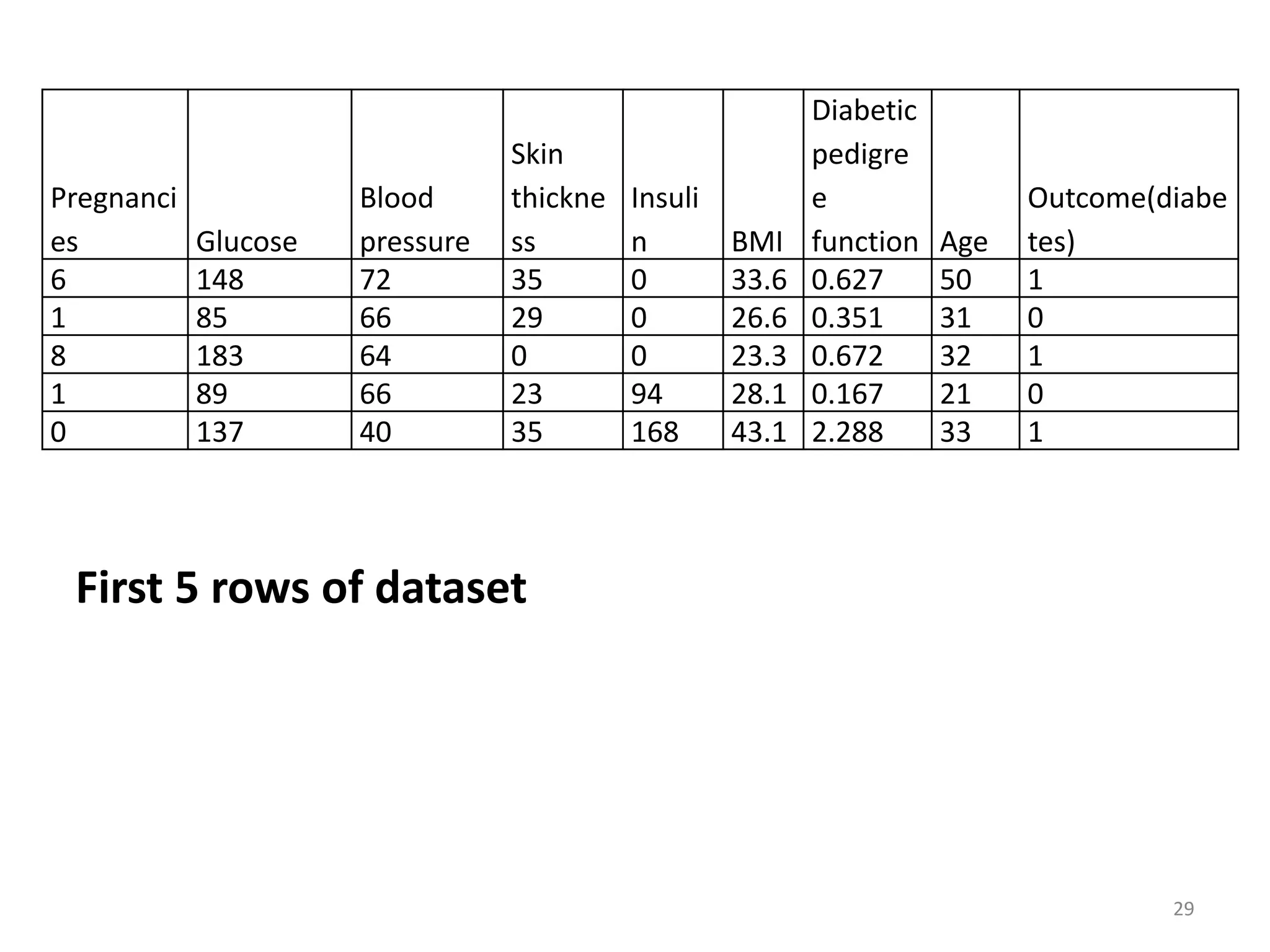
![for i in range(5):
print(i+1 , ':' , dataset[i])
# Print 1st
5 rows of dataset
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/labprogram6-230216103524-1f943651/75/lab-program-6-pdf-28-2048.jpg)